Abstract
Optical burst switching provides a feasible paradigm for the next IP over optical backbones. However its burst loss performance can be highly affected by burst contention. In this paper we discuss traffic engineering approaches for path selection with the objective to minimize contention using only topological information. The discussed strategies are based on balancing the traffic across the network in order to reduce congestion without incurring into link state protocol penalties. The routing strategies are evaluated by simulation on an optical burst switching model specifically developed for the purpose with OMNeT++. Results show that our strategies outperform the traditionally used shortest path routing to an extent that depends on the network connectivity.
1. Introduction
Optical burst switching (OBS) [1,2] is considered as an efficient switching candidate for the core of IP over optical networks. OBS avoids the inefficient resource utilization of optical circuit switching (OCS) and the requirements of buffers, optical logic processing and synchronization problems of optical packet switching (OPS). OBS is widely presented as combining the merits of both OCS and OPS while avoiding their respective shortcomings. In OBS the basic transport unit is the burst, an aggregate message that can be considered as an optical “super packet” containing multiple IP packets going to the same egress node and (if used) classified by some quality of service (QoS) criteria. Bursts are assembled at the ingress nodes and their transmission is preceded by dedicated setup messages, transmitted on a dedicated control channel with the purpose of reserving bandwidth along the path for the upcoming data bursts. Based on the information carried by each setup message, the intermediate nodes reserve switching resources along a certain path, providing an optical channel through which a data burst can be transmitted, after an adequate delay, from source to final destination without any optical-electrical-optical (OEO) conversion [2,3].
OBS, like other switching paradigms, does not perform well in overloaded scenarios and can present low reliability since it generally uses one-way reservation protocols, where data bursts are transmitted without confirmation that resources along the path will be successfully reserved to establish the required end-to-end transparent connection. Consequently, whenever the number of simultaneous reservation attempts exceed the number of available resources, some will fail and owing to the lack of sophisticated optical buffers will result in burst loss. Burst loss degrades the global network performance since dropping may lead to significant IP data losses or rescheduling of lost data with significant impact on any end-to-end delay sensitive applications running in the network layers above. Therefore, minimizing burst loss is a key factor for the practical implementation of OBS networks and any related QoS support.
Considerable effort has been devoted to the study of different methods to handle contention, including, burst scheduling, optical buffering, burst segmentation, wavelength conversion, and deflection routing [4,5]. These are mainly reactive mechanisms driven by burst contention and requiring extra hardware and/or software components at each core node, significantly increasing their cost and complexity, leading to scalability impairments. A simple and cost efficient solution is to deploy contention mechanisms at the edge nodes. This approach has been followed by using burst assembly mechanisms [6,7], by path selection and wavelength assignment [8,9] or by balancing the traffic load between alternate paths [10,11,12]. Path selection mechanisms at the ingress nodes can alleviate contention when compared with typical shortest path (SP) routing approaches. In fact, although successfully used in both circuit switching and packet switching networks, SP routing does not take into consideration the traffic load offered to the network, and it often causes certain links to become congested while other links remain underutilized [10]. This is highly undesirable in bufferless OBS networks, since a few highly congested links can lead to unacceptably high burst loss values for the entire network, corroborating contention avoidance strategies as an important feature in the OBS field.
The aim of this paper is to discuss three static routing strategies intended to minimize the global network contention and the overall burst loss as a preliminary foundation for the development of end-to-end QoS policies. The algorithms presented here (already proposed as ongoing research work in [13,14]) are discussed together for the first time in the context of the QoS provisioning technologies. In addition, the issue of complexity is also addressed for the first time in this article, providing comparative information concerning the sizes of the instances of the ILP problems, as well as the computation times involved in their resolution. This work follows a traffic engineering (TE) approach that uses only topological information to be integrated in an integer linear programming (ILP) formulation from which optimized routes are obtained. These routes are primarily intended to be used alone as single-path static routes to provide load-balancing without the need for extra link-state signalization, but a combined use with other technologies is not precluded.
The benefits of TE over SP are well-known. In fact load balancing is being successfully used in IP networks to map traffic from congested areas to lightly loaded ones, and several proposals were already deployed for the wavelength routed (WR) networks. However, these approaches cannot be directly applied to OBS networks. Different from IP networks where buffers are intensively used, and different from WR networks where wavelengths can be treated as virtual links between ingress/egress pairs with no data loss on the transmission path, buffering in OBS is minimal and wavelengths are statistically shared among many different ingress/egress pairs, leading to a certain finite burst loss probability. These and other intrinsic features of OBS (like the streamline effect, for example) manifestly justify further TE research on the context of OBS networks.
It is also well known that static strategies may have limitations if the traffic pattern is changing over time. However, it is worth pointing out that, by its nature, OBS technology is mainly tailored to support transport backbones presenting aggregate traffic demands that are expected to change relatively slowly. In fact those traffic demands have been recently characterized as quasi-stationary [15]. Moreover, despite being widely believed that the dynamic operation of RWA helps to overcome the inefficiencies of static allocations (in terms of wavelength utilization), recent simulation studies show some static RWA algorithms which perform closely to dynamic ones, in particular in networks without wavelength conversion capability where the benefit of dynamic approaches is not significant [16,17].
The paper is organized as follows. After this introductory section with the objective and the motivation for the proposed work, some OBS intrinsic problems are stated together with a brief state of the art that extends itself into Section 2. In Section 2 the OBS network functionality is presented together with the adopted QoS perspective. Section 3 presents the simulation model and describes the OBS simulator developed for testing. Section 4 presents the routing strategies for burst loss reduction. In Section 5 results are presented and discussed. Finally, Section 6 concludes the paper with final remarks.
2. OBS Networks
An OBS network consists of OBS capable nodes interconnected by optical fiber links supporting multiple WDM channels. In this meshed networks, nodes can be either edge nodes or core nodes (see Figure 1 and Figure 3). Edge nodes are primarily responsible for assembling data packets into bursts, and scheduling the bursts for transmission on outgoing wavelength channels. This nodes, also commonly referred as edge routers, are to be located at the boundary of the OBS network, providing inter-working facilities between the client networks and the OBS network. Core nodes are mainly responsible for switching and forwarding bursts through output ports and for handling contentions. This nodes, also referred as core routers, compose the inner core of the OBS network, and comprise an optical switching fabric, a switch control unit, and processors for routing and signaling. Users, outside the OBS network, are typically electronic IP routers equipped with legacy networking cards through which packet traffic is forwarded (and received) to (and from) the OBS network.
IP packets from client networks go through a burst assembly/disassembly process at the edge of the OBS network. The burst, the fundamental transmission and switching unit in OBS networks, is composed of data payload and a separated control packet (CP). The data payload contains the actual data packets after being aggregated and assembled into a bigger transport unit called data burst, or burst for short. The CP carries all the relevant information of the corresponding burst in order to drive scheduling operations in the core network. The information carried by the CP can include, for example, the length of the burst and its class of service. In OBS networks the CP and the burst are transmitted separately on different channels (wavelengths) allowing for great network flexibility and scalability. In fact, while the CP undergoes OEO conversion at each intermediate core node, the burst is transmitted all-optically through the core. These features allow for two important savings [2]: first, with the assembly/disassembly process deployed at the edge, data needs to be buffered only at the edge nodes where electronic RAM is available, cheap and abundant; secondly, having data and control signals transmitted separately, costly OEO conversions are only required on a few control channels instead of a large number of data channels. The main functions carried out by OBS nodes are described bellow, after being contextualized in a IP over OBS layered architecture and followed by a discussion on adopted QoS perspective.
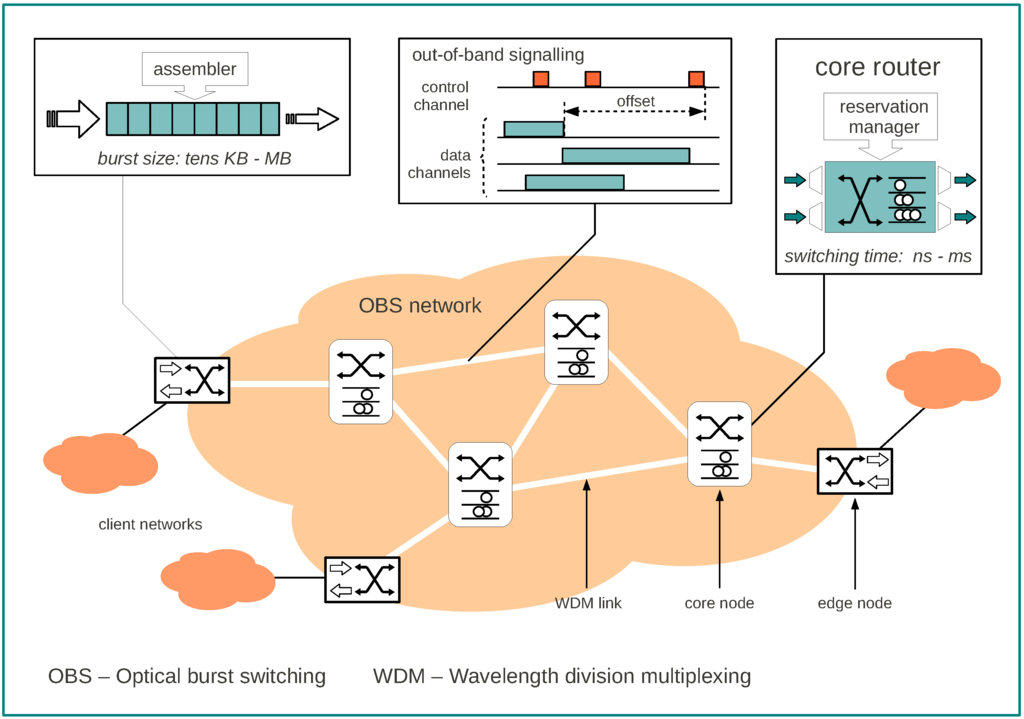
Figure 1.
