The Prediction of the In Vitro Release Curves for PLGA-Based Drug Delivery Systems with Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PLGA Carrier Characteristics
2.2. Drug Molecular Descriptors
2.3. The Dataset Construction and Experimental Conditions
2.4. Model Design and Training
2.5. Comparative Semi-Empirical Models
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Training and Verification Results for Neural Networks
3.2. Comparison Between DrugNet and Semi-Empirical Models
3.2.1. The Semi-Empirical Models
3.2.2. DrugNet
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trucillo, P. Drug carriers: Classification, administration, release profiles, and industrial approach. Processes 2021, 9, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghitman, J.; Biru, E.I.; Stan, R.; Iovu, H. Review of hybrid PLGA nanoparticles: Future of smart drug delivery and theranostics medicine. Mater. Des. 2020, 193, 108805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danhier, F.; Ansorena, E.; Silva, J.M.; Coco, R.; Le Breton, A.; Préat, V. PLGA-based nanoparticles: An overview of biomedical applications. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.; Ahmed, N.; ur Rehman, A. Recent applications of PLGA based nanostructures in drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagreca, E.; Onesto, V.; Di Natale, C.; La Manna, S.; Netti, P.A.; Vecchione, R. Recent advances in the formulation of PLGA microparticles for controlled drug delivery. Prog. Biomater. 2020, 9, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzegar-Jalali, M. Kinetic analysis of drug release from nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 11, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, L.P.; Ghazali, M.; Ashrafi, H.; Azadi, A. A comparison of models for the analysis of the kinetics of drug release from PLGA-based nanoparticles. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Peng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shukla, A.J. Application of artificial neural networks in the design of controlled release drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1201–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekoya, O.C.; Yibowei, M.E.; Adekoya, G.J.; Sadiku, E.R.; Hamam, Y.; Ray, S.S. A mini-review on the application of machine learning in polymer nanogels for drug delivery. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, S141–S144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, P.; Atyabi, F.; Dinarvand, R. The significance of artificial intelligence in drug delivery system design. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 151, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafienia, M.; Amiri, M.; Janmaleki, M.; Sadeghian, A. Application of artificial neural networks in controlled drug delivery systems. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2010, 24, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, J.; Ibrić, S.; Betz, G.; Đurić, Z. Optimization of matrix tablets controlled drug release using Elman dynamic neural networks and decision trees. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 428, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshari, S.H.; Chang, D.P.; Wang, N.B.; Zarraga, I.E.; Rajagopal, K.; Lenhoff, A.M.; Wagner, N.J. Data-driven development of predictive models for sustained drug release. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 3582–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Householder, K.T.; DiPerna, D.M.; Chung, E.P.; Wohlleb, G.M.; Dhruv, H.D.; Berens, M.E.; Sirianni, R.W. Intravenous delivery of camptothecin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for the treatment of intracranial glioma. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 479, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malathi, S.; Nandhakumar, P.; Pandiyan, V.; Webster, T.J.; Balasubramanian, S. Novel PLGA-based nanoparticles for the oral delivery of insulin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar]
- Alai, M.; Lin, W.J. Application of nanoparticles for oral delivery of acid-labile lansoprazole in the treatment of gastric ulcer: In vitro and in vivo evaluations. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 4029–4041. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donnell, A.; Moollan, A.; Baneham, S.; Ozgul, M.; Pabari, R.M.; Cox, D.; Kirby, B.P.; Ramtoola, Z. Intranasal and intravenous administration of octa-arginine modified poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles facilitates central nervous system delivery of loperamide. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.B.; Cho, H.Y.; Kim, D.D.; Choi, H.G.; Lee, Y.B. Preparation and evaluation of tacrolimus-loaded nanoparticles for lymphatic delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 74, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Gu, X. Preparation, characterization, and in vivo study of rhein-loaded poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles for oral delivery. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 2301–2309. [Google Scholar]
