Failure Mode and Effect Analysis for Cyber-Physical Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Provide a CBTC risk prevention analysis.
- Propose a novel approach to the FMEA’s RPN estimation, concerning CPSs’ risk analysis importance.
- Provide a CBTC risk analysis through our version of the FMEA RPN calculation.
2. Related Work
2.1. CPS Risk Assessment
2.2. RPN Estimation Improvement
3. Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
4. New RPN Criteria and Formula
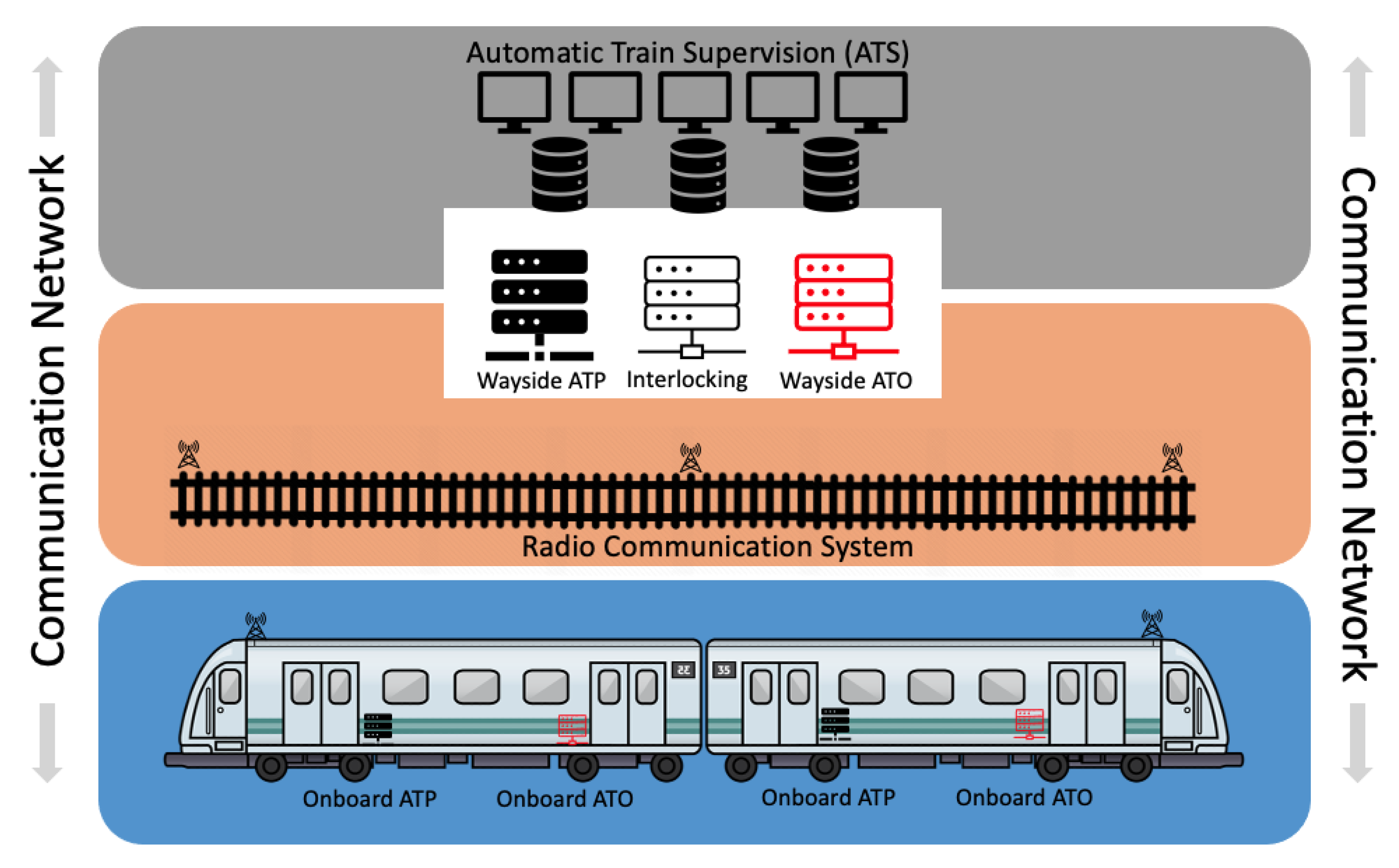
5. Communications-Based Train Control
CBTC Risk Prevention Analysis
6. Failure Mode and Effect Analysis Application
6.1. System Subdivision
6.2. Failure Modes, Causes, and Effects
6.3. Risk Priority Number Calculation
- Wrong control message injection:
- Message Dropping:
- Signal Jamming:
- Communication Delay:
6.4. Prevention Actions Recording
- Wrong control message injection
- Originating seed and salt variation method for authentication.
