A Novel Low-Complexity Fault Diagnosis Algorithm for Energy Internet in Smart Cities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Our Contribution
- The , along with the , is applied to detect faulty cluster-heads in a centralized manner with a high accuracy; meanwhile, the messages exchanged are no more than such that the corresponding energy cost is reduced.
- We develop to determine the faulty state of every cluster-member within each cluster of a faulty cluster-head, while the cluster with a fault-free cluster-head can easily make a decision by simply comparing the data between the cluster-head and cluster-members. By doing so, the diagnosis accuracy is increased significantly, and the message complexity, which is only , implies that the energy cost is further reduced.
2. System Model
3. The Proposed Strategy
3.1. - and -based Centralized Fault Diagnosis
3.1.1. -based State Prediction
3.1.2. -based Faulty Cluster-Heads Identification
3.2. Modified Three Sigma Rule-based Fault Diagnosis
4. Performance Analysis
4.1. Theoretical Analysis
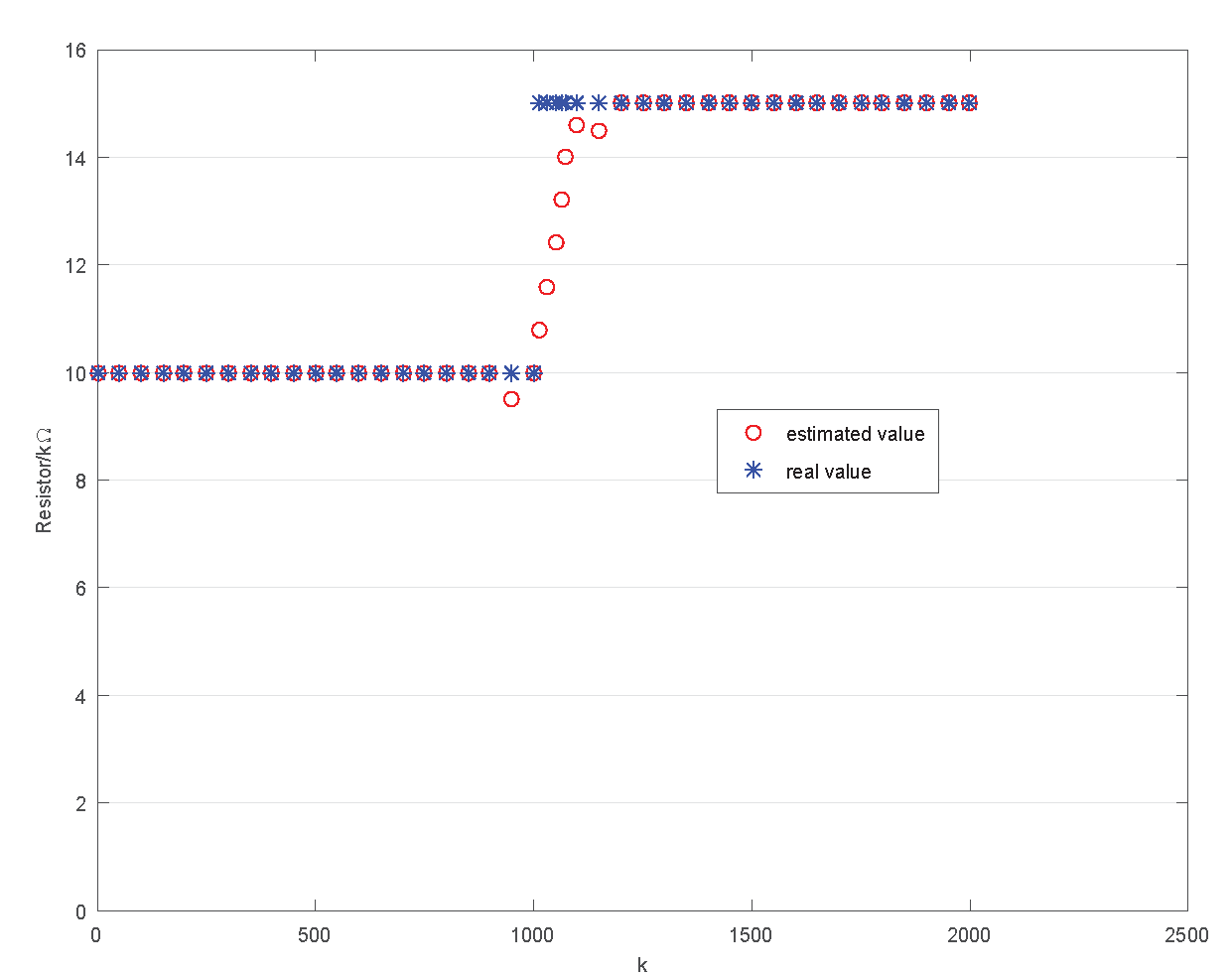
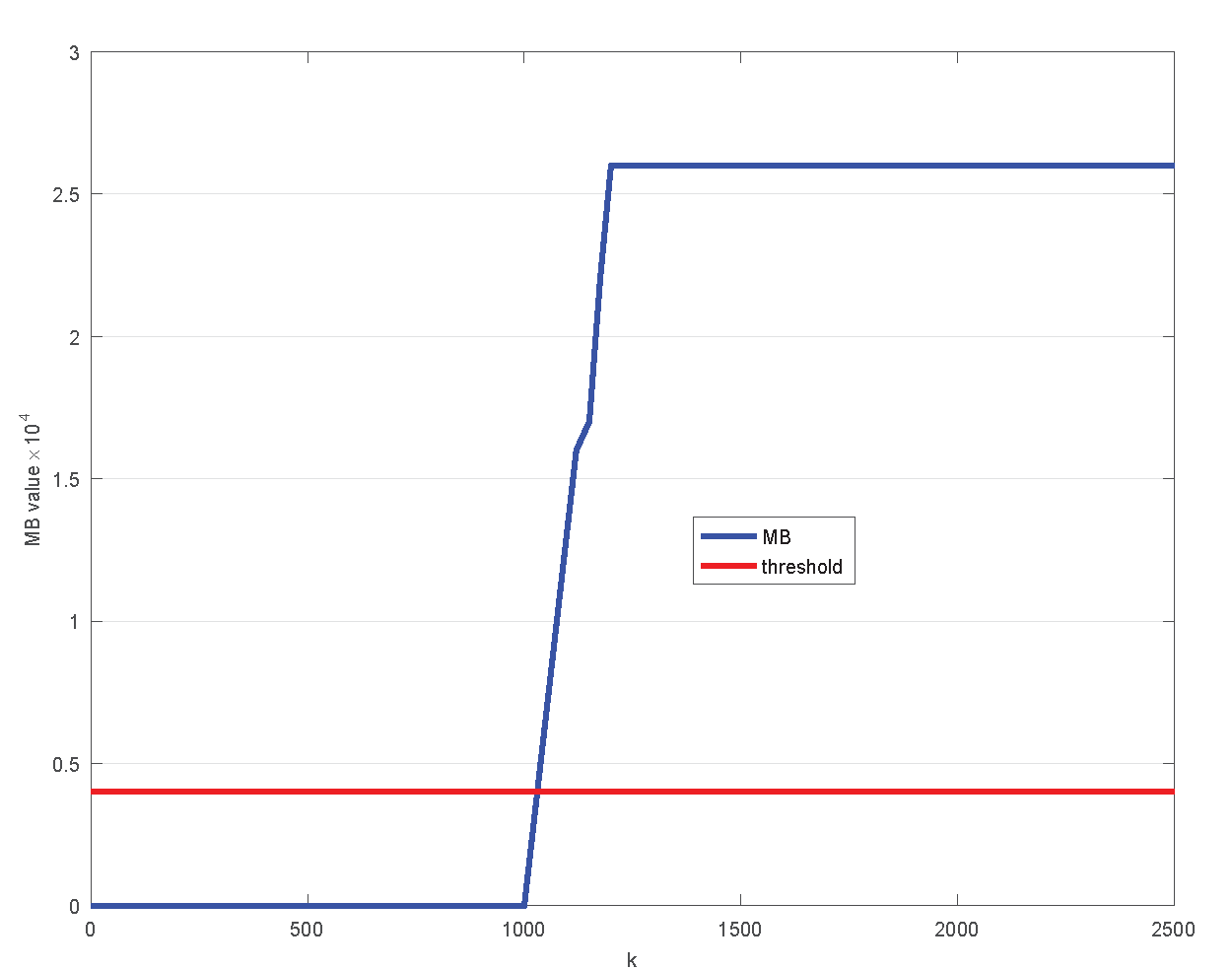
4.2. Validation Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, K.; Gu, L.; He, X.; Guo, S.; Sun, Y.; Vinel, A.; Shen, J. Distributed energy management for vehicle-to-grid networks. IEEE Netw. 2017, 31, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, P.; Guo, S. Energy management for EV charging in software-defined green vehicle-to-grid network. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, K.; Li, P.; Xia, R.; Guo, S.; Guo, M. Renewable energy-aware big data analytics in geo-distributed data centers with reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ouyang, Z.; Krishnan, R.; Shu, L.; He, L. A game theory based energy management system using price elasticity for smart grids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2015, 11, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Guo, S.; Wu, J. Green industrial Internet of Things architecture: an energy-efficient perspective. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2016, 54, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.P.; Uma, C.; Elias, K. Everything you wanted to know about smart cities: The internet of things is the backbone. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2016, 5, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yu, J.; Yu, Y.; Qian, Y.; Zeng, D.; Guo, S.; Xiang, Y.; Wu, J. A survey on Energy Internet: architecture, approach and emerging technologies. IEEE Syst. J. 2018, 12, 2403–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hu, X.; Li, H.; Li, P.; Zeng, D.; Guo, S. A survey on energy Internet communications for sustainability. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Comput. 2017, 2, 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, H.; Feng, Y.; Tian, G. Big data analytics for system stability evaluation strategy in the energy Internet. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Wang, K.; He, L. Probabilistic model checking and scheduling implementation of energy router system in energy internet for green cities. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, K.; Huang, H.; Liu, B. QoE-driven big data architecture for smart city. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimovic, M. Greening the Future: Green Internet of Things (G-IoT) as a Key Technological Enabler of Sustainable Development. In Internet of Things and Big Data Analytics Toward Next-Generation Intelligence; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 283–313. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Shao, Y.; Xie, L.; Wu, J.; Guo, S. Adaptive and fault-tolerant data processing in healthcare iot based on fog computing. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Shao, Y.; Shu, L.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Y. Mobile big data fault-tolerant processing for eHealth networks. IEEE Netw. 2016, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Lin, Y.; Xu, W. LightChain: a lightweight blockchain system for industrial internet of things. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 3571–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Lu, C.; Liu, H. Fault Diagnosis for the Heat Exchanger of the Aircraft Environmental Control System Based on the Strong Tracking Filter. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daroogheh, N.; Meskin, N.; Khorasani, K. A Dual Particle Filter-Based Fault Diagnosis Scheme for Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2017, 26, 1317–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Zhu, X. Intelligent Particle Filter and Its Application on Fault Detection of Nonlinear System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 3852–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Shmaliy, Y.; Liu, F. Fast Kalman-Like Optimal Unbiased FIR Filtering with Applications. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 2284–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Qin, L.; Zhou, D. Fault Tolerant Control for an Internet-Based Three-Tank System: Accommodation to Sensor Bias Faults. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 64, 2266–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Shao, T.; Chen, S.; Wen, C. Carrier Tracking Estimation Analysis by Using the Extended Strong Tracking Filtering. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Yu, T.; Jian, H.; Liu, T. Design of adaptive robust square-root cubature Kalman filter with noise statistic estimator. Appl. Math. Comput. 