Hydrologic Alteration at the Upper and Middle Part of the Yangtze River, China: Towards Sustainable Water Resource Management Under Increasing Water Exploitation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
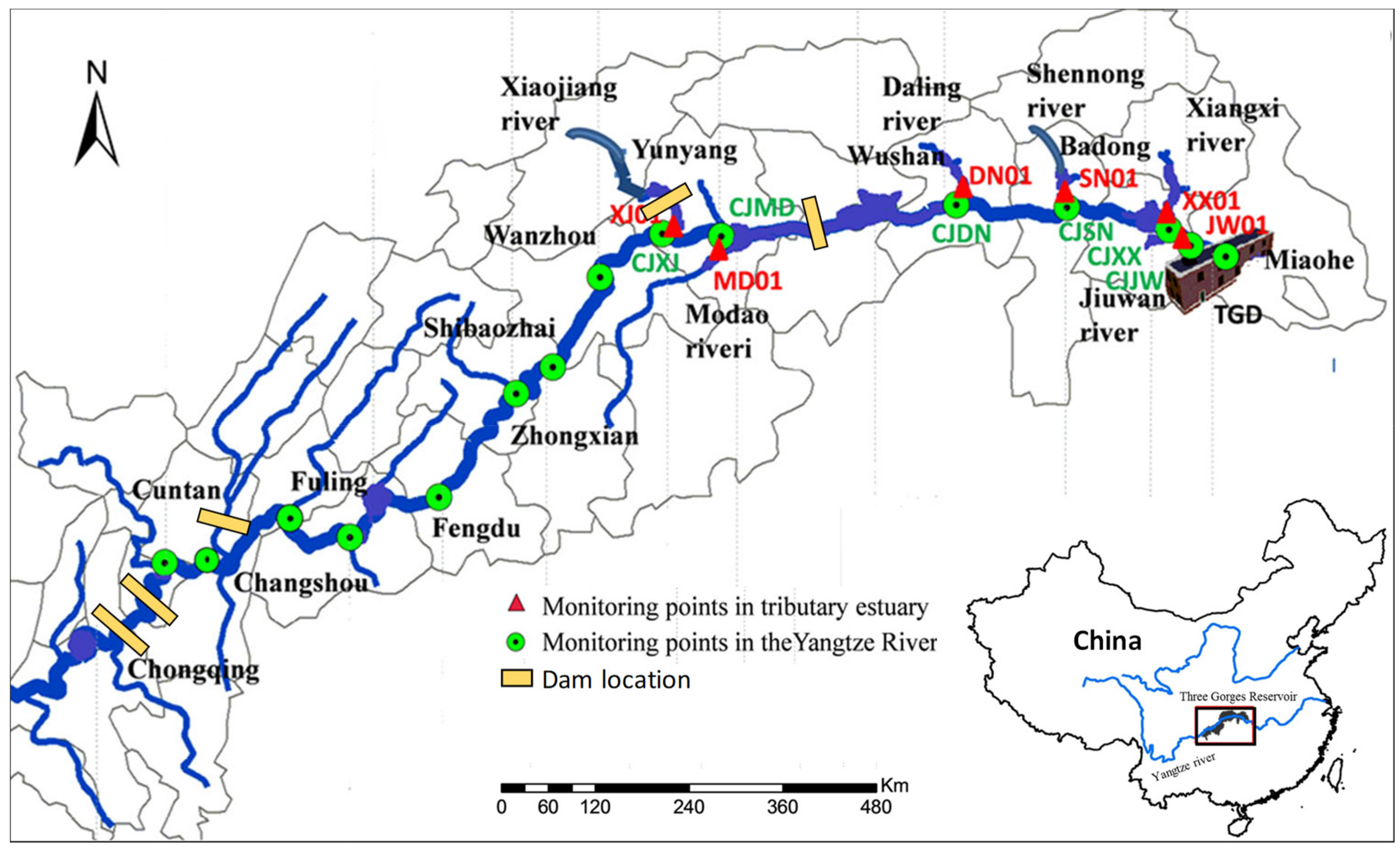
2. Study Area and Datasets
3. Methodology
Indicators of Hydrologic Alteration (IHA)
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Magnitude of Monthly Flow
4.2. Extreme Conditions
4.3. Timings of Annual Extreme Water
4.4. High and Low Pulses in Flow
4.5. Rate and Frequency of Flow Changes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.-J.; Jian-Yun, Z.; Shahid, S.; El Mahdi, A.; Rui-min, H.; Zhen-Xin, B.; Ali, M. Water resources management strategy for adaptation to droughts in China. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2012, 17, 923–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, N.; Pour, S.H.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, T.; Ahmed, K.; Chung, E.S.; Nawaz, N.; Wang, X. Spatial distribution of secular trends in rainfall indices of Peninsular Malaysia in the presence of long-term persistence. Meteorol. Appl. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Chung, E.-S.; Wang, X.-J.; Harun, S.B. Climate Change Uncertainties in Seasonal Drought Severity-Area-Frequency Curves: Case of Arid Region of Pakistan. J. Hydrol. 2019, 570, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Ismael, A.; Heryansyah, A.; Nawaz, N. Long Term Historic Changes in the Flow of Lesser Zab River, Iraq. Hydrology 2019, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardıçlıoğlu, M.; Kuriqi, A. Calibration of channel roughness in intermittent rivers using HEC-RAS model: Case of Sarimsakli creek, Turkey. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, D.E.; Craig, J.F.; Davidson, N.; Delany, S.; Seddon, M. Biodiversity impacts of large dams. Backgr. Pap. 2001, 1, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, J.M.; Lyu, S. The impact of water-intake for a tributary on the flow and saline intrusion in the lower Han River. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2017, 21, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billington, D.P.; Jackson, D.C.; Melosi, M.V. The History of Large Federal Dams: Planning, Design and Construction; US Department of the Interior, Bureau of Reclamation: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2005.
- Kuriqi, A.; Ardiçlioglu, M.; Muceku, Y. Investigation of seepage effect on river dike’s stability under steady state and transient conditions. Pollack Period. 2016, 11, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.D.; Postel, S.; Revenga, C.; Scudder, T.; Lehner, B.; Churchill, A.; Chow, M. Lost in development’s shadow: The downstream human consequences of dams. Water Altern. 2010, 3, 14–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sakaris, P.C. A review of the effects of hydrologic alteration on fisheries and biodiversity and the management and conservation of natural resources in regulated river systems. In Current Perspectives in Contaminant Hydrology and Water Resources Sustainability; InTech: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kuriqi, A.; Ardiçlioǧlu, M. Investigation of hydraulic regime at middle part of the Loire River in context of floods and low flow events. Pollack Period. 2018, 13, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriqi, A.; Pinheiro, A.; Sordo-Ward, A.; Garrote, L. Trade-off between environmental flow policy and run-of-river hydropower generation in Mediterranean climate. Eur. Water 2017, 60, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Kuriqi, A.; Rivaes, R.; Sordo-Ward, A.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Garrote, L. Comparison and validation of hydrological e-flow methods through hydrodynamic modelling. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference, Vienna, Austria, 23–28 April 2017; p. 13634. [Google Scholar]