OBS network (adapted from [18]).
2.1. IP over OBS Model
Beyond reliable physical implementation of OBS networks, a number of very specific procedures are involved in the communication process. In computer-communication networks these procedures (protocols) are normally organized into hierarchical layers of general functionality that can be easily associated to well known reference models. An OBS network architecture can also be represented in layers as a set of protocols that provide services and exchange data. In fact, a layered architecture with well-defined interfaces between layers is crucial for the deployment of OBS networks, both in terms of their internal functioning and their interoperability with the other networks. As referred in a recent multilayered approach for OBS [19], in an IP over OBS hierarchy, the IP layer treats the OBS as its link layer, while the OBS operates on top of the optical layer. Therefore, as a data transport system, the OBS network architecture implements the lower three layers of the reference model, namely physical, data link, and network. In order to understand the way OBS functions, it is important to have some understanding of what happens in this lower network layers.
Figure 2 depicts a functional block diagram of the main functions that need to be executed by edge nodes and core nodes at the medium access control (MAC) layer and optical layer (physical). At the MAC layer, source and destination edge nodes perform the functions of burst assembly and disassembly, offset computation, CP generation, routing and wavelength assignment (RWA) and signaling. At the optical layer, intermediate core nodes are mainly responsible for scheduling and contention resolution of bursts in-transit. These MAC and optical layers offer a set of services that guarantee, for example, certain burst blocking probabilities to the client IP routers located in the layer above [20]. The “quality” of those services is, therefore, strongly dependent on the mechanisms implemented in these lower layers. Those mechanisms are represented with functional blocks in Figure 2 and will be described next.

Figure 2.
Functional block diagram of IP over OBS (adapted from [20]).
2.2. Functional Mechanisms of OBS Nodes
Depending on their sending/receiving status, OBS edge nodes can be viewed either as ingress or as egress nodes. When acting as ingress nodes (see Figure 3(a)), edge nodes are responsible for burst assembly and connection setup mechanisms. Core nodes are located in the core of OBS networks where a transparent switching of bursts from one optical fiber to another takes place (see Figure 1). Core nodes (see Figure 3(b)) perform, the following main functions: scheduling of resources and contention resolution.
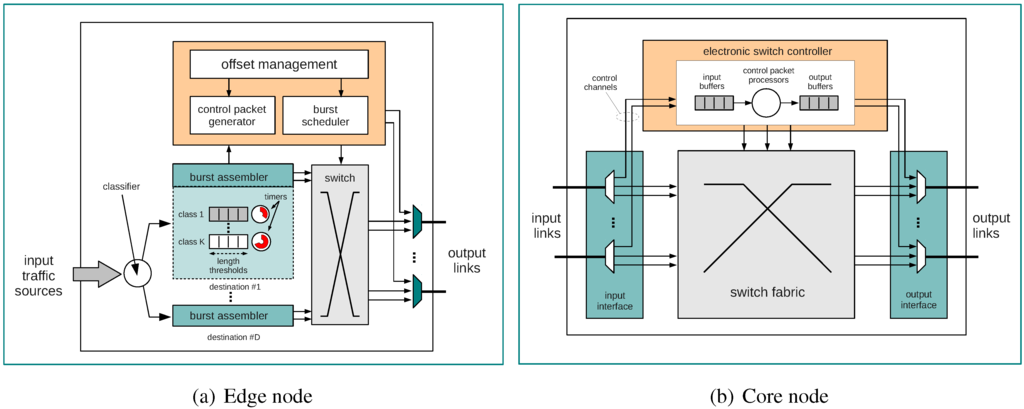
Figure 3.
Functional architecture of OBS nodes (adapted from [18]).
2.2.1. Burst Assembly
This is the process of assembling incoming data packets into bursts. In general, each edge node maintains multiple queues to aggregate the data packets from client networks according to their destinations and QoS requirements (see Figure 3(a)). A burst is then assembled from one of these queues according to a given assembly algorithm whose purpose is to decide when to stop the data aggregation process. Several assembly algorithms have been proposed and investigated up to date [6,7,21,22], but they usually have to take the following parameters into account: a preset timer, minimum burst size and maximum burst size. The timer is used by the edge node to decide when to assemble a new burst. The minimum and maximum burst size parameters determine the length of the assembled burst. These parameters require careful setting because long bursts can hold network resources for long time periods, prone to higher burst losses, while short bursts result in increased number of CPs.
2.2.2. Signaling
For transporting an assembled burst over the optical core a temporary connection must be established between a given pair of edge nodes. This procedure, by which the allocation and configuration of network resources required for burst transmission is accomplished, starts with signaling and proceeds with routing and wavelength assignment. Signaling is, therefore, an important aspect of any network architecture. It specifies the protocol by which connection requests are handled, and its operation determines whether or not the network resources are efficiently utilized. For OBS networks it is even more critical due to the bufferless nature of the core network where contention for resources can lead to data loss. In OBS networks signaling is implemented out-of-band, either by means of a dedicated wavelength channel or by means of a separate control network, and can rely on a distributed approach using one-way reservation or on a centralized approach using end-to-end reservation. Several variations of signaling protocols exist for OBS depending on how and when the resources along a route are reserved for a burst. Their underlying principles can be characterized by the following general attributes [23,24]: direction of the connection setup, which can be one-way or two-way; the starting point where the resource reservation process initiates, where source initiation or destination initiation can be considered; reservation/release of wavelength channels, where explicit or implicit schemes can be adopted.
2.2.3. Routing
This is the process of selecting the paths along which to send the network traffic. Thus, it is also considered a crucial functionality for network performance. In OBS networks, a routing process is used to decide the path of a burst through the core network and this can be accomplished in three different ways: on a hop-by-hop basis, based on the generalized multiprotocol label switching (GMPLS), or using explicit pre-calculated setup. When routing is done on a hop-by-hop basis, like in the IP networks, a fast table look-up algorithm must be used to determine the next hop. In the second approach, routing is done by deploying GMPLS based routing protocols to compute explicit or constraint-based routes at OBS edge nodes as described in [25]. The third approach is to use explicit pre-planned setup connections, which can be established via constraint-based route label distribution protocol (CR-LDP) or resource reservation protocol with traffic engineering (RSVP-TE). Explicit routing is very useful in a constraint based routed OBS network where the traffic routes have to meet certain QoS metrics such as delay, hop count, bit error rate, or bandwidth [26].
2.2.4. Wavelength Assignment
This mechanism is used to determine on which particular wavelength to transmit the burst. Along the selected path, each link must also be assigned a wavelength on which the bursts are carried. In OBS networks wavelength assignment with and without wavelength conversion at the intermediate nodes is possible, whereby wavelength conversion may be fixed, limited-range, full-range, or sparse [20]. Most studies assume full wavelength conversion capabilities throughout the network, and this is also here the case. It should be noted, however, that economic and technical considerations are likely to dictate a more limited and sparse deployment of wavelength converters in the optical network. Therefore, wavelength assignment policies are also expected to be an important component of OBS networks [9].
2.2.5. Scheduling of Resources
Reservation of resources in the core concerns the capability to ensure undisturbed switching and transmission of bursts from input ports to output ports. This process relies on the information carried on each CP about the corresponding burst, which can include, for instance, the offset and the size. Based on this information, core nodes schedule the resources inside the local optical switching fabrics such that bursts can cut through them. The resource scheduling schemes proposed for OBS networks can be classified based on the duration of the reservation, i.e., taking into account the moment when the reservation of a channel started and the moment when that reservation is released (see Figure 4): immediate reservation, delayed reservation, explicit release, and implicit release. These four mechanisms determine the occupancy of resources inside the switching fabrics for a certain burst. It should be noted that the adopted scheduling scheme is closely related with signaling and also depends on the burst assembly process used by the edge nodes, since the information that the CP can provide depends on the assembly algorithm from which it was generated.

Figure 4.
Reservation and release schemes in OBS.
2.2.6. Contention Resolution
OBS networks provide connectionless transport through wavelength channels that support statistical multiplexing. In this working condition it is quite possible that several bursts contend with each other at the intermediate nodes. This can occur because connection requests made by OBS edge nodes generally use one-way reservation protocols in which bursts are transmitted without confirmation that resources along the path will be successfully reserved. Therefore, if a burst arrives at an OBS node and all local resources are already taken, or if two or more simultaneously arriving bursts compete for the same resource, we have contention and (potentially) burst loss. Burst loss is a critical issue with significant impact on any end-to-end application running in the upper layers reducing its overall performance. Since contention is the primary cause of burst loss, contention resolution is one of the main design objectives in OBS networks. The general solution to burst contention is to move all but one burst “out of the way”. In OBS networks this can be accomplished by actions in the time, space or wavelength domains, or any combination therefrom. In fact, since time, space and wavelength are independent, any technique from any domain can be combined, resulting in a potential high number of different contention resolution schemes. Typical approaches for contention resolution using each of the above mentioned three domains can include: optical buffering (time domain), deflection routing (space domain), and wavelength conversion (wavelength domain). It is worth mentioning that these are usually reactive mechanisms driven by burst contention, while the proposals in this article take a more preventive approach in which the space domain is used by the appropriate selection of routing paths in order to avoid congestion, followed by a reactive wavelength conversion attempt if contention occurs.
