Flux-Modulated Permanent Magnet Machines: Challenges and Opportunities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- High torque for effective propulsion, especially at low speeds;
- High efficiency over a wide torque and speed range to reduce electricity consumption;
- Robust structure and good fault tolerance capability;
- Compact size and acceptable cost.
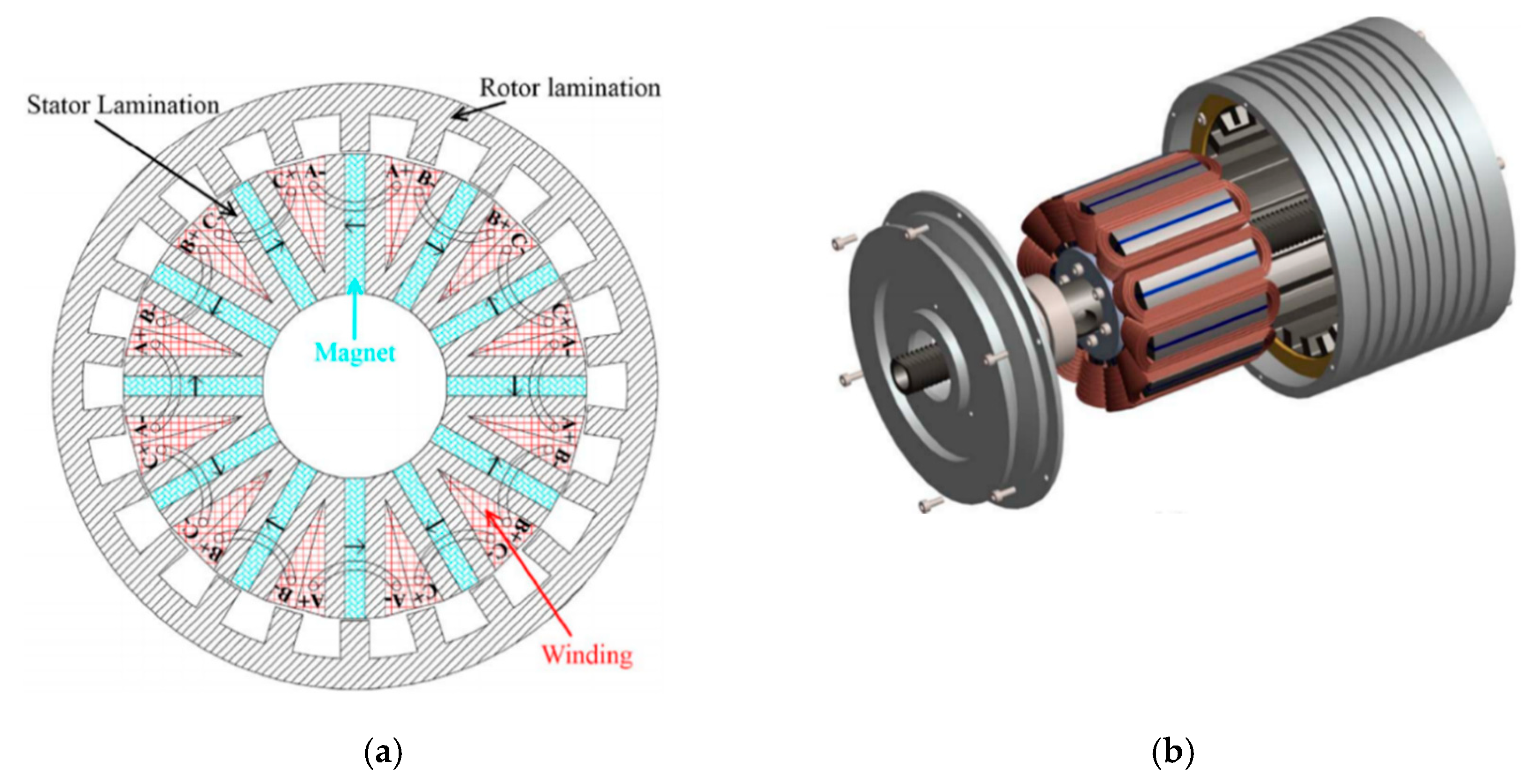
2. Surface-Type FMPM Machines
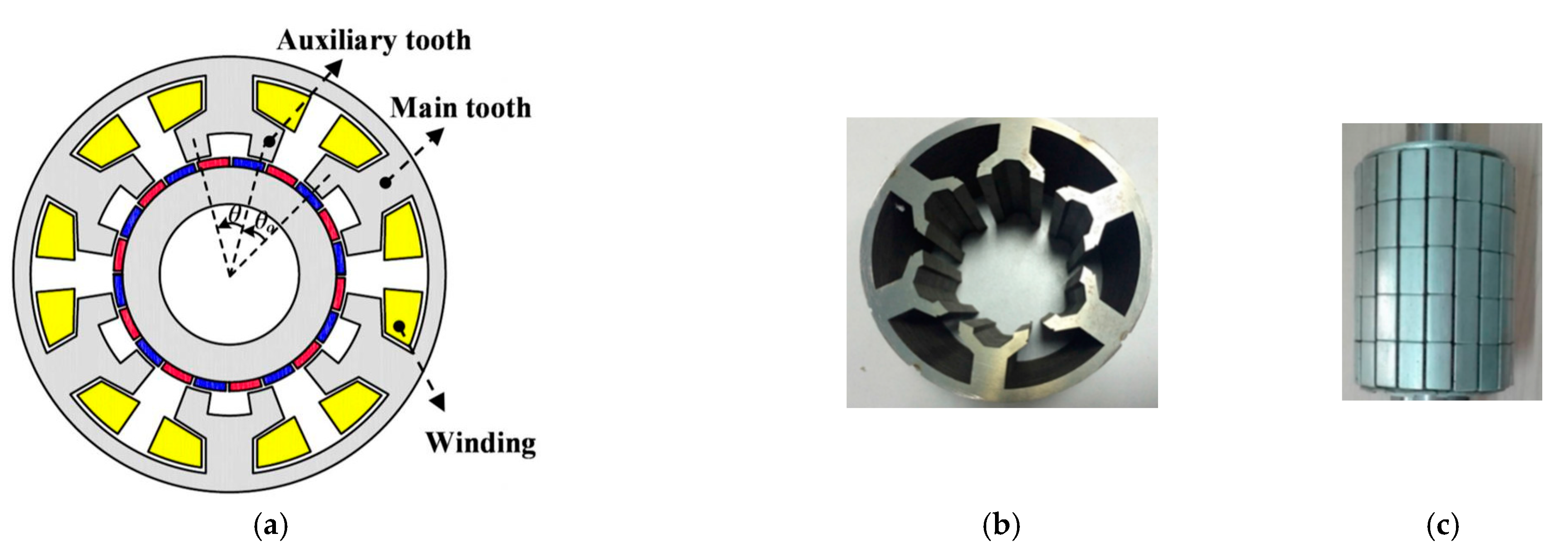
3. Spoke-Type FMPM Machines
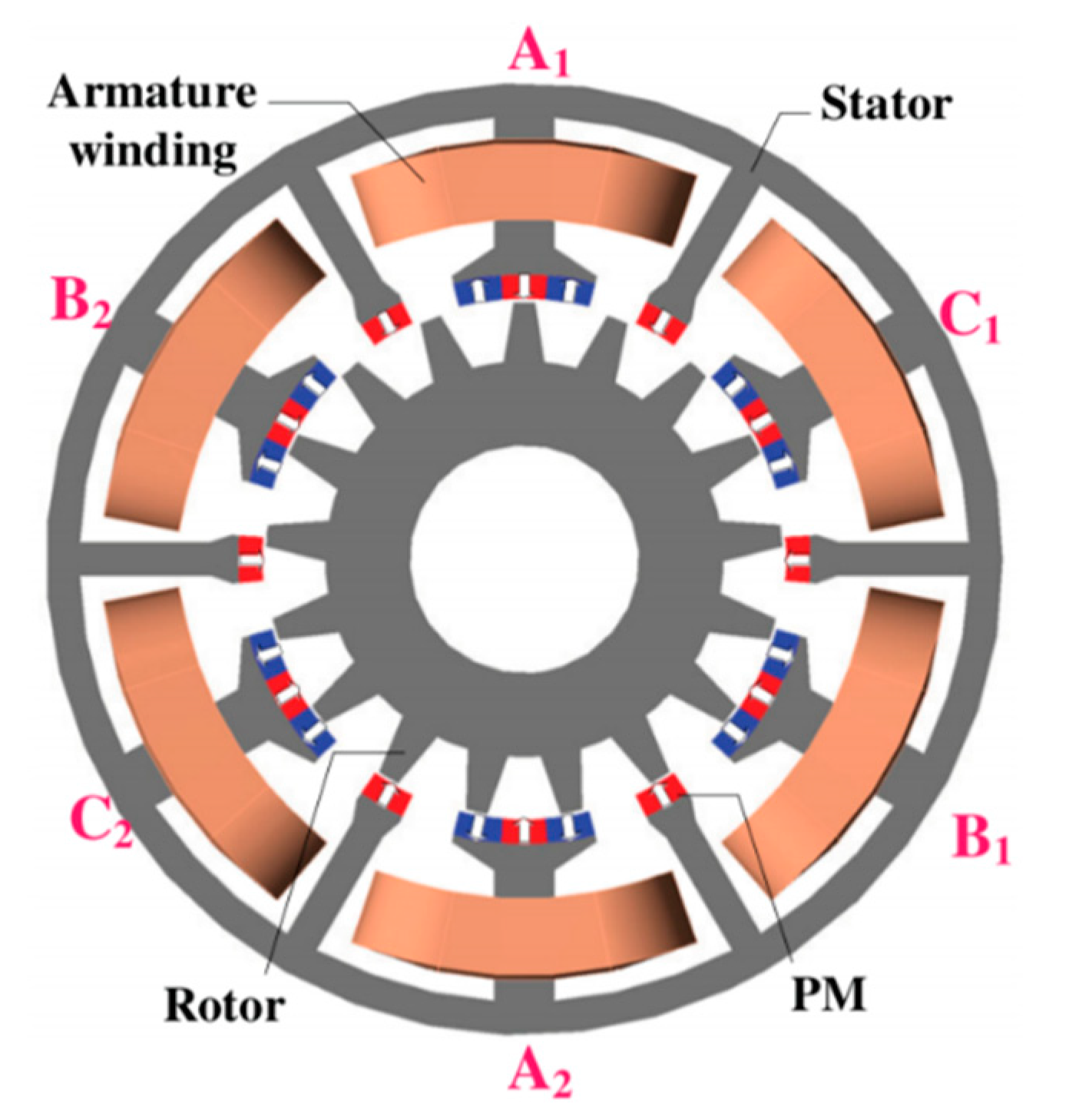
4. Partitioned Stator FMPM Machines
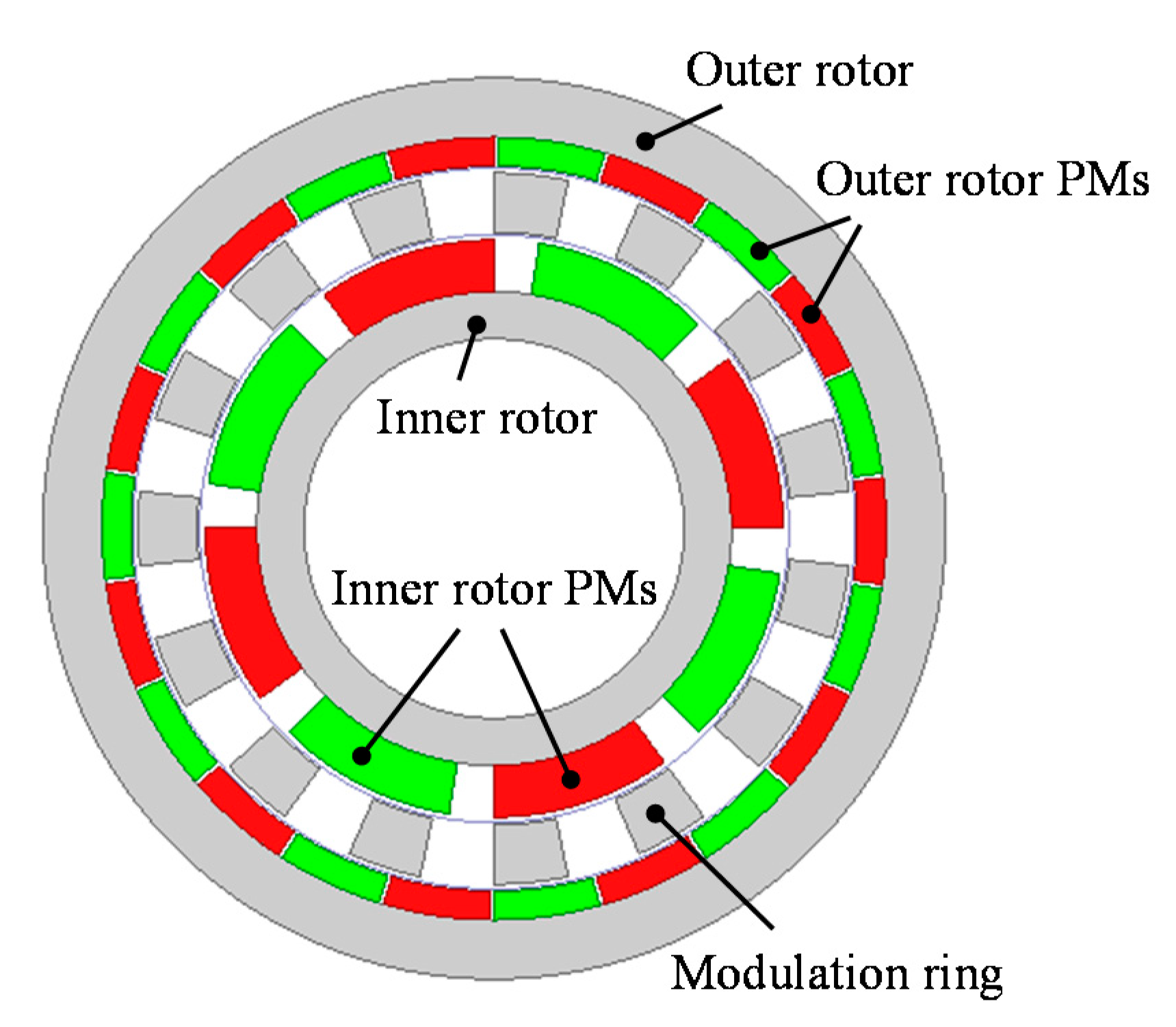
5. Bidirectional FMPM Machines
6. Discussion and Conclusions
- Surface-type FMPM machines have simple structures and are easy to manufacture. The PMs are glued on the surface of the rotor or the stator teeth. However, the weak mechanical strength of PMs limits the application of surface-type FMPM machines in high speeds. Meanwhile, the PMs have a demagnetization risk because the armature flux passes through the PMs.
- Spoke-type FMPM machines can achieve higher torque density than surface-type FMPM machines due to the flux-focusing effect of the spoke PM array. The drawback is a complicated mechanical structure, since the PMs have to be inserted into the stator or the rotor.
- PS-FMPM machines are good improvements on regular stator-PM machines. The separate stators not only increase the space for the installation of armature coils and PMs but also protect the PMs from being demagnetized by the hot armature coils. A tradeoff is that PS-FMPM machines have to be designed with two stators, which have higher manufacturing challenge.
- Bidirectional FMPM machines can achieve higher torque density than their unidirectional FMPM machine counterparts without increasing mechanical complexity. The PMs on the stator and the rotor can generate electromagnetic torque separately. The machine inside space can be fully utilized, and the PM arrangement is flexible.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chau, K.T.; Chan, C.C.; Liu, C. Overview of Permanent-Magnet Brushless Drives for Electric and Hybrid Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 2246–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyoseok, S.; Niguchi, N.; Hirata, K. Characteristic Analysis of Surface Permanent-Magnet Vernier Motor According to Pole Ratio and Winding Pole Number. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murariu, G.; Dragu, M.; Roşu, B.; Epure, S.; Vlad, C. Updating an electric propulsion UAV device for long range missions. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th International Symposium on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ISEEE), Galati, Romania, 18–20 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Barzkar, A.; Ghassemi, M. Electric Power Systems in More and All Electric Aircraft: A Review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 169314–169332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nøland, J.K.; Leandro, M.; Suul, J.A.; Molinas, M. High-Power Machines and Starter-Generator Topologies for More Electric Aircraft: A Technology Outlook. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 130104–130123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlioglu, B.; Morris, C.T. More Electric Aircraft: Review, Challenges, and Opportunities for Commercial Transport Aircraft. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2015, 1, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Niu, S. Design of Dual-Electrical-Port DC-Coil-Free Hybrid-Excited Machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 1328–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Niu, S. A novel DC-coil-free hybrid-excited machine with consequent-pole PM rotor. Energies 2018, 11, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, G.; Jahns, T.M. Analysis and Design Recommendations to Mitigate Demagnetization Vulnerability in Surface PM Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcaro, M.; Bianchi, N. Interior PM Machines Using Ferrite to Replace Rare-Earth Surface PM Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.L.; Wang, Q.; Niu, S.; Fu, W.N. A Novel Magnetic-Geared Tubular Linear Machine With Halbach Permanent-Magnet Arrays for Tidal Energy Conversion. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, K.; Howe, D. A novel high-performance magnetic gear. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2001, 37, 2844–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jian, L.; Chau, K.T.; Jiang, J.Z. A Magnetic-Geared Outer-Rotor Permanent-Magnet Brushless Machine for Wind Power Generation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2009, 45, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Shen, J.X.; Luk, P.C.K.; Fei, W.Z.; Wang, C.F.; Hao, H. Development of a Magnetic-Geared Permanent-Magnet Brushless Motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 4578–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atallah, K.; Rens, J.; Mezani, S.; Howe, D. A Novel “Pseudo” Direct-Drive Brushless Permanent Magnet Machine. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2008, 44, 4349–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouheraoua, M.; Wang, J.; Atallah, K. Slip Recovery and Prevention in Pseudo Direct Drive Permanent-Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 2291–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Lipo, T.A. Operation and Design Principles of a PM Vernier Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 3656–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Qu, R.; Li, D.; Gao, Y. Influence of Pole Ratio and Winding Pole Numbers on Performance and Optimal Design Parameters of Surface Permanent-Magnet Vernier Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 3707–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Li, D.; Qu, R.; Jiang, D.; Li, J. Advanced High Torque Density PM Vernier Machine With Multiple Working Harmonics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 5295–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhong, J.; Chau, K.T. A Novel Flux-Controllable Vernier Permanent-Magnet Machine. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 4238–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Hua, W.; Wang, W.; Huang, W. Analysis of Back-EMF in Flux-Reversal Permanent Magnet Machines by Air Gap Field Modulation Theory. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 3344–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lin, H.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Lyu, S.; Liu, Y. Design and Analysis of Novel Asymmetric-Stator-Pole Flux Reversal PM Machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Zhu, Z.Q. Influence of Adjacent Teeth Magnet Polarities on the Performance of Flux Reversal Permanent Magnet Machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Khatab, M.F.; Li, H.; Liu, Y. A Novel Axial Flux Magnetically Geared Machine for Power Split Application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 5954–5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatab, M.F.H.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Li, H.Y.; Liu, Y. Comparative study of novel axial flux magnetically geared and conventional axial flux permanent magnet machines. Ces Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2018, 2, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Gardner, M.C.; Toliyat, H.A. Design and Analysis of an Axial Flux Magnetically Geared Generator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Li, D.; Qu, R.; Li, J.; Jiang, D. Analysis