- Long term IP/MAC mapping table.
- Message Dropping
- Query node after messages are sent.
- Time communications between two nodes with a limit waitable timer.
- Signal Jamming
- Low transmission power deteriorates chances for attacker signal location.
- Transmission of short pulses on a broad spectrum of a frequency band at the same time.
- Communication Delay
- Originating seed and salt variation method for authentication.
- Long term IP/MAC mapping table.
- IP/MAC binding allows to prioritize traffic with static IP assignment reservation.
6.5. Discussion
7. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lyu, X.; Ding, Y.; Yang, S.H. Safety and security risk assessment in cyberphysical systems. IET-Cyber-Phys. Syst. Theory Appl. 2019, 4, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Kang, R.; Li, Z. Risk assessment method for cyber security of cyber physical systems. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Reliability Systems Engineering (ICRSE’15), Beijing, China, 21–23 October 2015; p. 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.; Schwartz, G.; Hussain, A. In quest of benchmarking security risks to cyber-physical systems. IEEE Netw. 2013, 27, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatis, D. Failure Mode and Effect Analysis: FMEA from Theory to Execution; ASQ Quality Press: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.M.; Chin, K.S.; Poon, G.K.K.; Yang, J.B. Risk evaluation in failure mode and effects analysis using fuzzy weighted geometric mean. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Lu, T.; Guo, X.; Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Gao, Y. Security analysis on Cyber-Physical System using attack tree. In Proceedings of the 2013 Ninth International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 16–18 October 2013; pp. 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruchkin, I.; Rao, A.; De Niz, D.; Chaki, S.; Garlan, D. Eliminating inter-domain vulnerabilities in cyber-physical systems: An analysis contracts approach. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM Workshop on Cyber-Physical Systems-Security and/or Privacy, Co-located with CCS’15, Denver, CO, USA, 16 October 2015; pp. 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Hong, J.E. Failure detection and prevention for cyber-physical systems using ontology-based knowledge base. Computers 2018, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, K.M.; Lim, C.P. Fuzzy FMEA with a guided rules reduction system for prioritization of failures. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2006, 23, 1047–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; You, J.X.; Fan, X.J.; Lin, Q.L. Failure mode and effects analysis using D numbers and grey relational projection method. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 4670–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Tian, J.; Zhao, T. Failure mode prioritization by improved RPN calculation method. Reliab. Maintainab. Symp. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabak, M.; Özveri, O. The Usage of MCDM Techniques in Failure Mode and Effect Analysis. J. Econ. Manag. Res. 2015, 4, 94–108. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, F.; Yarmohammadian, M.H.; Haghshenas, A.; Fallah, A.; Ferdosi, M. Revised risk priority number in failure mode and effects analysis model from the perspective of healthcare system. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2018, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpitella, S.; Certa, A.; Izquierdo, J.; La Fata, C.M. A combined multi-criteria approach to support FMECA analyses: A real-world case. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2018, 169, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciani, L.; Guidi, G.; Patrizi, G. A Critical Comparison of Alternative Risk Priority Numbers in Failure Modes, Effects, and Criticality Analysis. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 92398–92409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreafico, C.; Russo, D.; Rizzi, C. A state-of-the-art review of FMEA/FMECA including patents. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2017, 25, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, W. Modelling Failure Modes and Effects Analysis. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 1993, 10, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto da Mobilidade e dos Transportes, IP. Apuramento de Indicadores Comuns de Segurança (in Portuguese). Technical Report; 2015. Available online: http://www.imt-ip.pt/sites/IMTT/Portugues/TransportesFerroviarios/CaminhodeFerro/GuiasdeApoio/Documents/Guia_Implementa%C3%A7%C3%A3o_ICS_v3.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2020).
