- Article
How Healthcare Professionals Perceive Emergency Pediatric Care Provision in Two Public Hospitals in Greece: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Eleni Vathi,
- Konstantinos Petsios and
- Eleni Evangelou
- + 6 authors
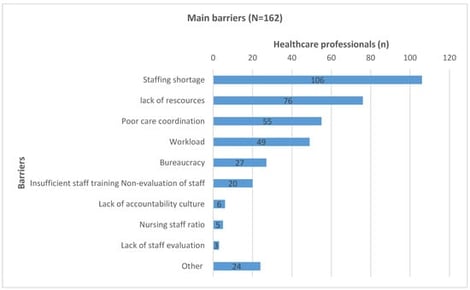
Background/Objectives: High-quality pediatric emergency care requires timely access, effective communication, privacy, pain management, comfort, and child- and family-centered practices; however, implementation may be constrained by several barriers. The aim of the study was to evaluate the quality of pediatric emergency care as perceived by healthcare professionals, with emphasis on child-centered care and variations based on workplace and professional characteristics. Methods: A cross-sectional survey was performed in the emergency departments in two tertiary public pediatric hospitals in Athens, Greece. A study-developed 14-item Quality of Care Assessment Scale with paired ratings of agreement with quality principles and implementation in practice was completed by 162 professionals (122 doctors, 24 nurses, 16 assistant nurses). Independent items evaluated perceived barriers, overall assessments (0–100), and information provided to parents/children (5-point Likert scale). Inferential tests and descriptive statistics were also used (p < 0.05). Results: There was a significant degree of agreement with quality principles, but there was a constant lack of implementation (principle–practice gap). The primary perceived weakness was waiting times; child-friendly settings and privacy during examinations and information-giving were also lacking. Internal consistency ranged from good to acceptable (implementation α = 0.800; agreement α = 0.711). Children were most frequently rated as “moderately informed” (48.1%), while parents were most frequently rated as “quite informed” (50.0%). Compared to the organization of care (mean 60.85), perceived safety was higher (mean 73.27). Perceptions varied by age, educational level, profession, department, shift rotations, and hospital. The main barriers were workload (30.2%), poor coordination (34.0%), and lack of resources (46.9%). Conclusions: Health professionals seem to perceive that consistent delivery of child-centered care is impaired by organizational and structural limitations. Reducing the standards-to-practice gap requires targeted system-level interventions that focus on staffing, care organization, environment, and professional support.
5 February 2026