The Design and Optimization of a Novel Hybrid Excitation Generator for Vehicles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Overall Structural Design
3. Principle of Operation Analysis
4. Magnetic Circuit Analysis
5. Determination of the Main Parameters
5.1. Parameters of the Permanent Magnet
5.2. Parameters of the Excitation Coil
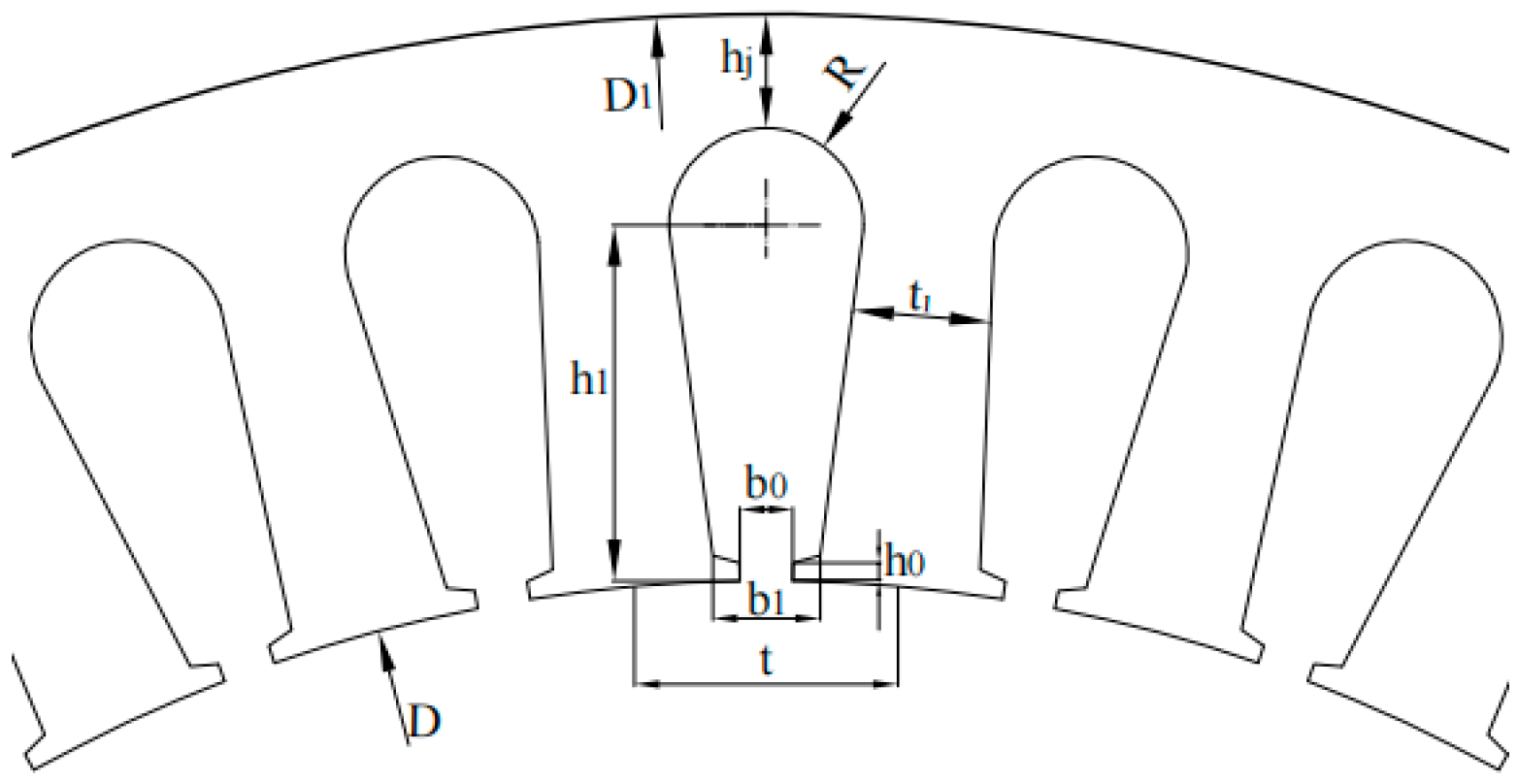
5.3. Parameters of the Stator
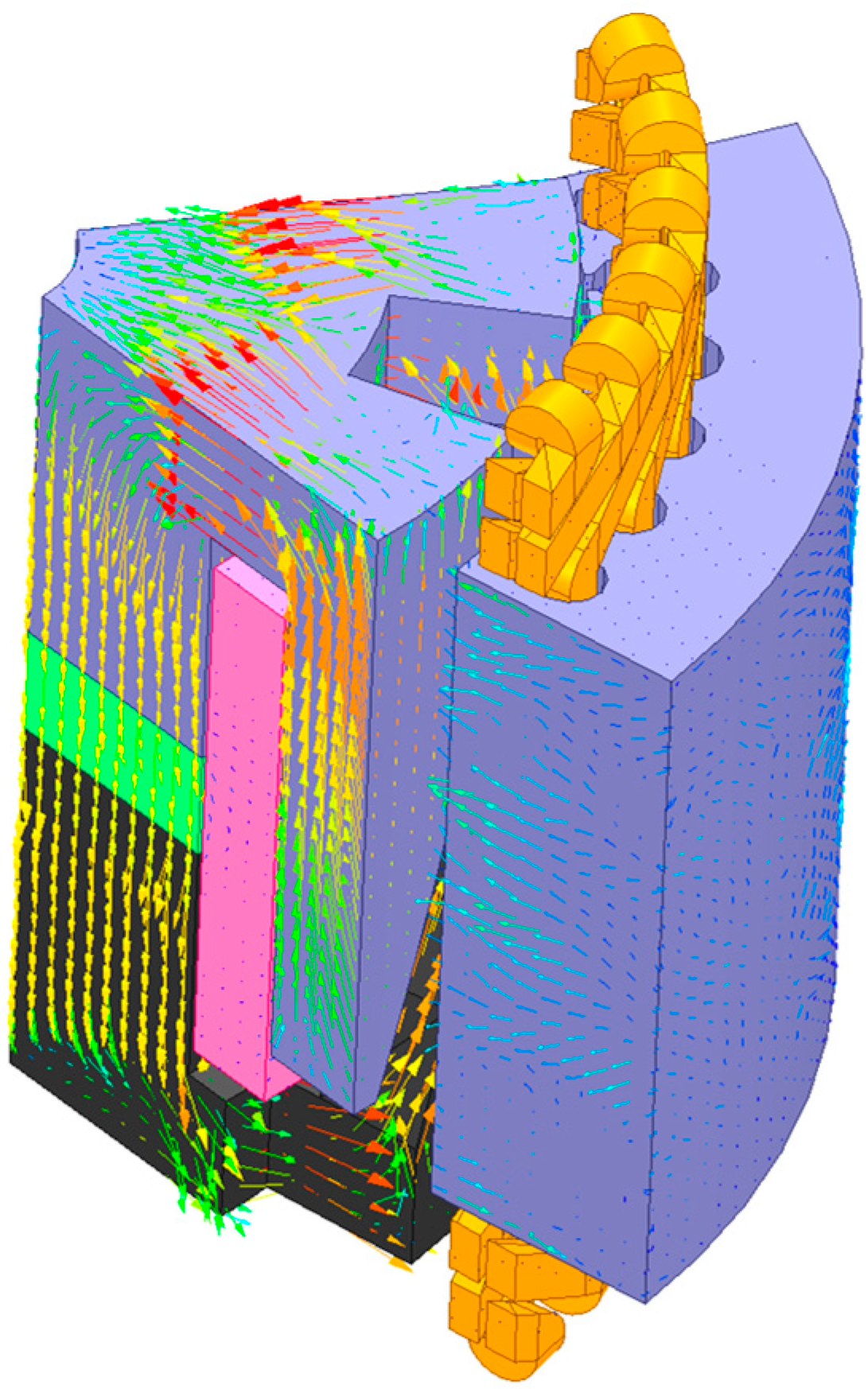
6. Establishment of the Finite Element Model
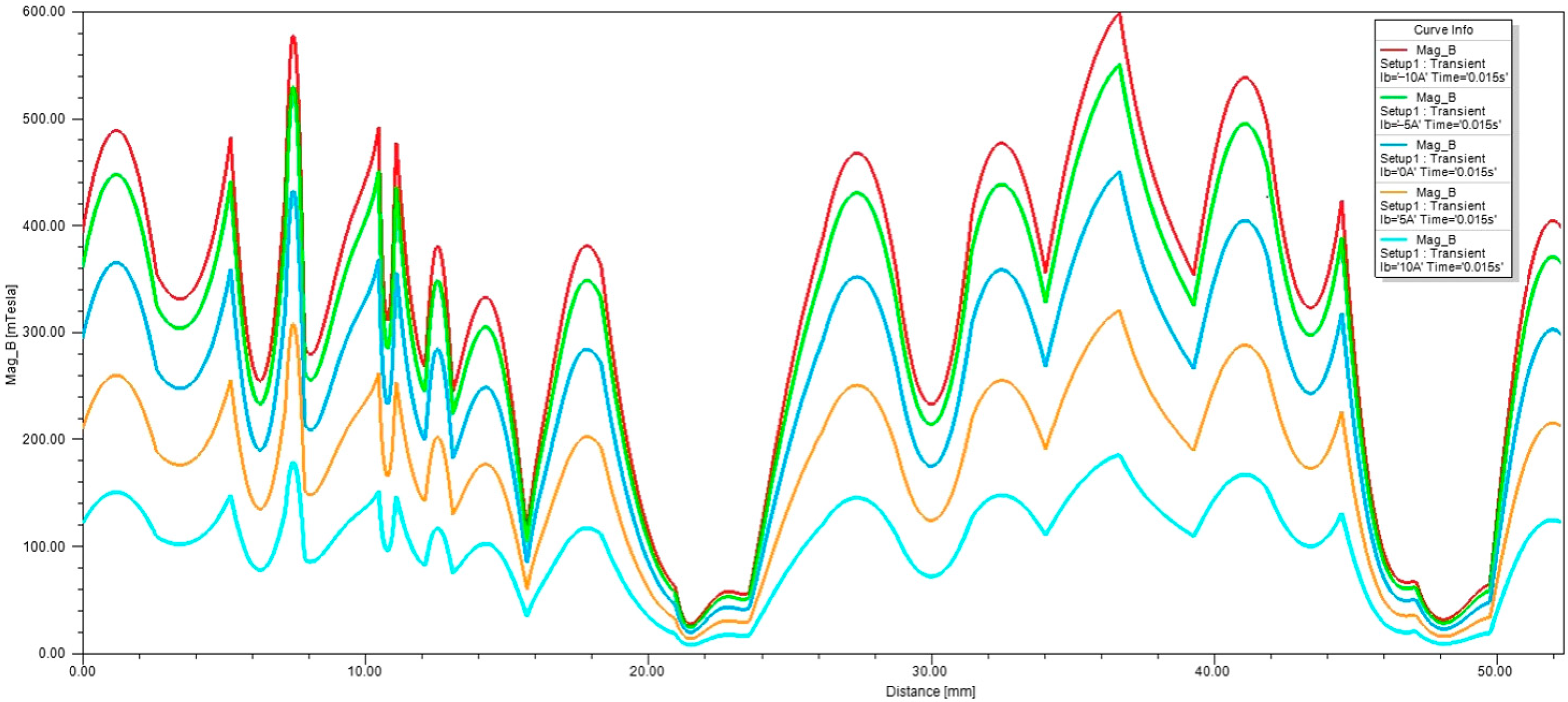
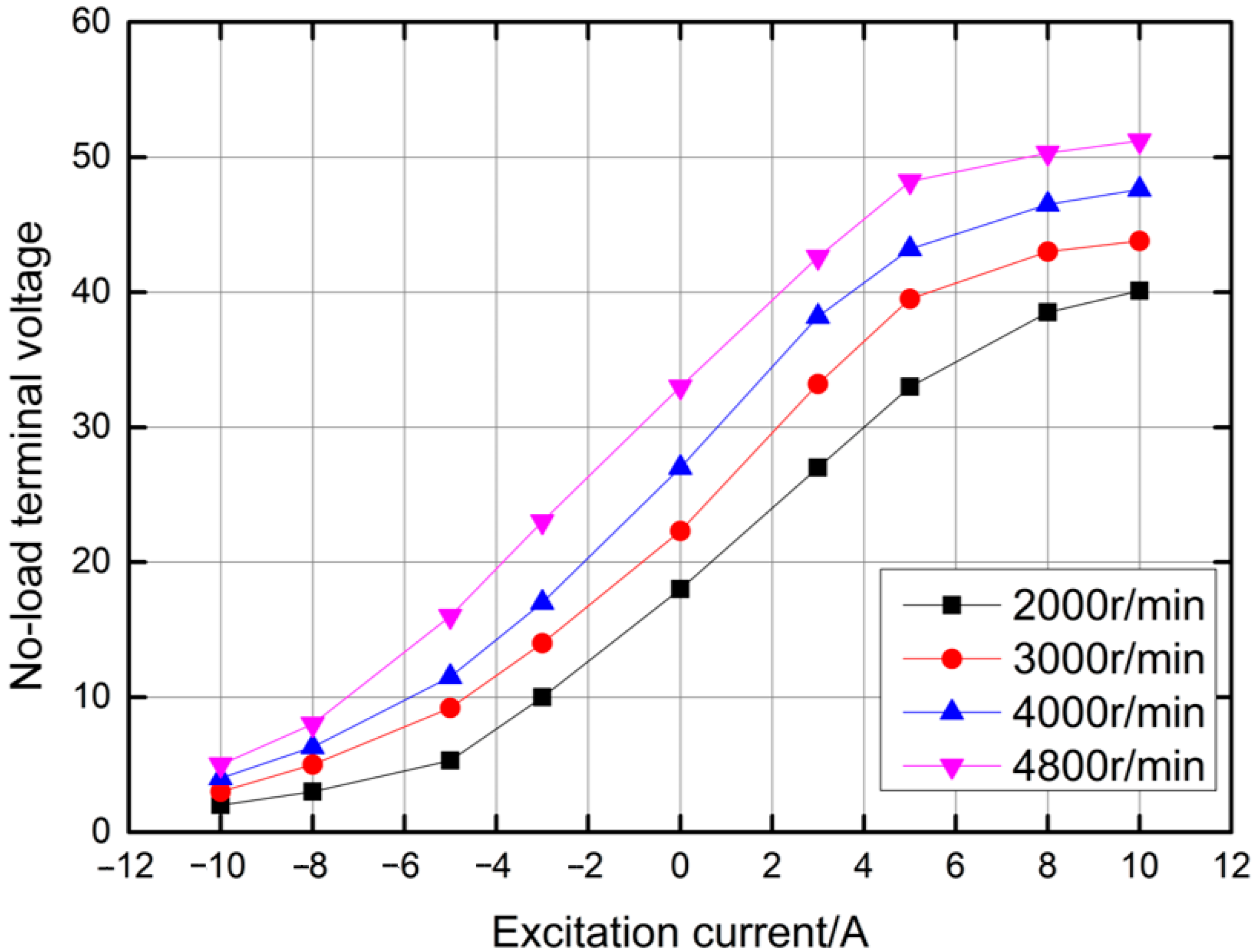
