Ambient Environmental Parameter Estimation for Reliable Diffusive Molecular Communications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. System Model of Diffusive Molecular Communications
2.1. System Overview
2.2. CIR for Diffusive Molecular Communication
2.3. Effect of Temperature Change on CIR
2.4. Effect of Transmitter Molecule Volume on CIR
3. Proposed Demodulation Method with Estimation of Ambient Environmental Parameters
3.1. Conventional Threshold-Based Demodulation Method
3.2. Proposed MLSE Demodulation Method
4. Performance Evaluation and Discussion
4.1. Computer Simulation Configuration
4.2. Number of Received Molecules
4.3. BER Improvement by MLSE Demodulation
4.4. Evaluation of BER Characteristics with Respect to Temperature
4.5. Effect of Environmental Temperature on Communication Performance
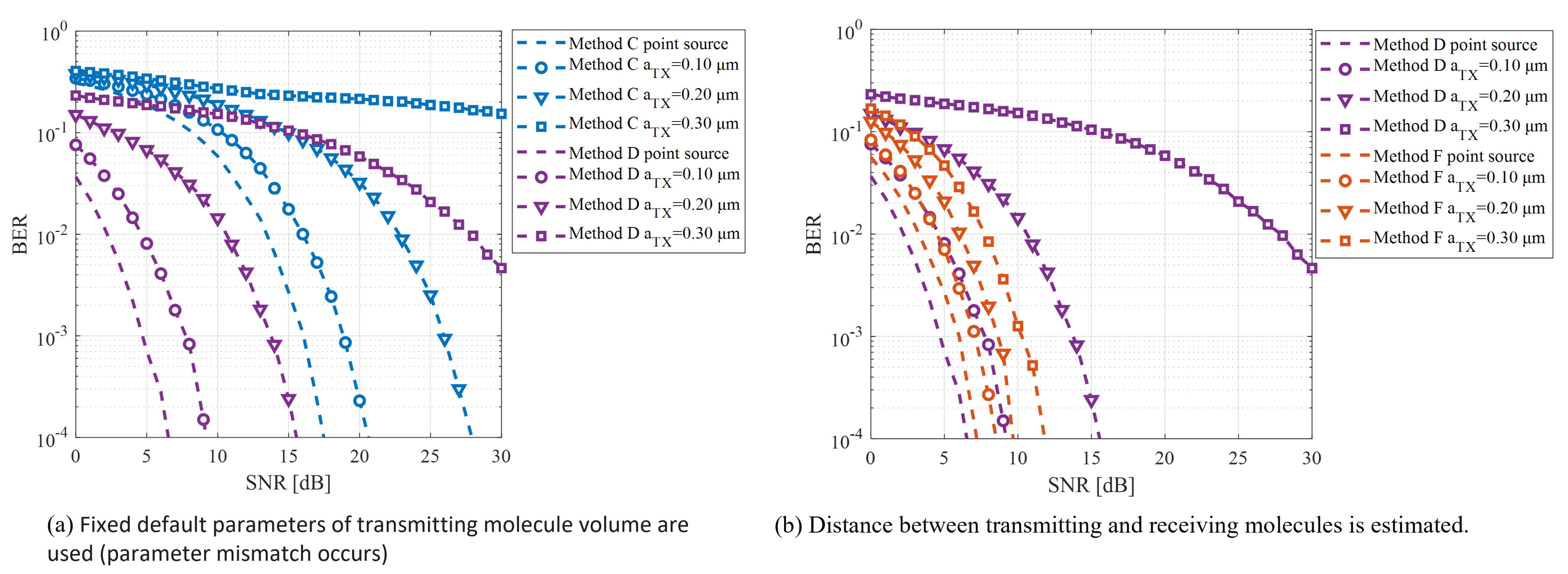
4.6. Effect of Transmitter Molecule Volume on Communication Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MC | Molecular Communication |
| DDS | Drug Delivery System |
| SIPONs | Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles |
| MIMO | Multiple-Input Multiple-Output |
| CIR | Channel Impulse Response |
| BER | Bit Error Rate |
| GFP | Green Fluorescent Protein |
| OOK | On-Off Keying |
| MLSE | Maximum Likelihood Sequence Estimation |
| FEM | Finite Element Method |
| AWGN | Additive White Gaussian Noise |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise power Ratio |
References
- Abd El-atty, S.M.; Gharsseldien, Z.M.; Lizos, K.A. On performance of SISO nanonetworks-based molecular communications. In Proceedings of the 2014 6th International Conference on New Technologies, Mobility and Security (NTMS), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 30 March–2 April 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kuran, M.S.; Yilmaz, H.B.; Demirkol, I.; Farsad, N.; Goldsmith, A. A survey on modulation techniques in molecular communication via diffusion. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 7–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, D.; Almpanis, A.; Noel, A.; Deng, Y.; Schober, R. A survey of molecular communication in cell biology: Establishing a new hierarchy for interdisciplinary applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1494–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Eckford, A.W.; Haraguchi, T. Molecular Communication; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kuscu, M.; Dinc, E.; Bilgin, B.A.; Ramezani, H.; Akan, O.B. Transmitter and receiver architectures for molecular communications: A survey on physical design with modulation, coding, and detection techniques. Proc. IEEE 2019, 107, 1302–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamali, V.; Ahmadzadeh, A.; Wicke, W.; Noel, A.; Schober, R. Channel modeling for diffusive molecular communication—A tutorial review. Proc. IEEE 2019, 107, 1256–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hiyama, S.; Moritani, Y.; Suda, T. Molecular communication. J. Inst. Electron. Inf. Commun. Eng. 2006, 89, 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, T.; Enomoto, A. Recent research and development in molecular communication technology. Natl. Inst. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2008, 54, 73–88. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Helali, A.; Liang, B.; Nasser, N. Novel molecular signaling method and system for molecular communication in human body. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 119361–119375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manocha, P.; Chandwani, G.; Das, S. Characterization of dielectrophoresis based relay-assisted molecular communication using analogue transmission line. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 33352–33359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yang, L. Error performance analysis of diffusive molecular communication systems with on-off keying modulation. IEEE Trans. Mol. Biol. Multi-Scale Commun. 2017, 3, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsad, N.; Pan, D.; Goldsmith, A. A novel experimental platform for in-vessel multi-chemical molecular communications. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM 2017), Singapore, 4–8 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Grebenstein, L.; Kirchner, J.; Peixoto, R.S.; Zimmermann, W.; Wicke, W.; Ahmadzadeh, A.; Jamali, V.; Fischer, G.; Weigel, R.; Burkovski, A.; et al. Biological optical-to-chemical signal conversion interface: A small-scale modulator for molecular communications. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 2019, 18, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Unterweger, H.; Kirchner, J.; Wicke, W.; Ahmadzadeh, A.; Ahmed, D.; Jamali, V.; Alexiou, C.; Fischer, G.; Schober, R. Experimental molecular communication testbed based on magnetic nanoparticles in duct flow. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 19th International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), Kalamata, Greece, 25–28 June 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Nakano, T.; Mahfuz, M.; Guo, W. Bio-Inspired Information and Communication Technologies; Springer Press: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadzadeh, A.; Arjmandi, H.; Burkovski, A.; Schober, R. Comprehensive reactive receiver modeling for diffusive molecular communication systems: Reversible binding, molecule degradation, and finite number of receptors. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 2016, 15, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, L.S.; Yeh, P.C.; Chen, K.C.; Akyildiz, I.F. MIMO communications based on molecular diffusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM2012), Anaheim, CA, USA, 3–7 December 2012; pp. 5380–5385. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, P.; Zhao, L.; Eckford, A.W. Improving receiver performance of diffusion-based molecular MIMO communication. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 18th International Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO), Cork, Ireland, 23–26 July 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Alshammri, G.H.; Ahmed, W.K.M.; Lawrence, V.B. Sequential training-based receiver for On-OFF-keying diffusion-based molecular communications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 18th International Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO), Cork, Ireland, 23–26 July 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Okaie, Y.; Nakano, T. Mobile molecular communication through multiple measurements of the concentration of molecules. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 179606–179615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadzadeh, A.; Jamali, V.; Noel, A.; Schober, R. Diffusive mobile molecular communications over time-variant channels. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2017, 21, 1265–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, B.; Fiorini, P.; Peeters, S.; Majeed, B.; de Beeck, M.O.; Yamashita, I.; Van Hoof, C. A micro-PCR chamber suitable for integration into a monolithic silicon lab-on-a-chip platform. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 25th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Paris, France, 29 January–2 February 2012; pp. 761–764. [Google Scholar]