- Gabinete de Prevenção e Investigação de Acidentes com Aeronaves e de Acidentes Ferroviários (GPIAAF) (in Portuguese). Investigation Activities Annual Report—Rail Transportation. Technical Report; 2018. Available online: http://www.gisaf.gov.pt/?lnk=1282ca70-b489-4691-8079-6d8f784788ec (accessed on 12 August 2020).
- Caruso, M.; Tornaghi, M.; Negro, P. Applicability of the Sustainable Structural Design (SSD) method at Urban/Regional/National Level. JRC Tech. Rep. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Taxing Energy Use 2019: Country Note—Portugal. Technical Report. 2019. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/tax/tax-policy/taxing-energy-use-iceland.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2020).
- Xu, J.; Chen, L.; Gao, W.; Zhao, M. CBTC Simulation Platform Design and Study. J. Comput. Commun. 2015, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Schmittner, C.; Ma, Z.; Temple, W.; Dong, X.; Jones, D.; Sanders, W. Security Analysis of Urban Railway Systems: The Need for a Cyber-Physical Perspective; SAFECOM 2015 Workshops; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, J.; Soler, J. Radio Communication for Communications-Based Train Control (CBTC): A Tutorial and Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 1377–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Bu, B. Security analysis for CBTC systems under attack-defense confrontation. Electronics 2019, 8, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayana, S.; Revadigar, G.; Karachiwala, J.S.; Sravana Kumar, S.L.; Hu, Y.C.; Chang, S.Y.; Yau, D.K. Signal jamming attacks against communication-based train control: Attack impact and countermeasure. In Proceedings of the 11th ACM Conference on Security and Privacy in Wireless and Mobile Networks, Stockholm, Sweden, 18–20 June 2018; pp. 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, L. A Bayesian game based defense scheme for CBTC systems under Man-in-the-middle attacks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference, ITSC, Auckland, New Zealand, 27–30 October 2019; pp. 2172–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Won, Y.; Park, I.H.; Eun, Y.; Park, K.J. Cyber-Physical Vulnerability Analysis of Communication-Based Train Control. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 6353–6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, I.; Aguado, M. Cyber security analysis of the European train control system. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaragno, A.; Bandara, K.R.S.; Fewell, A.; Wijesekera, D. Rail Radio Intrusion Detection System (RRIDS) for Communication Based Train Control (CBTC). In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Rail Transportation (ICIRT), Birmingham, UK, 23–25 August 2016; pp. 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.Y.; Kim, D.; Kim, J. Enhanced ARP: Preventing ARP Poisoning-Based Man-in-the-Middle Attacks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2010, 14, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Zhu, S. Message Dropping Attacks in Overlay Networks: Attack Detection and Attacker Identification. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. Secur. 2006, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Occurrence | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (O) | Nearly Impossible | Failure Almost Inevitable | ||||||||
| Severity | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| (S) | No Effect | Hazardous Effect | ||||||||
| Detectability | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| (D) | Almost Certain | Absolute Uncertainty | ||||||||
| Level | Description | Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Low | Reduced number of light injuries 1 ≤ LI ≤ 10 7400 € ≤ C ≤ 74,000 € |
| 2 | Low | Moderate number of light injuries 10 < LI ≤ 30 81,400€ < C ≤ 222,000 € |
| 3 | Low | High number of light injuries LI > 30 C > 222,000 € |
| 4 | Moderate | High number of light injuries Reduced number of serious injuries LI ⩾ 30 1 ≤ SI ≤ 10 773,400 € ≤ C ≤ 1,203,000 € |
| 5 | Moderate | High number of light injuries Moderate number of serious injuries LI > 30 10 < SI ≤ 30 1,203,000 € ≤ C ≤ 3,331,000 € |
| 6 | Moderate | High number of light injuries and serious injuries LI > 30 SI > 30 C > 3,444,000 € |
| 7 | High | Reduced number of serious injuries and fatalities 1 ≤ SI ≤ 10 1 ≤ F ≤ 10 910,000 € ≤ C ≤ 11,252,000 € |
| 8 | High | Moderate number of serious injuries and fatalities 10 < SI ≤ 30 10 ≤ F ≤ 30 8,137,400 € ≤ C ≤ 27,312,000 € |
| 9 | Catastrophic | High number of fatalities F > 30 C > 24,090,000 € |
| 10 | Catastrophic | High number of serious injuries and fatalities SI > 30 F > 30 C > 27,312,000 € |
| Level | Description | Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Low | Low damage to the railway track (≤ 1000 m) 0 < C ≤ 250,000 € |
| 2 | Low | Low damage to 1 or more bogies 250,000 € < C ≤ 500,000 € |
| 3 | Low | Low damage to the railway track and 1 or more bogies 500,000 € < C ≤ 750,000 € |
| 4 | Moderate | 1 or more bogies derailment 750,000 € < C ≤ 1,250,000 € |
| 5 | Moderate | 1 or more bogies derailment and access points destruction 1 250,000 € < C ≤ 1,750,000 € |
| 6 | Moderate | Serious damage to the railway track (> 1000 m) 1 or more bogies derailment and access points destruction 750,000 € < C ≤ 2,250,000 € |
| 7 | High | 2 trains collision 2,250,000 € < C ≤ 3,250,000 € |
| 8 | High | 2 trains collision and access points destruction 3,250,000 € < C ≤ 4,250,000 € |
| 9 | Catastrophic | 2 trains collision, access points destruction and severe damage to the railway track 4,250,000 € < C ≤ 6,250,000 € |
| 10 | Catastrophic | 2 trains collision, 1 or more bogies derailment, access points destruction and serious damage to the railway track C > 6,250,000 € |
| Level | Description | Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Low | C ≤ 25,000 € (± 12 h) |
| 2 | Low | 25,000 € < C ≤ 50,000 € |
| 3 | Low | 50,000 € < C ≤ 75,000 € |
| 4 | Moderate | 75,000 € < C ≤ 100,000 € |
| 5 | Moderate | 100,000 € < C ≤ 125,000 € |
| 6 | Moderate | 125,000 € < C ≤ 150,000 € |
| 7 | High | 150,000 € < C ≤ 175,000 € |
| 8 | High | 175,000 € < C ≤ 200,000 € |
| 9 | Very High | 200,000 € < C ≤ 225,000 € |
| 10 | Very High | C > 225,000 € |
| Level | Description | Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Low | 0 < QCO2 ≤ 500 tCO2 0 < RSSD(CO2) ≤ 12,500 € |
| 2 | Low | 500 < QCO2 ≤ 1000 tCO2 2,500 < RSSD(CO2) ≤ 25,000 € |
| 3 | Low | 1000 < QCO2 ≤ 1500 tCO2 25,000 < RSSD(CO2) ≤ 37,500 € |
| 4 | Moderate | 1500 < QCO2 ≤ 2000 tCO2 37,500 < RSSD(CO2) ≤ 50,000 € |
| 5 | Moderate | 2000 < QCO2 ≤ 2500 tCO2 50,000 < RSSD(CO2) ≤ 62,500 € |
