Abstract
Functional foods include cold-pressed oils, which are a rich source of antioxidants and bioactive n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids. The aim of this study was to assess the quality of rapeseed oils supplemented with Spanish sage and cress oils. Seven oil mixtures consisting of 70% of rapeseed oil and 30% of sage and/or cress oil were prepared for the analyses. The oil mixtures were analyzed to determine their acid value, peroxide value, oxidative stability, and fatty acid composition. In terms of the acid value and the peroxide value, all mixtures met the requirements for cold-pressed vegetable oils. The enrichment of the rapeseed oil with α-linolenic acid-rich fats resulted in a substantially lower ratio of n-6 to n-3 acids in the mixtures than in the rapeseed oil. The mixture of the rapeseed oil with the sage and cress oils in a ratio of 70:10:20 exhibited higher oxidative stability than the raw materials used for enrichment and a nearly 20% α-linolenic acid content. The oils proposed in this study can improve the ratio of n-6:n-3 acids in modern diets. Additionally, mixing the cress seed oils with rapeseed oil and chia oil resulted in a reduction in the content of erucic acid in the finished product. This finding indicates that cress seeds, despite their high content of erucic acid, can be used as food components. The production of products with a positive effect on human health is one of the most important factors in the sustainable development of agriculture.
1. Introduction
The results available from health and nutrition research increase public awareness of the relationship between health and diet. Therefore, functional food is becoming increasingly popular among consumers. The idea of functional food originates from Japan, where a national program of studies on the relationship between food science and medicine was introduced in 1984. Functional food is defined as follows: “a food can be regarded as ‘functional’ if it is satisfactorily demonstrated to affect beneficially one or more target functions in the body, beyond adequate nutritional effects, in a way that is relevant to either an improved state of health and well-being and/or reduction of risk of disease. Functional foods must remain foods and they must demonstrate their effects in amounts that can normally be expected to be consumed in the diet: these are not pills or capsules, but part of a normal food pattern” [1,2,3]. The production of such food may be one of the most important aspects of strategies for sustainable development. The essence of the sustainable development of food production is the production of products with a positive effect on human health [4].
Functional foods include cold-pressed oils, as they are a rich source of antioxidants such as tocopherols and polyphenols, and hence exhibit high antioxidant activity. These also contain polyunsaturated fatty acids from the n-3 and n-6 groups as well as sterols, which exert a bioactive effect [5,6]. Seeds or fruits of plants that are traditionally regarded as oil-bearing species, e.g., rape, soybean, sunflower, olives, etc., are used for pressing oils. Also, oils pressed from unusual plant materials such as nuts and sage or garden cress seeds are gaining popularity.
Rapeseed oil is one of the most frequently consumed vegetable oils, and it is one of the most valuable edible fats, mainly due to the high content (approx. 90%) of 18-carbon unsaturated acids. It is produced from rapeseed varieties with a low level of erucic acid and is characterized by the presence of fatty acids that are desirable in human and animal diets and are present in ratios that are similar to those in the most valuable oils, e.g., olive oil. Furthermore, it is rich in many bioactive compounds, whose presence in food is the current focus of attention. These are primarily antioxidant compounds. The oil is also a source of essential unsaturated fatty acids from the n-6 and n-3 groups. The content of linoleic and α-linolenic acids in rapeseed oil is usually approx. 20% and 10%, respectively [7,8]. It also exhibits good oxidative stability, which is better than that of soybean and sunflower oils [9]. The oxidative stability of rapeseed oil can be improved by supplementation with natural antioxidants contained in spices (dried rosemary, oregano) and in resin from trees of the Burseraceae family [10,11]. Research was also conducted on the stability of mixtures of rapeseed oil with linseed oil. Mixtures of rapeseed oil with 25% and 50% linseed oil were found to have the best properties [12].
It is important to maintain an appropriate n-6:n-3 ratio of polyunsaturated fatty acids. Most reports in the literature indicate that the n-6:n-3 ratio should range from 1:1 to 4:1. However, modern diets usually contain up to 20-fold higher levels of n-6 than n-3 fatty acids [13]. Therefore, in terms of sustainable development strategies, it is vital to enrich food with n-3 acids, e.g., α-linolenic acid, which originates from vegetable oils such as Spanish sage or garden cress oils [14,15]. The production of products that have a positive effect on human health is one of the most important element in the sustainable development of agriculture.
Seeds of Spanish sage (Salvia hispanica L.) contain large amounts of fat (30%–40%), which is rich in essential fatty acids, in particular α-linolenic acid. This may account for 68% of all fatty acids [14,16]. Sage seeds are also characterized by a high level of antioxidants, which may be helpful in preventing diseases related to oxidative DNA damage [17,18].
Garden cress (Lepidium sativum L.) is a good source of n-3 fatty acids. It is an annual plant from the family Brassicaceae (Cruciferae). Its seeds contain large amounts of fat (28%). Its main fatty acids are oleic acid (30%) and α-linolenic acid (32%) representing the n-3 group. Cress seeds also contain a high level of polyphenols and are a source of bioactive glycosides [15,19]. It has been found that the isoflavone glycoside isolated from L. sativum seeds can improve liver function and the serum lipid profile. It can also reduce the generation of free radicals through induction of an antioxidant defense mechanism and acts as a potential antioxidant against paracetamol poisoning [20].
