New Insights into Risk Genes and Their Candidates in Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
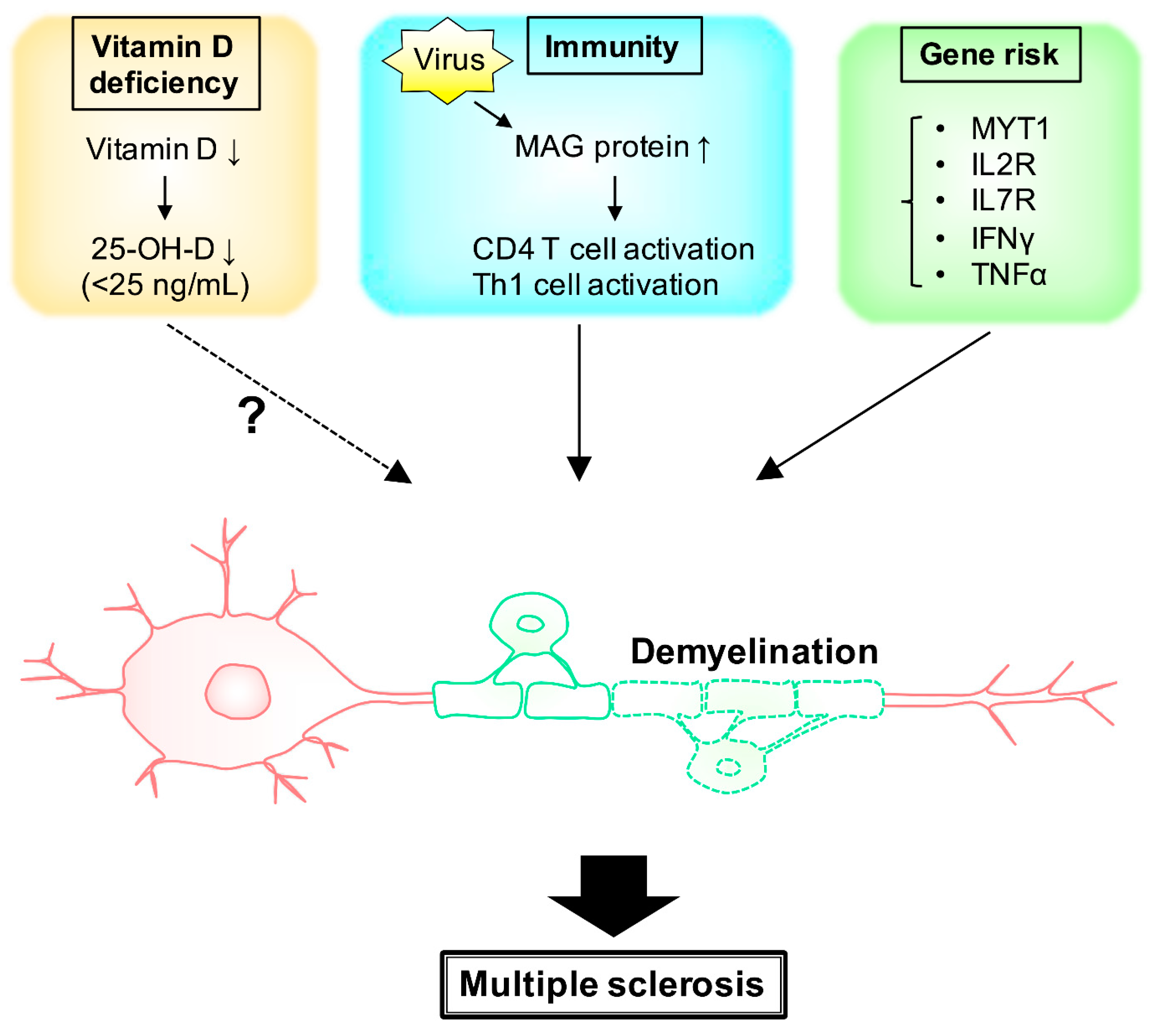
2. MS and Environmental Factors (Vitamin D)
3. MS and Environmental Factors (Immunity)
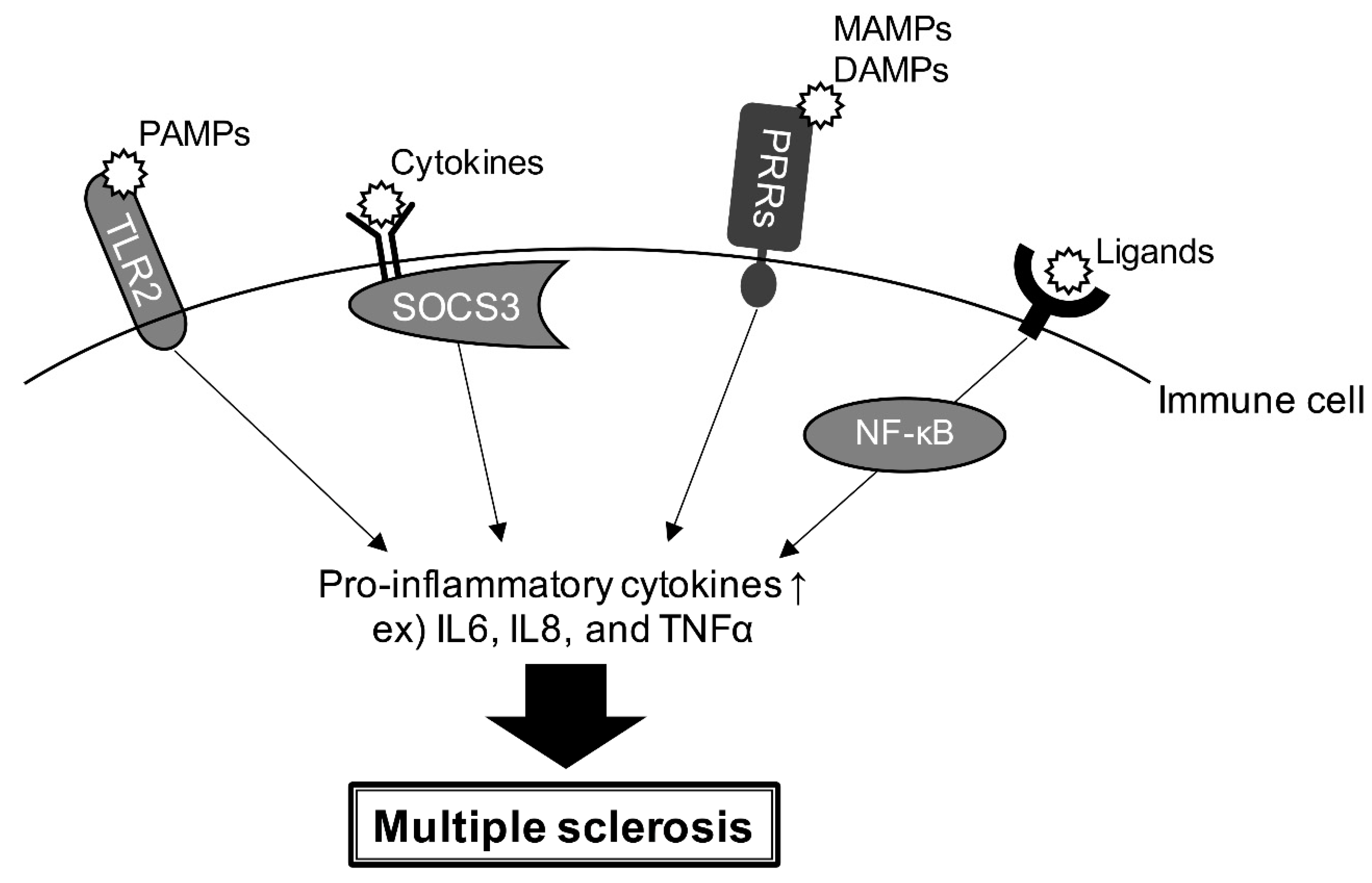
4. Gene Risk and Signaling Pathway
5. Conclusions and Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simons, M.; Nave, K.A. Oligodendrocytes: Myelination and axonal xsupport. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 8, a020479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barateiro, A.; Brites, D.; Fernandes, A. Oligodendrocyte development and myelination in neurodevelopment: Molecular mechanisms in health and disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 656–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz, B.; Popko, B. Molecular control of oligodendrocyte development. Trends Neurosci. 2019, 42, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, K.L.; Dahl, K.D.; Gallo, V.; Macklin, W.B. Intrinsic and extrinsic regulators of oligodendrocyte progenitor proliferation and differentiation. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2021, 116, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lublin, F.D.; Reingold, S.C. Defining the clinical course of multiple sclerosis: Results of an international survey. National Multiple Sclerosis Society (USA) Advisory Committee on Clinical Trials of New Agents in Multiple Sclerosis. Neurology 1996, 46, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaser, A.; Stahmann, A.; Meissner, T.; Flachenecker, P.; Horakova, D.; Zaratin, P.; Brichetto, G.; Pugliatti, M.; Rienhoff, O.; Vukusic, S.; et al. Multiple sclerosis registries in Europe—An updated mapping survey. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2019, 27, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houzen, H.; Kondo, K.; Horiuchi, K.; Niino, M. Consistent increase in the prevalence and female ratio of multiple sclerosis over 15 years in northern Japan. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, P.; Chandraratna, D.; Angood, C.; Tremlett, H.; Baker, C.; Taylor, B.V.; Thompson, A.J. Atlas of Multiple Sclerosis 2013: A growing global problem with widespread inequity. Neurology 2014, 83, 1022–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierrot-Deseilligny, C.; Souberbielle, J.C. Vitamin D and multiple sclerosis: An update. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2017, 14, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohara, C.; Hase, M.; Liebert, R.; Wu, N. The burden of multiple sclerosis in Japan. J. Med. Econ. 2017, 20, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfredsson, L.; Olsson, T. Lifestyle and Environmental Factors in Multiple Sclerosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a028944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baecher-Allan, C.; Kaskow, B.J.; Weiner, H.L. Multiple sclerosis: Mechanisms and immunotherapy. Neuron 2018, 97, 742–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawcer, S.; Ban, M.; Maranian, M.; Yeo, T.W.; Compston, A.; Kirby, A.; Daly, M.J.; De Jager, P.L.; Walsh, E.; Lander, E.S.; et al. A high-density screen for linkage in multiple sclerosis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 77, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics, C.; Hafler, D.A.; Compston, A.; Sawcer, S.; Lander, E.S.; Daly, M.J.; De Jager, P.L.; de Bakker, P.I.; Gabriel, S.B.; Mirel, D.B.; et al. Risk alleles for multiple sclerosis identified by a genomewide study. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, R.; Giovannoni, G. Multiple sclerosis—A review. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemond, C.C.; Bakshi, R. Magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a028969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S., Jr.; Blizzard, L.; Otahal, P.; Van der Mei, I.; Taylor, B. Latitude is significantly associated with the prevalence of multiple sclerosis: A meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannath, V.A.; Filippini, G.; Di Pietrantonj, C.; Asokan, G.V.; Robak, E.W.; Whamond, L.; Robinson, S.A. Vitamin D for the management of multiple sclerosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 9, CD008422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoln, M.R.; Schneider, R.; Oh, J. Vitamin D as disease-modifying therapy for multiple sclerosis? Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 17, 691–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munger, K.L.; Levin, L.I.; Hollis, B.W.; Howard, N.S.; Ascherio, A. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and risk of multiple sclerosis. JAMA 2006, 296, 2832–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.F.; Briggs, F.B.; Shao, X.; Gianfrancesco, M.A.; Kockum, I.; Harbo, H.F.; Celius, E.G.; Bos, S.D.; Hedstrom, A.; Shen, L.; et al. Multiple sclerosis risk loci and disease severity in 7,125 individuals from 10 studies. Neurol. Genet. 2016, 2, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harroud, A.; Manousaki, D.; Butler-Laporte, G.; Mitchell, R.E.; Davey Smith, G.; Richards, J.B.; Baranzini, S.E. The relative contributions of obesity, vitamin D, leptin, and adiponectin to multiple sclerosis risk: A Mendelian randomization mediation analysis. Mult. Scler. 2021, 27, 1994–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scazzone, C.; Agnello, L.; Bivona, G.; Lo Sasso, B.; Ciaccio, M. Vitamin D and genetic susceptibility to multiple sclerosis. Biochem. Genet. 2021, 59, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, L.; Clarke, L.; Khalilidehkordi, E.; Butzkueven, H.; Taylor, B.; Broadley, S.A. Vitamin D for the treatment of multiple sclerosis: A meta-analysis. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 2893–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, J.; Yaqubi, M.; Futhey, N.C.; Sedaghat, S.; Baufeld, C.; Blain, M.; Baranzini, S.; Butovsky, O.; Antel, J.; White, J.H.; et al. Vitamin D regulates MerTK-dependent phagocytosis in human myeloid cells. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasamy, A.; Trabzuni, D.; Forabosco, P.; Smith, C.; Walker, R.; Dillman, A.; Sveinbjornsdottir, S.; North American Brain Expression Consortium, U.K.B.E.C.; Hardy, J.; Weale, M.E.; et al. Genetic evidence for a pathogenic role for the vitamin D3 metabolizing enzyme CYP24A1 in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2014, 3, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Scazzone, C.; Agnello, L.; Sasso, B.L.; Ragonese, P.; Bivona, G.; Realmuto, S.; Iacolino, G.; Gambino, C.M.; Bellia, C.; Salemi, G.; et al. Klotho and vitamin D in multiple sclerosis: An Italian study. Arch. Med. Sci. 2020, 16, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi-Milasi, F.; Mahnam, K.; Shakhsi-Niaei, M. In silico study of the association of the HLA-A*31:01 allele (human leucocyte antigen allele 31:01) with neuroantigenic epitopes of PLP (proteolipid protein), MBP (myelin basic protein) and MOG proteins (myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein) for studying the multiple sclerosis disease pathogenesis. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 2526–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolbec, K.; Chalkley, J.; Sudhakar, P. Atypical MOG antibody disease presenting with typical multiple sclerosis lesions. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 44, 102342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarius, S.; Ruprecht, K.; Stellmann, J.P.; Huss, A.; Ayzenberg, I.; Willing, A.; Trebst, C.; Pawlitzki, M.; Abdelhak, A.; Gruter, T.; et al. MOG-IgG in primary and secondary chronic progressive multiple sclerosis: A multicenter study of 200 patients and review of the literature. J. Neuroinflam. 