| 6 | Moderate | 2500 < QCO2 ≤ 3000 tCO2 62,500 < RSSD(CO2) ≤ 65,000 € |
| 7 | High | 3000 < QCO2 ≤ 3500 tCO2 65,000 < RSSD(CO2) ≤ 67,500 € |
| 8 | High | 3500 < QCO2 ≤ 4000 tCO2 67,500 < RSSD(CO2) ≤ 70,000 € |
| 9 | Very High | 4000 < QCO2 ≤ 4500 tCO2 70,000 < RSSD(CO2) ≤ 72,500 € |
| 10 | Very High | QCO2 > 4500 tCO2 RSSD(CO2) > 72,500 € |
| Category | RPN |
|---|---|
| Very Low | [1–2] |
| Low | [2–4] |
| Moderate | [4–6] |
| High | [6–8] |
| Catastrophic | [8–10] |
| Original RPN | Our Approach | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Example 1 | Example 2 | Example 3 | |||||||||||||||||
| Social | Infra Structure | Environ Mental | Delay | RPN | Social | Infrastr | >Environ | Delay | RPN | Social | Infrastr | Environ | Delay | RPN | Social | Infrastr | Environ | Delay | RPN |
| 0.5 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.05 | 0.05 | ||||||||
| 7 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 28 | 7 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 5.05 | 7 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4.75 | 7 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 5.2 |
| 7 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 112 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 5.2 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 5.3 |
| 7 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 252 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5.35 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5.25 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5.4 |
| 7 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 448 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5.5 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5.5 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5.5 |
| 7 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 35 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 5.4 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 5.6 |
| 7 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 140 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 5.55 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 5.25 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 5.7 |
| 7 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 315 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 5.7 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 5.5 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 5.8 |
| 7 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 560 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 5.85 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 5.75 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 5.9 |
| 7 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 42 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 5.75 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 5.25 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| 7 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 168 | 7 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 5.9 | 7 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 5.5 | 7 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 6.1 |
| 7 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 378 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 6.05 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 5.75 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 6.2 |
| 7 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 672 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 6.2 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 6.3 |
| 7 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 49 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 6.1 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 5.5 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 6.4 |
| 7 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 196 | 7 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 6.25 | 7 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 5.75 | 7 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 6.5 |
| 7 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 441 | 7 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 6.4 | 7 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 6.6 |
| 7 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 784 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 6.55 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 6.25 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 6.7 |
| 8 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 32 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 5.55 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 5.25 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 5.7 |
| 8 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 128 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 5.7 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 5.5 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 5.8 |
| 8 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 288 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5.85 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5.75 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5.9 |
| 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 512 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6 |
| 8 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 40 | 8 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 5.9 | 8 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 5.5 | 8 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 6.1 |
| 8 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 160 | 8 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 6.05 | 8 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 5.75 | 8 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 6.2 |
| 8 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 360 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 6.2 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 6.3 |
| 8 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 640 | 8 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 6.35 | 8 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 6.25 | 8 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 6.4 |
| 8 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 48 | 8 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 6.25 | 8 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 5.75 | 8 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 6.5 |
| 8 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 192 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 6.4 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 6.6 |