Polyunsaturated fatty acids from the n-3 group enhance the nutritional value of food products but also increase the susceptibility to fat oxidation. Spanish sage seeds are rich in essential fatty acids; yet, the low oxidative stability of the oil pressed from this raw material is a shortcoming. Additionally, the nutritional value of cress seed oil may be reduced by the elevated content of erucic acid.
The aim of this study was to verify the quality of a composition of rapeseed oil supplemented with oils from Spanish sage and cress seeds in various proportions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Material
The research material included seven different oil mixtures based on rapeseed oil. Seeds of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.), Spanish sage (Salvia hispanica L.), and garden cress (Lepidium sativum L.) were used to obtain the experimental oils. The seeds were analyzed for moisture [21] and fat content [22]. The moisture contents were approximately 7% and the fat contents were typical for the seeds of the plants (Table 1).

Table 1.
Humidity and fat content in the seeds used for oil pressing and pressing yields.
Individual batches of seeds were cold pressed in a Farmet DUO screw press (Czech Republic) with a capacity of 18–25 kg∙h−1, engine power 2.2 kW, and screw speed 1500 rpm equipped with a 10-mm diameter nozzle. Before starting, the press was heated to 50 °C. After pressing, the oil was left for natural sedimentation for 5 days in refrigerated conditions (10 ± 1 °C) and then decanted. The pressing efficiency was calculated based on the weight of the seeds used for the process, the fat content of the seeds, and the weight of the pressed oil. The following formula was used to calculate the pressing efficiency (W):
where:
- mo—weight of oil (kg),
- ms—weight of seeds (kg),
- f—fat content in seeds (%)
The highest yield of 79% was obtained from the rapeseeds, whereas the lowest value, i.e., approximately 42%, was noted for the cress seeds (Table 1).
The acid value (AV), peroxide value (PV), oxidative stability, and fatty acid composition in the pressed oil were also determined.
2.2. Research Methods
The oils were mixed in 500-ml amber glass bottles at appropriate weight ratios. Seven mixtures of oil marked from M1 to M7 were prepared for the analyses with 70% of rapeseed oil (R) and 30% of Spanish sage and/or cress oils. The proportions of the individual oils and the symbols denoting the individual mixtures are presented in Table 2. The oil mixtures were analyzed for their acid value (AV), peroxide value (PV), oxidative stability, and fatty acid composition.

Table 2.
Experimental setup.
The acid value was determined with the titration method using a cold solvent and expressed in mg KOH per 1 g oil [23]. The peroxide value was estimated by titration with iodometric determination of the end point and expressed in mmol O2 per 1 kg of oil [24]. Oxidative stability was assessed in the Rancimat accelerated oxidation test [25]. The test was carried out using a Metrohm 893 Professional Biodiesel Rancimat device. Oil samples (3.00 ± 0.01 g) were weighed, placed in a measuring vessel, and exposed to air at a flow rate of 20 l/h at 120 °C. The results were expressed as the induction time determined from the curve inflection point using the StabNet1.0 software provided by the manufacturer. The fatty acid composition was determined using gas chromatography (a Bruker 436GC chromatograph with an FID detector) following the relevant standards [26,27]. Fatty acid methyl esters were separated on a BPX 70 capillary column (60 m × 0.25 mm, 25 μm) with nitrogen as the carrier gas.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
All determinations were made in triplicate. The arithmetic mean of the replicates was assumed as the result. The results were analyzed statistically using the StatSoft Polska STATISTICA 10.0 program. The significance of differences between the mean values of the determined parameters was verified using Tukey’s test. The calculations were made at the significance level α = 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
The determined acid and peroxide values, which determine the quality of pressed oils, are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Chemical properties of the analyzed oils.
The highest acid value (4.77 mg KOH∙g−1 fat) was determined for the chia seed oil. This value was only slightly higher than the requirements specified for this parameter (LK ≤ 4 mg∙g−1) in the Codex Alimentarius [28]. As demonstrated by Krygier et al. [29], the acid value of oil depends on the quality of seeds used for pressing and increases with the increasing amounts of damaged seeds, which is explained by the authors by the greater activity of lipolytic enzymes present in such material.
The peroxide value, which reflects the amount of primary oxidation products, ranged from 1.00 to 1.85 mmol O2∙kg−1 in the analyzed oils and did not exceed the maximum value of 10 mmol O2∙kg−1 specified in the Codex Alimentarius [28].
