Combined Cognitive and Motor Training Improves Reading, Writing and Motor Coordination in Dyslexic Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
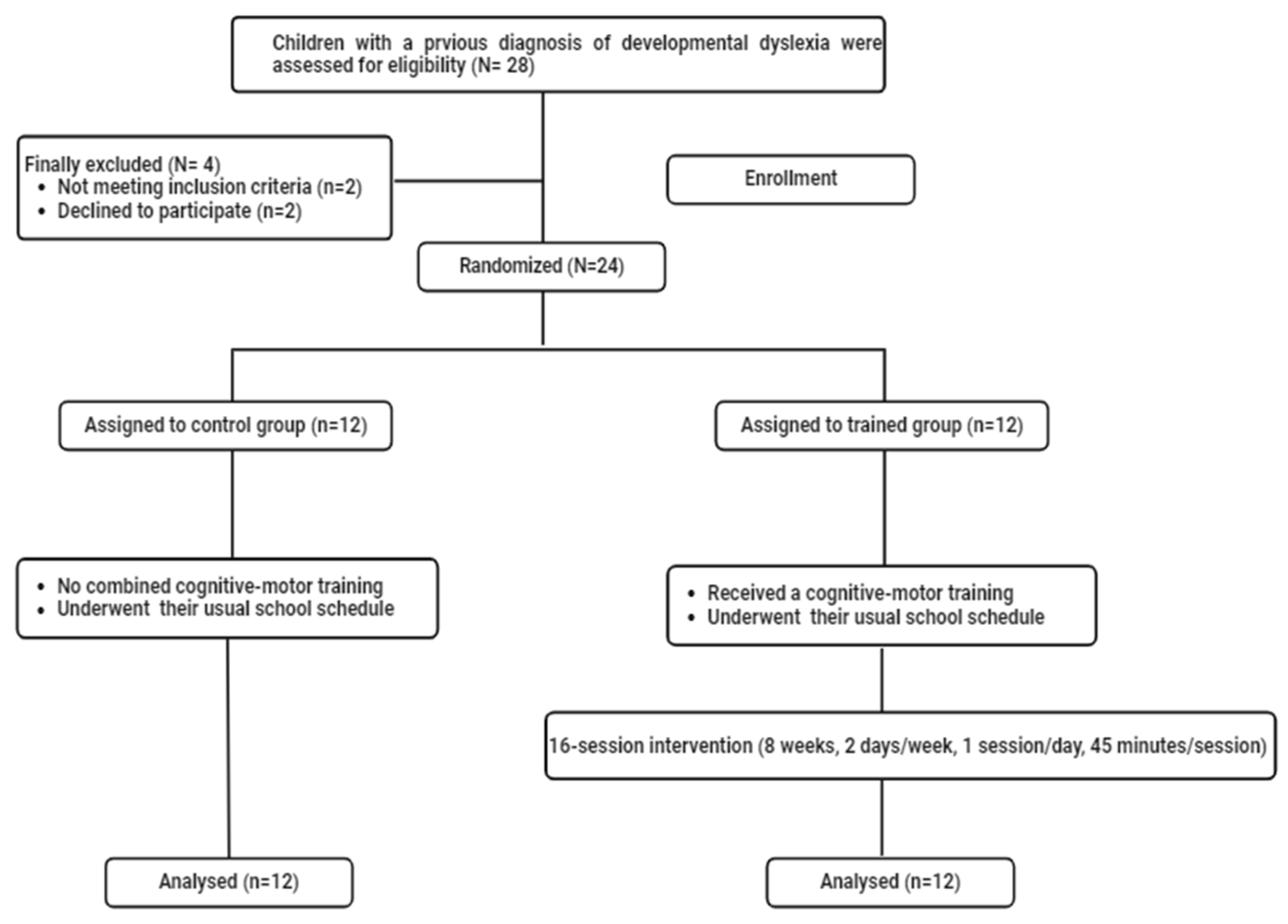
2.1. Sample Size and Participants
2.2. Cognitive Evaluation
2.2.1. Reading Evaluation
2.2.2. Writing Evaluation
2.2.3. Combined Cognitive and Motor Training Program
2.3. Motor Evaluation
2.3.1. Visuospatial Orientation Evaluation
2.3.2. Upper Limb Coordination Evaluation
2.4. Experimental Procedure
2.5. Data Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cognitive Abilities
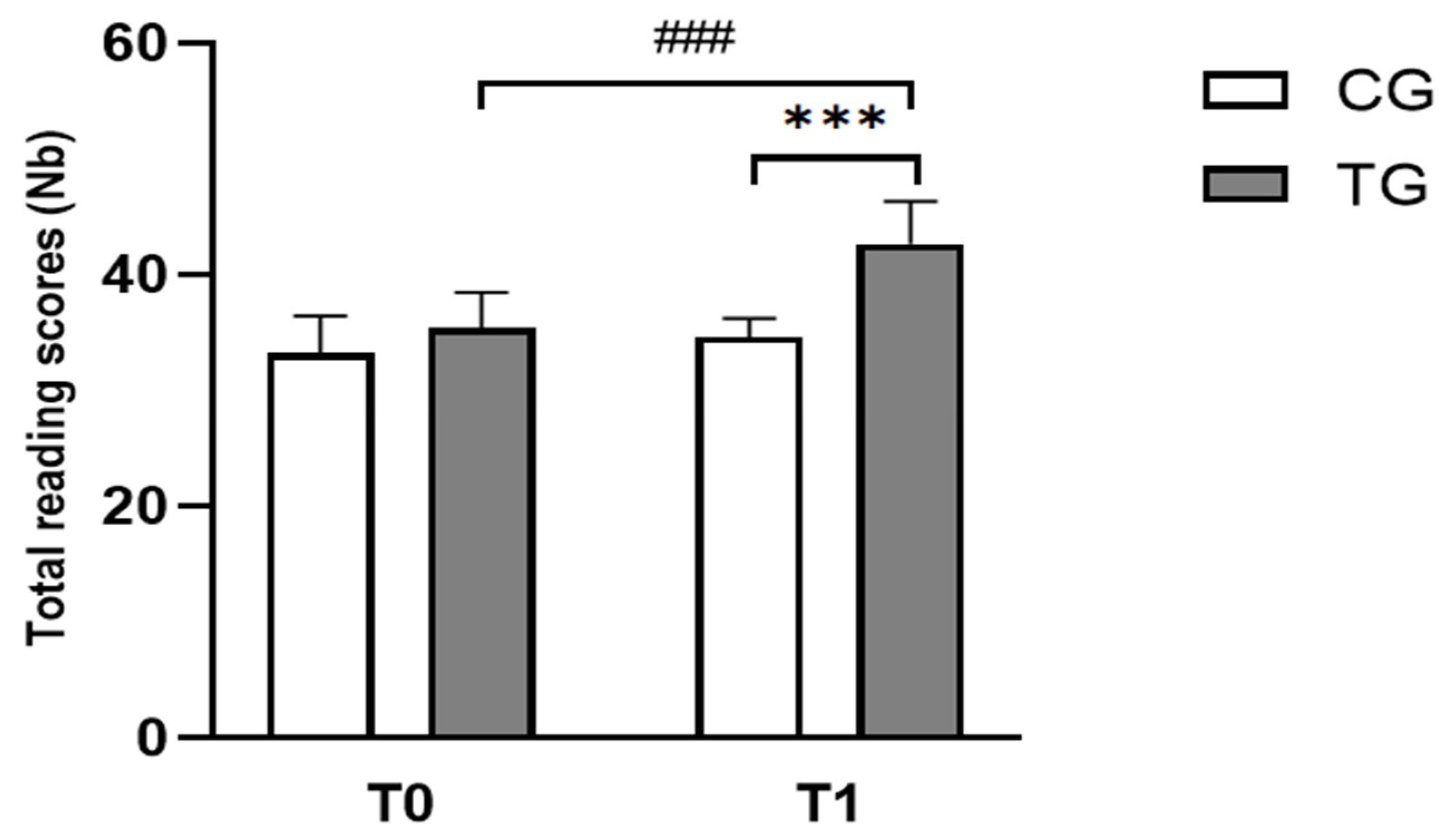
3.1.1. Reading Test
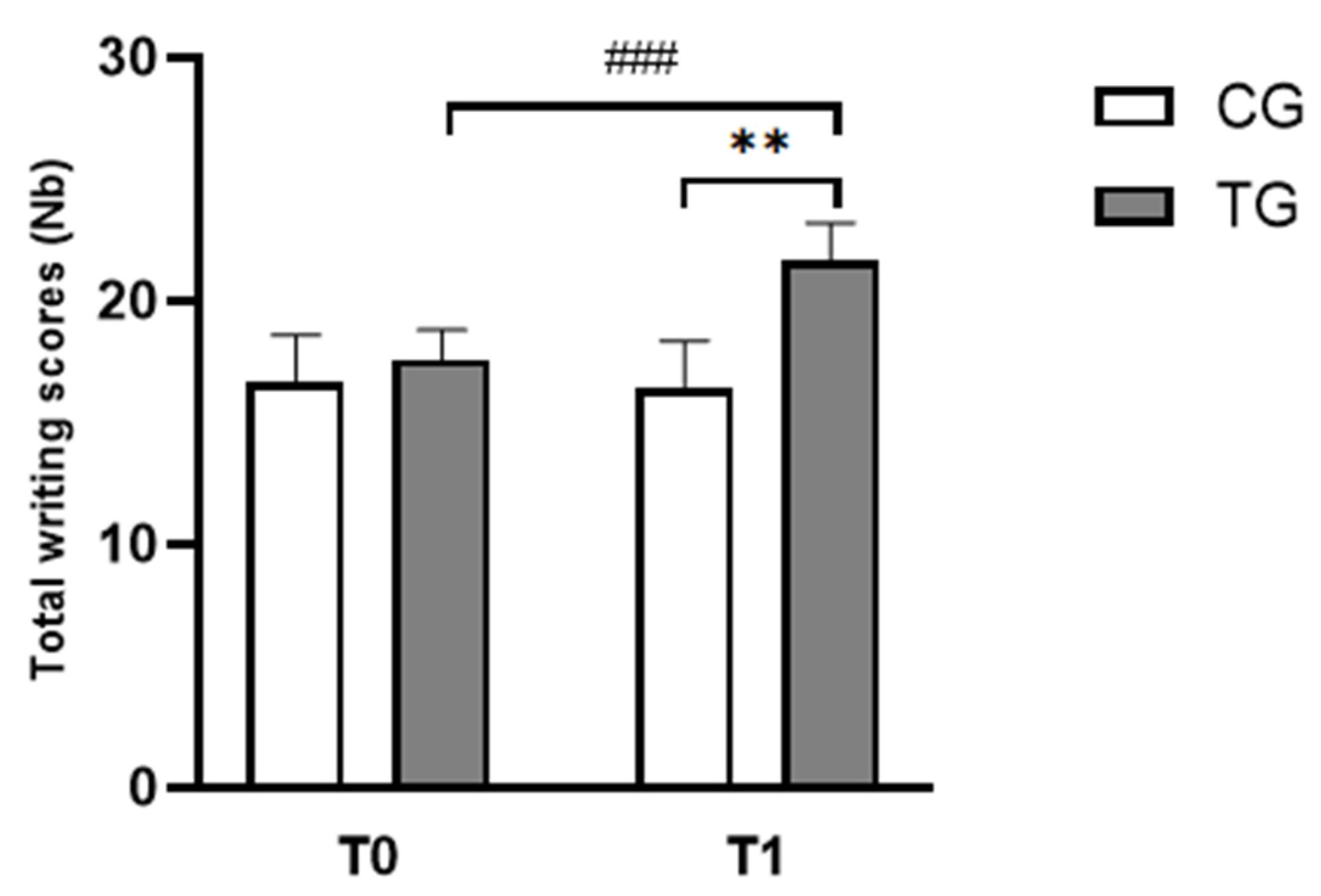
3.1.2. Writing Test
3.2. Motor Abilities
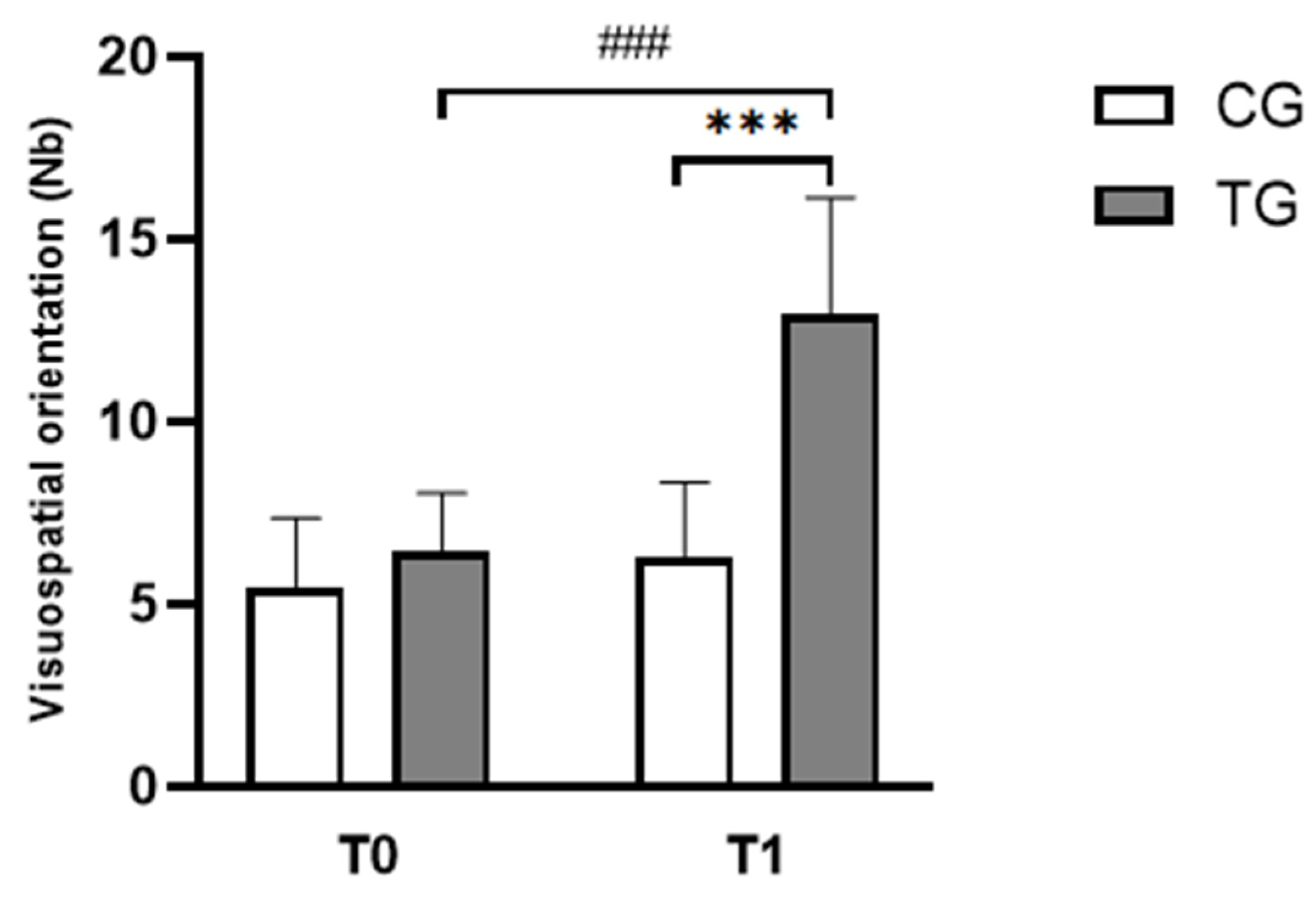
3.2.1. Visuospatial Orientation Test
3.2.2. Upper Limb Coordination Test
4. Discussion
4.1. Cognitive Performances
4.2. Motor Performances
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | America’s Children and the Environment |
| DD | Developmental Dyslexia |
| BALE | Batterie Analytique du Langage Ecrit |
| BOT-2 SF | Bruininks–Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency, Second Edition, Short Form |
| ELFE | Évaluation de la Lecture en FluencE |
| JLOT | Judgment of Line Orientation Test |
| ODÉDYS 2 | Outil de DÉpistage des DYSlexies Version 2 |
| VWM | Verbal Working Memory |
| VWM-B | Verbal Working Memory-Balance |
| WISC-IV | Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children, Fourth Edition |
References
