Abstract
In Multimedia Internet of Things (IoT), in order to reduce the bandwidth consumption of wireless channels, Motion-Compensated Frame Rate Up-Conversion (MC-FRUC) is often used to support the low-bitrate video communication. In this paper, we propose a spatial predictive algorithm which is used to improve the performance of MC-FRUC. The core of the proposed algorithm is a predictive model to split a frame into two kinds of blocks: basic blocks and absent blocks. Then an improved bilateral motion estimation is proposed to compute the Motion Vectors (MVs) of basic blocks. Finally, with the spatial correlation of Motion Vector Field (MVF), the MV of an absent block is predicted based on the MVs of its neighboring basic blocks. Experimental results show that the proposed spatial prediction algorithm can improve both the objective and the subjective quality of the interpolated frame, with a low computational complexity.
1. Introduction
Normally, films are played with 24 frames per second and TV programs are broadcasted with a standard frame rate of 30 Hz. Especially in Multimedia Internet of Things (IoT), limited by the bandwidth of wireless channels, the lower frame rate is required when encoding video sequences. Low frame rate can basically meet people’s entertainment needs, but motion blur would occur when a mass of fast movements exists in the video sequences. It is known that video sequences at a high frame rate contain fewer blurs or block artifacts and provide people with a better visual experience. Therefore, in the receiver of Multimedia IoT, we should increase the frame rate of video sequences in order to attract the eyes of the audience. To meet the needs described above, Motion-Compensated Frame Rate Up-Conversion (MC-FRUC) can often be used to convert low-frame-rate videos to high-frame-rate ones.
MC-FRUC, which is gaining extensive attention from scholars in recent years [1,2,3,4,5], is a video processing technique interpolating several new frames between two adjacent original frames. It has a standard flow including Motion Estimation (ME), Motion Vector Smoothing (MVS), Motion Vector Mapping (MVM) and Motion-Compensated Interpolation (MCI), among which the former three are combined to provide the Motion Vector Field (MVF) of the middle frame, and MCI is used to interpolate the new frame according to the above MVF [6].
The quality of the interpolated frames is heavily influenced by the accuracy of MVF, so lots of researches are focused on ME, MVS and MVM. ME is a process of predicting the MVF between two adjacent original frames [7]. Block matching algorithm (BMA), the typical method among various ME algorithms, has an advantage of low complexity over pixel-wise ME [8,9]. The size of one standard block is much smaller than that of one frame, and the pixels of most objects are distributed in different contiguous blocks. In light of that, 3D Recursive Search (3DRS) was proposed based on the spatiotemporal correlation [10]. To track MVs as truly as possible, MVS imposes some smoothness constraints on BMA [11], so that more MV outliers can be effectively suppressed. MVS can also be explicitly implemented by median filtering and penalty terms [12], but this explicit approach increases the computational complexity. After MVS, MVM is used to deduce the MVF of the intermediate frame from the MVF between adjacent original frames [13]. Forward MVM is a common strategy which maps halved MVs along their directions to blocks where they are pointed [14,15]. Little temporal mismatch occurs when performing forward MVM, but some blocks in the intermediate frame could have multiple MVs or no MV, thus introducing overlaps and holes. According to the assumption of temporal symmetry, the bilateral MVM directly performs the Bilateral ME (BME) [16] on the intermediate frame, which avoids block artifacts. However, due to the varying statistics of video sequences, MV outliers always exist, which results in edge blurring and block artifacts in the process of MCI. Some advanced MCI approaches, e.g., Overlapped Block Motion Compensation (OBMC) [17], can reduce some bad effects resulting from MV outliers. Fractal interpolation also can be performed to predict the pixels at fractional coordinates and effectively reduces blurring and block artifacts by providing a pleasant zoom and slow motion [18]. Various research results on ME, MVS, MVM and MCI can be combined flexibly with the MC-FRUC with different performances. Recently, some state-of-the-art methods are continually presented, e.g., Li et al. [19] proposed a MC-FRUC using patch-based sparseland model, Tsai et al. [20] constructed the hierarchical motion field and an MV mapping stage to improve the performance of MC-FRUC and Li et al. [21] used multiple ME schemes to jointly interpolate the frames. However, the performance improvements of these works are at the costs of computational complexity. Similar to natural images, the MVF of video frames also has local stationary statistics [22], which can help MCFI to reduce the computational complexity.
The existing works throw a lot of computations to suppress MV outliers, but the improvement of MV precision is far from satisfactory. We expect a good balance between computations and MVF accuracy, so a Spatial Prediction-based Motion-Compensated Frame Interpolation (SP-MCFI) is proposed in this paper. The contributions of SP-MCFI are listed as follows:
- (1)
- A predictive model defines two kinds of blocks: basic block and absent block. BME is directly performed to compute the MV of basic blocks.
- (2)
- To speed up BME, the Successive Elimination Algorithm (SEA) [23] is used to reduce search candidates, and the block matching is performed with a subsampling pattern.