2.3. QoS Support
Different applications have different requirements regarding the handling of their traffic in the network. For instance, applications such as voice and video cannot tolerate long queuing delays and may need to be given higher priority than regular email or browsing traffic, which are called elastic applications. This is a significant issue for any supporting transport network since current IP provides only best effort service, while some mission-critical and real-time applications might require high QoS support with low values of delay, jitter and loss. To provide a feasible paradigm for the next IP over optical backbones, it is desirable that OBS architectures support different classes of user traffic. In OBS it is not possible to adopt neither the solution used in wavelength routed (WR) networks, nor the QoS developments for IP networks. In fact, while in WR networks the optical connections between ingress and egress pairs are treated as virtual links where QoS mechanisms developed for IP networks can be directly applied, in OBS, wavelengths are statistically shared among many connections between different pairs of nodes, leading to a finite burst loss probability on the transmission path which renders the WR approach unusable. QoS developments for IP can hardly be adapted to OBS networks since they rely on intensive buffering and electronic processing for service class isolation, while in OBS buffering is minimal and optical processing is still in its infancy. Therefore, intrinsic OBS features present new challenges for QoS provisioning, requiring the participation of several network entities along the end-to-end paths. Considering the separation between control and data planes, several new algorithms were proposed in literature, either taking advantage of the offset times between CPs and data bursts along with reservation, scheduling and contention resolution policies, or by exploring traffic engineering approaches like routing and load balancing (see Figure 5). While the first are mainly node-based mechanisms used for QoS differentiation, the later are edge-to-edge mechanisms within the core network to facilitate end-to-end QoS provisioning [27]. The work reported here can be classified in this second category.
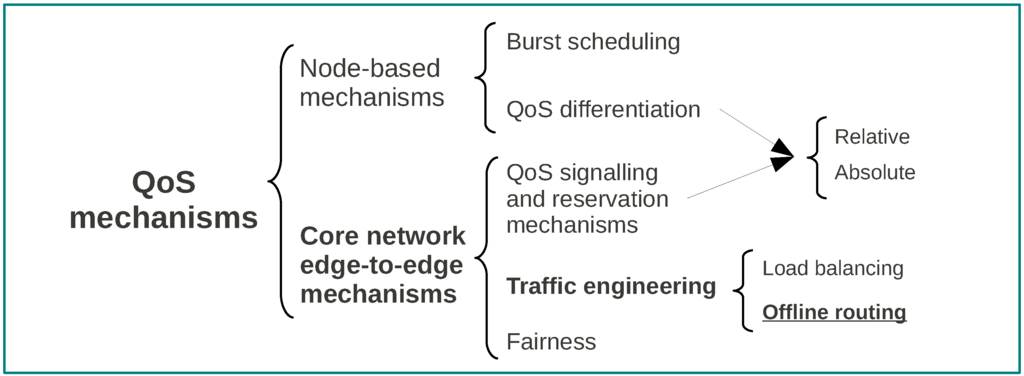
Figure 5.
QoS mechanisms in OBS (based on [27]).
2.3.1. Differentiated QoS Provisioning
In general, differentiated QoS provisioning can be achieved by introducing differentiation at some point in the network. In OBS networks this differentiation can be included in the functional mechanisms described in the subsection above, and various proposed schemes providing QoS can be classified in the following four categories based on the stage at which service differentiation is performed [28]: assembly-time schemes, reservation schemes, scheduling schemes, and contention resolution schemes.
The assembly-time category includes differentiation preformed during the assembly of packets into bursts. Examples of these schemes include a burst length differentiation technique which assigns different burst sizes for different classes of traffic [29]; prioritized assembly using composite burst assembly techniques along with burst segmentation [6,22,30,31]; and intentional dropping, where lower priority bursts are intentionally dropped at assembly under certain predetermined conditions [28,32], some of theme providing absolute QoS differentiation in OBS networks [8,33,34].
The reservation category comprises service differentiation schemes using different reservation policies for different classes. Proposals in this category include offset-time based mechanisms, providing service differentiation in terms of burst loss probability by setting different offset times for bursts with different priorities [35,36,37,38,39]; the forward resource reservation scheme, where the authors present a transmission mechanism embedded at ingress nodes to efficiently reduce the end-to-end delay [40]; preemptive reservation protocols, where a node may drop, or preempt, a low priority burst already scheduled to make room for a high priority one (similar to intentional dropping but more efficient, because it drops only those necessary to schedule the high priority burst) [41,42,43,44], and a probabilistic variant to provide relative burst loss rate differentiation by setting different preemption probabilities for multiple classes of traffic [45,46]; and wavelength limited schemes where lower priority bursts are restricted to use only a certain set of wavelengths, while those with higher priority can use a larger, or complete, set of wavelengths [34,47].
Proposals in the scheduling category provide differentiated QoS by allocating different amounts of bandwidth to different service classes [48], where the processing of a low priority control packet is delayed at the core node by a certain period of time, allowing higher priority CPs which arrive later to reserve bandwidth ahead of the low priority bursts; a slot-based prioritized scheduling scheme is also proposed in [49]; and an approach relying on a centralized request server that performs the scheduling for the entire network trying to minimize delay [50].
Contention is the major cause of burst loss in OBS networks. Considering that most of the QoS mechanisms of OBS networks have burst loss or blocking probability as their main QoS metrics of interest, then, contention resolution is also considered in most of them. Examples of such mechanisms using priorities and burst segmentation can be found in [6,30,31]. Once in OBS networks data loss may occur when bursts contend for network resources, there have been several proposals to resolve contentions in order to minimize burst loss (some presented above). These localized contention resolution techniques react to contention, but do not address the more fundamental problem of congestion. Hence, there is a room for network level contention avoidance using TE techniques in order to minimize burst loss. This can be achieved by load-balanced routing techniques, as described bellow.
2.3.2. Traffic Engineering
Traffic engineering (TE) has long been considered an essential mechanism for any next generation networks (NGN) used to improve its overall performance. A network without TE is, in most cases, operated under the simplest way to route traffic flows based on the fixed shortest path. Despite the benefits of such simplicity, it can cause some traffic load unbalance in the network, i.e., a large amount of traffic may traverse a certain set of links, while there can be little traffic load on other links. The disadvantage of such an unbalance is poor network capacity utilization, making it difficult to guarantee a certain level of performance to data flows requiring, for example, less than a certain level of delay, jitter or dropping probability. To improve such an unbalanced situation and increase the network capacity utilization, TE tries to best balance link utilization in the network to avoid congestion on some links, creating ground for QoS guarantees. This can be accomplished by load balancing and offline routing (see Figure 5).
The key form of TE is load balancing, in which traffic from congested areas is diverted to lightly loaded areas. In doing so, load balancing frees up network resources at bottleneck links and helps the network to provide better QoS to end users [27]. Several load balancing algorithms have been proposed for OBS networks, some of them [51,52] for example, adopting an offline approach formulated as an optimization problem and solved by ILP. Dynamic and adaptive approaches for best effort traffic can be found in [11,53] and [54] respectively, considering wavelength conversion restrictions in [12,55], and considering the streamline effect in [56].
Offline routing is another load-balanced related form of TE focused on the selection of paths with the objective of balancing the traffic across the network links in order to reduce congestion and improve the overall performance. This are complex problems usually solved by ILP optimization or heuristics. Examples can be found in [10,15,57] and also in the routing strategies next discussed in Section 4 of this article.
3. Simulation Model
The simulation model described in this paper is deployed in two stages as depicted in Figure 6. The first stage, which comprises the determination of routing paths, is the optimization stage and was developed using the IBM ILOG CPLEX optimizer [58]. In this stage routing problems are formulated using ILP, which is a widely used approach to address both high level and system level synthesis. The second stage comprises the application of a routing solution. This is the simulation stage in stricto sensu, where the optimized paths produced on the first stage are incorporated into an OBS network simulation scenario developed within the OMNeT++ simulation environment [59] and some programming effort mainly in C++, but also comprising some middleware scripts developed in Perl for easy integration of the two stages mentioned above.
3.1. First Stage—Routing Path Determination
The aim of the routing strategies proposed is to produce edge-router-based routing solutions able to minimize burst contention using only topological network information. We assume that the network operates with source based routing, that is, the ingress edge node selects a path for a burst that enters the network from a set of K previously calculated paths. Therefore, this 1st stage comprises itself two parts: first, the calculation of K eligible paths for each pair of nodes, and second, the selection of one path from the set of K eligible paths for each pair of nodes so that the chosen paths minimize the global network contention. For the first part, the K most link disjoint shortest paths are determined. For the second part the following three optimization strategies for contention avoidance have been calculated: the minimize Maximum Congested Link (MCL), based on the idea that the more a certain link is included in the chosen paths for source-destination pairs, the highest the blocking probability can be [13]; the minimize Maximum End-to-end Congested (MEC) path, based on the idea that blocking may occur at any link traversed by a burst along the path [13]; and one Streamline Based Pre-planned Routing (SBPR) strategy [14] considering the streamline effect, a reported phenomenon unique to OBS networks wherein bursts traveling in a common link are streamlined and do not contend with each other until they diverge [15]. Mathematical formulations for these routing strategies will be presented in Section 4.