2018, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, R.; Messina, S.; Roca-Fernandez, A.; Leite, M.I.; Kong, Y.; Palace, J.A. Quantitative spinal cord MRI in MOG-antibody disease, neuromyelitis optica and multiple sclerosis. Brain 2021, 144, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.; Yu, M.; Soderstrom, M.; Weerth, S.; Baig, S.; Solders, G.; Link, H. Multiple MAG peptides are recognized by circulating T and B lymphocytes in polyneuropathy and multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2002, 9, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, J.R.; Johnson, D.; Brady, R.O.; Tourtellotte, W.W.; Quarles, R.H. Antibodies to myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) in the cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients. J. Neuroimmunol. 1989, 22, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sospedra, M.; Martin, R. Immunology of multiple sclerosis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 23, 683–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawcer, S.; Franklin, R.J.M.; Ban, M. Multiple sclerosis genetics. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banwell, B.; Giovannoni, G.; Hawkes, C.; Lublin, F. Multiple sclerosis is a multifaceted disease. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2014, 3, 553–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, E.J.; Bailey, S.L.; Castenada, C.V.; Waldner, H.; Miller, S.D. Epitope spreading initiates in the CNS in two mouse models of multiple sclerosis. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, B.L.; Sicotte, N.L. Microglia in multiple sclerosis: Friend or foe? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, H.; Kurtoic, D.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Weber, P.; Putz, B.; Muller-Myhsok, B.; Weber, F.; Andlauer, T.F.M. Gene expression in spontaneous experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis is linked to human multiple sclerosis risk genes. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, H.; Yin, P.; Song, J.; Jiang, F.; Tang, Z.; Fan, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Y.; et al. Identification and clinical validation of key extracellular proteins as the potential biomarkers in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 753929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scazzone, C.; Agnello, L.; Lo Sasso, B.; Salemi, G.; Gambino, C.M.; Ragonese, P.; Candore, G.; Ciaccio, A.M.; Giglio, R.V.; Bivona, G.; et al. FOXP3 and GATA3 polymorphisms, vitamin D3 and multiple sclerosis. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mescheriakova, J.Y.; van Nierop, G.P.; van der Eijk, A.A.; Kreft, K.L.; Hintzen, R.Q. EBNA-1 titer gradient in families with multiple sclerosis indicates a genetic contribution. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eftekharian, M.M.; Komaki, A.; Mazdeh, M.; Arsang-Jang, S.; Taheri, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Expression profile of selected MicroRNAs in the peripheral blood of multiple sclerosis patients: A multivariate statistical analysis with ROC Curve to find new biomarkers for fingolimod. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 68, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridolfi, E.; Fenoglio, C.; Cantoni, C.; Calvi, A.; De Riz, M.; Pietroboni, A.; Villa, C.; Serpente, M.; Bonsi, R.; Vercellino, M.; et al. Expression and genetic analysis of MicroRNAs involved in multiple sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 4375–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.S.; Rao, V.T.S.; Durafourt, B.A.; Bedell, B.J.; Ludwin, S.K.; Bar-Or, A.; Antel, J.P. miR-155 as a multiple sclerosis-relevant regulator of myeloid cell polarization. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 74, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Taheri, M. A comprehensive review of non-coding RNAs functions in multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 879, 173127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingelfinger, F.; Gerdes, L.A.; Kavaka, V.; Krishnarajah, S.; Friebel, E.; Galli, E.; Zwicky, P.; Furrer, R.; Peukert, C.; Dutertre, C.A.; et al. Twin study reveals non-heritable immune perturbations in multiple sclerosis. Nature 2022, 603, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handunnetthi, L.; Handel, A.E.; Ramagopalan, S.V. Contribution of genetic, epigenetic and transcriptomic differences to twin discordance in multiple sclerosis. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2010, 10, 1379–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ramagopalan, S.V.; Dyment, D.A.; Ebers, G.C. Genetic epidemiology: The use of old and new tools for multiple sclerosis. Trends Neurosci. 2008, 31, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics, C.; Beecham, A.H.; Patsopoulos, N.A.; Xifara, D.K.; Davis, M.F.; Kemppinen, A.; Cotsapas, C.; Shah, T.S.; Spencer, C.; Booth, D.; et al. Analysis of immune-related loci identifies 48 new susceptibility variants for multiple sclerosis. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics, C.; Wellcome Trust Case Control, C.; Sawcer, S.; Hellenthal, G.; Pirinen, M.; Spencer, C.C.; Patsopoulos, N.A.; Moutsianas, L.; Dilthey, A.; Su, Z.; et al. Genetic risk and a primary role for cell-mediated immune mechanisms in multiple sclerosis. Nature 2011, 476, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics, C. Multiple sclerosis genomic map implicates peripheral immune cells and microglia in susceptibility. Science 2019, 365, eaav7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Manuel, A.M.; Dai, Y.; Zhao, Z. Prioritization of risk genes in multiple sclerosis by a refined Bayesian framework followed by tissue-specificity and cell type feature assessment. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresle, M.M.; Jordan, M.A.; Stankovich, J.; Spelman, T.; Johnson, L.J.; Laverick, L.; Hamlett, A.; Smith, L.D.; Jokubaitis, V.G.; Baker, J.; et al. Multiple sclerosis risk variants regulate gene expression in innate and adaptive immune cells. Life Sci. Alliance 2020, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonasdottir, A.; Thorlacius, T.; Fossdal, R.; Jonasdottir, A.; Benediktsson, K.; Benedikz, J.; Jonsson, H.H.; Sainz, J.; Einarsdottir, H.; Sigurdardottir, S.; et al. A whole genome association study in Icelandic multiple sclerosis patients with 4804 markers. J. Neuroimmunol. 2003, 143, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omraninava, M.; Mehranfar, S.; Vahedi, P.; Razi, B.; Imani, D.; Aslani, S.; Feyzinia, S. Association between IL7 Receptor Alpha (Il7ra) gene rs6897932 polymorphism and the risk of multiple sclerosis: A meta-regression and meta-analysis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 48, 102687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharzadeh, M.; Najafi-Ghalehlou, N.; Poor, B.M.; Asgharzadeh, V.; Pourostadi, M.; Vegari, A.; Kafil, H.S.; Fadaee, M.; Farhoudi, M.; Rashedi, J. IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha gene polymorphisms in multiple sclerosis patients in Northwest Iran. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2021, 21, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barizzone, N.; Cagliani, R.; Basagni, C.; Clarelli, F.; Mendozzi, L.; Agliardi, C.; Forni, D.; Tosi, M.; Mascia, E.; Favero, F.; et al. An investigation of the role of common and rare variants in a large italian multiplex family of multiple sclerosis patients. Genes 2021, 12, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium. Electronic address, c.c.y.e.; International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics, C. Low-frequency and rare-coding variation contributes to multiple sclerosis risk. Cell 2018, 175, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorosina, M.; Barizzone, N.; Clarelli, F.; Anand, S.; Lupoli, S.; Salvi, E.; Mangano, E.; Bordoni, R.; Roostaei, T.; Mascia, E.; et al. A multi-step genomic approach prioritized TBKBP1 gene as relevant for multiple sclerosis susceptibility. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 4510–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics, C. A systems biology approach uncovers cell-specific gene regulatory effects of genetic associations in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Gibson, S.A.; Buckley, J.A.; Qin, H.; Benveniste, E.N. Role of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in regulation of innate immunity in neuroinflammatory diseases. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 189, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, J.A. Colony-stimulating factors in inflammation and autoimmunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, M.; Zhou, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, M.; Jing, Y.; Ma, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, L. Illumination of molecular pathways in multiple sclerosis lesions and the immune mechanism of matrine treatment in EAE, a mouse model of MS. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 640778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.Q.; Szodoray, P.; Zeher, M. Toll-like receptor pathways in autoimmune diseases. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 50, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccala, M.; Barizzone, N.; Boggio, E.; Gigliotti, L.; Sorosina, M.; Basagni, C.; Bordoni, R.; Clarelli, F.; Anand, S.; Mangano, E.; et al. Genomic and functional evaluation of TNFSF14 in multiple sclerosis susceptibility. J. Genet. Genom. 2021, 48, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steri, M.; Orru, V.; Idda, M.L.; Pitzalis, M.; Pala, M.; Zara, I.; Sidore, C.; Faa, V.; Floris, M.; Deiana, M.; et al. Overexpression of the Cytokine BAFF and autoimmunity risk. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1615–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolic, I.; Stojkovic, L.; Stankovic, A.; Stefanovic, M.; Dincic, E.; Zivkovic, M. Association study of rs7799039, rs1137101 and rs8192678 gene variants with disease susceptibility/severity and corresponding LEP, LEPR and PGC1A gene expression in multiple sclerosis. Gene 2021, 774, 145422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørbaek, C.; Elmquist, J.K.; Frantz, J.D.; Shoelson, S.E.; Flier, J.S. Identification of SOCS-3 as a potential mediator of central leptin resistance. Mol. Cell. 1998, 1, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deerhake, M.E.; Biswas, D.D.; Barclay, W.E.; Shinohara, M.L. Pattern recognition receptors in multiple sclerosis and its animal models. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cui, C.; Ma, X.; Luo, W.; Zheng, S.G.; Qiu, W. Nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB)-mediated inflammation in multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rosa, V.; Galgani, M.; Porcellini, A.; Colamatteo, A.; Santopaolo, M.; Zuchegna, C.; Romano, A.; De Simone, S.; Procaccini, C.; La Rocca, C.; et al. Glycolysis controls the induction of human regulatory T cells by modulating the expression of FOXP3 exon 2 splicing variants. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 1174–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, K.M.; Mirshafiey, A. Role of proangiogenic factors in immunopathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Iran J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hassani, N.; Salmaninejad, A.; Aslani, S.; Kamali-Sarvestani, E.; Vessal, M. The association between PD-1 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to multiple sclerosis. Immunol. Med. 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelic, M.; Pontarelli, F.; Woodworth, L.; Zhu, C.; Mahan, A.; Ren, Y.; LaMorte, M.; Gruber, R.; Keane, A.; Loring, P.; et al. RIPK1 activation mediates neuroinflammation and disease progression in multiple sclerosis. Cell. Rep. 2021, 35, 109112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| SNP Region | Gene | Protein | Possible Role of Nearest Gene |