- (3)
- The MV of absent blocks will be accurately recovered from MVs of its neighboring basic blocks.
Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed SP-MCFI algorithm generates a pleasant up-converted video, and meanwhile, it has a low computational complexity.
2. Proposed SP-MCFI Algorithm
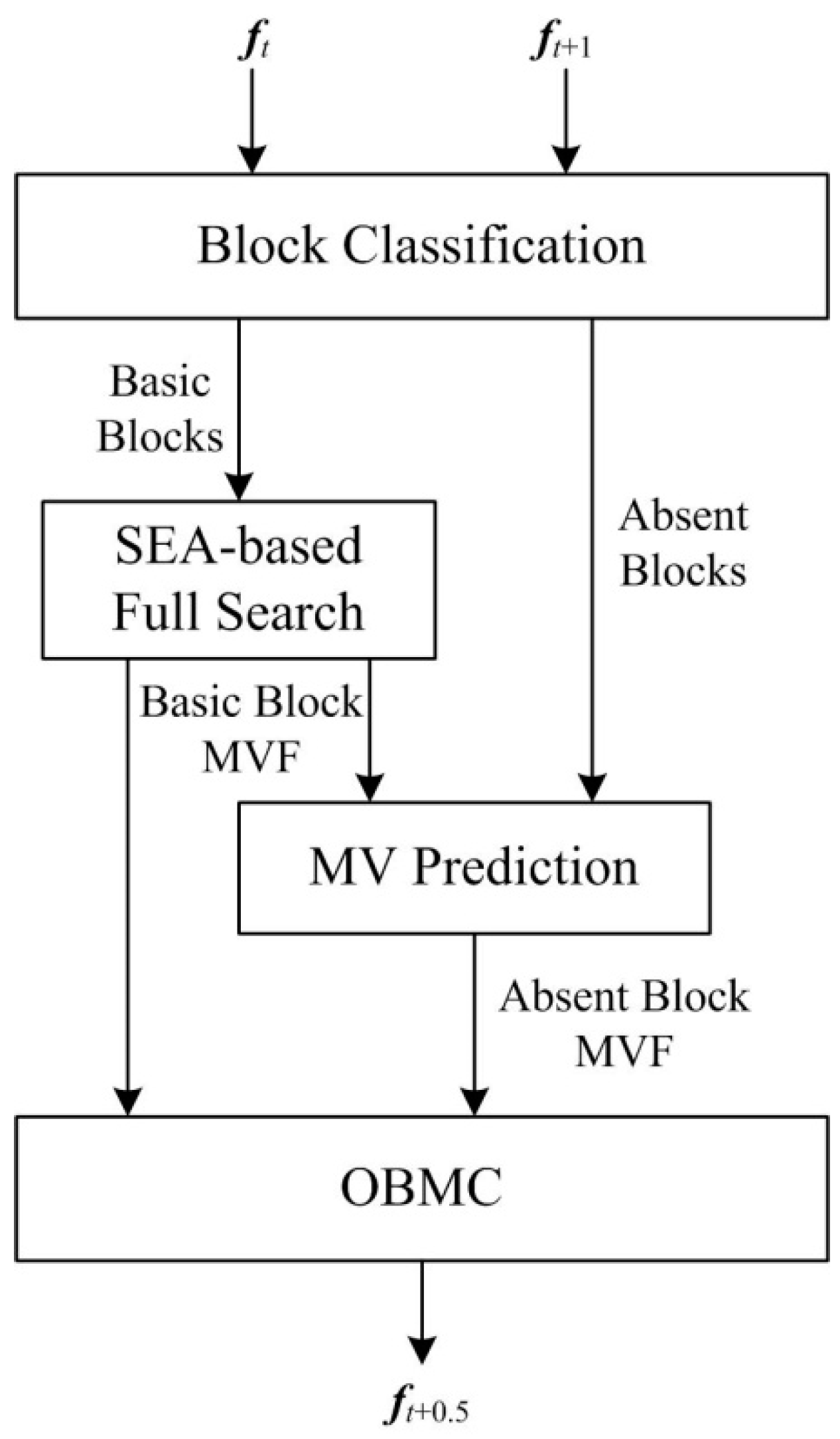
Figure 1 shows the flowchart of the proposed SP-MCFI algorithm. First, a block classification is done to divide the frame into basic blocks and absent blocks. Second, the full search ME based on advanced SEA is utilized to track the MVs of basic blocks. Then, the spatial prediction method is used to achieve the MVs of absent blocks according to the motion information of basic blocks. Finally, the MVs of the two types of blocks are combined to compensate the image of the interpolated frame ft+0.5 with the pixel values of two reference frames ft and ft+1.
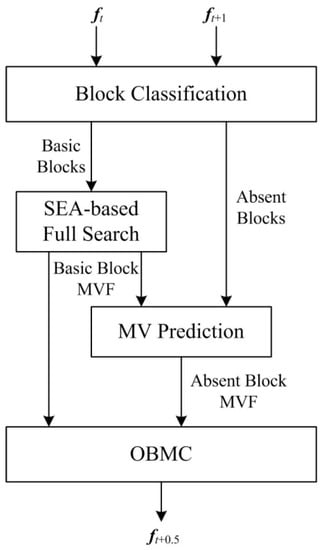
Figure 1.