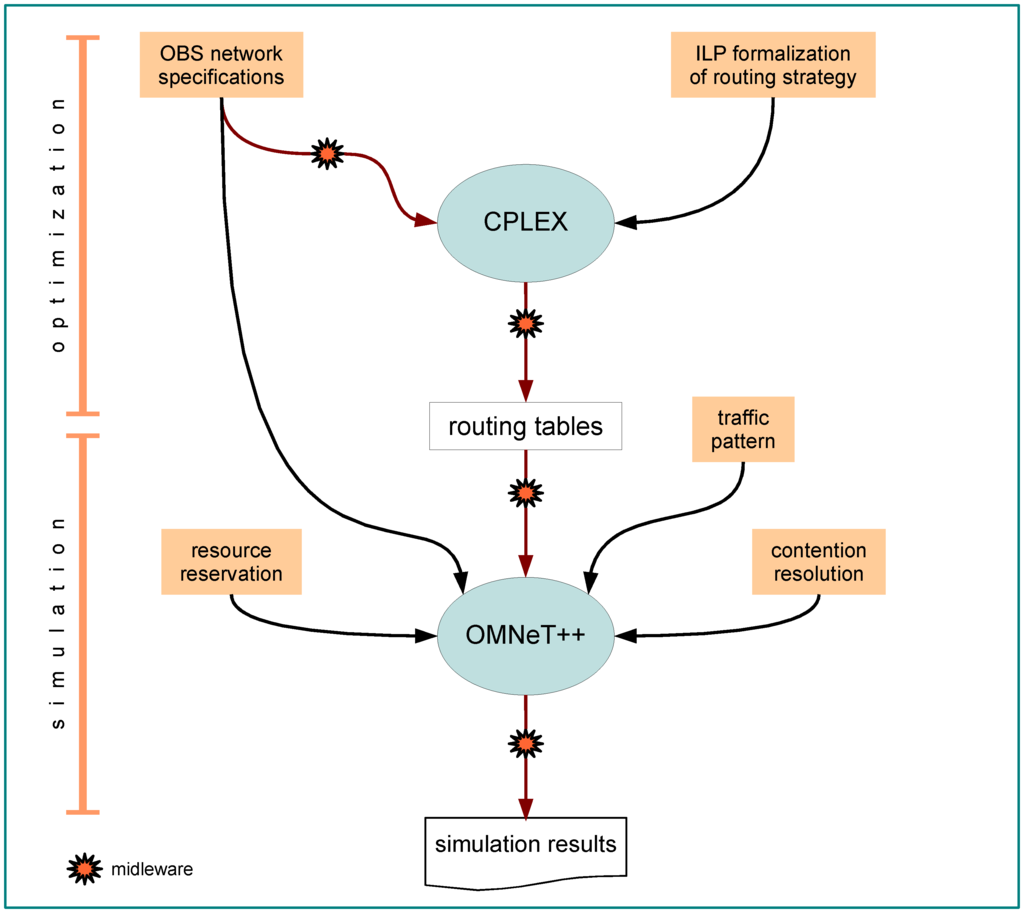
Figure 6.
Conceptual view of the simulation methodology.
3.2. Second Stage—Routing Path Application
The functional architecture of our OBS model has similar characteristics to the ones presented in [3,60], assuming, like it is done in these proposals, that each node can support both new input traffic generated by the client networks and the in transitu traffic passing all-optically from source to final destination. The simulation studies were done on different networks, including two from North America (ARPANET and NSFNET) one European (COST239) and one with a random configuration of nodes, whose topologies are depicted in Figure 7. Some physical parameters of these networks are presented in Table 1, in which the average degree is considered the average number of physical connections per node, and the physical connectivity is defined as the normalized number of bidirectional links with respect to a physically fully connected network of the same size [61]. The nodes are connected by links representing optical fibers with the same characteristics, i.e., having 16 wavelengths per link with a transmission capacity of 10 gigabits per second (per wavelength).
This simulation model was conceived to work in a stochastic self-driven way. Thus, it generates its own input data traffic, representing the load offered to the OBS network to be switched and forwarded. Since in this model we are mainly interested in a comparative evaluation of alternative routing strategies, the issue of packet aggregation and burst assembly is not considered. This means that the traffic used in the network is already burst based traffic after the assembly process.
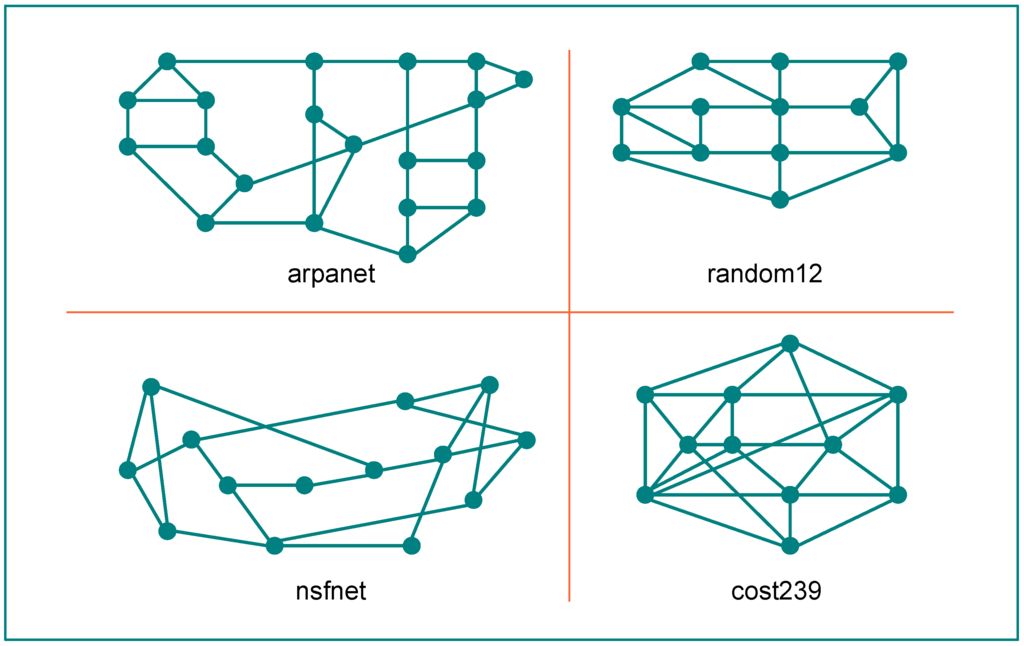
Figure 7.
Network topologies under study.

Table 1.
Network physical parameters.
| Network | Num of | Num of | Degree | Connectivity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nodes | links | (av) | (stdev) | ||
| ARPANET | 20 | 62 | 3.1 | 0.45 | 0.16 |
| NSFNET | 14 | 42 | 3.0 | 0.55 | 0.23 |
| RANDOM12 | 12 | 42 | 3.5 | 0.67 | 0.32 |
| COST239 | 11 | 52 | 4.7 | 0.65 | 0.47 |
Traffic pattern: The traffic characteristics of an OBS network are highly dependent on the burst assembly algorithm in use [60,62,63]. Both theoretical and simulation results show a smoothing effect resultant from a reduction in the degree of self-similarity of the input packeted traffic. In [63] it is argued that, despite of long range dependence, the burst arrival process can be assumed to be Poisson in low timescales. As a consequence, there is nearly no influence of self-similarity on blocking probability, while the influence is significant in optical buffers dimensioning. Therefore, in our approach, the adopted traffic pattern is based on a Poisson arrival pattern assuming a previous burst length threshold assembly method, generating messages that are bytes.
Signaling scheme: The bursts are forwarded through the core backbone reproducing the relevant actions of the JET signaling scheme, i.e., using delayed reservation and implicit release. The CP processing time is assumed to be 10 μs and average switching time in a core node is also 10 μs, although other values from 12.5 μs down to 1 μs could be adopted depending on the technology in place (current state-of-art or foreseeable in the near future). The timings assumed by this configuration parameters are in agreement to the ones widely used in OBS research, like in [64,65], for example.
Routing: The model employs source routing in which a complete routing decision is taken at the ingress edge node. Like the approach adopted in [10,54], the path over which the burst must travel is carried by the CP that precedes the transmission of each burst and is not modified by downstream nodes. The adopted path is fetched from the edge nodes routing tables, previously populated by the results of the path selection strategies calculated during the 1st stage of this model.
Contention resolution: The core nodes do not employ any buffering in the data path and they do not use deflection routing. It is generally assumed that the nodes are capable of performing a full wavelength conversion. Blocking occurs only if there are no free wavelengths available to accomplish the next hop on a predetermined path to a certain destination. If scheduling fails, the burst is simply dropped and no further contention resolution method is adopted.
Together with the network topology description, the OBS simulation model, which is composed of OBS capable nodes interconnected by optical fibers, is based on the modules depicted in Figure 8, whose functionality, generically described in Section 2, will be succinctly presented next from the simulation point of view.
