Global Analysis of Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure and Sustainable Energy Sources Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Technological EV Infrastructure
2.1. EV Charging Standards
2.2. Standards of Charging Connectors
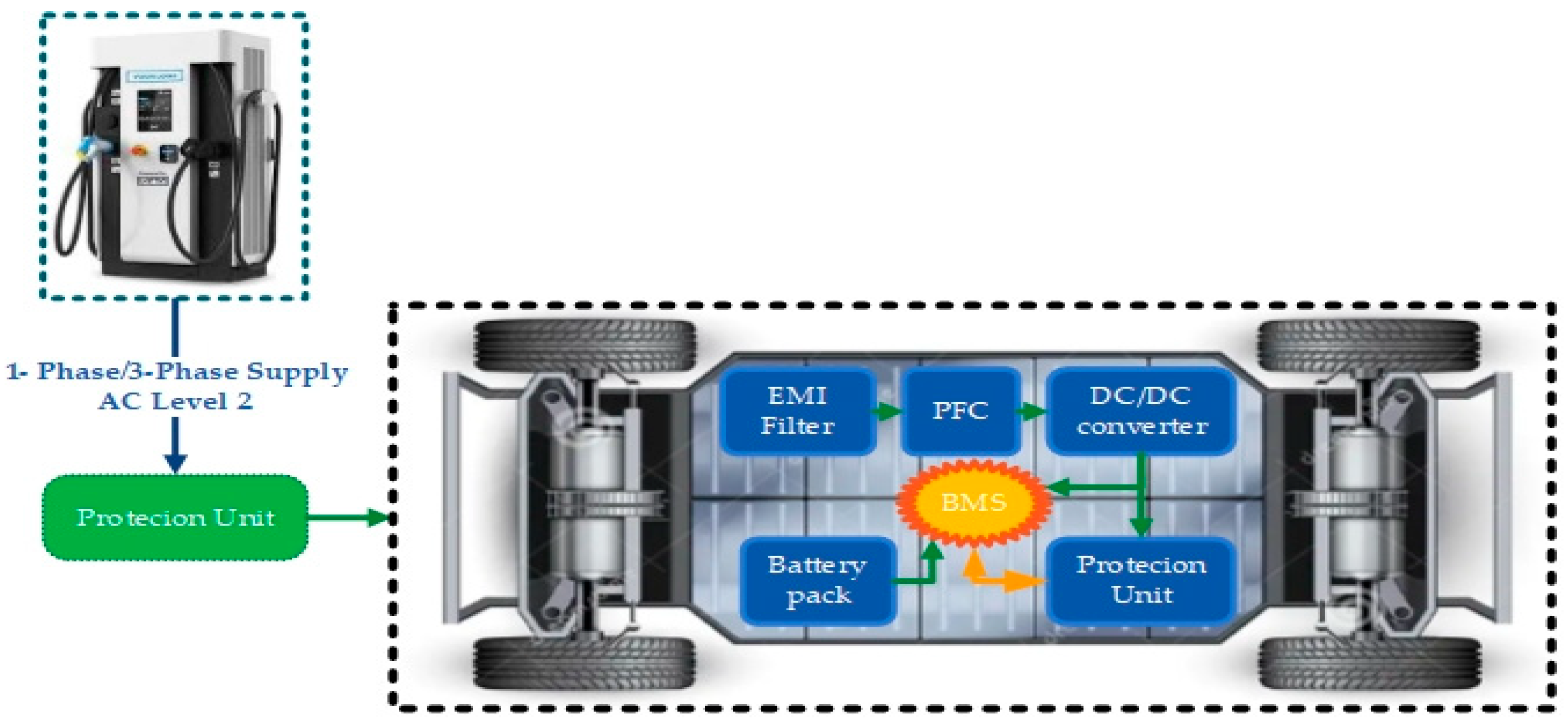
2.3. EV Charging Technologies
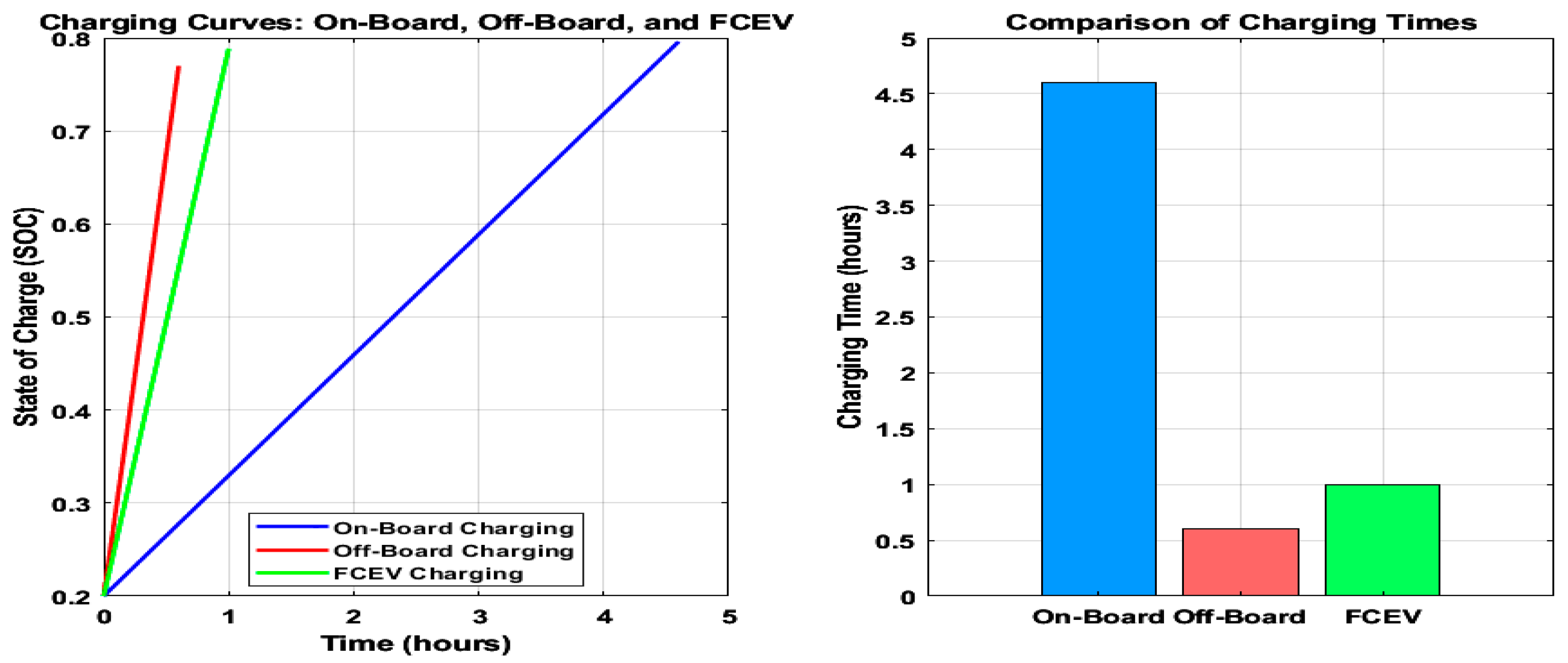
- ton-board: Charging time for on-board charging (hours);
- toff-board: Charging time for on-board charging (hours);
- Ereq: Energy required to charge the battery (kWh);
- Pon-board: Charging power provided by the on-board charger (kW);
- Poff-board: Charging power provided by the off-board charger (kW);
- ηon-board/off-board: Efficiency of the on-board/off-board charging system.
