A Celecoxib-Loaded Emulsion Gel for Enhanced Drug Delivery and Prevention of Postoperative Adhesion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of CEL-Loaded Pectin-Emulsion Gel
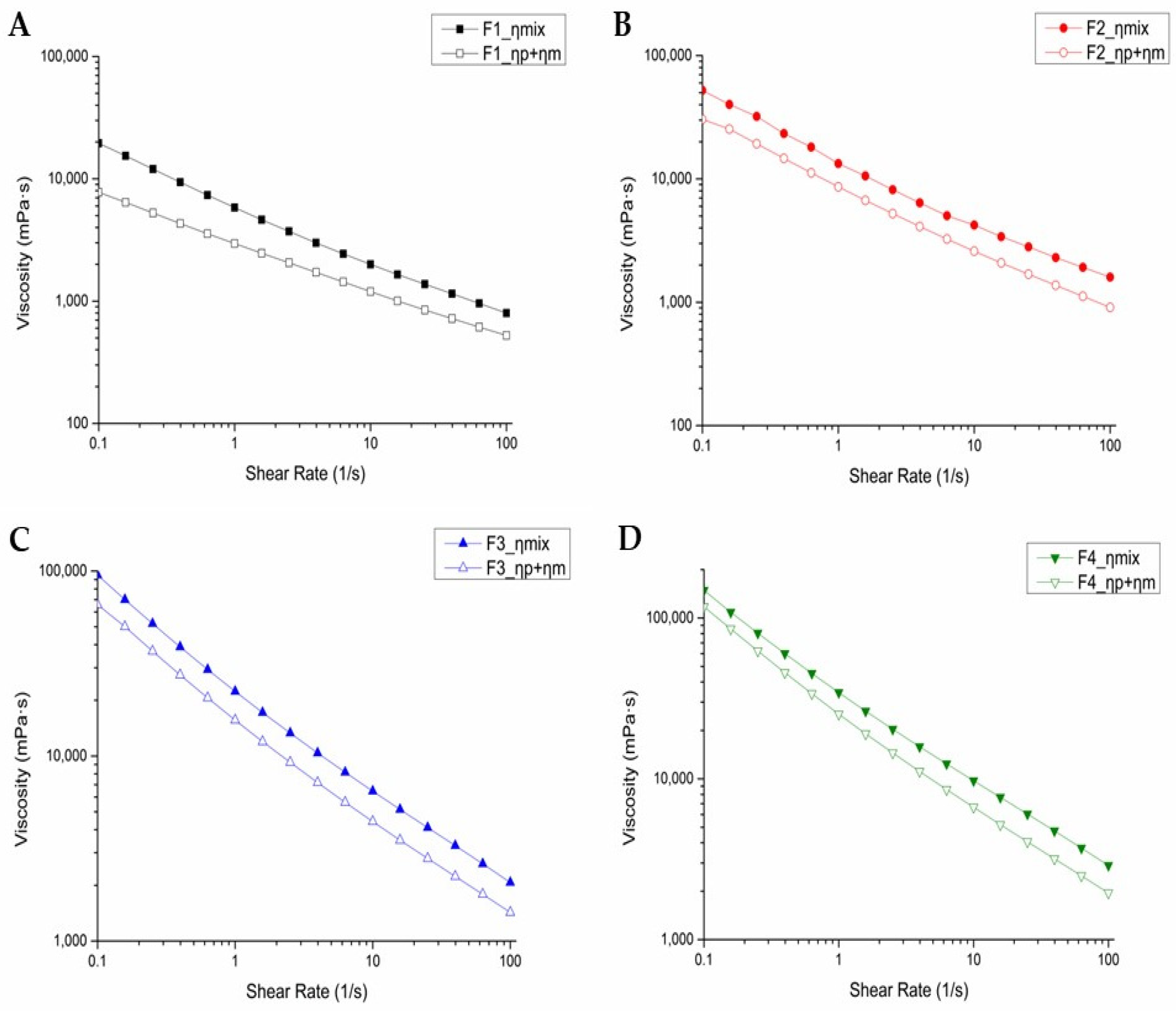
2.3. Rheological and Viscosity Analysis
2.4. In Vitro Mucoadhesion Evaluation
- ηmix: viscosity of emulsion and 10% mucin suspension mixture,
- ηp: viscosity of emulsion diluted with PBS buffer,
- ηm: viscosity of 5% mucin suspension.