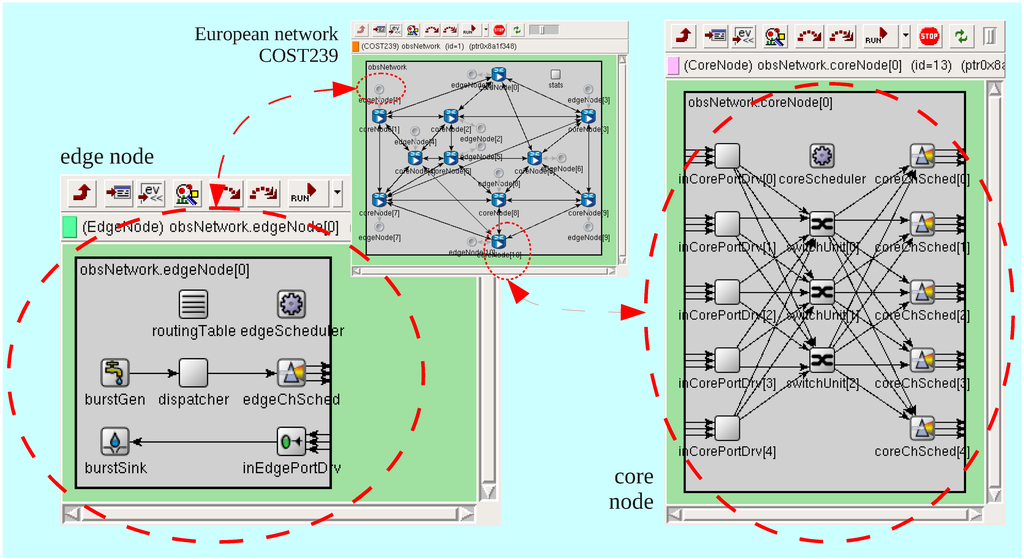
Figure 8.
Screenshots of the OBS simulator (simplified view).
3.2.1. Edge Node Simulator
Edge nodes connect multiple subnetworks running on top of legacy link layer protocols to the OBS network. They can be considered either ingress or egress nodes. When acting as ingress node, edge nodes are responsible for aggregating the incoming packets into bursts, for taking the initial (and here also permanent) routing decision, and for scheduling the bursts for transmission on outgoing channels. In our model, we assume the burst as the basic transport unit of interest. Hence, the issues of packet aggregation and burst assembly are considered out of scope. It is worth noting that the traffic generator developed here is a burst generator, generating messages based on a Poisson process with a symmetric all-to-all traffic matrix. Thus, whenever a Poisson process timer expires, a new burst is generated, a destination address is chosen at random between all other nodes in the network, a route to the destination node is taken from the source nodes routing table, and an initial wavelength is selected among the free ones. The model uses source-based routing, which is our first way of addressing contentions with an a priory action on the space domain. The burst, together with all its relevant information, is then retained in a system queue organized by destination address, and the connection-setup process starts with the sending of a CP on the appropriate dedicated channel. The CP is always transmitted before the corresponding burst and separated from it by the adequate offset time. The model calculates this offset time in order to allow the CP to be processed at each subsequent node, before the burst arrival, and in such a way that an optical path can be properly reserved for burst delivery.
3.2.2. Core Node Simulator
Core nodes are responsible for processing CP reservations, for switching the bursts from an input to an output port without OEO conversion, and for handling contentions. Signaling in OBS is typically implemented using one out-of-band channel, meaning that CPs are transmitted on a wavelength different from the group of wavelengths used to transmit bursts. This model uses for the transmission of CPs. Several signaling schemes have been proposed for burst scheduling but the Just in Time (JIT) and the Just Enough Time (JET) are two of the most popular protocols using distributed signaling. These are both one-way and source-initiated signaling schemes, which means that the bursts are sent to the core network without waiting for acknowledgments regarding the success or failure of the reservation attempts. Despite being closely related, they differ in the duration of the reservations. The JIT protocol uses immediate reservation with the data channel being reserved as soon as the CP reaches the node, while JET delays the channel reservation until the burst arrival (see Figure 4). This technique, together with the implicit release, makes JET more efficient than JIT regarding bandwidth utilization, resulting in lower blocking rates and low end-to-end delay [5]. For these reasons our strategies are evaluated under a JET-type behavior scheme.
Together with burst forwarding without leaving the optical domain, core nodes are also responsible for taking contention resolution actions. Contention occurs when multiple bursts from different sources are destined for the same output port at the same time [66]. In addition to the initial path selection strategies adopted on the edge nodes, in handling burst contentions, the core nodes are assumed by default to be equipped with devices having full wavelength conversion capability. This means that, by default, no end-to-end wavelength continuity constraint exists, and that any incoming wavelength can be shifted to any outgoing wavelength, if one is available. As a result, only if there is no wavelength available on the output port the burst will be dropped without any further contention resolution action.
4. Routing Strategies
In the following discussion let be the graph representing an OBS network, where is the set of nodes, and the set of unidirectional fiber links. We define a path over which a burst must travel, v, as a connected series of directed links, written as , from source node to destination node . The set of paths that can be used by a burst from s to d is defined as and the set including all is defined as . We also define if link is included in v, otherwise, and if the two paths v and share at least one link. When taking a specific node as a reference point, a link coming out of that node can be denoted as and a link coming into that node can be denoted as . The total number of elements in , and is denoted by N, L and V. A demand matrix can be considered, where represents a relative load from source node s to destination node d. Although the traffic demands are included in the formulations for a demonstrative purpose, still they are skipped in the performed simulations.
We consider three path selection strategies: MCL, MEC and SBPR. These strategies are formulated in three ILP problems for which a single path for each pair of nodes must be selected. That is, for the overall network and for each strategy, paths must be chosen and resources allocated for burst delivery. For each strategy, input information includes a set of K eligible paths which are computed in advance. The optimization problems are solved in our simulation model by CPLEX optimizers, and the results obtained are used to populate the routing tables in order to achieve a global contention reduction.
4.1. MCL Path Selection Strategy
This strategy is based on the idea that the more a certain link is included in the chosen paths for source-destination pairs, the highest the blocking probability will be. This situation is represented on the small network of Figure 9(a) where, considering the paths between nodes 0→3, 1→5, 2→3 and 2→5, the SP algorithm can bring excessive load to the link 1–3 leaving other links underutilized. Therefore, paths for source-destination pairs should be selected with the objective of minimizing the blocking probability of the link with highest expected contention value, denoted by . This is achieved by the following ILP optimization problem:
Subject to
where is a binary variable that indicates if v is used to carry bursts from node to node . Equation (2) is a constraint stating that one path must be found for each pair of nodes. Each path is selected from the corresponding set of available paths. Equation (3) states that the expected congestion at a link must not exceed .
With this algorithm, and for the same scenario presented, we can see in Figure 9(b) that the traffic is now more evenly distributed, increasing the network utilization to avoid the highly congested situation presented in Figure 9(a). It should be noticed, however, that on this attempt to spread the traffic throughout the network some paths can became longer (like the case of path 2→3). This observation was the driving force to the next strategy.
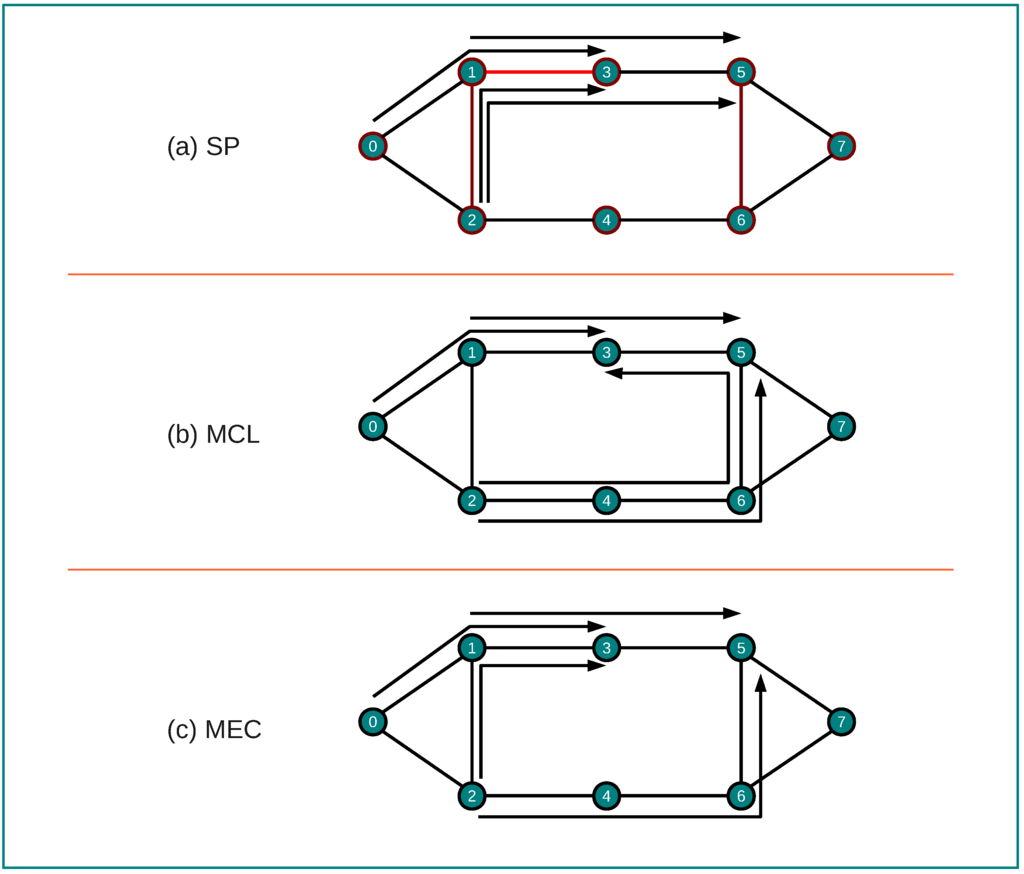
Figure 9.
A small illustrative example of SP, MCL, and MEC.
4.2. MEC Path Selection Strategy
This strategy is based on the idea that blocking may occur at any link traversed by a burst along the path. Therefore, paths for source-destination pairs should be selected so that demands have the smallest probability of contending with other demands at every link from source to destination, minimizing the end-to-end blocking. This is achieved by the following ILP optimization problem, where denotes the value of the path having the highest number of contends.