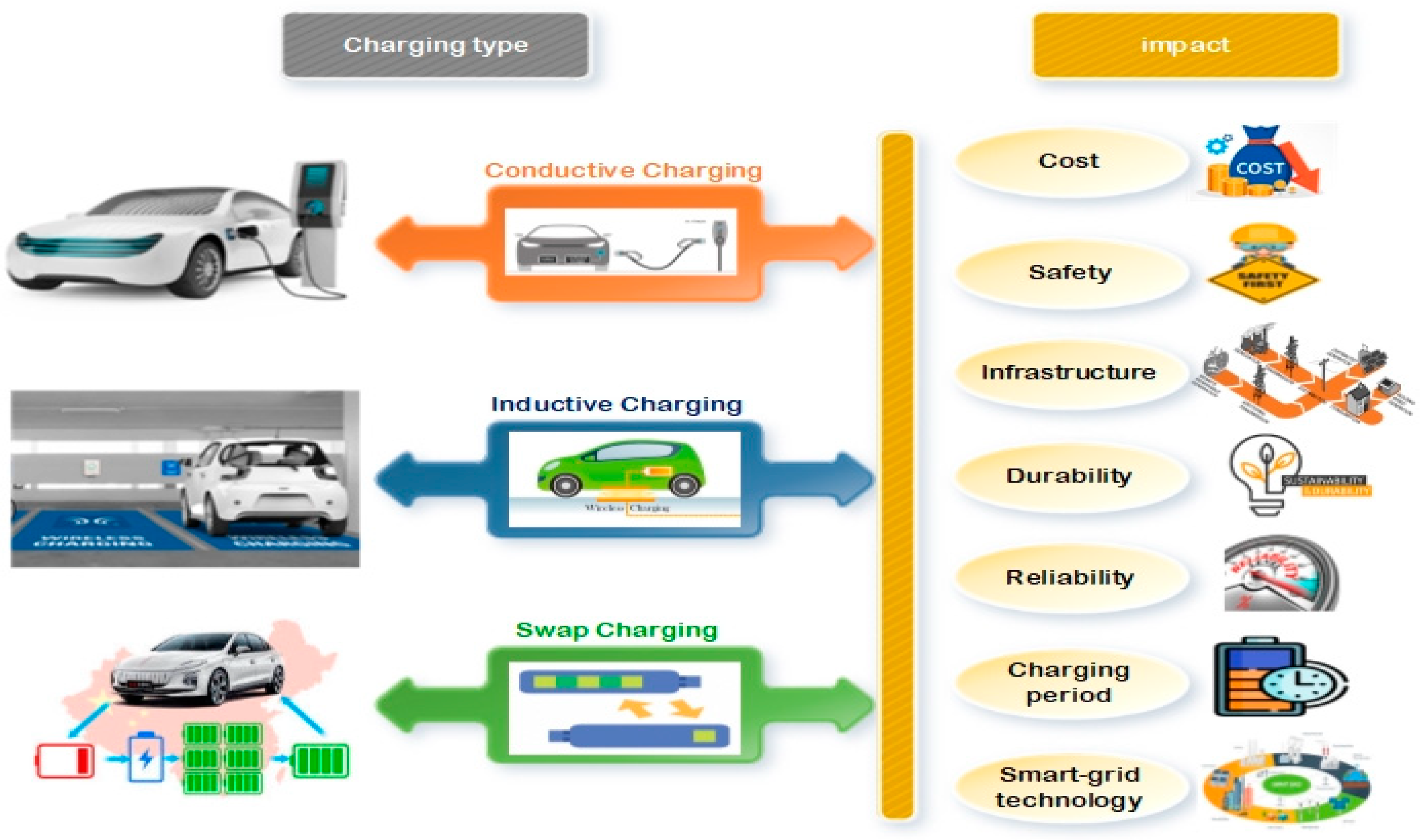
3. Various Charging Modes
4. Parameters of Leading EVs
5. Need for Forecasting Models to Predict EV Charging Demand
6. Charging Infrastructure
7. Essential Need for RE
8. Advantages and Drawbacks of Different Sources of Renewable Energies
9. Energy Storage Solutions
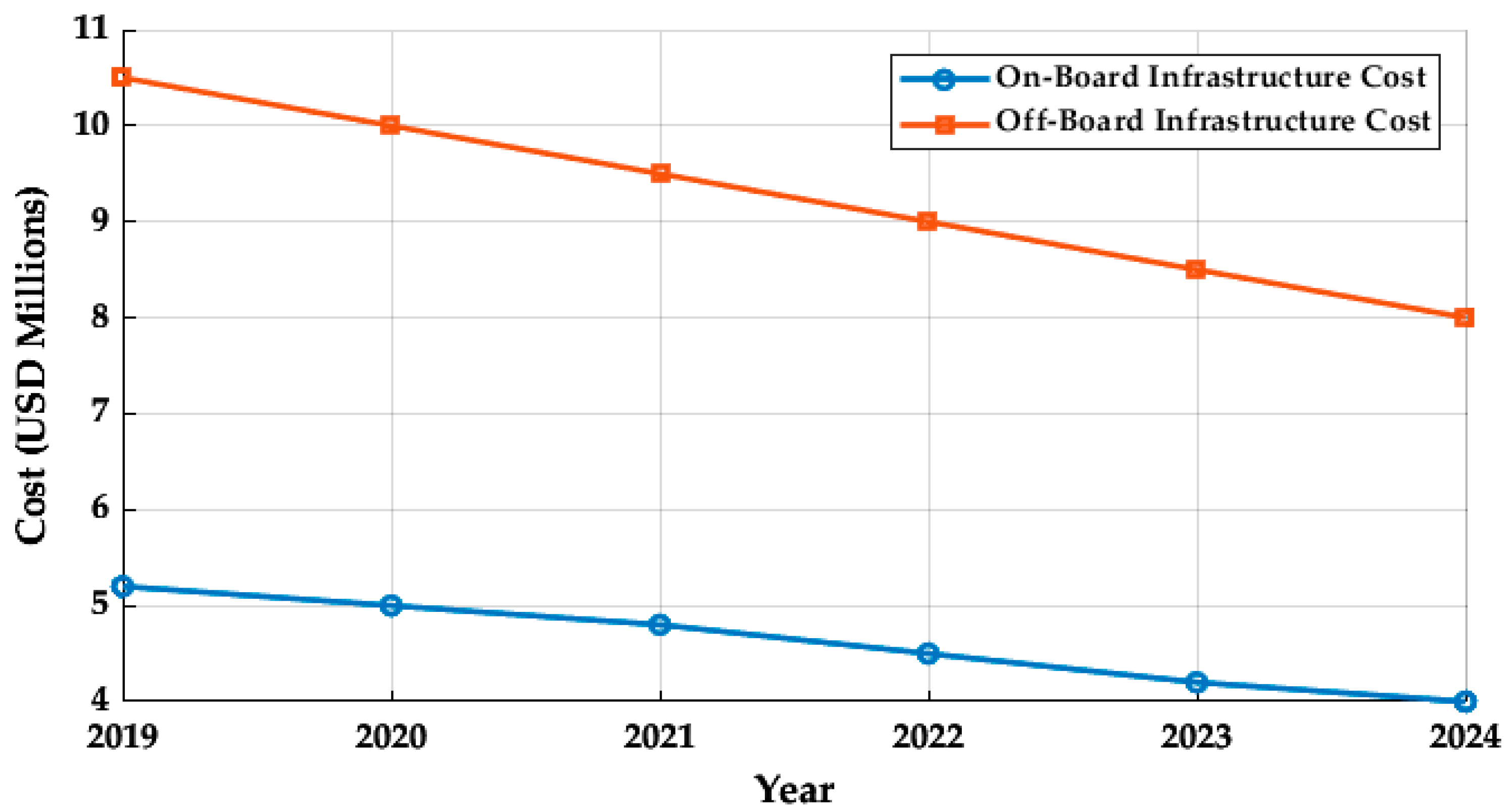
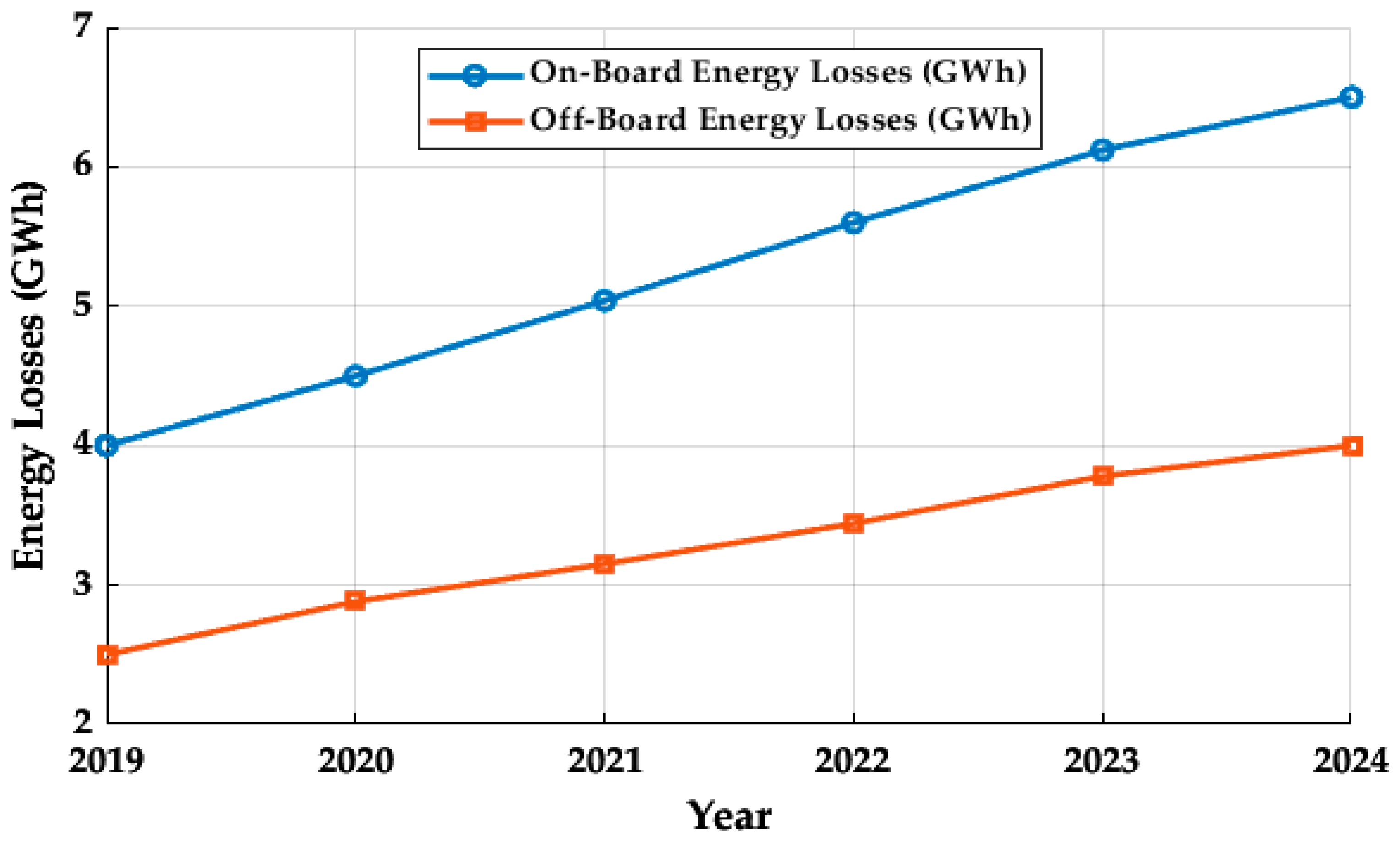
10. Cost Analysis of Charging Infrastructure
11. Future Developments in EV Charging and Sustainable Energy Integration
12. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| AC | Alternating Current |
| BEVs | Battery electric vehicles |
| BSSs | Battery swapping stations |
| DC | Direct Current |
| EV | Electric vehicle |
| ES | Energy storage |
| FC | Fuel cell |
| FCEVs | Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles |
| GB | Guobiao |
| HEVs | Hybrid Electric Vehicles |
| IEEE | Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers |
| IoT | Internet of things |
| ICE | Internal combustion engine |
| IEC | International Electrotechnical Commission |
| NaNiCl2 | Sodium nickel chloride |
| Na2S | Sodium sulfide |
| Ni-MH | Nickel-metal hydride |
| Ni-Cd | Nickel-cadmium |
| Na-ion | Sodium-ion |
| SAE | Society of Automotive Engineers |
| SC | Supercapacitors |
| SOC | State of charge |
| PHEVs | Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| UCs | Ultracapacitors |
| RE | Renewable enrgy |
| V2G | Vehicle to grid |
References
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). IEC 62196-2:2022: Plugs, Socket-Outlets, Vehicle Connectors and Vehicle Inlets—Conductive Charging of Electric Vehicles—Part 2: Dimensional Compatibility Requirements for AC Pin and Contact-Tube Accessories. 2022. Available online: https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/64364 (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- European Commission. A European Strategy for Low-Emission Mobility, Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions. 2016. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A52016DC0501 (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Barreto, R.; Faria, P.; Vale, Z. Electric Mobility: An Overview of the Main Aspects Related to the Smart Grid. Electronics 2022, 11, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, A.A.; Edpuganti, A.; Khadkikar, V.; Zeineldin, H. A Novel Simultaneous AC and DC Charging Scheme for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2024, 39, 1534–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Fulton, L.; Kendall, A. A Review of Charging Infrastructure Requirements for US Electric Light-Duty Vehicles. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 200, 114608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Hynan, P.; von Jouanne, A.; Yokochi, A. Current Li-Ion Battery Technologies in Electric Vehicles and Opportunities for Advancements. Energies 2019, 12, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkholy, M.; Said, T.; Elymany, M.; Senjyu, T.; Gamil, M.M.; Song, D.; Ueda, S.; Lotfy, M.E. Techno-Economic Configuration of a Hybrid Backup System within a Microgrid Considering Vehicle-to-Grid Technology: A Case Study of a Remote Area. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 301, 118032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Pérez, N.; Gonzalez-Garrido, A.; Gallarreta, A.; Justel, D.; González-Pérez, M.; González-Ramos, J.; Arrizabalaga, A.; Asensio, F.J.; Bidaguren, P. Communications and Data Science for the Success of Vehicle-to-Grid Technologies: Current State and Future Trends. Electronics 2024, 13, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul, S.; Qadir, F.; Ahmad, F.; Mohsin, A.; Al-Wahedi, A.; Iqbal, A.; Ali, A. Navigating the Complex Realities of Electric Vehicle Adoption: A Comprehensive Study of Government Strategies, Policies, and Incentives. Energy Strategy Rev. 2024, 53, 101379. [Google Scholar]
- Szumska, E.M. Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure along Highways in the EU. Energies 2023, 16, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.F.C.; Marques, D.C.; Tavares, L.; Dantas, N.K.L.; Fernandes, A.L.; Tuo, J.; de Medeiros, L.H.A.; Rosas, P. Energy and Demand Forecasting Based on Logistic Growth Method for Electric Vehicle Fast Charging Station Planning with PV Solar System. Energies 2022, 15, 6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Chen, B.; Liu, X.C.; Wei, R.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z. An Agent-Based Modeling Approach for Public Charging Demand Estimation and Charging Station Location Optimization at Urban Scale. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2023, 101, 101949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmouna, A.; Borderiou, L.; Becherif, M. Charging Stations for Large-Scale Deployment of Electric Vehicles. Batteries 2024, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakam, Y.; Gaga, A.; Elhadadi, B. Exploring the State of Electric Vehicles: An Evidence-Based Examination of Current and Future Electric Vehicle Technologies and Smart Charging Stations. Energy Rep. 2024, 11, 4102–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshil, B.; Nagababu, G. Strategies and Models for Optimal EV Charging Station Site Selection. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1372, 012106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, M.W.; González, R.C.; Hatzell, M.C. Optimizing Geographic Locations for Electric Vehicle Battery Recycling Preprocessing Facilities in California. RSC Sustain. 2024, 2, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.U.; Umar, S.; Qureshi, M.S. Life Cycle Analysis of Solar-Powered Electric Vehicles: Environmental and Economic Perspectives. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. Innov. 2024, 3, 96–115. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Basset, M.; Gamal, A.; Hezam, I.M.; Sallam, K.M. Sustainability assessment of optimal location of electric vehicle charge stations: A conceptual framework for green energy into smart cities. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 11475–11513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, J. Multi-objective dynamic economic emission dispatch integration with renewable energy sources and plug-in electrical vehicle using equilibrium optimizer. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 8555–8586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, S.; Ahshan, R.; Al Abri, R.; Al-Badi, A.; Albadi, M. Techno-economic and environmental assessment of renewable energy sources, virtual synchronous generators, and electric vehicle charging stations in microgrids. Appl. Energy 2024, 353, 122028. [Google Scholar]
- Aslankaya, E.; Yılmaz, A.; Bayrak, G. Enhancing power quality in vehicle-to-grid (V2G) operations of FCEVs through the integration of real-time digital IIR filters in power calculations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 75, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Dargaville, R. The Optimal Infrastructure Design for Grid-to-Vehicle (G2V) Service: A Case Study Based on the Monash Microgrid. Energies 2024, 17, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, F. Electric Vehicles: Benefits, Challenges, and Potential Solutions for Widespread Adaptation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.S. Optimal allocation of electric vehicles charging infrastructure, policies and future trends. J. Energy Storage 2021, 43, 103291. [Google Scholar]
- Mosleuzzaman; Shamsuzzaman, H.M.; Hussain, D. Engineering Challenges and Solutions in Smart Grid Integration With Electric Vehicles. Acad. J. Sci. Technol. Eng. Math. Educ. 2024, 4, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manousakis, N.M.; Karagiannopoulos, P.S.; Tsekouras, G.J.; Kanellos, F.D. Integration of Renewable Energy and Electric Vehicles in Power Systems: A Review. Processes 2023, 11, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Saif, O.; Abo-Adma, M.; Fahmy, A.; Elazab, R. Strategies and sustainability in fast charging station deployment for electric vehicles. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, A.; Iqbal, S.; Rehman, A.U.; Elbarbary, Z.M.S.; Kotb, H.; Selim, A.; Kamel, S. Integration of solar based charging station in power distribution network and charging scheduling of EVs. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1086793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajanovic, A.; Haas, R. On the economics and the future prospects of battery electric vehicles. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, H. Hydrogen refueling of a fuel cell electric vehicle. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 75, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, M.; Fragiacomo, P. Hydrogen refueling station: Overview of the technological status and research enhancement. J. Energy Storage 2023, 61, 106758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Cho, M.; Hardman, S. Do plug-in hybrid adopters switch to battery electric vehicles (and vice versa)? Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2023, 119, 103752. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, L.; Ahmad, M.; Khattak, S.I. Impact of innovation in hybrid electric vehicles-related technologies on carbon dioxide emissions in the 15 most innovative countries. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2023, 196, 122859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://x-engineer.org/battery-electric-vehicle-bev/ (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Available online: https://www.honda-nyon.ch/actus/details/4774/premiere-mondiale-au-h2-fc-expo-de-tokyo-honda-cr-v-e-fcev (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Available online: https://skill-lync.com/blogs/types-of-hybrid-electric-vehicle-and-the-recent-trends-in-the-hev-market (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Available online: https://grupomsdealer.es/mitsubishi-anuncia-la-fecha-de-presentacion-del-nuevo-outlander-phev-en-europa-y-desvela-cuando-llegara-a-espana-su-renovado-suv-hibrido/ (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Habib, S.; Khan, M.M.; Abbas, F.; Sang, L.; Shahid, M.U.; Tang, H. A comprehensive study of implemented international standards, technical challenges, impacts and prospects for electric vehicles. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 13866–13890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommana, B.; Kumar, J.S.V.S.; Nuvvula, R.S.S.; Kumar, P.P.; Khan, B.; Muthusamy, S.; Inapakurthi, R. A comprehensive examination of the protocols, technologies, and safety requirements for electric vehicle charging infrastructure. J. Adv. Transp. 2023, 2023, 7500151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaymaz, H. Operational charging methods for electric buses: A case study for BRT Istanbul. Int. J. Heavy Veh. Syst. 2023, 30, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempton, W.; McGee, R.T.; Ejzak, G.A. A Universal Electric Vehicle Outlet and Portable Cable for North America. World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 15, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Wu, Y.; Wu, X.; Sun, Y.; Teng, D.; Liu, Y. Research and development review of power converter topologies and control technology for electric vehicle fast-charging systems. Electronics 2023, 12, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaman, S.; Verbrugge, B.; Garcia, O.H.; Abdel-Monem, M.; Oliver, B.; Geury, T.; Hegazy, O. Development and validation of V2G technology for electric vehicle chargers using combo CCS type 2 connector stand-ards. Energies 2022, 15, 7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, R.; Keshmiri, N.; Emadi, A. On-board chargers for high-voltage electric vehicle powertrains: Future trends and challenges. IEEE Open J. Power Electron. 2023, 4, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateen, S.; Amir, M.; Haque, A.; Bakhsh, F.I. Ultra-fast charging of electric vehicles: A review of power electronics converter, grid stability and optimal battery consideration in multi-energy systems. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2023, 35, 101112. [Google Scholar]
- Mastoi, M.S.; Zhuang, S.; Munir, H.M.; Haris, M.; Hassan, M.; Usman, M.; Bukhari, S.S.H.; Ro, J.-S. An in-depth analysis of electric vehicle charging station infrastructure, policy implications, and future trends. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 11504–11529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchanathan, S.; Vishnuram, P.; Rajamanickam, N.; Bajaj, M.; Blazek, V.; Prokop, L.; Misak, S. A Comprehensive Review of the Bidirectional Converter Topologies for the Vehicle-to-Grid System. Energies 2023, 16, 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Mikkili, S. Advancements in EV international standards: Charging, safety and grid integration with challenges and impacts. Int. J. Green Energy 2024, 21, 2672–2698. [Google Scholar]
- Martini, D.; Aimar, M.; Borghetti, F.; Longo, M.; Foiadelli, F. Innovative Energy Approach for Design and Sizing of Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure. Infrastructures 2024, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.; Cappellucci, J.; Heinrich, A.; Cost, E. Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Trends from the Alternative Fueling Station Locator: Fourth Quarter 2023. Tech. Rep. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, V.S.; Bhavya, Y.V.; Udaya Sagar, V.; Chandrasekar, V. Implementation and Test Bench Development of GB/T 27930-2015 Communication Protocol for Electric Vehicle Charger. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 7380–7388. [Google Scholar]
- Kilic, A. Charging Techniques, Infrastructure, and Their Influences. Eng. Perspect. 2023, 3, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). IEC 62196 Plugs, Socket-Outlets, Vehicle Connectors and Vehicle Inlets—Conductive Charging of Electric Vehicles. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEC_62196 (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Parthasarathy, T.N.; Narayanamoorthy, S.; Devi, N.S.K.; Pamucar, D.; Simic, V.; Kang, D. An Idiosyncratic Interval Valued Picture q-Rung Orthopair Fuzzy Decision-Making Model for Electric Vehicle Battery Charging Technology Selection. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 26, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WKhan, W.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, F.; Alam, M.S. A comprehensive review of fast charging infrastructure for electric vehicles. Smart Sci. 2018, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, M.; Ahmad, F.; Panigrahi, B.K. Design, simulation and analysis of a fast charging station for electric vehicles. Energy Storage 2021, 3, e263. [Google Scholar]