|---|---|---|---|
| rs6742 | rtel1 | RTEL1 | DNA helicase |
| rs32658 | fam170a | FAM170A | DNA binding activator |
| rs137955 | rpl3 | RPL3 | ribosomal protein |
| rs140522 | hdac10 | HDAC10 | deacetylase |
| rs198398 | mtor | MTOR | rapamycin kinase |
| rs244656 | ppp2ca | PPP2CA | catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase |
| rs249677 | arhgap26 | ARHGAP26 | GTPase activating protein |
| rs354033 | znf862 | ZNF862 | zinc finger protein |
| rs405343 | axin1 | AXIN1 | cytoplasmic protein |
| rs438613 | eomes | EOMES | DNA binding domain |
| rs483180 | notch2 | NOTCH2 | notch receptor |
| rs531612 | rela | RELA | proto-oncogene transcription factor |
| rs631204 | tnfaip3 | TNFAIP3 | cytokine |
| rs701006 | arhgap9 | ARHGAP9 | GTPase activating protein |
| rs719316 | atxn1 | ATXN1 | DNA binding protein |
| rs735542 | myc | MYC | proto-oncogene transcription factor |
| rs760517 | lgals1 | LGALS1 | galactoside binding protein |
| rs802730 | ptprk | PTPRK | protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor |
| rs883871 | rara | RARA | retinoic acid receptor |
| rs962052 | rnd3 | RND3 | Rho family GTPase |
| rs983494 | cd48 | CD48 | immune response regulator |
| rs1014486 | il12a | IL12A | cytokine |
| rs1026916 | hoxa13 | HOXA13 | homeobox |
| rs1076928 | pim1 | PIM1 | proto-oncogene kinase |
| rs1077667 | c3 | C3 | complement component |
| rs1087056 | znf438 | ZNF438 | zinc finger protein |
| rs1112718 | ide | IDE | insulin enzyme |
| rs1177228 | commd1 | COMMD1 | copper metabolism |
| rs1250551 | zmiz1 | ZMIZ1 | zinc finger protein |
| rs1323292 | rgs1 | RGS1 | G Protein Signaling |
| rs1365120 | traf6 | TRAF6 | adaptor protein |
| rs1399180 | gata3 | GATA3 | transcription factor |
| rs1415069 | bcar3 | BCAR3 | anti-estrogen resistance protein |
| rs1465697 | atf5 | ATF5 | transcription factor |
| rs1738074 | synj2 | SYNJ2 | inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase |
| rs1800693 | cd9 | CD9 | immune response regulator |
| rs2084007 | ppp2ca | PPP2CA | catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase |
| rs2150879 | rps6kb1 | RPS6KB1 | ribosomal protein |
| rs2248137 | znf217 | ZNF217 | zinc finger protein |
| rs2269434 | celf1 | CELF1 | alternative splicing |
| rs2286974 | litaf | LITAF | cytokine |
| rs2289746 | alcam | ALCAM | immunoglobulin receptor |
| rs2317231 | cd1e | CD1E | immune response regulator |
| rs2327586 | sgk1 | SGK1 | serine/threonine kinase |
| rs2331964 | cd86 | CD86 | immune response regulator |
| rs2364485 | cd9 | CD9 | immune response regulator |
| rs2469434 | cd226 | CD226 | immune response regulator |
| rs2546890 | il12b | IL12B | cytokine |
| rs2585447 | znf217 | ZNF217 | zinc finger protein |
| rs2590438 | bcl6 | BCL6 | immune signaling receptor |
| rs2705616 | mapk10 | MAPK10 | MAPK |
| rs2726479 | cxxc4 | CXXC4 | zinc finger protein |
| rs2836438 | ets2 | ETS2 | transcription factor |
| rs2986736 | camta1 | CAMTA1 | transcription activator |
| rs3184504 | arpc3 | ARPC3 | cell polymerization |
| rs3737798 | cd48 | CD48 | immune response regulator |
| rs3809627 | mapk3 | MAPK3 | MAPK |
| rs3923387 | plec | PLEC | cytoskeleton |
| rs4262739 | ets1 | ETS1 | proto-oncogene transcription factor |
| rs4325907 | rpl24 | RPL24 | ribosomal protein |
| rs4409785 | maml2 | MAML2 | cytoplasmic protein |
| rs4728142 | smo | SMO | G protein-coupled receptor |
| rs4796224 | acaca | ACACA | acetyl-CoA carboxylase |
| rs4808760 | ifi30 | IFI30 | lysosomal thiol reductase |
| rs4812772 | mybl2 | MYBL2 | proto-oncogene transcription factor |
| rs4820955 | lif | LIF | cytokine |
| rs4896153 | bclaf1 | BCLAF1 | BCL transcription factor |
| rs4939490 | fads1 | FADS1 | fatty acid desaturase |
| rs4940730 | malt1 | MALT1 | caspase-like protease |
| rs5756405 | rac2 | RAC2 | GTP binding protein |
| rs6020055 | cebpb | CEBPB | transcriptional activator protein |
| rs6032662 | cd40 | CD40 | immune response regulator |