A flowchart of the proposed SP-MCFI algorithm.
2.1. Block Classification
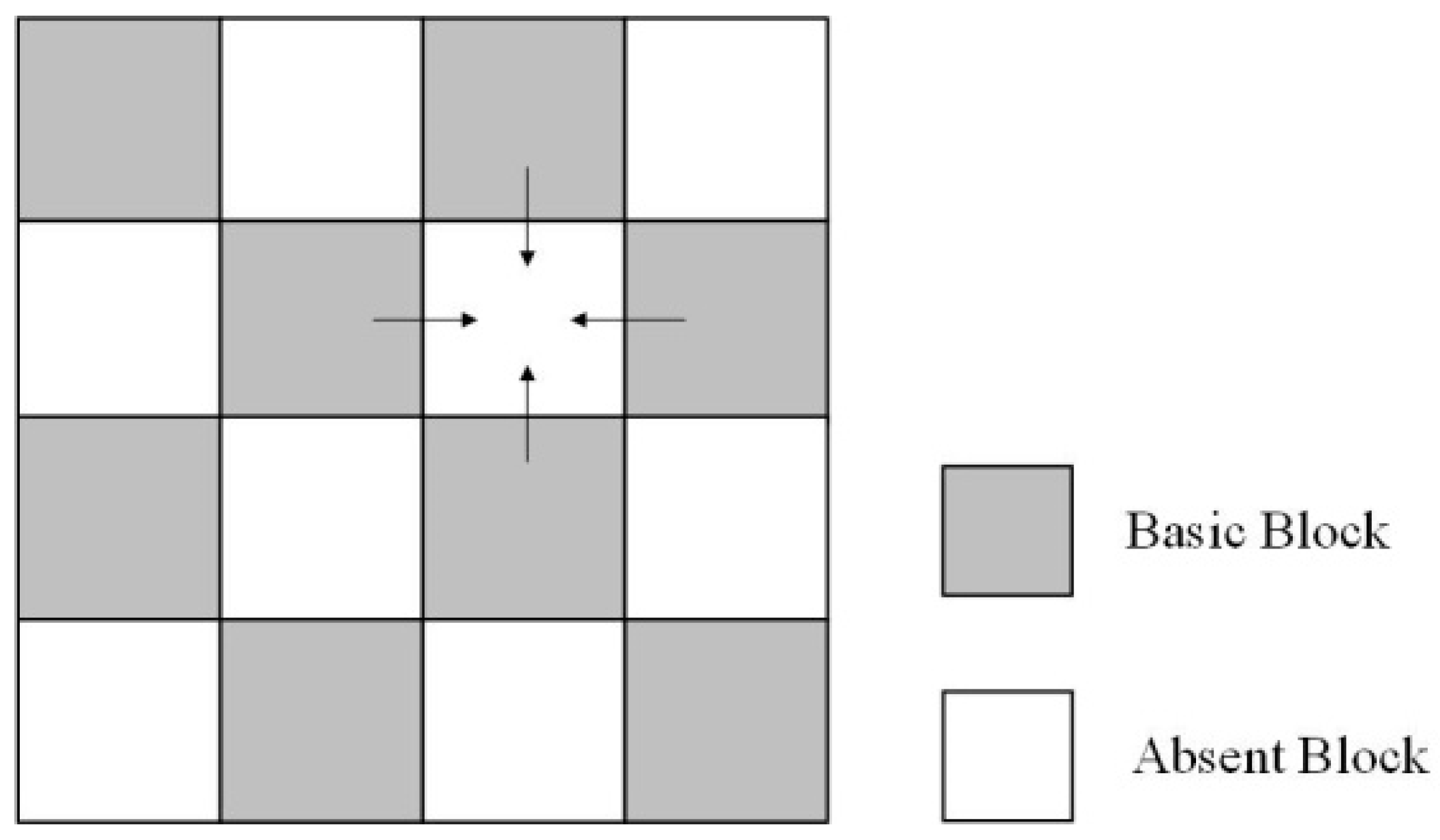
The key to spatial prediction technology is based on the effective use of spatial correlation, and the premise of applying this technique lies in the block classification. Figure 2 shows the block classification model in the spatial prediction technique. The gray blocks represent basic blocks, and the remaining blocks are absent blocks. The two kinds of blocks alternate in horizontal and vertical directions. The MVs of the basic blocks are accurately obtained through BME algorithm, and then the MV of each absent block is calculated by effectively using the motion information of basic blocks adjacent to it.