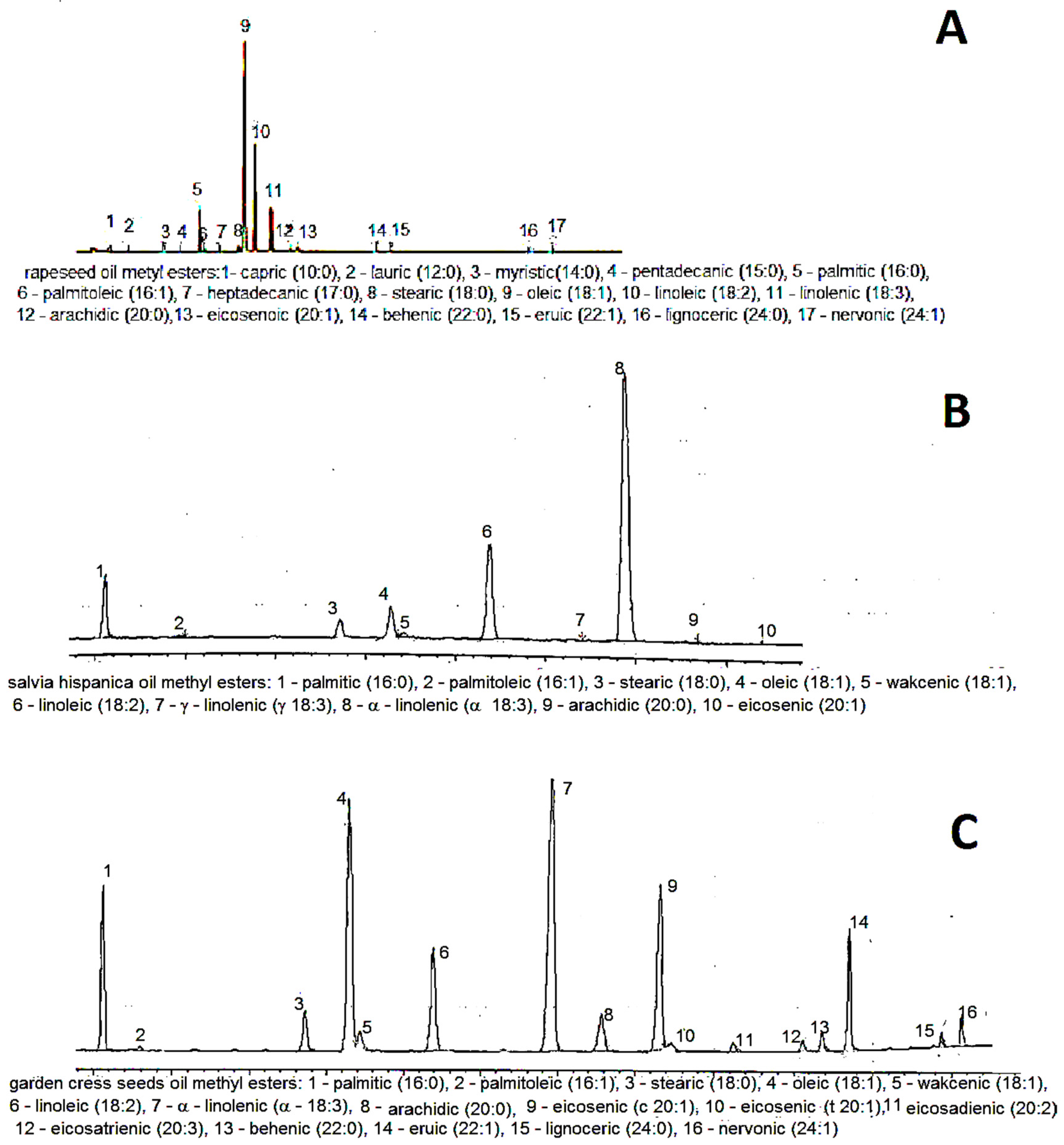
Sample gas chromatograms of each oil are shown in Figure 1. The analyzed rapeseed oil had a typical fatty acid composition [30]. The content of unsaturated fatty acids exceeded 91% (Table 4).
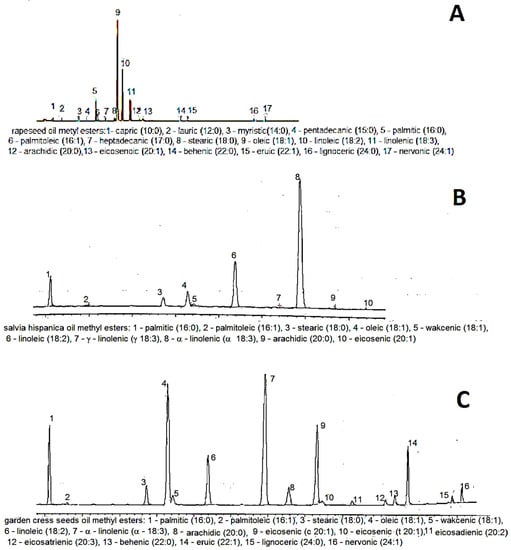
Figure 1.
Typical gas chromatogram of: A—rapeseed oil, B—Spanish sage seed oil, C—cress seed oil.

Table 4.
Fatty acid composition of the oils (% of FA sum).
