A Quantitative Assessment of Comprehensive Ecological Risk for a Loess Erosion Gully: A Case Study of Dujiashi Gully, Northern Shaanxi Province, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- How can an evaluation system that fully reflects regional ecological risks be constructed?
- (2)
- How can risk management categories based on the results of risk assessment be conducted to promote regional sustainability?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source and Processing
2.3. Ecological Risk Assessment Framework
2.3.1. Risk Probability
2.3.2. Sensitivity
2.3.3. Impairment
3. Results
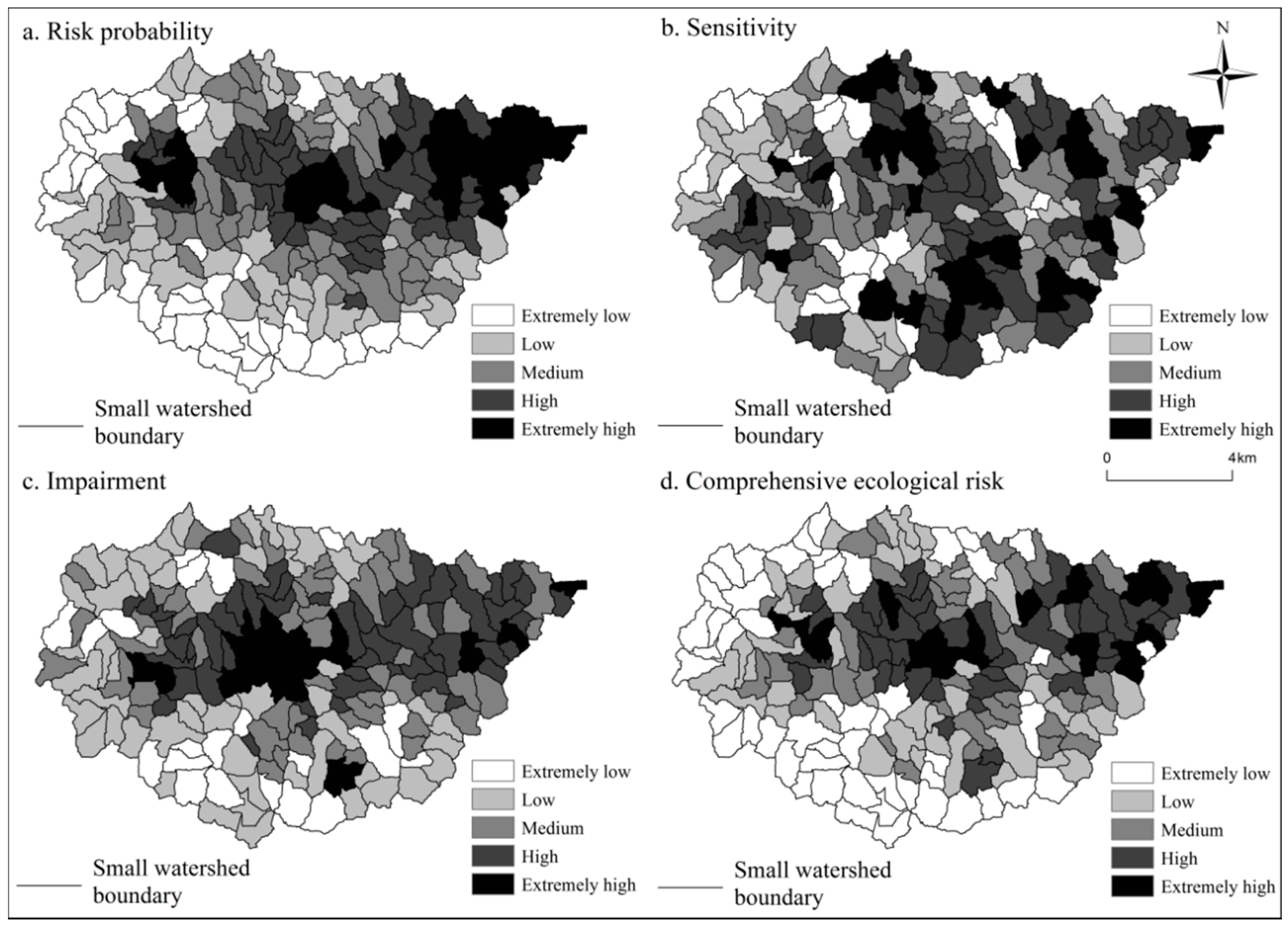
3.1. Spatial Differences in Criteria Layers
3.2. Spatial Differences in Comprehensive Ecological Risk and Analysis of the Section Line
3.3. Risk Management Categories
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, B.J. Geography: From knowledge, science to decision making support. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 1923–1932. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; You, N.S.; Meng, J.J. Dynamic ecological risk assessment and management of land use in the middle reaches of the Heihe River based on landscape patterns and spatial statistics. Sustainability 2016, 8, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.F.; Peng, J.; Wang, Y.L.; Wu, W.B.; Yang, P.; Liu, Y.X.; Song, Z.Q.; Hsueh, I.C. Characteristics of landscape system in the context of global change. Prog. Geogr. 2017, 36, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Forbes, V.E.; Calow, P. Developing predictive systems models to address complexity and relevance for ecological risk assessment. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2013, 9, E75–E80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollino, C.A.; Thomas, C.R.; Hart, B.T. Introduction to models and risk assessment. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2012, 18, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Dang, W.X.; Liu, Y.X.; Zong, M.L.; Hu, X.X. Review on landscape ecological risk assessment. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 664–677. [Google Scholar]
- Suter, G.W.; Norton, S.B.; Barnthouse, L.W. The evolution of frameworks for ecological risk assessment from the Red Book ancestor. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2003, 9, 1349–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, W.G. Twenty years before and hence: Ecological risk assessment at multiple scales with multiple stressors and multiple endpoints. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2003, 9, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zong, M.L.; Hu, Y.N.; Liu, Y.X.; Wu, J.S. Assessing Landscape ecological risk in a mining city: A case study in Liaoyuan City, China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 8312–8334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzabeygi, M.; Abbasnia, A.; Yunesian, M.; Nodehi, R.N.; Yousefi, N.; Hadi, M.; Mahvi, A.H. Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment in drinking water of Sistan and Baluchistan, Southeastern Iran. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2017, 23, 1893–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protano, C.; Zinna, L.; Giampaoli, S.; Romano, S.V.; Chiavarini, S.; Vitali, M. Heavy Metal Pollution and Potential Ecological Risk in Rivers: A Case Study from Sounthern Italy. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toixcol. 2014, 92, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.F.; Wang, R.S.; Li, Z.G.; Li, F.; Wu, J.S.; Huang, J.L.; Yu, Y.Y. Comprehensive assessment of urban ecological risks: The case of Huaibei City. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 6204–6214. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.Y.; Peng, J.; Zhao, S.Q.; Hu, Z.C.; Wang, Y.L. Ecological risk assessment of landslide disasters in mountainous areas of Southwest China: A case study in Dali Bai Autonomous Prefecture. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 1544–1561. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Q.W.; Zhang, X.W.; Ma, H.K.; Wu, J.S. Review of landscape ecological risk and an assessment framework based on ecological services: ESRISK. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 843–855. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Z.Y.; Xu, X.G.; Lin, H.P.; Wang, X.L. Regional ecological risk assessment of in the Liaohe River Delta wetlands. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2001, 21, 365–373. [Google Scholar]
- Malekmohammadi, B.; Blouchi, L.R. Ecological risk assessment of wetland ecosystems using multi criteria decision making and geographic information system. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 41, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.H. Ecological risk assessment of the Yulin coal mining area based on the petarmethod. Resour. Sci. 2011, 33, 1914–1923. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.H.; Wang, L.; Li, J.Y. Regional ecological risk assessment in catchment area along the Weihe River based on GIS. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2009, 29, 5523–5534. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, J.F.; Guo, J.K. The ecological risk assessment of Taihu Lake watershed. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 2896–2906. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Xie, X.P. Regional ecological risk assessment in Nansi Lake based on RS and GIS. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.L.; Wang, P.; Huang, H.S. Ecological risk assessment of land use change in the Poyang Lake eco-economic zone, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 328–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Yang, J.X.; Tang, W.W. Spatially explicit landscape-level ecological risks induced by land use and land cover change in a national ecologically representative region in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 14192–14215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, J.P. A long-term site study for the ecological risk migration of landscapes and its driving forces in the Sanjiang Plain from 1976 to 2013. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 3729–3740. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, X.P.; Chen, X.; Kong, F.X. Ecological risk assessment of an ecological migrant resettlement region based on landscape structure: A case study of Hongsibu in Ningxia. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 2672–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Ghulam, A.; Kung, H. Ecological risk assessment and prediction of Ebinur Lake region based on Land use/Land cover change. China Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 3465–3474. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.N.; Zhu, J.; Wu, S.H.; Zhou, S.L.; Li, B.J. Assessment of Land Ecological Risks Driven by Multi-sources: A Case Study of Sheyang County, Jiangsu Province. J. Nat. Resour. 2016, 31, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.W.; Fang, X.N. Landscape sustainability and landscape sustainability science. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 2453–2459. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, H.; Chen, H.; Mao, N.Z.; Nie, X. Landscape sustainable development in highly sensitive ecological fragile areas. Res Sci. 2018, 40, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.Y.; Sun, Y.J.; Wu, L.X. Comprehensive evaluation of ecological risk of land during 1990–2012 in Yulin City. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2017, 25, 656–664. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Shi, P.J.; Wu, N. Spatial identification of ecological risk and development balance in loess hilly and gully region: A case study of Lanzhou. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2018, 38, 380–389. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Lo´pez-Carr, D.; Tan, Y.; Liang, X.Y. China’s Grain for Green policy and farm dynamics: Simulating household land-use responses. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2016, 16, 1147–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Marter-Kenyon, J.; López-Carr, D.; Liang, X.Y. Land cover and landscape changes in Shaanxi Province during China’s Grain for Green Program (2000–2010). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Xie, P.; Liu, Y.X.; Hu, X.X. Integrated ecological risk assessment and spatial development trade-offs in low-slope hilly land: A case study in Dali Bai Autonomous Prefecture, China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 1747–1761. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.S.; Mao, J.Y.; Lin, Q.; Li, J.C. Urban growth boundary based on the evaluation of habitat quality: Taking the Yangtze River Delta as an Example. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2017, 37, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.F.; Wang, S.; Ren, L.; Zeng, Z.Z. Spatial distribution of rainstorm hazard risk based on EW-AHP in mountainous scenic area of China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2017, 23, 925–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.T.; Yang, L.; Cai, G.J.; Mo, B.R.; Chai, C.S. A quantitative health evaluation of an eco-economy in the Semi-Arid Loess Plateau of China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2015, 21, 1884–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.X.; Wang, Y.L.; Peng, J.; Zhang, T.; Wei, H. Urban landscape ecological risk assessment based on the 3D framework of adaptive cycle. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 1052–1067. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.Y.; He, D.J.; You, W.B.; Deng, X.P.; Tan, Y.; Ji, Z.R. Disaster ecological risk assessment in Dongshan Island: Spatio-temporal evolution. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 5027–5037. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhong, Y.X.; Feng, X.H.; Hu, L.T.; Zheng, L. Ecological risk pattern of Poyang Lake basin based on land use. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 7850–7857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, R.L.; Hunsaker, C.T.; O’neill, R.V.; Jackson, B.L. Ecological risk assessment at the regional scale. Ecol. Appl. 1991, 1, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.G.; He, C.Y.; Li, X.B. Landscape ecological risk assessment of natural/semi-natural landscapes in fast urbanization regions—A case study in Beijing, China. J. Nat. Resour. 2008, 23, 33–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C.P.; Jiang, B.; Kinzig, A.P.; Lee, K.N.; Ouyang, Z.Y. Linking ecosystem characteristics to final ecosystem services for public policy. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, S.; Rebecca, C.K.; Spencer, W. InVEST 3.3.0 User’s Guide[M/OL]. 2015. Available online: http://data.natural capital project.org/nightly-build/invest-users-guide/html/habitat quality.html (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Mei, Y.J. The Study on the Quantification and Integrated Assessment of Landscape Services in the Fragile Area: The Study of Mizhi County of Shannxi Province; Northwest University: Xi’an, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.F.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.C. Spatio-temporal variation on habitat quality and its mechanism within the transitional area of the Three Natural Zones: A case study in Yuzhong county. Geogr. Res. 2018, 37, 419–432. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Huang, S.L. Landscape ecological risk responses to land use change in the Luanhe River Basin, China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 16631–16652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Pu, R.L.; Gong, H.B.; Ye, M.Y.; Feng, B.X. Evolution characteristics of landscape ecological risk patterns in coastal zones in Zhejiang Province, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, K.; Ding, Q.L.; Men, M.X.; Xu, H. Spatial distribution of land use and its relationship with terrain factors in hilly area. Geogr. Res. 2015, 34, 909–921. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Q.; Liu, D.; Liu, X.W. Ecological risk assessment and spatial prevention tactic of land destruction in mining city. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2013, 29, 245–254. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.N.; Zhang, T.Z. Integration of ecosystem services into ecological risk assessment for implementation in ecosystem based river management: A case study of the Yellow River, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2013, 19, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.D.; Wang, J.; Fu, B.J.; Qiu, Y. Land-use change in a small catchment of northern Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2001, 86, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Target Layer | Criteria Layer | Index Layer/Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Comprehensive ecological risk | Risk probability | Landslide hazard risk/0.25 |
| Flood hazard risk/0.23 | ||
| Soil pollution risk/0.35 | ||
| External pressure risk/0.17 | ||
| Sensitivity | Habitat quality/1 | |
| Impairment | Landscape loss index/0.62 | |
| Population density/0.22 | ||
| Food production/0.16 |
| Threat Factor | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Habitat Type | Habitat | Residential | Transportation Corridors | Industrial Land | Wasteland | Farmland |
| Water body | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.85 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| Orchard | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Forest | 1 | 0.75 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.75 |
| Grassland | 0.6 | 0.55 | 0.5 | 0.55 | 0.8 | 0.35 |
| Max-distance/km | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.25 | |
| Weight | 1 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.05 | 0.2 | |
| Name | Calculation Methods |
|---|---|
| Landscape fragmentation index (Ci) | |
| Landscape isolation index (Si) | |
| Landscape dominance index (DOi) | |
| Landscape disturbance index (Ei) | |
| Landscape vulnerability index (Fi) | Construction land (grade 1; lowest), forest (grade 2), grassland (grade 3), orchard (grade 4), farmland (grade 5), water body (grade 6) and wasteland (grade 7; highest) [37] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Liang, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Mao, N. A Quantitative Assessment of Comprehensive Ecological Risk for a Loess Erosion Gully: A Case Study of Dujiashi Gully, Northern Shaanxi Province, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10093239
Liu D, Liang X, Chen H, Zhang H, Mao N. A Quantitative Assessment of Comprehensive Ecological Risk for a Loess Erosion Gully: A Case Study of Dujiashi Gully, Northern Shaanxi Province, China. Sustainability. 2018; 10(9):3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10093239
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Di, Xiaoying Liang, Hai Chen, Hang Zhang, and Nanzhao Mao. 2018. "A Quantitative Assessment of Comprehensive Ecological Risk for a Loess Erosion Gully: A Case Study of Dujiashi Gully, Northern Shaanxi Province, China" Sustainability 10, no. 9: 3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10093239
APA StyleLiu, D., Liang, X., Chen, H., Zhang, H., & Mao, N. (2018). A Quantitative Assessment of Comprehensive Ecological Risk for a Loess Erosion Gully: A Case Study of Dujiashi Gully, Northern Shaanxi Province, China. Sustainability, 10(9), 3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10093239





