2.1. Resource-Based View (RBV)
The Resource-Based View (RBV) perceives that its resources fundamentally control an organization’s success. These resources are named assets or capabilities. The assets can be tangible or intangible [
38], though the capabilities are intangible, including abilities and information [
39]. Besides, the capital equipment, learning and abilities of representatives, and firm goodwill are the resources of a firm [
40]. As indicated by RBV, the principal factors in deciding the sustainable competitive advantage for a firm are its resources [
40]. These general important and rare intangible resources are vital for making and keeping up a competitive advantage. Because of these particular resources, a firm progresses towards sufficiently proficient for creating and conveying creative as well as top-notch items and administrations, and it also makes a distinction among other company’s products [
40,
41]. RBV is given in
Figure 2, which shows that resources are based on tangible and intangible, which must be heterogeneous and immobile. These resources finally influence competitive advantage.
In addition, the RBV centres around the match between organizational capabilities and available opportunities. This clarifies the disappointment of visual failure of organizational systems. It turns out to be genuine where there is a mismatch between organizational capabilities and opportunities. In the present study, social and technological challenges are the resources of SMEs. Better management of social responsibility, better values and beliefs of employees, IT managerial resources and better IT implementation are the resources of the company. These resources are increasing the sustainable competitive advantage among SMEs.
Alluding to the consequences of asset-based perspective of the firm, it accentuates on the significance of resources for making and supporting competitive advantage. In this manner, organizations ought to have the potential for distinguishing and making appropriate utilization of their accessible asset [
42]. Further to this, Barney [
43] referenced that the inward and outer condition both have been significantly underscored. Consequently, organizations ought to get most refreshed data identified from candidates, markets and clients. In conclusion, the third consequence of RBV on organizational success is for organizational capabilities. The organizational capabilities incorporate people with specific range of abilities and experience, data and process, in case, if ultimately used can deliver creative results with high quality for surpassing client desires [
44]. Likewise, it is entrenched that the organizational capabilities upgrade the esteem of accessible asset for their viable use [
45,
46]. As per Teece, Pisano and Shuen [
39] the sustainable competitive advantage creation links with a dynamic process for organizations to develop and get the dynamic business condition. Therefore, this sustainable competitive advantage increases sustainable business performance among SMEs with the help of internal resources, including social and technological factors. Additionally, it is recommended that the improvement of dynamic capabilities procedures need to be founded on the learning along with organizational learning exercises [
47,
48].
Further to this, one of the complications of RBV on business success is identified with organizational capabilities. The organizational capabilities include human asset (that are skilled, capable, and experienced), data, and specific procedures that could be responsively used to deliver high-quality results, for example, enhanced business success and different advancements [
44]. Corporate enterprise is a procedure, and it has stable connection with the human resource that at last, helps organizations to enhance their sustainable business performance.
