Using Moss Walls for Air Quality Monitoring: Extending Their Utility Beyond Traditional Green Infrastructure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Moss Collection and Moss Wall Location
2.2. Technical Solution: Moss Walls with Self-Sustaining Systems for Moss Communities
2.3. Experiment Design
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.4.1. Toxic Elements
2.4.2. Lipids and Tocopherols
2.4.3. Nucleic Acid Extraction
2.4.4. RT-qPCR
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Moss Walls and Toxic Element Bioaccumulation
3.2. Lipids and Tocopherols
3.3. The rbcL Gene Expression in MWs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ERI | Ecological Risk Index |
| MW | Moss wall |
| RF | Risk Factorfactor |
References
- Julinova, P.; Beckovsky, D. Perspectives of moss species in urban ecosystems and vertical living-architecture: A review. In Advances in Engineering Materials, Structures and Systems: Innovations, Mechanics and Applications; Zingoni, A., Ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glime, J.M. Adaptive Strategies: Growth and Life Forms. In Bryophyte Ecology; Glime, J.M., Ed.; Michigan Technological University, International Association of Bryologists: Houghton, MI, USA, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Zechmeister, H.G.; Möslinger, L.; Korjenic, A.; Streit, E.; Sulejmanovski, A.; Frank, P.N.; Hummel, E. Viability of Living Moss for Indoor Green Walls: A Study on Temperature, Humidity, and Irrigation. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez Gutiérrez, R.; Blom, J.; Belmans, B.; De Bock, A.; Van den Bergh, L.; Audenaert, A. Preliminary Research on Moss-Based Biocomposites as an Alternative Substrate in Moss Walls. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Li, X. Air pollution and public health: An empirical study based on inter-provincial panel data. Popul. J. 2017, 39, 5–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mohsen, M.; Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L. Particulate matter concentrations and heavy metal contamination levels in the railway transport system of Sydney, Australia. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2018, 62, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ares, A.; Aboal, J.R.; Carballeira, A.; Giordano, S.; Adamo, P.; Fernández, J. Moss bag biomonitoring: A methodological review. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 432, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribacheva, N.; Gecheva, G.; Zhiyanski, M.; Pavlova-Traykova, E.; Yaneva, R. Active and passive moss monitoring of trace elements in urban and mountain areas, Bulgaria. For. Ideas 2021, 27, 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, W.; Nickel, S.; Schönrock, S.; Meyer, M.; Wosniok, W.; Harmens, H.; Frontasyeva, M.V.; Alber, R.; Aleksiayenak, J.; Barandovski, L.; et al. Spatially valid data of atmospheric deposition of heavy metals and nitrogen derived