- Petts, G.E. Instream Flow Science For Sustainable River Management. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2009, 45, 1071–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayes, D.S.; Brandle, J.M.; Seliger, C.; Zeiringer, B.; Ferreira, T.; Schmutz, S. Advancing towards functional environmental flows for temperate floodplain rivers. Sci Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olden, J.D.; Poff, N. Redundancy and the choice of hydrologic indices for characterizing streamflow regimes. River Res. Appl. 2003, 19, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Peng, W.; Huang, W.; Qu, X.; Singh, S.K. Quantitative Assessment of Flow Regime Alteration Using a Revised Range of Variability Methods. Water 2018, 10, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, E. Combined Effect of Danjiangkou Reservoir and Cascade Reservoirs on Hydrologic Regime Downstream. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2018, 23, 05018008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.; Kiesel, J.; Guse, B.; Fohrer, N. Towards an improved understanding of hydrological change–linking hydrologic metrics and multiple change point tests. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2018, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.D.; Tao, X.; Xu, C.Y.; Chen, X. A spatial assessment of hydrologic alteration caused by dam construction in the middle and lower Yellow River, China. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2008, 22, 3829–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnansaari, T.; Monk, W.; Baird, D.; Curry, R. Review of approaches and methods to assess Environmental Flows across Canada and internationally. DFO Can. Sci. Advis. Secr. Res. Doc. 2012, 39, 1–74. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, B.D.; Baumgartner, J.V.; Powell, J.; Braun, D.P. A method for assessing hydrologic alteration within ecosystems. Conserv. Biol. 1996, 10, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.; Liang, S. Effects of dams on river flow regime based on IHA/RVA. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2015, 368, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, B.; Yang, D.; Zhao, T.; Yang, H. Changes in the eco-flow metrics of the Upper Yangtze River from 1961 to 2008. J. Hydrol. 2012, 448–449, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.; Hou, J.; Qian, J. Assessment of multi-objective reservoir operation in the middle and lower Yangtze River based on a flow regime influenced by the Three Gorges Project. Ecol. Inform. 2017, 38, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriqi, A.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Sordo-Ward, A.; Garrote, L. Influence of hydrologically based environmental flow methods on flow alteration and energy production in a run-of-river hydropower plant. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 1028–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koel, T.M.; Sparks, R.E. Historical patterns of river stage and fish communities as criteria for operations of dams on the Illinois River. River Res. Appl. 2002, 18, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiau, J.-T.; Wu, F.-C. Feasible diversion and instream flow release using range of variability approach. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2004, 130, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Milliman, J.; Li, P.; Xu, K. 50,000 dams later: Erosion of the Yangtze River and its delta. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2011, 75, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, X.; Giorgi, F.; Chen, Z.; Yu, D. Climate effects of the Three Gorges Reservoir as simulated by a high resolution double nested regional climate model. Quat. Int. 2012, 282, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Lewis, Q.W.; Wu, J.; Huang, F. A framework to assess the cumulative impacts of dams on hydrological regime: A case study of the Yangtze River. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 3045–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Kuriqi, A.; Abubaker, S.; Kisi, O. Long-Term Trends and Seasonality Detection of the Observed Flow in Yangtze River Using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s Innovative Trend Method. Water 2019, 11, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. OECD Environmental Performance Reviews: China; OECD: Paris, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Beusen, A.H.; Van Beek, L.P.; Mogollón, J.M.; Ran, X.; Bouwman, A.F. Exploring spatiotemporal changes of the Yangtze River (Changjiang) nitrogen and phosphorus sources, retention and export to the East China Sea and Yellow Sea. Water Res. 2018, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Lu, X. Model of water regulation in the Yangtze River Basin and its effects using remote sensing techniques. In Proceedings of the IAHS International Commission on Continental Erosion Symposium, Chengdu, China, 11–15 October 2012; IAHS-AISH Publication: Wallingford, UK, 2012; Volume 356, pp. 235–243. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yang, D.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qi, Y. Characterizing spatiotemporal variations of hourly rainfall by gauge and radar in the mountainous Three Gorges region. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2014, 53, 873–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, J.; Song, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; He, B. Spatial and temporal patterns of stable water isotopes along the Yangtze River during two drought years. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Shepherd, M. Precipitation changes near Three Gorges Dam, China. Part I: A spatiotemporal validation analysis. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-S.; Wang, H.-J.; Saito, Y.; Milliman, J.; Xu, K.; Qiao, S.; Shi, G. Dam impacts on the Changjiang (Yangtze) River sediment discharge to the sea: The past 55 years and after the Three Gorges Dam. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, A. The Three Gorges Project on the Yangtze River in China. Geography 2004, 89, 111–126. Available online: jstor.org/stable/40573956.
- Yu, H.C.; Liu, H.D.; Huang, Z.Q.; Shi, G.C. Experimental study on time-dependent behavior of silty mudstone from the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2017, 21, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, Z.; Gupta, H.; Wu, G.; Li, D. Impact of the Three Gorges Dam on the hydrology and ecology of the Yangtze River. Water 2016, 8, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fang, X.; Wen, Z.; Chen, Q.; Ma, M.; Huang, Y.; Wu, S.; Yang, L. Spatio-Temporal Patterns and Impacts of Sediment Variations in Downstream of the Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.-H.; Xu, H.; Ji, D.-B.; Cui, Y.-J.; Liu, D.-F.; Song, L.-X. Characteristic of the water temperature lag in Three Gorges Reservoir and its effect on the water temperature structure of tributaries. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, R.; Richter, B.D. Application of the Indicators of hydrologic alteration software in environmental flow setting. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 1400–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Vogel, R.M.; Kroll, C.N.; Poff, N.L.; Olden, J.D. Development of representative indicators of hydrologic alteration. J. Hydrol. 2009, 374, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.D.; Baumgartner, J.V.; Braun, D.P.; Powell, J. A spatial assessment of hydrologic alteration within a river network. Regul. Rivers Res. Manag. Int. J. Devoted River Res. Manag. 1998, 14, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, R.M.; Sieber, J.; Archfield, S.A.; Smith, M.P.; Apse, C.D.; Huber-Lee, A. Relations among storage, yield, and instream flow. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.; Baumgartner, J.; Wigington, R.; Braun, D. How much water does a river need? Freshw. Biol. 1997, 37, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, W.; Cowan, T.; Briggs, P.; Raupach, M. Rising temperature depletes soil moisture and exacerbates severe drought conditions across southeast Australia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Opperman, J.J.; Tickner, D.; Speed, R.; Guo, Q.; Chen, D. Managing the Three Gorges Dam to implement environmental flows in the Yangtze River. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Q.; Yuan, J. Changes in dominant discharge and their influential factors in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River after the Three Gorges Dam impoundment. Adv. Water Sci 2018, 29, 331–338. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z. Dams altered Yangtze River phosphorus and restoration countermeasures. J. Lake Sci. 2018, 30, 865–880. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Fujiwara, M.; Winemiller, K.O.; Lin, P.; Li, M.; Liu, H. Regime shift in fish assemblage structure in the Yangtze River following construction of the Three Gorges Dam. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ran, X.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Wu, W.; Li, M.; Zang, J. Response of the sediment geochemistry of the Changjiang River (Yangtze River) to the impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 83, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.-M.; Edwards, J.; Guan, Z.; Lv, S.; Li, S.-Z.; Zhang, L.-J.; Feng, J.; Feng, N.; Zhou, X.-N.; Xu, J. Change patterns of oncomelanid snail burden in areas within the Yangtze River drainage after the three gorges dam operated. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2019, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-J.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Shamsuddin, S.; Oyang, R.-l.; Guan, T.-S.; Xue, J.-G.; Zhang, X. Impacts of climate variability and changes on domestic water use in the Yellow River Basin of China. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2017, 22, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Chang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, T. Influence of Three Gorges Dam on Downstream Low Flow. Water 2019, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Dai, Z.; Van Gelder, P.; Gao, J. Linking three Gorges Dam and downstream hydrological regimes along the Yangtze River, China. Earth Space Sci. 2015, 2, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Chen, P.; Deng, J.; Xu, Q.; Tang, R.; Feng, Z.; Xiong, Y. Estimations and changes of the dominant discharge in Three Gorges Reservoir channel. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sojka, M.; Jaskuła, J.; Wicher-Dysarz, J.; Dysarz, T. Assessment of dam construction impact on hydrological regime changes in lowland river–A case of study: The Stare Miasto reservoir located on the Powa River. J. Water Land Dev. 2016, 30, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Sun, T. Assessing effects of dam operation on flow regimes in the lower Yellow River. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Group 1: Magnitude of Monthly Water Flow Rates (m3/s) | Group 2: Magnitude and Duration of Annual Extreme Water Flow Rates (m3/s) | Group 3: Timing of Annual Extreme Water Flow Rates | Group 4: Frequency and Duration of High and Low Pulses | Group 5: Rate and Frequency of Water Flow Rate Changes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 1-Day minimum | Date of minimum | Low pulse count | Rise rate |
| February | 3-Day minimum | Date of maximum | Low pulse duration | Fall rate |
| March | 7-Day minimum | High pulse count | Number of reversals | |
| April | 30-Day minimum | High pulse duration | ||
| May | 90-Day minimum | |||
| June | 1-Day maximum | |||
| July | 3-Day maximum | |||
| August | 7-Day maximum | |||
| September | 30-Day maximum | |||
| October | 90-Day maximum | |||
| November | Base flow index (dimensionless) | |||
| December |
| Month | Cuntan Station | Miaohe Station | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Impact (m3/s) | Post-Impact (m3/s) | Relative Change (%) | Pre-Impact (m3/s) | Post-Impact (m3/s) | Relative Change (%) | |
| January | 4100 | 4110 | 0.24 | 4800 | 5180 | 7.92 |
| February | 3560 | 3580 | 0.56 | 4450 | 4370 | −1.80 |
| March | 4190 | 4120 | −1.67 | 5250 | 5011 | −4.55 |
