Application of Microbiological Screening Tests in Assessment of Environmental Exposure to Antibiotics: Preliminary Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
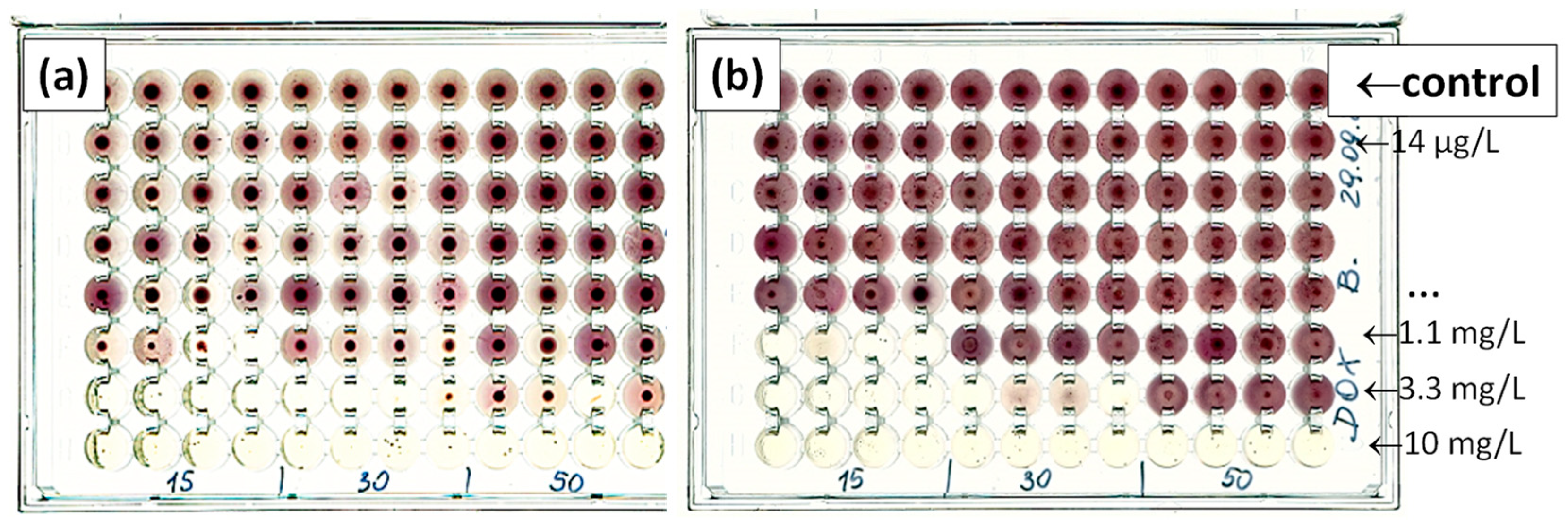
2. Results and Discussion
- Water collected from an aquarium (Figure 4, Aquarium) with a controlled culture of Carassius auratus;
- Water collected directly from a source (Figure 4, Source), free of anthropogenic pollution;
- Water collected from ponds with Salmo irideus and Acipenser baerii culture (Figure 4, Aquaculture) directly fed with spring water, where no antibiotics were used in the culture;
- Water from an undrained pond (Figure 4, Ponds) stocked with fish and used by anglers in a park;
- Water from an artificial reservoir (Figure 4, Reservoir) directly fed with spring water and used for recreation in the summer season;
- Effluent from the mechanical–biological wastewater treatment plant (Figure 4, effluent) located in Sosnowiec-Zagórze (Poland)supplied mainly with municipal and hospital wastewater;
- Water from a drainage ditch (Figure 4, Leachate) fed with leachate from vegetable gardens and domestic wastewater from several residential buildings.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Antibiotics
3.2. Water Samples Used as Inoculum
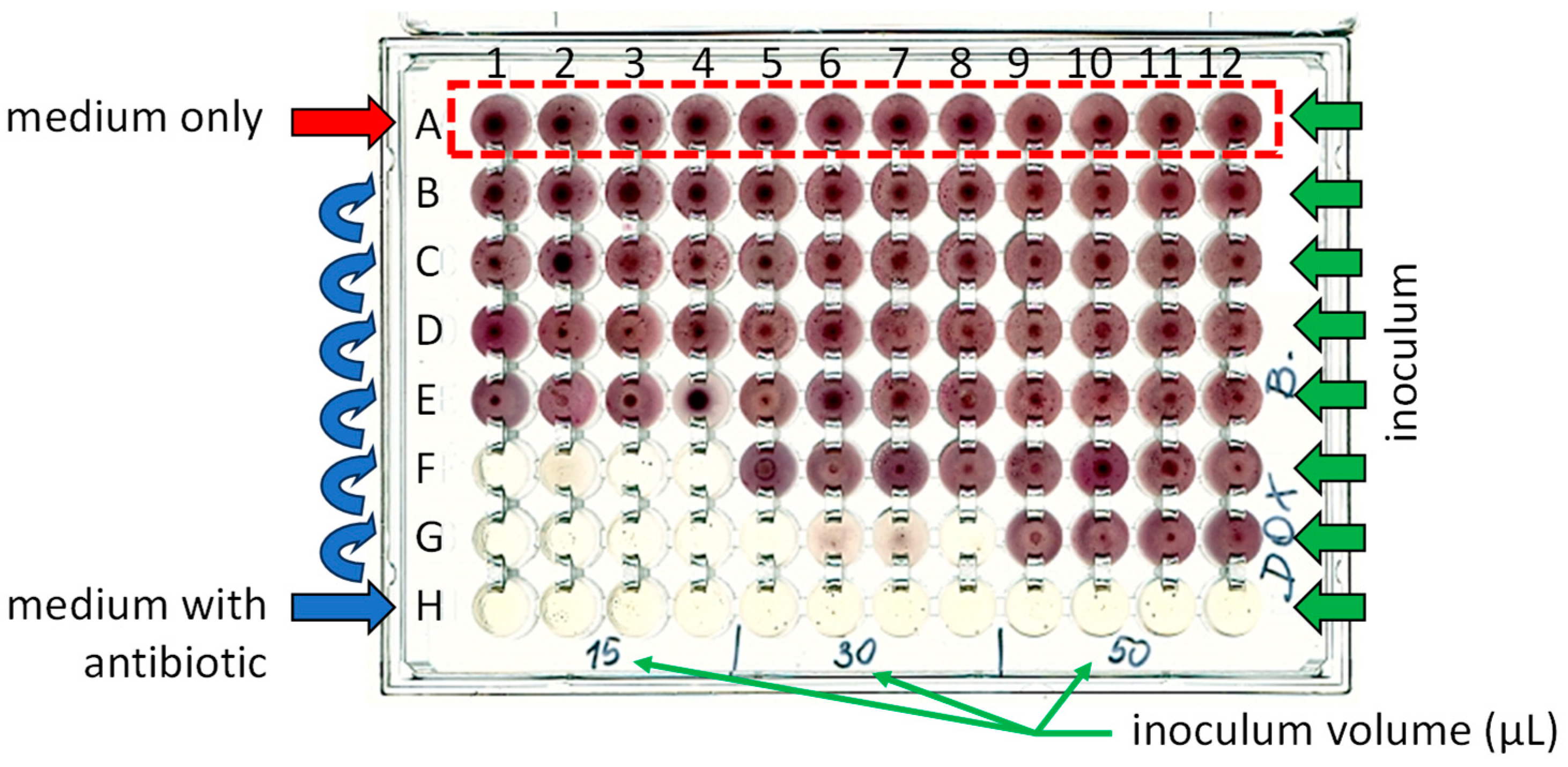
3.3. Procedure for Preparation of Test Plate
3.4. Assessment of Microbial Susceptibility
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larsson, D.G.J.; Flach, C.-F. Antibiotic Resistance in the Environment. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemper, N. Veterinary Antibiotics in the Aquatic and Terrestrial Environment. Ecol. Indic. 2008, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernier, S.P.; Surette, M.G. Concentration-Dependent Activity in Natural Environments. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 40125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, S.A.; Ramachandran, A.; Perron, G.G. Antibiotic Pollution in the Environment: From Microbial Ecology to Public Policy. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Yin, G.; Liu, M.; Chen, C.; Jiang, Y.; Hou, L.; Zheng, Y. A Systematic Review of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Estuarine and Coastal Environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, P.; Loureiro, L.; Matos, A. Transfer of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria between Intermingled Ecological Niches: The Interface between Humans, Animals and the Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasiri, M.; Sano, D.; Suzuki, S. Understanding Human Health Risks Caused by Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria (ARB) and Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARG) in Water Environments: Current Knowledge and Questions to be Answered. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 2016–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Peoples, A.J.; Ludwig, K.C.; Maity, S.; Derks, M.G.N.; De Benedetti, S.; Krueger, A.M.; Vermeulen, B.J.A.; Harbig, T.; Lavore, F.; et al. An Antibiotic from an Uncultured Bacterium Binds to an Immutable Target. Cell 2023, 186, 4059–4073.e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melcrová, A.; Maity, S.; Melcr, J.; de Kok, N.A.W.; Gabler, M.; van der Eyden, J.; Stensen, W.; Svendsen, J.S.M.; Driessen, A.J.M.; Marrink, S.J.; et al. Lateral Membrane Organization as Target of an Antimicrobial Peptidomimetic Compound. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geser, N.; Stephan, R.; Hächler, H. Occurrence and Characteristics of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Food Producing Animals, Minced Meat and Raw Milk. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliu, E.-M.; Vahjen, W.; Zentek, J. Types and Prevalence of Extended–Spectrum Beta–Lactamase Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Poultry. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2017, 18, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DANMAP. Use of Antimicrobial Agents and Occurrence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria from Food Animals, Food and Humans in Denmark; 2022. Diagnostic Infectious Disease Preparedness, Statens Serum Institut, National Food Institute, Technical University of Denmark, Kongens Lyngby. Available online: https://www.danmap.org/-/media/institutter/foedevareinstituttet/danmap-site/report-2022/danmap_2022_low_version-3.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- He, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Mathieu, J.; Stadler, L.; Senehi, N.; Sun, R.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Antibiotic Resistance Genes from Livestock Waste: Occurrence, Dissemination, and Treatment. NPJ Clean Water 2020, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Wan, W.; Mao, D.; Wang, C.; Mu, Q.; Qin, S.; Luo, Y. Occurrence and Distribution of Sulfonamides, Tetracyclines, Quinolones, Macrolides, and Nitrofurans in Livestock Manure and Amended Soils of Northern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4545–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolliver, H.A.S.; Gupta, S.C. Antibiotic Losses from Unprotected Manure Stockpiles. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, M.Z.; Ramon-Portugal, F.; Huesca, A.; Angastiniotis, K.; Simitopoulou, M.; Kefalas, G.; Ferrari, P.; Levallois, P.; Fourichon, C.; Wolthuis-Fillerup, M.; et al. Residues of Veterinary Antibiotics in Manures from Pig and Chicken Farms in a Context of Antimicrobial Use Reduction by Implementation of Health and Welfare Plans. Environ. Res. 2023, 238, 117242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eintrag von Arzneimitteln und Deren Verhalten und Verbleib in der Umwelt, Literaturstudie Fachbericht 2; Landesamt für Natur, Umwelt und Verbraucherschutz Nordrhein-Westfalen: Dusseldorf, Germany, 2007; Available online: https://www.lanuv.nrw.de/fileadmin/lanuvpubl/3_fachberichte/30002.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Wang, H.; Chu, Y.; Fang, C. Occurrence of Veterinary Antibiotics in Swine Manure from Large-Scale Feedlots in Zhejiang Province, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 98, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Liguoro, M.; Poltronieri, C.; Capolongo, F.; Montesissa, C. Use of Sulfadimethoxine in Intensive Calf Farming: Evaluation of Transfer to Stable Manure and Soil. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massé, D.; Saady, N.; Gilbert, Y. Potential of Biological Processes to Eliminate Antibiotics in Livestock Manure: An Overview. Animals 2014, 4, 146–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Qiang, Z.; Ben, W.; Chen, M. Residual Veterinary Antibiotics in Swine Manure from Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations in Shandong Province, China. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Yan, J.; Li, H.; Hu, H. Long-Term Manure Application Increased the Levels of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in a Greenhouse Soil. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2017, 121, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, A.; André, S.; Viana, P.; Nunes, O.C.; Manaia, C.M. Antibiotic Resistance, Antimicrobial Residues and Bacterial Community Composition in Urban Wastewater. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1875–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, H.; Fricker, C.; Brown, R.S.; Majury, A.; Liss, S.N. Antibiotic Resistance Genes as an Emerging Environmental Contaminant. Environ. Rev. 2016, 24, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Manaia, C.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Ploy, M.C.; Michael, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban Wastewater Treatment Plants as Hotspots for Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria and Genes Spread into the Environment: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gothwal, R.; Shashidhar, T. Antibiotic Pollution in the Environment: A Review. Clean-Soil Air Water 2015, 43, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazal, H. Pharmaceuticals Contamination in the Environment. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 103, 104251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, E.; Hornek-Gausterer, R.; Saçan, M.T. Single and Mixture Toxicity of Pharmaceuticals and Chlorophenols to Freshwater Algae Chlorella Vulgaris. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 129, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-L.; Wong, M.-H. Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs): A Review on Environmental Contamination in China. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jjemba, P.K. Excretion and Ecotoxicity of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products in the Environment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2006, 63, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ying, G.; Su, H.; Stauber, J.L.; Adams, M.S.; Binet, M.T. Growth-inhibiting Effects of 12 Antibacterial Agents and Their Mixtures on the Freshwater Microalga Pseudokirchneriella Subcapitata. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Kumar, R.; Kishor, K.; Mlsna, T.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D. Pharmaceuticals of Emerging Concern in Aquatic Systems: Chemistry, Occurrence, Effects, and Removal Methods. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3510–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Lu, C.; Liao, Q.; Gudda, F.O.; Ling, W. Antibiotics in Animal Manure and Manure-Based Fertilizers: Occurrence and Ecological Risk Assessment. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 127006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Beck, I.-C. Effects of Sulfonamide and Tetracycline Antibiotics on Soil Microbial Activity and Microbial Biomass. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenart-Boroń, A.; Prajsnar, J.; Guzik, M.; Boroń, P.; Grad, B.; Żelazny, M. Antibiotics in Groundwater and River Water of Białka—A Pristine Mountain River. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, F.; Calısto-Ulloa, N.; Gómez-Fuentes, C.; Gómez, M.; Ferrer, J.; González-Rocha, G.; Bello-Toledo, H.; Botero-Coy, A.M.; Boıx, C.; Ibáñez, M.; et al. Occurrence of Antibiotics and Bacterial Resistance in Wastewater and Sea Water from the Antarctic. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 363, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansson, E.; Fick, J.; Janzon, A.; Grabic, R.; Rutgersson, C.; Weijdegård, B.; Söderström, H.; Larsson, D.G.J. Pyrosequencing of Antibiotic-Contaminated River Sediments Reveals High Levels of Resistance and Gene Transfer Elements. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.G.J. Antibiotics in the Environment. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 119, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.L. Natural Antibiotic Resistance and Contamination by Antibiotic Resistance Determinants: The Two Ages in the Evolution of Resistance to Antimicrobials. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 19026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cytryn, E. The Soil Resistome: The Anthropogenic, the Native, and the Unknown. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2013, 63, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoloni, A.; Bartalesi, F.; Mantella, A.; Dell’Amico, E.; Roselli, M.; Strohmeyer, M.; Barahona, H.G.; Barrón, V.P.; Paradisi, F.; Rossolini, G.M. High Prevalence of Acquired Antimicrobial Resistance Unrelated to Heavy Antimicrobial Consumption. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielson, J.; Kühn, I.; Colque-Navarro, P.; Hart, M.; Iversen, A.; McKenzie, D.; Möllby, R. Microplate-Based Microbial Assay for Risk Assessment and (Eco)Toxic Fingerprinting of Chemicals. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 485, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhia, K.; Dando, T.; Clive Thompson, K. Intra-Laboratory Evaluation of Microbial Assay for Risk Assessment (MARA) for Potential Application in the Implementation of the Water Framework Directive (WFD). J. Environ. Monit. 2007, 9, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadhia, K. ISTA13-International Interlaboratory Comparative Evaluation of Microbial Assay for Risk Assessment (MARA). Environ. Toxicol. 