by moss surveys for pollution risk assessments of ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 10457–10476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Eiriksson, F.F.; Thorsteinsdóttir, M.; Simonsen, H.T. Valuable fatty acids in bryophytes—Production, biosynthesis, analysis and applications. Plants 2019, 8, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, T.; Ghnaya, T.; Abdelly, C. Nickel, cadmium and lead phytotoxicity and potential of halophytic plants in heavy metal extraction. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 11, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulbaki, A.S.; Alsamadany, H.; Alzahrani, Y.; Olayinka, B.U. Rubisco and abiotic stresses in plants: Current assessment. Turk. J. Bot. 2022, 46, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandalio, L.M.; Dalurzo, H.C.; Gómez, M.; Romero-Puertas, M.C.; Del Río, L.A. Cadmium-induced changes in the growth and oxidative metabolism of pea plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2001, 52, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galmés, J.; Aranjuelo, I.; Medrano, H.; Flexas, J. Variation in Rubisco content and activity under variable climatic factors. Photosynth. Res. 2013, 117, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huihui, Z.; Xin, L.; Zisong, X.; Yue, W.; Zhiyuan, T.; Meijun, A.; Yuehui, Z.; Wenxu, Z.; Nan, X.; Guangyu, S. Toxic effects of heavy metals Pb and Cd on mulberry (Morus alba L.) seedling leaves: Photosynthetic function and reactive oxygen species (ROS) metabolism responses. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 195, 110469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, H.; Hussain, S.J.; Al-Huqail, A.A.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Al-Huqail, A.A.; Khan, M.I.R. Hydrogen sulphide and salicylic acid regulate antioxidant pathway and nutrient balance in mustard plants under cadmium stress. Plant Biol. 2022, 24, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marraccini, P.; Freire, L.P.; Alves, G.S.C.; Vieira, N.G.; Vinecky, F.; Elbelt, S.; Ramos, H.J.; Montagnon, C.; Vieira, L.G.; Leroy, T.; et al. RBCS1 expression in coffee: Coffea orthologs, Coffea arabica homeologs, and expression variability between genotypes and under drought stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, F.; Dind, G.; Liu, W.; Zhan, D.; Wu, H.; Guo, W. Comparative study of responses in the brown algae Sargassum thunbergii to zinc and cadmium stress. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2018, 36, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gecheva, G.; Mollov, I.; Yahubyan, G.; Gozmanova, M.; Apostolova, E.; Vasileva, T.; Nikolova, M.; Dimitrova-Dyulgerova, I.; Radoukova, T. Can biomarkers respond upon freshwater pollution?—A moss-bag approach. Biology 2021, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozzi, F.; Giordano, S.; Aboal, J.R.; Adamo, P.; Bargagli, R.; Boquete, T.; Di Palma, A.; Real, C.; Reski, R.; Spagnuolo, V.; et al. Best options for the exposure of traditional and innovative moss bags: A systematic evaluation in three European countries. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chonova, P.; Gecheva, G.; Gribacheva, N. Air pollution biomonitoring in urban ecosystems with Aesculus hippocastanum. Ecol. Balk. 2019, 11, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Nagl, C.; Schneider, J.; Thielen, P. Implementation of the Ambient Air Quality Directive; European Parliament: Brussels, Belgium, 2016; 93p. [Google Scholar]
- Gribacheva, N.; Gecheva, G.; Stefanova, V. Air pollution monitoring with mosses in Western Rhodopes, Bulgaria. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 2019, 51, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmens, H.; Norris, D.A.; Steinnes, E.; Kubin, E.; Piispanen, J.; Alber, R.; Aleksiayenak, Y.; Blum, O.; Coşkun, M.; Dam, M.; et al. Mosses as biomonitors of atmospheric heavy metal deposition: Spatial patterns and temporal trends in Europe. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 3144–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinnes, E.; Rühling, Å.; Lippo, H.; Mäkinen, A. Reference materials for large-scale metal deposition surveys. Accredit. Qual. Assur. 1997, 2, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.A.; Carballeira, A. Evaluation of contamination, by different elements, in terrestrial mosses. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 40, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ter Braak, C.J.F.; Šmilauer, P. CANOCO Reference Manual and CanoDraw for Windows User’s Guide: Software for Canonical Community Ordination (Version 4.5). Section on Permutation Methods; Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2002; Available online: https://research.wur.nl/en/publications/canoco-reference-manual-and-canodraw-for-windows-users-guide-soft (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Harmens, H.; Norris, D.A.; Sharps, K.; Mills, G.; Alber, R.; Aleksiayenak, Y.; Blum, O.; Cucu-Man, S.M.; Dam, M.; De Temmerman, L.; et al. Heavy metal and nitrogen concentrations in mosses are declining across Europe whilst some “hotspots” remain in 2010. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 200, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurukova, L.; Gecheva, G.; Popgeorgiev, G. “Ecological hot spots” atmospheric assessment with mosses in Bulgaria. C. R. Acad. Bulg. Sci. 2014, 67, 683–686. [Google Scholar]
- Hristeva, Y.; Gecheva, G.; Yurukova, L. Bryophytes in Protected Territories of Plovdiv City (Bulgaria): Preliminary Species List and First Data of Air Pollution Monitoring. Ecol. Balk. 2011, 3, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Urošević, M.A.; Lazo, P.; Stafilov, T.; Nečemer, M.; Andonovska, K.B.; Balabanova, B.; Hristozova, G.; Papagiannis, S.; Stihi, C.; Suljkanović, M.; et al. Active biomonitoring of potentially toxic elements in urban air by