Draft Animals, Farm Machines and Sustainable Agricultural Production: Insight from China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Agricultural Production Transition from Draft Animal Use to Farm Machine Use
3. Data and Descriptive Statistics
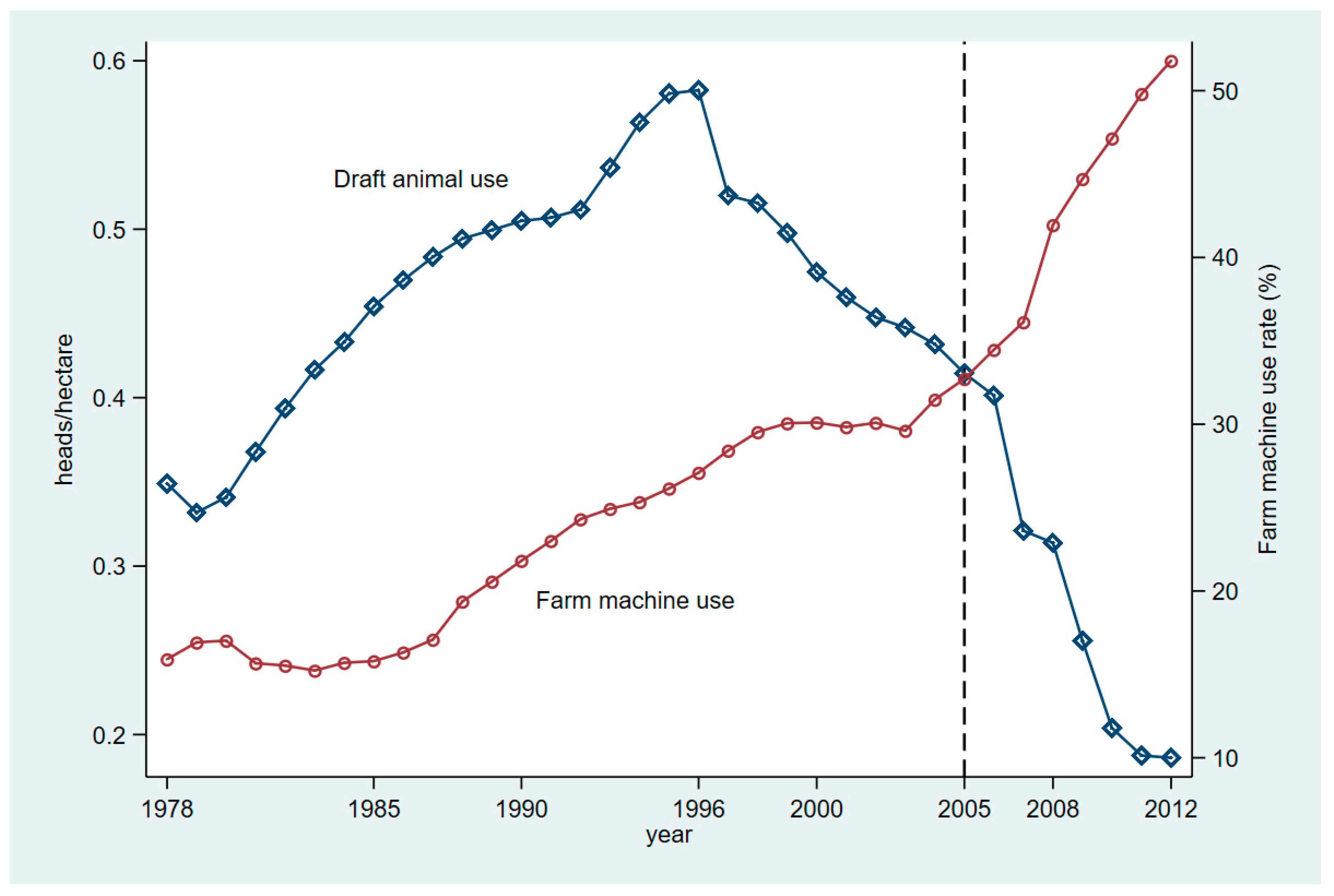
3.1. Data Source
3.2. Descriptive Statistics
4. Empirical Models
4.1. Pooled Mean Group (PMG) Model
4.2. Production Function Model with Fixed Effects
5. Empirical Results and Discussions
5.1. Results for Unit Root (IPS) Test and Cointergration Tests
5.2. Impact of Farm Machine Use on Draft Animal Use
5.3. Impact of Draft Animal Use and Farm Machine Use on Agricultural Productivity
6. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

| Variable | Without Time Trend | With Time Trend | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistic Value | p-Value | Statistic Value | p-Value | |
| Draft animal use | −3.362 | 0.000 | −6.031 | 0.000 |
| Farm machine use | −4.751 | 0.000 | −4.817 | 0.000 |
| Agricultural productivity | −10.991 | 0.000 | −8.109 | 0.000 |
| Labour | −7.799 | 0.000 | −7.101 | 0.000 |
| Fertiliser | −11.884 | 0.000 | −11.986 | 0.000 |
| Transportation | −7.529 | 0.000 | −7.895 | 0.000 |
| Off-farm income | −10.046 | 0.000 | −9.929 | 0.000 |
| Education | −5.336 | 0.000 | −6.232 | 0.000 |
| Tests | Statistics | Draft Animal Use Model | Production Function Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Westerlund test | Variance ratio | −2.429 (0.008) | −1.462 (0.072) |
| Pedroni test | Modified Philips-Perron test | −2.947 (0.002) | −4.672 (0.000) |
| Philips-Perron test | −5.156 (0.000) | −1.560 (0.059) | |
| Augmented Dickey-Fuller test | −5.690 (0.000) | −1.285 (0.010) |
| Variables | FE Model | FD Model |
|---|---|---|
| Farm machine use | −1.608 (−1.87) * | −0.977 (−3.60) *** |
| Labour | 0.032 (0.11) | 0.507 (3.59) *** |
| Fertiliser | 0.075 (0.55) | 0.118 (3.12) *** |
| Transportation | −1.143 (−3.56) *** | −0.254 (−2.41) ** |
| Off-farm income | −0.617 (−3.10) *** | −0.132 (−1.23) |
| Education | 0.037 (0.40) | −0.080 (−1.74) * |
| Log Likelihood | −508.652 | 80.542 |
| Observations | 980 | 952 |
| Period I | Period II | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Draft Animal Use | Farm Machine Use | Year | Draft Animal Use | Farm Machine Use |
| 1978 | 0.185 | −0.161 | 1998 | −0.001 | 0.041 |
| 1979 | 0.186 | −0.168 | 1999 | 0.011 | 0.011 |
| 1980 | 0.186 | −0.175 | 2000 | −0.008 | 0.017 |
| 1981 | 0.169 | −0.152 | 2001 | −0.011 | 0.018 |
| 1982 | 0.159 | −0.139 | 2002 | −0.024 | 0.037 |
| 1983 | 0.145 | −0.123 | 2003 | −0.039 | 0.037 |
| 1984 | 0.130 | −0.103 | 2004 | −0.049 | 0.054 |
| 1985 | 0.105 | −0.052 | 2005 | −0.061 | 0.075 |
| 1986 | 0.103 | −0.051 | 2006 | −0.074 | 0.103 |
| 1987 | 0.097 | −0.043 | 2007 | −0.079 | 0.102 |
| 1988 | 0.087 | −0.032 | 2008 | −0.083 | 0.106 |
| 1989 | 0.082 | −0.030 | 2009 | −0.100 | 0.131 |
| 1990 | 0.090 | −0.045 | 2010 | −0.119 | 0.172 |
| 1991 | 0.069 | −0.016 | 2011 | −0.127 | 0.182 |
| 1992 | 0.055 | 0.002 | 2012 | −0.129 | 0.170 |
| 1993 | 0.056 | −0.012 | |||