| 8 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 432 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 6.55 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 6.25 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 6.7 |
| 8 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 768 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 6.7 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 6.5 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 6.8 |
| 8 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 56 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 6.6 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 6.9 |
| 8 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 224 | 8 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 6.75 | 8 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 6.25 | 8 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 7 |
| 8 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 504 | 8 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 6.9 | 8 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 6.5 | 8 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 7.1 |
| 8 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 896 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 7.05 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 6.75 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 7.2 |
| 9 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 36 | 9 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 6.05 | 9 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 5.75 | 9 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 6.2 |
| 9 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 144 | 9 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 6.2 | 9 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 9 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 6.3 |
| 9 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 324 | 9 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 6.35 | 9 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 6.25 | 9 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 6.4 |
| 9 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 576 | 9 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6.5 | 9 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6.5 | 9 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6.5 |
| 9 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 45 | 9 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 6.4 | 9 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 9 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 6.6 |
| 9 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 180 | 9 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 6.55 | 9 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 6.25 | 9 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 6.7 |
| 9 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 405 | 9 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 6.7 | 9 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 6.5 | 9 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 6.8 |
| 9 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 720 | 9 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 6.85 | 9 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 6.75 | 9 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 6.9 |
| 9 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 54 | 9 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 6.75 | 9 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 6.25 | 9 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| 9 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 216 | 9 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 6.9 | 9 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 6.5 | 9 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 7.1 |
| 9 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 486 | 9 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 7.05 | 9 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 6.75 | 9 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 7.2 |
| 9 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 864 | 9 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 7.2 | 9 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 7 | 9 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 7.3 |
| 9 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 63 | 9 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 7.1 | 9 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 6.5 | 9 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 7.4 |
| 9 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 252 | 9 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 7.25 | 9 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 6.75 | 9 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 7.5 |
| 9 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 567 | 9 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 7.4 | 9 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 9 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 7.6 |
| 9 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 1008 | 9 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 7.55 | 9 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 7.25 | 9 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 7.7 |
| 10 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 40 | 10 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 6.55 | 10 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 6.25 | 10 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 6.7 |
| 10 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 160 | 10 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 6.7 | 10 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 6.5 | 10 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 6.8 |
| 10 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 360 | 10 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 6.85 | 10 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 6.75 | 10 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 6.9 |
| 10 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 640 | 10 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 7 | 10 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 7 | 10 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 7 |
| 10 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 50 | 10 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 6.9 | 10 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 6.5 | 10 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 7.1 |