2.5. Evaluation of Particle Size and Zeta Potential
2.6. In Vitro Evaluation of Emulsion-Gel Degradation
2.7. In Vitro CEL Release Test
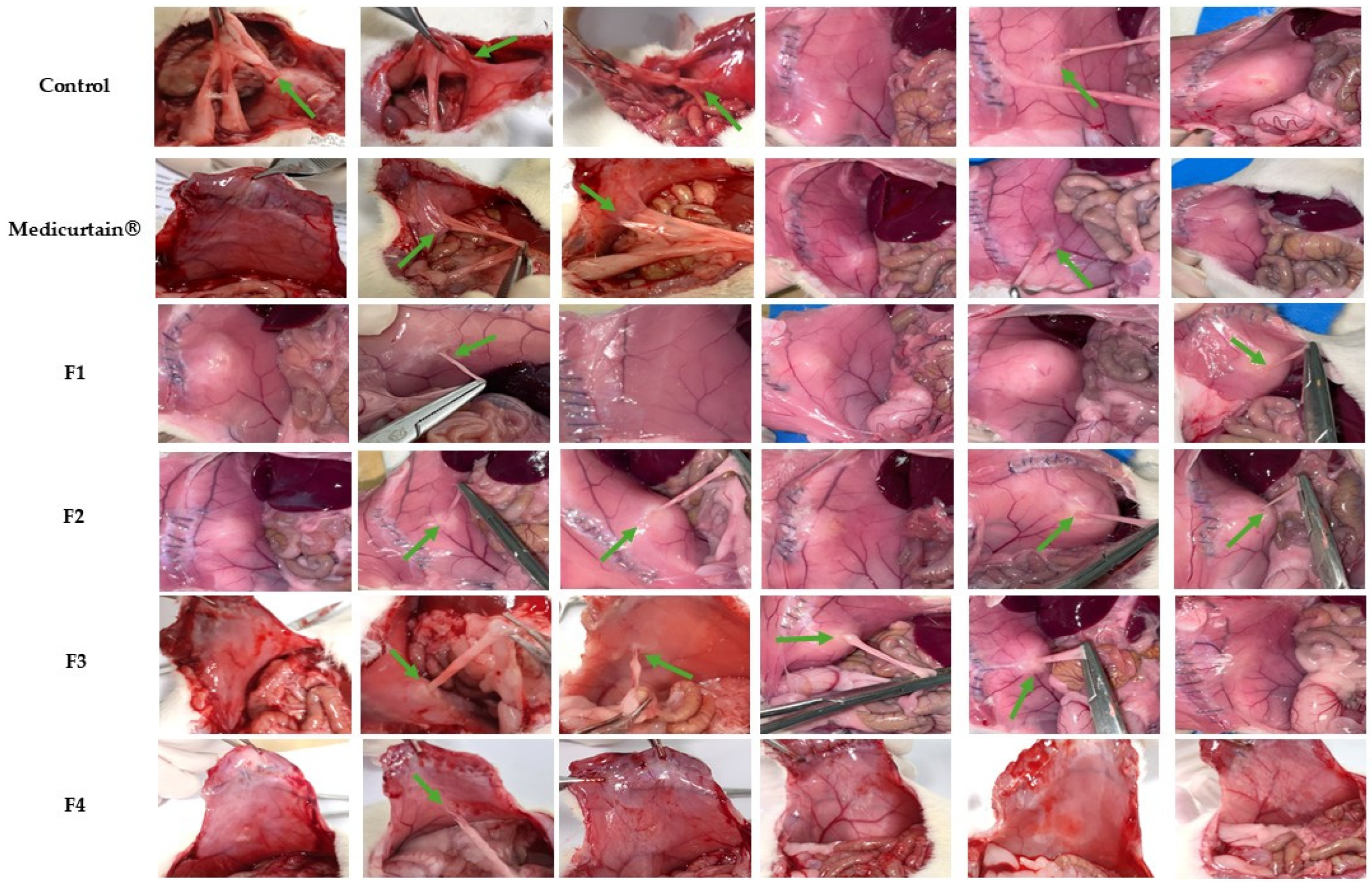
2.8. In Vivo Evaluation of Intraperitoneal Anti-Adhesion Effects
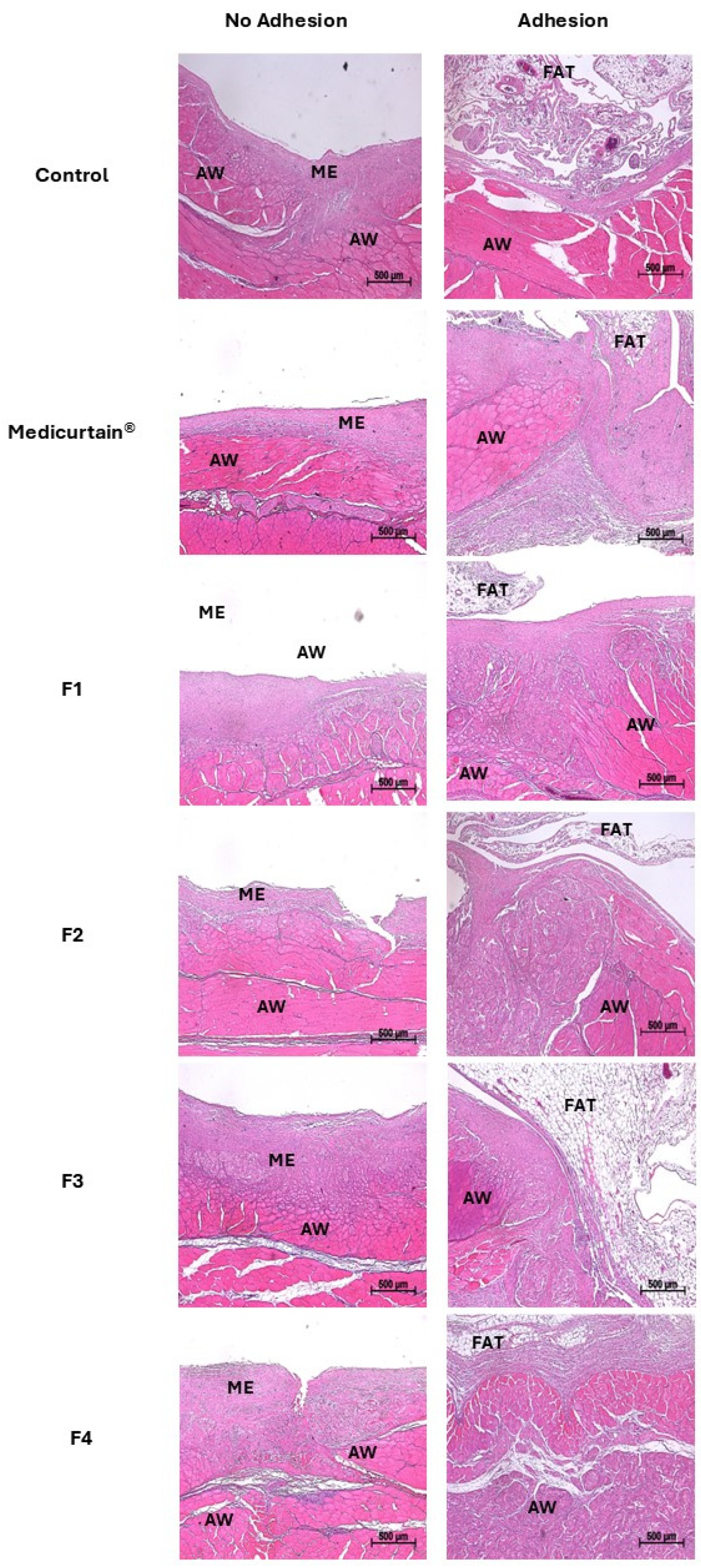
2.9. Histopathological Evaluation of Intraperitoneal Tissue
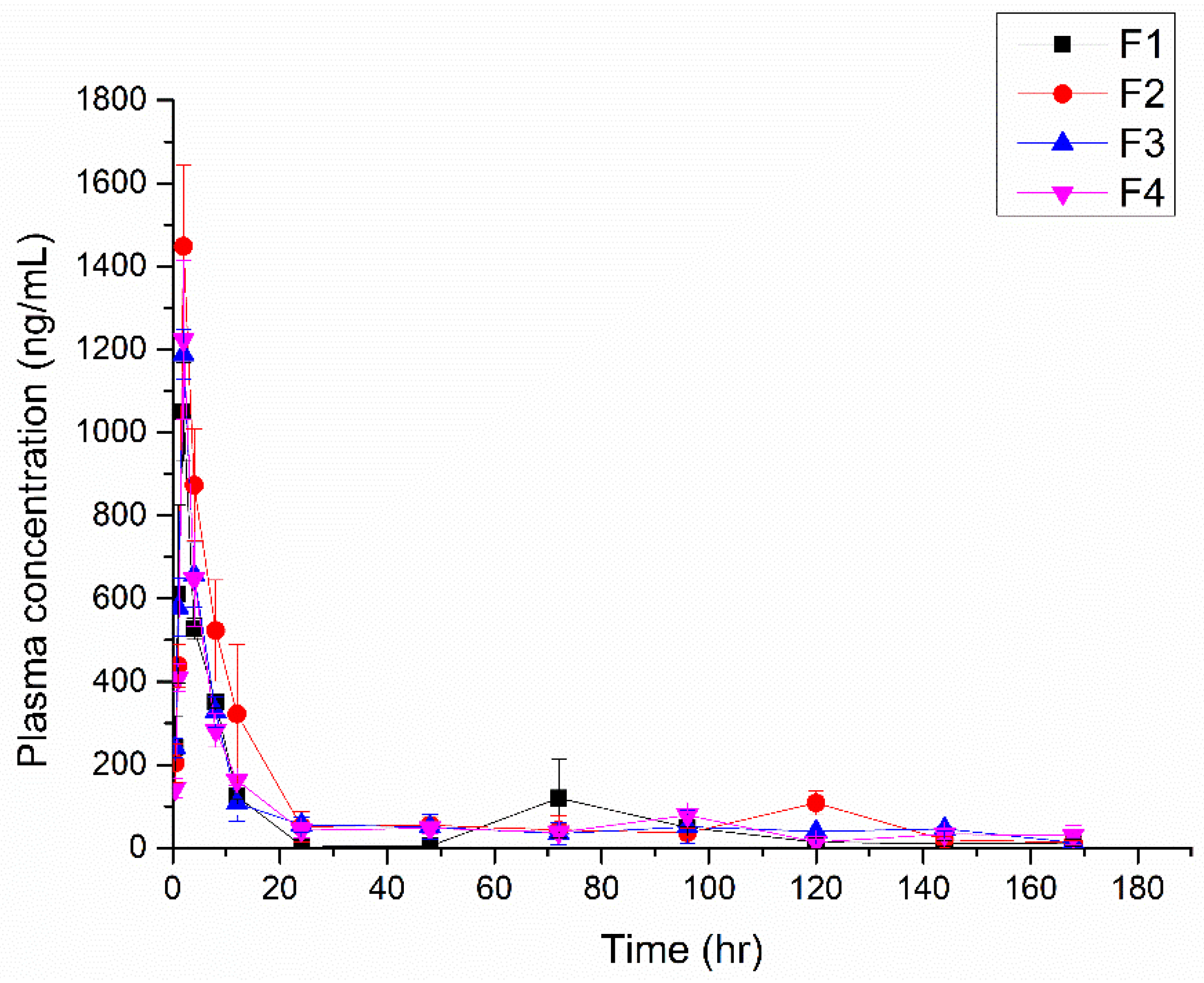
2.10. In Vivo Pharmacokinetics (PK) Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rheology and Viscosity of Emulsion Gels
3.2. In Vitro Mucoadhesion Assessment
3.3. Particle-Size and Zeta-Potential Measurements
3.4. In Vitro Assessment of Emulsion-Gel Degradation
3.5. In Vitro Assessment of CEL Release
3.6. In Vivo Evaluation of Intraperitoneal Anti-Adhesion Effects
3.7. Histopathological Analysis of Intraperitoneal Tissue
3.8. In Vivo PK
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ten Broek, R.P.; Strik, C.; Issa, Y.; Bleichrodt, R.P.; van Goor, H. Adhesiolysis-related morbidity in abdominal surgery. Ann. Surg. 2013, 258, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Cheng, R.; das Neves, J.; Tang, J.; Xiao, J.; Ni, Q.; Liu, X.; Pan, G.; Li, D.; Cui, W. Advances in biomaterials for preventing tissue adhesion. J. Control. Release 2017, 261, 318–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatehi Hassanabad, A.; Zarzycki, A.N.; Jeon, K.; Dundas, J.A.; Vasanthan, V.; Deniset, J.F.; Fedak, P.W. Prevention of post-operative adhesions: A comprehensive review of present and emerging strategies. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arung, W.; Meurisse, M.; Detry, O. Pathophysiology and prevention of postoperative peritoneal adhesions. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyendyk, J.P.; Schoenecker, J.G.; Flick, M.J. The multifaceted role of fibrinogen in tissue injury and inflammation. Blood 2019, 133, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, A.-G. Trends of anti-adhesion adjuvant-review. Biomater. Res. 2013, 17, 138–145. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Feng, X.; Liu, B.; Yu, Y.; Sun, L.; Liu, T.; Wang, Y.; Ding, J.; Chen, X. Polymer materials for prevention of postoperative adhesion. Acta Biomater. 