| 1994 | 0.050 | −0.005 | |||
| 1995 | 0.049 | −0.011 | |||
| 1996 | 0.041 | 0.004 | |||
| 1997 | 0.001 | 0.041 | |||
References
- Kienzle, J.; Ashburner, J.E.; Sims, B.G. Mechanization for Rural Development: A Review of Patterns and Progress from around the World. In Integrated Crop Management (FAO) No. 20; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Guthiga, P.M.; Karugia, J.T.; Nyikal, R.A. Does use of draft animal power increase economic efficiency of smallholder farms in Kenya? Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2007, 22, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrema, G.; Soni, P. A Regional Strategy for Sustainable Agricultural Mechanization: Sustainable Mechanization across Agri-Food Chains in Asia and the Pacific Region; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.; Goodwin, B. Agricultural Mechanization and Non-Farm Labor Supply of Farm Households: Evidence from Bangladesh. In Proceedings of the the 2016 Agricultural & Applied Economics Association Annual Meeting, Boston, MA, USA, 31 July–2 August 2015; Volume 1, pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yamauchi, F.; Huang, J. Rising wages, mechanization, and the substitution between capital and labor: Evidence from small scale farm system in China. Agric. Econ. 2016, 47, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhong, F. Machinery investment decision and off-farm employment in rural China. China Econ. Rev. 2012, 23, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, B.; Hilmi, M.; Kienzle, J. Agricultural Mechanization: A Key Input for Sub-Saharan African Smallholders. In Integrated Crop Management Integrated Crop Management (FAO) eng v. 23; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pingali, P. Chapter 54 Agricultural Mechanization: Adoption Patterns and Economic Impact. Handb. Agric. Econ. 2007, 3, 2779–2805. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Renwick, A.; Grafton, Q. Farm machinery use, off-farm employment and farm performance in China. Aust. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2018, 62, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotons-Martínez, J.M.; Martin-Gorriz, B.; Torregrosa, A.; Porras, I. Economic evaluation of mechanical harvesting of lemons. Outlook Agric. 2018, 47, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Miah, M.A.M.; Hossain, S. Impact of farm mechanization on labour use for wheat cultivation in northern Bangladesh. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2011, 21, 589–594. [Google Scholar]
- Benin, S. Impact of Ghana’s agricultural mechanization services center program. Agric. Econ. 2015, 46, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binswanger, H.P. Agricultural Mechanization: A Comparative Historical Perspective. World Bank Res. Obs. 1986, 1, 27–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, W.K.; Matlon, P.J. Utilization, Profitability, and the Adoption of Animal Draft Power in West Africa. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 1990, 72, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, F. Increasing wage, mechanization, and agriculture production in China. China Econ. Rev. 2017, 46, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X.; Cossar, F.; Houssou, N.; Kolavalli, S. Mechanization in Ghana: Emerging demand, and the search for alternative supply models. Food Policy 2014, 48, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, K.D. Economic factors in the choice of an early form of capital: Draught animals in early twentieth century South Africa. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2000, 7, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.G. Effects of Technological-Change and Institutional Reform on Production Growth in Chinese Agriculture. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 1991, 73, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, F. Rising real wages, mechanization and growing advantage of large farms: Evidence from Indonesia. Food Policy 2016, 58, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshima, H.; Nin-Pratt, A.; Diao, X. Mechanization and Agricultural Technology Evolution, Agricultural Intensification in Sub-Saharan Africa: Typology of Agricultural Mechanization in Nigeria. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2013, 95, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, S. China has reached the Lewis turning point. China Econ. Rev. 2011, 22, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayami, Y.; Kawagoe, T. Farm Mechanization, Scale Economies and Polarization. J. Dev. Econ. 1989, 31, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Reardon, T. The Rapid Rise of Cross-Regional Agricultural Mechanization Services in China. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2013, 95, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, M.H.; Shin, Y.; Smith, R.P. Pooled Mean Group Estimation of Dynamic Heterogeneous Panels Stable. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1999, 94, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iii, E.F.B.; Frank, M.W.; Blackburne, E.F.; Frank, M.W. Estimation of nonstationary heterogeneous panels. Stata J. 2007, 7, 197–208. [Google Scholar]
- Kangasniemi, M.; Mas, M.; Robinson, C.; Serrano, L. The economic impact of migration: Productivity analysis for Spain and the UK. J. Product. Anal. 2012, 38, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachewe, F.; Headey, D. Urban Wage Behaviour and Food Price Inflation in Ethiopia. J. Dev. Stud. 2017, 53, 1207–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, K.S.; Pesaran, M.H.; Shin, Y. Testing for unit roots in heterogeneous panels. J. Econ. 2003, 115, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerlund, J. Testing for error correction in panel data. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 2007, 69, 709–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroni, P. Panel cointegration: Asymptotic and finite sample properties of pooled time series tests with an application to the PPP hypothesis. Econ. Theory 2004, 20, 597–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulai, A.; Tietje, H. Estimating technical efficiency under unobserved heterogeneity with stochastic frontier models: Application to northern German dairy farms. Eur. Rev. Agric. Econ. 2007, 34, 393–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latruffe, L.; Bravo-Ureta, B.E.; Carpentier, A.; Desjeux, Y.; Moreira, V.H. Subsidies and technical efficiency in agriculture: Evidence from European dairy farms. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2017, 99, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Yan, C.; Mei, X.; He, W.; Bing, S.H.; Ding, L.; Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Fan, T. Long-term effect of chemical fertilizer, straw, and manure on soil chemical and biological properties in northwest China. Geoderma 2010, 158, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhtiar, S.M.; Sakurai, K. Effects of organic manure and chemical fertilizer on soil fertility and productivity of plant and ratoon crops of sugarcane. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2005, 51, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Abdulai, A.; Goetz, R. Agricultural Cooperatives and Investment in Organic Soil Amendments and Chemical Fertilizer in China. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2018, 100, 502–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Abdulai, A.; Ma, C. The effects of off-farm work on fertilizer and pesticide expenditures in China. Rev. Dev. Econ. 2018, 22, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | Definition | Mean | S.D. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Draft animal use | Draft animal use per hectare (head) | 0.448 | 0.312 |
| Farm machine use | The farm machine use rate | 0.272 | 0.202 |
| Agricultural productivity | Gross agricultural production value per hectare (Yuan) a | 4622.578 | 4815.123 |
| Labour | Labour input per hectare (person) | 1.987 | 0.724 |
| Fertiliser | Fertiliser input (kg/hectare) | 224.553 | 121.782 |
| Transportation | The road length per square kilometre (km/km2) | 0.360 | 0.337 |
| Off-farm income | The proportion of off-farm income to rural households’ total income per capita | 0.323 | 0.175 |
| Education | The average schooling year of rural people (year) | 6.868 | 1.503 |
| Ploughing | The rate of land ploughed by machines | 0.401 | 0.243 |
| Sowing | The rate of land sowed by machines | 0.234 | 0.254 |
| Harvesting | The rate of land harvested by machines | 0.144 | 0.245 |
| Variables | Model (1) | Model (2) | Model (3) | Model (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adjustment coefficients | −0.184 (−4.19) *** | −0.170 (−4.27) *** | −0.170 (−3.98) *** | −0.224 (−4.87) *** |
| Long-run coefficients | ||||
| Farm machine use | −2.818 (−4.88) *** | |||
| Ploughing | −1.194 (−2.27) ** | |||
| Sowing | −1.256 (−2.83) *** | |||
| Harvesting | −2.876 (−6.95) *** | |||
| Labour | 0.215 (0.93) | 0.377 (1.43) | 0.050 (0.18) | 0.409 (2.04) ** |
| Fertiliser | 0.165 (1.17) | 0.061 (0.44) | 0.115 (0.80) | 0.086 (0.71) |
| Transportation | −5.136 (−8.92) *** | −5.907 (−8.94) *** | −7.162 (−9.23) *** | −2.991 (−7.56) *** |
