Topical Administration of Vitamin D2 Combined with Colloidal Silver Nanoparticles Promotes Wound Repair and Protection Against Skin Irritation and UVB Irradiation in 3D Reconstructed Human Skin Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Vitamin D2 and Silver Nanoparticle Cream Extract
2.3. Construction of the Reconstructed Human Skin Model
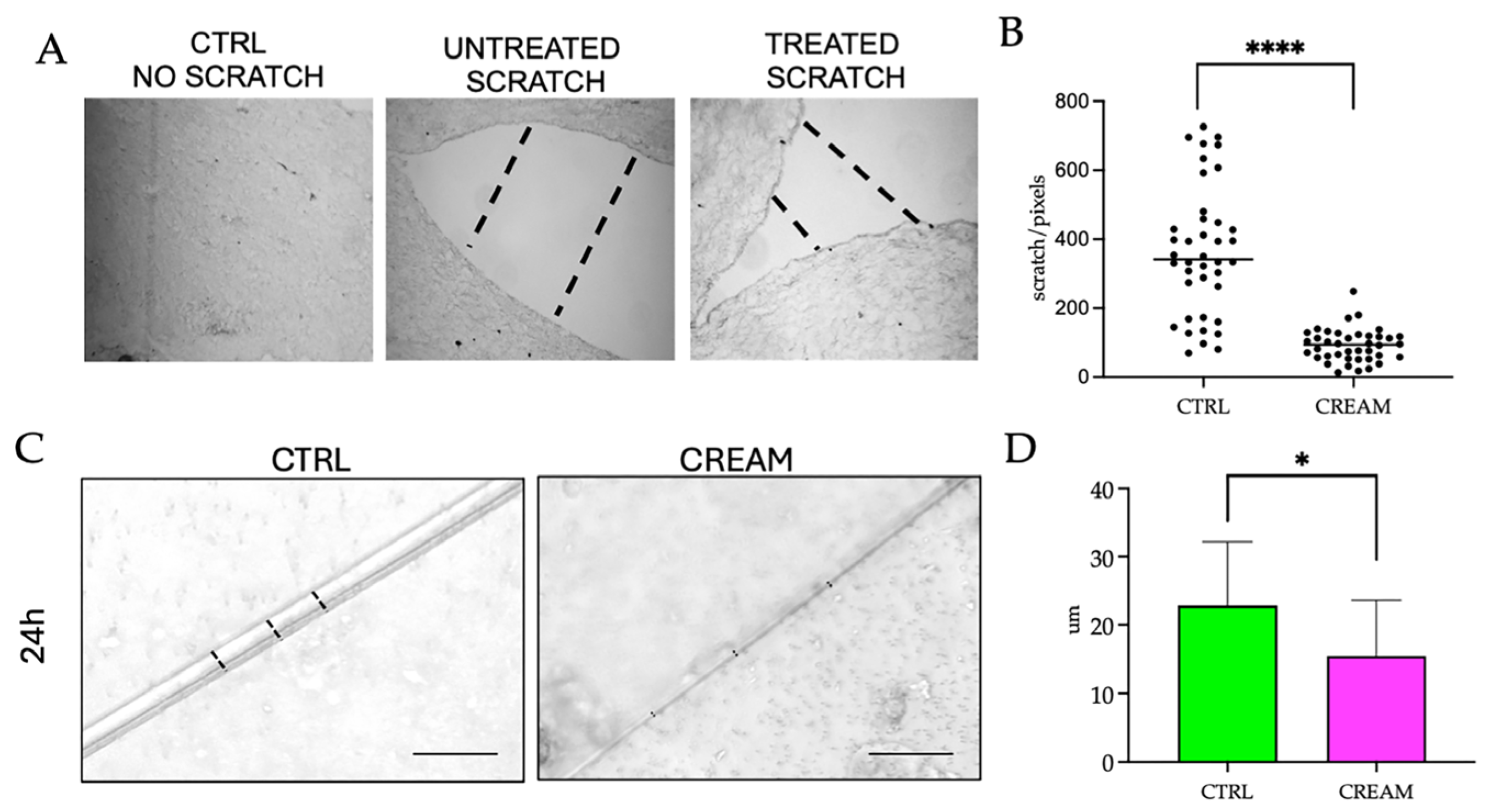
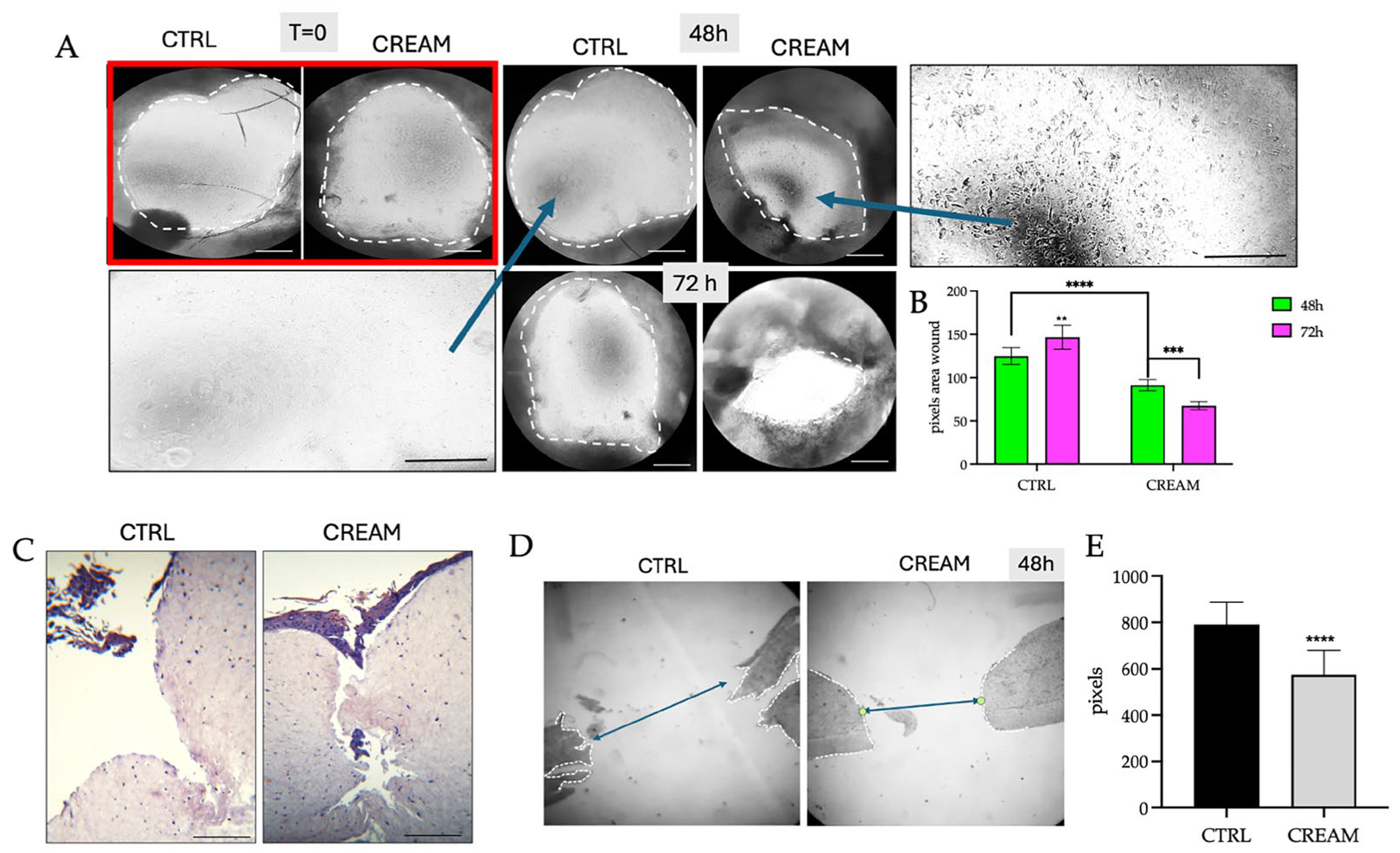
2.4. Wound Healing Measurements on Reconstructed Human Skin Models
2.5. Skin Irritation and UVB Irradiation Treatments on Reconstructed Human Skin Models
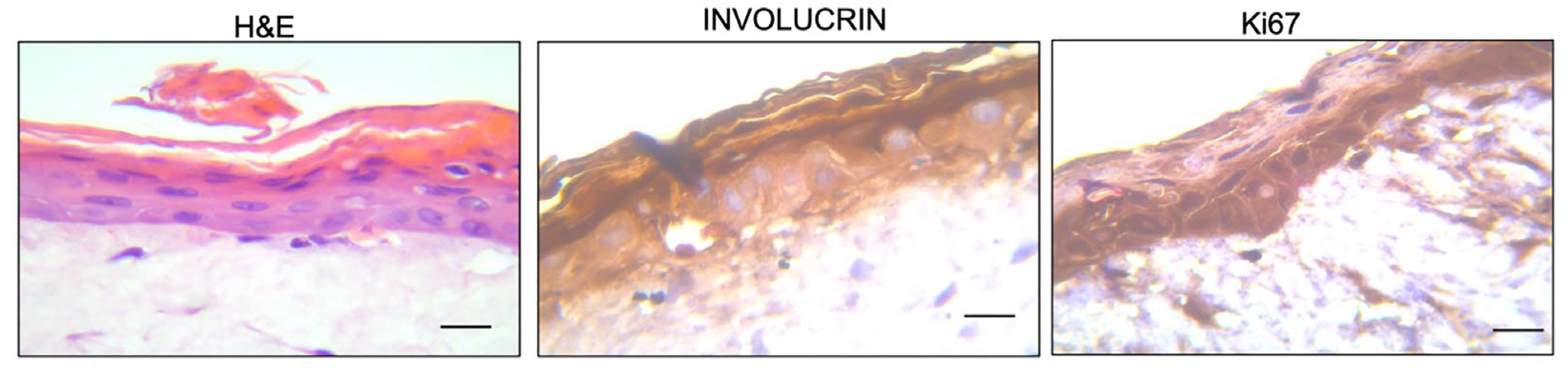
2.6. Morphological Assessment and Immunohistochemical Detection of Involucrin and Ki67
2.7. Viability Measurements
2.8. Determination of Interleukin 1Alpha
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Wound Healing Efficacy of the of Vitamin D2 and Silver Nanoparticle Cream Extract
3.2. Protective Efficacy of the of Vitamin D2 and Silver Nanoparticle Cream Extract in Skin Irritation
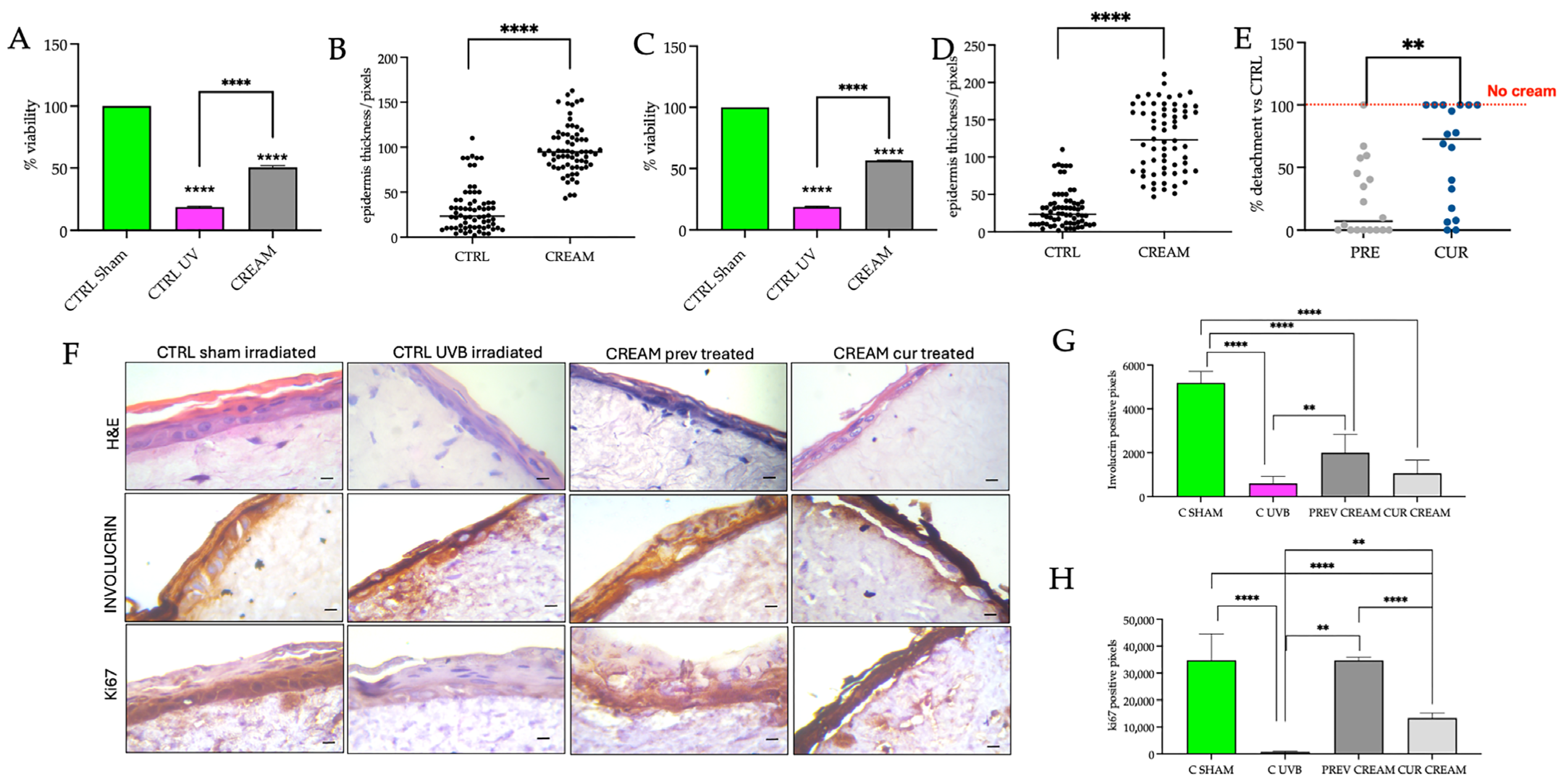
3.3. Protective and Curative Efficacy of the Vitamin D2 and Silver Nanoparticle Cream Extract in Ultraviolet B Irradiation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2D | Two-Dimensional |
| 3D | Three-Dimensional |
| AgNPs | Silver Nanoparticles |
| CTRL | Control |
| DEJ | Dermal-Epidermal Junction |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| HBSS | Hanks’ Balanced Salt Solution |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| IL-1α | Interleukin 1alpha |
| RHS | Reconstructed Human Skin |
| SB | Stratum Basal |
| SC | Stratum Corneum |
| SG | Stratum Granulosum |
| SS | Stratum Spinosum |
| SDS | Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate |
| USD | United States dollar |
| UVB | Ultraviolet B light |
| VD2 | Vitamin D2 |
| VD3 | Vitamin D3 |
References
- Skin Repair Market Size and Growth 2024 to 2033. Available online: https://www.precedenceresearch.com/skin-repair-market (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Global Sun Protection Market 2024–2033. Available online: https://www.custommarketinsights.com/report/sun-protection-market/ (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Michalak, M. Plant extracts as skin care and therapeutic agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resende, D.I.S.P.; Jesus, A.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Sousa, E.; Cruz, M.T.; Cidade, H.; Almeida, I.F. Up-to-date overview of the use of natural ingredients in sunscreens. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janjetovic, Z.; Slominski, A.T. Promising functions of novel vitamin D derivatives as cosmetics: A new fountain of youth in skin aging and skin protection. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat-Ali, M.; Bubshait, D.A.; Al-Turki, H.A.; Al-Dakheel, D.A.; Al-Olayani, W.S. Topical delivery of vitamin d3: A randomized controlled pilot study. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2014, 10, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crintea, A.; Dutu, A.G.; Sovrea, A.; Constantin, A.M.; Samasca, G.; Masalar, A.L.; Ifju, B.; Linga, E.; Neamti, L.; Tranca, R.A.; et al. Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery: An Overview with Emphasis on Vitamin D and K Transportation. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavda, V.P.; Acharya, D.; Hala, V.; Vora, L.; Dawre, S. Sunscreens: A comprehensive review with the application of nanotechnology. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 86, 104720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.S.; Panja, A.; Dutta, S.; Prasun, P. Advancements in nanoparticles for skin care: A comprehensive review of properties, applications, and future perspectives. Discov. Mater. 2024, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanli, T.; Kilfoyle, B.E.; Zhang, Z.; Michniak-Kohn, B.B. Polymeric nanospheres for topical delivery of vitamin D3. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 516, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldi, S.; Ceccarini, M.R.; Patria, F.; Beccari, T.; Mandarano, M.; Ferri, I.; Lazzarini, A.; Curcio, F.; Albi, E. The effect of vitamin D3 and silver nanoparticles on HaCaT Cell Viability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patria, F.F.; Ceccarini, M.R.; Codini, M.; Conte, C.; Perioli, L.; Beccari, T.; Albi, E. A role for neutral sphingomyelinase in wound healing induced by keratinocyte proliferation upon 1a, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, A.; Tandi, A.; Moharana, S.; Chakroborty, S.; Mohapatra, S.S.; Mondal, A.; Dey, S.; Chandra, P. Silver nanoparticle for biomedical applications: A review. Hybrid. Adv. 2024, 6, 100184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, G.; Cataldi, S.; Mandarano, M.; Albi, E. Agaric extract and colloidal silver promote skin health and wound repair. Appl. Cosmetol. 2023, 41, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, E.; Fink, J.; Pignet, A.-L.; Schwarz, A.; Schellnegger, M.; Nischwitz, S.P.; Holzer-Geissler, J.C.J.; Kamolz, L.