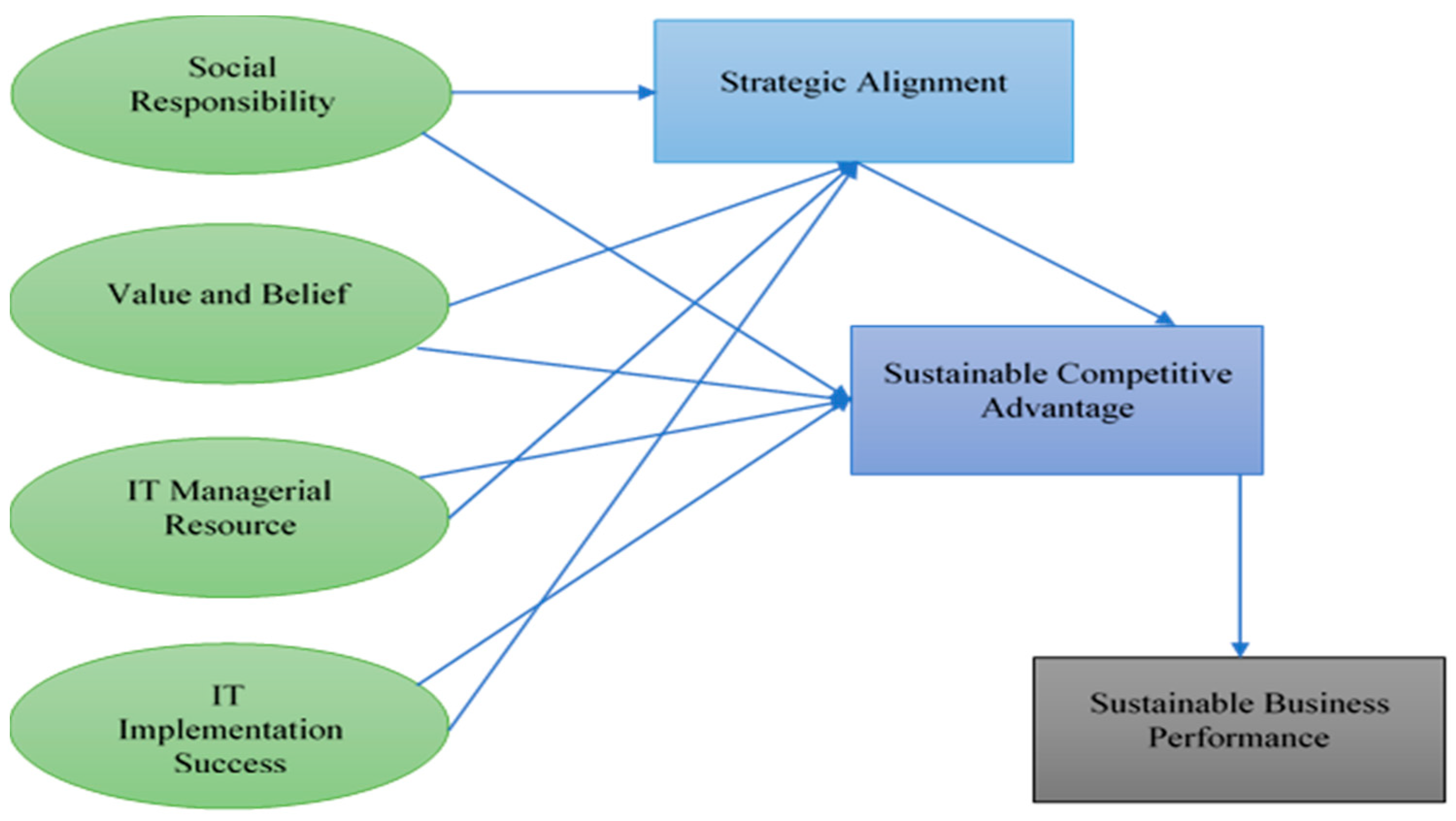
Essentially, the objective of this study is to examine the roles of social and technological challenges in achieving a sustainable competitive advantage and sustainable business performance. In consistent with RBV, social and technological factors are the resources of a company, which influence positively on sustainable competitive advantage, and ultimately increase the sustainable business performance. These variables have been underpinned by the RBV theory, as suggested in the literature, shown in
Figure 3.
According to RBV, the key features in determining the sustainable competitive advantage for an organization are its resources, both internal as well as external [
40]. These rare, valuable, and inimitable intangible strategic resources are the engine for creating as well as sustaining competitive advantage. Because of these unique resources, a firm becomes proficient enough for producing as well as delivering innovative and high-quality products and services, and it creates a difference [
41]. Moreover, the RBV emphasizes the available match between organizational capabilities as well as opportunities. This clarifies that the failure for blind imitation of organizational strategies becomes true where there is a mismatch between organizational capabilities and existing opportunities.