- Chereddy, K.K.; Lopes, A.; Koussoroplis, S.; Payen, V.; Moia, C.; Zhu, H.; Sonveaux, P.; Carmeliet, P.; des Rieux, A.; Vandermeulen, G.; et al. Combined effects of PLGA and vascular endothelial growth factor promote the healing of non-diabetic and diabetic wounds. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 1975–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, M.J.; Loureiro, J.A.; Gomes, B.; Frasco, M.F.; Coelho, M.A.; Pereira, M.C. PLGA nanoparticles as a platform for vitamin D-based cancer therapy. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1306–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruozi, B.; Belletti, D.; Sharma, H.S.; Sharma, A.; Muresanu, D.F.; Mössler, H.; Forni, F.; Vandelli, M.A.; Tosi, G. PLGA nanoparticles loaded cerebrolysin: Studies on their preparation and investigation of the effect of storage and serum stability with reference to traumatic brain injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 52, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darvishi, B.; Manoochehri, S.; Kamalinia, G.; Samadi, N.; Amini, M.; Mostafavi, S.H.; Maghazei, S.; Atyabi, F.; Dinarvand, R. Preparation and antibacterial activity evaluation of 18-β-glycyrrhetinic acid loaded PLGA nanoparticles. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2015, 14, 373. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pahuja, R.; Seth, K.; Shukla, A.; Shukla, R.K.; Bhatnagar, P.; Chauhan, L.K.S.; Saxena, P.N.; Arun, J.; Chaudhari, B.P.; Patel, D.K.; et al. Trans-blood brain barrier delivery of dopamine-loaded nanoparticles reverses functional deficits in parkinsonian rats. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4850–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, R.; Kan, P.L.; Awad, G.; Mortada, N.; Abd-Elhameed, E.S.; Alpar, O. Enhanced properties of discrete pulmonary deoxyribonuclease I (DNaseI) loaded PLGA nanoparticles during encapsulation and activity determination. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 408, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolate, A.; Kore, G.; Lesimple, P.; Baradia, D.; Patil, S.; Hanrahan, J.W.; Misra, A. Polymer assisted entrapment of netilmicin in PLGA nanoparticles for sustained antibacterial activity. J. Microencapsul. 2015, 32, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menale, C.; Piccolo, M.T.; Favicchia, I.; Aruta, M.G.; Baldi, A.; Nicolucci, C.; Barba, V.; Mita, D.G.; Crispi, S.; Diano, N. Efficacy of piroxicam plus cisplatin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles in inducing apoptosis in mesothelioma cells. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, X.Y.; Mei, X.G. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of thienorphine-loaded PLGA nanoparticles. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ren, H.; Han, M.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, Z.F.; Lu, P.; Wang, J.J.; Wang, J.Q.; Mao, Q.J.; Gao, J.Q.; Ouyang, H.W. Repair of spinal cord injury by inhibition of astrocyte growth and inflammatory factor synthesis through local delivery of flavopiridol in PLGA nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6585–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.; Kumar, A.; Sawant, K. Enhanced bioavailability and intestinal uptake of Gemcitabine HCl loaded PLGA nanoparticles after oral delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 60, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verderio, P.; Pandolfi, L.; Mazzucchelli, S.; Marinozzi, M.R.; Vanna, R.; Gramatica, F.; Corsi, F.; Colombo, M.; Morasso, C.; Prosperi, D. Antiproliferative effect of ASC-J9 delivered by PLGA nanoparticles against estrogen-dependent breast cancer cells. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 2864–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, U.; Joshi, G.; Sawant, K. Improvement in antihypertensive and antianginal effects of felodipine by enhanced absorption from PLGA nanoparticles optimized by factorial design. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 35, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Pai, R.S. Optimization (Central Composite Design) and Validation of HPLC Method for Investigation of Emtricitabine Loaded Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles: In Vitro Drug Release and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Studies. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 583090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, D.S.; Athawale, R.B.; Bajaj, A.N.; Shrikhande, S.S.; Goel, P.N.; Nikam, Y.; Gude, R.P. Unraveling the cytotoxic potential of Temozolomide loaded into PLGA nanoparticles. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ghasemian, E.; Vatanara, A.; Rouholamini Najafabadi, A.; Rouini, M.R.; Gilani, K.; Darabi, M. Preparation, characterization and optimization of sildenafil citrate loaded PLGA nanoparticles by statistical factorial design. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, L.; Liu, X.; Yu, H.; Mei, L.; Liu, Z. Effects of Caryota mitis profilin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles in a murine model of allergic asthma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4553–4562. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Czyszczon, E.A.; Reineke, J.J. Delineating intracellular pharmacokinetics of paclitaxel delivered by PLGA nanoparticles. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2013, 3, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.j.; Yuan, Y.; Xing, E.m.; Qin, Y.; Peng, Z.j.; Zhang, Z.p.; Yang, K.y. Optimization of parameters for preparation of docetaxel-loaded PLGA nanoparticles by nanoprecipitation method. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 2013, 33, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, P.; Tuccillo, F.M.; Federico, A.; Napolitano, M.; Borrelli, A.; Melisi, D.; Rimoli, M.G.; Palaia, R.; Arra, C.; Carinci, F. Ibuprofen delivered by poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid)(PLGA) nanoparticles to human gastric cancer cells exerts antiproliferative activity at very low concentrations. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5683–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.S.; Sawant, K.K. Modified nanoprecipitation method for preparation of cytarabine-loaded PLGA nanoparticles. Aaps Pharmscitech. 2010, 11, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, K.L.; Thulasidasan, A.K.T.; Deepa, G.; Anto, R.J.; Kumar, G.V. Purely aqueous PLGA nanoparticulate formulations of curcumin exhibit enhanced anticancer activity with dependence on the combination of the carrier. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 425, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, J.S.; Weller, C.E.; Booth, C.J.; Babar, I.A.; Liang, X.; Slack, F.J.; Saltzman, W.M. Prevention of K-Ras-and Pten-mediated intravaginal tumors by treatment with camptothecin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2011, 1, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannitelli, A.; Grande, R.; Di Stefano, A.; Di Giulio, M.; Sozio, P.; Bessa, L.J.; Laserra, S.; Paolini, C.; Protasi, F.; Cellini, L. Potential antibacterial activity of carvacrol-loaded poly (DL-lactide-co-glycolide)(PLGA) nanoparticles against microbial biofilm. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5039–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; You, L.; Sun, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, P. Shikonin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: A promising strategy for Psoriasis Treatment. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleraky, N.E.; Attia, M.A.; Safwat, M.A. Sertaconazole-PLGA nanoparticles for management of ocular keratitis. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 95, 105539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Chen, F.; Bao, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, M.; He, C.; Wang, Y. Preparation, characterization, and anticancer efficacy of evodiamine-loaded PLGA nanoparticles. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaeifard, P.; Abdi-Ali, A.; Soudi, M.R.; Gamazo, C.; Irache, J.M. Amikacin loaded PLGA nanoparticles against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 93, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, A.; Paolino, D.; Costa, N.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D. Zein-vs PLGA-based nanoparticles containing rutin: A comparative investigation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 118, 111538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmak, G.; Öztürk, M.G.; Gümüşderelioğlu, M. Salinomycin encapsulated PLGA nanoparticles eliminate osteosarcoma cells via inducing/inhibiting multiple signaling pathways: Comparison with free salinomycin. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 101834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

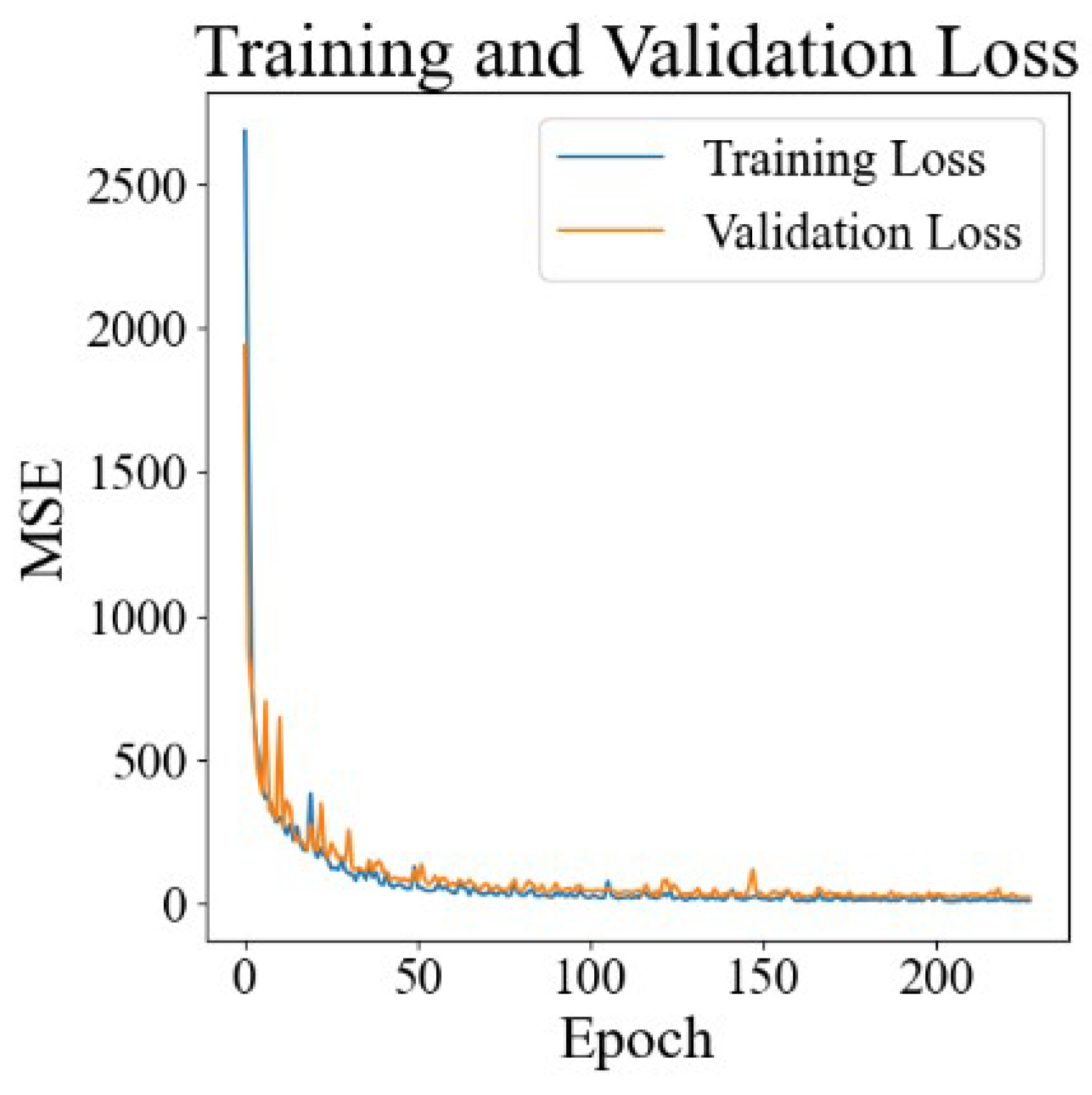
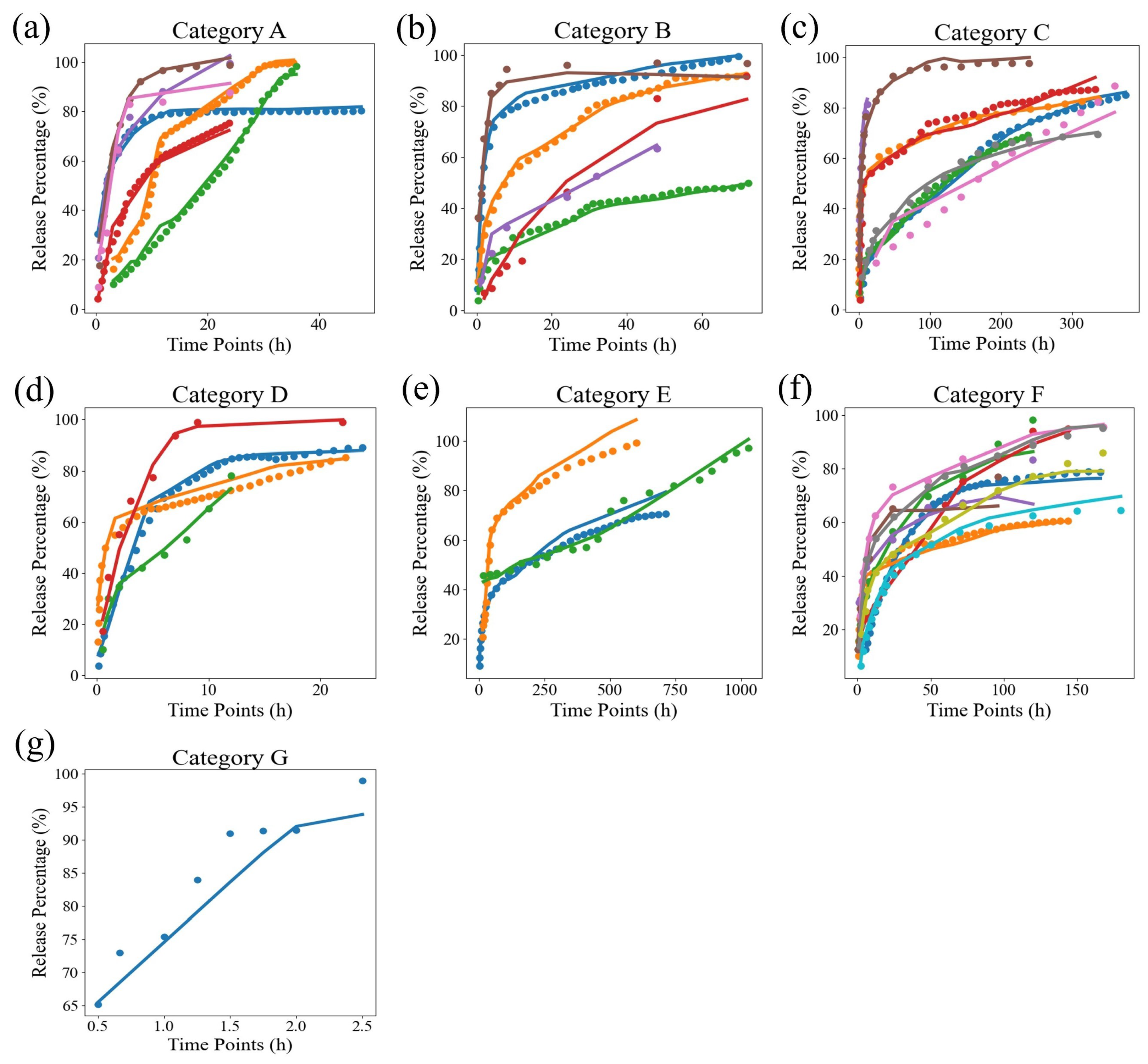
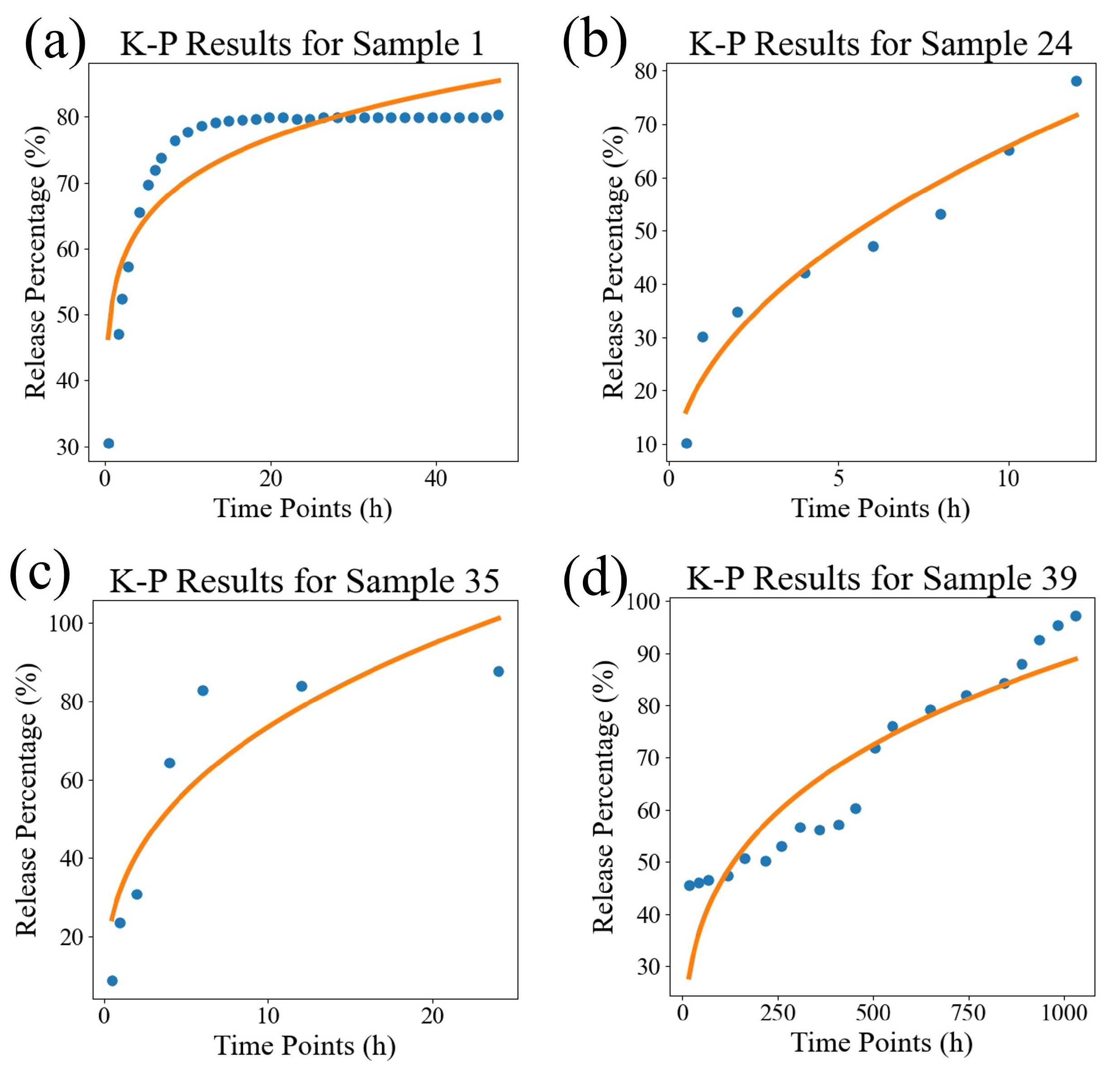
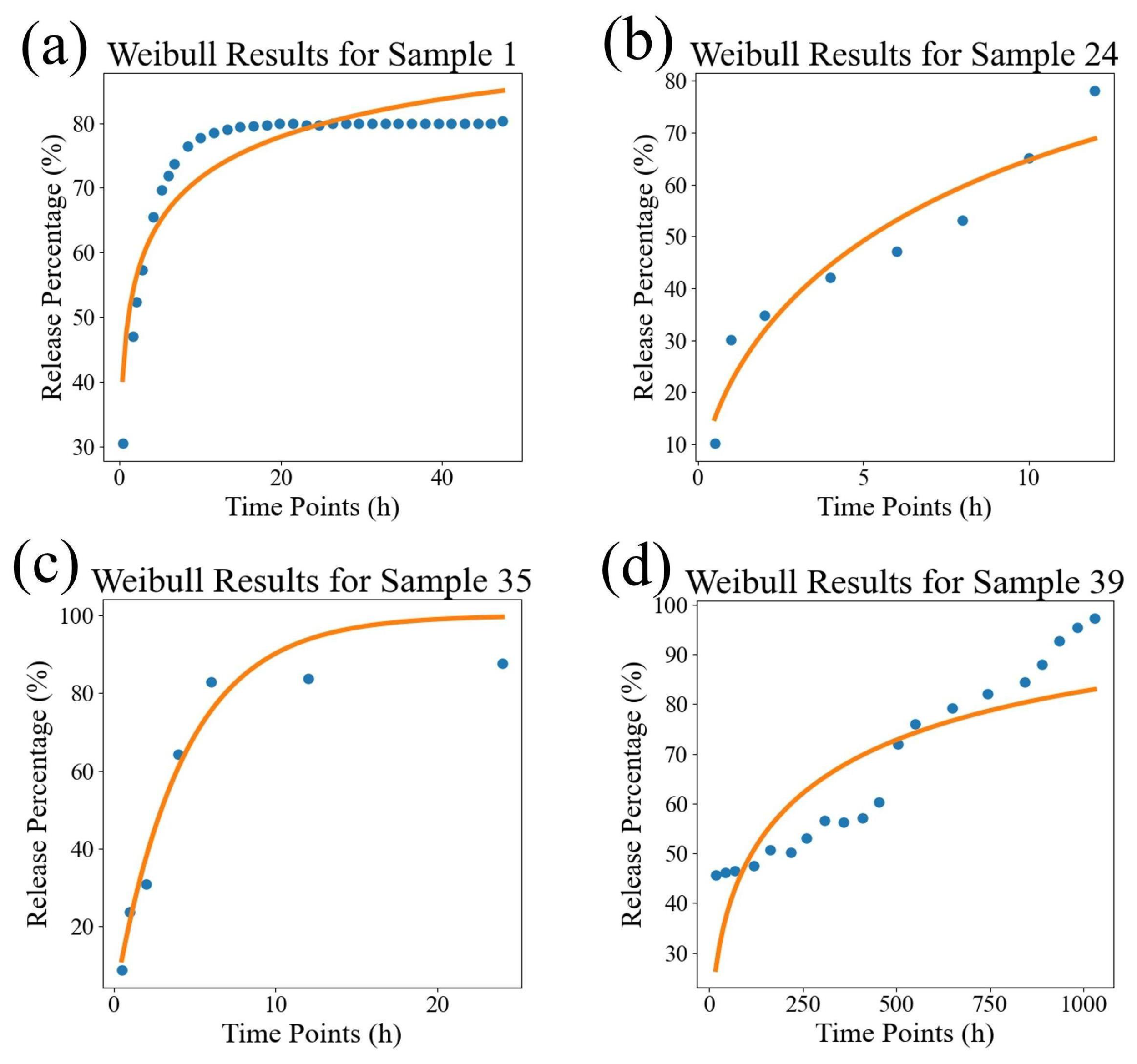

| Drug Name | Source | Release Time Scale | Point Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Camptothecin | [14] | 20–40 (h) | 33 |
| Insulin | [15] | 20–40 (h) | 37 |
| Insulin | [15] | 20–40 (h) | 33 |
| Lansoprazole | [16] | 20–40 (h) | 35 |
| Loperamide | [17] | 40–80 (h) | 35 |
| Tacrolimus | [18] | 200–400 (h) | 35 |
| Rhein | [19] | 10–20 (h) | 35 |
| VEGF | [20] | 400–1000 (h) | 35 |
| Calcitriol | [21] | 100–200 (h) | 35 |
| Cerebrolysin | [22] | 10–20 (h) | 35 |
| 18--glycyrrhetinic acid | [23] | 40–80 (h) | 35 |
| 18--glycyrrhetinic acid | [23] | 40–80 (h) | 35 |
| Dopamine | [24] | 100–200 (h) | 35 |
| DNaseI | [25] | 200–400 (h) | 35 |
| Netilmicin | [26] | 200–400 (h) | 35 |
| Cisplatin | [27] | 200–400 (h) | 35 |
| Thienorphine | [28] | 200–400 (h) | 8 |
| Flavopiridol | [29] | 40–80 (h) | 8 |
| Gemcitabine | [30] | 100–200 (h) | 11 |
| ASC-J9 | [31] | 200–400 (h) | 21 |
| Felodipine | [32] | 100–200 (h) | 11 |
| Emtricitabine | [33] | 200–400 (h) | 15 |
| Temazolamide | [34] | 100–200 (h) | 10 |
| Sildenafil | [35] | 10–20 (h) | 8 |
| Caryota mitis Profilin | [36] | 200–400 (h) | 16 |