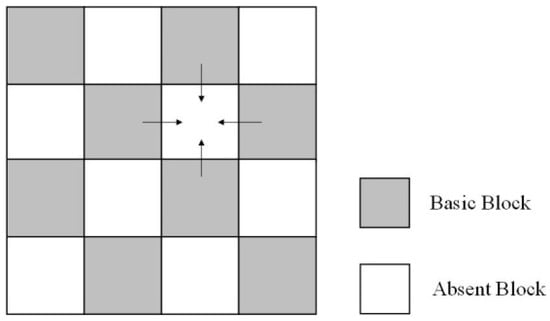
Figure 2.
The block classification model.
2.2. BME for Basic Block
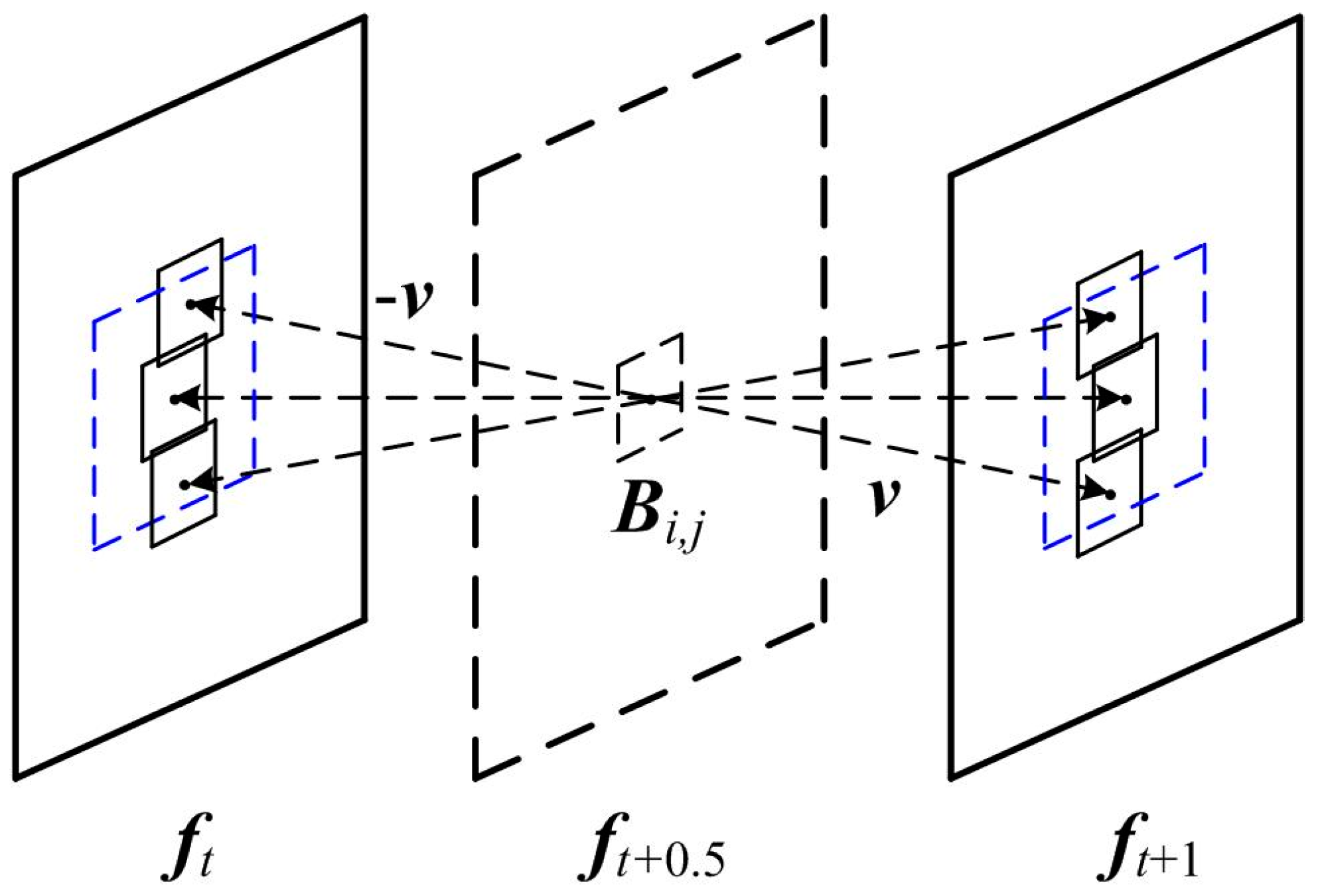
The MV of an absent block is predicted by the MVs of its neighboring basic blocks. A better ME algorithm is needed to guarantee that any basic block has an accurate MV. Therefore, a full search ME is introduced to perform BME algorithm on the basic blocks. As Figure 3 shows, the advantage of a full search ME is that it can match the optimal motion trajectory within the search window, but meanwhile, the disadvantage is obvious. Assuming that the search radius is 8 and the standard block is 16 × 16 in size, we can find that 289 blocks need to be searched in order to find the best matching block. Taking the CIF format as an example, a single video frame of 396 such matching blocks can mean a huge amount of computation for the full search ME algorithm. Therefore, this paper introduces an advanced SEA to reduce the computational complexity.