two distinct moss species and two analytical techniques: A pan-Southeastern European study. Air Qual. Atmos. Hlth. 2023, 16, 595–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembitsky, V.M. Lipids of bryophytes. Prog. Lipid Res. 1993, 32, 281–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guschina, I.A.; Harwood, J.L. Lipid metabolism in the moss Rhytidiadelphus squarrosus (Hedw.) Warnst, from lead-contaminated and non-contaminated populations. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- De Agostini, A.; Cogoni, A.; Cortis, P.; Vacca, A.; Becerril, J.M.; Hernández, A.; Esteban, R. Heavy metal tolerance strategies in metallicolous and non-metallicolous populations of mosses: Insights of γ+β-tocopherol regulatory role. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2022, 194, 104738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, I.; Backlund, A. Structure and function of Rubisco. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 46, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottier, M.; Gilis, D.; Boutry, M. The Hidden Face of Rubisco. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, M.T.; Cummings, M.P.; Durbin, M.L. The evolution of plant nuclear genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 7791–7798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarte, S.; Tiedemann, R. A gene duplication/loss event in the ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate-carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) small subunit gene family among accessions of Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 1861–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, A.; Feiz, L. Rubisco assembly in the chloroplast. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreitzer, R.J.; Salvucci, M.E. Rubisco: Structure, regulatory interactions, and possibilities for a better enzyme. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2002, 53, 449–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
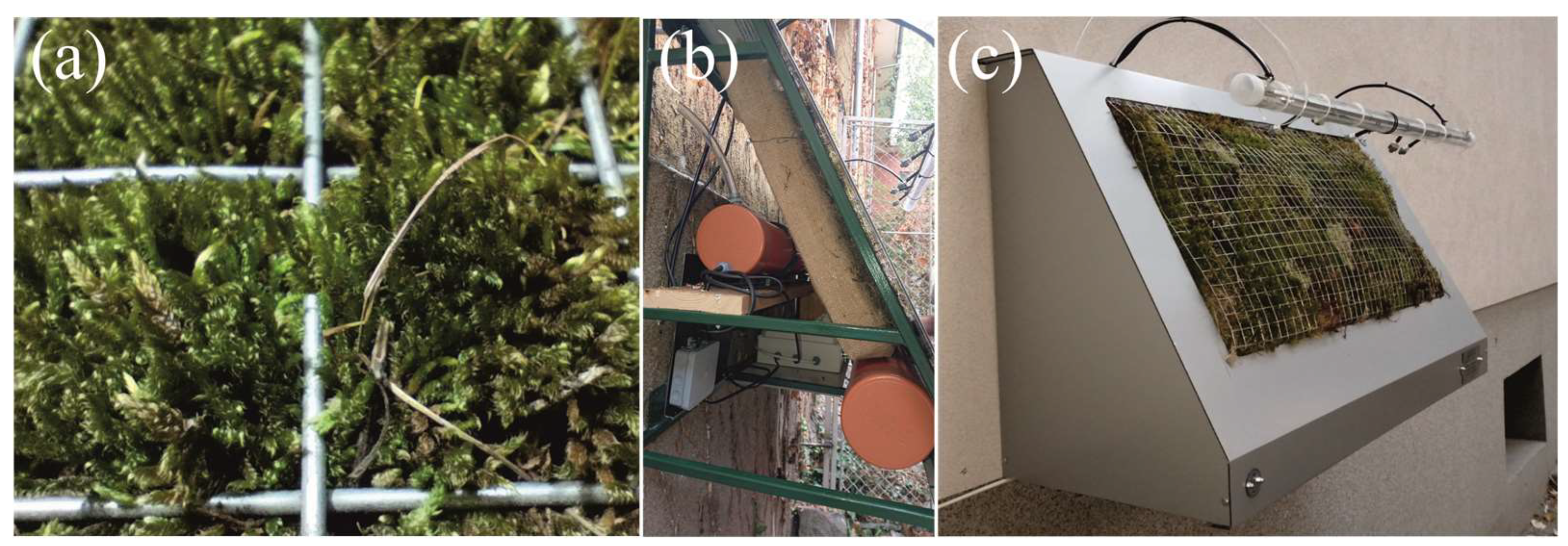
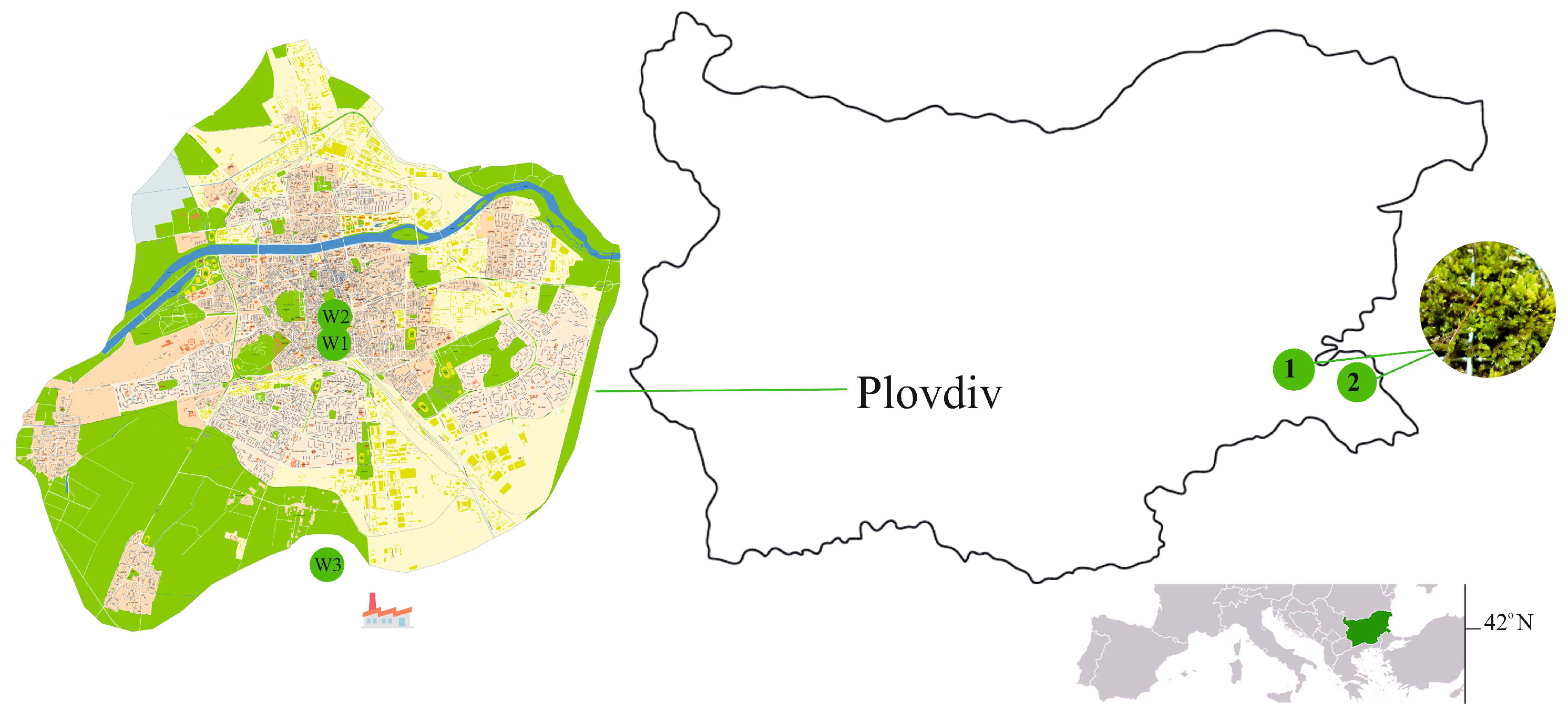



| Location | Name | Coordinates | Characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Strandja Mountain | Protected area Mouth of Izvorska River | 42.400833, 27.431306 | A low-stemmed oak plantation. |
| 2 | Strandja Mountain | Ropotamo Reserve | 42.315225, 27.754692 | Maslen nos region. A coppiced oak plantation. |
| 3 | Plovdiv | Moss wall 1 (MW1) | 42.13747, 24.75123 | A transport-oriented site in the center of the city. Close to a central hub for major traffic flows. |
| 4 | Plovdiv | Moss wall 2 (MW2) | 42.14758, 24.75089 | A low-impacted urban location within Plovdiv’s old city. |
| 5 | Kuklen village | Moss wall 3 (MW3) | 42.03388, 24.77881 | Approximately 15 km south of Plovdiv. Close to the KCM 2000 industrial complex, Bulgaria’s largest non-ferrous metal production company, situated within the Kuklen Industrial Zone. |