| Paclitaxel | [37] | 100–200 (h) | 6 |
| Docetaxel | [38] | 100–200 (h) | 10 |
| Ibuprofen | [39] | 0–10 (h) | 8 |
| Cytarabine | [40] | 20–40 (h) | 7 |
| Curcumin | [41] | 100–200 (h) | 13 |
| Curcumin | [41] | 100–200 (h) | 12 |
| Camptothecin | [42] | 400–1000 (h) | 25 |
| Carvacrol | [43] | 20–40 (h) | 10 |
| Shikonin | [44] | 40–80 (h) | 6 |
| Sertaconazole | [45] | 20–40 (h) | 7 |
| Evodiamine | [46] | 100–200 (h) | 18 |
| Amikacin | [47] | 10–20 (h) | 8 |
| Rutin | [48] | 40–80 (h) | 10 |
| Salinomycin | [49] | 400–1000 (h) | 20 |
| Sample ID | Source | K-P | Weibull | DrugNet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [14] | 27.629 | 17.656 | 2.459 |
| 2 | [15] | 46.751 | 15.429 | 6.175 |
| 3 | [15] | 3.34 | 25.584 | 4.767 |
| 4 | [16] | 14.638 | 4.699 | 5.708 |
| 5 | [17] | 63.628 | 21.99 | 6.719 |
| 6 | [18] | 5.557 | 5.647 | 3.146 |
| 7 | [19] | 49.384 | 9.898 | 5.586 |
| 8 | [20] | 2.746 | 1.875 | 15.638 |
| 9 | [21] | 47.466 | 19.981 | 2.201 |
| 10 | [22] | 16.702 | 12.046 | 20.248 |
| 11 | [23] | 8.957 | 4.159 | 3.05 |
| 12 | [23] | 2.944 | 1.832 | 3.461 |
| 13 | [24] | 9.013 | 6.269 | 3.987 |
| 14 | [25] | 32.36 | 24.187 | 2.616 |
| 15 | [26] | 1.554 | 4.597 | 2.049 |
| 16 | [27] | 39.187 | 29.911 | 8.516 |
| 17 | [28] | 6.631 | 1.129 | 12.594 |
| 18 | [29] | 26.738 | 9.755 | 45.325 |
| 19 | [30] | 3.147 | 12.502 | 17.529 |
| 20 | [31] | 73.67 | 6.492 | 9.065 |
| 21 | [32] | 8.806 | 28.458 | 3.737 |
| 22 | [33] | 3.032 | 13.482 | 37.949 |
| 23 | [34] | 7.718 | 11.115 | 35.374 |
| 24 | [35] | 26.282 | 33.064 | 15.017 |
| 25 | [36] | 6.708 | 3.505 | 4.098 |
| 26 | [37] | 25.273 | 7.703 | 46.85 |
| 27 | [38] | 30.68 | 11.166 | 2.797 |
| 28 | [39] | 4.523 | 6.805 | 16.989 |
| 29 | [40] | 40.652 | 3.897 | 13.56 |
| 30 | [41] | 29.529 | 12.047 | 8.091 |
| 31 | [41] | 5.611 | 8.519 | 7.5 |
| 32 | [42] | 60.37 | 27.353 | 19.663 |
| 33 | [43] | 104.735 | 0.918 | 12.06 |
| 34 | [44] | 2.705 | 3.831 | 11.066 |
| 35 | [45] | 176.78 | 52.661 | 46.605 |
| 36 | [46] | 20.648 | 11.06 | 5.895 |
| 37 | [47] | 123.463 | 10.139 | 25.502 |
| 38 | [48] | 124.397 | 11.997 | 15.682 |
| 39 | [49] | 54.805 | 87.494 | 10.724 |
| avg | - | 34.327 | 14.894 | 13.333 |
| Sample ID | Source | K-P | Weibull | DrugNet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [14] | 0.786 | 0.863 | 0.981 |
| 2 | [15] | 0.928 | 0.976 | 0.991 |
| 3 | [15] | 0.996 | 0.966 | 0.994 |
| 4 | [16] | 0.967 | 0.989 | 0.987 |
| 5 | [17] | 0.892 | 0.963 | 0.989 |
| 6 | [18] | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.994 |