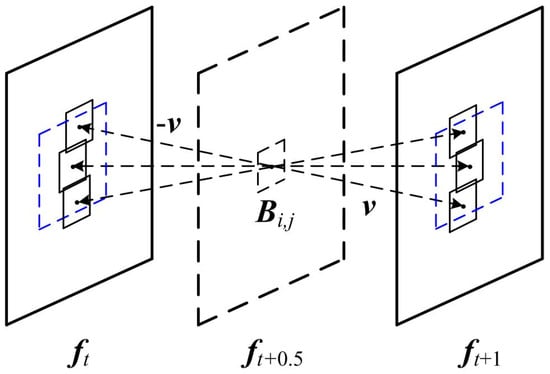
Figure 3.
An illustration of a full search ME.
Assuming that the resolution of the interpolated frame ft+0.5 is M × N and the block size is s × s, each frame would include M × N/s2 standard blocks, and M and N must be divisible by s. The pixel coordinate (i, j) of the upper left corner of each block is used as a reference, and the luminance accumulation sum P of the block (i, j) is calculated respectively in the tth frame and the (t + 1)th frame as follows:
where ft(i + m, j + n) and ft+1(i + m, j + n) denote the luminance at the coordinate of (i + m, j + n) respectively in ft and ft+1 and (m, n) is the coordinate of pixel in the block.
The top-left pixel of the current basic block is set to p (p = (i, j)), then, the candidate blocks in the search window are traversed symmetrically in two reference frames. For reference frame ft+1, the offset of the nth candidate block is = (x, y), and the offset of nth candidate block in the reference frame ft is . When the search window radius is r, x, y ∈ [−r, r], the initial offset is set to (r, r), then the initial difference D0 of the current basic block is calculated in the following formula:
where Bt(i − r, j − r) is the vector in which all the pixels of block (i − r, j − r) in ft are arranged in rows and ||•||1 is the l1-norm of the vector. After calculating D0, the is updated to the next candidate block in the search window; if the following inequality is satisfied,
then the difference Dn of the nth candidate block is calculated as follows:
Update the motion vector vs of the current basic block as follows:
Then, the updated D0 = min{Dn, D0}; otherwise, vs remains unchanged. All the candidate blocks in the search window should be traversed symmetrically according to the above process.
2.3. MV Prediction for Absent Block
After tracking the MVs of the basic blocks by a full search ME, the motion vectors va1, va2, va3 and va4 of the four basic blocks adjacent to the current absent block are selected as candidates. The candidate vector set Vc is composed of the above vectors as follows:
The coordinate of the upper left pixel of the current absent block is set to p, and then the motion vector vp of the absent block is calculated based on the Sum of Bi-direction Absolute Difference (SBAD):
where Bt(p − v) is the vector in which all the pixels of block (p − v) in ft are arranged in rows, ||•||1 is the l1-norm of the vector and v is a candidate vector.
After the MV prediction of the absent blocks is completed, all the MVs of the two kinds of blocks are assembled into the MVF Vt+0.5 of the interpolated frame ft+0.5. The OBMC technique is used to calculate the value of the pixel p = (i, j) in ft+0.5 as follows:
where
vi,j is the MV of Vt+0.5 at p; k represents the three types of the overlapping part: it denotes the non-overlapping part when it is set to 1, the overlapping part of two blocks when it is set to 2 and the overlapping part of four blocks when it is set to 3; and the value of coefficient ω is set to the corresponding value based on the change of k.
3. Experimental Results
In this section, the performance of the proposed SP-MCFI algorithm is evaluated by testing on different video sequences, and then the results are compared with recent state-of-the-arts ME algorithms Dual-ME from [24] and DS-ME from [25]. All test sequences used for the experiments are in the standard CIF (352 × 288) formats and 30 frame/s. In the proposed algorithm, we need to set the two parameters: block size s and radius r of the search window. To make a good balance between the interpolation quality and computational complexity, s and r are both set to be 16. The comparing algorithms keep their original parameter settings. The quality of the interpolated frames will be evaluated from subjective and objective perspectives, and the objective evaluation is to be done by using the Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Structural SIMilarity (SSIM) [26]. All experiments are conducted on a Windows machine with an Intel Core i7 3.40 GHz CPU and a memory of 8 GB. All algorithms are implemented in MATLAB.
