Persistent Organic Pollutants in Tagus Estuary Salt Marshes: Patterns of Contamination and Plant Uptake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Collection Sites
2.2. Sample Pre-Processing
2.3. Granulometry Analysis
2.4. Total Organic Carbon
2.5. OCPs and PCBs Extraction and Quantification
2.6. Statistical Analysis
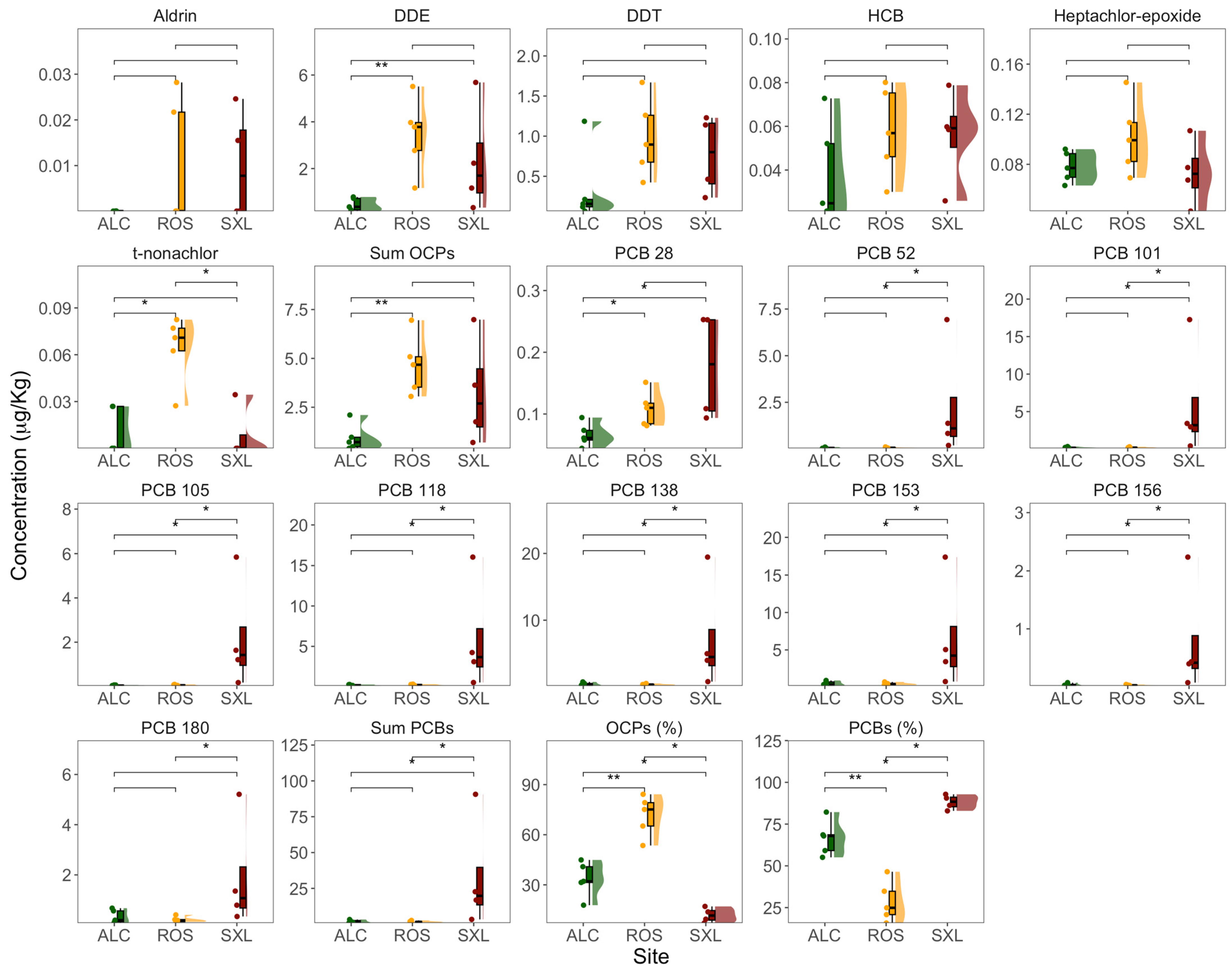
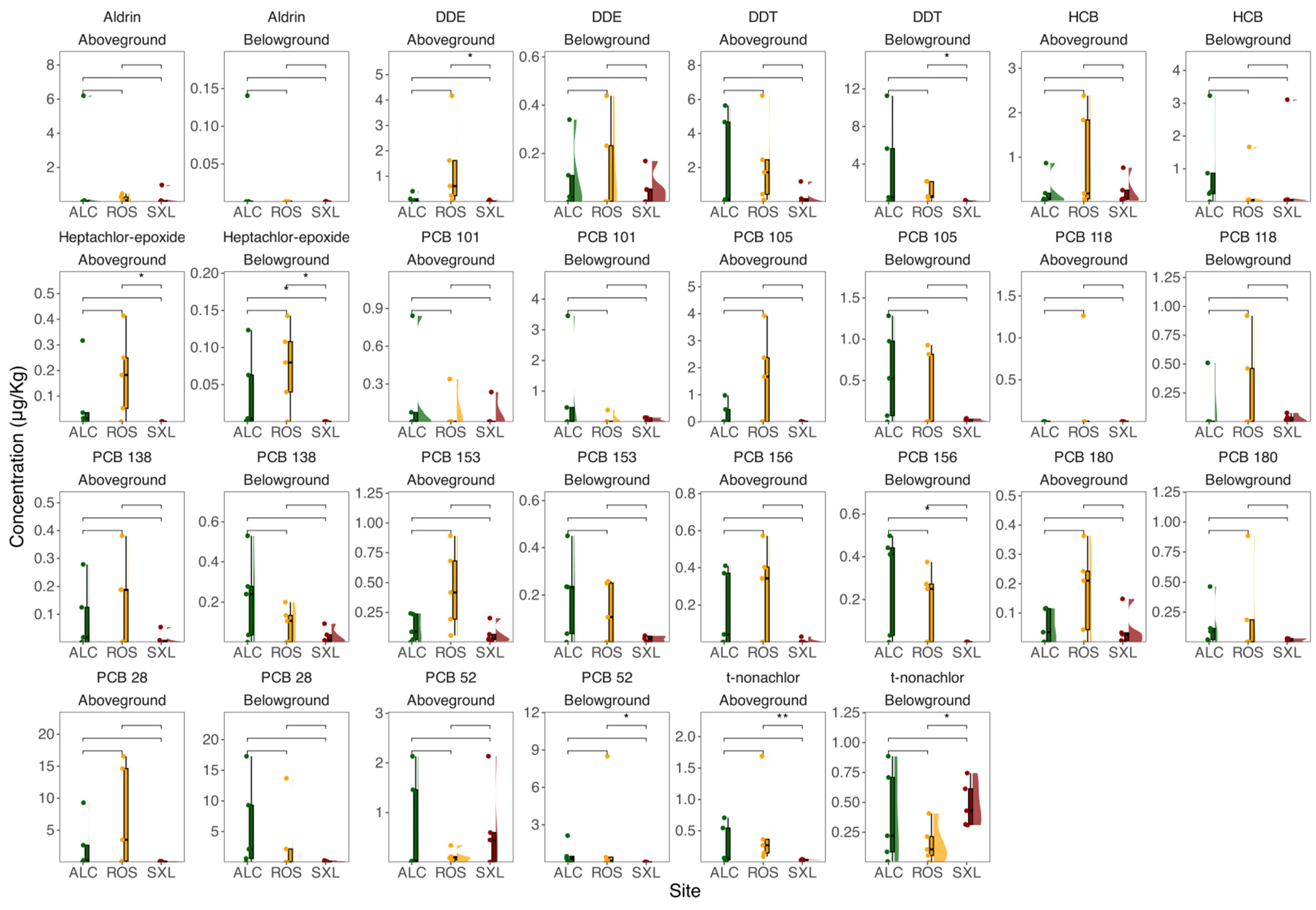
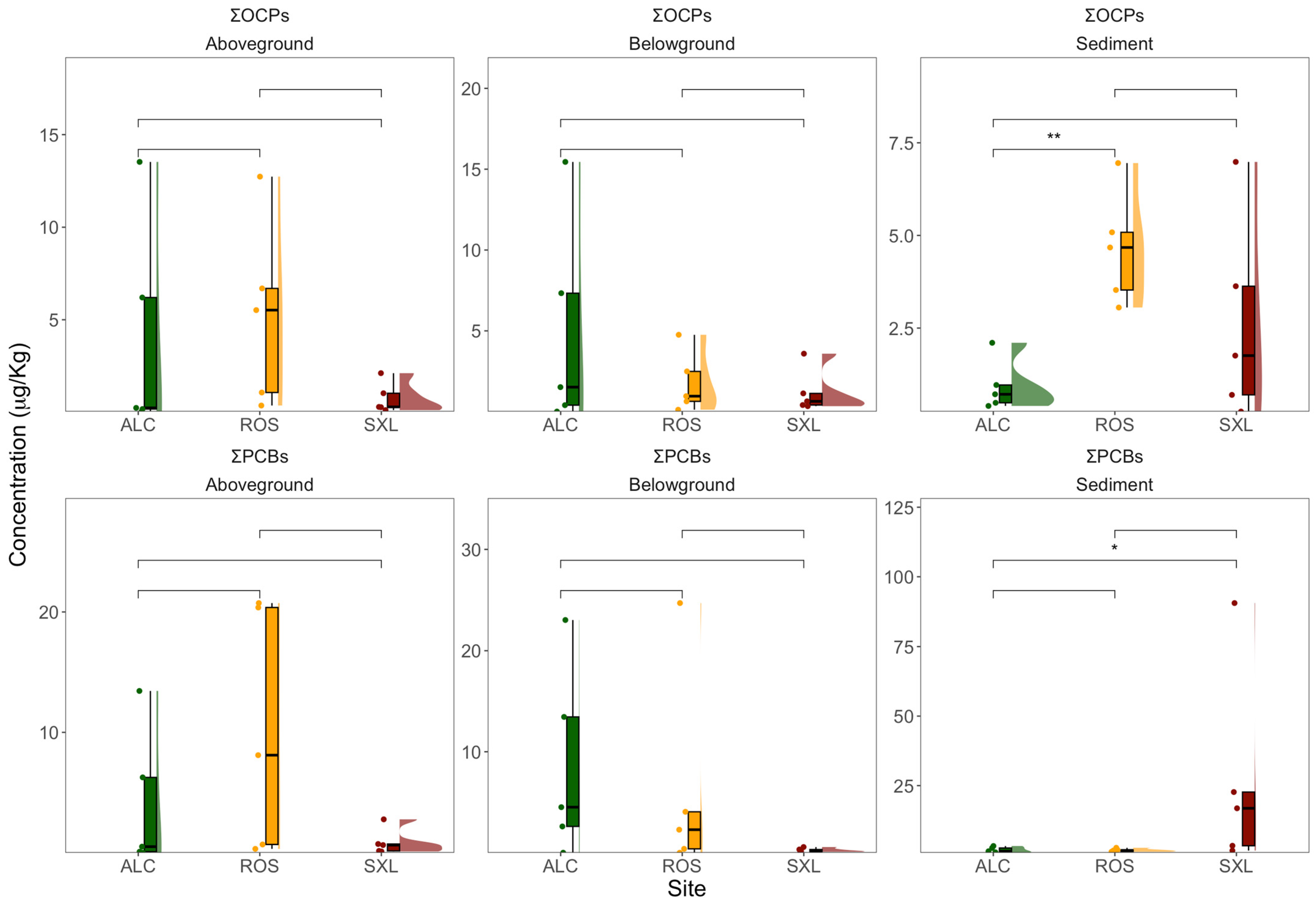
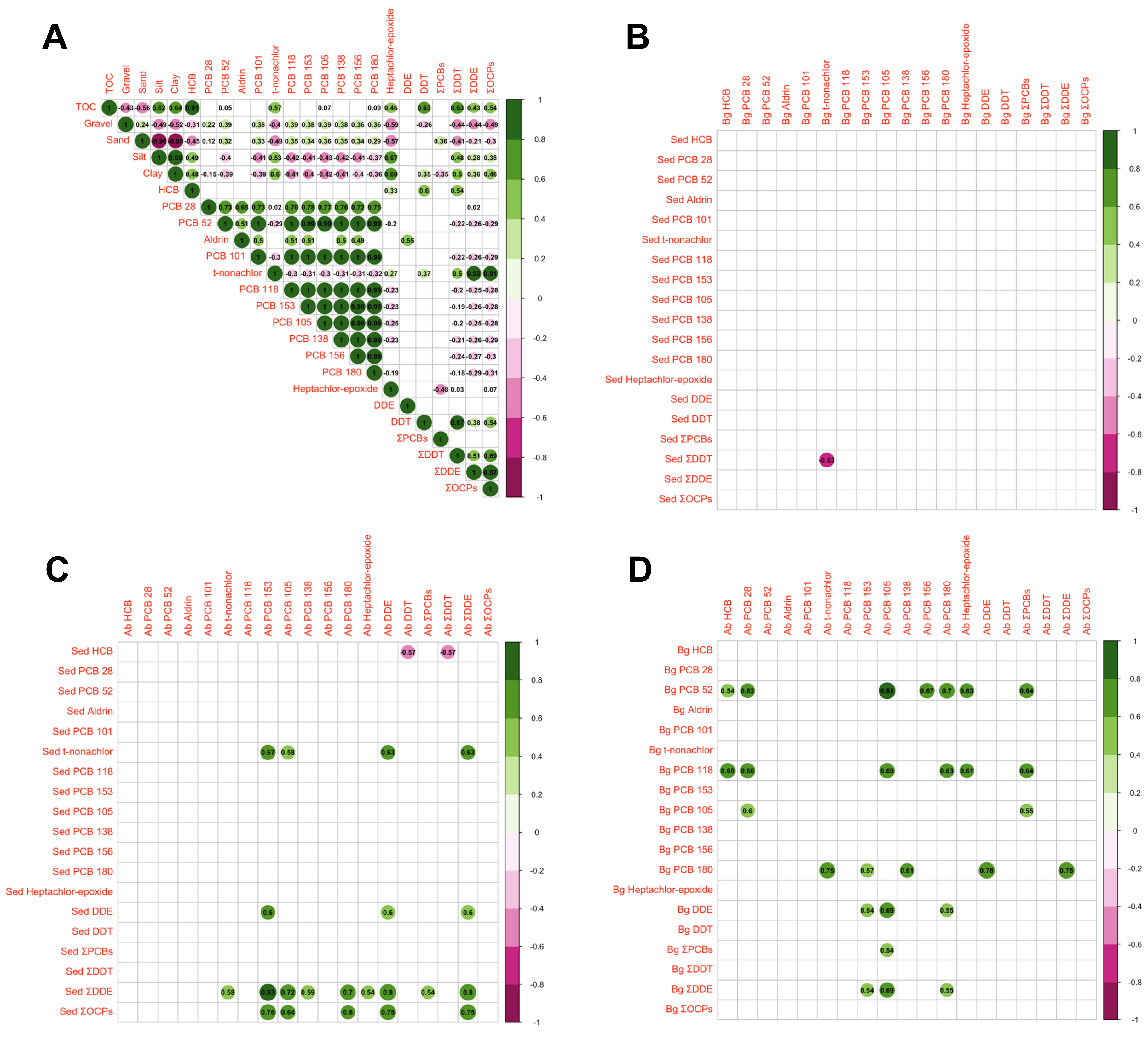
3. Results
3.1. Sediment Composition
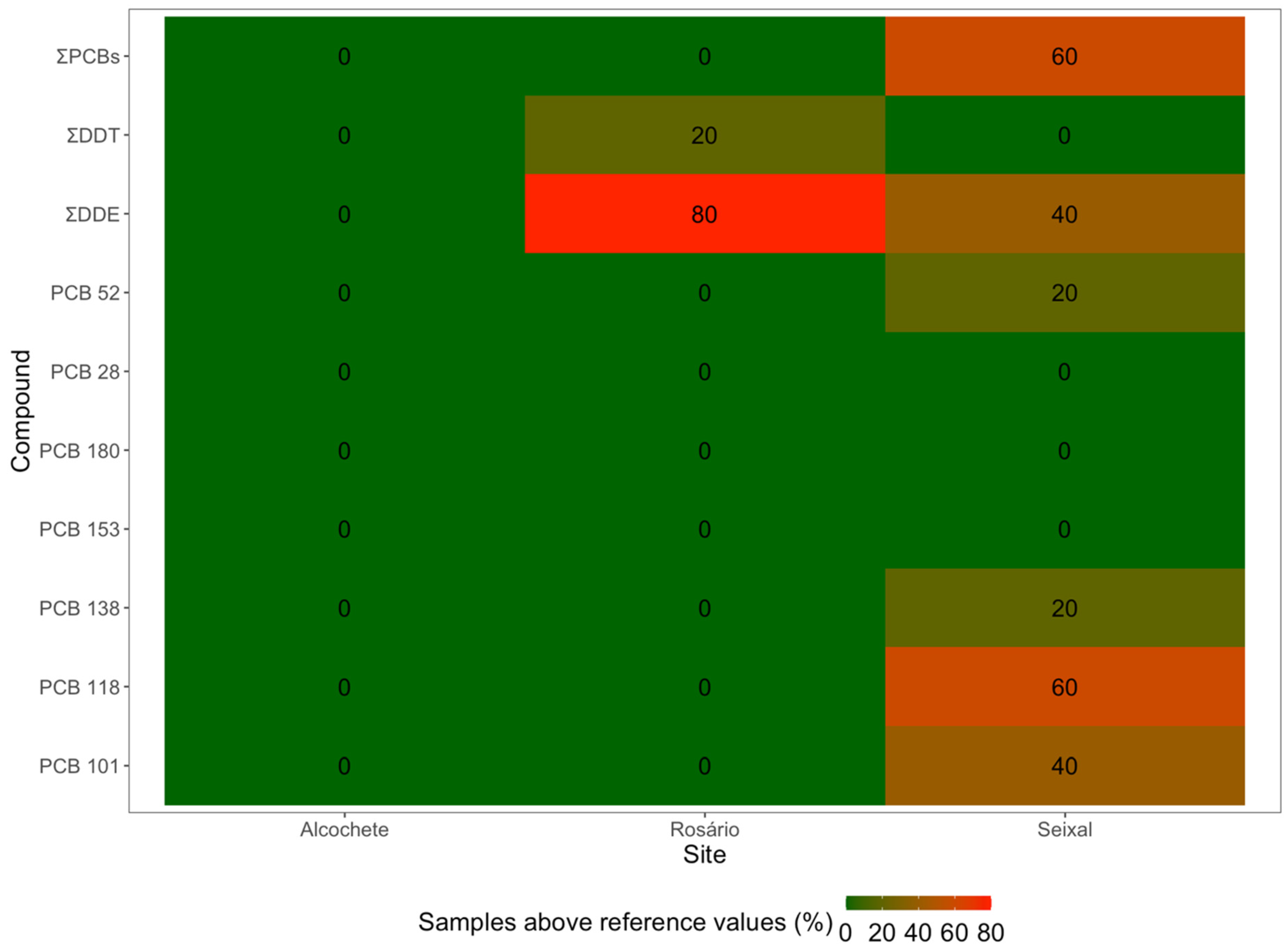
3.2. OCPs and PCBs in Sediments and Plants
3.3. Correlation and Multivariate Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Talley, L.D.; Pickard, G.L.; Emery, W.J.; Swift, J.H. Descriptive Physical Oceanography: An Introduction; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sekerci, Y.; Petrovskii, S. Mathematical Modelling of Plankton–Oxygen Dynamics under the Climate Change. Bull. Math. Biol. 2015, 77, 2325–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arceo-Carranza, D.; Chiappa-Carrara, X.; Chávez López, R.; Yáñez Arenas, C. Mangroves as Feeding and Breeding Grounds. In Mangroves: Ecology, Biodiversity and Management; Rastogi, R.P., Phulwaria, M., Gupta, D.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 63–95. ISBN 9789811624940. [Google Scholar]
- Doherty, E.; Murphy, G.; Hynes, S.; Buckley, C. Valuing ecosystem services across water bodies: Results from a discrete choice experiment. Ecosyst. Serv. 2014, 7, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.W.; Yáñez-Arancibia, A.; Kemp, W.M.; Crump, B.C. Introduction to Estuarine Ecology. In Estuarine Ecology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–18. ISBN 978-1-118-41278-7. [Google Scholar]
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B. Editorial-The Economics of Aquatic Ecosystems: An Introduction to the Special Issue. Water Econ. Policy 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elphick, C.S.; Shriver, W.G.; Greenberg, R. Estuarine Wildlife. In Estuarine Ecology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 292–312. ISBN 978-1-119-53465-5. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, B.; Carreiras, J.; Caçador, I. Climate Change Impacts on Salt Marsh Blue Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorous Stocks and Ecosystem Services. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, J.M.; Caçador, I.; Caetano, M.; Chaínho, P.; Costa, L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; Pereira, L.; Pinto, L.; Ramos, J.; Seixas, S. Estuários. In Rios de Portugal: Comunidades, Processos e Alterações; Coimbra University Press: Coimbra, Portugal, 2019; pp. 382–421. [Google Scholar]