Subject to
where is a binary variable that indicates if v is used to carry bursts from node to node , and is a binary variable that indicates if v and have both been selected to carry bursts and share at least one link. Similarly to the previous strategy, the constraint expressed on Equation (6) states that one path must be found for each pair of nodes. Equation (7) forces to be 1 if v and share a link and have both been selected to carry bursts. Otherwise, and due to the minimizing nature of the objective function, will be 0. Equation (8) states that the contending value of a source-destination pair must not exceed .
4.3. SBPR path selection strategy
This strategy takes into account the streamline effect [56] assuming that contention at a certain link can be strongly dependent on the number of input streams to the link. This is so because bursts traveling in a common link are streamlined and do not contend with each other until they diverge [67]. This happens because OBS networks are bufferless and once contentions are resolved at the first link where they merge, no further contentions will happen among them thereafter. However, like was depicted in Figure 10, those bursts may still contend with other bursts that merge at downstream nodes [67]. This phenomenon has impact in load balancing and must also be considered for path selection approaches. Taking into account that we are using full wavelength conversion, on a potentially contending situation, the wavelength of the contending burst may change at any hop. Therefore, at any particular node, all the arriving bursts can contend with each other regardless of their incoming links. This situation results in a somewhat more flexible streamline effect where a global potential joining point exists on each core node. In this case, our approach considers that routes must be chosen with the objective of minimize “load” differences at the output links. In fact, by dividing the total number of incoming links by the number of output links, a lower value of input links per output link is obtained, naturally favoring the creation of a lower number of inbound paths going to the same output link, while favoring the creation of widely dispersed paths at downstream. This is the principle behind this SBPR strategy.

Figure 10.
An illustrative example of the streamline effect.
The main goal of the next objective function is to minimize , a global bound that stores the highest number of routes competing for an output link. The second component of the objective function is a secondary goal so that routes having a small number of hops are chosen if multiple solutions exist for a given value.
Subject to
where is a binary variable that indicates if v is used to carry bursts from node to node . Equation 11 states that one path must be found for each pair of nodes. Each path is selected from the corresponding set of available paths. For a specific node i, Equation 12 stores in the highest number of selected routes competing for an output link of node i. Note that an attempt will be made to evenly distribute the routes among all output links in order to keep low. Equation 13 stores in the highest value from all . A global bound is being stored in , the variable that will be minimized.
5. Results and Discussion
In this section we provide simulation results that compare the performance of the proposed path selection schemes with the SP. In the evaluation of our strategies, results are plotted with burst loss values normalized to the number of bursts that enter the network backbone against the average load. The graphs presented in Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14 show the performance of our MCL, MEC and SBPR strategies applied to the four networks represented in Figure 7 having its nodes equipped with wavelength converters, i.e., where, on a contending situation, the contending burst can have its wavelength changed, as a measure of last resort, before being dropped. These graphs show that the plotted burst loss values for the proposed strategies are always bellow the reference curve for the SP routing, whose plotted values are in agreement with the ones generally presented in literature [10]. This means that the optimization effort required by the strategies is being productive in reducing contention, resulting clearly in better performance with respect to burst loss. These graphs show also that burst loss values decrease from Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14. Taking into account that simulations were done under absolutely similar conditions with regard to the number of bursts generated per source node (), arrival pattern, traffic load variation, and number of K shortest paths per pair of nodes being provided to each strategy, we assume that the progressive gain of the proposed algorithms is also related with the way nodes are connected in OBS networks. In fact, these graphs are presented in ascending order of physical connectivity (see Table 1), which corroborates the work in [68] where the influence of nodal degree on the performance of OBS networks is analyzed. These algorithms are, therefore, more efficient in highly connected networks, and this explains why they provide better results for the COST239 topology than for the ARPANET topology.
Among the three proposals the SBPR presents almost always the best performance, which means that reducing the number of upstream links competing for the same downstream link by balancing the potential load at the output links is more productive than the approaches in MCL and MEC. It is worth pointing out that this results from SBPR are obtained with an ILP problem that converges to an optimal solution in less then one second, like it is mentioned in Table 2 where the CPLEX total root+branch&cut time spent is reported (except for MEC). Results show also that MEC behaves almost always better than MCL, but the algorithm of MEC is significantly more expensive in terms of computation complexity, considering the sizes of the instances of the optimization problems both in terms of number of constraints and number of relevant variables involved (see Table 2). In fact, the ILP formulation of the MEC algorithm is so heavy that its optimization stage was intentionally terminated after a solution has been found bellow 1% of the optimal value, rendering what can be considered a near-optimal solution obtained in some tens of minutes. The exception to the prevalence of MEC over MCL is the case of the COST239 network where the opposite happens, probably because its high connectivity makes it possible to obtain alternative paths with a similar reduced number of hops. In fact, alternative longer paths means more possibilities of contention, and potentially higher values of burst loss. For these reasons, and considering that the algorithm of SBPR is also light in terms of computation, SBPR can be considered the best choice for the networks under test, in particular for the more connected ones, where lower levels of burst loss can be achieved.

Table 2.
Sizes of instances and reported time spent in the optimization problems.
| MCL | MEC | SBPR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| number of constraints | 442 | 1299220 | 462 | |
| ARPANET | number of variables | 1141 | 1299601 | 1161 |
| total time spent in sec. | 0.02 | 0.01 | ||
| number of constraints | 224 | 297934 | 238 | |
| NSFNET | number of variables | 547 | 298117 | 561 |
| total time spent in sec. | 0.02 | 0.02 | ||
| number of constraints | 174 | 156684 | 186 | |
| RANDOM12 | number of variables | 397 | 156817 | 409 |
| total time spent in sec. | 0.01 | 0.01 | ||
| number of constraints | 162 | 108790 | 173 | |
| COST239 | number of variables | 331 | 108901 | 342 |
| total time spent in sec. | 0.02 | 0.02 |
This routing strategies may serve as a basis for the development of QoS policies. If it is truth that the concept of QoS in communication systems is closely related to the network performance of the underlying routing system [69], these strategies, with the obtained results, can be considered as service related primitives allowing for the implementation of high-level differentiation. For instance, considering the curves for burst loss in Figure 14, it is possible to exploit the “no loss” bound of the SBPR algorithm to guarantee no burst loss at all until an average load of 54% of the capacity, and a burst loss ratio of 1 burst in 100,000 for an average traffic load of 80% of the capacity. Obviously, other policies are possible taking advantage of these optimally routed traffic patterns that can be exploited for end-to-end QoS provisioning.

Figure 11.
Proposed strategies vs. SP for Arpanet.

Figure 12.
Proposed strategies vs. SP for Nsfnet.
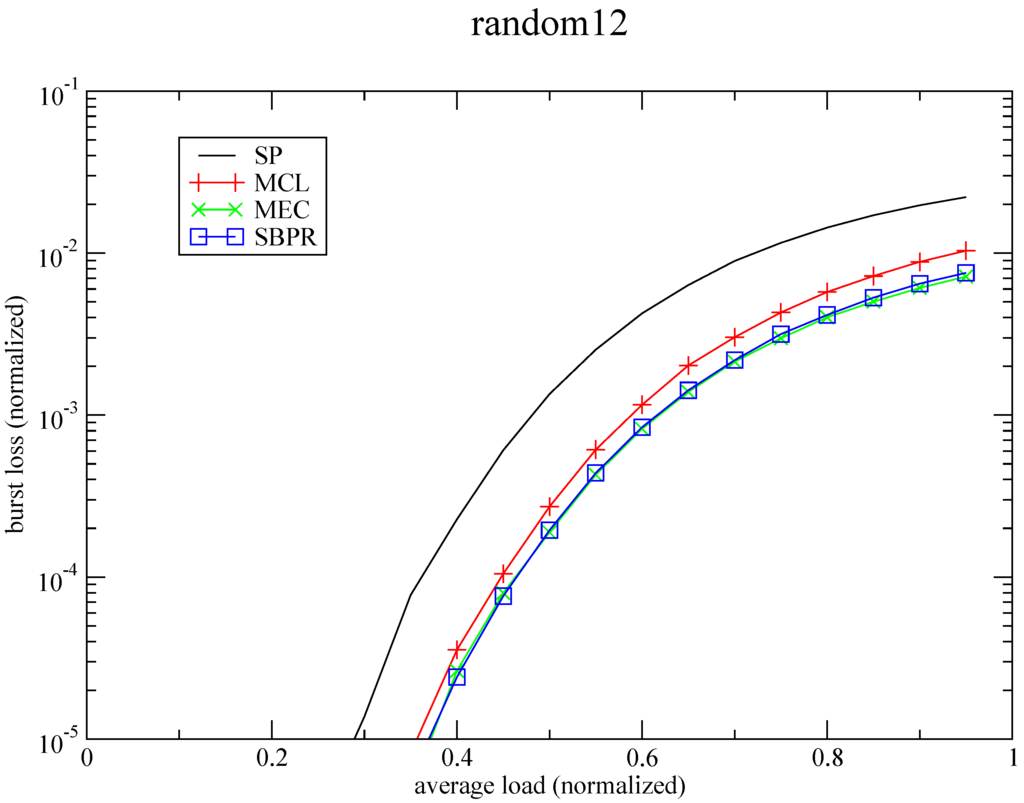
Figure 13.
Proposed strategies vs. SP for Random12.