3.1. Subjective Evaluation
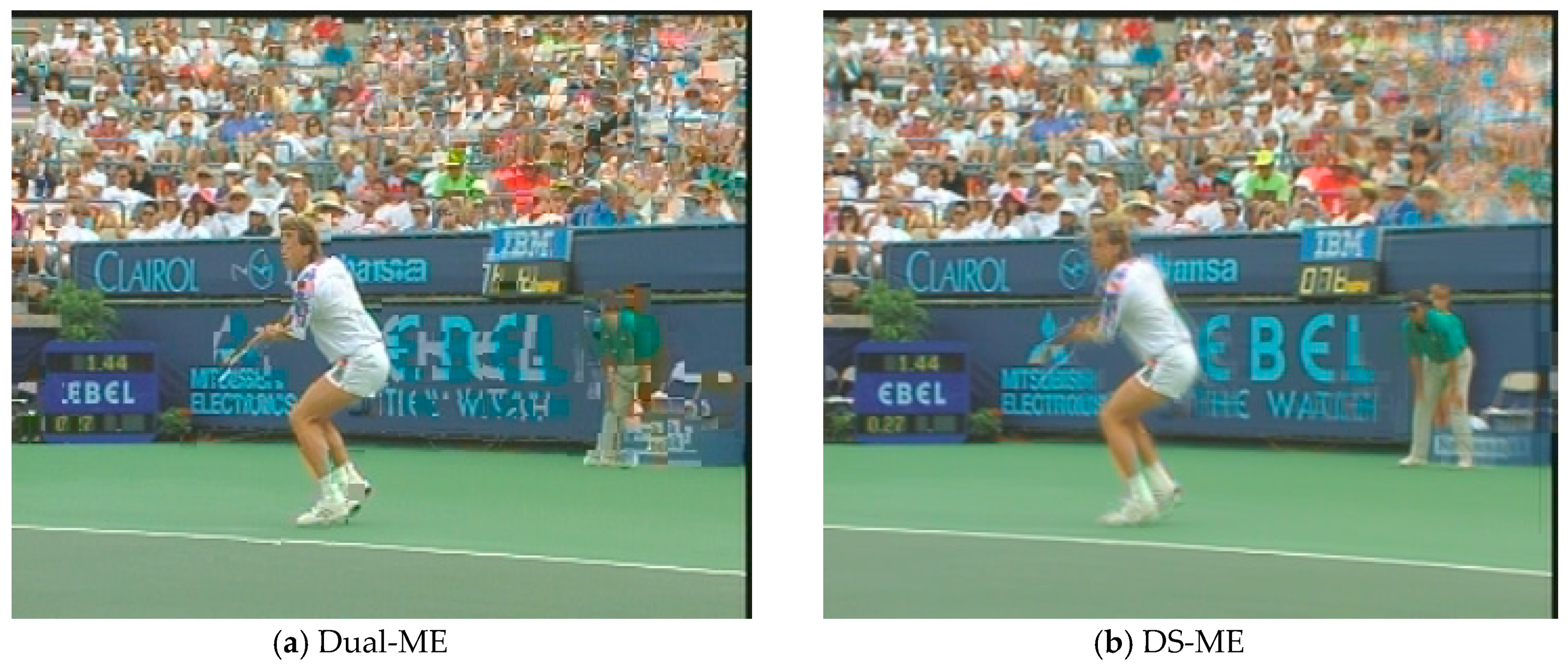
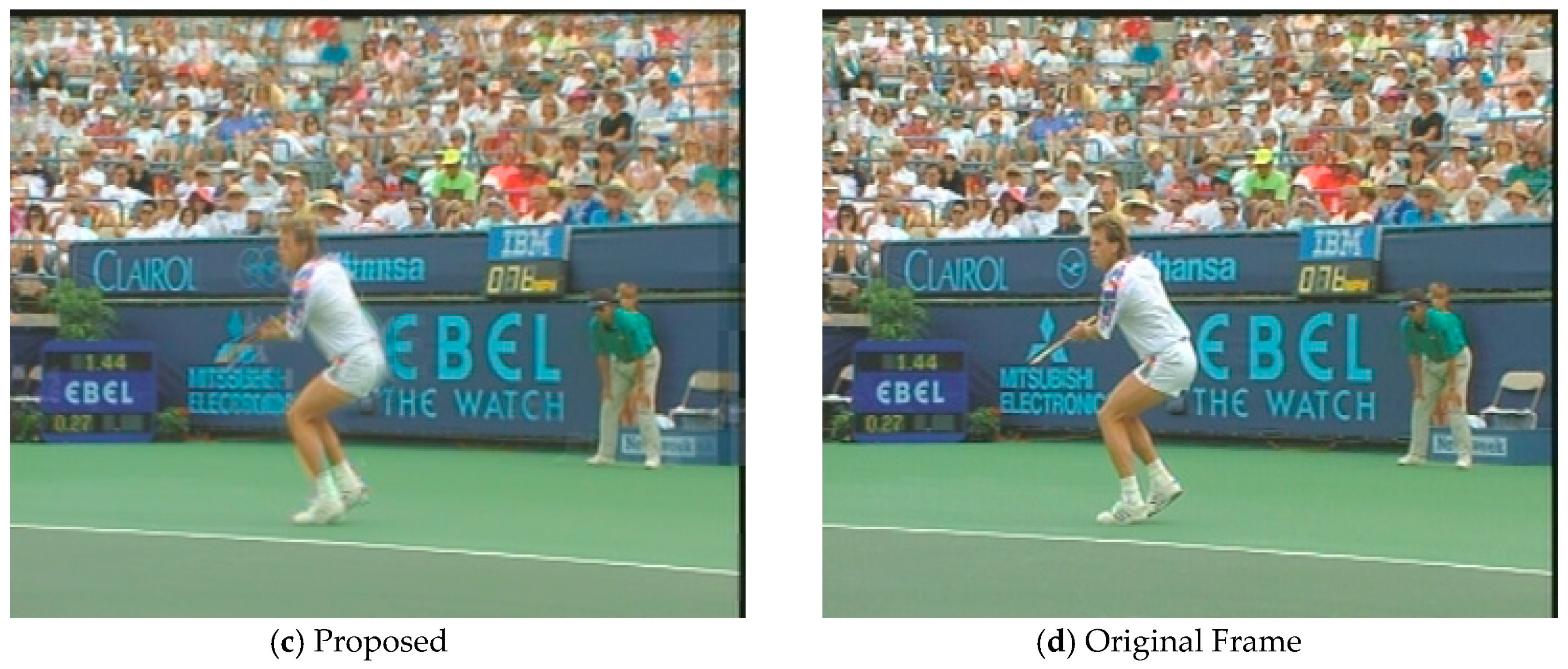
In order to evaluate the subjective visual quality of the proposed SP-MCFI algorithm, we select the video sequences Foreman and Stefan to perform contrast experiments among which Foreman contains moderate scene motion while Stefan has a mass of sharp movements. Figure 4 and Figure 5 shows the interpolated frames of the comparing algorithms and proposed algorithm, and the 78th frame of Foreman and the 88th frame of Stefan are respectively captured as examples. Observing the interpolated frames, we can see that obvious blur and block artifacts appear in the face part when using the comparing algorithms, while the proposed algorithm works out the face part more clearly. As for the interpolated Stefan frames by the two comparing algorithms, there are a large number of blurred backgrounds and malposed billboard fonts while the proposed algorithm can reduce the background blur and provide more details. In general, the proposed algorithm can provide a better subjective visual quality than the comparing algorithms.

Figure 4.
A visual comparison of the Foreman sequence between the three methods.
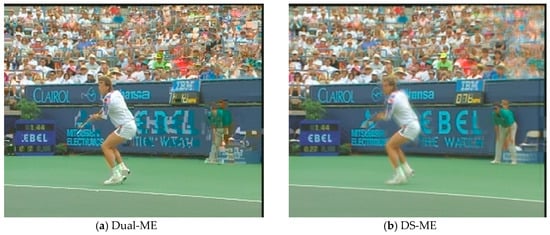
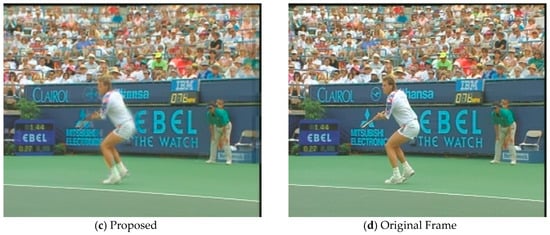
Figure 5.
A visual comparison of the Stefan sequence between the three methods.
3.2. Objective Evaluation
Table 1 shows the PSNR values for different FRUC techniques. For the nine test video sequences, the proposed algorithm significantly improves the PSNR value by a maximum of 2.72 dB and achieves the purpose of improving the quality of the interpolated frame when compared with the Dual-ME method. The DS-ME method can be effectively utilized in the video sequences which are relatively static or contain fewer motions, such as Foreman and Mother. But for videos containing a large number of movements, such as Bus, City, Football, Mobile and Stefan, our algorithm can track the object’s trajectory more precisely, and the PSNR value can be improved by up to 3.21 dB when compared with DS-ME. The SSIM values of different FRUC techniques are shown in Table 2. By comparison, we can see that our proposed algorithm is