-P.; Kotzbeck, P. Human in vitro skin models for wound healing and wound healing disorders. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piasek, A.M.; Levkovych, I.; Musolf, P.; Chmielewska, H.; Ścieżyńska, A.; Sobiepanek, A. Building up skin models for numerous applications—From two-Dimensional (2D) monoculture to three-Dimensional (3D) multiculture. J. Vis. Exp. 2023, 200, e65773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, F.; Augello, F.R.; Ciafarone, A.; Ciummo, V.; Altamura, S.; Cinque, B.; Palumbo, P. 3D Models currently proposed to investigate human skin aging and explore preventive and reparative approaches: A descriptive review. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truzzi, F.; Saltari, A.; Palazzo, E.; Lotti, R.; Petrachi, T.; Dallaglio, K.; Gemelli, C.; Grisendi, G.; Dominici, M.; Pincelli, C.; et al. CD271 mediates stem cells to early progeny transition in human epidermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Pintado, M.; Tavaria, F.K. A systematic review of natural products for skin applications: Targeting inflammation, wound healing, and photo-aging. Phytomedicine 2023, 115, 154824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincelli, C.; Haake, A.R.; Benassi, L.; Grassilli, E.; Magnoni, C.; Ottani, D.; Polakowska, R.; Franceschi, C.; Giannetti, A. Autocrine Nerve Growth Factor Protects Human Keratinocytes from Apoptosis Through its High Affinity Receptor (TRK): A Role for BCL-2. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1997, 109, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, L.G.; Wu, X.; Guan, J.L. Wound-healing assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2005, 294, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Truzzi, F.; Dilloo, S.; Chang, X.; Whittaker, A.; D’Amen, E.; Dinelli, G. Basic three-dimensional (3D) intestinal model system with an immune component. J. Vis. Exp. 2023, 199, e65484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandárová, H.; Hayden, P.; Klausner, M.; Kubilus, J.; Sheasgreen, J. An in vitro skin irritation test (SIT) using the EpiDerm reconstructed human epidermal (RHE) model. J. Vis. Exp. 2009, 13, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Bhat, S.S.; Singh, N.; Venkanna, B.U.; Mohamed, R.; Rao, R.P. Cell-Based Model systems for validation of various efficacy-based claims for cosmetic ingredients. Cosmetics 2022, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltari, A.; Truzzi, F.; Quadri, M.; Lotti, R.; Palazzo, E.; Grisendi, G.; Tiso, N.; Marconi, A.; Pincelli, C. CD271 Down-regulation promotes melanoma progression and invasion in three-dimensional models and in Zebrafish. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 2049–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, M.; Fullard, N.; Costello, L.; Bradbury, S.; Markiewicz, E.; O’Reilly, S.; Darling, N.; Ritchie, P.; Määttä, A.; Karakesisoglou, I.; et al. Bioengineering the microanatomy of human skin. J. Anat. 2019, 234, 438–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoio, P.; Ventura, S.; Leite, M.; Oliva, A. Pigmented Full-Thickness Human Skin Model Based on a Fibroblast-Derived Matrix for Long-Term Studies. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods J. Anat. 2021, 27, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastar, I.; Stojadinovic, O.; Yin, N.C.; Ramirez, H.; Nusbaum, A.G.; Sawaya, A.; Patel, S.B.; Khalid, L.; Isseroff, R.R.; Tomic-Canic, M. Epithelialization in wound healing: A Comprehensive Review. Adv. Wound Care 2014, 3, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghalbzouri, A.; Hensbergen, P.; Gibbs, S.; Kempenaar, J.; van der Schors, R.; Ponec, M. Fibroblasts facilitate re-epithelialization in wounded human skin equivalents. Lab. Investig. 2004, 84, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balko, S.; Kerr, E.; Buchel, E.; Logsetty, S.; Raouf, A.A. Robust and standardized approach to quantify wound closure using the scratch assay. Methods Protoc. 2023, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landén, N.X.; Li, D.; Ståhle, M. Transition from inflammation to proliferation: A critical step during wound healing. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3861–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lee, P.Y.; Ho, C.M.; Lui, V.C.; Chen, Y.; Che, C.M.; Tam, P.K.; Wong, K.K. Silver nanoparticles mediate differential responses in keratinocytes and fibroblasts during skin wound healing. Chem. Med. Chem. 2010, 5, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Wu, P.; Ho, J.K.; Jin, R.; Zhang, L.; Shao, H.; Han, C. Silver nanoparticle loaded collagen/chitosan scaffolds promote wound healing via regulating fibroblast migration and macrophage activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, E.-Y.; Jin, H.; Park, Y. Assessing the antioxidant, cytotoxic, apoptotic and wound healing properties of silver nanoparticles green-synthesized by plant extracts. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 101, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, K.; Chen, Z.; Ganapa, T.; Wu, B.M.; Tawil, B.; Linsley, C.S. Keratinocyte migration in a three-dimensional in vitro wound healing model co-cultured with fibroblasts. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 15, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, S.; Krieg, T.; Smola, H. Keratinocyte-fibroblast interactions in wound healing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyavambiza, C.; Meyer, M.; Meyer, S. Cellular and molecular events of wound healing and the potential of silver based nanoformulations as wound healing agents. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitoussi, R.; Vie, K.; Mathieu, É.; Gooris, É.; Hemmerlé, J. TEM assessments of the restructuring effects of an emollient cream on the stratum corneum. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. Sci. Appl. 2011, 1, 8847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kim, H.; Choi, J.; Oh, S.M.; Park, J.; Park, K. Skin corrosion and irritation test of sunscreen nanoparticles using reconstructed 3D human skin model. Environ. Health Toxicol. 2014, 29, e2014004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Choi, J.; Lee, H.; Park, J.; Yoon, B.I.; Jin, S.M.; Park, K. Skin corrosion and irritation test of nanoparticles using reconstructed three-dimensional human skin model, EpiDermTM. Toxicol. Res. 2016, 32, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F.F.; Nowakowski, S.; Kluger, P.J. Improvement of a three-layered in vitro skin model for topical application of irritating substances. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komine, M.; Rao, L.S.; Freedberg, I.M.; Simon, M.; Milisavljevic, V.; Blumenberg, M. Interleukin-1 induces transcription of keratin K6 in human epidermal keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 116, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masri, S.; Fauzi, M.B.; Rajab, N.F.; Lee, W.H.; Zainal Abidin, D.A.; Siew, E.L. In vitro 3D skin culture and its sustainability in toxicology: A narrative review. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2024, 52, 476–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Orazio, J.; Jarrett, S.; Amaro-Ortiz, A.; Scott, T. UV radiation and the skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 12222–12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernerd, F.; Asselineau, D. Successive alteration and recovery of epidermal differentiation and morphogenesis after specific UVB-damages in skin reconstructed in vitro. Dev. Biol. 1997, 183, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelièvre, D.; Canivet, F.; Thillou, F.; Tricaud, C.; Le Floc’h, C.; Bernerd, F. Use of reconstructed skin model to assess the photoprotection afforded by three sunscreen products having different SPF values against DNA lesions and cellular alterations. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2024, 19, 100213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Kang, W.; Choi, D.; Roh, J.; Park, T. Dihydromyrcenol modulates involucrin expression through the Akt signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravcová, M.; Libra, A.; Dvořáková, J.; Víšková, A.; Muthný, T.; Velebný, V.; Kubala, L. Modulation of keratin 1, 10 and involucrin expression as part of the complex response of the human keratinocyte cell line HaCaT to ultraviolet radiation. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2013, 6, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Hong, Y.D.; Son, E.D.; Cho, S.Y. β-endorphin suppresses ultraviolet B irradiation-induced epidermal barrier damage by regulating inflammation-dependent mTORC1 signaling. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Chang, R.; Ye, T.; Li, Z.; Huang, R.; Wang, Z.; Deng, J.; Xia, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. Dermal injection of recombinant filaggrin-2 ameliorates UVB-induced epidermal barrier dysfunction and photoaging. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, T.; Hachiya, A.; Kusaka, A.; Sriwiriyanont, P.; Visscher, M.O.; Morita, K.; Muto, M.; Miyachi, Y.; Sugiyama, Y.; Inoue, S. Characterization of tight junctions and their disruption by UVB in human epidermis and cultured keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.J.S.; Vani, M.G.; Wang, S.Y. Limonene protects human skin keratinocytes against UVB-induced photodamage and photoaging by activating the Nrf2-dependent antioxidant defense system. Environ. Toxicol. 2022, 37, 2897–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, T.L.; Lonkhuyzen, D.; Dawson, R.; Kimlin, M.; Upton, Z. Characterization of a human skin equivalent model to study the effects of ultraviolet B radiation on keratinocytes. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2013, 20, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Los Santos Gomez, P.; Costello, L.; Goncalves, K.; Przyborski, S. Comparison of photodamage in non-pigmented and pigmented human skin equivalents exposed to repeated ultraviolet radiation to investigate the role of melanocytes in skin photoprotection. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1355799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, S.; Tyagi, N.; Bhardwaj, A.; Rusu, L.; Palanki, R.; Vig, K.; Singh, S.R.; Singh, A.P.; Palanki, S.; Miller, M.E.; et al. Silver nanoparticles protect human keratinocytes against UVB radiation-induced DNA damage and apoptosis: Potential for prevention of skin carcinogenesis. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiprasongsuk, A.; Janjetovic, Z.; Kim, T.K.; Jarrett, S.G.; D’Orazio, J.A.; Holick, M.F.; Tang, E.K.Y.; Tuckey, R.C.; Panich, U.; Li, W.; et al. Protective effects of novel derivatives of vitamin D3 and lumisterol against UVB-induced damage in human keratinocytes involve activation of Nrf2 and p53 defense mechanisms. Redox Biol. 2019, 24, 101206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.Y.; Sun, D.S.; Chang, H.H. Silver nanoparticles protect skin from ultraviolet B-induced damage in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Truzzi, F.; Tibaldi, C.; Dilloo, S.; Saltari, A.; Levesque, M.P.; Arcangeli, F.; Garzi, A.; Ruggiero, G.; Dinelli, G. Topical Administration of Vitamin D2 Combined with Colloidal Silver Nanoparticles Promotes Wound Repair and Protection Against Skin Irritation and UVB Irradiation in 3D Reconstructed Human Skin Models. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040472
Truzzi F, Tibaldi C, Dilloo S, Saltari A, Levesque MP, Arcangeli F, Garzi A, Ruggiero G, Dinelli G. Topical Administration of Vitamin D2 Combined with Colloidal Silver Nanoparticles Promotes Wound Repair and Protection Against Skin Irritation and UVB Irradiation in 3D Reconstructed Human Skin Models. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(4):472. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040472
Chicago/Turabian StyleTruzzi, Francesca, Camilla Tibaldi, Silvia Dilloo, Annalisa Saltari, Mitchell P. Levesque, Fabio Arcangeli, Alfredo Garzi, Giuseppe Ruggiero, and Giovanni Dinelli. 2025. "Topical Administration of Vitamin D2 Combined with Colloidal Silver Nanoparticles Promotes Wound Repair and Protection Against Skin Irritation and UVB Irradiation in 3D Reconstructed Human Skin Models" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 4: 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040472
APA StyleTruzzi, F., Tibaldi, C., Dilloo, S., Saltari, A., Levesque, M. P., Arcangeli, F., Garzi, A., Ruggiero, G., & Dinelli, G. (2025). Topical Administration of Vitamin D2 Combined with Colloidal Silver Nanoparticles Promotes Wound Repair and Protection Against Skin Irritation and UVB Irradiation in 3D Reconstructed Human Skin Models. Pharmaceutics, 17(4), 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040472