| Off-farm income | −0.362 (−1.54) | −0.291 (−1.08) | −0.576 (−2.39) ** | −0.451 (−2.00) ** |
| Education | 0.083 (1.67) * | 0.018 (0.31) | 0.026 (0.45) | −0.004 (−0.08) |
| Short-run coefficients | ||||
| Farm machine use | 0.587 (1.34) | |||
| Ploughing | 0.284 (1.53) | |||
| Sowing | 3.717 (1.07) | |||
| Harvesting | −0.079 (−0.07) | |||
| Labour | 0.191 (1.40) | 0.105 (0.70) | 0.119 (0.78) | 0.130 (0.93) |
| Fertiliser | 0.123 (3.05) *** | 0.104 (2.03) ** | 0.135 (2.71) *** | 0.158 (3.25) *** |
| Transportation | 0.539 (2.24) ** | 0.590 (2.14) ** | 0.942 (2.66) *** | 0.432 (1.88) * |
| Off-farm income | 0.014 (0.31) | −0.005 (−0.07) | 0.063 (1.06) | 0.067 (1.16) |
| Education | −0.071 (−1.81) * | −0.040 (−0.90) | −0.052 (−1.34) | 0.047 (1.09) |
| Constant | −0.085 (−3.34) *** | 0.094 (4.19) *** | 0.145 (4.91) *** | 0.014 (0.63) |
| Log Likelihood | 655.712 | 651.438 | 667.195 | 663.056 |
| Observation | 952 | 952 | 952 | 952 |
| Variable | Cobb–Douglas Form | Translog Form |
|---|---|---|
| Draft animal use | 0.047 (3.707) *** | 0.270 (3.386) *** |
| Farm machine use | −0.041 (−2.086) ** | −0.130 (−1.129) |
| Labour | −0.044 (−0.883) | −0.716 (−2.381) ** |
| Fertiliser | 0.048 (1.918) * | 0.735 (4.275) *** |
| t | 0.064 (37.263) *** | 0.039 (4.600) *** |
| Draft animal use × Draft animal use | 0.008 (0.730) | |
| Draft animal use × Farm machine use | 0.010 (0.614) | |
| Draft animal use × Labour | 0.024 (1.011) | |
| Draft animal use × Fertiliser | 0.048 (2.184) ** | |
| Draft animal use × t | −0.008 (−6.994) *** | |
| Farm machine use × Farm machine use | −0.010 (−0.586) | |
| Farm machine use × Labour | −0.080 (−1.367) | |
| Farm machine use × Fertiliser | −0.078 (−2.586) *** | |
| Farm machine use × t | 0.010 (6.275) *** | |
| Labour × Labour | −0.038 (−0.261) | |
| Labour × Fertiliser | −0.309 (−4.599) *** | |
| Labour × t | 0.036 (10.034) *** | |
| Fertiliser × Fertiliser | 0.137 (3.147) *** | |
| Fertiliser × t | −0.001 (−0.388) | |
| t × t | −0.002 (−9.948) *** | |
| Constant | −1.998 (−22.473) *** | −0.889 (−2.322) ** |
| R2 | 0.919 | 0.953 |
| Likilyhood Ratio (LR) test | Chi2(15) = 525.080 *** | |
| AIC | −460.661 | −955.738 |
| BIC | −431.336 | −853.099 |
| Observation | 980 | 980 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Ma, W.; Li, G. Draft Animals, Farm Machines and Sustainable Agricultural Production: Insight from China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10093015
Zhou X, Ma W, Li G. Draft Animals, Farm Machines and Sustainable Agricultural Production: Insight from China. Sustainability. 2018; 10(9):3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10093015
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xiaoshi, Wanglin Ma, and Gucheng Li. 2018. "Draft Animals, Farm Machines and Sustainable Agricultural Production: Insight from China" Sustainability 10, no. 9: 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10093015
APA StyleZhou, X., Ma, W., & Li, G. (2018). Draft Animals, Farm Machines and Sustainable Agricultural Production: Insight from China. Sustainability, 10(9), 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10093015