| rs6072343 | plcg1 | PLCG1 | phospholipase |
| rs6427540 | cd48 | CD48 | immune response regulator |
| rs6496663 | iqgap1 | IQGAP1 | GTPase activating protein |
| rs6533052 | nfkb1 | NFKB1 | cytokine |
| rs6564681 | maf | MAF | proto-oncogene kinase |
| rs6589706 | kmt2a | KMT2A | Lysine Methyltransferase |
| rs6589939 | clmp | CLMP | transmembrane protein |
| rs6670198 | prdm16 | PRDM16 | zinc finger protein |
| rs6672420 | runx3 | RUNX3 | transcription factor |
| rs6738544 | stat1 | STAT1 | transcription activator |
| rs6789653 | zbtb38 | ZBTB38 | zinc finger protein |
| rs6837324 | tec | TEC | tyrosine kinase |
| rs6911131 | hivep2 | HIVEP2 | zinc finger protein |
| rs6990534 | myc | MYC | proto-oncogene transcription factor |
| rs7222450 | crhr1 | CRHR1 | G-protein coupled receptor |
| rs7260482 | apoe | APOE | apoprotein |
| rs7731626 | map3k1 | MAP3K1 | MAPK kinase |
| rs7855251 | anp32b | ANP32B | RNA polymerase binding protein |
| rs7975763 | mphosph9 | MPHOSPH9 | M phase phosphoprotein |
| rs7977720 | olr1 | OLR1 | low density lipoprotein receptor |
| rs8062446 | nlrc5 | NLRC5 | cytokine receptor |
| rs9308424 | batf3 | BATF3 | basic leucine zipper protein |
| rs9568402 | rnaseh2b | RNASEH2B | ribonuclease |
| rs9591325 | rnaseh2b | RNASEH2B | ribonuclease |
| rs9610458 | ube2l3 | UBE2L3 | ubiquitin conjugating enzyme |
| rs9808753 | ifnar2 | IFNAR2 | interferon receptor |
| rs9843355 | cd80 | CD80 | immune response regulator |
| rs9863496 | satb1 | SATB1 | matrix protein |
| rs9878602 | rybp | RYBP | DNA binding protein |
| rs9900529 | grb2 | GRB2 | growth factor receptor |
| rs9909593 | rara | RARA | retinoic acid receptor |
| rs9955954 | malt1 | MALT1 | caspase-like protein |
| rs9992763 | rpl34 | RPL34 | ribosomal protein |
| rs10063294 | slc1a3 | EAA1 | transporter |
| rs10191360 | cxcr4 | CXCR4 | chemokine receptor |
| rs10230723 | ikzf1 | IKAROS | DNA binding protein |
| rs10245867 | hoxa13 | HOXA13 | homeobox |
| rs10271373 | tbxas1 | TBXAS1 | lipid synthase |
| rs10801908 | atp1a1 | ATP1A1 | transporting subunit |
| rs10936182 | il12a | IL12A | cytokine |
| rs10936602 | mecom | MDS1 And EVI1 Complex Locus | zinc finger protein |
| rs10951042 | mad1l1 | MAD1 | cell cycle controller |
| rs10951154 | hoxa4 | HOXA4 | homeobox |
| rs11079784 | npepps | NPEPPS | peptidase |
| rs11083862 | c5ar1 | C5AR1 | complement component receptor |
| rs11125803 | adcy3 | ADCY3 | adenylate cyclase |
| rs11161550 | bcl10 | BCL10 | immune signaling receptor |
| rs11231749 | esrra | ESRRA | estrogen related receptor |
| rs11256593 | pfkfb3 | PFKFB3 | phosphofructo kinase |
| rs11578655 | extl2 | EXTL2 | glycosyltransferase |
| rs11749040 | dab2 | DAB2 | adaptor protein |
| rs11809700 | rpl5 | RPL5 | ribosomal protein |
| rs11852059 | ptger2 | PTGER2 | prostaglandin receptor |
| rs11899404 | lpin1 | LPIN1 | lipid phosphohydrolase |
| rs11919880 | cnot10 | CNOT10 | transcription complex |
| rs12133753 | cdc7 | CDC7 | cell cycle kinase |
| rs12147246 | rcor1 | RCOR1 | transcription factor |
| rs12211604 | rreb1 | RREB1 | binding protein |
| rs12365699 | kmt2a | KMT2A | methyltransferase |
| rs12434551 | zfp36l1 | ZFP36L1 | zinc finger protein |
| rs12478539 | zfp36l2 | ZFP36L2 | zinc finger protein |
| rs12588969 | rcor1 | RCOR1 | chromatin binding |
| rs12609500 | tyk2 | TYK2 | tyrosine kinase |
| rs12614091 | cd28 | CD28 | immune response regulator |
| rs12622670 | aplf | APLF | component of the cellular response |
| rs12722559 | pfkfb3 | PFKFB3 | glycolysis-related biphosphatase |
| rs12832171 | cd9 | CD9 | immune response regulator |
| rs12925972 | maf | MAF | proto-oncogene kinase |
| rs12971909 | map2k2 | MAP2K2 | MAPK kinase |
| rs13066789 | bcl6 | BCL6 | immune signaling receptor |
| rs13136820 | uchl1 | UCHL1 | ubiquitin hydrolase |
| rs13327021 | eomes | EOMES | DNA binding domain |
| rs13385171 | sertad2 | SERTAD2 | transcription activator |
