Post-Materialist Values of Smart City Societies: International Comparison of Public Values for Good Enough Governance
Abstract
:1. Introduction and Background
2. Methodology
3. Results
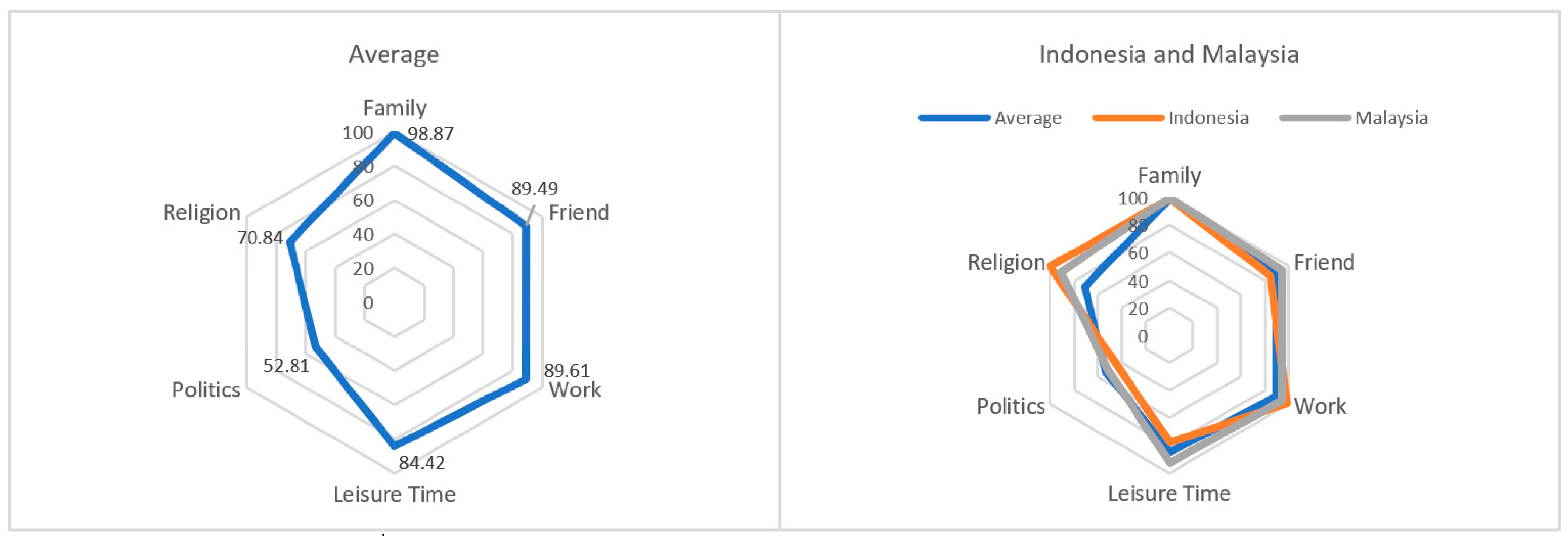
3.1. Important Values in Life
3.2. Qualities to Develop
3.3. Materialist vs. Post-Materialist Values
4. Discussion
4.1. Political Participation Values to Prioritize under the Principle of Long-Term Good Enough Governance to Realize the Smart City Society
4.2. Dichotomous Challenges in Building Qualities of Future Smart Citizen and Society
4.3. Possibilities for Building the Post-Materialist Smart City Society
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Han, H.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Ioppolo, G.; Sabatini-Marques, J. The making of smart cities: Are Songdo, Masdar, Amsterdam, San Francisco and Brisbane the best we could build? Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komninos, N.; Panori, A.; Kakderi, C. Smart cities beyond algorithmic logic: Digital platforms, user engagement and data science. In Smart Cities in the Post-Algorithmic Era: Integrating Technologies, Platforms and Governance; Komninos, N., Kakderi, C., Eds.; Edward Elgar: Northampton, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Yuan, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, Q. From digital to sustainable: A scientometric review of smart city literature between 1990 and 2019. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummitha, R.K.R.; Crutzen, N. How do we understand smart cities? An evolutionary perspective. Cities 2017, 67, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchin, R.; Lauriault, T.P.; Mcardle, G. Smart cities and the politics of urban data. In Smart Urbanism: Utopian Vision or False Dawn? Marvin, S., Luque-Ayala, A., McFarlane, C., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2016; pp. 16–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Corchado, J.M.; Mehmood, R.; Li, R.Y.M.; Mossberger, K.; Desouza, K. Responsible urban innovation with local government artificial intelligence (AI): A conceptual framework and research agenda. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex 2021, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartswood, M.; Grimpe, B.; Jirotka, M.; Anderson, S. Towards the ethical governance of smart society. In Social Collective Intelligence; Miorandi, D., Maltese, V., Rovastos, M., Nijholt, A., Stewart, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 3–30. [Google Scholar]
- Staletić, N.; Labus, A.; Bogdanović, Z.; Despotović-Zrakić, M. Citizens’ readiness to crowdsource smart city services: A developing country perspective. Cities 2020, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckinsey Global Institute. Smart cities: Digital Solutions for a More Livable Future; Mckinsey & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rotta, M.J.R.; Sell, D.; dos Santos Pacheco, R.C.; Yigitcanlar, T. Digital commons and citizen coproduction in smart cities: Assessment of Brazilian municipal e-government platforms. Energies 2019, 12, 2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meijer, A.; Bolívar, M.P.R. Governing the smart city: Scaling-up the search for socio-techno synergy. In Proceedings of the European Group for Public Administration (EGPA), Edinburgh, UK, 11–13 September 2013; pp. 100–113. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. Good Governance and its Benefits on Economic Development: An Overview of Current Trends. Available online: https://pdf4pro.com/cdn/good-governance-and-its-benefits-on-economic-development-442998.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Grindle, M.S. Good enough governance: Poverty reduction and reform in developing countries. Gov. An. Int. J. Policy, Adm. Inst. 2004, 17, 525–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grindle, M.S. Good enough governance revisited. Dev. Policy Rev. 2007, 25, 553–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premat, C. Smart cities in a digital nation: Are Swedish cities enough innovative? In Smarter as the New Urban. Agenda a Comprehensive View of the 21st Century City; Gil-Garcia, J.R., Nam, T., Pardo, T.A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 207–224. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.H.; Cheah, T.C. A study of Malaysia’s smart cities initiative progress in comparison of neighbouring countries (Singapore & Indonesia). J. Crit. Rev. 2020, 7, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, K.L.A.; Lau, S.L.; Chua, H.N.; Ling, M.H.; Iranmanesh, V.; Kwan, S.C.C. Greater Kuala Lumpur as a smart city: A case study on technology opportunities. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST), Chiangmai, Thailand, 3–6 February 2016; pp. 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokolo, A.J.; Majid, M.A.; Romli, A. A trivial approach for achieving smart city: A way forward towards a sustainable society. In Proceedings of the 21st Saudi Computer Society National Computer Conference (NCC), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 25–26 April 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, J.A.; Lim, S.B.; Yigitcanlar, T. Social inclusion indicators for building citizen-centric smart cities: A systematic literature review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.B.; Malek, J.A.; Hussain, M.Y.; Tahir, Z. Citizen participation in building citizen-centric smart cities. Geografia Malays. J. Soc. 2018, 14, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.B.; Malek, J.A.; Hussain, M.Y.; Tahir, Z. The behaviours and job positions of citizens in smart cities’ development. Plan. Malays. 2019, 17, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.B.; Malek, J.A.; Hussain, M.Y.; Tahir, Z. Participation in e-government services and smart city programs: A case study of Malaysian local authority. Plan. Malays. 2020, 18, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.B.; Malek, J.A.; Hussain, M.Y.; Tahir, Z. Malaysia smart CITY framework: A trusted framework for shaping smart Malaysian citizenship? In Handbook of Smart Cities; Augusto, J.C., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wok, S.; Mohamed, S. Internet and social media in Malaysia: Development, challenges and potentials. In The Evolution of Media Communication; Acuña, B.P., Ed.; Intechopen: London, UK, 2017; pp. 45–64. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.B.; Malek, J.A.; Hussain, M.Y.; Tahir, Z.; Saman, N.H.M. SDGs, smart urbanisation, and politics: Stakeholder partnerships and environmental cases in Malaysia. J. Sustain. Sci. Manag. 2021, 16, 190–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. World Bank Country and Lending Groups. Available online: https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519 (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Serajuddin, U.; Hamadeh, N. New World Bank Country Classifications by Income Level: 2020–2021. Available online: https://blogs.worldbank.org/opendata/new-world-bank-country-classifications-income-level-2020–2021 (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Noack, R. World’s Least Religious Countries. Available online: https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/worldviews/wp/2015/04/14/map-these-are-the-worlds%02least-religious-countries/ (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Worldometer. Countries in the World by Population. 2021. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/population-by-country/ (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Feng, B. Chinese Respondents Top Materialism Poll. Available online: https://sinosphere.blogs.nytimes.com/2013/12/20/chinese-respondents-top-materialism-poll/?mtrref=undefined&assetType=PAYWALL (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Haerpfer, C.; Inglehart, R.; Moreno, A.; Welzel, C.; Kizilova, K.; Diez-Medrano, J.; Lagos, M.; Norris, P.; Ponarin, E.; Puranen, B.; et al. World Values Survey: Round Seve—Country-Pooled Datafile; JD Systems Institute & WVSA Secretariat: Madrid, Spain; Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Alemán, J.; Woods, D. Value orientations from the World Values Survey: How comparable are they cross-nationally? Comp. Polit. Stud. 2016, 49, 1039–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglehart, R.F. After postmaterialism: An essay on China, Russia and the United States: A comment. Can. J. Sociol. 