- Jamali, V.; Farsad, N.; Schober, R.; Goldsmith, A. Diffusive molecular communications with reactive signaling. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kansas City, MO, USA, 20–24 May 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Noel, A.; Cheung, K.C.; Schober, R. A unifying model for external noise sources and ISI in diffusive molecular communication. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2014, 32, 2330–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Number of A molecules | 5000 | |
|---|---|---|
| Diffusion coefficient of A molecule | ||
| Transmitter and receiver distance | μm | |
| a | Radius of receiver distance | μm |
| Forward reaction constant | ||
| Backward reaction constant | ||
| Degradation reaction constant | ||
| M | Number of recepters | 3000 |
| Radius of recepter | nm | |
| T | Temperature | 15, 25, 35 °C |
| Radius of Transmitter | 0, 0.10, 0.20, 0.30 μm |
| Training sequence length | 1 bit | |
|---|---|---|
| L | Data sequence length | 10 bits |
| Symbol interval duration | ms |
| Detection Method | Ambient Environment Parameters | Parameters in Detection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional | Method A | Threshold | Known in advance | Exact parameters used |
| Proposed | Method B | MLSE | (perfectly matched) | |
| Method C | Threshold | Unknown | Default parameters used | |
| Method D | MLSE | (mismatch occurs) | ||
| Method E | Threshold | Ambient parameters estimated | ||
| Method F | MLSE |
| Demodulation Method | Ambient Environment Parameters | Required SNR [dB] |
|---|---|---|
| Method A | 25 °C | 16.0 |
| Method A | 35 °C | 16.0 |
| Method B | 25 °C | 9.2 |
| Method B | 35 °C | 12.5 |
| Method C | 35 °C | - |
| Method D | 35 °C | - |
| Method E | 35 °C | 15.5 |
| Method F | 35 °C | 13.0 |
| Demodulation Method | Ambient Environment Parameters | Required SNR [dB] |
|---|---|---|
| Method C | left 35 °C, right 30 °C | 20.2 |
| Method D | left 35 °C, right 30 °C | 21.9 |
| Method E | left 35 °C, right 30 °C | 16.1 |
| Method F | left 35 °C, right 30 °C | 12.1 |
| Method C | left 30 °C, right 35 °C | 22.5 |
| Method D | left 30 °C, right 35 °C | 27.7 |
| Method E | left 30 °C, right 35 °C | 15.8 |
| Method F | left 30 °C, right 35 °C | 12.8 |
| Demodulation Method | Ambient Environment Parameters | Required SNR [dB] |
|---|---|---|
| Method C | point source | 16.0 |
| Method C | μm | 18.8 |
| Method C | μm | 25.9 |
| Method C | μm | - |
| Method D | point source | 4.6 |
| Method D | μm | 7.7 |
| Method D | μm | 13.8 |
| Method D | μm | - |
| Method F | point source | 6.0 |
| Method F | μm | 7.0 |
| Method F | μm | 8.6 |
| Method F | μm | 10.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toriyama, S.; Hasegawa, S.; Kirchner, J.; Fischer, G.; Anzai, D. Ambient Environmental Parameter Estimation for Reliable Diffusive Molecular Communications. Future Internet 2022, 14, 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi14110311
Toriyama S, Hasegawa S, Kirchner J, Fischer G, Anzai D. Ambient Environmental Parameter Estimation for Reliable Diffusive Molecular Communications. Future Internet. 2022; 14(11):311. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi14110311
Chicago/Turabian StyleToriyama, Shota, Shoma Hasegawa, Jens Kirchner, Georg Fischer, and Daisuke Anzai. 2022. "Ambient Environmental Parameter Estimation for Reliable Diffusive Molecular Communications" Future Internet 14, no. 11: 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi14110311
APA StyleToriyama, S., Hasegawa, S., Kirchner, J., Fischer, G., & Anzai, D. (2022). Ambient Environmental Parameter Estimation for Reliable Diffusive Molecular Communications. Future Internet, 14(11), 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi14110311







