Grazing Affects the Ecological Stoichiometry of the Plant–Soil–Microbe System on the Hulunber Steppe, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Discription of the Experimental Site
2.2. Sampling and Chemical Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
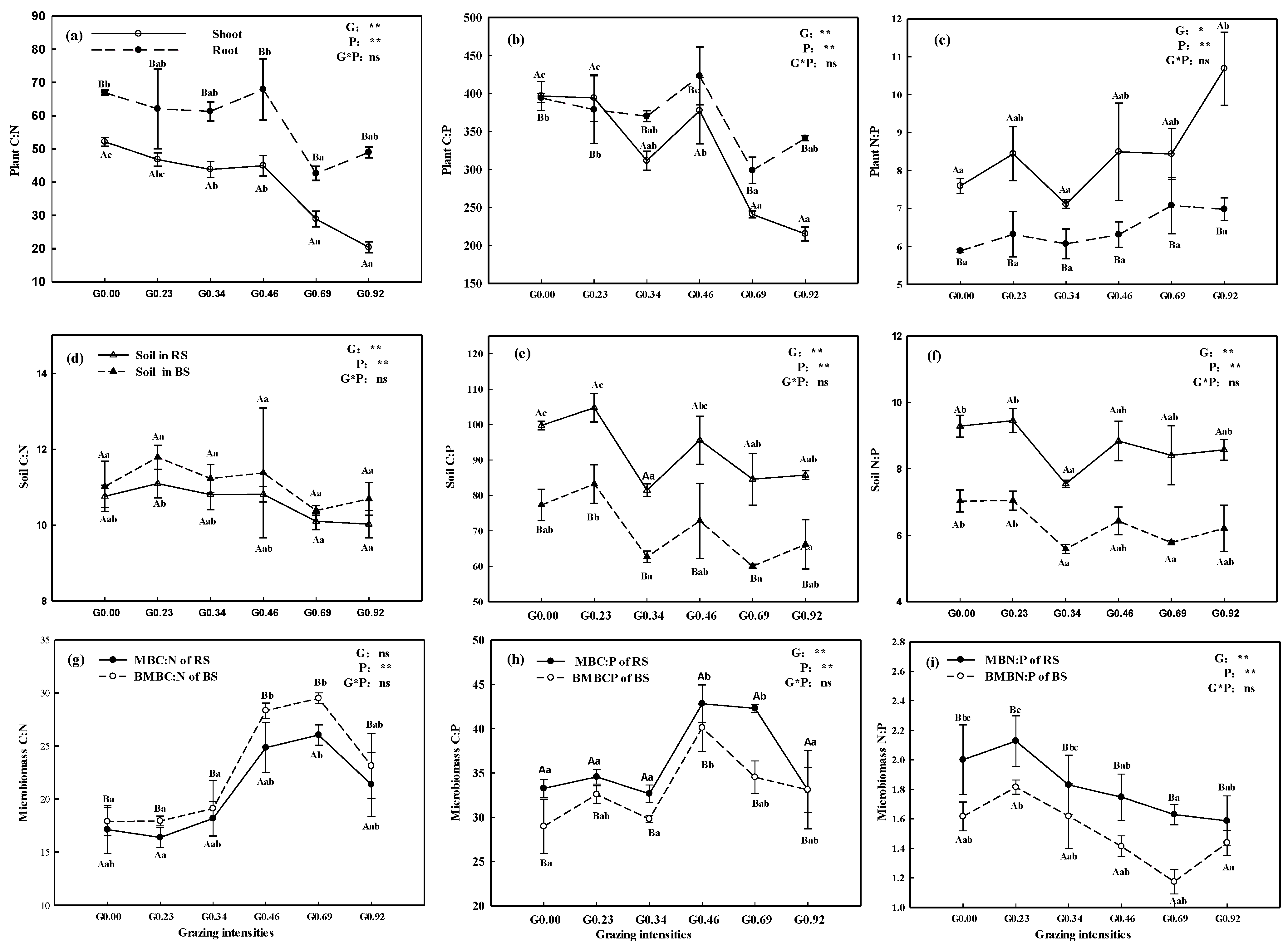
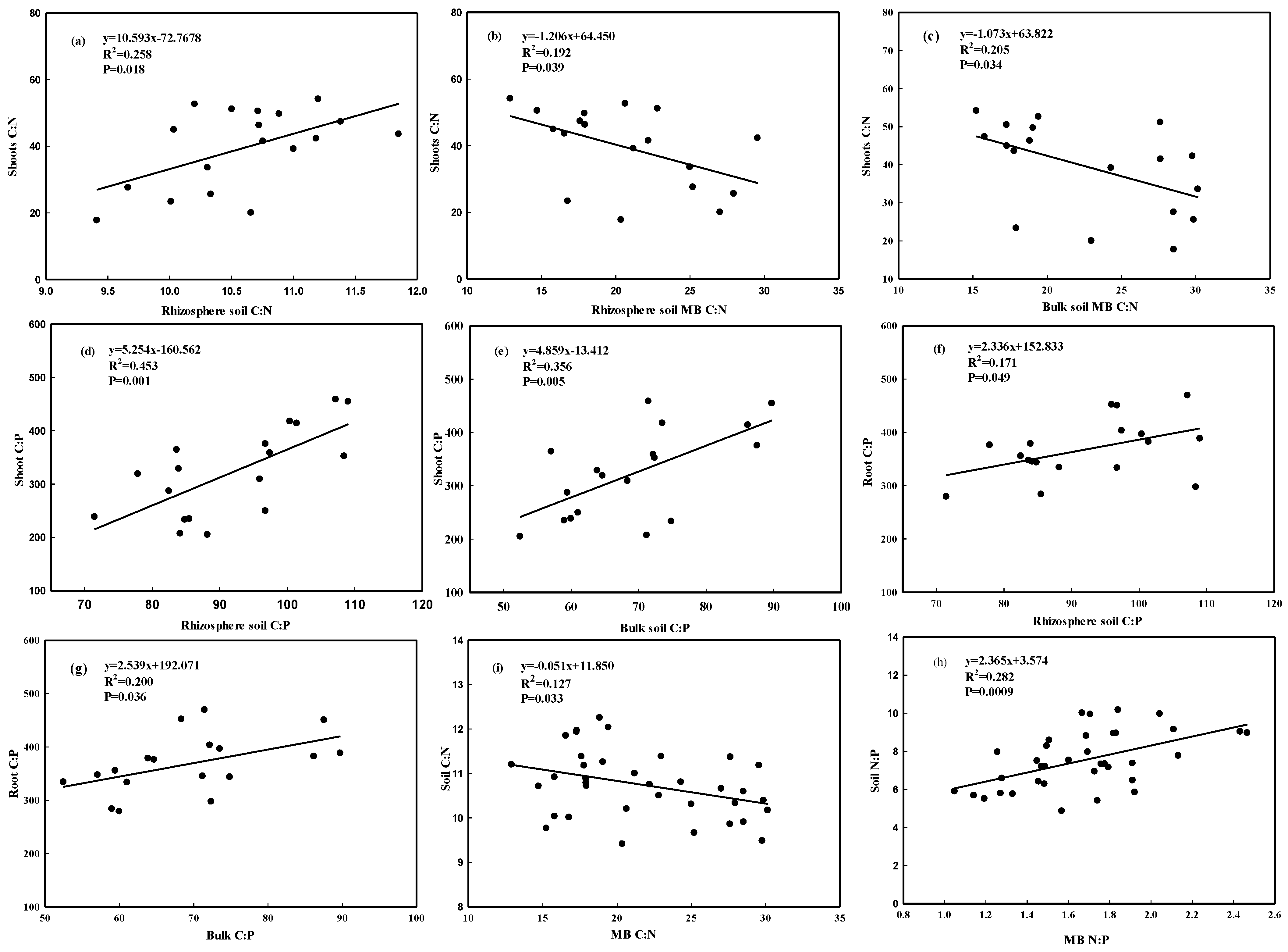
3. Results
3.1. Nutrients in Plants and Soil
3.2. Stoichiometric Characteristics in Plants and Soil
3.3. Relationships of Nutrients and the Stoichiometry between Soil and Plants
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Grazing on Stoichiometric Characteristics of Plants
4.2. Effects of Grazing on Stoichiometric Characteristics of Soil
4.3. Responses of Microbial Biomass to Grazing
4.4. Linkages between Above- and Belowground Nutrients
4.5. Role of the Rhizosphere in Nutrient Cycles
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knapp, A.K.; Fay, P.A.; Blair, J.M.; Collins, S.L.; Smith, M.D.; Carlisle, J.D.; Harper, C.W.; Danner, B.T.; Lett, M.S.; McCarron, J.K. Rainfall variability, carbon cycling, and plant species diversity in a mesic grassland. Science 2002, 298, 2202–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, M.; Stringer, L.C. Climate Change and Desertification: Anticipating, Assessing & Adapting to Future Change in Drylands; Agropolis International: Montpellier, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge, D.J.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Travers, S.K.; Val, J.; Oliver, I. Do grazing intensity and herbivore type affect soil health? Insights from a semi-arid productivity gradient. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 54, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaughton, S.J. Grazing as an optimization process: Grass-ungulate relationships in the serengeti. Am. Nat. 1979, 113, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.Y.; Zhou, X.H.; He, Y.H.; Shao, J.J.; Hu, Z.H.; Liu, R.Q.; Zhou, H.M.; Hosseinibai, S. Grazing intensity significantly affects belowground carbon and nitrogen cycling in grassland ecosystems: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.A.; Zhu, Q.A.; Zhan, W.; Xu, Y.Y.; Zhu, E.X.; Gao, Y.H.; Li, S.Q.; Zheng, Q.Y.; Zhu, D.; He, Y.X.; et al. The linkage between vegetation and soil nutrients and their variation under different grazing intensities in an alpine meadow on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 110, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Yang, X.D.; Ives, A.R.; Feng, Z.L.; Sha, L.Q. Effects of seasonal and perennial grazing on soil fauna community and microbial biomass carbon in the subalpine meadows of Yunnan, Southwest China. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessema, Z.K.; de Boer, W.F.; Baars, R.M.T.; Prins, H.H.T. Changes in soil nutrients, vegetation structure and herbaceous biomass in response to grazing in a semi-arid savanna of Ethiopia. J. Arid Environ. 2011, 75, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.W.; Elser, J.J. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Elser, J.J.; Sterner, R.W.; Galford, A.E.; Chrzanowski, T.H.; Findlay, D.L.; Mills, K.H.; Paterson, M.J.; Stainton, M.P.; Schindler, D.W. Pelagic C:N:P stoichiometry in a eutrophied lake: Responses to a whole-lake food-web manipulation. Ecosystems 2000, 3, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.L.; Fang, X.; Xiang, W.H.; Deng, X.W.; Peng, C.H. Stoichiometric and nutrient resorption characteristics of dominant tree species in subtropical Chinese forests. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 11033–11043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.J.; Huang, Z.Y.; Zhang, K.L.; Cornelissen, J.H.C. C:N:P stoichiometry of artemisia species and close relatives across northern China: Unravelling effects of climate, soil and taxonomy. J. Ecol. 2015, 103, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.X.; Ren, H.Y.; Li, W.H.; Lan, Z.C. Scale-dependent effects of grazing on plant C:N:P stoichiometry and linkages to ecosystem functioning in the Inner Mongolia grassland. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elser, J.J.; Fagan, W.F.; Kerkhoff, A.J.; Swenson, N.G.; Enquist, B.J. Biological stoichiometry of plant production: Metabolism, scaling and ecological response to global change. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batjes, N.H. Total carbon and nitrogen in the soils of the world. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 65, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.B.; Wu, J.P.; Liu, W.F.; Yuan, Y.H.; Hu, L.; Cai, Q.K. Linkages of plant and soil C:N:P stoichiometry and their relationships to forest growth in subtropical plantations. Plant Soil 2015, 392, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineiro, G.; Paruelo, J.M.; Oesterheld, M. Potential long-term impacts of livestock introduction on carbon and nitrogen cycling in grasslands of southern South America. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2006, 12, 1267–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyburn, J.; McKenzie, P.; Crawley, M.J.; Fornara, D.A. Effects of grassland management on plant C:N:P stoichiometry: Implications for soil element cycling and storage. Ecosphere 2017, 8, e01963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.F.; Wu, J.G.; Clark, C.M.; Pan, Q.M.; Zhang, L.X.; Chen, S.P.; Wang, Q.B.; Han, X.G. Grazing alters ecosystem functioning and C:N:P stoichiometry of grasslands along a regional precipitation gradient. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 49, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; Wardle, D.A. Herbivore-mediated linkages between aboveground and belowground communities. Ecology 2003, 84, 2258–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.A. Ungulate and topographic control of nitrogeN: Phosphorus stoichiometry in a temperate grassland; soils, plants and mineralization rates. Oikos 2008, 117, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Zhao, N.; Liu, C.C.; Yang, H.; Li, M.L.; Yu, G.C.; Wilcox, K.; Yu, Q.; He, N.P. C:N:P stoichiometry in China’s forests: From organs to ecosystems. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusewell, S. N:P ratios in terrestrial plants: Variation and functional significance. New Phytol. 2004, 164, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.; Carrillo, Y.; Boot, C.M.; Rocca, J.D.; Pendall, E.; Wallenstein, M.D. Rhizosphere stoichiometry: Are C:N:P ratios of plants, soils, and enzymes conserved at the plant species-level? New Phytol. 2014, 201, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.R.; Tang, H.J.; Xin, X.P.; Chen, B.R.; Murray, P.J.; Yan, Y.C.; Wang, X.; Yang, G.X. Grazing intensity and driving factors affect soil nitrous oxide fluxes during the growing seasons in the Hulunber meadow steppe of China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 054004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.W.; Chen, B.R.; Yan, R.R.; Yan, Y.C.; Sun, X.B.; Xu, L.J.; Xin, X.P. Quantitative monitoring of grazing intensity in the temperate meadow steppe based on remote sensing data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 40, 2227–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, D.R.; Gautam, R.K.; Yousuf, B.; Mishra, A.; Jha, B. Nutrients, microbial community structure and functional gene abundance of rhizosphere and bulk soils of halophytes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 91, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, V.S.; Mapfumo, E.; Dick, A.C.; Naeth, M.A.; Okine, E.K.; Chanasyk, D.S. Grazing intensity impacts on pasture carbon and nitrogen flow. J. Range Manag. 2002, 55, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.D.; Hao, X.Y.; Zhao, M.L.; Wang, M.J.; Ellert, B.H.; Willms, W.; Wang, M.J. Effect of grazing intensity on carbon and nitrogen in soil and vegetation in a meadow steppe in Inner Mongolia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 125, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.L.; Wang, S.P.; Pang, Z.; Wang, C.S.; Kardol, P.; Zhou, X.Q.; Rui, Y.C.; Lan, Z.C.; Wang, Y.F.; Xu, X.L. Grazing modifies inorganic and organic nitrogen uptake by coexisting plant species in alpine grassland. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Acharya, K.; Kyle, M.; Cotner, J.; Makino, W.; Markow, T.; Watts, T.; Hobbie, S.; Fagan, W.; Schade, J.; et al. Growth rate-stoichiometry couplings in diverse biota. Ecol. Lett. 2003, 6, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greenwood, K.L.; Hutchinson, K.J. Root characteristics of temperate pasture in New South Wales after grazing at three stocking rates for 30 years. Grass Forage Sci. 1998, 53, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.Y.; Zhang, J.N.; Zhang, Y.S.; Li, G.; Wang, Q.; Yang, D.L. Effects of grazing on plant root distribution and soil physicochemical properties in Stipa baicalensis grassland. Chin. J. Ecol. 2010, 29, 1715–1721. [Google Scholar]