2017, 61, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Xue, B.; Liao, J.; Qu, Y.; Qian, Z. Polymeric hydrogels for post-operative adhesion prevention: A review. Mater. Express 2017, 7, 417–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Priyadarshi, R.; Łopusiewicz, Ł.; Biswas, D.; Chandel, V.; Rhim, J.-W. Recent progress in pectin extraction, characterization, and pectin-based films for active food packaging applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitseva, O.; Khudyakov, A.; Sergushkina, M.; Solomina, O.; Polezhaeva, T. Pectins as a universal medicine. Fitoterapia 2020, 146, 104676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirawong, N.; Kennedy, R.A.; Sriamornsak, P. Viscometric study of pectin–mucin interaction and its mucoadhesive bond strength. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moote, C. Efficacy of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the management of postoperative pain. Drugs 1992, 44, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolettas, A.; Lazaridis, G.; Baka, S.; Mpoukovinas, I.; Karavasilis, V.; Kioumis, I.; Pitsiou, G.; Papaiwannou, A.; Lampaki, S.; Karavergou, A. Postoperative pain management. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, S62. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, P.; Knaus, E.E. Evolution of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibition and beyond. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 11, 81s–110s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colville-Nash, P.R.; Willoughby, D.A. COX-1, COX-2 and articular joint disease: A role for chondroprotective agents. Biorheology 2002, 39, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Soria, M.; Herrero-Beaumont, G.; Moreno-Rubio, J.; Calvo, E.; Santillana, J.; Egido, J.; Largo, R. Long-term NSAID treatment directly decreases COX-2 and mPGES-1 production in the articular cartilage of patients with osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 1484–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghazaly, M.A.; Nada, A.S.; El-Hazek, R.M.; Khayyal, M.T. Effect of selective COX-2 inhibitor, celecoxib on adjuvant-induced arthritis model in irradiated rats. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2010, 86, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, A.K.; Alwayn, I.P.; Nose, V.; Flynn, E.; Sampson, D.; Zurakowski, D.; Folkman, J.; Puder, M. Prevention of intra-abdominal adhesions using the antiangiogenic COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib. Ann. Surg. 2005, 242, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K.; Miyake, S.; Mizuno, M.; Oka, N.; Kusunoki, S.; Yamamura, T. Selective COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib prevents experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through COX-2-independent pathway. Brain 2006, 129, 1984–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, L.; Hong, J.; Kim, D.M.; Lee, G.; Park, E.J.; Baik, S.H.; Hwang, S.-J. A novel thermosensitive poloxamer-hyaluronic acid-kappa-carrageenan-based hydrogel anti-adhesive agent loaded with 5-fluorouracil: A preclinical study in Sprague-Dawley rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 621, 121771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-J.; Dinh, L.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Sung, Y.; Yeo, S.; Hwang, S.-J. Polysaccharide-based emulsion gels for the prevention of postoperative adhesions and as a drug delivery system using 5-fluorouracil. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 661, 124386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirovy, M.; Krupova, M.; Hyspler, R.; Ticha, A.; Kolackova, M.; Andrys, C.; Radochova, V.; Astapenko, D.; Odlozilová, S.; Kotek, J. Lipid emulsions prevent postoperative abdominal adhesions. Asian J. Surg. 2023, 46, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edsman, K.; Hägerström, H. Pharmaceutical applications of mucoadhesion for the non-oral routes. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2005, 57, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.K.