2008, 23, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamek, E.; Baran, W. Degradation of Veterinary Antibiotics by the Ozonation Process: Product Identification and Ecotoxicity Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 134026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamek, E.; Masternak, E.; Sapińska, D.; Baran, W. Degradation of the Selected Antibiotic in an Aqueous Solution by the Fenton Process: Kinetics, Products and Ecotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, T.J. Methods for Screening and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity: A Review of Protocols, Advantages, and Limitations. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2024, 14, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamek, E.; Baran, W.; Sobczak, A. Assessment of the Biodegradability of Selected Sulfa Drugs in Two Polluted Rivers in Poland: Effects of Seasonal Variations, Accidental Contamination, Turbidity and Salinity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 313, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufaner, F. Relationship between Physicochemical Parameters in Çıldır Lake (Turkey): Predicted Total Organic Carbon as a Lake Pollution Indicator. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 4085–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexy, R.; Kümpel, T.; Kümmerer, K. Assessment of Degradation of 18 Antibiotics in the Closed Bottle Test. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, J.D.; Moon, G. Re-Evaluation of a Microbiological Acceptable Daily Intake for Tylosin Based on Its Impact on Human Intestinal Microflora. Toxicol. Res. 2024, 40, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Antibiotic Group | Antibiotic | Concentration (mg/kg Dry Weight) | Matrix | Year | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imidazole | Furazolidone | ~0.3 | - | 2015 | [15] |
| Macrolides | Tylosin | 8.1 | Beef manure stockpile | 2008 | [16] |
| Tilmicosin | 18.93 | Swine manure | 2023 | [17] | |
| Sulphonamides | Sulphadiazine | 91 | Turkey manure | 2007 | [18] |
| Sulphamethazine | 167 | Swine manure | 2007 | [18] | |
| Sulphamerazine | 16.50 | - | 2017 | [19] | |
| Sulphadimethoxine | 395.73 | Calf manure | 2007 | [20] | |
| Tetracyclines | Oxytetracycline | 354 | Swine manure | 2014 | [21] |
| Tetracycline | 136.00 | Swine manure | 2011 | [22] | |
| Chlortetracycline | 764.4 | Swine manure | 2011 | [22] | |
| Doxycycline | 99.198 | Poultry manure | 2023 | [17] | |
| Trimethoprim | Trimethoprim | 17.0 | Turkey manure | 2007 | [18] |
| Antibiotic Classification | Name | Abbreviation | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Manufacturer/Supplier | Purity | Maximum Concentration Used in Experiments 1 (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penicillins | Ampicillin sodium salt | AMP | 371.4 | Sigma-Aldrich | 91.0–100.5% | 100 |
| Tetracyclines | Doxycycline hyclate | DOX | 512.9 | Sigma-Aldrich | ≥98% | 10 or 50 |
| Imidazole derivatives | Metronidazole | MET | 171.2 | Fluka | ≥98% | 200 |
| Sulphonamides | Sulfathiazole sodium salt | STZ | 277.3 | Sigma-Aldrich | >99% | 300 |
| Trimethoprim | Trimethoprim | TMP | 290.3 | Sigma-Aldrich | ≥98% | 100 |
| Macrolides | Tylosin tartrate | TYL | 1066.2 | Sigma-Aldrich | potency: ≥800 units/mg | 200 |
| Abbreviated Name | Brief Description | Geographical Coordinates of the Sampling Location in Decimal Format | Sampling Month | TOC (mgC/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Przemsza | The moderately polluted Przemsza River; the catchment area includes agricultural and industrial areas | 50.25903590, 19.13729930 | March | 10.4 ± 0.5 |