| rs13414105 | alk | ALK | tyrosine kinase |
| rs17051321 | qrfpr | QRFPR | pyroglutamylated receptor |
| rs17724508 | maf | MAF | proto-oncogene kinase |
| rs17741873 | camk2g | CAMK2G | CAM kinase |
| rs17780048 | tnfaip3 | TNFAIP3 | cytokine |
| rs28703878 | pkia | PKIA | protein kinase inhibitor |
| rs28834106 | dnm2 | DNM2 | GTP binding protein |
| rs34026809 | kmt2a | KMT2A | methyltransferase |
| rs34536443 | tyk2 | TYK2 | tyrosine kinase |
| rs34681760 | adcy2 | ADCY2 | adenylate cyclase |
| rs34695601 | fos | FOS | proto-oncogene transcription factor |
| rs34723276 | extl2 | EXTL2 | glycosyltransferase |
| rs34947566 | litaf | LITAF | cytokine |
| rs35218683 | deaf1 | DEAF1 | zinc finger protein |
| rs35486093 | bcl10 | BCL10 | adaptor protein |
| rs35540610 | sp110 | SP110 | nuclear body protein |
| rs35703946 | irf8 | IRF8 | cytokine |
| rs55858457 | mad1l1 | MAD1L1 | cell cycle controller |
| rs56095240 | maml2 | MAML2 | transcriptional activator |
| rs57116599 | il1b | IL1B | cytokine |
| rs58166386 | rasal3 | RASAL3 | Ras GTPase activating protein |
| rs58394161 | rpl5 | RPL5 | ribosomal protein |
| rs59655222 | znf281 | ZNF281 | zinc finger protein |
| rs60600003 | elmo1 | ELMO1 | adaptor protein |
| rs61708525 | plxnc1 | PLXNC1 | transmembrane receptor |
| rs61863928 | egr2 | EGR2 | transcription factor |
| rs61884005 | arntl | ARNTL | transcriptional activator |
| rs62013236 | acsbg1 | ACSBG1 | acyl-CoA synthetase |
| rs62420820 | tnfaip3 | TNFAIP3 | cytokine |
| rs67111717 | nsd1 | NSD1 | transcriptional regulator |
| rs67934705 | rpl11 | RPL11 | ribosomal protein |
| rs71329256 | cd86 | CD86 | immune response regulator |
| rs72922276 | pde4b | PDE4B | phosphodiesterase |
| rs72928038 | rragd | RRAGD | Ras related GTPase binding protein |
| rs72989863 | march1 | MARCH1 | ubiquitin protein ligase |
| rs73414214 | pik3cg | PIK3CG | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| chr1:154983036 | arhgef2 | ARHGEF2 | Rho/Rac guanine nucleotide exchanger |
| chr1:32738415 | hdac1 | HDAC1 | histone deacetylase |
| chr2:112492986 | anapc1 | ANAPC1 | anaphase-promoting complex |
| chr3:100848597 | rpl24 | RPL24 | ribosomal protein |
| chr3:112693983 | cd200 | CD200 | immune response regulator |
| chr3:121783015 | cd86 | CD86 | immune response regulator |
| chr5:40429250 | dab2 | DAB2 | DAB adaptor protein |
| chr6:119215402 | mcm9 | MCM9 | ATP hydrolysis activity |
| chr6:130348257 | arhgap18 | ARHGAP18 | Ras GTPase activating protein |
| chr6:14691215 | jarid2 | JARID2 | transcriptional repressor |
| chr7:50328339 | ikzf1 | IKZF1 | zinc finger protein |
| chr8:129177769 | myc | MYC | proto-oncogene transcription factor |
| chr8:95851818 | rad54b | RAD54B | DEAD-like helicase |
| chr11:118783424 | kmt2a | KMT2A | lysine methyltransferase |
| chr11:14868316 | pde3b | PDE3B | phosphodiesterase |
| chr13:100026952 | dock9 | DOCK9 | Cdc42 guanine nucleotide exchanger |
| chr14:88523488 | kcnk10 | KCNK10 | potassium channel protein |
| chr16:11213951 | litaf | LITAF | cytokine |
| chr16:11353879 | litaf | LITAF | cytokine |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shirai, R.; Yamauchi, J. New Insights into Risk Genes and Their Candidates in Multiple Sclerosis. Neurol. Int. 2023, 15, 24-39. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15010003
Shirai R, Yamauchi J. New Insights into Risk Genes and Their Candidates in Multiple Sclerosis. Neurology International. 2023; 15(1):24-39. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleShirai, Remina, and Junji Yamauchi. 2023. "New Insights into Risk Genes and Their Candidates in Multiple Sclerosis" Neurology International 15, no. 1: 24-39. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15010003
APA StyleShirai, R., & Yamauchi, J. (2023). New Insights into Risk Genes and Their Candidates in Multiple Sclerosis. Neurology International, 15(1), 24-39. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15010003