- Leijon, J.; Boström, C. Charging electric vehicles today and in the future. World Electr. Veh. J. 2022, 13, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.R.; Alam, M.S.; Sarwar, A.; Asghar, M.J. A Comprehensive Review on Electric Vehicles Charging Infrastructures and Their Impacts on Power Quality of the Utility Grid. eTransportation 2019, 1, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemberton, S.; Nobajas, A.; Waller, R. Rapid charging provision, multiplicity and battery electric vehicle (BEV) mobility in the UK. J. Transp. Geogr. 2021, 95, 103137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipu, M.S.H.; Mamun, A.A.; Ansari, S.; Miah, M.S.; Hasan, K.; Meraj, S.T.; Abdolrasol, M.G.M.; Rahman, T.; Maruf, M.H.; Sarker, M.R.; et al. Battery Management, Key Technologies, Methods, Issues, and Future Trends of Electric Vehicles: A Pathway toward Achieving Sustainable Development Goals. Batteries 2022, 8, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadaoui, A.; Ouassaid, M.; Maaroufi, M. Overview of integration of power electronic topologies and advanced control techniques of ultra-fast EV charging stations in standalone microgrids. Energies 2023, 16, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savari, G.F.; Sathik, M.J.; Raman, L.A.; El-Shahat, A.; Hasanien, H.M.; Almakhles, D.; Aleem, S.H.A.; Omar, A.I. Assessment of charging technologies, infrastructure and charging station recommendation schemes of electric vehicles: A review. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 14, 101938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iam, I.-W.; Choi, C.-K.; Lam, C.-S.; Mak, P.-I.; Martins, R.P. A constant-power and optimal-transfer-efficiency wireless inductive power transfer converter for battery charger. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.-T.; Vu, V.-B.; Gohil, G.; Fahimi, B. Coil-to-coil efficiency optimization of double-sided LCC topology for electric vehicle inductive chargers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 11242–11252. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Fang, C. Double-assistant evolutionary multitasking algorithm for enhanced electric vehicle routing with backup batteries and battery swapping stations. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On-Ouen, A.; Arbking, J.; Phakdee, N. Optimized selection of motorcycle battery swapping stations under flexible demand by using distance function and gis technique. EECTI Trans. Comput. Inf. Technol. (ECTI-CIT) 2023, 17, 432–439. [Google Scholar]
- Sayarshad, H.R.; Mahmoodian, V. An Intelligent Method for Dynamic Distribution of Electric Taxi Batteries Between Charging and Swapping Stations. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 65, 102605. [Google Scholar]
- Adu-Gyamfi, G.; Song, H.; Obuobi, B.; Nketiah, E.; Wang, H.; Cudjoe, D. Who will adopt? Investigating the adoption intention for battery swap technology for electric vehicles. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 156, 111979. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, S.; Sun, L. Research on location planning of urban charging stations and battery-swapping stations for electric vehicles. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 508–522. [Google Scholar]
- Sachan, S.; Deb, S.; Singh, S.N. Different charging infrastructures along with smart charging strategies for electric vehicles. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 60, 102238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Triel, F.; Lipman, T.E. Modeling the future California electricity grid and renewable energy integration with electric vehicles. Energies 2020, 13, 5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, M.; Ismail, M.; Hoornweg, D.; Metcalfe, M. Planning for variable renewable energy and electric vehicle integration under varying degrees of decentralization: A case study in Lusaka, Zambia. Energy 2018, 151, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakkar, R.; Gupta, R.; Agrawal, S.; Tanwar, S.; Sharma, R.; Alkhayyat, A.; Neagu, B.-C.; Raboaca, M.S. A Review on Standardizing Electric Vehicles Community Charging Service Operator Infrastructure. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, G.; Vaithilingam, C.; Norhisam, M.; Naidu, K.; Ahmed, M. A Comprehensive Review on System Architecture and International Standards for Electric Vehicle Charging Stations. J. Energy Storage 2021, 42, 103099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amry, Y.; Elbouchikhi, E.; Le Gall, F.; Ghogho, M.; El Hani, S. Electric vehicle traction drives and charging station power electronics: Current status and challenges. Energies 2022, 15, 6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triviño-Cabrera, A.; González-González, J.M. Wireless Power Transfer for Electric Vehicles: Foundations and Design Approach, 1st ed.; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.; Tavakoli, R.; Pantic, Z.; Onar, O.C. Advances in High-Power Wireless Charging Systems: Overview and Design Considerations. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2020, 6, 886–919. [Google Scholar]
- Musavi, F.; Eberle, W. Overview of Wireless Power Transfer Technologies for Electric Vehicle Battery Charging. IET Power Electron. 2014, 7, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Tarar, M.O.; Hassan, N.U.; Naqvi, I.H. Techno-economic framework for electric vehicle battery swapping stations. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 9, 4458–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyundai. Available online: https://www.hyundai.com/fr/fr/voiture-electrique.html (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Tesla Model 3. Available online: https://www.tesla.com/ownersmanual/model3/pl_pl/GUID-E414862C-CFA1-4A0B-9548 (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- MINI Cooper SE. Available online: https://www.mini.com.pl/pl_PL/home/range/electric.html (accessed on 28 January 2023).