Oleic acid was the main fatty acid (55.22%). The rapeseed oil contained the highest amount of linoleic acid (24.24%) and the lowest level of α-linolenic acid (10.34%). The ratio of n-6 to n-3 acids of 2:3 was equally low.
The Spanish sage oil had a high level of unsaturated fatty acids (89.43%), which is consistent with results reported by other authors [31,32]. The main acids were represented by α-linolenic acid (63.40%) followed by linoleic acid (20.80%). Such a high amount of α-linolenic acid resulted in a very low ratio of n-6 to n-3 acids in chia seed oil, i.e., 0.3.
The cress seed oil exhibited the greatest variety of fatty acids. Palmitic acid (9.02%), stearic acid (3.06%), and arachidonic acid (3.64%) represented saturated fatty acids. Mono-unsaturated fatty acids were represented by oleic acid (20.68%) as well as eicosenoic acid (13.8%) and erucic acid (5.98%). The content of essential unsaturated fatty acids (linoleic and linolenic) accounted for 9.08% and 30.03% of the sum of fatty acids, respectively. The lower content of linoleic acid than that determined in the other oils resulted in a low ratio of n-6 to n-3 acids, as in the Spanish sage oil (0:3). Additionally, there were small amounts of eicosadienoic, eicosatrienoic, lignoceric, and nervonic acids, which were not present in the other oils. The results obtained in the present study are similar to those reported by other authors investigating cress seeds [33,34], although the analyzed oil had almost two-fold higher content of erucic acid than the value determined by Moser et al. [34]. Due to its properties, erucic acid is classified as an anti-nutritional compound. The presence of erucic acid in cress oil is a drawback and limits the application of cress seeds as a raw material for oil pressing.
The oils used in the analyses had different values of oxidative stability (Table 3). The longest induction time was recorded for the rapeseed oil (4.40 h). It was similar to values reported by other authors [30,35]. The oxidative stability of vegetable oils is determined by the fatty acid composition: the greater the number of unsaturated bonds, the greater the susceptibility to oxidation. The chia seed oil exhibited the highest content of polyunsaturated fatty acids (over 84%) and hence the lowest oxidative stability (0.65 h).
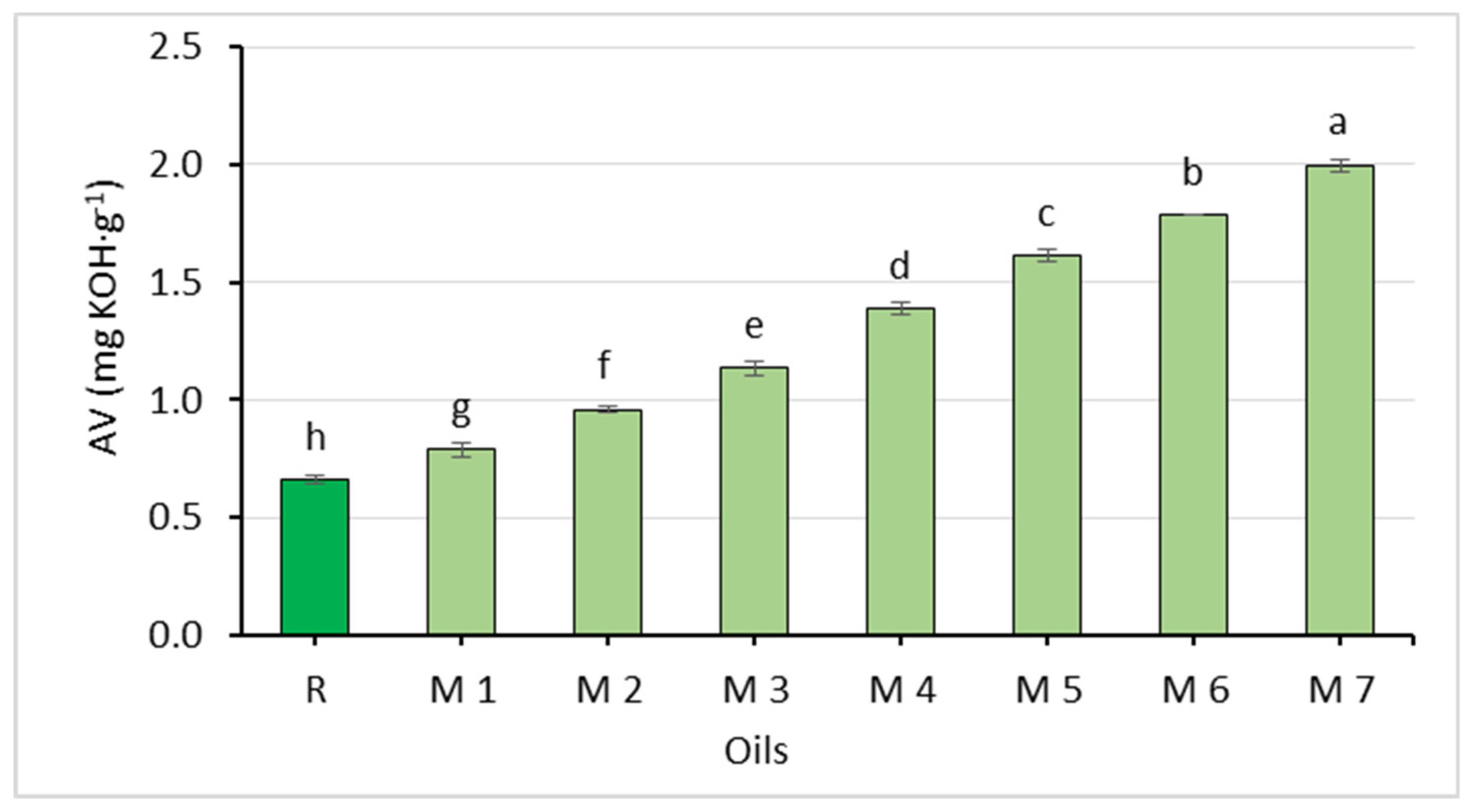
The chemical properties of the oil mixtures are shown in Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4 and Table 5. The oils differed in their acid value and oxidative stability. The acid value ranged from 0.79 to 2.00 mg∙g−1 and increased with higher amounts of the Spanish sage oil.