- Salazar-Mendías, C.; Lendínez, M.L. Mediterranean Halophytic Flora and Vegetation in the Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal). In Handbook of Halophytes: From Molecules to Ecosystems towards Biosaline Agriculture; Grigore, M.-N., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2021; pp. 325–368. ISBN 978-3-030-57635-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kennish, M.J. Anthropogenic Drivers of Estuarine Change. In Climate Change and Estuaries; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; ISBN 978-1-00-312609-6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, B.; Jin, M.; Wang, R.; Ding, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Chen, Q.; Tao, R.; Fu, J.; et al. Anthropogenic-induced ecological risks on marine ecosystems indicated by characterizing emerging pollutants in Pearl River Estuary, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 172030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, P.G.; Dolbeth, M.; Sousa, R.; Relvas, P.; Santos, R.; Silva, A.; Quintino, V. Chapter 7—The Portuguese Coast. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation, 2nd ed.; Sheppard, C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 189–208. ISBN 978-0-12-805068-2. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, P. Saltmarshes in a time of change. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 39–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caçador, I.; Duarte, B. Mechanisms of Salt Stress Tolerance in Halophytes: Biophysical and Biochemical Adaptations. In Managing Salt Tolerance in Plants; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Pooja; Devi, A.; Garg, C.; Kumari, A.; Mann, A.; Kumar, A. Behavior of Halophytes and Their Tolerance Mechanism under Different Abiotic Stresses. In Ecophysiology, Abiotic Stress Responses and Utilization of Halophytes; Hasanuzzaman, M., Nahar, K., Öztürk, M., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 25–38. ISBN 9789811337628. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, B.; Caçador, I.; Marques, J.C.; Croudace, I.W. Tagus estuary salt marshes feedback to sea level rise over a 40-year period: Insights from the application of geochemical indices. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, B.; Santos, D.; Marques, J.C.; Caçador, I. Biophysical probing of Spartina maritima photo-system {II} changes during prolonged tidal submersion periods. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 77, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.A.; Jarvis, J.C. Estuarine Seagrass and Climate Change. In Climate Change and Estuaries; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; ISBN 978-1-00-312609-6. [Google Scholar]