7. No-Load Characteristics Analysis
8. Influence of the Structural Parameters on Performance
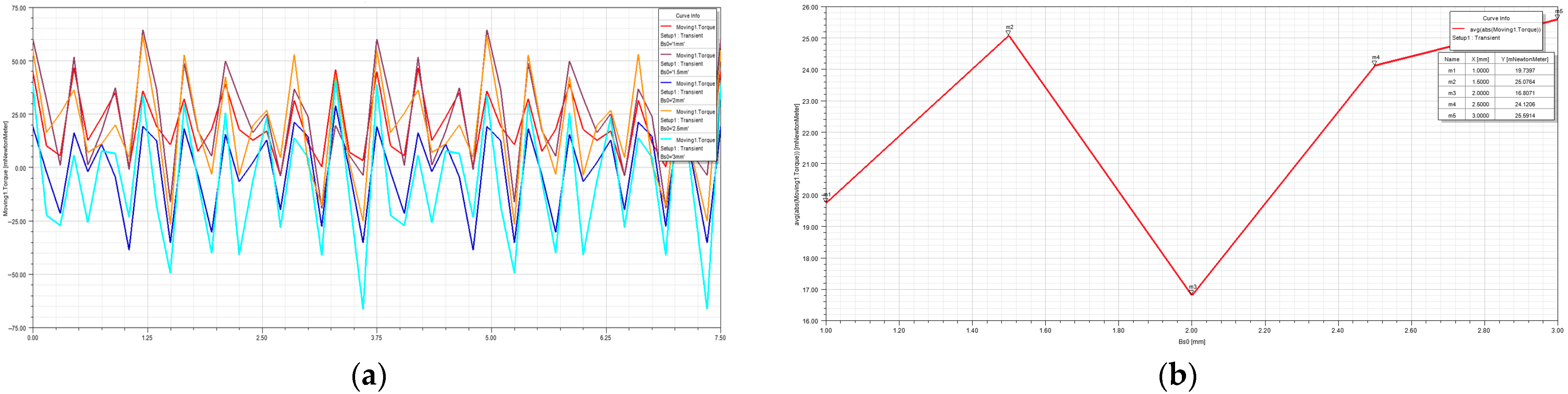
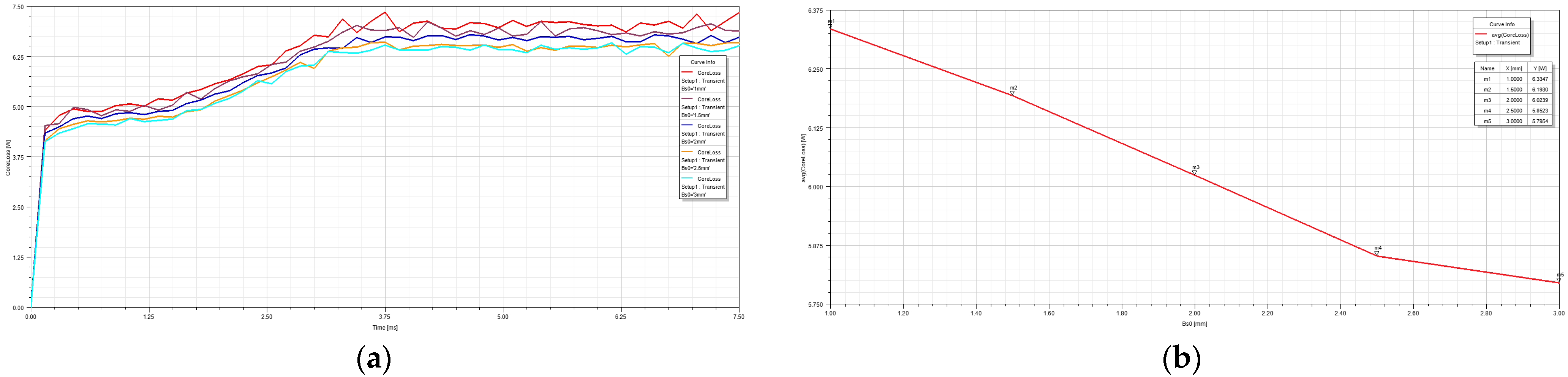
8.1. Influence of the Slot Width
8.2. Influence of the Permanent Magnet Thickness
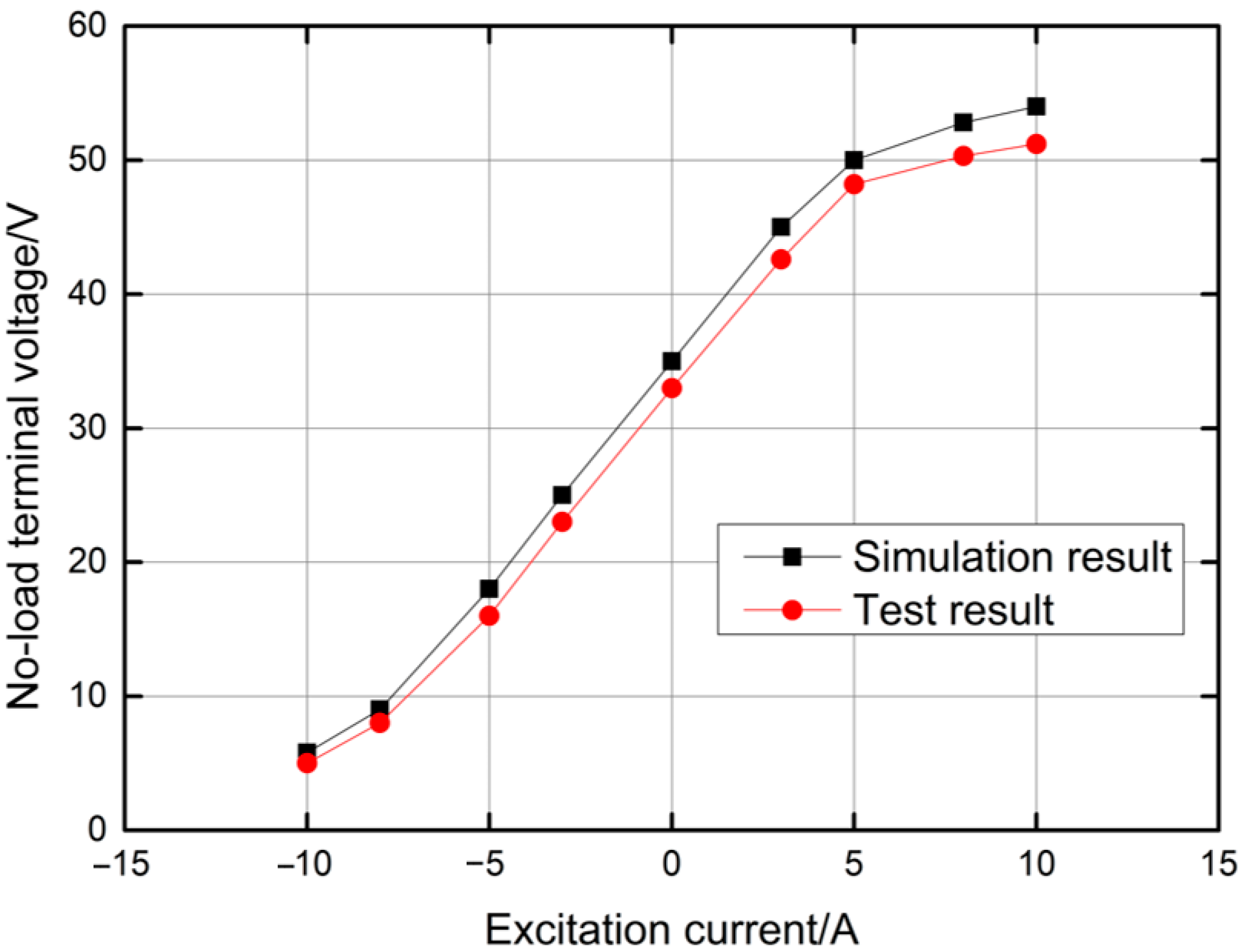
9. Experimental Analysis
10. Conclusions
- In the novel HEG, the permanent magnet and excitation winding share the same magnetic circuit and common excitation, which reduces the excitation loss. The structural parameters were designed based on the