of a Dual-Rotor, Toroidal-Winding, Axial-Flux Vernier Permanent Magnet Machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 1920–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.T.; Zhu, Z.Q. Winding Configurations and Optimal Stator and Rotor Pole Combination of Flux-Switching PM Brushless AC Machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, W.; Luk, P.C.K.; Shen, J.X.; Wang, Y.; Jin, M. A Novel Permanent-Magnet Flux Switching Machine With an Outer-Rotor Configuration for In-Wheel Light Traction Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 1496–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Li, Y.; Cetin, E.; Sarlioglu, B. Influence of Rotor Tooth Shaping on Cogging Torque of Axial Flux-Switching Permanent Magnet Machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, J.R.; Ardebili, M. Design and Control of a Novel Yokeless Axial Flux-Switching Permanent-Magnet Motor. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkaman, H.; Ghaheri, A.; Keyhani, A. Design of Rotor Excited Axial Flux-Switching Permanent Magnet Machine. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2018, 33, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.T.; Zhu, Z.Q. Comparison of All- and Alternate-Poles-Wound Flux-Switching PM Machines Having Different Stator and Rotor Pole Numbers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2010, 46, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Zhang, G.; Cheng, M. Flux-Regulation Theories and Principles of Hybrid-Excited Flux-Switching Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 5359–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, R.L.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Jewell, G.W. Hybrid-Excited Flux-Switching Permanent-Magnet Machines With Iron Flux Bridges. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 1726–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.T.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Iwasaki, S.; Deodhar, R.P. A Novel Hybrid-Excited Switched-Flux Brushless AC Machine for EV/HEV Applications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Su, P.; Tong, M.; Meng, J. Investigation of a Five-Phase E-Core Hybrid-Excitation Flux-Switching Machine for EV and HEV Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Lin, H.; Xu, P.L.; Zhan, H.L.; Fang, S.; Huang, Y. Design Synthesis of Switched Flux Hybrid-Permanent Magnet Memory Machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Qu, R.; Lipo, T.A. High-Power-Factor Vernier Permanent-Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 3664–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.S.; Lipo, T.A. Design of an Improved Dual-Stator Ferrite Magnet Vernier Machine to Replace an Industrial Rare-Earth IPM Machine. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 2062–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Qu, R.; Xu, W.; Li, J.; Lipo, T.A. Design Procedure of Dual-Stator Spoke-Array Vernier Permanent-Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 2972–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.S.; Lipo, T.A. Torque Performance Comparison Between a Ferrite Magnet Vernier Motor and an Industrial Interior Permanent Magnet Machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 2088–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Z.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Shi, J.T. Novel Doubly Salient Permanent Magnet Machines With Partitioned Stator and Iron Pieces Rotor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.J.; Zhu, Z.Q. Novel Partitioned Stator Switched Flux Permanent Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi Qiang, Z.; Zhong Ze, W.; Evans, D.J.; Wen Qiang, C. Novel Electrical Machines Having Separate PM Excitation Stator. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Z.; Zhu, Z.Q. Partitioned Stator Flux Reversal Machine With Consequent-Pole PM Stator. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.J.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Zhan, H.L.; Wu, Z.Z.; Ge, X. Flux-Weakening Control Performance of Partitioned Stator-Switched Flux PM Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 2350–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Hua, H.; Wu, D.; Shi, J.T.; Wu, Z.Z. Comparative Study of Partitioned Stator Machines With Different PM Excitation Stators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Zhan, H. Novel Consequent-Pole Hybrid Excited Machine with Separated Excitation Stator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Zhu, Z.Q. Novel Parallel Hybrid Excited Machines With Separate Stators. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 31, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Zhu, Z.Q. Novel partitioned stator hybrid excited machines with magnets on slot openings. J. Eng. 2019, 2019, 3568–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Zhu, Z.Q. Novel Partitioned Stator Hybrid Excited Switched Flux Machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q. Overview of novel magnetically geared machines with