- Hyundai Ioniq 5. Available online: https://www.hyundai.com/fr/fr/modeles/ioniq5.html (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Ford Mustang Mach-E GT. Available online: https://www.ford.pl/ (accessed on 28 January 2023).
- BMW i4 Gran Coupe. Available online: https://www.bmw.fr/fr/tous-les-modeles/bmw-i/i4/bmw-i4-gran-coupe.html (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- KIA EV6 AWD. Available online: https://www.kia.com/pl/modele/ev6 (accessed on 28 January 2023).
- Porsche Cayenne. Available online: https://www.porsche.com/middle-east/fr/models/cayenne (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Nissan Leaf N-Connecta. Available online: https://www.nissan.pl/pojazdy/nowe-pojazdy/leaf/ (accessed on 28 January 2023).
- Wang, L.; Qin, Z.; Slangen, T.; Bauer, P. Grid impact of electric vehicle fast charging stations: Trends, standards, issues and mitigation measures—An overview. Open J. Power Electron. 2021, 2, 56–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadi, S.A.; Matsumoto, H.; Moshirvaziri, M. Active saturation mitigation in high-density dual-active-bridge DC–DC converter for on-board EV charger applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 35, 4376–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastoi, M.S.; Zhuang, S.; Munir, H.M.; Haris, M.; Hassan, M. A study of charging-dispatch strategies and vehicle-to-grid technologies for electric vehicles in distribution networks. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 1777–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmings, T.; Goves, C. Utilising Mobile Network Data for Transport Modelling: Recommendations Paper; Department for Transport: London, UK, 2017.
- Zannat, K.E.; Choudhury, C.F.; Hess, S.; Watling, D. Investigating the relative accuracy of GPS, GSM and CDR data for inferring spatiotemporal travel trajectories. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 18, 3013–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdoğan, B.; Tural, M.K.; Khoei, A.A. Finding an energy efficient path for plug-in electric vehicles with speed optimization and travel time restrictions. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 176, 108987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, Z.; Nowaczyk, S. Enhancing energy efficiency in connected vehicles for traffic flow optimization. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 2574–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakikes; Nathanail, E.; Savrasovs, M. Techniques for smart urban logistics solutions’ simulation: A systematic review. In Reliability and Statistics in Transportation and Communication: Selected Papers from the 18th International Conference on Reliability and Statistics in Transportation and Communication, RelStat’18, Riga, Latvia, 17–20 October 2018; 68 LNNS; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 551–561. [Google Scholar]
- Karakikes, I.; Nathanail, E. Simulation techniques for evaluating smart logistic solutions for sustainable urban distribution. Procedia Eng. 2017, 178, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Ren, Q.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X. Predictive Model for EV Charging Load Incorporating Multimodal Travel Behavior and Microscopic Traffic Simulation. Energies 2024, 17, 2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Mu, Y.; Jin, S.; Dong, X.; Jia, H. Modeling Electric Vehicle Charging Load Dynamics: A Spatial-Temporal Approach Integrating Trip Chains and Dynamic User Equilibrium. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2024, 16, 582–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Esparza, E.; Masegosa, A.D.; Oliva, D. A new hyper-heuristic based on adaptive simulated annealing and reinforcement learning for the capacitated electric vehicle routing problem. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 252 Pt B, 124197. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, R.; Aggarwal, A.; Bedi, J. A meta-heuristic-based energy efficient route modeling for EVs integrating start/stop and recapturing energy effect. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 91, 104420. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Chen, X.; Qiu, R.; Hou, S. Electric vehicle industry sustainable development with a stakeholder engagement system. Technol. Soc. 2021, 67, 101771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Fang, H.; Jiang, H.; Bai, J.; Havyarimana, V.; Chen, H.; Jiao, L. Understanding Private Car Aggregation Effect via Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Trajectory Data. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2023, 53, 2346–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachan, S.; Singh, P.P. Charging infrastructure planning for electric vehicle in India: Present status and future challenges. Reg. Sustain. 2022, 3, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenna, M.; Foiadelli, F.; Leone, C.; Longo, M. Electric Vehicles Charging Technology Review and Optimal Size Estimation. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2020, 15, 2539–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.; Singh, A.K.; Rathore, R.S.; Bajaj, M.; Gupta, D. Revolutionizing Load Management: A Novel Technique to Diminish the Impact of Electric Vehicle Charging Stations on the Electricity Grid. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2024, 65, 103784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, M.; Chaves-Ávila, J.P.; Magdy, G.; Sánchez-Miralles, Á. Review of positive and negative impacts of electric vehicles charging on electric power systems. Energies 2020, 13, 4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metais, M.O.; Jouini, O.; Perez, Y.; Berrada, J.; Suomalainen, E. Too much or not enough? Planning electric vehicle charging infrastructure: A review of modeling options. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 153, 111719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Wang, B.; Zhang, P.; Luh, P.B. Decentralised online charging scheduling for large populations of electric vehicles: A cyber-physical system approach. Int. J. Parallel, Emergent Distrib. Syst. 2013, 28, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Anduri, S.; Veerendra, G.T.N.; Rao, K.V.; Babu, P.S.S.A. Renewable Energy Present Status and Future Potentials in India: An Overview. Innovation and Green Development. 2022. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4323017 (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Fares, R. Renewable Energy Intermittency Explained: Challenges, Solutions and Opportunities. Scientific American. 2023. Available online: https://www.scientificamerican.com/blog/plugged-in/renewable-energy-intermittency-explained-challenges-solutions-and-opportunities/ (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Owusu, P.A.; Asumadu-Sarkodie, S. A review of renewable energy sources, sustainability issues and climate change mitigation. Cogent Eng. 2016, 3, 1167990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, S.; Cezar, G.V.; Min, L.; Azevedo, I.M.L.; Rajagopal, R. Charging infrastructure access and operation to reduce the grid impacts of deep electric vehicle adoption. Nat. Energy 2022, 7, 932–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dik, A.; Omer, S.; Boukhanouf, R.; Vehicles, E. Safe, and Green EV Penetration. Energies 2022, 15, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, S.; Lopez, A.; Watson, A.; Grue, N.; Leisch, J.E. Renewable Energy Data; Analysis, and Decisions: A Guide for Practitioners; National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2018.