| April | 4515 | 4475 | −0.89 | 6830 | 6200 | −9.22 |
| May | 7140 | 8120 | 13.73 | 10,300 | 10,540 | 2.33 |
| June | 12,400 | 11,250 | −9.27 | 15,200 | 15,350 | 0.99 |
| July | 20,600 | 27,900 | 35.44 | 23,700 | 30,140 | 27.17 |
| August | 19,800 | 19,700 | −0.51 | 22,700 | 21,130 | −6.92 |
| September | 19,300 | 19,650 | 1.81 | 22,350 | 22,300 | −0.22 |
| October | 12,100 | 9250 | −23.55 | 13,900 | 10,500 | −24.46 |
| November | 6795 | 5945 | −12.51 | 7800 | 7587 | −2.73 |
| December | 4590 | 4360 | −5.01 | 5690 | 5861 | 3.01 |
| IHA Factor | Cuntan Station | Miaohe Station | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Impact (m3/s) | Post-Impact (m3/s) | Relative Change (%) | Pre-Impact (m3/s) | Post-Impact (m3/s) | Relative Change (%) | |
| 1-day minimum | 3200 | 3240 | 1.25 | 3910 | 3625 | −7.29 |
| 3-day minimum | 3227 | 3287 | 1.86 | 3973 | 3817 | −3.93 |
| 7-day minimum | 3293 | 3371 | 2.37 | 4061 | 3930 | −3.23 |
| 30-day minimum | 3628 | 3569 | −1.63 | 4326 | 4317 | −0.21 |
| 90-day minimum | 3811 | 3878 | 1.76 | 4681 | 4791 | 2.35 |
| 1-day maximum | 46,500 | 45,500 | −2.15 | 45,800 | 54,400 | 18.78 |
| 3-day maximum | 41,,770 | 44,600 | 6.78 | 44,430 | 49,900 | 12.31 |
| 7-day maximum | 35,840 | 38,460 | 7.31 | 40,740 | 44,540 | 9.33 |
| 30-day maximum | 26,270 | 29,980 | 14.12 | 31,690 | 34,010 | 7.32 |
| 90-day maximum | 21,550 | 26,450 | 22.74 | 25,820 | 28,460 | 10.22 |
| Number of zero-days | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Base flow index | 0.30 | 0.31 | 3.19 | 0.31 | 0.30 | −1.56 |
| IHA Factor | Cuntan Station | Miaohe Station | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Impact | Post-Impact | Relative Change (%) | Pre-Impact | Post-Impact | Relative Change (%) | |
| Date of minimum | 46 | 38 | −17.39 | 41 | 47 | 14.63 |
| Date of maximum | 247 | 206 | −16.59 | 229 | 206 | −10.04 |
| IHA Factor | Cuntan Station | Miaohe Station | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Impact | Post-Impact | Relative Change (%) | Pre-Impact | Post-Impact | Relative Change (%) | |
| Low pulse count | 5 | 4 | −20 | 5 | 9 | 80 |
| Low pulse duration | 4 | 10.5 | 162.5 | 11 | 2 | −81.81 |
| High pulse count | 5 | 3 | −40 | 6 | 5 | −16.66 |
| High pulse duration | 6 | 14 | 133.33 | 5 | 5 | 0 |
| IHA Factor | Cuntan Station | Miaohe Station | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Impact (m3/s) | Post-Impact (m3/s) | Relative Change (%) | Pre-Impact (m3/s) | Post-Impact (m3/s) | Relative Change (%) | |
| Rise rate | 270 | 155 | −42.59 | 450 | 365 | −18.88 |
| Fall rate | −230 | −250 | 8.69 | −400 | −463 | 15.75 |
| Number of reversals | 124 | 77 | −37.90 | 131 | 143 | 9.16 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, R.; Kuriqi, A.; Abubaker, S.; Kisi, O. Hydrologic Alteration at the Upper and Middle Part of the Yangtze River, China: Towards Sustainable Water Resource Management Under Increasing Water Exploitation. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5176. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195176
Ali R, Kuriqi A, Abubaker S, Kisi O. Hydrologic Alteration at the Upper and Middle Part of the Yangtze River, China: Towards Sustainable Water Resource Management Under Increasing Water Exploitation. Sustainability. 2019; 11(19):5176. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195176
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Rawshan, Alban Kuriqi, Shadan Abubaker, and Ozgur Kisi. 2019. "Hydrologic Alteration at the Upper and Middle Part of the Yangtze River, China: Towards Sustainable Water Resource Management Under Increasing Water Exploitation" Sustainability 11, no. 19: 5176. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195176
APA StyleAli, R., Kuriqi, A., Abubaker, S., & Kisi, O. (2019). Hydrologic Alteration at the Upper and Middle Part of the Yangtze River, China: Towards Sustainable Water Resource Management Under Increasing Water Exploitation. Sustainability, 11(19), 5176. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195176