| September | 13.5 ± 0.3 | |||
| December | 13.0 ± 1.0 | |||
| Brynica | The heavily polluted Brynica River; the catchment area includes an industrial area | 50.25894507, 19.13701568 | March | 18.0 ± 0.4 |
| September | 20.3 ± 0.3 | |||
| December | 17.7 ± 0.3 | |||
| Aquarium | Water from C. auratus culture in a 50 L aquarium, without plants, without gravel substrate, with a sponge filter, and fed with bacteria-free water | - | April | 18.2 ± 0.5 |
| Source | Water from the source of Sztoła River, free from anthropogenic pollution; metronidazole was applied in culture | 50.23925120, 19.50705237 | April | <3.0 |
| Aquaculture | Water from a commercial freshwater fish farm, including S. irideus and A. baerii; ponds were fed directly with spring water, and no antibiotics were used in the culture | 50.43250454, 19.18074069 | April | 4.2 ± 0.3 |
| Pond | Water from a small undrained pond in the park, stocked with fish and used for recreation by anglers | 50.34197738, 19.18572344 | April | 4.1 ± 0.2 |
| Reservoir | Water from artificial reservoir Pogoria 3; the reservoir is fed directly with spring water and is used for recreation in the summer season; | 50.35563921, 19.21286766 | April | 7.5 ± 0.5 |
| Effluent | Treated wastewater from the mechanical–biological wastewater treatment plant with a sludge bioreactor; the wastewater treatment plant is mainly supplied with municipal and hospital wastewater from the Sosnowiec-Zagórze housing estate (approximately 50,000 residents) | 50.30227793, 19.20080535 | April | 24.1 ± 0.7 |
| Leachate | Water from a drainage ditch fed with leachate from vegetable gardens and domestic wastewater from several residential buildings | 50.30592077, 19.20361633 | April | >30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madej-Knysak, D.; Adamek, E.; Kośmider, L.; Baran, W. Application of Microbiological Screening Tests in Assessment of Environmental Exposure to Antibiotics: Preliminary Studies. J. Xenobiot. 2024, 14, 1187-1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14030067
Madej-Knysak D, Adamek E, Kośmider L, Baran W. Application of Microbiological Screening Tests in Assessment of Environmental Exposure to Antibiotics: Preliminary Studies. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2024; 14(3):1187-1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14030067
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadej-Knysak, Daria, Ewa Adamek, Leon Kośmider, and Wojciech Baran. 2024. "Application of Microbiological Screening Tests in Assessment of Environmental Exposure to Antibiotics: Preliminary Studies" Journal of Xenobiotics 14, no. 3: 1187-1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14030067
APA StyleMadej-Knysak, D., Adamek, E., Kośmider, L., & Baran, W. (2024). Application of Microbiological Screening Tests in Assessment of Environmental Exposure to Antibiotics: Preliminary Studies. Journal of Xenobiotics, 14(3), 1187-1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14030067