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Wirtz, D.; Hanes, J. Micro-and macrorheology of mucus. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarn, A.; Lapworth, R. Biochemical analysis of ascitic (peritoneal) fluid: What should we measure? Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2010, 47, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntourakis, D.; Katsimpoulas, M.; Tanoglidi, A.; Barbatis, C.; Karayannacos, P.E.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Machairas, A. Adhesions and healing of intestinal anastomoses: The effect of anti-adhesion barriers. Surg. Innov. 2016, 23, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, H.; Zainal, N.F.A.; Hess, M.; Chan, C.H. Basic principle and good practices of rheology for polymers for teachers and beginners. Chem. Teach. Int. 2022, 4, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, D.; Schmitt, V.; Leal-Calderon, F.; Langevin, D. On the possible role of surface elasticity in emulsion stability. Langmuir 2009, 25, 5565–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherian, A.R.; Fustier, P.; Ramaswamy, H.S. Effect of added oil and modified starch on rheological properties, droplet size distribution, opacity and stability of beverage cloud emulsions. J. Food Eng. 2006, 77, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, F.; Arslan, N. Effect of temperature and concentration on viscosity of orange peel pectin solutions and intrinsic viscosity–molecular weight relationship. Carbohydr. Polym. 1999, 40, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimaraes, G.C.; Coelho Júnior, M.C.; Garcia Rojas, E.E. Density and kinematic viscosity of pectin aqueous solution. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2009, 54, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, L.A.; Rehman, T.U.; Khan, M. Synthesis of graphene oxide doped poly(2-acrylamido-2-methyl propane sulfonic acid) [GO@p(AMPS)] composite hydrogel with pseudo-plastic thixotropic behavior. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 3921–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahham, A.; Stewart, P.; Marriott, J.; Mainwaring, D.E. Flow and injection characteristics of pharmaceutical parenteral formulations using a micro-capillary rheometer. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 270, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacua, K.; Ordoñez, F.; Zapata, C.; Herrera, B.; Pabón, E.; Buitrago-Sierra, R. Surfactant concentration and pH effects on the zeta potential values of alumina nanofluids to inspect stability. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 583, 123960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fadlilah, F.N.; Yang, Q.; Hong, Y.; Wu, D.; Peng, M.; Peng, X.; Wu, J.; Luo, Y. A biodegradable shape memory polyurethane film as a postoperative anti-adhesion barrier for minimally invasive surgery. Acta Biomater. 2024, 189, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; De Baerdemaeker, A.; Poelaert, J.; Madder, A.; Hoogenboom, R.; Ballet, S. Controlled-release of opioids for improved pain management. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S. Understanding the burst release phenomenon: Toward designing effective nanoparticulate drug-delivery systems. Ther. Deliv. 2021, 12, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Celecoxib | PEG 400 | Pectin | Water | P 407 | Montanox® 80 | Soybean Oil | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 0.03 | 2.0 | 0.5 | 5.04 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 2.4 |
| F2 | 0.03 | 2.0 | 0.6 | 4.94 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 2.4 |
| F3 | 0.03 | 2.0 | 0.7 | 4.84 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 2.4 |
| F4 | 0.03 | 2.0 | 0.8 | 4.74 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 2.4 |
| Grade | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| 0 | No adhesions |
| 1 | Tiny, filmy adhesions easy to separate |
| 2 | Dense adhesion that require tension to divide |
| 3 | Dense adhesions that require division by scissors |
| 4 | Other intraabdominal organs involved, with conglomerate formed |