theory of a permanent magnet generator and the design method of an electric excitation generator.
- A three-dimensional model of a claw-pole series magnetic circuit HEG was established, the no-load characteristics of the generator were analyzed and the magnetic induction in the air gap was obtained when the value of the excitation current in the excitation winding was different. It was shown that the output voltage could be controlled by changing the value and direction of the excitation current.
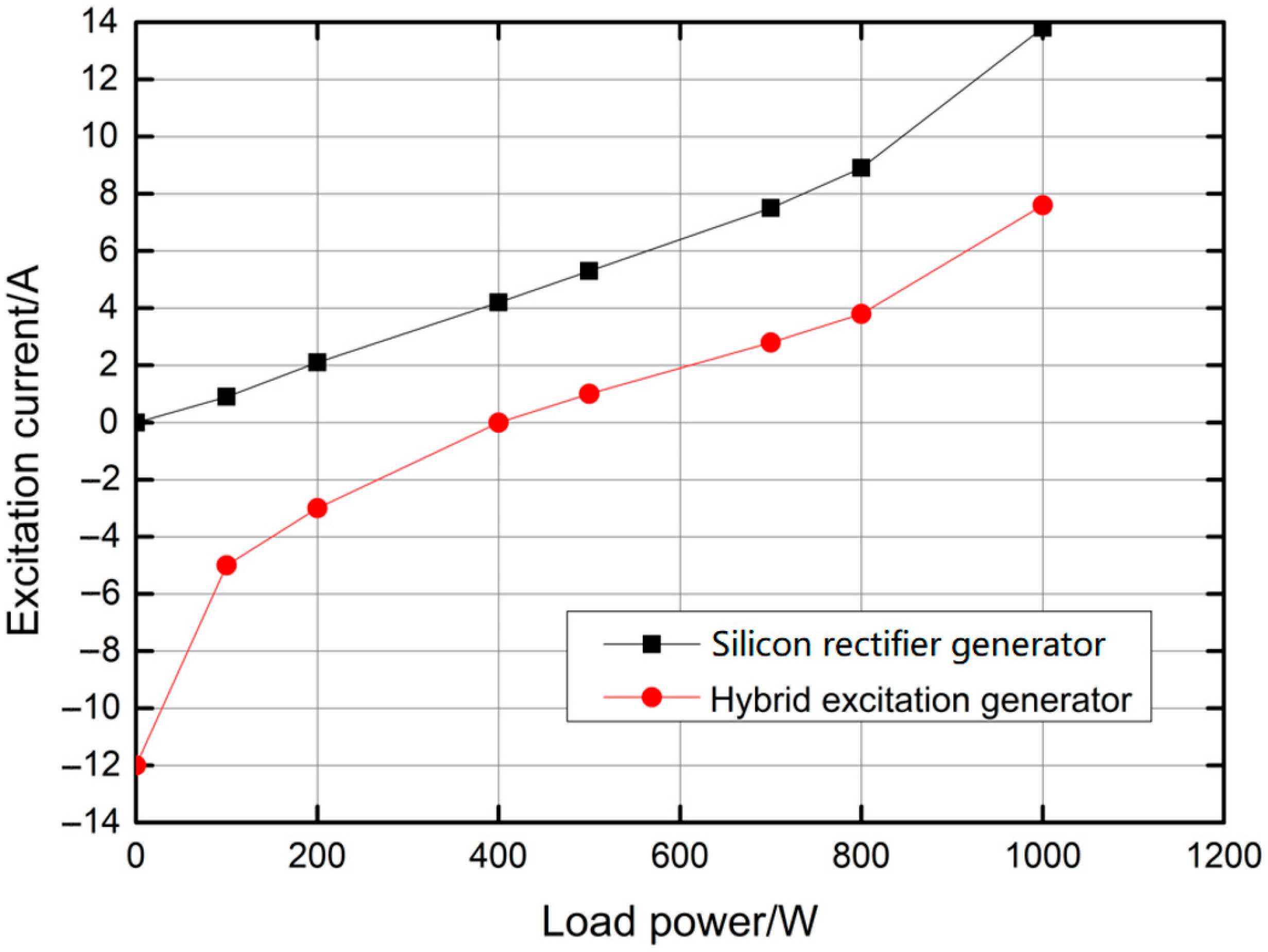
- The influence of the slot width on the cogging torque, the flux linkage and the iron loss were analyzed, as well as the influence of the permanent magnet thickness on the output voltage. Based on the analysis results, the structural parameters were optimized. According to the results of the optimization analysis, a prototype was made and a test was conducted. The experimental results show that the prototype made according to the optimized results displayed good no-load and output performances, and it saved on excitation consumption compared with a silicon rectifier generator.
11. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.R.; Wang, D.; Hua, W. Overview and prospect of structure principle, design and operation control technology of hybrid excitation motor. Proc. CSEE 2020, 40, 7834–7850+8221. [Google Scholar]
- Prajzendanc, P.; Paplicki, P. Performance evaluation of an axial flux machine with a hybrid excitation design. Energies 2022, 15, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Zhang, X.; Si, T.; Tong, L.; Ma, Q.; Xu, M. Analysis of the rotor magnetomotive force of built-in radial Permanent Magnet Generator for Vehicle. Int. J. Rotating Mach. 2021, 2021, 5319615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, X.; Yin, H.; Geng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, L. Analysis of magnetic field and electromagnetic performance of a new hybrid excitation synchronous motor with dual-V type magnets. Energies 2020, 13, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y. Current situation and development trend of generator for automobile manufacturing. Mod. Manuf. Technol. Equip. 2017, 23, 146–148. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Cheng, M.; Zhao, W.X. Review and prospect of hybrid excitation motor technology. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2018, 23, 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Capponi, F.G.; Borocci, G.; Donato, G.D.; Caricchi, F. Flux regulation strategies for hybrid excitation synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 3838–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardach, M. Torque and back-emf in hybrid excited claw pole generator. COMPEL-Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2018, 4, 1342–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malanciuc, A.; Simion, A.; Livadaru, L.; Munteanu, A.; Afanasov, C. FEM-based Analysis of a Hybrid Synchronous Generator with Skewed Stator slots. Adv. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2011, 11, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, Y.; Schleicher, K.; Klöpzig, M. A novel hybrid excited synchronous machine for (H)EV applications. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Berlin, Germany, 2–5 September 2014; pp. 353–359. [Google Scholar]
- Hlioui, S.; Vido, L.; Amara, Y.; Gabsi, M.; Miraoui, A.; Lécrivain, M. Magnetic equivalent circuit model of a hybrid excitation synchronous machine. Compel Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2008, 27, 1000–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Zhang, X.; Tong, L.; Ma, Q.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. Performance optimization analysis of hybrid excitation generator with the electromagnetic rotor and embedded permanent magnet rotor for vehicle. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 163640–163653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhao, W.; Xu, L.; Ji, J. A novel parallel hybrid excitation field modulated machine with efficient utilization of multi-working harmonics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Lin, N.; Zhang, X.B.; Wang, D.; Guo, Y.J.; Wei, K. Study on Mathematical Model of interleaved pole Hybrid excitation synchronous generator. Proc. CSEE 2022, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, S.H.; Zhu, Z.C. Calculation of stator iron consumption of a Tooth harmonic excitation hybrid excitation generator with a rectifying load. Water Resour. Power 2020, 38, 160–163. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.Z.; Song, X.J.; Chen, Z. Design and test of slender salient pole hybrid excitation generator for while drilling. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2022, 17, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Hu, W.; Lei, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, A.; Wang, S.; Shi, L. Development of brushless claw pole electrical excitation and combined permanent magnet hybrid excitation generator for vehicles. Energies 2020, 13, 4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Yao, S.C. Design and Research of a new straight claw Hybrid excitation claw pole Motor. Mech. Electr. Eng. 2019, 36, 539–543. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Analysis of a novel surface-mounted permanent magnet motor with hybrid magnets for low cost and low torque pulsation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, X.; Geng, H.; Gao, T.; You, D. Electromagnetic design and flux regulation analysis of new hybrid excitation generator for electric vehicle range extender. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2021, 18, 5547517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.S.; Jo, B.W.; Kim, K.C. Analysis of an IPMSM hybrid magnetic equivalent circuit. Energies 2021, 14, 5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.H. Structure Designing and characteristic study of HECPG with magnetic circuit series connection. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2015, 24, 1–6+12. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, K. A new parallel hybrid excitation machine: Permanent-magnet variable-reluctance machine with bidirectional field-regulating capability. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiriz, E.; Onbilgin, G. Comparative study of new axial field permanent magnet hybrid excitation machines. Electr. Power Appl. 2017, 11, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Zhao, X.; Deng, X. Design and analysis of a novel hybrid excitation flux reversal machine. Appl. Comput. Electromagn. Soc. J. 2021, 36, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, R.Y. Theory and Design of Modern Permanent Magnet Motor, 2nd ed.; Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, D.; Baek, J. Optimal design of a six-Phase permanent-magnet-assisted synchronous reluctance motor to convert into three phases for fault-tolerant improvement in a traction system. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Gao, H. Optimization and performance improvement of a hybrid excitation synchronous machine with modular magnetic-shunting rotor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 4381–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knypiski, K.; Nowak, L.; Demenko, A. Optimization of the synchronous motor with hybrid permanent magnet excitation system. Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2015, 32, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi-aghdam, S.R.; Feyzi, M.R.; Ebrahimi, Y. A new switched reluctance motor design to reduce torque ripple using finite element fuzzy optimization. Iran. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2012, 8, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.P.; Cui, T.X. Magnetic field analysis and calculation of the hybrid excitation claw Pole generator Based on Ansoft. Electr. Mach. Technol. 2013, 33, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Qing, Y.H. Hybrid excitation synchronous machine adaptive speed region control and experimental verification. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2018, 58, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, L.; Yu, L. Phase displacement characteristics of a parallel hybrid excitation brushless DC generator. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Finite-Element analysis of hybrid excitation machine with isolated magnetic paths. Electr. Mach. Control Appl. 2019, 36, 6–9+28. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, G.H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C. Optimization analysis of stator permanent magnet axial flux switching hybrid excitation motor. J. Mach. Des. 2017, 34, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, Y.H.; Liu, C. Analysis and calculation of electromagnetic and temperature field in a hybrid excitation synchronous generator. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2016, 3, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.R.; Zhang, C. New Rare Earth Permanent Magnet Material and Permanent Magnet Motor; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
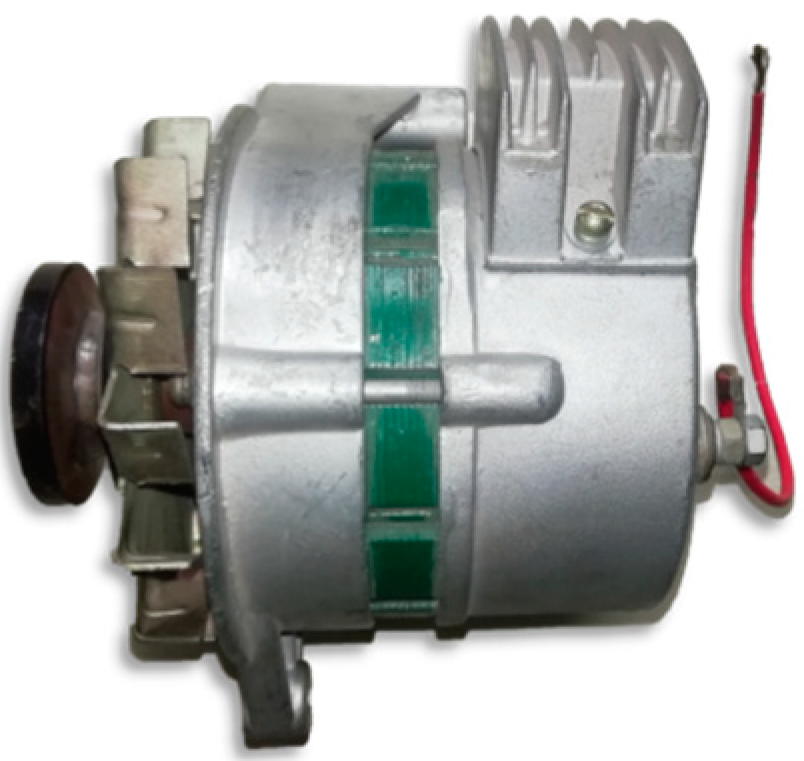
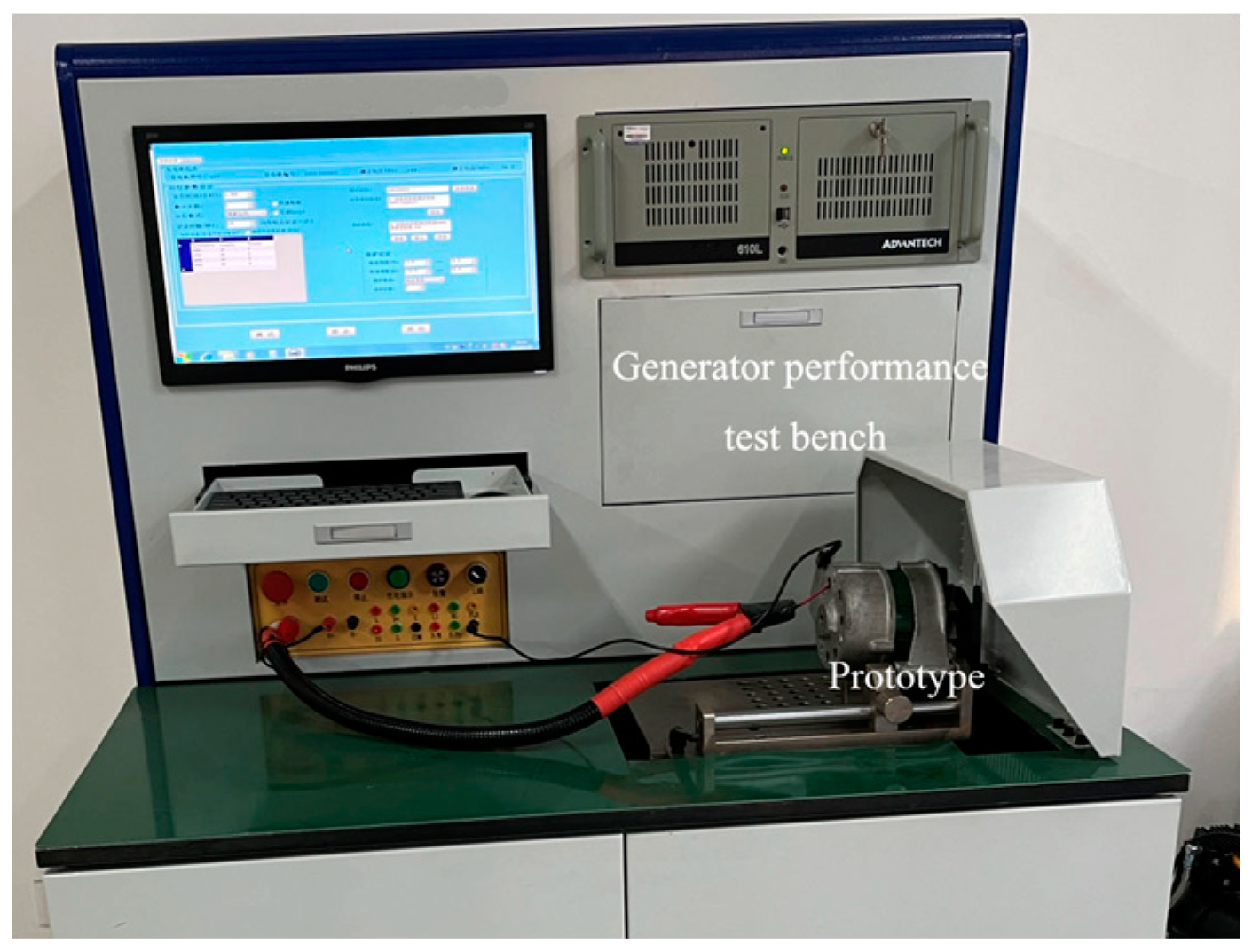
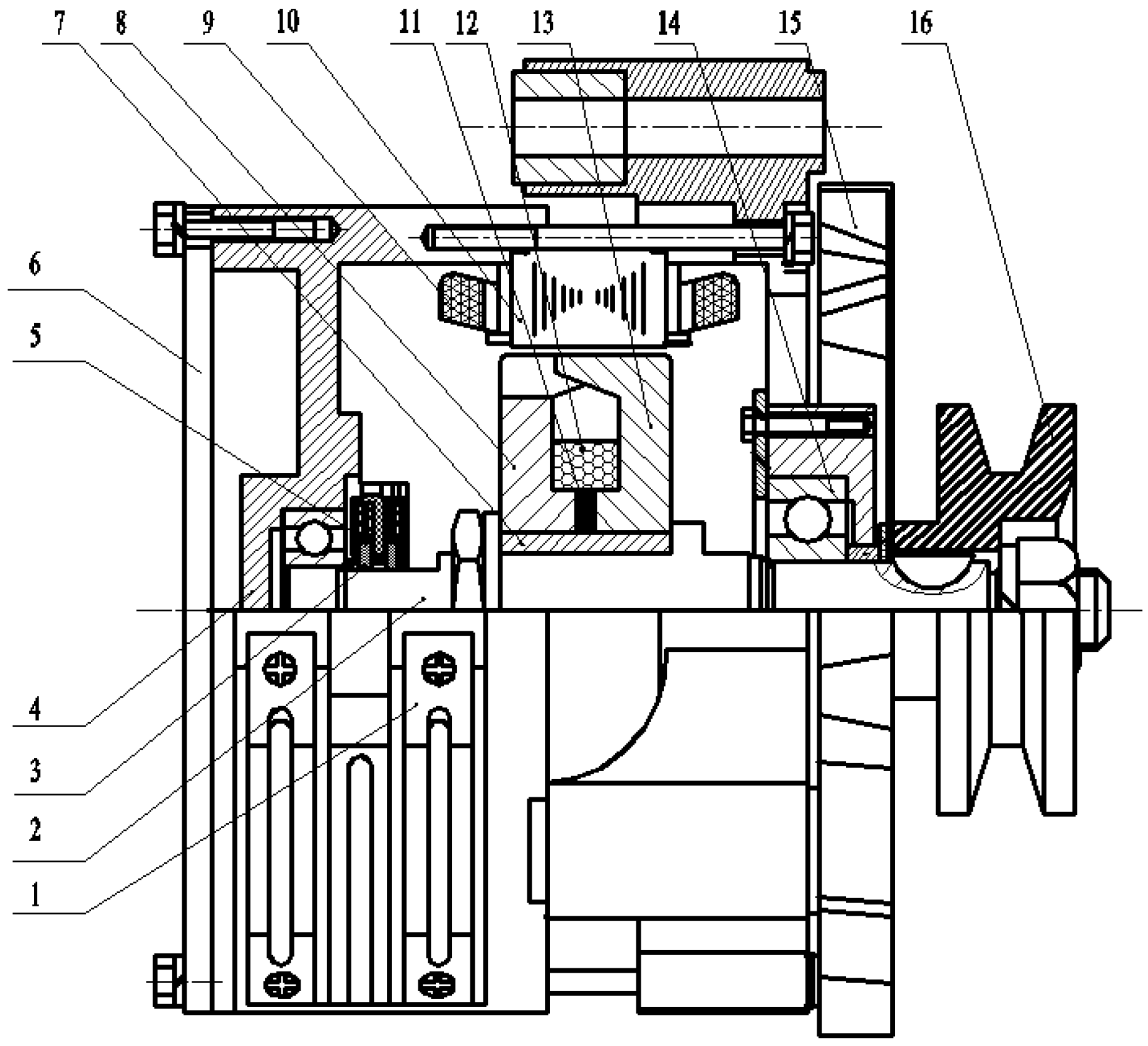

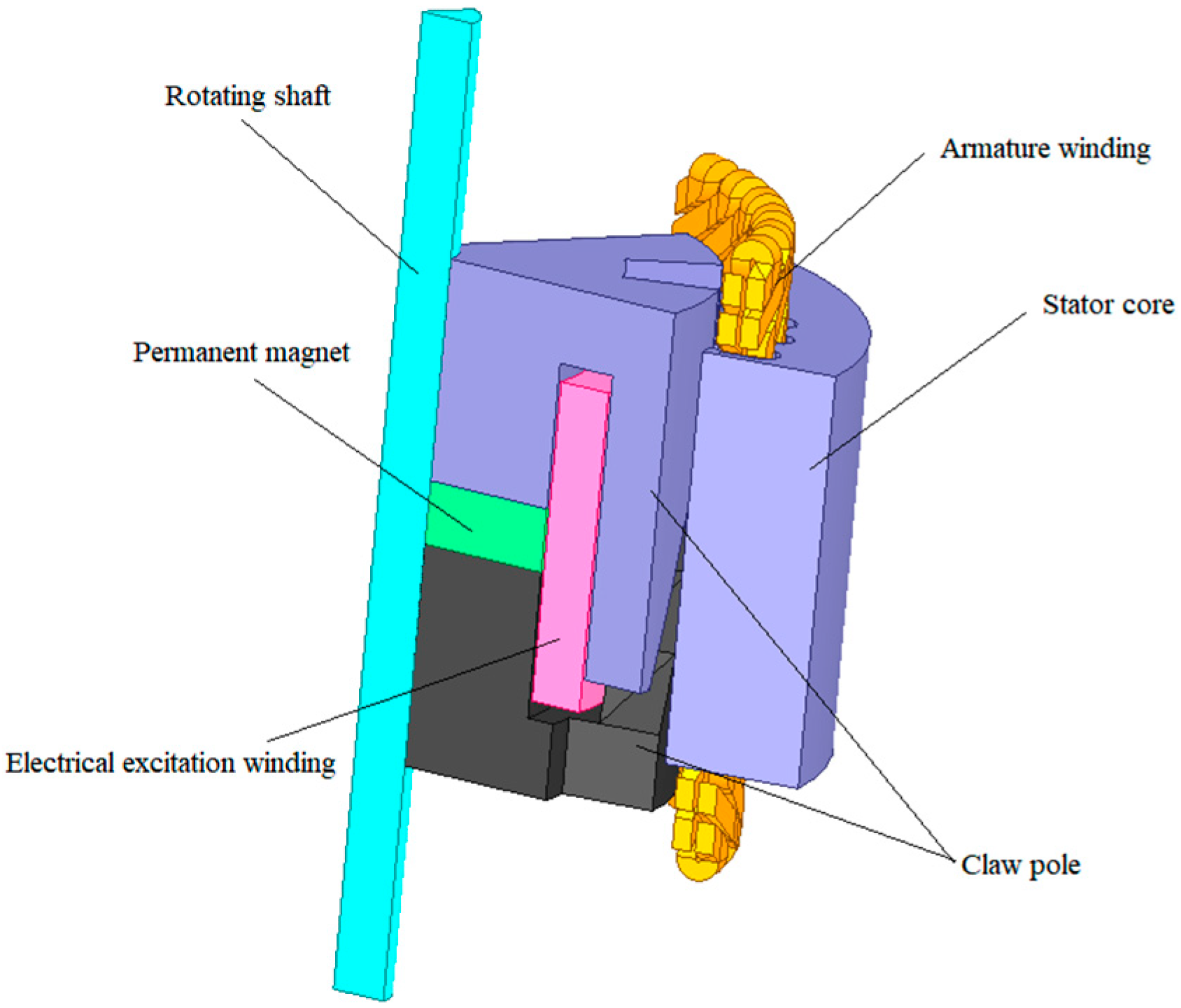






| Technical Indexes | Rated Voltage (V) | Rated Power (W) | Rated Speed (r/min) | Insulation Class | Protection Level | Working Temperature | Output Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | 14 | 1000 | 4000 | E | IP23 | From −40 °C to −75 °C | Direct current |
| Parameters of Permanent Magnet | Outside Diameter (mm) | Inside Diameter (mm) | Thickness (mm) | Volume (mm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 60 | 26 | 10 | 22,965.04 |