Makadok [
42] described that the essence of RBV process is to consider the use of resources at the completest to build up the unique core competencies for the accomplishment of competitive advantage. For attaining the desired competitive strategic position, firms can develop their competencies by observing into factors such as human competencies, internal organizational strategies, regulations as well as suitable information sources [
41]. In the context of this study, IT implementation, IT managerial resource, social responsibility, values and beliefs are the core competencies of any organization for a competitive advantage, which is crucial for sustainable business performance.
2.2. Hypotheses Development
The success of any businesses depends on having some advantages compared to their competitors. Therefore, the key objective of strategy is to attain a competitive advantage as well as performance [
49,
50]. For achieving this goal, specific strategies and challenges, such as social responsibility, values and beliefs, IT managerial resources, IT implementation success and strategy alignment to gain a competitive advantage in a competitive environment are needed. In any case, regardless of whether businesses are competent to pick up a competitive advantage and accomplish a more elevated amount of profitability, they lose this competitive advantage after some time. This is because their systems are generally duplicated.
Accomplishing a competitive advantage empowers a firm to raise effective obstructions and accomplish a sustainable competitive advantage [
51]. In any case, anticipating imitation does not keep going forever. Along these lines, the firm will pick up the greatest profit by any competitive advantages. Accomplishing better development basically needs specific core values. The entrance to some competitive advantage would be essential for building this solid and separated centre [
52].
As indicated by Prahalad and Hamel [
46], “similar formidable” standards for item cost and quality combine to that of Western and Japanese organizations. These standards are increasingly imperative as qualifying criteria for success in the rivalry and imperative as sources of sustainable competitive advantage. They further recommend that the genuine wellspring of sustainable competitive advantage is identified with an organization’s capacity to unite innovations and aptitudes generation in abilities that enable the business to adjust rapidly to growing openings. Kanterholds [
53,
54] proposed that organizations must constantly concentrate on their skills, put resources into improvement, and de-underline exercises that do not add value. Therefore, they will be fruitful. Achievement in changing the conditions is ensured by characterizing the capabilities and sorting out it to help and expand them.
Onkvisit and Shaw [
55] argue that organization in the previous decades had contributed to turning into lean and adaptable to react quickly to condition and market changes. They likewise benchmarked continuously to accomplish the best practice and outsourced to accomplish efficiencies. The companies are prominent for inferring competitive advantage by operational adequacy. These ventures have blown-up in securing sustainable competitive advantage despite the fact that they have prevailed with regards to accomplishing operational enhancements, effectiveness and competitive advantage [
55]. To gain sustainable competitive advantage, social responsibility, values and beliefs, IT managerial resources, IT implementation success and strategy alignment are needed.
Various researchers work on the social responsibility of companies [
56,
57,
58,
59,
60,
61]; however, these studies misses with the roles of achieving a competitive advantage and sustainable business performance. It is found that the social responsibility of organization affects sustainable competitive advantage [
62,
63,
64,
65]. Better social responsibility achievement increases the competitive advantage of companies. However, lose control of social responsibility decreases the competitive advantage.
While the job of business, society continues changing after some time, there has been no concurrence on what social responsibility remains among the spectators or to what degree is the limit of social responsibility as it is interpreted differently by individuals. What social responsibility shows, among experts that actualizes it inside their organizations contrasts from what it intends to experts trying to establish it as a discipline [
66].
Organization’s responsibilities in creating nations are characterized distinctively dependent on the social (particularly national setting) [
66]. For instance, social responsibility among organizations in Malaysia is halfway persuaded by religious conviction [
66], in Argentina, it is halfway impacted by the monetary emergency in 2001 [
67], while corporate social responsibility in South Africa centre around the issues of racial imbalance because of the one of a kind inheritance of politically-sanctioned racial segregation. Malaysian organizations generally centre on beneficent exercises that revolve around the Muslim and Chinese religious occasions, while South African nations centre on the strengthening of the black individuals of the country. Thus, it may be said that corporate social responsibility or social responsibility implies distinctive things to various individuals from various countries [
66]. All these factors have significant influence to gain or sustain competitive advantage.