| 7 | [19] | 0.924 | 0.985 | 0.991 |
| 8 | [20] | 0.992 | 0.994 | 0.954 |
| 9 | [21] | 0.891 | 0.954 | 0.995 |
| 10 | [22] | 0.949 | 0.963 | 0.938 |
| 11 | [23] | 0.984 | 0.993 | 0.995 |
| 12 | [23] | 0.98 | 0.988 | 0.977 |
| 13 | [24] | 0.952 | 0.966 | 0.979 |
| 14 | [25] | 0.931 | 0.948 | 0.994 |
| 15 | [26] | 0.996 | 0.987 | 0.994 |
| 16 | [27] | 0.914 | 0.934 | 0.981 |
| 17 | [28] | 0.982 | 0.997 | 0.966 |
| 18 | [29] | 0.974 | 0.990 | 0.955 |
| 19 | [30] | 0.996 | 0.983 | 0.976 |
| 20 | [31] | 0.888 | 0.99 | 0.986 |
| 21 | [32] | 0.988 | 0.96 | 0.995 |
| 22 | [33] | 0.993 | 0.971 | 0.917 |
| 23 | [34] | 0.975 | 0.964 | 0.885 |
| 24 | [35] | 0.933 | 0.915 | 0.961 |
| 25 | [36] | 0.981 | 0.990 | 0.989 |
| 26 | [37] | 0.957 | 0.987 | 0.920 |
| 27 | [38] | 0.94 | 0.978 | 0.994 |
| 28 | [39] | 0.961 | 0.941 | 0.854 |
| 29 | [40] | 0.942 | 0.994 | 0.981 |
| 30 | [41] | 0.957 | 0.983 | 0.988 |
| 31 | [41] | 0.988 | 0.981 | 0.983 |
| 32 | [42] | 0.902 | 0.956 | 0.968 |
| 33 | [43] | 0.856 | 0.999 | 0.983 |
| 34 | [44] | 0.991 | 0.988 | 0.964 |
| 35 | [45] | 0.808 | 0.943 | 0.949 |
| 36 | [46] | 0.937 | 0.966 | 0.982 |
| 37 | [47] | 0.843 | 0.987 | 0.967 |
| 38 | [48] | 0.718 | 0.973 | 0.964 |
| 39 | [49] | 0.829 | 0.727 | 0.967 |
| avg | - | 0.934 | 0.965 | 0.970 |
| Evaluation Indicators | K-P | Weibull | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSE | 39.317 | 15.882 | 12.662 |
| 0.065 | 0.046 | 0.031 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, K. The Prediction of the In Vitro Release Curves for PLGA-Based Drug Delivery Systems with Neural Networks. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040513
Zhang Z, Zhang B, Chen R, Zhang Q, Wang K. The Prediction of the In Vitro Release Curves for PLGA-Based Drug Delivery Systems with Neural Networks. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(4):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040513
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zheng, Bolun Zhang, Ren Chen, Qian Zhang, and Kangjun Wang. 2025. "The Prediction of the In Vitro Release Curves for PLGA-Based Drug Delivery Systems with Neural Networks" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 4: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040513
APA StyleZhang, Z., Zhang, B., Chen, R., Zhang, Q., & Wang, K. (2025). The Prediction of the In Vitro Release Curves for PLGA-Based Drug Delivery Systems with Neural Networks. Pharmaceutics, 17(4), 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040513