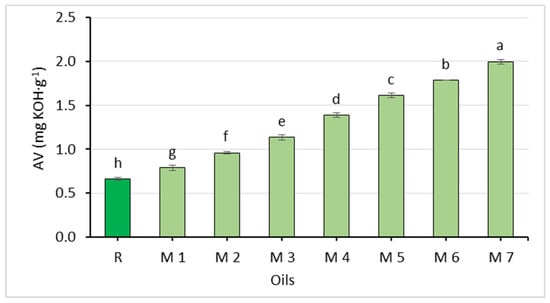
Figure 2.
Comparison of the acid value of rapeseed oil (R) and oil mixtures (abc—statistically significant differences, p ≤ 0.05).
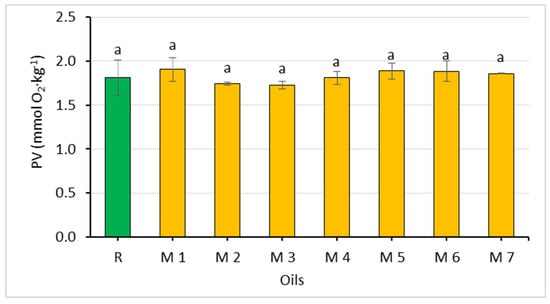
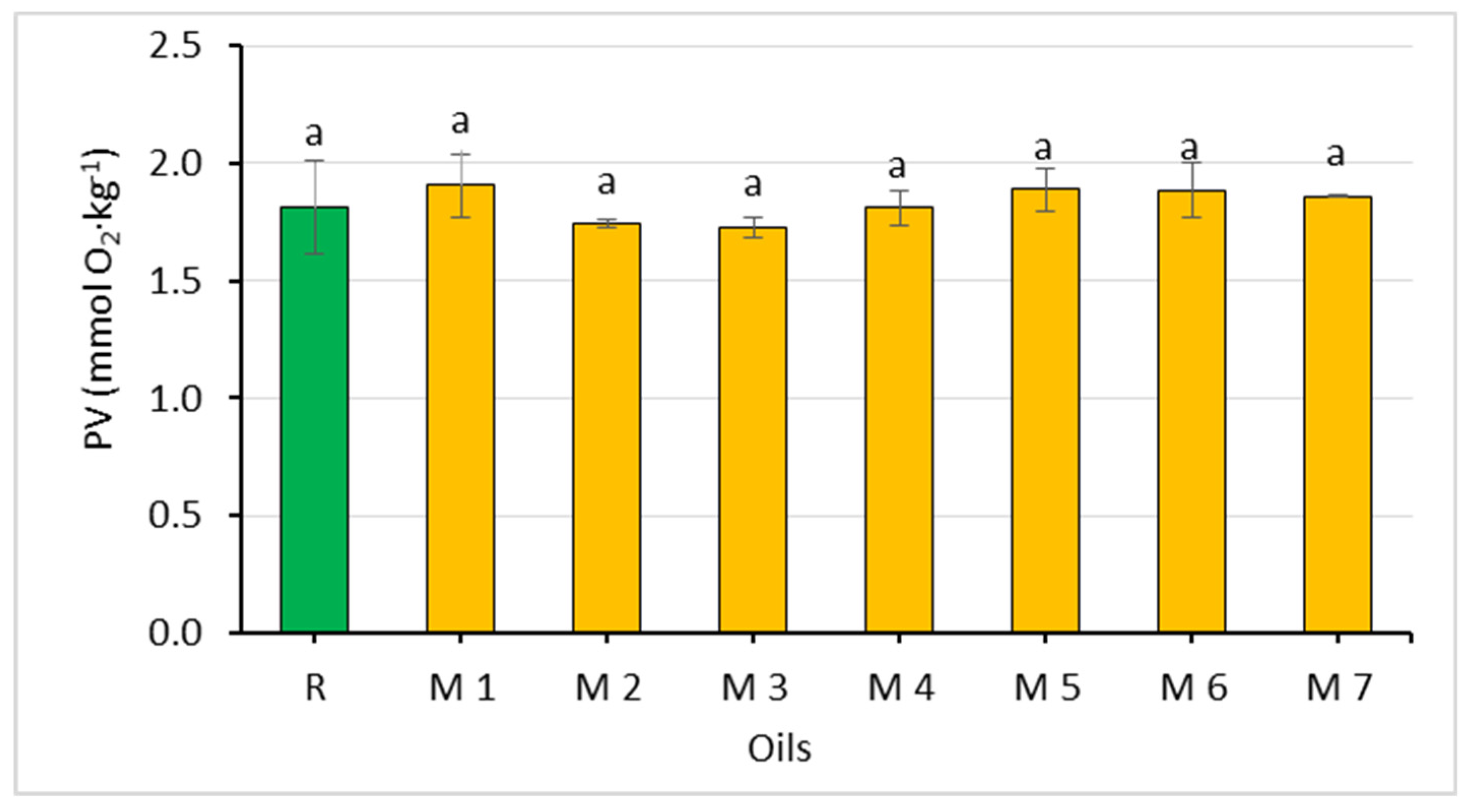
Figure 3.