- Nikalje, G.C.; Yadav, K.; Penna, S. Halophyte Responses and Tolerance to Abiotic Stresses. In Ecophysiology, Abiotic Stress Responses and Utilization of Halophytes; Hasanuzzaman, M., Nahar, K., Öztürk, M., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 1–23. ISBN 9789811337628. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, B.; Caetano, M.; Almeida, P.R.; Vale, C.; Caçador, I. Accumulation and biological cycling of heavy metal in four salt marsh species, from Tagus estuary (Portugal). Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1661–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wu, J.; Yan, L.; Yu, L.; Liu, J.; Yan, C. A comparative study of sediment-bound trace elements and iron-bearing minerals in S. alterniflora and mudflat regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reboreda, R.; Caçador, I. Copper, zinc and lead speciation in salt marsh sediments colonised by Halimione portulacoides and Spartina maritima. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.K.; Singh, R.; Rajput, V.D.; Singh, V.K. Halophytes for the sustainable remediation of heavy metal-contaminated sites: Recent developments and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallou, A.; Erraji, H.; Al Masmoudi, Y.; Abbatantuono, F.; Ali, S.A.; Mabrouki, J.; Moustaqim, K.E.L.; Salcedo, F.P.; Vivaldi, G.A. Phytoremediation of Contaminated Environments Using Halophytes: General Overview. In Integrated Solutions for Smart and Sustainable Environmental Conservation; Mabrouki, J., Azrour, M., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Germany, 2024; pp. 143–163. ISBN 978-3-031-55787-3. [Google Scholar]
- Roe, R.A.L.; MacFarlane, G.R. The potential of saltmarsh halophytes for phytoremediation of metals and persistent organic pollutants: An Australian perspective. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 180, 113811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caçador, I.; Neto, J.M.; Duarte, B.; Barroso, D.V.; Pinto, M.; Marques, J.C. Development of an Angiosperm Quality Assessment Index (AQuA-Index) for ecological quality evaluation of Portuguese water bodies—A multi-metric approach. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 25, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Gómez, S. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in Spartina. Funct. Plant Biol. 2013, 40, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Aníbal, J.; Duarte, D.; Chícharo, L. Sarcocornia fruticosa and Spartina maritima as heavy metals remediators in an European southwestern salt marsh (Ria Formosa, Portugal). J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2015, 16, 1468–1477. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, P.; Gorito, A.M.; Fernandes, J.P.; Mucha, A.P.; Almeida, C.M.R. Saltmarsh plants role in metals retention and the potential of vegetation for metal removal in the long term. Nat.-Based Solut. 2024, 5, 100110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrin, V.L.; La Colla, N.S.; Schwab, F.; Domini, C.; Botté, S.E. Evaluating metal phytorremediation and biondication potential of Spartina alterniflora in a South American estuary. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 193, 106292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girones, L.; Oliva, A.L.; Negrin, V.L.; Marcovecchio, J.E.; Arias, A.H. Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in coastal wetlands: A review of their occurrences, toxic effects, and biogeochemical cycling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, H. South Africa and the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants: Science policy. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2004, 100, 323–328. [Google Scholar]
- De Voogt, P.; Brinkman, U.A.T. CHAPTER 1—Production, properties and usage of polychlorinated biphenyls. In Halogenated Biphenyls, Terphenyls, Naphthalenes, Dibenzodioxins and Related Products, 2nd ed.; Kimbrough, R.D., Jensen, A.A., Eds.; Topics in Environmental Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; pp. 3–45. [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer, R.B.; Caquet, T.; Siimes, K.; Mueller, R.; Lagadic, L.; Liess, M. Effects of pesticides on community structure and ecosystem functions in agricultural streams of three biogeographical regions in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 382, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, O.M.L.; Basheer, A.A.; Khattab, R.A.; Ali, I. Health and environmental effects of persistent organic pollutants. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 263, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, G.; Akoto, O.; Oppong, C. Persistent organochlorine pesticide residues in fish, sediments and water from Lake Bosomtwi, Ghana. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolopoulou-Stamati, P.; Maipas, S.; Kotampasi, C.; Stamatis, P.; Hens, L. Chemical Pesticides and Human Health: The Urgent Need for a New Concept in Agriculture. Front. Public Health 2016, 4, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, L.; Roose, L.; Bersuder, P.; Kotterman, M.; Haarich, M.; Vorkamp, K. Determination of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Sediment and Biota; ICES Techniques in Marine Environmental Science (TIMES): International Council for the Exploration of the Sea: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren, K.; Tysklind, M.; Ishaq, R.; Broman, D.; van Bavel, B. Polychlorinated Naphthalene Levels, Distribution, and Biomagnification in a Benthic Food Chain in the Baltic Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 5005–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaraj, R.; Megha, P.; Sreedev, P. Review Article. Organochlorine pesticides, their toxic effects on living organisms and their fate in the environment. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2016, 9, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrozek, E.; Leidy, R.B. Investigation of selective uptake of polychlorinated biphenyls bySpartina alterniflora Loisel. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1981, 27, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrozek, E.; Seneca, E.D.; Hobbs, L.L. Polychlorinated biphenyl uptake and translation by Spartina alterniflora loisel. Water Air Soil Pollut 1982, 17, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrozek, E.; Queen, W.H.; Hobbs, L.L. Effects of polychlorinated biphenyls on growth of Spartina alterniflora Loisel. Environ. Exp. Bot. 1983, 23, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, P. Uptake of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) by the macroalga, Cladophora glomerata. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1987, 38, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.; Vernisseau, A.; Marchand, P.; Le Bizec, B.; Ramos, F.; Pardal, M.A. Distribution of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in sediment and plants from a contaminated salt marsh (Tejo estuary, Portugal). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 2540–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, P.N.; Basto, M.C.P.; Silva, M.F.G.M.; Machado, A.; Bordalo, A.A.; Vasconcelos, M.T.S.D. Ability of salt marsh plants for TBT remediation in sediments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulding, T.; Sousa, P.M.; Silva, G.; Medeiros, J.P.; Carvalho, F.; Metelo, I.; Freitas, C.; Lopes, N.; Chainho, P.; Costa, J.L. Shifts in Estuarine Macroinvertebrate Communities Associated with Water Quality and Climate Change. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caçador, I.; Costa, J.L.; Duarte, B.; Silva, G.; Medeiros, J.P.; Azeda, C.; Castro, N.; Freitas, J.; Pedro, S.; Almeida, P.R.; et al. Macroinvertebrates and fishes as biomonitors of heavy metal concentration in the Seixal Bay (Tagus estuary): Which species perform better? Ecol. Indic. 2012, 19, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgueiro, N.; Caçador, I. Short-term sedimentation in Tagus estuary, Portugal: The influence of salt marsh plants. Hydrobiologia 2007, 587, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa-Dias, A.; Melo, R.A. Long-term abundance patterns of macroalgae in relation to environmental variables in the Tagus Estuary (Portugal). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 76, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gameiro, C.; Cartaxana, P.; Brotas, V. Environmental drivers of phytoplankton distribution and composition in Tagus Estuary, Portugal. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 75, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cereja, R.; Brotas, V.; Cruz, J.P.C.; Rodrigues, M.; Brito, A.C. Tidal and Physicochemical Effects on Phytoplankton Community Variability at Tagus Estuary (Portugal). Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz de Carvalho, R.; Feijão, E.; Kletschkus, E.; Marques, J.C.; Reis-Santos, P.; Fonseca, V.F.; Papenbrock, J.; Caçador, I.; Duarte, B. Halophyte bio-optical phenotyping: A multivariate photochemical pressure index (Multi-PPI) to classify salt marsh anthropogenic pressures levels. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 119, 106816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PORDATA Censos 2021: Densidade Populacional. Available online: http://www.pordata.pt (accessed on 9 May 2024).