Despite the fact that no universal definition has been available for social responsibility, yet numerous private organizations allude to social responsibility as an approach to coordinate the ecological, social and the monetary complications of their business exercises in the regularly developing business world [
68,
69]. Therefore, it ends up obvious for business organizations to be dependable to stay current, and it participates in-light of the differed partners. In the present time of modern globalization, companies and business organizations have gone past the restriction of their country state and this prevalence of the global organization past the restriction of their country has brought about an increment in the interest for greater responsibility and straightforward worldwide business [
68].
Business organizations challenge to react to a trustworthy responsibility agenda [
68]. Globalization and the challenge for restricted resources have kept corporate social responsibility in the focal point of discussion among business network and Government. Numerous advocates were guaranteed in the talk on corporate social responsibility in the western world, where it is guaranteed that corporate social responsibility is not a greater amount of corporate philanthropy, it is fairly an essential logic for extensive, medium and little ventures to gain comparative advantage and sustainable business performance among various companies [
68]. Various studies proved that social responsibility has important roles in achieving a sustainable competitive advantage [
70,
71]. In line with social responsibility, values and beliefs are equally important in achieving sustainable competitive advantage.
Values and beliefs are important roles to gain sustainable competitive advantage, and these are the challenges in SMEs. The values and beliefs of organizational individuals tremendously affect numerous measurements of IT in organizations. These incorporate the method for overseeing IT in organizations. For instance, if business administrators do not trust that IT is strategic this may characterize how they oversee and manage IT-related issues [
72]. This measurement is a point of worry about the values and beliefs of organizational members because it influences in achieving a sustainable competitive advantage. Values and beliefs can fundamentally shape the career, including conduct and practices. These beliefs are moulded all through one’s profession dependent on the experience which one has with IT. Real impacts are probably going to originate from experience with IT both from past work environments and from current industry or the organization. Values and beliefs ought not to be mistaken for culture. While the idea of culture is present in the administration classification, actually begins from human conduct [
73,
74,
75,
76]. Culture is an idea which includes values and beliefs, yet it is additionally moulded by stories, control frameworks, structures, and legislative issues. These culture issues have vital role in shaping competitive advantage. Singular values and beliefs are, for sure, a sufficient power to affect competitive advantage. Therefore, IT issues have a relationship with values and beliefs [
26] and competitive advantage.
Thus, better values and beliefs have the ability to resolve various IT challenges. Values and beliefs are one of the challenges in proper IT implementation. An attitude of organization towards new technology adoption has important challenge [
77]. There values and beliefs belong to the culture of organization. Culture of the organization has a significant link with technological adoption in which attitude has essential role and has an important link with achieving a competitive advantage [
78,
79,
80,
81].
H1: There is a relationship between social responsibility and sustainable competitive advantage.
H2: There is a relationship between values and beliefs and sustainable competitive advantage.
SMEs are also facing new technological challenges including IT managerial resources and IT implementation success. Good managerial resources for IT are vital to implement new technology, which is a challenge among most of the companies. This antecedent concerns the dimension of the association from business and IT managers in seller determination, contract transaction and the executives, and the structure as well as usage of the IT projects. Freeman and Sharp [
82] expressed that IT achievement, for the most part, reflects a successful connection between business supervisors and IT, and it is the principal supporter of effective seller relations. Chan et al. [
83] clarified that IT partners are bound to be trusted and counselled in the basic leadership process. They turn out to be increasingly mindful of both existing and new business openings and have the reasonable learning not merely in working inside existing markets, yet also with a recently developing business sector which has an impact on competitive advantage. A prior examination by Boynton et al. [
84] surveyed administrative IT learning of the business’ tasks and systems, found that more elevated amounts of administrative IT information emphatically anticipated a higher utilization of IT resources.