- Gu, C.; Bi, H.-Y. Auditory Processing Deficit in Individuals with Dyslexia: A Meta-Analysis of Mismatch Negativity. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 116, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburn, S.M.; Flowers, D.L.; Napoliello, E.M.; Eden, G.F. Cerebellar Function in Children with and without Dyslexia during Single Word Processing. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 41, 120–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Key Findings of America’s Children and the Environment. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/americaschildrenenvironment/key-findings-americas-children-and-environment (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Bishop, D.V.M. The Interface between Genetics and Psychology: Lessons from Developmental Dyslexia. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20143139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, S.; Shankweiler, D.; Mann, V. Speech Perception and Memory Coding in Relation to Reading Ability. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 1983, 35, 345–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruck, M. Persistence of Dyslexics’ Phonological Deficits. Dev. Psychol.—Dev. Psychol. 1992, 28, 874–886. Available online: https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/0012-1649.28.5.874 (accessed on 21 February 2025). [CrossRef]
- Snowling, M.J. Phonological Processing and Developmental Dyslexia. J. Res. Read. 1995, 18, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, J. What Is Developmental Dyslexia? Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, M.; Tokoglu, F.; Sun, Z.; Schafer, R.J.; Skudlarski, P.; Gore, J.C.; Constable, R.T. Connectivity–Behavior Analysis Reveals That Functional Connectivity between Left BA39 and Broca’s Area Varies with Reading Ability. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Hoeft, F.; Zhang, L.; Shu, H. Neuroanatomical Anomalies of Dyslexia: Disambiguating the Effects of Disorder, Performance, and Maturation. Neuropsychologia 2016, 81, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosnan, M.; Demetre, J.; Hamill, S.; Robson, K.; Shepherd, H.; Cody, G. Executive Functioning in Adults and Children with Developmental Dyslexia. Neuropsychologia 2002, 40, 2144–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facoetti, A.; Lorusso, M.L.; Paganoni, P.; Cattaneo, C.; Galli, R.; Mascetti, G.G. The Time Course of Attentional Focusing in Dyslexic and Normally Reading Children. Brain Cogn. 2003, 53, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolson, R.I.; Fawcett, A.J. Automaticity: A New Framework for Dyslexia Research? Cognition 1990, 35, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, J.F.; Riddell, P.M.; Fowler, S. Disordered Vergence Control in Dyslexic Children. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1988, 72, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallal, P. Auditory Temporal Perception, Phonics, and Reading Disabilities in Children. Brain Lang. 1980, 9, 182–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Floch, A.; Ropars, G. Left-Right Asymmetry of the Maxwell Spot Centroids in Adults without and with Dyslexia. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 284, 20171380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blythe, H.; Kirkby, J.; Liversedge, S. Comments on: “What Is Developmental Dyslexia?” Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 26. The Relationship between Eye Movements and Reading Difficulties. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, R.I.; Fawcett, A.J.; Dean, P. Developmental Dyslexia: The Cerebellar Deficit Hypothesis. Trends Neurosci. 2001, 24, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, R.I.; Fawcett, A.J. Dyslexia, Dysgraphia, Procedural Learning and the Cerebellum. Cortex 2011, 47, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, M.; Kearns, D.M.; Hayes, J.B.; Bazis, P.; Cooper, S. Why Children With Dyslexia Struggle With Writing and How to Help Them. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Sch. 2018, 49, 843–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berninger, V.W.; Nielsen, K.H.; Abbott, R.D.; Wijsman, E.; Raskind, W. Writing Problems in Developmental Dyslexia: Under-Recognized and Under-Treated. J. Sch. Psychol. 2008, 46, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-García, C.; Afonso, O.; Cuetos, F.; Suárez-Coalla, P. Handwriting Production in Spanish Children with Dyslexia: Spelling or Motor Difficulties? Read. Writ. 2021, 34, 565–593. [Google Scholar]
- Iversen, S.; Berg, K.; Ellertsen, B.; Tønnessen, F.-E. Motor Coordination Difficulties in a Municipality Group and in a Clinical Sample of Poor Readers. Dyslexia 2005, 11, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, S.J. Identifying and Teaching Children and Young People with Dyslexia and Literacy Difficulties: An Independent Report from Sir Jim Rose to the Secretary of State for Children, Schools and Families; Department for Children, Schools and Families: London, UK, 2009.
