Ergogenic and Sympathomimetic Effects of Yohimbine: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
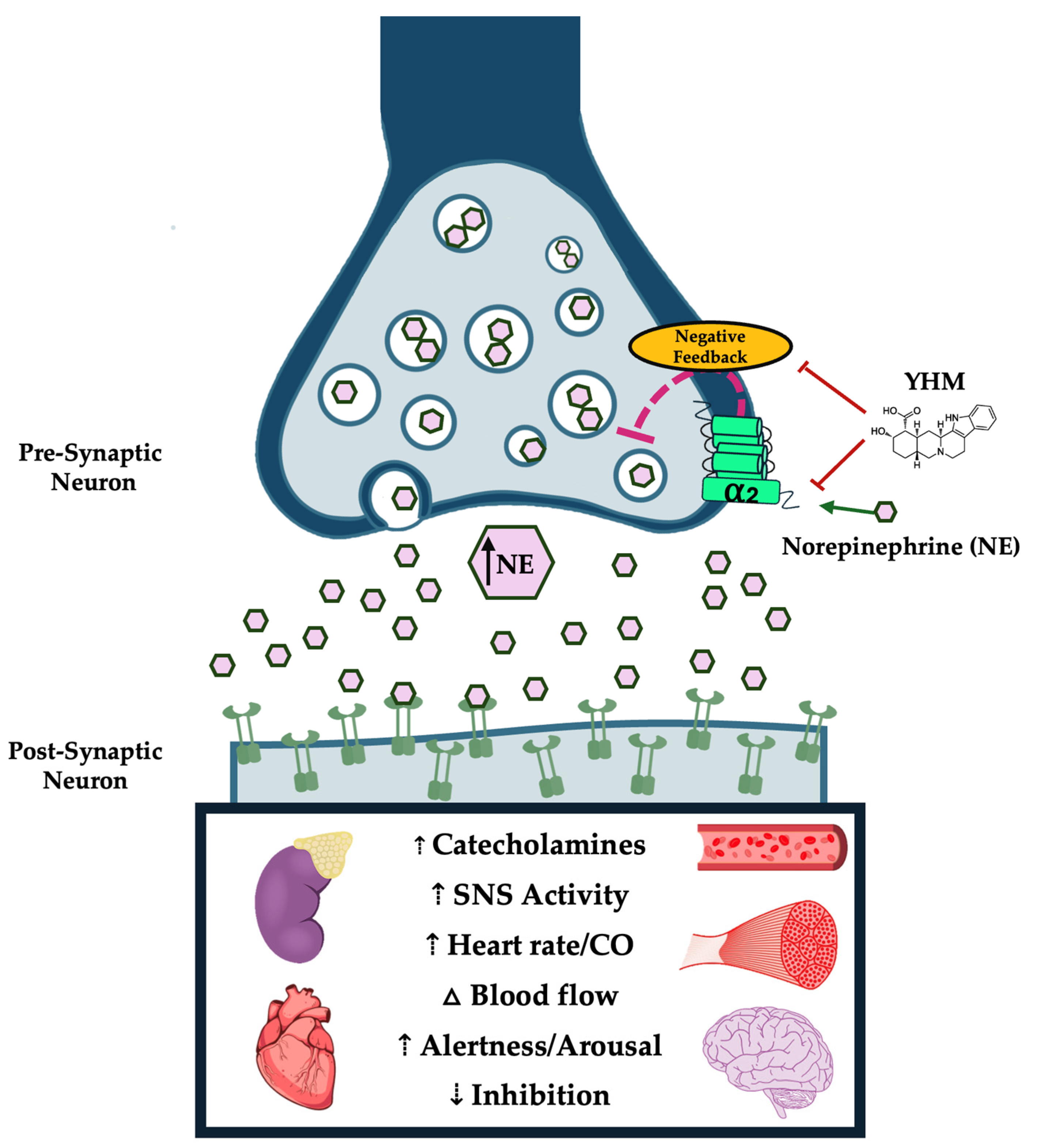
2. Primary Mechanism of Action
3. Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability
4. Yohimbine and Exercise
| Study | Conditions | Dosage | Ingestion Period | Exercise | Primary Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ostojic et al. (2006) [3] | PL, YHM | 20 mg | Daily; 21 days | Sprint (Cycle) | ↓ Fat Mass, ↔ Performance |
| Al-Kuraishy et al. (2014) [15] | PL, YHM | 5 mg | 2 h | Cycling | ↑ VO2, ↑ Distance,↑ Speed, ↑ Caloric Expenditure |
| Barnes et al. (2022) [17] | PL, YHM | 2.5 mg | 20 min prior | Sprint (Cycle) | ↑ Power, ↑ HR, ↔ RPE, ↑ Epinephrine, ↓ Lactate |
| Williams et al. (2023) [8] | PL, YHM | 5 mg | 20 min prior | Bench Press | ↔ Power or Velocity, ↑ RTF, ↑ Alertness, ↑ Motivation |
| Ballmann & Rogers et al. (2024) [14] | PL (AM), YHM (AM), Control (PM) | 2.5 mg | 20 min prior | Rowing | ↑ Power, ↓Time to Completion, ↔ HR or RPE, ↓ Lactate, ↑ Hypoxanthine |
4.1. Aerobic
4.2. Anaerobic
5. Considerations for Safety and Usage
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tam, S.W.; Worcel, M.; Wyllie, M. Yohimbine: A clinical review. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 91, 215–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teloken, C.; Rhoden, E.L.; Sogari, P.; Dambros, M.; Vargas Souto, C.A. Therapeutic effects of high dose yohimbine hydrochloride on organic erectile dysfunction. J. Urol. 1998, 159, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostojic, S.M. Yohimbine: The effects on body composition and exercise performance in soccer players. Res. Sports Med. 2006, 14, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, A. Yohimbine in erectile dysfunction: The facts. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2000, 12, S70–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotanska, M.; Marcinkowska, M.; Knutelska, J.; Zygmunt, M.; Sapa, J. Yohimbine improves lipid and carbohydrate profiles without reduction in body weight in obese leptin-deficient ob/ob mice. J. Pre-Clin. Clin. Res. 2018, 12, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P.A.; Wang, Y.H.; Maller, G.; DeSouza, R.; Khan, I.A. Pharmaceutical quantities of yohimbine found in dietary supplements in the USA. Drug Test. Anal. 2016, 8, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, O.G.; Zubieta, J.K.; Grunhaus, L.; Minoshima, S. Effects of yohimbine on cerebral blood flow, symptoms, and physiological functions in humans. Psychosom. Med. 2000, 62, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.D.; Boag, L.E.; Helton, C.L.; Middleton, M.L.; Rogers, R.R.; Sternenberg, L.H.; Ballmann, C.G. Effects of Acute Yohimbine Hydrochloride Ingestion on Bench Press Performance in Resistance-Trained Males. Muscles 2022, 1, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.R.; Hollister, A.S.; Robertson, D. Influence of yohimbine on blood pressure, autonomic reflexes, and plasma catecholamines in humans. Hypertension 1983, 5, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murburg, M.M.; Villacres, E.C.; Ko, G.N.; Veith, R.C. Effects of yohimbine on human sympathetic nervous system function. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1991, 73, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, E.; Rea, R.F.; Hoffman, A.; Goldstein, D.S. Yohimbine increases sympathetic nerve activity and norepinephrine spillover in normal volunteers. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1991, 260, R142–R147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, M.F. Pre-exercise administration of yohimbine may enhance the efficacy of exercise training as a fat loss strategy by boosting lipolysis. Med. Hypotheses 2002, 58, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.; Anderson, D.; Harre, N.; Wade, N. Case study: Two fatal case reports of acute yohimbine intoxication. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2013, 37, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballmann, C.G.; Rogers, R.R.; Barnes, M.E.; Cowan, C.R.; Elwell, C.C.; Luiken, K.A.; Lehman, G.Y.; Kaylor, J.C.; Simpson, E.G.; Westbrooks, S.B. Yohimbine Ingestion Mitigates Morning-Associated Decrements in High-Intensity Exercise Performance. Nutraceuticals 2024, 4, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M Al-Kuraishy, H.; AN Abood, H.; Al-Gareeb, I.A. Ergogenic Effects of Yohimbine: Standardized Cycling Clinical Study. Kerbala J. Med. 2014, 7, 1850–1855. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, M.E.; Cowan, C.R.; Boag, L.E.; Hill, J.G.; Jones, M.L.; Nixon, K.M.; Parker, M.G.; Parker, S.K.; Raymond, M.V.; Sternenberg, L.H.; et al. Effects of Acute Yohimbine Hydrochloride Supplementation on Repeated Supramaximal Sprint Performance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, M.E.; Williams, T.; Cowan, C.R.; Torres, B.A.; Clark, W.T.; Rogers, R.R.; Harms, L.R.; Ballmann, C.G. The Effects of Acute Rauwolscine (α-Yohimbine) Ingestion on Repeated Wingate Sprint Performance in Healthy Males. Top. Exerc. Sci. Kinesiol. 2023, 4, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hai-Bo, L.; Yong, P.; Lu-qi, H.; Jun, X.; Pei-Gen, X. Mechanism of selective inhibition of yohimbine and its derivatives in adrenoceptor α2 subtypes. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 783058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannitti, J.A., Jr.; Thoms, S.M.; Crawford, J.J. Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonists: A review of current clinical applications. Anesth. Prog. 2015, 62, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koganei, H.; Takeuchi, A.; Kimura, T.; Satoh, S. Effects of yohimbine and desipramine on adrenal catecholamine release in response to splanchnic nerve stimulation in anesthetized dogs. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 18, 1207–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waluga; Janusz; Karpel; Hartleb; Nowak. Cardiovascular effects of ephedrine, caffeine and yohimbine measured by thoracic electrical bioimpedance in obese women. Clin. Physiol. 1998, 18, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, J.; Nakatsu, S.; Fenemore, J.; Condra, M.; Surridge, D.; Morales, A. The pharmacokinetics of yohimbine in man. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1987, 32, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, F.; Nascimento, N.; Cerqueira, J.; Morais, M.; Regadas, R.; Gonzaga-Silva, L. Yohimbine relaxes the human corpus cavernosum through a non-adrenergic mechanism involving the activation of K+ ATP-dependent channels. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2009, 21, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, S.; Jenkins, D. Factors affecting the rate of phosphocreatine resynthesis following intense exercise. Sports Med. 2002, 32, 761–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabir, N.R.; Firoz, C.K.; Zughaibi, T.A.; Alsaadi, M.A.; Abuzenadah, A.M.; Al-Asmari, A.I.; Alsaieedi, A.; Ahmed, B.A.; Ramu, A.K.; Tabrez, S. A literature perspective on the pharmacological applications of yohimbine. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 2849–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galitzky, J.; Taouis, M.; Berlan, M.; Riviere, D.; Garrigues, M.; Lafontan, M. α2-Antagonist compounds and lipid mobilization: Evidence for a lipid mobilizing effect of oral yohimbine in healthy male volunteers. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1988, 18, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, A.M.; Critchley, H.D.; Duka, T. The impact of Yohimbine-induced arousal on facets of behavioural impulsivity. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 1783–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Messing, R.B.; Sparber, S.B. Learning enhancement and behavioral arousal induced by yohimbine. Life Sci. 1987, 41, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, A.C.; Lijffijt, M.; Lane, S.D.; Cox, B.; Steinberg, J.L.; Moeller, F.G. Norepinephrine and impulsivity: Effects of acute yohimbine. Psychopharmacology 2013, 229, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Corre, P.; Dollo, G.; Chevanne, F.; Le Verge, R. Biopharmaceutics and metabolism of yohimbine in humans. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 9, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millan, M.J.; Newman-Tancredi, A.; Audinot, V.; Cussac, D.; Lejeune, F.; Nicolas, J.P.; Cogé, F.; Galizzi, J.P.; Boutin, J.A.; Rivet, J.M. Agonist and antagonist actions of yohimbine as compared to fluparoxan at α2-adrenergic receptors (AR) s, serotonin (5-HT) 1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D and dopamine D2 and D3 receptors. Significance for the modulation of frontocortical monoaminergic transmission and depressive states. Synapse 2000, 35, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hedner, T.; Edgar, B.; Edvinsson, L.; Hedner, J.; Persson, B.; Pettersson, A. Yohimbine pharmacokinetics and interaction with the sympathetic nervous system in normal volunteers. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1992, 43, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, J.R.; Kang, J.; Ratamess, N.A.; Hoffman, M.W.; Tranchina, C.P.; Faigenbaum, A.D. Examination of a pre-exercise, high energy supplement on exercise performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2009, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, J.R.; Kang, J.; Ratamess, N.A.; Rashti, S.L.; Faigenbaum, A.D. Thermogenic effect of a high energy, pre-exercise supplement. Kinesiology 2008, 40, 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- Lutsch, D.J.; Camic, C.L.; Jagim, A.R.; Stefan, R.R.; Cox, B.J.; Tauber, R.N.; Henert, S.E. Effects of a multi-ingredient preworkout supplement versus caffeine on energy expenditure and feelings of fatigue during low-intensity treadmill exercise in college-aged males. Sports 2020, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, D.N.; Kraemer, W.J.; Volek, J.S.; Spiering, B.A.; Judelson, D.A.; Hoffman, J.R.; Maresh, C.M. Anticipatory responses of catecholamines on muscle force production. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 102, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tank, J.; Heusser, K.; Diedrich, A.; Brychta, R.J.; Luft, F.C.; Jordan, J. Yohimbine attenuates baroreflex-mediated bradycardia in humans. Hypertension 2007, 50, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, W.; Zappe, D.; Tankersley, C.; Derr, J. Effect of systemic yohimbine on the control of skin blood flow during local heating and dynamic exercise. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 1994, 266, H371–H376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Fruhbeck, G.; Aguado, M.; Milagro, F.I.; Margareto, J.; Martinez, A.J. Divergent effects of an α2-adrenergic antagonist on lipolysis and thermogenesis: Interactions with a β3-adrenergic agonist in rats. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2001, 8, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafontan, M.; Berlan, M.; Galitzky, J.; Montastruc, J.-L. Alpha-2 adrenoceptors in lipolysis: α2 antagonists and lipid-mobilizing strategies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 55, 219S–227S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, J.; Lim, K. Nutrition supplements to stimulate lipolysis: A review in relation to endurance exercise capacity. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2016, 62, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uth, N.; Sørensen, H.; Overgaard, K.; Pedersen, P.K. Estimation of O2max from the ratio between HRmax and HRrest–the Heart Rate Ratio Method. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 91, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahon, A.D.; Stephens, B.R.; Cole, A.S. Exercise responses in boys with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Effects of stimulant medication. J. Atten. Disord. 2008, 12, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toner, M.M.; Kirkendall, D.; Delio, D.; Chase, J.; Cleary, P.; Fox, E. Metabolic and cardiovascular responses to exercise with caffeine. Ergonomics 1982, 25, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, D.G.; Jacobs, I.; Zamecnik, J. Effects of caffeine, ephedrine and their combination on time to exhaustion during high-intensity exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1998, 77, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drust, B.; Waterhouse, J.; Atkinson, G.; Edwards, B.; Reilly, T. Circadian rhythms in sports performance—An update. Chronobiol. Int. 2005, 22, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazer, H.J.; Jordan, C.L.; Pederson, J.A.; Rogers, R.R.; Williams, T.D.; Marshall, M.R.; Ballmann, C.G. Effects of time-of-day training preference on resistance-exercise performance. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2021, 92, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumar, A.M.; Huntington, A.F.; Rogers, R.R.; Kopec, T.J.; Williams, T.D.; Ballmann, C.G. Acute beetroot juice supplementation attenuates morning-associated decrements in supramaximal exercise performance in trained sprinters. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roatta, S.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Farina, D. Sympathetic-induced changes in discharge rate and spike-triggered average twitch torque of low-threshold motor units in humans. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 5561–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roatta, S.; Farina, D. Sympathetic actions on the skeletal muscle. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2010, 38, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitts, R.H. The cross-bridge cycle and skeletal muscle fatigue. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 104, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Green, T.A.; Theobald, D.E.; Birnbaum, S.G.; Graham, D.L.; Zeeb, F.D.; Nestler, E.J.; Winstanley, C.A. Yohimbine increases impulsivity through activation of cAMP response element binding in the orbitofrontal cortex. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, S.; Mers, A.; Banta, G.; Steigerwalt, S.; Lockette, W. Effect of the alpha 2-adrenergic antagonist yohimbine on orthostatic tolerance. Hypertension 1990, 15, 877–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, E.; Pittler, M. Yohimbine for erectile dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J. Urol. 1998, 159, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources Added to Food (ANS). Scientific Opinion on the evaluation of the safety in use of Yohimbe (Pausinystalia yohimbe (K. Schum.) Pierre ex Beille). EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3302. [Google Scholar]
- Kearney, T.; Tu, N.; Haller, C. Adverse drug events associated with yohimbine-containing products: A retrospective review of the California Poison Control System reported cases. Ann. Pharmacother. 2010, 44, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimolai, N. An overview of yohimbine in sports medicine. In Sustained Energy for Enhanced Human Functions and Activity; Academic Press: London, UK, 2017; pp. 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Han, X.; Zhu, J.; Du, L.; Liu, L.; Gong, W. Severe acute intoxication with yohimbine: Four simultaneous poisoning cases. Forensic Sci. Int. 2021, 320, 110705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampreti, A.; Lonati, D.; Locatelli, C.; Rocchi, L.; Campailla, M.T. Acute neurotoxicity after yohimbine ingestion by a body builder. Clin. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridwell, R.E.; Yoo, M.J.; Grove, J.J.; Ng, P.C. Chest pain from supplement use in an active duty soldier: A case report. Mil. Med. 2020, 185, e1857–e1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drevin, G.; Palayer, M.; Compagnon, P.; Zabet, D.; Jousset, N.; Briet, M.; Abbara, C. A fatal case report of acute yohimbine intoxication. Forensic Toxicol. 2020, 38, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, H.; Brandl, P.; Kockott, G.; Schmitz, J.; Wiegand, M.; Schadrack, J.; Gierend, M. Double-blind, placebo-controlled safety and efficacy trial with yohimbine hydrochloride in the treatment of nonorganic erectile dysfunction. Int. J. Impot. Res. 1997, 9, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Porrill, S.L.; Rogers, R.R.; Ballmann, C.G. Ergogenic and Sympathomimetic Effects of Yohimbine: A Review. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 1837-1848. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16060131
Porrill SL, Rogers RR, Ballmann CG. Ergogenic and Sympathomimetic Effects of Yohimbine: A Review. Neurology International. 2024; 16(6):1837-1848. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16060131
Chicago/Turabian StylePorrill, Sophia L., Rebecca R. Rogers, and Christopher G. Ballmann. 2024. "Ergogenic and Sympathomimetic Effects of Yohimbine: A Review" Neurology International 16, no. 6: 1837-1848. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16060131
APA StylePorrill, S. L., Rogers, R. R., & Ballmann, C. G. (2024). Ergogenic and Sympathomimetic Effects of Yohimbine: A Review. Neurology International, 16(6), 1837-1848. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16060131