- NP EN 932-2 Norma Portuguesa: NP EN 932–2; Ensaios das Propriedades Gerias dos Agregados Parte 2: Métodos de Redução de Amostras Laboratoriais. Instituto Português da Qualidade: Caparica, Portugal, 2002.
- NP EN 933-2 Norma Portuguesa: NP EN 933–2; Ensaios para Determinação das Caraterísticas Geométricas dos Agregados Parte 2: Determinação da Distribuição Granulométrica Peneiros de Ensaio, Dimensão Nominal das Aberturas. Instituto Português da Qualidade: Caparica, Portugal, 1999.
- NP EN 9331-1 Norma Portuguesa: NP EN 9331–1; Ensaios das Propriedades Geométricas dos Agregados Parte 1—Análise Granulométrica: Método da Peneiração. Instituto Português da Qualidade: Caparica, Portugal, 2014.
- ISO 13320 ISO 13320:2020 (E); Particle Size Analysis–Laser Diffraction Methods. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Baird, R.; Eaton, A.; Rice, E. (Eds.) Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-0-87553-287-5. [Google Scholar]
- Giergielewicz-Możajska, H.; Dąbrowski, Ł.; Namieśnik, J. Accelerated Solvent Extraction (ASE) in the Analysis of Environmental Solid Samples—Some Aspects of Theory and Practice. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2001, 31, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.E.; Jones, B.A.; Ezzell, J.L.; Porter, N.L.; Avdalovic, N.; Pohl, C. Accelerated Solvent Extraction: A Technique for Sample Preparation. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehotay, S.J. Determination of pesticide residues in foods by acetonitrile extraction and partitioning with magnesium sulfate: Collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 2007, 90, 485–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 10382 ISO 10382:2002(E); Soil Quality—Determination of Organochlorine Pesticides and Polychlorinated Bipheyls—Gas Chromatography Method with Electron Capture Detection. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
- Lyytikäinen, M.; Kukkonen, J.V.K.; Lydy, M.J. Analysis of Pesticides in Water and Sediment Under Different Storage Conditions Using Gas Chromatography. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2003, 44, 0437–0444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OSPAR Background Document on CEMP Assessment Criteria for QSR 2010; OSPAR Comission: London, UK, 2009. Available online: https://www.ospar.org/documents?v=7167 (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- US EPA. Guidelines for Ecological Risk Assessment; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2014-11/documents/eco_risk_assessment1998.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; The R Foundation, Vienna University of Economics and Business: Vienna, Austria, 2021.