- Barela, J.A.; Dias, J.L.; Godoi, D.; Viana, A.R.; De Freitas, P.B. Postural Control and Automaticity in Dyslexic Children: The Relationship between Visual Information and Body Sway. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 1814–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulème, N.; Gérard, C.-L.; Bucci, M.P. The Effect of Training on Postural Control in Dyslexic Children. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hare, A.; Khalid, S. The Association of Abnormal Cerebellar Function in Children with Developmental Coordination Disorder and Reading Difficulties. Dyslexia 2002, 8, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoodley, C.J.; Fawcett, A.J.; Nicolson, R.I.; Stein, J.F. Impaired Balancing Ability in Dyslexic Children. Exp. Brain Res. 2005, 167, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, S.; Quercia, P.; Michel, C.; Pozzo, T.; Bonnetblanc, F. Cognitive Demands Impair Postural Control in Developmental Dyslexia: A Negative Effect That Can Be Compensated. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 462, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, R.L.; Leij, A. van der. Testing the Automatization Deficit Hypothesis of Dyslexia Via a Dual-Task Paradigm. J. Learn. Disabil. 1994, 27, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, M. Neuroanatomical Markers for Dyslexia: A Review of Dyslexia Structural Imaging Studies. Neuroscientist 2004, 10, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibby, M.Y.; Fancher, J.B.; Markanen, R.; Hynd, G.W. A Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Analysis of the Cerebellar Deficit Hypothesis of Dyslexia. J. Child. Neurol. 2008, 23, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, C.; Kuldau, J.; Maron, L.; Ricciuti, N.; Mahoney, B.; Bengtson, M.; Debose, C. Identical Neural Risk Factors Predict Cognitive Deficit in Dyslexia and Schizophrenia. Neuropsychology 2008, 22, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rae, C.; Harasty, J.A.; Dzendrowskyj, T.E.; Talcott, J.B.; Simpson, J.M.; Blamire, A.M.; Dixon, R.M.; Lee, M.A.; Thompson, C.H.; Styles, P.; et al. Cerebellar Morphology in Developmental Dyslexia. Neuropsychologia 2002, 40, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boets, B.; de Beeck, H.O.; Vandermosten, M.; Scott, S.K.; Gillebert, C.R.; Mantini, D.; Bulthé, J.; Sunaert, S.; Wouters, J.; Ghesquière, P. Intact but Less Accessible Phonetic Representations in Adults with Dyslexia. Science 2013, 342, 1251–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, M.; Lardy, C.; Desiles, T.; Commeiras, C.; Chobert, J.; Besson, M. Music and Dyslexia: A New Musical Training Method to Improve Reading and Related Disorders. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, R. The Cerebellum and the Reading Process; Nova Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Palmis, S.; Velay, J.; Habib, M.; Anton, J.; Nazarian, B.; Sein, J.; Longcamp, M. The Handwriting Brain in Middle Chilhood. Dev. Sci. 2021, 24, e13046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivo, G.; Persson, J.; Hedenius, M. Exploring Brain Plasticity in Developmental Dyslexia through Implicit Sequence Learning. NPJ Sci. Learn. 2024, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldani, S.; Gerard, C.-L.; Peyre, H.; Bucci, M.P. Visual Attentional Training Improves Reading Capabilities in Children with Dyslexia: An Eye Tracker Study During a Reading Task. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldani, S.; Moiroud, L.; Miquel, C.; Peiffer, V.; Florian, A.; Bucci, M.P. Short Vestibular and Cognitive Training Improves Oral Reading Fluency in Children with Dyslexia. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonacina, S.; Cancer, A.; Lanzi, P.L.; Lorusso, M.L.; Antonietti, A. Improving Reading Skills in Students with Dyslexia: The Efficacy of a Sublexical Training with Rhythmic Background. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Fawcett, A.J. Cognitive-Motor Training Improves Reading-Related Executive Functions: A Randomized Clinical Trial Study in Dyslexia. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdar, C.C.; Cihan, M.; Yücel, D.; Serdar, M.A. Sample Size, Power and Effect Size Revisited: Simplified and Practical Approaches in Pre-Clinical, Clinical and Laboratory Studies. Biochem. Med. 2021, 31, 27–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocq, M.-A.; Guelfi, J.-D. Disgnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders—Fourth Edition—Text Revised (DSM-IV-TR); American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler, D.; Kodama, H. Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—Fourth Edition (WISC-IV); The Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier-Roux, M.; Lequette, C.; Pouget, G.; Valdois, S.; Zorman, M. BALE: Batterie Analytique Du Langage Écrit; Groupe Cogni-Sciences, Laboratoire de Psychologie et NeuroCognition: Grenoble, France, 2010; Available online: https://www1.ac-grenoble.fr/article/cognisciences-121593 (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Jacquier-Roux, M.; Valdois, S.; Zorman, M. ODÉDYS 2: Outil de Dépistage des DYSlexies, Version 2; Groupe Cogni-Sciences, Laboratoire de Psychologie et NeuroCognition: Grenoble, France, 2005; Available online: https://www1.ac-grenoble.fr/article/cognisciences-121593 (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Benton, A.L.; Varney, N.R.; Hamsher, K.D. Visuospatial Judgment. A Clinical Test. Arch. Neurol. 1978, 35, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calamia, M.; Markon, K.; Denburg, N.L.; Tranel, D. Developing a Short Form of Benton’s Judgment of Line Orientation Test: An Item Response Theory Approach. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2011, 25, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruininks, R.H.; Bruininks, B.D. Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency, 2nd ed.; AGS Publishing: Circle Pines, MN, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Radanović, D.; Đorđević, D.; Stanković, M.; Pekas, D.; Bogataj, Š.; Trajkovic, N. Test of Motor Proficiency Second Edition (BOT-2) Short Form: A Systematic Review of Studies Conducted in Healthy Children. Children 2021, 8, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark-Carter, D. Doing Quantitative Psychological Research: From Design to Report. 1997. Available online: https://psycnet.apa.org/record/1997-36613-000 (accessed on 16 December 2024).
- Hopkins, W.G. A Scale of Magnitudes for Effect Statistics. A New View Stat. 2002, 502, 321. [Google Scholar]
- Mersin, Y.; Çebi, M. An In-Depth Examination of Visuospatial Functions in a Group of Turkish Children with Dyslexia. J. Neurobehav. Sci. 2021, 8, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaedi, R.H. An Assessment of the Motor Performance Skills of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder in the Gulf Region. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cognisciences. Site de l’académie de Grenoble. Available online: https://www1.ac-grenoble.fr/article/cognisciences-121593 (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Moroso, A.; Ruet, A.; Lamargue-Hamel, D.; Munsch, F.; Deloire, M.; Coupé, P.; Ouallet, J.-C.; Planche, V.; Moscufo, N.; Meier, D.S.; et al. Posterior Lobules of the Cerebellum and Information Processing Speed at Various Stages of Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramezani, M.; Behzadipour, S.; Fawcett, A.J.; Joghataei, M.T. Verbal Working Memory-Balance Program Training Alters the Left Fusiform Gyrus Resting-State Functional Connectivity: A Randomized Clinical Trial Study on Children with Dyslexia. Dyslexia 2023, 29, 264–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovagnoli, G.; Vicari, S.; Tomassetti, S.; Menghini, D. The Role of Visual-Spatial Abilities in Dyslexia: Age Differences in Children’s Reading? Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, L.; Davies, S.J.; Sumner, E.; Green, C. Individual Differences in the Development of Early Writing Skills: Testing the Unique Contribution of Visuo-Spatial Working Memory. Read. Writ. 2014, 27, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olive, T.; Passerault, J.-M. The Visuospatial Dimension of Writing. Writ. Commun. 2012, 29, 326–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rival, C.; Olivier, I.; Ceyte, H.; Bard, C. Age-Related Differences in the Visual Processes Implied in Perception and Action: Distance and Location Parameters. J. Exp. Child. Psychol. 2004, 87, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipowska, M.; Czaplewska, E.; Wysocka, A. Visuospatial Deficits of Dyslexic Children. Med. Sci. Monit. 2011, 17, CR216–CR221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanowicz, M.; Adryjanek, A.; Rożyńska, M. Uczeń z Dysleksją w Domu: Poradnik Nie Tylko Dla Rodziców; Wydawnictwo Pedagogiczne Operon: Gdynia, Poland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanowicz, M.; Kalka, D.; Krzykowski, G. Ryzyko Dysleksji: Problem i Diagnozowanie; Wydawnictwo Harmonia: Gdańsk, Poland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Przekoracka-Krawczyk, A.; Brenk-Krakowska, A.; Nawrot, P.; Rusiak, P.; Naskrecki, R. Unstable Binocular Fixation Affects Reaction Times But Not Implicit Motor Learning in Dyslexia. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 6470–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, Z.A.; Abdel-Aty, S.A.-R.; Elmeniawy, G.H.; Mahgoub, E.A.-M. Defects of Motor Performance in Children with Different Types of Specific Learning Disability. Drug Invent. Today 2020, 14, 302. [Google Scholar]
- Stošljević, M.; Adamović, M. Hand-Eye Coordination Ability in Students with Dyslexia. Belgrade Sch. Spec. Educ. Rehabil. 2012, 18, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald, K.; Milne, N.; Orr, R.; Pope, R. Associations between Motor Proficiency and Academic Performance in Mathematics and Reading in Year 1 School Children: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, K.; Milne, N.; Orr, R.; Pope, R. Relationships between Motor Proficiency and Academic Performance in Mathematics and Reading in School-Aged Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Gu, X. The Role of Executive Function in Linking Fundamental Motor Skills and Reading Proficiency in Socioeconomically Disadvantaged Kindergarteners. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2018, 61, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aadland, K.N.; Ommundsen, Y.; Aadland, E.; Brønnick, K.S.; Lervåg, A.; Resaland, G.K.; Moe, V.F. Executive Functions Do Not Mediate Prospective Relations between Indices of Physical Activity and Academic Performance: The Active Smarter Kids (ASK) Study. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaakkola, T.; Hillman, C.; Kalaja, S.; Liukkonen, J. The Associations among Fundamental Movement Skills, Self-Reported Physical Activity and Academic Performance during Junior High School in Finland. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 1719–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilukshika, K.V.K.; Nanayakkarawasam, P.P.; Wickramasinghe, V.P. The Effects of Upper Limb Exercises on Hand Writing Speed. Indian. J. Physiother. Occup. Ther. 2012, 6, 1–285. [Google Scholar]
| Clinical Characteristics | Mean (±SD) | |
|---|---|---|
| CG (n = 12) | TG (n = 12) | |
| Girls/boys (Nb) | 6/6 | 6/6 |
| Chronological age (years) | 9.25 ± 0.45 | 9.42 ± 0.51 |