2016, 41, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uhlaner, L.M.; Thurik, R.; Hutjes, J. Post-Materialism as a Cultural Factor Influencing Entrepreneurial Activity across Nations; Erasmus University Rotterdam: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU). Democracy Index 2020: In sickness and in health? Economist Intelligence Unit: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Inglehart, R.F. Religion’s Sudden Decline: What’s Causing It, and What Comes Next? Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, R. On the interpretation of World Values Survey Trust Question—Global Expectations vs. Local Beliefs; Discussion Paper No. 9872; Institute for the Study of Labor, University of Bonn: Bonn, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Curini, L.; Jou, W.; Memoli, V. How moderates and extremists find happiness: Ideological orientation, citizen-government proximity, and life satisfaction. Int. Polit. Sci. Rev. 2013, 2, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglehart, R. The silent revolution in Europe: Intergenerational change in post-industrial societies. Am. Polit. Sci. Rev. 1971, 65, 991–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inglehart, R. Modernization, existential security and cultural change: Reshaping human motivations and society. In Advances in Culture and Psychology; Gelfand, M., Chiu, C.Y., Hong, Y.-Y., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Roser, M. Materialism and Post-Materialism. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/materialism-and-post-materialism (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Cardullo, P.; Kitchin, R. Being a ‘citizen’ in the smart city: Up and down the scaffold of smart citizen participation in Dublin, Ireland. GeoJournal 2019, 84, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metaxiotis, K.; Carrillo, F.J.; Yigitcanlar, T. Knowledge-Based Development for Cities and Societies: Integrated Multi-Level Approaches; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Green, B. The Smart Enough City: Putting Technology in its Place to Reclaim Our Urban Future; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Kamruzzaman, M. Smart cities and mobility: Does the smartness of Australian cities lead to sustainable commuting patterns? J. Urban. Technol. 2019, 26, 21–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giffinger, R.; Fertner, C.; Kramar, H.; Kalasek, R.; Pichler, N.; Meijers, E. Smart Cities: Ranking of European Medium-Sized Cities; Centre of Regional Science, TU Vienna: Vienna, Austria, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Preston, S.; Mazhar, M.U.; Bull, R. Citizen engagement for co-creating low carbon smart cities: Practical lessons from Nottingham City Council in the UK. Energies 2020, 13, 6615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Cities and Local Governments (UCLG). Co-Creating the Urban Future: The Agenda of Metropolises, Cities and Territories; The Executive Summary; UCLG: Barcelona, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Desouza, K.; Butler, L.; Roozkhosh, F. Contributions and risks of artificial intelligence (AI) in building smarter cities: Insights from a systematic review of the literature. Energies 2020, 3, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Kankanamge, N.; Vella, K. How are smart city concepts and technologies perceived and utilized? A systematic geo-Twitter analysis of smart cities in Australia. J. Urban. Technol. 2021, 28, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Country | Geographical Location | Majority Religion | Economic Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indonesia | South-East Asia | Islam | Upper-middle income |
