IoT for Smart Cities: Machine Learning Approaches in Smart Healthcare—A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Perform a baseline study focusing on:
- ▪
- IoT
- ▪
- Smart HealthCare
- ▪
- Smart Cities
- ▪
- AI/ML in Smart Cities
- ▪
- Blockchain in Smart Cities
- Study existing literature;
- Study wireless sensor networks in relation to the IoT and smart cities;
- Understand and relate the IoT with smart healthcare;
- Study AI/ML applications in smart healthcare.
2. Related Work
3. Wireless Sensor Networks for Smart Cities
4. IOT and Healthcare
4.1. Patient Monitoring
4.2. Digital Drugs
4.3. Medical Equipment
4.4. Medical Institutions
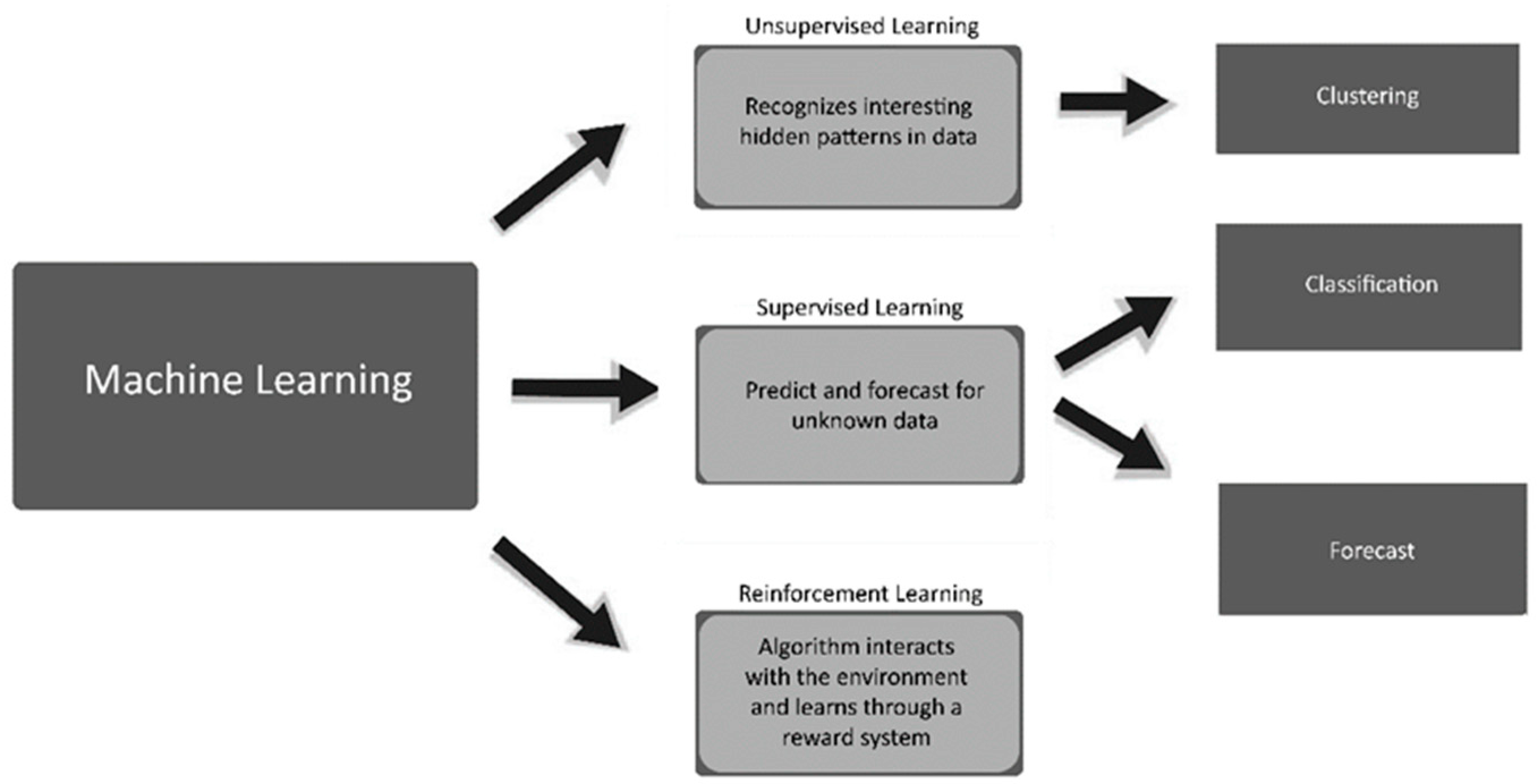
5. Machine Learning
5.1. Supervised Learning
5.2. Unsupervised Learning
5.3. Reinforcement Learning
5.4. Machine Learning Applications in Smart Cities
5.5. Applications of Machine Learning and AI in Healthcare
5.5.1. Health Monitoring and Prognosis
5.5.2. Treatment of the Acutely Ill
5.5.3. Decision Support Systems
5.5.4. Treatment of Chronic Illnesses
5.5.5. Respite Care
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shah, R.; Chircu, A. IoT and AI in healthcare: A systematic literature review. Issues Inf. Syst. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panarello, A.; Tapas, N.; Merlino, G.; Longo, F.; Puliafito, A. Blockchain and iot integration: A systematic survey. Sensors 2018, 18, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Zhi, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Shen, H.; Wang, Y. Artificial intelligence in healthcare: Past, present and future. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahl, M.; Barzilay, R.; Yedidia, A.B.; Locascio, N.J.; Yu, L.; Lehman, C.D. High-risk breast lesions: A machine learning model to predict pathologic upgrade and reduce unnecessary surgical excision. Radiology 2018, 286, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cugurullo, F. Exposing smart cities and eco-cities: Frankenstein urbanism and the sustainability challenges of the experimental city. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2018, 50, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cugurullo, F. Frankenstein Urbanism: Eco, Smart and Autonomous Cities, Artificial Intelligence and the End of the City; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Habibzadeh, H.; Soyata, T. Toward uniform smart healthcare ecosystems: A survey on prospects, security, and privacy considerations. In Connected Health in Smart Cities; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 9783030278441. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, S.; Zafar, N.A. A survey of security and privacy issues in IoT for smart cities. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Aerospace Science and Engineering ICASE, Islamabad, Pakistan, 14–16 November 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Fang, Y.; Wang, X.; Pei, Y.; Horn, B. A Survey on the status of smart healthcare from the universal village perspective. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE International Conference on Universal Village, Boston, MA, USA, 21–24 October 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arasteh, H.; Hosseinnezhad, V.; Loia, V.; Tommasetti, A.; Troisi, O.; Shafie-Khah, M.; Siano, P. Iot-based smart cities: A survey. In Proceedings of the EEEIC 2016 International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering, Florence, Italy, 7–10 June 2016; pp. 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsamhi, S.H.; Ma, O.; Ansari, M.S.; Almalki, F.A. Survey on collaborative smart drones and internet of things for improving smartness of smart cities. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 128125–128152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chai, Y.; Khan, F.; Jan, S.R.U.; Verma, S.; Menon, V.G.; Kavita; Li, X. A Comprehensive survey on machine learning-based big data analytics for iot-enabled smart healthcare system. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2021, 26, 234–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharel, J.; Reda, H.T.; Shin, S.Y. An architecture for smart health monitoring system based on fog computing. J. Commun. 2017, 12, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muhammad, K.; Khan, S.; Del Ser, J.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C. Deep learning for multigrade brain tumor classification in smart healthcare systems: A prospective survey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, S.; Miraz, M.H.; Prasanth, A.; Abdullah, M. Artificial intelligence enabled IoT: Traffic congestion reduction in smart cities. In Proceedings of the Smart Cities Symposium, Sakhir, Bahrain, 22–23 April 2018; IET Conference Publications: London, UK, 2018; pp. 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, Z.; Dhunny, Z.A. On big data, artificial intelligence and smart cities. Cities 2019, 89, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, U.; Khan, L.U.; Yaqoob, I.; Kazmi, S.M.A.; Salah, K.; Hong, C.S. Blockchain for IoT-based smart cities: Recent advances, requirements, and future challenges. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2021, 103007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cugurullo, F. Urban artificial intelligence: From automation to autonomy in the smart city. Front. Sustain. Cities 2020, 2, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Al-Turjman, F.; Mostarda, L.; Gagliardi, R. Applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning in smart cities. Comput. Commun. 2020, 154, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.; Nkenyereye, L.; Joshi, G.P.; Yang, E. Mitigating and monitoring smart city using internet of things. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2020, 65, 1059–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Cha, J.; Kim, T.W.; Park, J.H. Machine learning based distributed big data analysis framework for next generation web in IoT. Comput. Sci. Inf. Syst. 2021, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Azzaoui, A.E.L.; Kim, T.W.; Pan, Y.; Park, J.H. DeepBlockScheme: A deep learning-based blockchain driven scheme for secure smart city. Hum. Centric Comput. Inf. Sci. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fang, W.; Zhao, Q.; Ji, X.; Jia, G. Energy efficiency in internet of things: An overview. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2020, 63, 787–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Pan, Y.; Park, J.H. OTS scheme based secure architecture for energy-efficient iot in edge infrastructure. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 66, 2905–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullo, S.L.; Sinha, G.R. Advances in smart environment monitoring systems using iot and sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basics of Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) | Classification, Topologies, Applications. Available online: https://www.electronicshub.org/wireless-sensor-networks-wsn/ (accessed on 12 August 2021).
- Przydatek, B.; Song, D.; Perrig, A. SIA: Secure information aggregation in sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 5–7 November 2003; pp. 255–265. [Google Scholar]
- Bosman, H.H.; Iacca, G.; Tejada, A.; Wörtche, H.J.; Liotta, A. Ensembles of incremental learners to detect anomalies in ad hoc sensor networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 2015, 35, 14–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazal, T.M.; Hasan, M.K.; Hassan, R.; Islam, S.; Abdullah, S.; Afifi, M.A.; Kalra, D. Security vulnerabilities, attacks, threats and the proposed countermeasures for the Internet of Things applications. Solid State Technol. 2020, 63, 2513–2521. [Google Scholar]
- Bloch-Budzier, S. NHS using Google technology to treat patients. BBC News, 22 November 2016; 22. [Google Scholar]
- Hamet, P.; Tremblay, J. Artificial intelligence in medicine. Metabolism 2017, 69, S36–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpaydin, E. Introduction to Machine Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nordling, L. A fairer way forward for AI in health care. Nature 2019, 573, S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasan, M.K.; Ahmed, M.M.; Hashim, A.H.A.; Razzaque, A.; Islam, S.; Pandey, B. A novel artificial intelligence based timing synchronization scheme for smart grid applications. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 114, 1067–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Khalifa, O.O.; Hashim, A.-H.A.; Hasan, M.K.; Razzaque, M.A.; Pandey, B. Design and evaluation of a multihoming-based mobility management scheme to support inter technology handoff in PNEMO. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 114, 1133–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Hashim, A.-H.A.; Habaebi, M.H.; Hasan, M.K. Design and implementation of a multihoming-based scheme to support mobility management in NEMO. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2017, 95, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafi, N.S.; Hasan, M.K.; Abdallah, A.H. Traffic flow model for vehicular network. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Computer and Communication Engineering (ICCCE), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 3–5 July 2012; pp. 738–743. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtaruzzaman, M.; Shafie, A.A.; Raihan, S.M.; Hasan, M.K.; Ahsan, T.; Alam, M.S.; Haider, M.B. Golden ratio, the Phi, and its geometrical substantiation. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Student Conference on Research and Development, Cyberjaya, Malaysia, 19–20 December 2011; pp. 425–430. [Google Scholar]
- Nurelmadina, N.; Hasan, M.K.; Memon, I.; Saeed, R.A.; Zainol Ariffin, K.A.; Ali, E.S.; Mokhtar, R.A.; Islam, S.; Hossain, E.; Hassan, M.; et al. A systematic review on cognitive radio in low power wide area network for industrial IoT applications. Sustainability 2021, 13, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtaruzzaman, M.; Hasan, M.K.; Kabir, S.R.; Abdullah, S.N.H.S.; Sadeq, M.J.; Hossain, E. HSIC bottleneck based distributed deep learning model for load forecasting in smart grid with a comprehensive survey. IEEE Access 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, I.; Shaikh, R.A.; Hasan, M.K.; Hassan, R.; Haq, A.U.; Zainol, K.A. Protect mobile travelers information in sensitive region based on fuzzy logic in IoT technology. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
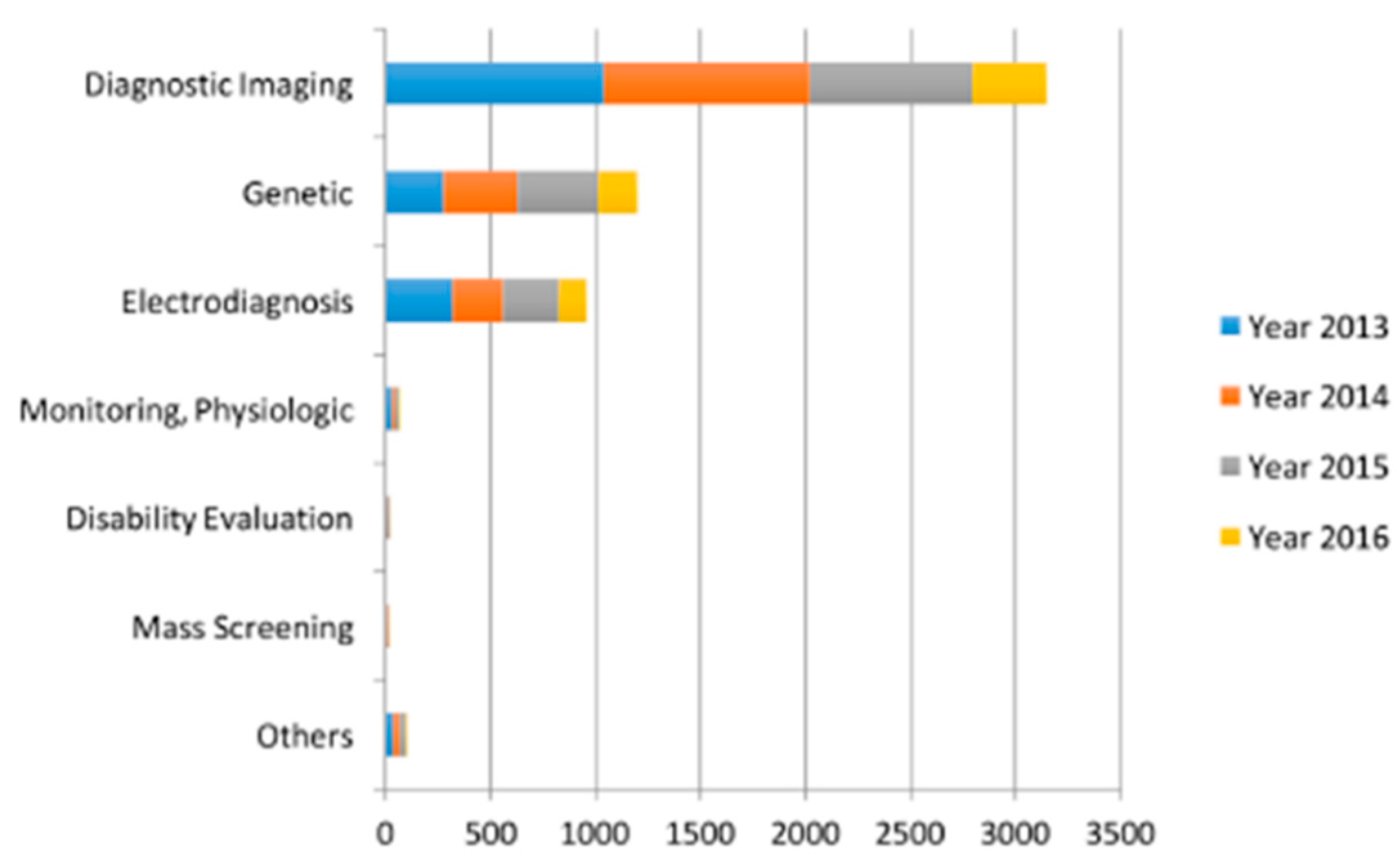






| Sr. | Title | Covered Areas | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smart Cities | Smart Healthcare | AI/ML | Security | ||
| 1 | Toward uniform smart healthcare ecosystems: A survey on prospects, security, and privacy considerations. [7] | N | Y | N | Y |
| 2 | A survey of security and privacy issues in IoT for smart cities [8] | Y | N | N | Y |
| 3 | A Survey on the Status of Smart Healthcare from the Universal Village Perspective [9] | Y | Y | N | N |
| 4 | IoT-based smart cities: A survey [10] | Y | N | N | N |
| 5 | A survey on collaborative smart drones and internet of things for improving smartness of smart cities. [11] | Y | N | N | N |
| 6 | A Comprehensive Survey on Machine Learning-Based Big Data Analytics for IoT-Enabled Smart Healthcare System [12] | Y | Y | Y | N |
| 7 | An architecture for smart health monitoring system based on fog computing [13] | N | Y | Y | N |
| 8 | Deep Learning for Multigrade Brain Tumor Classification in Smart Healthcare Systems: A Prospective Survey [14] | N | Y | Y | N |