- Pregitzer, K.S.; Laskowski, M.J.; Burton, A.J.; Lessard, V.C.; Zak, D.R. Variation in sugar maple root respiration with root diameter and soil depth. Tree Physiol. 1998, 18, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.Z.; Chen, Z.Z. Influences of stocking rates on C, N and P contents in plant-soil system. Acta Agrestia Sin. 1998, 6, 90–98. [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi, S.; Ritchie, M.E. Introduced grazers can restrict potential soil carbon sequestration through impacts on plant community composition. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSherry, M.E.; Ritchie, M.E. Effects of grazing on grassland soil carbon: A global review. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyman, H.A.; du Preez, C.C. Rangeland degradation in a semi-arid South Africa—II: Influence on soil quality. J. Arid Environ. 2005, 60, 483–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Oliva, F.; Tapia-Torres, Y.; Montiel-Gonzalez, C.; Perroni-Ventura, Y. Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus in Terrestrial Pools: Where Are the Main Nutrients Located in the Grasslands of the Cuatro Ciénegas Basin? In Ecosystem Ecology and Geochemistry of Cuatro Cienegas; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Liptzin, D. C:N:P stoichiometry in soil: Is there a “redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass? Biogeochemistry 2007, 85, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.F.; Thornton, P.E.; Post, W.M. A global analysis of soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in terrestrial ecosystems. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanin, N.; Fromin, N.; Buatois, B.; Hättenschwiler, S. An experimental test of the hypothesis of non-homeostatic consumer stoichiometry in a plant litter—Microbe system. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, A.E.; Allison, S.D.; Martiny, A.C. Phylogenetic constraints on elemental stoichiometry and resource allocation in heterotrophic marine bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 1398–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Chen, L.Y.; Peng, Y.F.; Ding, J.Z.; Li, F.; Yang, G.B.; Kou, D.; Liu, L.; Fang, K.; Zhang, B.B.; et al. Linking microbial C:N:P stoichiometry to microbial community and abiotic factors along a 3500-km grassland transect on the Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2016, 25, 1416–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, W.B.; Yan, R.R.; Ren, Y.; Jin, D.Y.; Xiong, W.; Zhang, G.S.; Cui, Z.L.; Xin, X.P.; Zhang, R.F. Grazing-induced microbiome alterations drive soil organic carbon turnover and productivity in meadow steppe. Microbiome 2018, 6, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.D.; Rovira, A.D. The rhizosphere and its management to improve plant growth. Adv. Agron. 1999, 66, 1–102. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, C.A.; Foster, B.L.; Gao, C. Temporal dynamics in rhizosphere bacterial communities of three perennial grassland species. Agronomy 2016, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, G.B.; Xue, S.; Wang, G.L.; Wang, J.; Song, Z.L. Effects of rhizosphere interactions of grass interspecies on the soil microbial properties during the natural succession in the loess plateau. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2018, 85, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uren, N.C. Types, amounts, and possible functions of compounds released into the rhizosphere by soil-grown plants. In The Rhizosphere; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 35–56. [Google Scholar]
- Raaijmakers, J.M.; Paulitz, T.C.; Steinberg, C.; Alabouvette, C.; Moenne-Loccoz, Y. The rhizosphere: A playground and battlefield for soilborne pathogens and beneficial microorganisms. Plant Soil 2009, 321, 341–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aira, M.; Gomez-Brandon, M.; Lazcano, C.; Baath, E.; Dominguez, J. Plant genotype strongly modifies the structure and growth of maize rhizosphere microbial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 2276–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| G0.00 | G0.23 | G0.34 | G0.46 | G0.69 | G0.92 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC | 1.15 ± 0.05a | 1.12 ± 0.04a | 1.16 ± 0.06a | 1.20 ± 0.09a | 1.19 ± 0.02a | 1.17 ± 0.02a |
| EN | 1.17 ± 0.06a | 1.20 ± 0.04a | 1.20 ± 0.04a | 1.24 ± 0.08a | 1.22 ± 0.03a | 1.25 ± 0.03a |
| EP | −0.88 ± 0.01a | −0.89 ± 0.05a | −0.89 ± 0.01a | −0.90 ± 0.02a | −0.86 ± 0.08a | −0.90 ± 0.09a |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, J.; Yan, R.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ning, C.; Hou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, X. Grazing Affects the Ecological Stoichiometry of the Plant–Soil–Microbe System on the Hulunber Steppe, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5226. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195226
Cao J, Yan R, Chen X, Wang X, Yu Q, Zhang Y, Ning C, Hou L, Zhang Y, Xin X. Grazing Affects the Ecological Stoichiometry of the Plant–Soil–Microbe System on the Hulunber Steppe, China. Sustainability. 2019; 11(19):5226. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195226
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Juan, Ruirui Yan, Xiaoyong Chen, Xu Wang, Qiang Yu, Yunlong Zhang, Chen Ning, Lulu Hou, Yongjuan Zhang, and Xiaoping Xin. 2019. "Grazing Affects the Ecological Stoichiometry of the Plant–Soil–Microbe System on the Hulunber Steppe, China" Sustainability 11, no. 19: 5226. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195226
APA StyleCao, J., Yan, R., Chen, X., Wang, X., Yu, Q., Zhang, Y., Ning, C., Hou, L., Zhang, Y., & Xin, X. (2019). Grazing Affects the Ecological Stoichiometry of the Plant–Soil–Microbe System on the Hulunber Steppe, China. Sustainability, 11(19), 5226. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195226