Comparison of the peroxide value of rapeseed oil (R) and oil mixtures (abc—statistically significant differences, p ≤ 0.05).
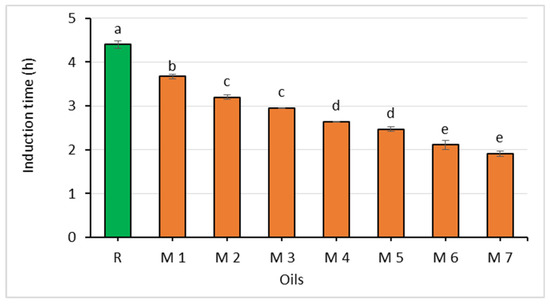
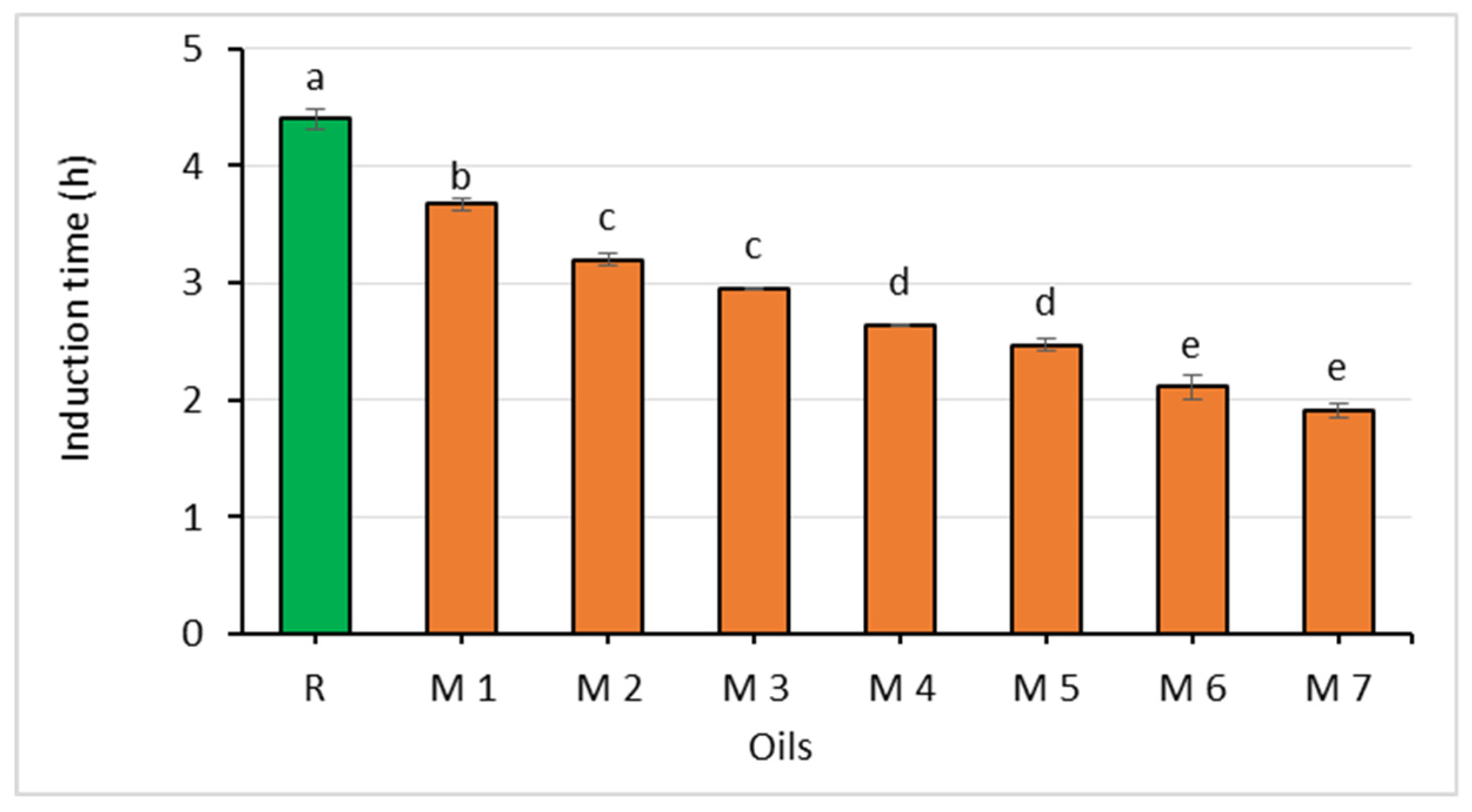
Figure 4.