| 9 | Artificial Intelligence enabled IoT: Traffic congestion reduction in smart cities. [15] | Y | N | Y | N |
| 10 | On big data, artificial intelligence and smart cities. [16] | Y | N | Y | N |
| 11 | Blockchain for IoT-based smart cities: Recent advances, requirements, and future challenges. [17] | Y | N | N | Y |
| 12 | Urban artificial intelligence: From automation to autonomy in the smart city. [18] | Y | N | Y | N |
| 13 | Applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning in smart cities [19] | Y | N | Y | N |
| 14 | Mitigating and monitoring smart city using internet of things [20] | Y | N | N | N |
| 15 | Machine learning based distributed big data analysis framework for next generation web in IoT [21] | Y | N | Y | N |
| 16 | DeepBlockScheme: A Deep Learning-Based Blockchain Driven Scheme for Secure Smart City. [22] | Y | N | Y | Y |
| 17 | Energy efficiency in internet of things: An overview [23] | N | N | N | Y |
| 18 | OTS Scheme Based Secure Architecture for Energy-Efficient IoT in Edge Infrastructure [24] | Y | Y | N | Y |
| Sr. | Smart Cities Application | ML Algorithm Type |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Smart healthcare | Rule based |
| Public safety | Pattern recognition | |
| Smart transportation | Semantic reasoning | |
| 2 | Smart home | Multiagent learning |
| Realtime traffic routing | Reinforcement learning | |
| 3 | Smart pipelines | HMM |
| 4 | Energy | Semi-supervised deep reinforcement learning |
| Water | ||
| Agriculture | ||
| Combatting pollution |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghazal, T.M.; Hasan, M.K.; Alshurideh, M.T.; Alzoubi, H.M.; Ahmad, M.; Akbar, S.S.; Al Kurdi, B.; Akour, I.A. IoT for Smart Cities: Machine Learning Approaches in Smart Healthcare—A Review. Future Internet 2021, 13, 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi13080218
Ghazal TM, Hasan MK, Alshurideh MT, Alzoubi HM, Ahmad M, Akbar SS, Al Kurdi B, Akour IA. IoT for Smart Cities: Machine Learning Approaches in Smart Healthcare—A Review. Future Internet. 2021; 13(8):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi13080218
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhazal, Taher M., Mohammad Kamrul Hasan, Muhammad Turki Alshurideh, Haitham M. Alzoubi, Munir Ahmad, Syed Shehryar Akbar, Barween Al Kurdi, and Iman A. Akour. 2021. "IoT for Smart Cities: Machine Learning Approaches in Smart Healthcare—A Review" Future Internet 13, no. 8: 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi13080218
APA StyleGhazal, T. M., Hasan, M. K., Alshurideh, M. T., Alzoubi, H. M., Ahmad, M., Akbar, S. S., Al Kurdi, B., & Akour, I. A. (2021). IoT for Smart Cities: Machine Learning Approaches in Smart Healthcare—A Review. Future Internet, 13(8), 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi13080218