significantly relatively better than the comparing methods and is only less effective than DS-ME in processing static videos. As is shown in Table 3, the running time of our algorithm is shorter than the DS-ME method and the Dual-ME method, which indicates that the spatial algorithm provides a lower computational complexity. It can be seen that the computational resource configuration of the proposed algorithm is more effective. By partitioning the frame and combining the advantages of a full search ME and spatial correlation, the calculation time can be saved while ensuring accuracy at the same time.

Table 1.
Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) (dB) comparison of different Motion Estimation (ME) methods for the test sequences.

Table 2.
The Structural SIMilarity (SSIM) comparison of different ME methods for the test sequences.

Table 3.
The average processing time (s/frame) comparison of different ME methods for the test sequences.
Table 4 presents PSNR and SSIM results of the proposed algorithm and three MC-FRUC algorithms proposed by References [19,20,21], respectively. The results of References [19,20,21] are directly taken from their originals. From Table 4, we can see that our algorithm obtains PSNR gains for several test sequences, e.g., the proposed algorithm is 0.23 dB higher than in Reference [21] for Foreman and 0.91 dB higher than in Reference [20] for Flower. In most cases, the PSNR values of our algorithm have the comparative results with References [19,20,21]. For SSIM evaluations, our algorithm obtains the highest SSIM values among all algorithms for Foreman, Flower and Mother but has the obvious SSIM degradations for sport sequences Football and Stefan, indicating that our algorithm can recover the good structures for sequences with low and medium motions. From above, it can be seen that our algorithm is competitive in terms of interpolation quality when compared with References [19,20,21]. Otherwise, in terms of computational complexity, our algorithm has advantages over References [19,20,21], e.g., Tsai et al. [20] costs 39.41 s on average to interpolate a CIF frame, but our algorithm only costs 4.35 s on average to interpolate a CIF frame.