Comparison of the oxidative stability of rapeseed oil (R) and oil mixtures (abc—statistically significant differences, p ≤ 0.05).

Table 5.
Fatty acid composition of the oil mixtures (% of FA sum).
Since the oils used to prepare the mixtures did not differ significantly in their peroxide value, the values of this parameter were similar in the oil mixtures as well (1.73–1.91 mmol O2∙kg−1). All mixtures met the requirements of acid and peroxide values for cold-pressed vegetable oils [28].
The fatty acid profile of the prepared oil mixtures reflected their raw material composition (Table 5). The highest content of saturated and mono-unsaturated fatty acids (11.40% and 52.20%, respectively) was determined for the M1 mixture consisting of 70% of rapeseed oil and 30% of cress seed oil, which was reflected in it showing the highest oxidative stability of all the oil mixtures. The induction time was only 0.73 h shorter than that of the rapeseed oil. The content of α-linolenic acid in the oil mixtures ranged from 16.18% to 23.02%.
The highest value for α-linolenic acid was determined for the M7 mixture containing 30% Spanish sage oil. Enrichment with this acid resulted in a substantially smaller ratio of n-6 to n-3 acids, i.e., in the range of 1.2 to 0.9, in the oil mixtures than in the rapeseed oil. As suggested by nutritional recommendations, there is a need to increase the intake of long-chain fatty acids from the n-3 group in the diet [36,37]. The oil mixtures proposed in this study can be used to enrich food with this component. According to the EU Commission Regulation of 2014 [38], the maximum allowable level of erucic acid in vegetable oils and fats is 50 g∙kg−1, i.e., 5%. By mixing the cress seed oil (containing 5.98% of this acid) with the rapeseed and Spanish sage oils, the erucic acid content was reduced below 2% in all of the analyzed mixtures.
The oxidative stability of the oils, which was expressed as the induction time ranged from 3.67 to 1.92 h and decreased with the increasing content of the Spanish sage oil. However, there were no statistically significant differences in the values for this parameter between mixtures with 5 and 10%, 15 and 20%, as well as 20 and 25% of the chia seed oil (Figure 4).
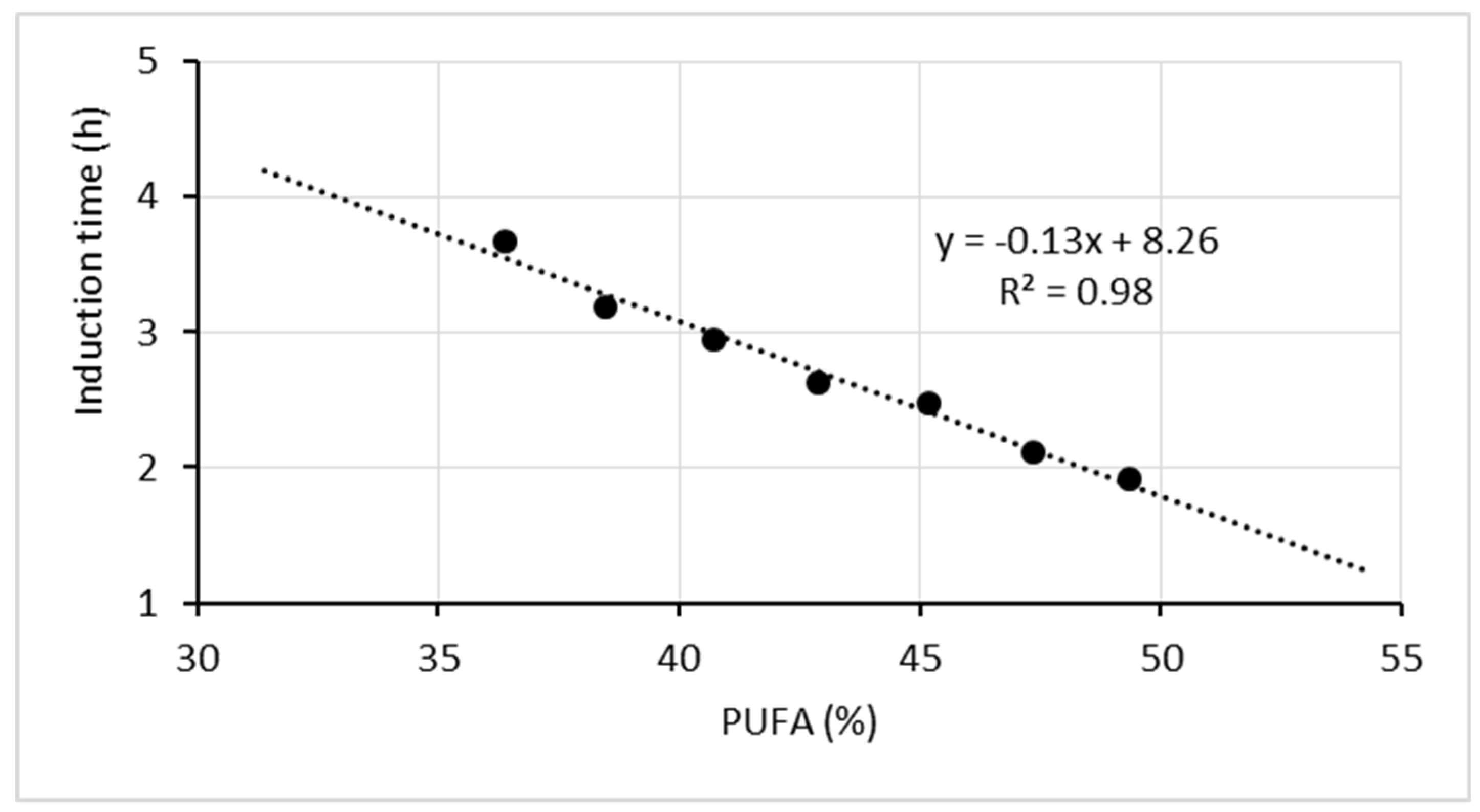
Fat oxidation susceptibility increases proportionally to the number of unsaturated bonds in individual fatty acids [30]. The dependence of oxidative stability of the experimental oil mixtures on the content of polyunsaturated fatty acids is presented graphically (Figure 5) as a linear function.
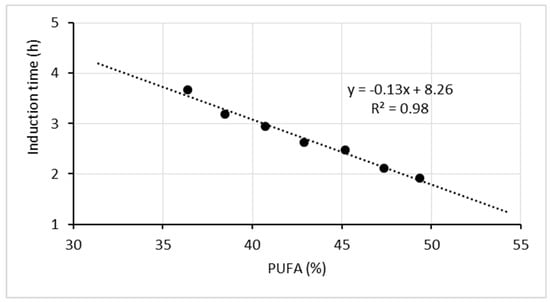
Figure 5.
Correlation between the oxidative stability of the oil mixtures and the content of polyunsaturated fatty acids.