- Mojumder, M.R.H.; Antara, F.A.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Alamri, B.; Alsharef, M. Electric Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technologies: Impact on the Power Grid and Battery. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntombela, M.; Musasa, K.; Moloi, K. A Comprehensive Review of the Incorporation of Electric Vehicles and Renewable Energy Distributed Generation Regarding Smart Grids. World Electr. Veh. J. 2023, 14, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guerrero, J.M.; Guan, Y.; Bazmohammadi, N. Microgrid an Energy Solution for Remote Islanded Communities in Indonesia. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 10th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC2024-ECCE Asia), Chengdu, China, 17–20 May 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 3799–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guerrero, J.M.; Guan, Y.; Golestan, S.; Cruz, J.D.L.; Koondhar, M.A.; Khan, B. A Comparison of Grid-Connected Local Hospital Loads with Typical Backup Systems and Renewable Energy System Based Ad Hoc Microgrids for Enhancing the Resilience of the System. Energies 2023, 16, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guerrero, J.M.; Guan, Y.; Cruz, J.D.L.; Aslam, M.J. Ad-Hoc Microgrids Planning for Rural Communities under Natural Disasters. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Energy, Power, Environment, Control, and Computing (ICEPECC), Gujrat, Pakistan, 8–9 March 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabnia, M.; Ali, M.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guan, Y.; Guerrero, J.M.; Khan, B.; Wijaya, F.D.; Perdana, A.P. Long-Term Renewable Energy Planning in the Indonesian Context: A Lombok Island Study Case. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Rajabnia, M.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guerrero, J.M.; Guan, Y.; Abusorrah, A.M. Planning of Community Microgrid for Improving the Resilience of System by Using HOMER Grid. In Proceedings of the 2023 25th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’2023 ECCE Europe), Aalborg, Denmark, 4–8 September 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Riaz, M.; Koondhar, M.A.; Akram, M.S.; Guerrero, J.M.; Vasquez, J.C.; Khan, B. Renewable Energy Sources-Based Hybrid Microgrid System for Off-Grid Electricity Solution for Rural Communities. Energy Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 3486–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, P.; Dutta, L.; Bordoloi, S.; Kalita, A.; Buragohain, P.; Bharali, S.; Azzopardi, B. Renewable energy integration with electric vehicle technology: A review of the existing smart charging approaches. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 183, 113518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Panda, K.P.; Naayagi, R.T.; Thakur, R.; Panda, G. Comprehensive review of electric vehicle technology and its impacts: Detailed investigation of charging infrastructure, power management, and control techniques. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dai, W.; Liu, B.; Li, J. Mechanical safety prediction of a battery-pack system under low speed frontal impact via machine learning. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2024, 160, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouka, K.; Masmoudi, A.; Abdelkafi, A.; Krichen, L. Dynamic energy management of an electric vehicle charging station using photovoltaic power. Sustain. Energy, Grids Netw. 2020, 24, 100402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B. Effective energy utilization through economic development for sustainable management in smart cities. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 4975–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercan, M.C.; Kayalica, O.; Kayakutlu, G.; Ercan, S. Economic model for an electric vehicle charging station with vehicle-to-grid functionality. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 6697–6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearnside, P.M. Environmental and Social Impacts of Hydroelectric Dams in Brazilian Amazonia: Implications for the Aluminum Industry. World Dev. 2016, 77, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.S.; Mahdi, A.J.; Bilal, M.; Sohail, H.M.; Ali, N.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Environmental impact and pollution-related challenges of renewable wind energy paradigm—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 683, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.S.; Ali, N.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Potential environmental impacts of wind energy development: A global perspective. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2020, 13, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, R.; Nygård, T.; Falkdalen, U.; Åstr, J.; Hamre, Ø.; Stokke, B.G. Paint it black: Efficacy of increased wind turbine rotor blade visibility to reduce avian fatalities. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 8927–8935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali, M.H.; Nouri, N.; Omrani, E.; Nasiri, A.; Otieno, W. An overview of the environmental, economic, and material developments of the solar and wind sources coupled with the energy storage systems. Int. J. Energy Res. 2017, 41, 1948–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breeze, P. Solar Integration and the Environmental Impact of Solar Power. Sol. Power Gener. 2016, 2016, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Bui, V.H.; Baek, J.W.; Kim, H.M. Stationary energy storage system for fast EV charging stations: Simultaneous sizing of battery and converter. Energies 2019, 12, 4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Huang, M.; Wang, L.Y.; Jiang, J. A bi-level optimization approach to charging load regulation of electric vehicle fast charging stations based on a battery energy storage system. Energies 2018, 11, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.; McDonough, M.K.; Miller, J.M.; Fahimi, B.; Balsara, P.T. Wireless Power Transfer for Vehicular Applications: Overview and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2018, 4, 3–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ruan, T.; Chen, Y.; Jin, F.; Peng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; Dou, S. Graphene-based composites for electrochemical energy storage, Energy Storage Mater. vol. 24, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Barman, P.; Dutta, L.; Azzopardi, B. Electric Vehicle Battery Supply Chain and Critical Materials: A brief survey of state of the art. Energies 2023, 16, 3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Bhatti, T.S. A review on electrochemical double-layer capacitors. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 2901–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, P. A historical review of electrode materials and electrolytes for electrochemical double layer supercapacitors and pseudocapacitors. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 2023, 61, 268–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Feng, J.; Fang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Yin, G.; Mao, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, F. An Energy-Oriented Torque-Vector Control Framework for Distributed Drive Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 9, 4014–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kularatna, N. DC Power Supplies Power Management and Surge Protection for Power Electronic Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Dougal, R.A. A compact digitally controlled fuel cell/battery hybrid power source. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Zhu, X.; Gergondet, P.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z. A Friction-Driven Strategy for Agile Steering Wheel Manipulation by Humanoid Robots. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2023, 4, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chu, J.; Sun, S. Development of a flywheel hybrid power system in vehicles without the electric drive device rated capacity limit. World Electr. Veh. J. 2022, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, T.H.; Frank, A.A. Design, demonstrations and sustainability impact assessments for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, M.Y.; Becherif, M.; Henni, A. Vehicle hybridization with fuel cell, supercapacitors and batteries by sliding mode control. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 2627–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solero, L.; Lidozzi, A.; Pomilio, J.A. Design of multiple-input power converter for hybrid vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2005, 20, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, K.; Dibaj, M.; Akrami, M. Analysing the Cost-Effectiveness of Charging Stations for Electric Vehicles in the U.K.’s Rural Areas. World Electr. Veh. J. 2021, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Yoon, G.; Kang, B.; Choi, M.-I.; Park, S.; Park, J.; Park, S. Enhancing Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure: A Techno-Economic Analysis of Distributed Energy Resources and Local Grid Integration. Buildings 2024, 14, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Bhattacharya, A.; Chakraborty, A.K. Allocation of Electric Vehicle Charging Station Considering Uncertainties. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2021, 25, 100422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.R.; Khan, I.A.; Hameed, S.; Asghar, M.S.J.; Ro, J.S. A Comprehensive Review on Structural Topologies, Power Levels, Energy Storage Systems, and Standards for Electric Vehicle Charging Stations and Their Impacts on Grid. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 128069–128094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Study | Focus Area | BEV Charging Infrastructure | FCEV Hydrogen Refueling Infrastructure | Renewable Energy Integration | Comparative Analysis of BEV vs. FCEV Infrastructure | Policy and Deployment Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [25] | Smart Grid Integration | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
| [26] | BEV Fast Charging | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| [27] | EV Infrastructure Cost Analysis | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
| [28] | Hydrogen Refueling Stations | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| This Study | Global EV Charging and Sustainable Energy Solutions | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
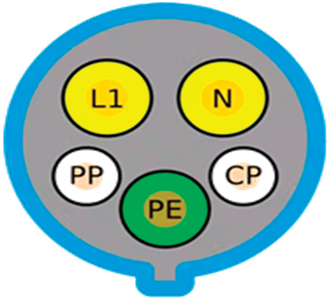 |  | 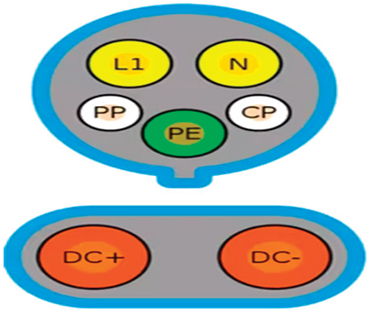 | 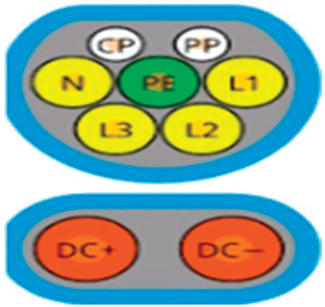 |
| SAE J1772 Type 1 | IEC 62196-2 Type 2 | SAE J1772 CCS/Combo 1 | IEC 62196-3 CCS/Combo 2 |
| USA/Japan | Europe/China | USA | Europe |
| AC charging | AC charging | DC fast charging/AC charging | DC fast charging/AC charging |
 |  | 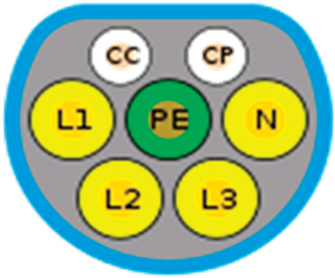 | 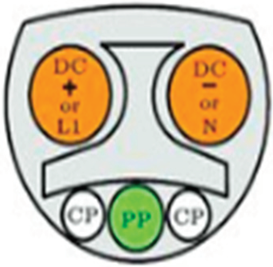 |
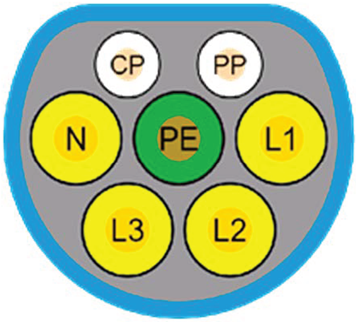
| GB/T BB.20234.3 | CHA DE MO | GB/T Type 2 20234.2 | Tesla |
| China | China | China | North USA/Europe |
| DC charging | DC charging | AC charging | AC and DC charging |
| Charging Type | Level | Power | Voltage | Maximum Current | Charging Time | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conductive (AC) | Level 1 | Up to 1.9 kW | 120 V AC | 16 A | 8–12 h | 85–90% |
| Level 2 | Up to 22 kW | 240 V AC | 32–80 A | 3–8 h | 90–95% | |
| Level 3 | Up to 43 kW | 400 V AC | 63–125 A | 30 min to 1 h | 95% and above | |
| Conductive (DC) | Level 4 | Up to 350 kW | 200–1000 V DC | 200–500 A | 20–40 min | 95% and above |
| Inductive | - | Up to 22 kW | 240 V AC | 32 A | Similar to AC | 90–95% |
| Swapping | - | System-dependent | - | - | Few minutes | Variable |
| Model | Level | Voltage (V) | Current (A) | Power (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Hyundai | Level 1 (DC) | 120 | 12 | Up to 2.4 |
| Level 2 (AC) | 240 | Up to 32 | Up to 7.2 | |
| Level 3 | 400 | Up to 250 | Up to 100 | |
 Tesla Model 3 | Level 1 (DC) | 120 | 12 | Up to 2.4 |
| Level 2 (AC) | 240 | Up to 48 | Up to 11.5 | |
| Level 3 | 400 to 800 | Up to 500 | Up to 250 | |
 Mini Electric (Mini Cooper SE) | Level 1 (DC) | 120 | 12 | Up to 2.4 |
| Level 2 (AC) | 240 | Up to 32 | Up to 7.4 | |
| Level 3 | 400 | Up to 125 | Up to 50 | |
 Hyundai Ioniq | Level 1 (DC) | 120 | 12 | Up to 2.4 |
| Level 2 (AC) | 240 | Up to 32 | Up to 7.2 | |
| Level 3 | 400 to 800 | Up to 500 | Up 150 | |
 Ford Mustang: Mach-E | Level 1 (DC) | 120 | 12 | Up to 2.4 |
| Level 2 (AC) | 240 | Up to 48 | Up to 11 | |
| Level 3 | 400 | Up to 375 | Up to 150 | |
 BMW i4 | Level 1 (DC) | 120 | 12 | Up to 2.4 |
| Level 2 (AC) | 240 | Up to 48 | Up to 11 | |
| Level 3 | 400 to 800 | Up to 500 | Up to 200 | |
 Kia EV6 | Level 1 (DC) | 120 | 12 | Up to 2.4 |
| Level 2 (AC) | 240 | Up to 48 | Up to 11 | |
| Level 3 | 400 to 800 | Up to 500 | Up 350 | |
 Porsche Taycan | Level 1 (DC) | 120 | 12 | Up to 2.4 |
| Level 2 (AC) | 240 | Up to 80 | Up to 19.2 | |
| Level 3 | 800 | Up to 650 | Up to 270 | |
 Nissan Leaf | Level 1 (DC) | 120 | 12 | Up to 2.4 |
| Level 2 (AC) | 240 | Up to 30 | Up to 6.6 | |
| Level 3 | 400 | Up to 125 | Up to 50 |
| Data Sources/References | Description |
|---|---|
| Survey data (e.g., household travel surveys, GPS-based surveys) [92,93] |
|
| Traffic flow volume [94,95] |
|
| Simulation data [96,97] |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the World Electric Vehicle Association. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nasri, S.; Mansouri, N.; Mnassri, A.; Lashab, A.; Vasquez, J.; Rezk, H. Global Analysis of Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure and Sustainable Energy Sources Solutions. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16040194
Nasri S, Mansouri N, Mnassri A, Lashab A, Vasquez J, Rezk H. Global Analysis of Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure and Sustainable Energy Sources Solutions. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2025; 16(4):194. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16040194
Chicago/Turabian StyleNasri, Sihem, Nouha Mansouri, Aymen Mnassri, Abderezak Lashab, Juan Vasquez, and Hegazy Rezk. 2025. "Global Analysis of Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure and Sustainable Energy Sources Solutions" World Electric Vehicle Journal 16, no. 4: 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16040194
APA StyleNasri, S., Mansouri, N., Mnassri, A., Lashab, A., Vasquez, J., & Rezk, H. (2025). Global Analysis of Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure and Sustainable Energy Sources Solutions. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 16(4), 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16040194