Better IT managerial resources have the ability to apply technology, which increases the competitive advantage, as it is proved from the literature that IT managerial resources, including IT skills, have a positive effect on competitive advantage [
85]. IT managerial resources are based on human resources and human resources have major roles in achieving a competitive advantage [
86,
87,
88,
89,
90]. Additionally, IT implementation is crucial. Implementation of new technology is more important when compared to simply introduce new technology.
Most of the companies are facing the issues while implementing a successful IT unit. Successful history of IT unit offers reliability to the IT unit and makes a complementary view of IT in the best administration [
91,
92,
93]. Likewise, it basically adds to the contribution of business directors in the arranging procedure [
94]. For the arrangement of business designs, two vital critical success factors found those are the confirmation of best administration in the IT division, and dependable administrations [
95]. Teo and Ang [
95] hypothesized that confirmation of best administration in IT builds their commitment to the strategic utilization of IT, making them bound to distribute appropriate asset for the arranging and improvement of IT applications.
H3: There is a relationship between IT managerial resources and sustainable competitive advantage.
H4: There is a relationship between IT implementation success and sustainable competitive advantage.
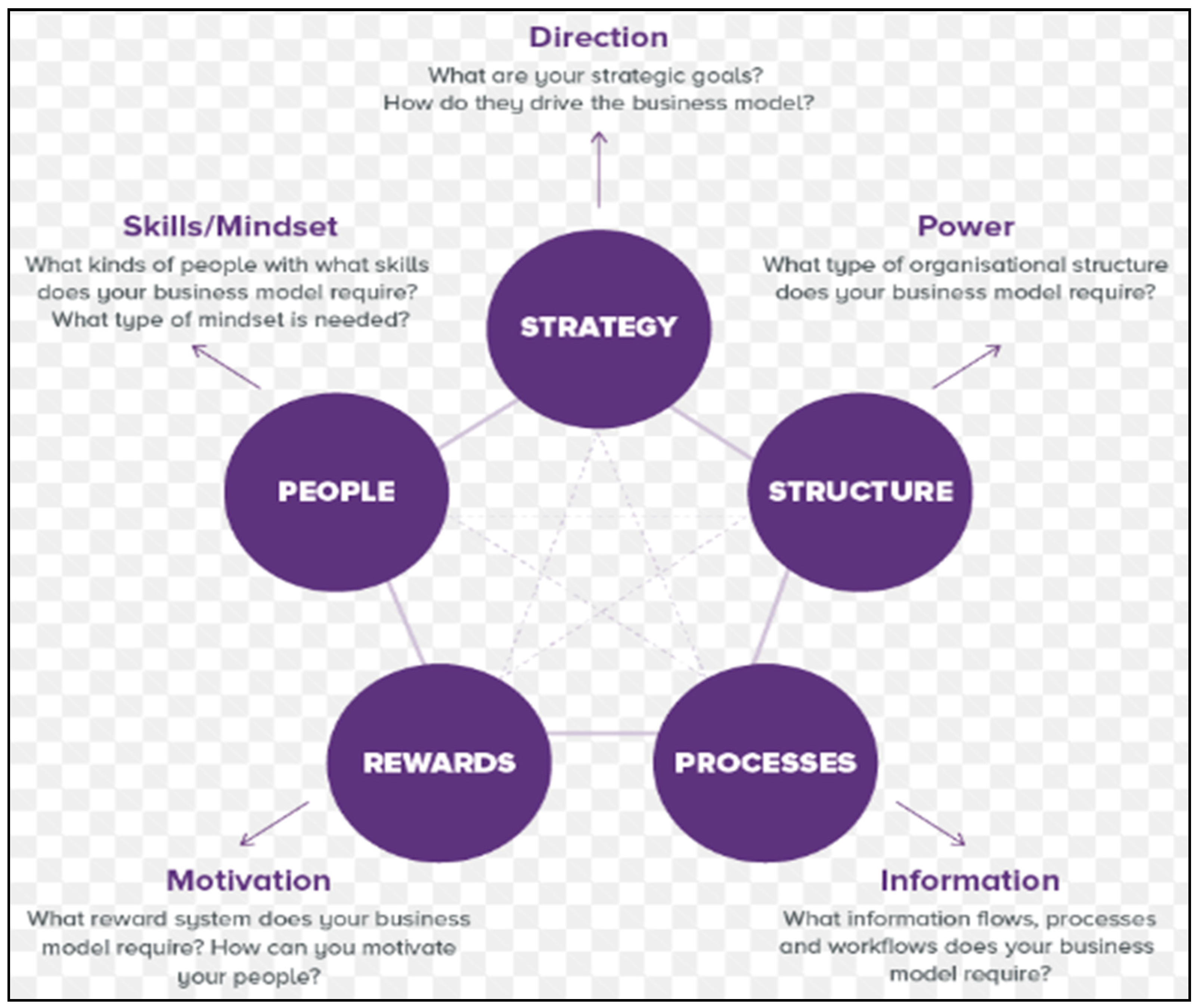
Consistent with social and new technological challenges, strategic alignment is one of the procedures and the outcome of connecting an organization’s structure as well as resources with its strategy and certain business environment. Strategic alignment comprises of matching skills to achieve certain goals regarding the plan of organization. It is a comprehensive procedure, which includes strategy, people, rewards and structure. It is a process which in line the organization structure with the business model that has a significant link with achieving a sustainable competitive advantage. Strategic alignment is shown in
Figure 4.
The alignment between the business strategy and its strategic decisions is a noticeable area of intention that stays on a high priority business, IT issues in which business and IT executives suffer [
96]. IT-business strategic alignment is viewed as a very imperative issue especially when IT turns into a fundamental piece of the business and is used for the utilization of unique business capabilities, consolidate organizations, rebuild businesses, and facilitate worldwide competition [