| Weight (kg) | 30.08 ± 1.65 | 30.33 ± 1.63 |
| Height (cm) | 130.67 ± 2.02 | 130.58 ± 1.73 |
| IQ (WISC-IV) | 103.92 ± 5.20 | 104.42 ± 4.19 |
| Activity Stage | Performed Exercises |
|---|---|
| Warm-Up (10 min) | Arm circles (forward/backward) |
| Cross-body arm swings | |
| Shoulder rolls | |
| Upper limb coordination (15 min) | 1. Ball Toss and Call-Out (5 min) |
| Toss a ball against a wall or with a partner, catching it with one or both hands. | |
| 2. Ball Passing (5 min) | |
| Pass a ball from one hand to the other while calling out confusion’s letters (e.g., “b/d” or “m/n” or “p/q”). | |
| 3. Handball Juggling (5 min) | |
| Hold a tennis ball in each hand and throw them in the air alternately, catching them with the same hand. Gradually increase the height and speed. | |
| Visuospatial orientation (15 min) | 1. Direction Changes (5 min) |
| Change direction through different orientations (e.g., “left” or “right” or “forward” or “backward”) according to verbal or visual instructions. | |
| 2. Draw and Follow (5 min) | |
| Draw a line representation of confusions’ letters (e.g., “b/d” or “m/n” or “p/q”). Follow the representation’s direction to reach the destination. | |
| Ball dribbling followed a path drawn that represented confusion among letters (e.g., “b/d” or “m/n” or “p/q”). | |
| 3. Mirror Exercises (5 min) | |
| A partner calls out or demonstrates movements (e.g., “step right and turn left”) while you mirror them. | |
| Cool-Down (5 min) | Stretch arms overhead and across the chest. |
| Deep breathing with arm raises. |
| Cognitive and Motor Parameters | Participants of this Study | Non-Dyslexic Population |
|---|---|---|
| Reading scores (Nb) | 33.96 ± 2.60 | 55.19 ± 4.42 [47] |
| Writing scores (Nb) | 16.54 ± 1.89 | 26.28 ± 3.65 [48] |
| Visuospatial orientation scores (Nb) | 5.92 ± 1.82 | 21.60 ± 2.89 [55] |
| Upper limb coordination scores (Nb) | 2.38 ± 1.10 | 10.20 ± 1.73 [56] |
| Cognitive Parameters | Groups | Means Values (±SD) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | ||
| Reading scores (Nb) | CG | 33.25 ± 3.22 | 35.42 ± 3.09 |
| TG | 34.67 ± 1.61 | 42.67 ± 3.70 ### | |
| Writing scores (Nb) | CG | 16.67 ± 1.92 | 17.58 ± 1.24 |
| TG | 16.42 ± 1.93 | 21.67 ± 1.44 ### | |
| Motor Parameters | Groups | Means Values (±SD) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | ||
| Visuospatial orientation scores (Nb) | CG | 5.42 ± 1.93 | 6.25 ± 2.09 |
| TG | 6.42 ± 1.62 | 12.92 ± 3.23 ### | |
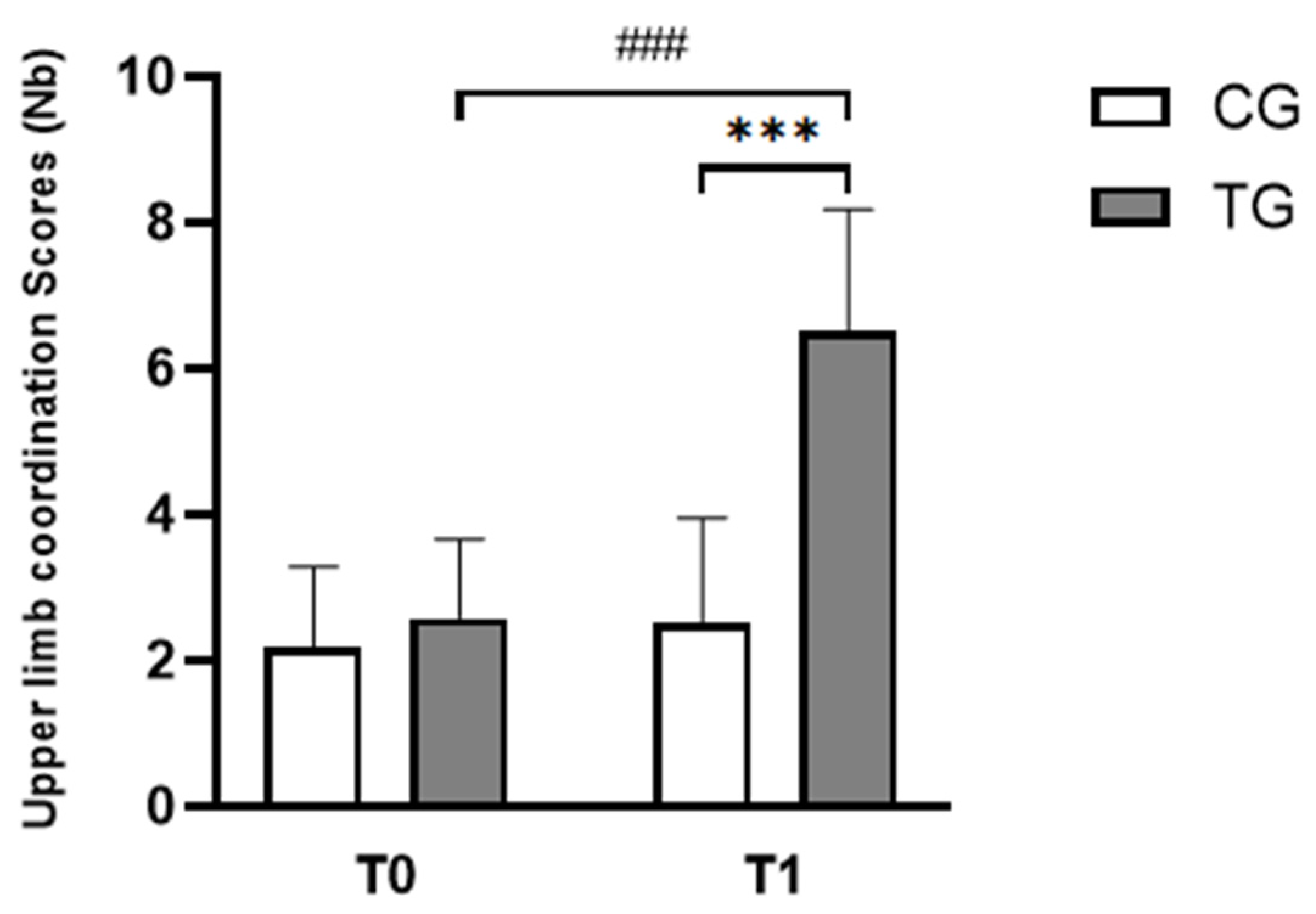
| Upper limb coordination scores (Nb) | CG | 2.17 ± 1.11 | 2.50 ± 1.45 |
| TG | 2.58 ± 1.08 | 6.50 ± 1.68 ### | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ben Dhia, A.; Bucci, M.-P.; Naffeti, C.; Ben Saad, H.; Hammouda, O.; Driss, T. Combined Cognitive and Motor Training Improves Reading, Writing and Motor Coordination in Dyslexic Children. Pediatr. Rep. 2025, 17, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17020046
Ben Dhia A, Bucci M-P, Naffeti C, Ben Saad H, Hammouda O, Driss T. Combined Cognitive and Motor Training Improves Reading, Writing and Motor Coordination in Dyslexic Children. Pediatric Reports. 2025; 17(2):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17020046
Chicago/Turabian StyleBen Dhia, Amal, Maria-Pia Bucci, Chokri Naffeti, Helmi Ben Saad, Omar Hammouda, and Tarak Driss. 2025. "Combined Cognitive and Motor Training Improves Reading, Writing and Motor Coordination in Dyslexic Children" Pediatric Reports 17, no. 2: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17020046
APA StyleBen Dhia, A., Bucci, M.-P., Naffeti, C., Ben Saad, H., Hammouda, O., & Driss, T. (2025). Combined Cognitive and Motor Training Improves Reading, Writing and Motor Coordination in Dyslexic Children. Pediatric Reports, 17(2), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17020046