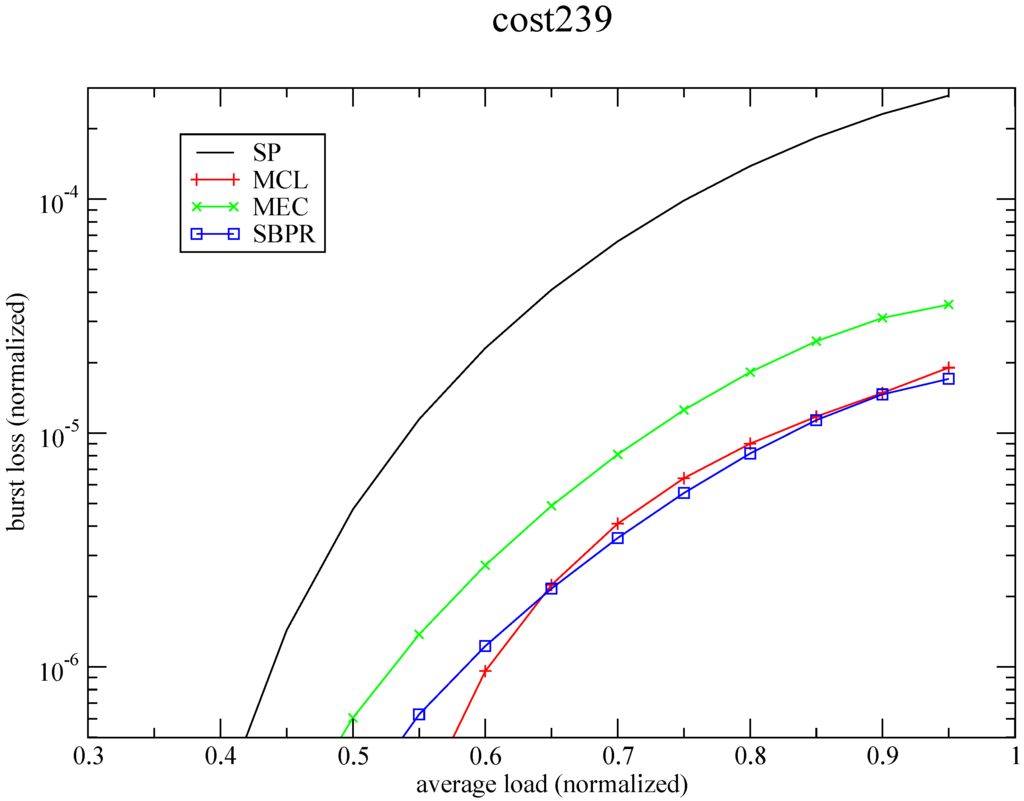
Figure 14.
Proposed strategies vs. SP for Cost239.
6. Conclusions
In this paper we take a TE approach which substantially reduces contention using only topological information. This approach uses static routing and has benefits in both network architecture, and network QoS.
Routing is preferentially done online and dynamically, based on “current” network resource availability. However, to support dynamic routing, the network may need to be flooded by frequent resource update messages, and additional hardware and software may need to be deployed at each OBS node hampering scalability. Pre-planned static routing can avoid both such signaling overhead and more complicated architecture condition. In addition, optimization techniques can be applied in pre-planned routing such that contention can be minimized, or substantially reduced, from a global point of view.
Considering the architecture, several advantages of our approach deserve to be highlighted: no extra hardware or software components are required on the core nodes for dynamic routing, no network flooding with signaling messages resulting from (over)active link state update protocols, no place for out-of-order arrivals, which are a disadvantage of some dynamic contention resolution schemes, also found on multipath routing schemes, typically requiring large memories at the edge nodes for re-ordering operations. These are important characteristics that permit to keep simple and cost-effective the architecture of the core nodes.
At this level, the service to be taken into account is the delivery of bursts to the correct destination and the quality of this service is described by its performance in terms of burst loss, i.e., the lesser the better. We demonstrate that burst loss can be minimized by appropriately choosing the paths that bursts must follow. That is, an effective choice of paths can lead to an overall QoS improvement for the network. The resolution of an ILP problem is involved in the process, which makes this approach mainly tailored for offline static routing. However, since eligible paths can be provided as input for the strategies, the solutions can be promptly reached. Taking into account the computation times involved (which have been found in a range of seconds for some instances presented in Table 2), the relatively infrequent update requests expected from changes in the OBS backbones whose topologies typically last for long time scales, and the quasi-stationary aggregate traffic demands at optical backbones, which are expected to change relatively slowly [15], this approach can be considered feasible for the real production of OBS networks by means of an operation process to be executed during the initial setup phase of the network.
Our results also show that the achieved performance improvement depends on the physical connectivity of the network, with more highly connected networks showing better performance. This happens because the proposed algorithms take advantage of more, short, alternative paths. Our strategies can provide an initial stage of improved performance, measured in terms of burst loss reduction, without incurring state dissemination protocol penalties. The routes obtained can be used alone, as single-path static routes to provide load-balancing without the need for additional control messages with regard to link status, or combined with other dynamic contention resolution schemes (deflection or segmentation, for example) and used occasionally as a default routing to assume whenever the network needs to recover from instability, favoring network resilience. Considering that any service performance at higher level is directly affected by the network performance, this strategies can also serve as a basis for the development of QoS policies.
Acknowledgments
The work reported in this paper was supported in part by the Foundation for Science and Technology within CEOT (unit 631) at the University of Algarve, Portugal, under the project PTDC/EEA-TEL/71678/2006
References
- Qiao, C.; Yoo, M. Optical Burst Switching (OBS)—A New Paradigm for an Optical Internet. JHSN 1999, 8, 69–84. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Qiao, C.; Yu, X. Optical burst switching: A new area in optical networking research. IEEE Network 2004, 18, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Vandenhoute, M.; Cankaya, H. Control architecture in optical burst-switched WDM networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2000, 18, 1838–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qiao, C. Recent progress in the scheduling algorithms in optical-burst-switched networks. J. Opt. Netw. 2004, 3, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jue, J.P.; Vokkarane, V.M. Optical Burst Switched Networks; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Vokkarane, V.; Vokkarane, V.; Jue, J. Prioritized burst segmentation and composite burst-assembly techniques for QoS support in optical burst-switched networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2003, 21, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Yang, O.W. Provision of differentiated performance in Optical Burst Switching networks based on burst assembly processes. Comput. Commun. 2007, 30, 3449–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Vokkarane, V.; Jue, J.; Chen, B. Absolute QoS differentiation in optical burst-switched networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2004, 22, 1781–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Rouskas, G. Wavelength Selection in OBS Networks Using Traffic Engineering and Priority-Based Concepts. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2005, 23, 1658–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Rouskas, G.N. Traffic engeneering approach to path selection in optical burst switching networks. OSA J. Opt. Netw. 2005, 4, 759–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mohan, G.; Chua, K. Dynamic load balancing in IP-over-WDM optical burst switching networks. Comput. Netw. 2005, 47, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Ortega, M.A.; Lopez-Ardao, J.C.; Rodriguez-Rubio, R.F.; Lopez-Garcia, C.; Fernandez-Veiga, M.; Suarez-Gonzalez, A. Performance analysis of adaptive multipath load balancing in WDM-LOBS networks. Comput. Commun. 2007, 30, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barradas, A.L.; Medeiros, M.C.R. Edge-Node Deployed Routing Strategies for Load Balancing in Optical Burst Switched Networks. ETRI J. 2009, 31, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barradas, A.L.; Medeiros, M.C.R. Pre-planned optical burst switched routing strategies considering the streamline effect. Photonic Netw. Commun. 2010, 19, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Mohan, G.; Chua, K.C. Route optimization in optical burst switched networks considering the streamline effect. Comput. Netw. 2008, 52, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata-Beghelli, A.; Bayvel, P. Dynamic Versus Static Wavelength-Routed Optical Networks. J. Lightwave Tech. 2008, 26, 3403–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K. Heuristic algorithms for routing and wavelength assignment in WDM optical networks. In Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Processing IPDPS, Sydney, Australia, December 2008; pp. 1–8.
- Klinkowski, M. Offset Time-Emulated Architecture for Optical Burst Switching—Modeling and Performance Evaluation. PhD Thesis, Department d’Arquitectura de Computadores, Universitat Politecnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain, November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Farahmand, F.; Vokkarane, V.M.; Jue, J.P.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C.; Freire, M.M. Optical burst switching network: A multi-layered approach. J. High Speed Netw. 2007, 16, 105–122. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, M. Optical burst switching. In Optical Switching Networks; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Chapter 9; pp. 103–134. [Google Scholar]
- Azodolmolky, S.; Tzanakaki, A.; Tomkos, I. Study of the Impact of Burst Assembly Algorithms in Optical Burst Switched Networks with Self-Similar Input Traffic. Transparent Opt. Network. 2006, 3, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Sarwar, S.; Wallentin, L.; Franzl, G.; van As, H.R. Composite burst assembly with high-priority packets in the middle of burst. In Proceedings of BROADNETS 2008: The 5th International Conference on Broadband Communications, Networks and Systems, London, UK, September 2008; pp. 140–145.
