Verteporfin Inhibits Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection via Inducing the Degradation of the Viral Gn Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
2.2. Chemicals and Antibodies
2.3. Immunofluorescent (IF) Assay
2.4. Cytotoxic Assay
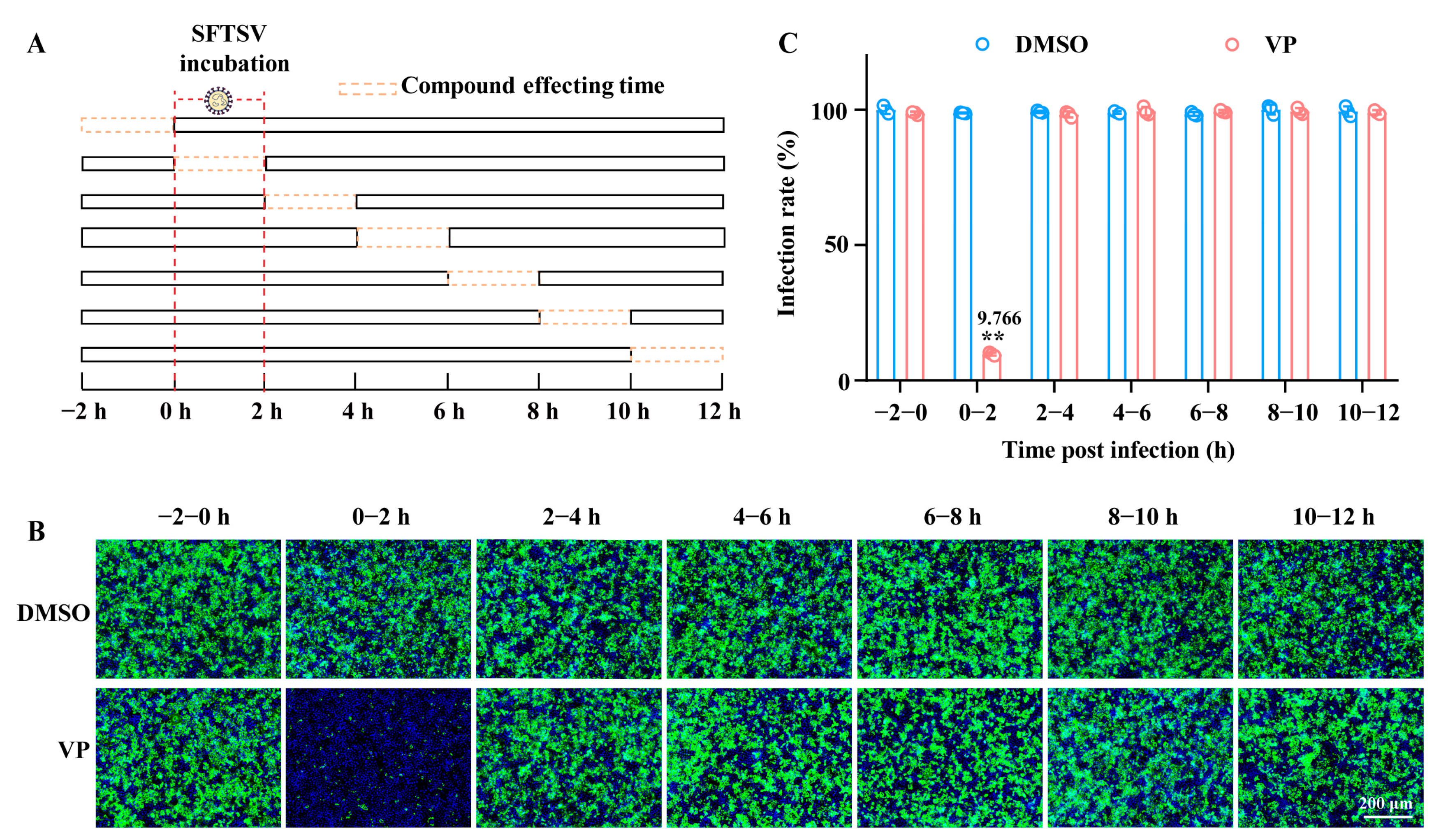
2.5. Time Window of Compound Affecting Assay
2.6. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.7. SFTSV Binding Assay
2.8. Endocytosis Assay
2.9. Membrane Fusion Assay
2.10. Drug Affinity Responsive Target Stability Assay (DARTS)
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
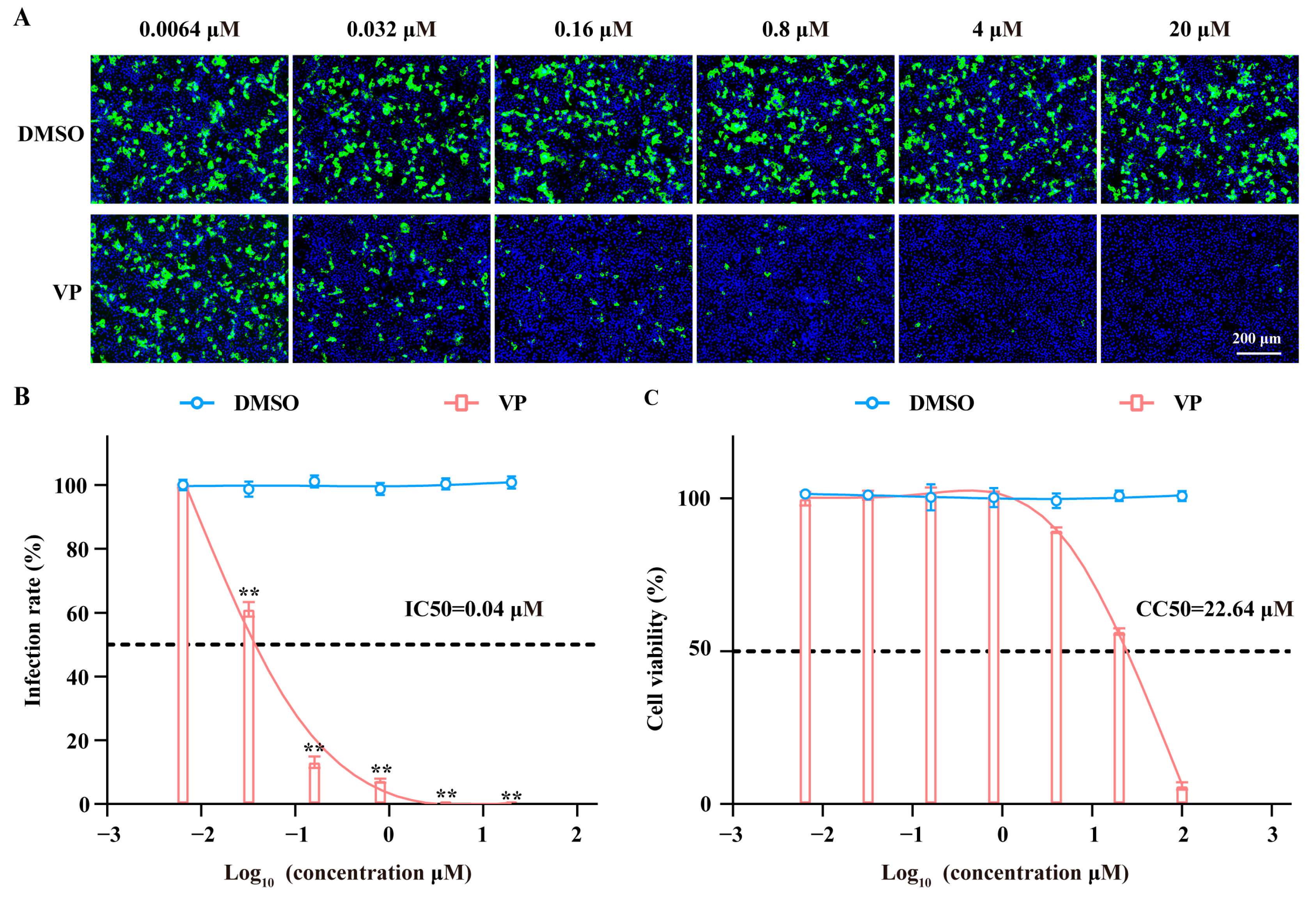
3.1. VP Has a Dose-Dependent Inhibition Effect on SFTSV Infection
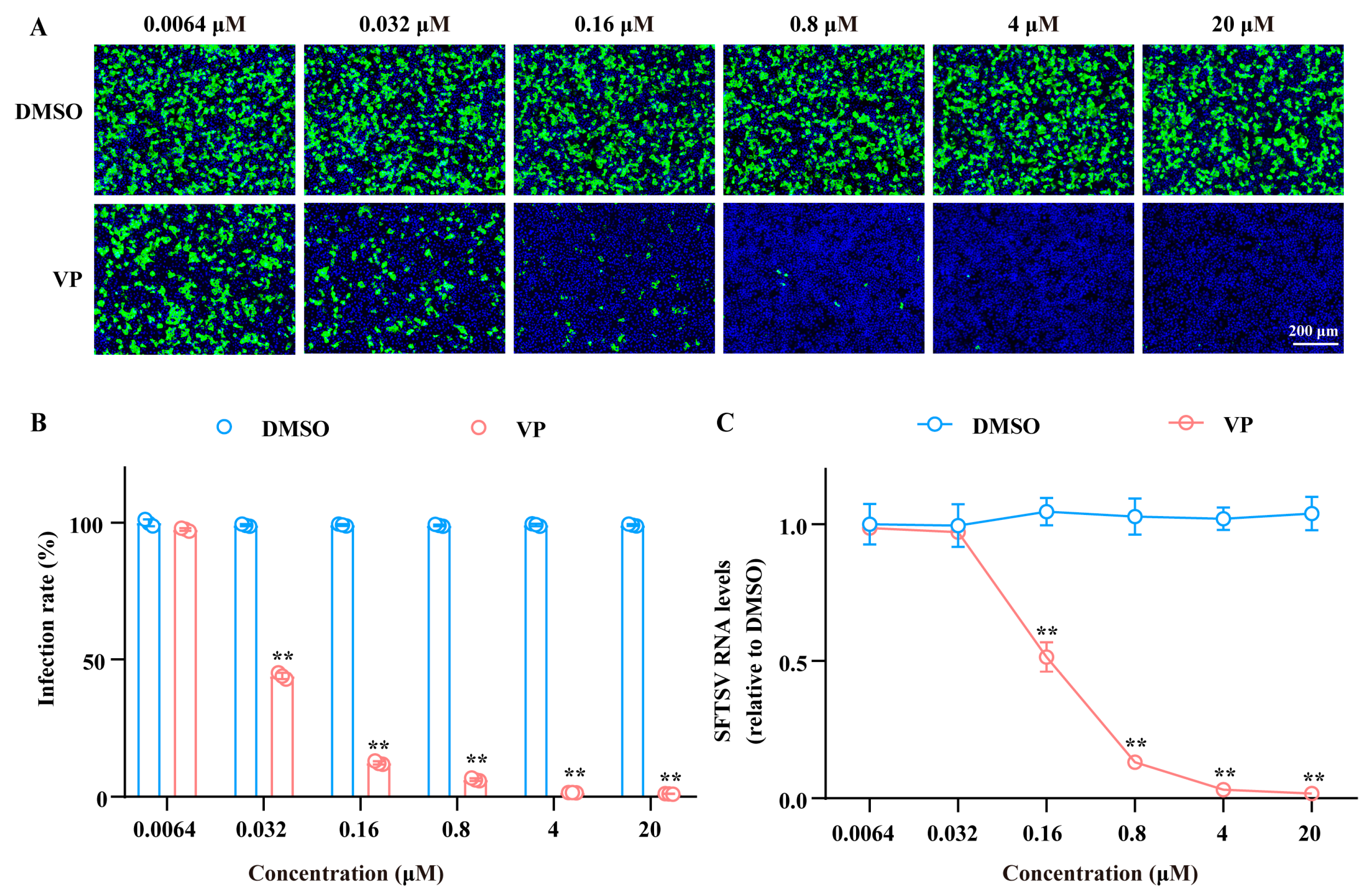
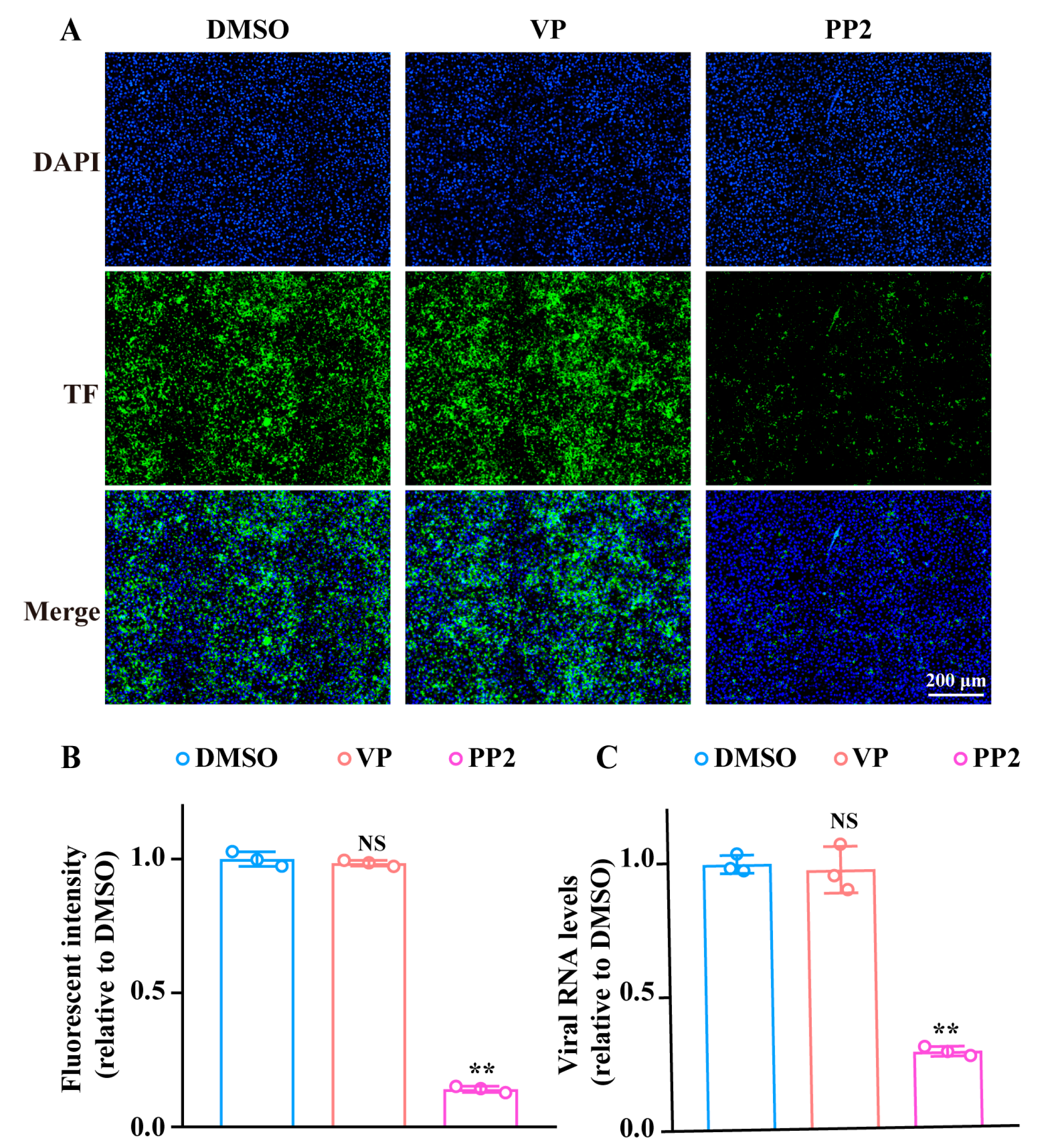
3.2. VP Suppresses SFTSV Infection via Blocking Viral Binding During the Early Entry Stage
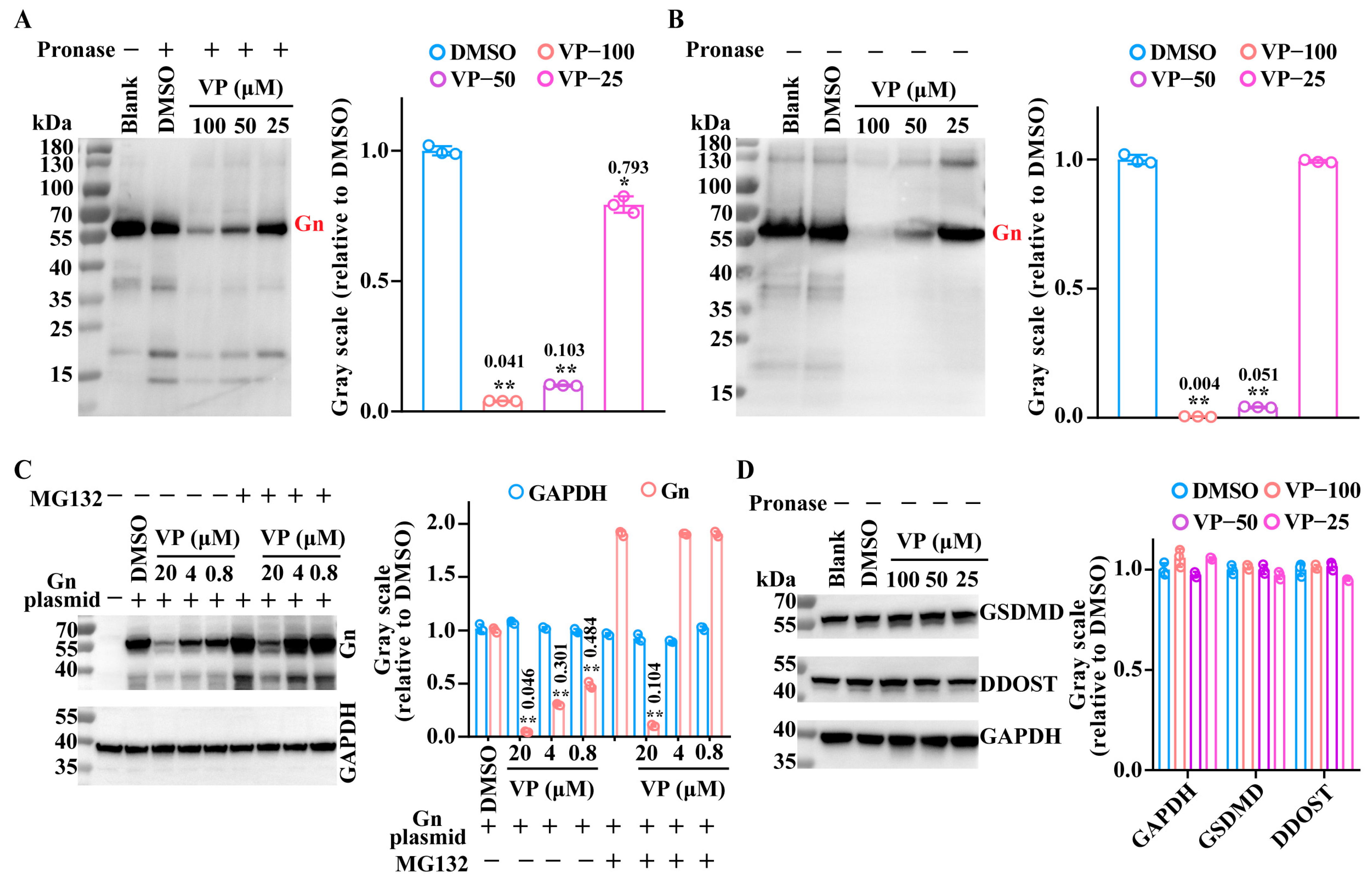
3.3. VP Inhibits the SFTSV Binding Process by Inducing Viral Gn Protein Degradation
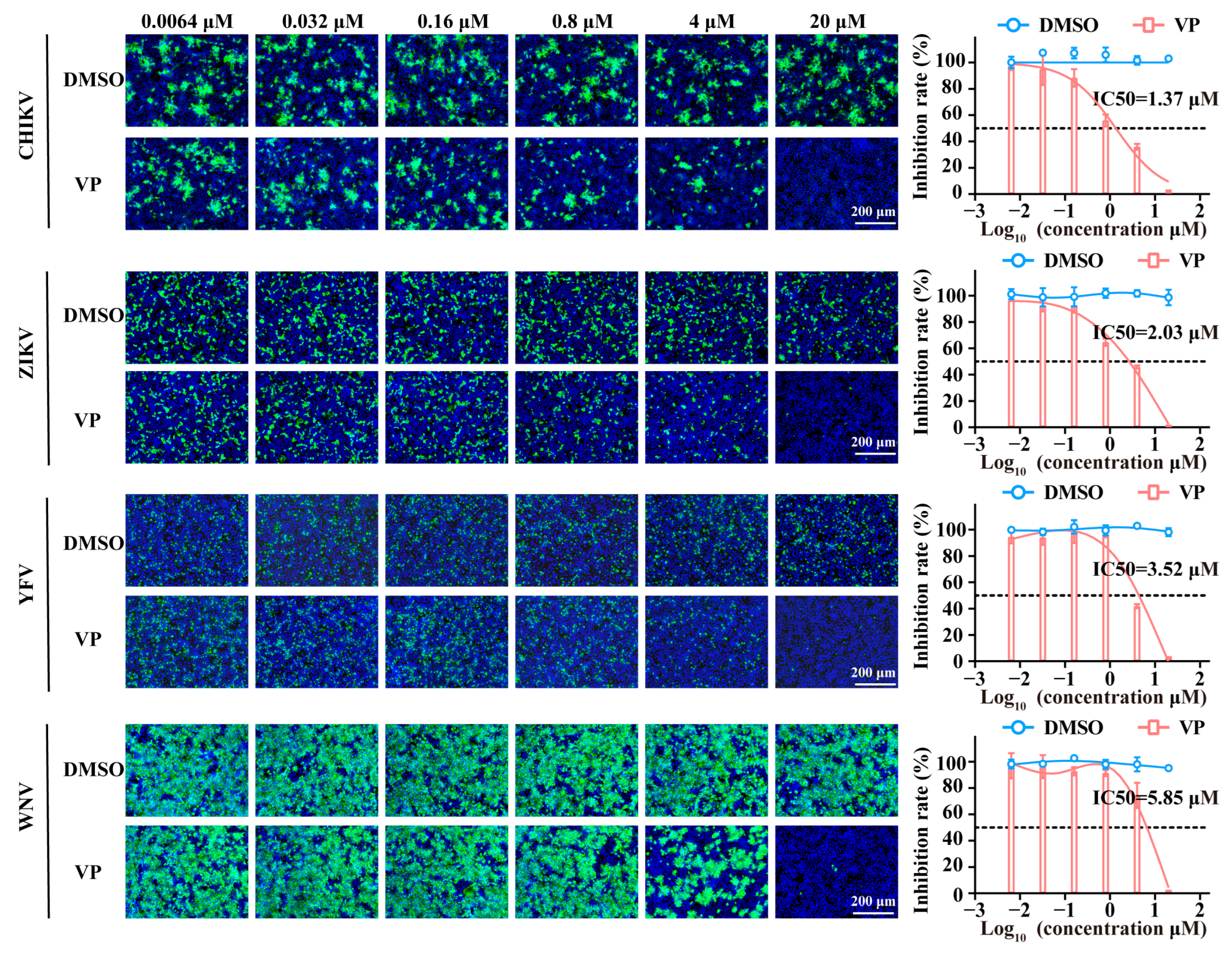
3.4. VP Exerts Broad Spectrum Antiviral Activity Against a Wide Range of Viruses
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Zhang, L.K.; Li, S.F.; Zhang, S.F.; Wan, W.W.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xin, Q.L.; Dai, K.; Hu, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.B.; et al. Calcium channel blockers reduce severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV) related fatality. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.K.; Yan, J.M.; Chu, M.; Li, B.; Gu, X.L.; Jiang, Z.Z.; Li, Z.M.; Liu, P.P.; Yu, T.M.; Zhou, C.M.; et al. Bunyavirus SFTSV nucleoprotein exploits TUFM-mediated mitophagy to impair antiviral innate immunity. Autophagy 2025, 21, 102–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.J.; Liang, M.F.; Zhang, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.D.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.F.; Popov, V.L.; Li, C.; et al. Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Shin, W.J.; Jung, J.U. Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus NSs Interacts with TRIM21 To Activate the p62-Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01684-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Hu, J.; Peng, Z.; Dai, Q.; Liu, W.; Liang, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, N.; Bao, C. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus human-to-human transmission. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Tian, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, L.; Li, M.; Zhao, Z.; Lei, X.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, X. Adenovirus type 5-expressing Gn induces better protective immunity than Gc against SFTSV infection in mice. NPJ Vaccines 2024, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Tian, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Wu, J.; Jiang, N.; Yuan, M.; Chen, D.; Su, A.; Xu, S.; et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus induces lactylation of m6A reader protein YTHDF1 to facilitate viral replication. EMBO Rep. 2024, 25, 5599–5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Lv, S.; Han, S.; Zhang, L.; Ding, H.; Wang, C.Y.; Xiao, G.; et al. CCR2 is a host entry receptor for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.; Park, S.J. Emerging Tick-Borne Dabie bandavirus: Virology, Epidemiology, and Prevention. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallapaty, S. The pathogens that could spark the next pandemic. Nature 2024, 632, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, K.; Kimura, M.; Sataka, A.; Hasegawa, H.; Tani, H.; Suzuki, T. Characterization of antibodies targeting severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus glycoprotein Gc. Arch. Virol. 2024, 169, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moming, A.; Shi, S.; Shen, S.; Qiao, J.; Yue, X.; Wang, B.; Ding, J.; Hu, Z.; Deng, F.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Fine mapping epitope on Glycoprotein-Gn from Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, P.; Yoo, B.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Woo, H.M.; Lim, H.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, S.; Lee, H. Characterization of high-affinity antibodies against the surface Gc protein of Dabie bandavirus/severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2024, 39, 101779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Gao, D.; Liao, L.; Sun, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Li, C.; Oladejo, B.O.; Li, S.; et al. Bispecific antibodies targeting two glycoproteins on SFTSV exhibit synergistic neutralization and protection in a mouse model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2400163121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, F.; Jiao, Y.; Oladejo, B.O.; Chai, Y.; Bi, Y.; Lu, S.; Dong, M.; Zhang, C.; et al. Structures of phlebovirus glycoprotein Gn and identification of a neutralizing antibody epitope. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7564–E7573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Li, F.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Huang, M.; Gao, X.; Su, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T. Interaction between the SFTSV envelope glycoprotein Gn and STING inhibits the formation of the STING-TBK1 complex and suppresses the NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Virol. 2024, 98, e0181523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, P.K. Verteporfin photodynamic therapy and anti-angiogenic drugs: Potential for combination therapy in exudative age-related macular degeneration. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2007, 23, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu-Chittenden, Y.; Huang, B.; Shim, J.S.; Chen, Q.; Lee, S.J.; Anders, R.A.; Liu, J.O.; Pan, D. Genetic and pharmacological disruption of the TEAD-YAP complex suppresses the oncogenic activity of YAP. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 1300–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, Y.; Yoon, K. Verteporfin is an effective inhibitor of HCMV replication. Virus Res. 2024, 350, 199475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, Z.P.; Dougherty, T.; Gollnick, S.; Schwartz, S.A.; Mahajan, S.D.; Kepner, J.; Sumlin, A.; Stewart, C.; Wallace, P.; Adal, A.; et al. Photopheresis in HIV-1 infected patients utilizing benzoporphyrin derivative (BPD) verteporfin and light. Curr. HIV Res. 2008, 6, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Wu, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Z.; Cai, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Protoporphyrin IX and verteporfin potently inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro and in a mouse model expressing human ACE2. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, E.; Li, W.; Mandeville, E.T.; Park, J.H.; Şencan, I.; Guo, S.; Shi, J.; Lan, J.; Lee, J.; Hayakawa, K.; et al. Potential circadian effects on translational failure for neuroprotection. Nature 2020, 582, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, C. Drug Affinity Responsive Target Stability (DARTS) Assay to Detect Interaction Between a Purified Protein and a Small Molecule. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2213, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Fang, Y.; Wu, X.; Bai, Y.; Dai, S.; et al. Antiviral activity and mechanism of the antifungal drug, anidulafungin, suggesting its potential to promote treatment of viral diseases. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Zheng, A. Entry of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. Virol. Sin. 2017, 32, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Wu, B.; Tang, H.; Luo, Z.; Xu, Z.; Ouyang, S.; Li, X.; Xie, J.; Yi, Z.; Leng, Q.; et al. Rifapentine is an entry and replication inhibitor against yellow fever virus both in vitro and in vivo. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.S.; Li, H.L.; Piao, X.H.; Yang, Z.Y.; Wang, S.M.; Ge, Y.W. Drug affinity responsive target stability (DARTS) accelerated small molecules target discovery: Principles and application. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 194, 114798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lu, Q.B.; Cui, N.; Li, H.; Wang, L.Y.; Liu, K.; Yang, Z.D.; Wang, B.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; et al. Case-fatality ratio and effectiveness of ribavirin therapy among hospitalized patients in china who had severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suemori, K.; Saijo, M.; Yamanaka, A.; Himeji, D.; Kawamura, M.; Haku, T.; Hidaka, M.; Kamikokuryo, C.; Kakihana, Y.; Azuma, T.; et al. A multicenter non-randomized, uncontrolled single arm trial for evaluation of the efficacy and the safety of the treatment with favipiravir for patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, S.; Guo, J.; Cao, J.; Jia, X.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, G.; Wang, W. Screening and Identification of Lassa Virus Entry Inhibitors from an FDA-Approved Drug Library. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00954-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrows, N.J.; Campos, R.K.; Powell, S.T.; Prasanth, K.R.; Schott-Lerner, G.; Soto-Acosta, R.; Galarza-Muñoz, G.; McGrath, E.L.; Urrabaz-Garza, R.; Gao, J.; et al. A Screen of FDA-Approved Drugs for Inhibitors of Zika Virus Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, L.M.; DeWald, L.E.; Shoemaker, C.J.; Hoffstrom, B.G.; Lear-Rooney, C.M.; Stossel, A.; Nelson, E.; Delos, S.E.; Simmons, J.A.; Grenier, J.M.; et al. A screen of approved drugs and molecular probes identifies therapeutics with anti-Ebola virus activity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 290ra89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plegge, T.; Hofmann-Winkler, H.; Spiegel, M.; Pöhlmann, S. Evidence that Processing of the Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Gn/Gc Polyprotein Is Critical for Viral Infectivity and Requires an Internal Gc Signal Peptide. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, H.; Shimojima, M.; Fukushi, S.; Yoshikawa, T.; Fukuma, A.; Taniguchi, S.; Morikawa, S.; Saijo, M. Characterization of Glycoprotein-Mediated Entry of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 5292–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudino, T.A. Targeted Cancer Therapy: The Next Generation of Cancer Treatment. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2015, 12, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Fei, Y.; Lu, B. Emerging New Concepts of Degrader Technologies. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 41, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbro, D.; Cowan-Jacob, S.W.; Moebitz, H. Ten things you should know about protein kinases: IUPHAR Review 14. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 2675–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xing, D.; Fei, Y.; Lu, B. Emerging degrader technologies engaging lysosomal pathways. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 8832–8876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielian, M.; Chanel-Vos, C.; Liao, M. Alphavirus Entry and Membrane Fusion. Viruses 2010, 2, 796–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.N.; Akhtar, R.; Abid, M.; Khan, S.A.; Rehman, Z.U.; Tayyub, M.; Malik, M.I.; Shahzad, M.K.; Mubeen, H.; Qadir, M.S.; et al. The interactions of flaviviruses with cellular receptors: Implications for virus entry. Virology 2022, 568, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer | Sequences |
|---|---|
| GAPDH | Forward primer: TGGGCTACACTGAGCACCAG |
| Reverse primer: AAGTGGTCGTTGAGGGCAAT | |
| SFTSV | Forward primer: TGGAGGCCTACTCTCTGTGG |
| Reverse primer: AGCCACTTCACCCGAACATC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, B.; Yu, C.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, P.; Qi, Z.; Qian, X. Verteporfin Inhibits Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection via Inducing the Degradation of the Viral Gn Protein. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040434
Wu B, Yu C, Lin Y, Zhao P, Qi Z, Qian X. Verteporfin Inhibits Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection via Inducing the Degradation of the Viral Gn Protein. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(4):434. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040434
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Bingan, Chenyang Yu, Yuxiang Lin, Ping Zhao, Zhongtian Qi, and Xijing Qian. 2025. "Verteporfin Inhibits Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection via Inducing the Degradation of the Viral Gn Protein" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 4: 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040434
APA StyleWu, B., Yu, C., Lin, Y., Zhao, P., Qi, Z., & Qian, X. (2025). Verteporfin Inhibits Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection via Inducing the Degradation of the Viral Gn Protein. Pharmaceutics, 17(4), 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040434