| Malaysia | South-East Asia | Islam | Upper-middle income |
| Iran | Middle East | Islam | Upper-middle income |
| Pakistan | South Asia | Islam | Lower-middle income |
| Nigeria | Africa | Islam | Lower-middle income |
| Brazil | Latin America | Christians (Catholics and Protestants) | Upper-middle income |
| China | East Asia | Chinese Buddhism and Folk Religions | Upper-middle income |
| United States | North America | Christians (Protestants and Catholics) | High-income |
| Germany | Europe | Christians (Protestants and Catholics) | High-income |
| Australia | Asia Pacific | Christians (Catholic and others) | High-income |
| Country | Population 2020 (Mil.) | Density (ppl/km2) | Urban Population (%) | Survey Sample Size | Year of Survey | Mode of Data Collection | Mode of Survey Length (Min.) | Urban Sampling (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indonesia | 274 | 151 | 56 | 3200 | June–Aug 2018 | CAPI | - | 29.5 |
| Malaysia | 32 | 99 | 78 | 1313 | Apr–May 2018 | CAWI | - | 63.0 |
| Iran | 84 | 52 | 76 | 1499 | Mac–Apr 2020 | PAPI | 86 to 120 | 74.0 |
| Pakistan | 221 | 587 | 35 | 1995 | Nov–Dec 2018 | CAPI | 46 to 65 | 33.3 |
| Nigeria | 206 | 226 | 52 | 1237 | Dec–Jan 2017 | CAPI | 66 to 85 | 49.0 |
| Brazil | 212 | 25 | 88 | 1762 | 2018 | CAPI | - | |
| China | 1439 | 153 | 61 | 3036 | Jul–Oct 2018 | PAPI | 46 to 65 | 61.1 |
| United States | 331 | 36 | 83 | 2596 | Apr–May 2017 | CAWI | Up to 45 | 88.4 |
| Germany | 84 | 240 | 76 | 1528 | Oct 2017–Mac 2018 | CAPI | 46 to 65 | 89.9 |
| Australia | 25 | 3 | 86 | 1813 | Apr–Aug 2018 | Mail/Post | Up to 45 | 78.5 |
| Total | - | - | - | 19,979 | - | - | - | - |
| Research Question | Item | Scale |
|---|---|---|
| RQ 1 | Q1–6 Important in Life: Family, Friend, Leisure Time, Politics, Work, and Religion | Question: For each of the following aspects, indicate how important it is in your life. Scale: Very Important, Rather Important, Not Very Important, Not at all |
| RQ 2 | Q7–17 Qualities to develop: Good manners, Tolerance and respect for other people, Feeling of responsibility, Independence, Religious and faith, Hard work, Obedience, Determination, Unselfishness, Thrift saving money and things, and Imagination | Question: Here is a list of qualities that children can be encouraged to learn at home. Which, if any, do you consider to be especially important? Please choose up to five. Scale: Important, Not mentioned. |
| RQ 3 | Q154-Materialist vs. Post-Materialist values | Question: If you had to choose, which one of the things on this card would you say is most important? Scale: Maintaining order in the nation; Giving people more say in important government decisions; Fighting rising prices; and Protecting freedom of speech |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, S.B.; Malek, J.A.; Yigitcanlar, T. Post-Materialist Values of Smart City Societies: International Comparison of Public Values for Good Enough Governance. Future Internet 2021, 13, 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi13080201
Lim SB, Malek JA, Yigitcanlar T. Post-Materialist Values of Smart City Societies: International Comparison of Public Values for Good Enough Governance. Future Internet. 2021; 13(8):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi13080201
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Seng Boon, Jalaluddin Abdul Malek, and Tan Yigitcanlar. 2021. "Post-Materialist Values of Smart City Societies: International Comparison of Public Values for Good Enough Governance" Future Internet 13, no. 8: 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi13080201
APA StyleLim, S. B., Malek, J. A., & Yigitcanlar, T. (2021). Post-Materialist Values of Smart City Societies: International Comparison of Public Values for Good Enough Governance. Future Internet, 13(8), 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi13080201