- Tang, Y.; Horikoshi, M.; Li, W. ggfortify: Unified Interface to Visualize Statistical Results of Popular R Packages. R J. 2016, 8, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. R Package “Corrplot”: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix (Version 0.92); The R Foundation: Vienna University of Economics and Business, Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, O.; Vale, C. DDT concentrations in surficial sediments of three estuarine systems in Portugal. Aquat. Ecol. 1999, 33, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, P.N.; Rodrigues, P.N.R.; Basto, M.C.P.; Vasconcelos, M.T.S.D. Organochlorine pesticides levels in Portuguese coastal areas. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, J.; Costa, P.M.; Caeiro, S.; Martins, M.; Ferreira, A.M.; Caetano, M.; Cesário, R.; Vale, C.; Costa, M.H. Evaluation of the potential of the common cockle (Cerastoderma edule L.) for the ecological risk assessment of estuarine sediments: Bioaccumulation and biomarkers. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 1496–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkhoff, T. City Population-Population Statistics, Charts and Map. Available online: https://www.citypopulation.de/ (accessed on 24 July 2024).
- Le, P.-C.; Le, D.-L.; Nguyen, D.D. Accumulation and distribution of persistent organic pollutants in surface sediment of the estuarine region and correlation between genetic and environmental factors: A case study. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.A.; Elkatory, M.R.; Ragab, S.; El Nemr, A. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in water-sediment system of southern Mediterranean: Concentration, source and ecological risk assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 196, 115692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Huang, W.; Dou, W.; You, J.; Jiao, H.; Sun, A.; Chen, J.; Shi, X.; et al. Occurrence, source, and ecological risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in the water–sediment system of Hangzhou Bay and East China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 179, 113735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buah-Kwofie, A.; Humphries, M.S. The distribution of organochlorine pesticides in sediments from iSimangaliso Wetland Park: Ecological risks and implications for conservation in a biodiversity hotspot. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, B.; Freitas, J.; Couto, T.; Valentim, J.; Dias, J.M.; Silva, H.; Marques, J.C.; Caçador, I. New multi-metric Salt Marsh Sediment Microbial Index (SSMI) application to salt marsh sediments ecological status assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 29, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frings, R.M. Downstream fining in large sand-bed rivers. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2008, 87, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jonge, L.W.; de Jonge, H.; Moldrup, P.; Jacobsen, O.H.; Christensen, B.T. Sorption of Prochloraz on Primary Soil Organomineral Size Separates. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pionke, H.B.; Chesters, G. Pesticide-Sediment-Water Interactions. J. Environ. Qual. 1973, 2, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Keller, A.A. Particle-Size Dependent Sorption and Desorption of Pesticides within a Water−Soil−Nonionic Surfactant System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3381–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qian, Y.; Jia, Q.; Weng, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Qiu, J. A national-scale distribution of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in cropland soils and major types of food crops in China: Co-occurrence and associated risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, A.D.; Amato, S.; Falconer, R.L. Emission of Chiral Organochlorine Pesticides from Agricultural Soils in the Cornbelt Region of the U.S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4592–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waliszewski, S.M.; Carvajal, O.; Infanzon, R.M.; Trujillo, P.; Aguirre, A.A.; Maxwell, M. Levels of Organochlorine Pesticides in Soils and Rye Plant Tissues in a Field Study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 7045–7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasali, H.; Pavlidis, G. Non-extractable Pesticide Residues in Soils. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 47: Pesticide Occurrence, Analysis and Remediation Vol. 1 Biological Systems; Inamuddin, M.I.A., Lichtfouse, E., Eds.; Sustainable Agriculture Reviews; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2021; pp. 203–226. ISBN 978-3-030-54712-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mottes, C.; Sabatier, P.; Evrard, O.; Cottin, N.; Arnaud, F.; Comte, I.; Piot, C.; Lesueur-Jannoyer, M.; Lichtfouse, E.; Poulenard, J. Pesticide resurrection. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 3357–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mil-Homens, M.; Vicente, M.; Grimalt, J.O.; Micaelo, C.; Abrantes, F. Reconstruction of organochlorine compound inputs in the Tagus Prodelta. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 540, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, M.D.; Kaley, R.G. Applications of polychlorinated biphenyls. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackova, M.; Macek, T.; Ocenaskova, J.; Burkhard, J.; Demnerova, K.; Pazlarova, J. Biodegradation of polychlorinated biphenyls by plant cells. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1997, 39, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Garrison, A.W.; Hoehamer, C.; Mazur, C.S.; Wolfe, N.L. Uptake and Phytotransformation of Organophosphorus Pesticides by Axenically Cultivated Aquatic Plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 6114–6120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezek, J.; Macek, T.; Mackova, M.; Triska, J. Plant metabolites of polychlorinated biphenyls in hairy root culture of black nightshade Solanum nigrum SNC-9O. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilken, A.; Bock, C.; Bokern, M.; Harms, H. Metabolism of different PCB congeners in plant cell cultures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1995, 14, 2017–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, B.; Almeida, P.R.; Cacador, I. Spartina maritima (cordgrass) rhizosediment extracellular enzymatic activity and its role in organic matter decomposition processes and metal speciation. Mar. Ecol. 2009, 9, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, S.; Duarte, B.; Raposo de Almeida, P.; Caçador, I. Metal speciation in salt marsh sediments: Influence of halophyte vegetation in salt marshes with different morphology. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 167, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriada-Pereira, M.; González-Castro, M.J.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S.; López-Mahía, P.; Prada-Rodríguez, D.; Fernández-Fernández, E. Organochlorine pesticides accumulation and degradation products in vegetation samples of a contaminated area in Galicia (NW Spain). Chemosphere 2005, 58, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglioranza, K.S.B.; de Moreno, J.E.A.; Moreno, V.J. Organochlorine pesticides sequestered in the aquatic macrophyte Schoenoplectus californicus (C.A. Meyer) Soják from a shallow lake in Argentina. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, P.N.; Rodrigues, P.N.R.; Evangelista, R.; Basto, M.C.P.; Vasconcelos, M.T.S.D. Can salt marsh plants influence levels and distribution of DDTs in estuarine areas? Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 93, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouldin, J.L.; Farris, J.L.; Moore, M.T.; Smith, S.; Cooper, C.M. Hydroponic uptake of atrazine and lambda-cyhalothrin in Juncus effusus and Ludwigia peploides. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commendatore, M.; Yorio, P.; Scenna, L.; Ondarza, P.M.; Suárez, N.; Marinao, C.; Miglioranza, K.S.B. Persistent organic pollutants in sediments, intertidal crabs, and the threatened Olrog’s gull in a northern Patagonia salt marsh, Argentina. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 136, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, R.; Durante, C.; Arcagni, M.; Juncos, R.; Seco Pon, J.; Crespo, E.; Narvarte, M. Effects of Pollution in Aquatic Food Chains. In Anthropogenic Pollution of Aquatic Ecosystems; Häder, D.-P., Helbling, E.W., Villafañe, V.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2021; pp. 61–89. ISBN 978-3-030-75602-4. [Google Scholar]
- Madgett, A.S.; Yates, K.; Webster, L.; McKenzie, C.; Brownlow, A.; Moffat, C.F. The concentration and biomagnification of PCBs and PBDEs across four trophic levels in a marine food web. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chormare, R.; Kumar, M.A. Environmental health and risk assessment metrics with special mention to biotransfer, bioaccumulation and biomagnification of environmental pollutants. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaynab, M.; Fatima, M.; Sharif, Y.; Sughra, K.; Sajid, M.; Khan, K.A.; Sneharani, A.H.; Li, S. Health and environmental effects of silent killers Organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyl. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2021, 33, 101511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K. Trophic transfer of organochlorine pesticides through food-chain in coastal marine ecosystem. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairy, M.; Brault, E.; Dickhut, R.; Harding, K.C.; Harkonen, T.; Karlsson, O.; Lehnert, K.; Teilmann, J.; Lohmann, R. Bioaccumulation of PCBs, OCPs and PBDEs in Marine Mammals from West Antarctica. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayele, S.; Mamo, Y.; Deribe, E.; Eklo, O.M. Organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in carnivorous waterbird and fish species from Lake Hawassa, Ethiopia. SN Appl. Sci. 2022, 4, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, C.M.; Mielke, K.C.; Pires, F.R.; Santos, J.B.D. Organic Pollutants Threatening Human Health. In Nanotechnology for Environmental Pollution Decontamination; Apple Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 3–37. ISBN 978-1-00-327956-3. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.J.; Catarino, F.; Bettencourt, A. The role of salt marshes in the Mira estuary (Portugal). Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2001, 9, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Lu, X.; Su, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Cao, X.; Li, Q.; Su, J.; Ittekkot, V.; et al. Major threats of pollution and climate change to global coastal ecosystems and enhanced management for sustainability. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, B.; Carreiras, J.; Feijão, E.; Reis-Santos, P.; Caçador, I.; Matos, A.R.; Fonseca, V.F. Fatty acid profiles of estuarine macroalgae are biomarkers of anthropogenic pressures: Development and application of a multivariate pressure index. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Human, L.R.D.; Feijão, E.; Cruz de Carvalho, R.; Caçador, I.; Reis-Santos, P.; Fonseca, V.; Duarte, B. Mediterranean salt marsh sediment metal speciation and bioavailability changes induced by the spreading of non-indigenous Spartina patens. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 243, 106921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cruz de Carvalho, R.; Cardoso, J.; Carreiras, J.A.; Santos, P.; Palma, C.; Duarte, B. Persistent Organic Pollutants in Tagus Estuary Salt Marshes: Patterns of Contamination and Plant Uptake. J. Xenobiot. 2024, 14, 1165-1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14030066
Cruz de Carvalho R, Cardoso J, Carreiras JA, Santos P, Palma C, Duarte B. Persistent Organic Pollutants in Tagus Estuary Salt Marshes: Patterns of Contamination and Plant Uptake. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2024; 14(3):1165-1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14030066
Chicago/Turabian StyleCruz de Carvalho, Ricardo, João Cardoso, João Albuquerque Carreiras, Paula Santos, Carla Palma, and Bernardo Duarte. 2024. "Persistent Organic Pollutants in Tagus Estuary Salt Marshes: Patterns of Contamination and Plant Uptake" Journal of Xenobiotics 14, no. 3: 1165-1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14030066
APA StyleCruz de Carvalho, R., Cardoso, J., Carreiras, J. A., Santos, P., Palma, C., & Duarte, B. (2024). Persistent Organic Pollutants in Tagus Estuary Salt Marshes: Patterns of Contamination and Plant Uptake. Journal of Xenobiotics, 14(3), 1165-1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14030066