Table 4.
PSNR and SSIM comparisons of different MC-FRUC methods for the test sequences.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, a spatial prediction-based MC-FRUC algorithm is proposed to improve the MVF accuracy of the interpolated frame. We design a predictive model to partition a frame into the basic block and the absent block. The MV of the basic block is first estimated by BME, and then the MV of the absent block is deduced from the MVs of its neighboring basic blocks. To reduce some redundant computations, bilateral SEA is designed to improve BME. Based on the spatial correlation of MVF, we have also designed an MV prediction to compute the MV of the absent block. Experimental results show that the proposed ME algorithm can improve both the objective and subjective quality of the interpolated frame with a low computational complexity.
Author Contributions
Y.L. contributed to the concept of the research, performed the data analysis and wrote the manuscript; W.M. helped perform the data analysis with constructive discussions and helped performed the experiment; H.Y. conducted the experiment and collected the data.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Innovation Team Support Plan of University Science and Technology of Henan Province (No. 19IRTSTHN014).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lu, Q.; Xu, N.; Fang, X. Motion-compensated frame interpolation with multiframe-based occlusion handling. J. Disp. Technol. 2016, 12, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaviani, H.R.; Shirani, S. Frame rate up-conversion using optical flow and patch-based reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2016, 26, 1581–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, Y.; Bruckstein, A.M. Motion-compensated coding and frame rate up-conversion: Models and analysis. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 2051–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.; Yang, G.; Li, L.; Li, R.; Sun, X. Detecting video frame rate up-conversion based on frame-level analysis of average texture variation. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Lu, Z. Motion-compensated frame interpolation with weighted motion estimation and hierarchical vector refinement. Neurocomputing 2016, 181, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, F.; Chien, S. Algorithm and architecture design of multi-rate frame rate up-conversion for ultra-HD LCD systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2016, 27, 2739–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Lei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Kwong, S. Fast motion estimation based on content property for low-complexity H.265/HEVC encoder. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 2016, 62, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Tai, S.C. Fast full-search block-matching algorithm for motion-compensated video compression. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2002, 45, 527–531. [Google Scholar]
- Dikbas, S.; Altunbasak, Y. Novel true-motion estimation algorithm and its application to motion-compensated temporal frame interpolation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 2931–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haan, G.D.; Biezen, P.W.A.C.; Huijgen, H.; Ojo, O.A. True motion estimation with 3-D recursive search block matching. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 1993, 3, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Lim, H.; Park, H.W. Iterative true motion estimation for motion-compensated frame interpolation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2013, 23, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparone, L.; Bartolini, M.B.F.; Cappellini, V. Adaptively weighted vector-median filters for motion fields smoothing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Atlanta, GA, USA, 9 May 1996; pp. 2267–2270. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, B.-T.; Lee, S.-H.; Ko, S.-J. New frame rate up-conversion using bi-directional motion estimation. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2000, 46, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Ma, S.; Gao, W. Side information generation with auto regressive model for low-delay distributed video coding. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2012, 23, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, B.-W.; Lee, G.-I.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, R.-H. Coarse-to-fine frame interpolation for frame rate up-conversion using pyramid structure. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2003, 49, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.D.; Han, J.W.; Kim, C.S.; Ko, S.J. Motion-compensated frame interpolation using bilateral motion estimation and adaptive overlapped block motion compensation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2007, 17, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orchard, M.T.; Sullivan, G.J. Overlapped block motion compensation: An estimation-theoretic approach. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1994, 3, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusto, D.D.; Murroni, M.; Soro, G. Slow motion replay of video sequences using fractal zooming. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2005, 51, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Fu, Z. Motion-compensated frame interpolation using patch-based sparseland model. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2017, 54, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.H.; Shi, A.T.; Huang, K.T. Accurate frame rate up-conversion for advanced visual quality. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 2016, 62, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Lv, Y.; Liu, Z. Multi-scheme frame rate up-conversion using space-time saliency. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.J.; Cho, K.R.; Kim, Y.H. Motion compensated frame rate up-conversion using extended bilateral motion estimation. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2007, 53, 1759–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Duanmu, C.J.; Zou, C. A multilevel successive elimination algorithm for block matching motion estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2000, 9, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.J.; Yoo, S.; Kim, Y.H. Dual motion estimation for frame rate up-conversion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2010, 20, 1909–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.G.; Kang, S.J.; Kim, Y.H. Direction-Select Motion Estimation for Motion-Compensated Frame Rate Up-Conversion. J. Disp. Technol. 2013, 9, 840–850. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).