| Sample | Storage Modulus (Pa) | Loss Modulus (Pa) | Loss Factor (tan δ) | δ (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 957.4 | 304.18 | 0.318 | 17.6 |
| F2 | 1761.9 | 528.11 | 0.300 | 16.7 |
| F3 | 6401.9 | 1153.8 | 0.180 | 10.2 |
| F4 | 7444.2 | 1285.3 | 0.173 | 9.8 |
| Sample | Particle Size (nm) | Size PDI | Zeta-Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 1121 ± 167.7 | 0.117 ± 0.08 | −39.40 ± 0.96 |
| F2 | 1041 ± 162.4 | 0.193 ± 0.05 | −34.45 ± 0.74 |
| F3 | 933 ± 57.7 | 0.119 ± 0.06 | −32.35 ± 0.48 |
| F4 | 987 ± 77.2 | 0.156 ± 0.03 | −32.39 ± 1.33 |
| Sample | Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax (h) | AUC(0→168 h) (ng·h/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 1048.9 ± 145.3 | 2 ± 0 | 11,095.2 ± 2679.3 |
| F2 | 1448.1 ± 239 | 2 ± 0 | 17,230.3 ± 4863.2 |
| F3 | 1187.7 ± 72.9 | 2 ± 0 | 12,941.2 ± 3715.7 |
| F4 | 1223.0 ± 234.1 | 2 ± 0 | 12,743.6 ± 740.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.-J.; Kim, Y.J.; Song, S.; Yeo, S.; Hwang, S.-J. A Celecoxib-Loaded Emulsion Gel for Enhanced Drug Delivery and Prevention of Postoperative Adhesion. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040427
Yang H, Kim D, Lee J-J, Kim YJ, Song S, Yeo S, Hwang S-J. A Celecoxib-Loaded Emulsion Gel for Enhanced Drug Delivery and Prevention of Postoperative Adhesion. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(4):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040427
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Heesang, Dongmin Kim, Jong-Ju Lee, Ye Ji Kim, Seungeun Song, Sooho Yeo, and Sung-Joo Hwang. 2025. "A Celecoxib-Loaded Emulsion Gel for Enhanced Drug Delivery and Prevention of Postoperative Adhesion" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 4: 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040427
APA StyleYang, H., Kim, D., Lee, J.-J., Kim, Y. J., Song, S., Yeo, S., & Hwang, S.-J. (2025). A Celecoxib-Loaded Emulsion Gel for Enhanced Drug Delivery and Prevention of Postoperative Adhesion. Pharmaceutics, 17(4), 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040427