| Background (Before Exposure) | RSD% | Maximum (Second Exposure Period) | RSD% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al, % | 0.35 | 4.7 | 0.60 | 7.4 |
| As, mg kg−1 | 1.21 | 6.2 | 1.62 | 9.9 |
| Cd, mg kg−1 | 0.08 | 15 | 0.24 | 9.6 |
| Co, mg kg−1 | 1.95 | 6.2 | 3.61 | 6.0 |
| Cr, mg kg−1 | 8.58 | 5.1 | 10.1 | 5.0 |
| Cu, mg kg−1 | 24.0 | 5.3 | 30.0 | 4.5 |
| Fe, % | 0.44 | 2.7 | 0.92 | 7.3 |
| Mn, mg kg−1 | 126 | 4.9 | 193 | 7.5 |
| Ni, mg kg−1 | 3.86 | 4.6 | 5.37 | 7.5 |
| Pb, mg kg−1 | 7.0 | 4.8 | 13.4 | 6.1 |
| Zn, mg kg−1 | 26.7 | 6.7 | 456 | 6.0 |
| RF | ERI | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | As | Cd | Pb | ||
| MW1-1 | 7 | 1 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 8 | 24 | 4 | 63 |
| MW1-2 | 15 | 2 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 13 | 35 | 5 | 93 |
| MW2-1 | 3 | 1 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 8 | 23 | 4 | 57 |
| MW2-2 | 8 | 2 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 9 | 37 | 5 | 75 |
| MW3-1 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 9 | 49 | 6 | 85 |
| MW3-2 | 17 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 11 | 92 | 10 | 147 |
| Sample | Total Lipids % | Tocopherols mg kg−1 |
|---|---|---|
| Background | 1.34 ± 0.02 a | 1921 ± 18 e |
| MW1-1 | 0.70 ± 0.01 c | 7277 ± 332 a |
| MW1-2 | 0.74 ± 0.02 c | 7066 ± 140 a,b |
| MW2-1 | 0.62 ± 0.03 d | 5111 ± 208 c |
| MW2-2 | 0.53 ± 0.02 e | 6722 ± 439 b |
| MW3-1 | 0.71 ± 0.04 c | 5543 ± 371 c |
| MW3-2 | 0.84 ± 0.01 b | 4545 ± 127 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gecheva, G.; Petkova, Z.; Damyanov, S.; Georgieva, D.; Baev, V.; Gozmanova, M.; Apostolova-Kuzova, E.; Yahubyan, G. Using Moss Walls for Air Quality Monitoring: Extending Their Utility Beyond Traditional Green Infrastructure. Int. J. Plant Biol. 2025, 16, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb16020044
Gecheva G, Petkova Z, Damyanov S, Georgieva D, Baev V, Gozmanova M, Apostolova-Kuzova E, Yahubyan G. Using Moss Walls for Air Quality Monitoring: Extending Their Utility Beyond Traditional Green Infrastructure. International Journal of Plant Biology. 2025; 16(2):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb16020044
Chicago/Turabian StyleGecheva, Gana, Zhana Petkova, Stoyan Damyanov, Deyana Georgieva, Vesselin Baev, Mariyana Gozmanova, Elena Apostolova-Kuzova, and Galina Yahubyan. 2025. "Using Moss Walls for Air Quality Monitoring: Extending Their Utility Beyond Traditional Green Infrastructure" International Journal of Plant Biology 16, no. 2: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb16020044
APA StyleGecheva, G., Petkova, Z., Damyanov, S., Georgieva, D., Baev, V., Gozmanova, M., Apostolova-Kuzova, E., & Yahubyan, G. (2025). Using Moss Walls for Air Quality Monitoring: Extending Their Utility Beyond Traditional Green Infrastructure. International Journal of Plant Biology, 16(2), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb16020044