partitioned stators. Iet Electr. Power Appl. 2018, 12, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Niu, S.; Yang, L. Design optimization and comparative study of novel dual-PM excited machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 9924–9933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Fu, W.N.; Ho, S.L. A Novel High Torque-Density Triple-Permanent-Magnet-Excited Magnetic Gear. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Niu, S.; Yang, S. Design Optimization and Comparative Study of Novel Magnetic-Geared Permanent Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Niu, S. A Novel Hybrid-Excited Flux Bidirectional Modulated Machine for Electric Vehicle Propulsion. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Hangzhou, China, 17–20 October 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Niu, S.; Ho, S.L.; Fu, W.; Zuo, S. Design and analysis of novel magnetic flux-modulated mnemonic machines. Iet Electr. Power Appl. 2015, 9, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Niu, S. Electromagnetic design and analysis of a novel fault-tolerant flux-modulated memory machine. Energies 2015, 8, 8069–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Niu, S.; Luo, X. A novel hybrid dual-PM machine excited by AC with DC bias for electric vehicle propulsion. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 6908–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Niu, S. A novel hybrid-excited dual-PM machine with bidirectional flux modulation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






















Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Niu, S. Flux-Modulated Permanent Magnet Machines: Challenges and Opportunities. World Electr. Veh. J. 2021, 12, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj12010013
Wang Q, Zhao X, Niu S. Flux-Modulated Permanent Magnet Machines: Challenges and Opportunities. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2021; 12(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj12010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qingsong, Xing Zhao, and Shuangxia Niu. 2021. "Flux-Modulated Permanent Magnet Machines: Challenges and Opportunities" World Electric Vehicle Journal 12, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj12010013
APA StyleWang, Q., Zhao, X., & Niu, S. (2021). Flux-Modulated Permanent Magnet Machines: Challenges and Opportunities. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 12(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj12010013