72].
Today’s Businesses are confronting a consistently expanding competition both at the local and worldwide level. Thus, it turns into a basic necessity for an organization to comprehend the nature of making a competitive advantage. A few researchers [
97,
98] showed that the literature proposes that the organizations could be competitive just if there is an alignment between the business and data innovation of the organizations. Therefore, alignment of strategies is most important to gain competitive advantage.
Various social and technological challenges in SMEs such as social responsibility, values and beliefs, IT managerial resources and IT implementation success can be managed through proper strategy alignment. IT managerial resources and IT implementation success challenge can be managed by allocating skilled people, and social issues can also be handled with aligning better strategies, which automatically increases the sustainable competitive advantage. As it is proved by different studies that strategic alignment and sustainable competitive advantage have a significant relationship [
99,
100,
101,
102].
In line with the above lines, increases in sustainable competitive advantage directly improve sustainable business performance. Literature suggested that companies should focus on competitive advantage in a competitive environment with a sustainable business performance at a satisfactory level. As it is found by various studies that sustainable competitive advantage has a significant relationship with sustainable business performance [
103,
104,
105]. Therefore, from the above discussion, the following hypotheses are proposed;
H4: There is a relationship between social responsibility and strategy alignment.
H5: There is a relationship between values and beliefs and strategy alignment.
H6: There is a relationship between IT managerial resources and strategy alignment.
H7: There is a relationship between IT implementation success and strategy alignment.
H8: Strategy alignment mediates the relationship between social responsibility and sustainable competitive advantage.
H9: Strategy alignment mediates the relationship between values and beliefs, and sustainable competitive advantage.
H10: Strategy alignment mediates the relationship between IT managerial resources and sustainable competitive advantage.
H11: Strategy alignment mediates the relationship between IT implementation success and sustainable competitive advantage.
H12: There is a relationship between strategy alignment and sustainable competitive advantage.
H13: There is a relationship between sustainable competitive advantage and sustainable business performance.