| 10 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 200 | 10 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 7.05 | 10 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 6.75 | 10 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 7.2 |
| 10 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 450 | 10 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 7.2 | 10 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 10 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 7.3 |
| 10 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 800 | 10 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 7.35 | 10 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 7.25 | 10 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 7.4 |
| 10 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 60 | 10 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 7.25 | 10 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 6.75 | 10 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 7.5 |
| 10 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 240 | 10 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 7.4 | 10 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 7 | 10 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 7.6 |
| 10 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 540 | 10 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 7.55 | 10 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 7.25 | 10 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 7.7 |
| 10 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 960 | 10 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 7.7 | 10 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 7.5 | 10 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 7.8 |
| 10 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 70 | 10 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 7.6 | 10 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 7.9 |
| 10 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 280 | 10 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 7.75 | 10 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 7.25 | 10 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 8 |
| 10 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 630 | 10 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 7.9 | 10 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 7.5 | 10 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 8.1 |
| 10 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 1120 | 10 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 8.05 | 10 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 7.75 | 10 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 8.2 |
| Original RPN | Our Approach | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Example 1 | Example 2 | Example 3 | |||||||||||||||||
| Social | Infra Structure | Environ Mental | Delay | RPN | Social | Infrastr | >Environ | Delay | RPN | Social | Infrastr | Environ | Delay | RPN | Social | Infrastr | Environ | Delay | RPN |
| 0.5 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.05 | 0.05 | ||||||||
| 7 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 112 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 5.2 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 5.3 |
| 9 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 405 | 9 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 6.7 | 9 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 6.5 | 9 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 6.8 |
| 10 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 1120 | 10 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 8.05 | 10 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 7.75 | 10 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 8.2 |
| RPN | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | Ex. 1 | Ex. 2 | Ex. 3 | Ex. 4 | |
| Average | 350.625 | 6.55 | 6.25 | 6.70 | 6.50 |
| Variance | 81,961.7 | 0.494 | 0.4688 | 0.525 | 0.0008 |
| Standard Deviation | 288.553 | 0.708 | 0.6901 | 0.7303 | 0.02 |
| Subsystems | Components |
|---|---|
| Local control system | Automatic train supervision (ATS) |
| Wayside system | Zone Controller (ZC) Computer-Based Interlocking (CI) |
| Vehicle onboard system | Automatic train protection (ATP) Automatic train operation (ATO) Vehicle Onboard Computer (VOBC) Data Communication System (DCS) |
| Train to the wayside communication system | Radio Communication System (RCS) Access Points (AP) |
| Failure Mode | Failure Cause | Failure Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Wrong Control Messages injection (Packet Spoofing) | Message Spoofing Attack | Unexpected abrupt braking Train location loss Train speed control loss Train full stop Train collision Train derailment |
| Message Dropping (Packet Dropping) | Message Dropping Attack | Train full stop Emergency braking; Change to conventional operation |
| Signal Jamming | Jamming Attack | Train full stop Emergency braking; Change to conventional operation |
| Communication Delay (Extensive packet duplication and forwarding) | Replay Attack | Train control performance breakdown Change to conventional operation |
| Failure Mode | Social | Infrastr | Environ | Delay | RPN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.1 | Original | Our Approach | |
| Wrong control message injection | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10,000 | 10 |
| Message dropping | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 12 | 2.45 |
| Signal jamming | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 12 | 2.45 |
| Communication Delay | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, J.; Carvalho, G.; Cabral, B.; Bernardino, J. Failure Mode and Effect Analysis for Cyber-Physical Systems. Future Internet 2020, 12, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12110205
Oliveira J, Carvalho G, Cabral B, Bernardino J. Failure Mode and Effect Analysis for Cyber-Physical Systems. Future Internet. 2020; 12(11):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12110205
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, João, Gonçalo Carvalho, Bruno Cabral, and Jorge Bernardino. 2020. "Failure Mode and Effect Analysis for Cyber-Physical Systems" Future Internet 12, no. 11: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12110205
APA StyleOliveira, J., Carvalho, G., Cabral, B., & Bernardino, J. (2020). Failure Mode and Effect Analysis for Cyber-Physical Systems. Future Internet, 12(11), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12110205