| Parameters | D (mm) | D1 (mm) | b0 (mm) | b1 (mm) | t (mm) | t1 (mm) | R (mm) | h1 (mm) | hj (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 101 | 145 | 2.7 | 5.4 | 8.8 | 3.7 | 4.3 | 18.9 | 4.1 |
| Parameters | Value | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of pole-pairs | 6 | Thickness of claw pole tip (mm) | 3 |
| Internal diameter of stator core (mm) | 101 | Root width of claw pole (mm) | 10 |
| Outside diameter of stator core (mm) | 145 | Root thickness of claw pole (mm) | 10 |
| Width of claw pole tip (mm) | 3 | External diameter of rotor yoke (mm) | 99 |
| Thickness of permanent magnet (mm) | 10 | External diameter of permanent magnet (mm) | 60 |
| Width of Slot (mm) | Average Cogging Torque (N·m) | Average Flux Linkage (Wb) | Average Iron Loss (W) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19.7397 | 0.0302 | 6.3347 |
| 1.5 | 25.0764 | 0.0300 | 6.1930 |
| 2 | 16.8071 | 0.0293 | 6.0239 |
| 2.5 | 24.1206 | 0.0291 | 5.8523 |
| 3 | 25.5914 | 0.0289 | 5.7964 |
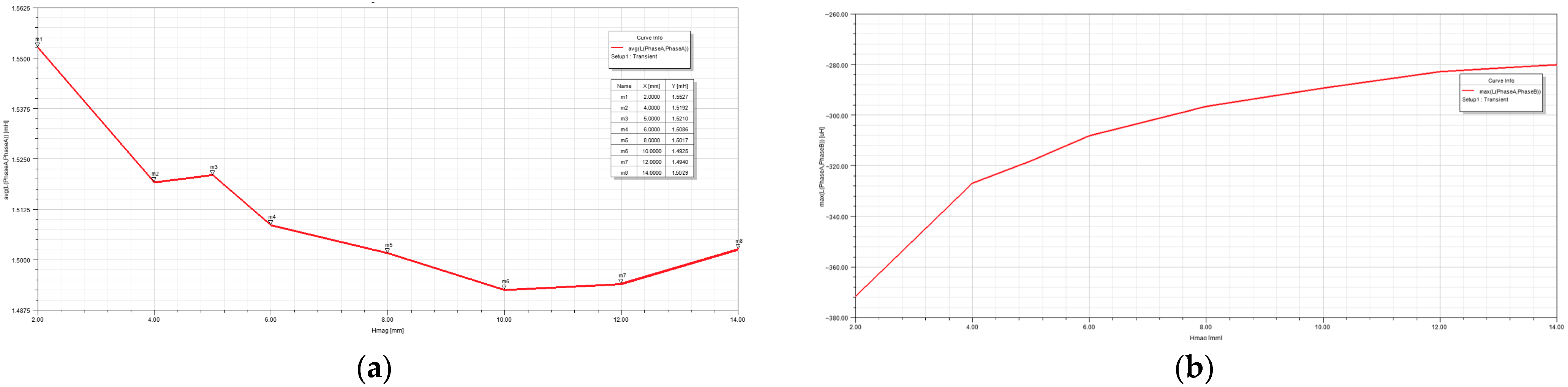
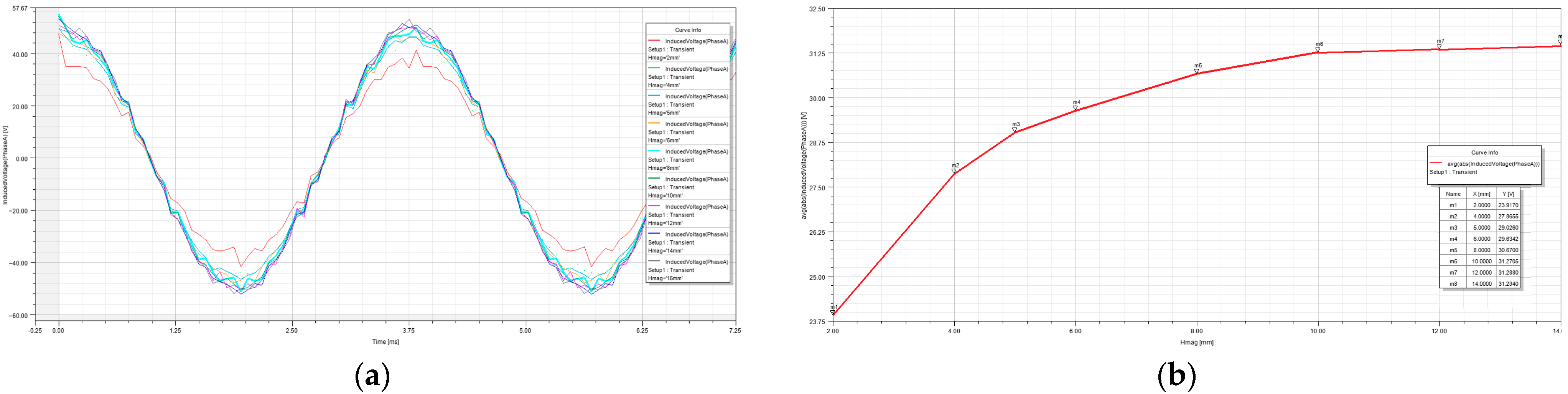
| Thickness of Permanent Magnet (mm) | Self-Inductance (mH) | Mutual Inductance (mH) | Average Induced Electromotive Force (V) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1.5527 | −0.3716 | 23.9170 |
| 4 | 1.5192 | −0.3268 | 27.8655 |
| 5 | 1.5210 | −0.3181 | 29.0260 |
| 6 | 1.5086 | −0.3081 | 29.6342 |
| 8 | 1.5017 | −0.2965 | 30.6700 |
| 10 | 1.4925 | −0.2893 | 31.2705 |
| 12 | 1.4940 | −0.2828 | 31.2880 |
| 14 | 1.4929 | −0.2801 | 31.2940 |
| Speed (r/min) | 2000 | 4000 | 4800 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load power (W) | 900 | 1000 | 1100 | 900 | 1000 | 1100 | 900 | 1000 | 1100 |
| Prototype voltage (V) | 13.8 | 13.7 | 13.5 | 14.3 | 14.1 | 14.0 | 14.3 | 14.2 | 14.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, J.; Gu, F.; Wang, L.; Ma, S.; Golmohammadi, A.-M.; Zhang, S. The Design and Optimization of a Novel Hybrid Excitation Generator for Vehicles. World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 15, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj15040139
Ma J, Gu F, Wang L, Ma S, Golmohammadi A-M, Zhang S. The Design and Optimization of a Novel Hybrid Excitation Generator for Vehicles. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2024; 15(4):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj15040139
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Jianwei, Fengyi Gu, Liwei Wang, Shilun Ma, Amir-Mohammad Golmohammadi, and Shaohang Zhang. 2024. "The Design and Optimization of a Novel Hybrid Excitation Generator for Vehicles" World Electric Vehicle Journal 15, no. 4: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj15040139
APA StyleMa, J., Gu, F., Wang, L., Ma, S., Golmohammadi, A.-M., & Zhang, S. (2024). The Design and Optimization of a Novel Hybrid Excitation Generator for Vehicles. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 15(4), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj15040139