- Jue, J.P.; Vokkarane, V.M. Signaling. In Optical Burst Switched Networks; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Chapter 4; pp. 37–56. [Google Scholar]
- Vokkarane, V.M. Intermediate-node-initiation (INI): A generalized signaling framework for optical burst-switched networks. Opt. Switching Netw. 2007, 4, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannie, E.E.A. Generalized Multi-Protocol Label Switching (GMPLS) Architecture. RFC 2004, RFC 3945. [Google Scholar]
- Battestilli, T.; Perros, H. An introduction to optical burst switching. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2003, 41, S10–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.C.; Gurusamy, M.; Liu, Y.; Phung, M.H. Edge-to-edge QoS Mechanisms. In Quality of Service in Optical Burst Switched Networks; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Chapter 5; pp. 111–176. [Google Scholar]
- Praveen, B.; Praveen, J.; Murthy, C.S.R. A survey of differentiated QoS schemes in optical burst switched networks. Opt. Switching Netw. 2006, 3, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkowski, M.; Careglio, D.; Spadaro, S.; Sole-Pareta, J. Impact of burst length differentiation on QoS performance in OBS networks. In Proceedings of 7th International Conference Transparent Optical Networks, Barcelona, Spain, July 2005; Volume 1, pp. 91–94.
- Vokkarane, V.; Vokkarane, V.; Zhang, Q.; Jue, J.; Chen, B. Generalized burst assembly and scheduling techniques for QoS support in optical burst-switched networks. In Proceedings of GLOBECOM ’02: IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, November 2002; Volume 3, pp. 2747–2751.
- Arakawa, Y.; Sakuta, M.; Sasase, I. QoS scheme with burst dropping in optical burst switching. In Proceedings of IEEE Pacific Rim Conference on Communications, Computers and signal Processing, Victoria, Canada, August 2003; Volume 1, pp. 397–400.
- Chen, Y.; Hamdi, M.; Tsang, D. Proportional QoS over OBS networks. In Proceedings of GLOBECOM ’01: IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, November 2001; Volume 3, pp. 1510–1514.
- Zhang, Q.; Vokkarane, V.; Chen, B.; Jue, J. Early drop scheme for providing absolute QoS differentiation in optical burst-switched networks. In Proceedings of 2003 Workshop on HPSR High Performance Switching and Routing, Torino, Italy, June 2003; pp. 153–157.
- Zhang, Q.; Vokkarane, V.; Chen, B.; Jue, J. Early drop and wavelength grouping schemes for providing absolute QoS differentiation in optical burst-switched networks. In Proceedings of GLOBECOM ’03: IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, December 2003; Volume 5, pp. 2694–2698.
- Yoo, M.; Qiao, C. New optical burst-switching protocol for supporting quality of service. In All-Optical Networking: Architecture, Control, and Management Issues; Senior, J.M., Qiao, C., Eds.; SPIE: Boston, MA, USA, November 1998; Volume 3531, pp. 396–405. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, M.; Qiao, C. Supporting multiple classes of services in IP over WDM networks. In Proceedings of GLOBECOM ’99: Global Telecommunications Conference, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, December 1999; Volume 1B, pp. 1023–1027.
- Yoo, M.; Qiao, C.; Dixit, S. QoS performance of optical burst switching in IP-over-WDM networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2000, 18, 2062–2071. [Google Scholar]
- Vu, H.L.; Zukerman, M. Blocking probability for priority classes in optical burst switching networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2002, 6, 214–216. [Google Scholar]
- Mikoshi, T.; Takenaka, T. Improvement of burst transmission delay using offset time for burst assembly in optical burt switching. In Proceedings of 7th Asia-Pacific Symposium on Information and Telecommunication Technologies, Bandos Island, Maldives, April 2008; pp. 13–18.
- Liu, J.; Ansari, N.; Ott, T. FRR for latency reduction and QoS provisioning in OBS networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2003, 21, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar]
- Loi, C.H.; Liao, W.; Yang, D.N. Service differentiation in optical burst switched networks. In Proceedings of GLOBECOM ’02: IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, November 2002; Volume 3, pp. 2313–2317.
- Guan, X.; Thng, I.L.J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, H. Providing absolute QoS through virtual channel reservation in optical burst switching networks. Comput. Commun. 2005, 28, 967–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, M.H.; Chua, K.C.; Mohan, G.; Motani, M.; Wong, T.C. An Absolute QoS Framework for Loss Guarantees in Optical Burst-Switched Networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2007, 55, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetto, G. Minimizing Preemption Probability to Efficiently Support Service Differentiation in Just-in-Time Based OBS Networks. In Proceedings of ICC ’08: IEEE International Conference on Communications, Beijing, China, May 2008; pp. 5219–5223.
- Yang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, S. A probabilistic preemptive scheme for providing service differentiation in OBS networks. In Proceedings of GLOBECOM ’03: IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, December 2003; Volume 5, pp. 2689–2693.
- Tan, C.W.; Mohan, G.; Lui, J.S. Achieving Multi-Class Service Differentiation in WDM Optical Burst Switching Networks: A Probabilistic Preemptive Burst Segmentation Scheme. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2006, 24, 106–119. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Ortega, M.; Lopez-Ardao, J.; Lopez-Garcia, C.; Argibay-Losada, P.; Rodriguez-Rubio, R.; Pineiro-Valladares, M. Loss differentiation in OBS networks without wavelength-conversion capability. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2008, 12, 903–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liu, M. Differentiated services and scheduling scheme in optical burst-switched WDM networks. In Proceedings of 10th IEEE International Conference on Networks, Atlanta, GA, USA, August 2002; pp. 23–27.
- Yang, M.; Zheng, S.; Verchere, D. A QoS supporting scheduling algorithm for optical burst switching WDMM networks. In Proceedings of IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, November 2001; Volume 1, pp. 86–91.
- Kozlovsky, E.; Bayvel, P. QoS Performance of WROBSS Network Architecture with Request Scheduling. In Next Generation Optical Network Design and Modelling; Kluwer: Torino, Italy, February 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.; Song, H.; Li, L.; Wang, S. Load-balancing contention resolution in LOBS based on GMPLS. In Proceedings of PDCAT’2003: the Fourth International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Computing, Applications and Technologies, Chengdu, China, August 2003; pp. 590–594.
- Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Zhu, K.; Datta, D.; Kim, Y.C.; Mukherjee, B. Pre-planned global rerouting for fault management in labeled optical burst-switched WDM networks. In Proceedings of IEEE GLOBECOM 2004, Dallas, TX, USA, November 2004; Volume 3, pp. 2004–2008.
- Thodime, G.; Vokkarane, V.; Jue, J. Dynamic congestion-based load balanced routing in optical burst-switched networks. In Proceedings of GLOBECOM ’03: IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, December 2003; Volume 5, pp. 2628–2632.
- Yang, L.; Rouskas, G. Adaptive path selection in OBS networks. J. Lightwave Tech. 2006, 24, 3002–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, Y.; Venkatesh, T.; Murthy, C. A Reinforcement Learning Framework for Path Selection and Wavelength Selection in Optical Burst Switched Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2007, 25, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, M.; Chua, K.; Mohan, G.; Motani, M.; Wong, T. The streamline effect in OBS networks and its application in load balancing. In Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Broadband Networks, Boston, MA, USA, October 2005; Volume 1, pp. 283–290.
- Chen, Q.; Mohan, G.; Chua, K.C. Offline Route Optimization Considering Streamline Effect in Optical Burst Switching Networks. In Proceedings of ICC ’06: IEEE International Conference on Communications, Istanbul, Turkey, June 2006; Volume 6, pp. 2562–2567.
- IBM ILOG CPLEX home page. Available online: http://www-01.ibm.com/software/integration/optimization/cplex/ (accessed on 21 October 2010).
- OMNeT++ home page. Available online: http://www.omnetpp.org (accessed on 21 October 2010).
- Yu, X.; Li, J.; Cao, X.; Chen, Y.; Qiao, C. Traffic statistics and performance evaluation in optical burst switched networks. J. Lightwave Tech. 2004, 22, 2722–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroni, S.; Bayvel, P. Wavelength requirements in arbitrarily connected wavelength-routed optical networks. J. Lightwave Tech. 1997, 15, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, A.; Callegati, F.; Tamil, L. On optical burst switching and self-similar traffic. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2000, 4, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izal, M.; Aracil, J. On the influence of self-similarity on optical burst switching traffic. In Proceedings of GLOBECOM ’02: IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, November 2002; Volume 3, pp. 2308–2312.
- Vokkarane, V.M.; Haridoss, K.; Jue, J.P. Threshold-based burst assembly policies for QoS support in optical burst-switched networks. In Proceedings of SPIE OptiComm 2002, Boston, MA, USA, July 2002; pp. 125–136.
- Gjessing, S.; Maus, A. Discrete Event Simulation of a large OBS Network. In Proceedings of International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Big Island, HI, USA, October 2005.
- Chua, K.C.; Gurusamy, M.; Liu, Y.; Phung, M.H. Quality of Service in Optical Burst Switched Networks; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Phung, M.; Shan, D.; Chua, K.; Mohan, G. Performance analysis of a bufferless OBS node considering the streamline effect. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2006, 10, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.J.P.C.; Freire, M.M.; Lorenz, P. The Role of Meshing Degree in Optical Burst Switching Networks Using Signaling Protocols with One-Way Reservation Schemes. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2005, 3420, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Masip-Bruin, X.; Yannuzzi, M.; Domingo-Pascual, J.; Fonte, A.; Curado, M.; Monteiro, E.; Kuipers, F.; Mieghem, P.V.; Avallone, S.; Ventre, G.; Aranda-Gutirrez, P.; Hollick, M.; Steinmetz, R.; Iannone, L.; Salamatian, K. Research challenges in QoS routing. Comput. Commun. 2006, 29, 563–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/.)