2015, 256, 352–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cui, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Liu, J.; Lai, J.; Lv, P. Research on Adaptive Multi-Source Information Fault-Tolerant Navigation Method Based on No-Reference System Diagnosis. Sensors 2019, 19, 2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; He, X. Detection of Intermittent fault for discrete-time systems with output dead-zone: a variant Tobit Kalman filtering approach. J. Control Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cisneros-Magaña, R.; Medina, A.; Anaya-Lara, O. Time-domain voltage sag state estimation based on the unscented Kalman filter for power systems with nonlinear components. Energies 2018, 11, 1411. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, B.C.; Ma, E.W.; Chow, T.W. Probabilistic fault detector for wireless sensor network. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 3703–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, M.; Nayak, A.; Roy, B.; Sarkar, S. Hypothesis testing and decision theoretic approach for fault detection in wireless sensor networks. Int. J. Parallel Emerg. Distrib. Syst. 2015, 30, 262–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, W.; Liu, K.; Liu, Y. Directional diagnosis for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2015, 26, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P. A new method for node fault detection in wireless sensor networks. Sensors 2009, 9, 1282–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panda, M.; Khilar, P.M. Distributed self fault diagnosis algorithm for large scale wireless sensor networks using modified three sigma edit test. Ad Hoc Netw. 2015, 25, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.P.; Sharma, T.P. rDFD: reactive distributed fault detection in wireless sensor networks. Wirel. Netw. 2016, 23, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, R.R.; Dash, T.; Khilar, P.M. An effective graph-theoretic approach towards simultaneous detection of fault(s) and cut(s) in wireless sensor networks. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2017, 30, e3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Peñate, S.; Valencia-Palomo, G.; López-Estrada, F.R.; Astorga-Zaragoza, C.-M.; Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Santos-Ruiz, I. Sensor fault diagnosis based on a H∞ sliding mode and unknown input observer for takagi-sugeno systems with uncertain premise variables. Asian J. Control 2019, 21, 339–353. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Ruiz, I.D.L.; López-Estrada, F.R.; Puig, V.; Pérez-Pérez, E.J.; Mina-Antonio, J.D.; Valencia-Palomo, G. Diagnosis of Fluid Leaks in Pipelines Using Dynamic PCA. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Huang, D.; He, H.; Zhou, W.; Han, Q.; Li, T. A novel framework for fault diagnosis using kernel partial least squares based on an optimal preference matrix. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 4315–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; He, H.; Xie, P.; Tang, Y. Stacked multilevel-denoising autoencoders: A new representation learning approach for wind turbine gearbox fault diagnosis. IEEE Transt. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 2391–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Huang, D.; Fu, S.; He, H.; Li, T. Optimized relative transformation matrix using bacterial foraging algorithm for process fault detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 2595–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, M.; Khilar, P.M. Distributed Byzantine fault detection technique in wireless sensor networks based on hypothesis testing. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2015, 48, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Yang, H.; Wang, L. Adaptive Unscented Kalman Filter Based Estimation and Filtering for Dynamic Positioning with Model Uncertainties. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2019, 17, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, W.E.; Shekhtman, B.; Suen, S.; Fisher, D.C. Upper bounds for the domination number of a graph. Congr. Numer. 1998, 132, 99–123. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, M.; Khilar, P.M. Distributed soft fault detection algorithm in wireless sensor networks using statistical test. In Proceedings of the 2012 2nd IEEE International Conference on Parallel, Distributed and Grid Computing, Solan, India, 6–8 Decemebr 2012. [Google Scholar]





| Symbols | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| i-th cluster | |
| i-th cluster-head of | |
| i-th meter | |
| Set of neighboring meters of | |
| State of a meter at time k | |
| data of | |
| Estimated value of | |
| Sample mean of | |
| Sample variance of | |
| Median of the data | |
| Median Absolute Deviation | |
| Standard Deviation | |
| Threshold for identifying fault state | |
| Probability of a meter being faulty | |
| p | Probability of a faulty meter detected as fault-free |
| Strong Tracking Unscented Kalman Filter | |
| Modified Bayes’ classification algorithm | |
| Modified Three Sigma test |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Lin, D.; Feng, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X. A Novel Low-Complexity Fault Diagnosis Algorithm for Energy Internet in Smart Cities. Future Internet 2020, 12, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12020026
Wang J, Zhang H, Lin D, Feng H, Wang T, Zhang H, Wang X. A Novel Low-Complexity Fault Diagnosis Algorithm for Energy Internet in Smart Cities. Future Internet. 2020; 12(2):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12020026
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiong, Hua Zhang, Dongliang Lin, Huibin Feng, Tao Wang, Hongyan Zhang, and Xiaoding Wang. 2020. "A Novel Low-Complexity Fault Diagnosis Algorithm for Energy Internet in Smart Cities" Future Internet 12, no. 2: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12020026
APA StyleWang, J., Zhang, H., Lin, D., Feng, H., Wang, T., Zhang, H., & Wang, X. (2020). A Novel Low-Complexity Fault Diagnosis Algorithm for Energy Internet in Smart Cities. Future Internet, 12(2), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12020026