As shown by the equation, a 5% increase in the PUFA content in the oil mixtures reduces oxidative stability by shortening the induction time by 0.65 h.
4. Conclusions
The oil mixtures proposed in this study are characterized by higher contents of n-3 fatty acids compared to rapeseed oil, and can therefore improve the n-6 to n-3 ratio in the modern diet. This is beneficial in terms of consumers’ health and complies with the principles of sustainable development of food production. The regression equation, developed using the study results, facilitates the precise determination of the properties of rapeseed, cress, and chia oil mixtures. The results indicated that a mixture of rapeseed, chia, and cress oils at a ratio of 70:10:20 exhibits higher oxidative stability than the individual enrichment raw materials, and a nearly 20% level of α-linolenic acid.
Furthermore, the mixture of cress seed oil with rapeseed and Spanish sage oils ensured reduced erucic acid content in the finished product. Hence, cress seeds, which are characterized by a high content of erucic acid can be used in the food industry, which is important for the sustainable development of agriculture and extensive use of its resources. This issue is also related to food security, which is one of the specific objectives of the strategy for sustainable development of rural areas, agriculture and fisheries for the years 2012–2020 in Poland. Within this objective, one of the priorities is the production of high-quality, agri-food products, which are safe for consumers [39].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S. (Agnieszka Sagan), D.A. and K.Z.; methodology, A.S. (Agnieszka Sagan), M.S. and D.A.; investigation, M.S., P.S. and A.S. (Agnieszka Starek); data curation, A.S. (Agnieszka Sagan), A.B.-K. and M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S. (Agnieszka Sagan), A.B.-K. and M.S.; writing—review and editing, D.A., P.S. and K.Z.; visualization, A.S. (Agnieszka Sagan), A.B.-K. and A.S. (Agnieszka Starek); supervision, D.A.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Cencic, A.; Chingwaru, W. The role of functional foods, nutraceuticals, and food supplements in intestinal health. Nutrients 2010, 2, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigliardi, B.; Galati, F. Innovation trends in the food industry: The case of functional foods. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2013, 31, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozen, A.E.; Pons, A.; Tur, J.A. Worldwide consumption of functional foods: A systematic review. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, B.K.; Norton, T.; Holden, N.M. Introduction. In Sustainable Food Processing; Tiwari, B.K., Norton, T., Holden, N.M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Obiedzińska, A.; Waszkiewicz-Robak, B. Oleje tłoczone na zimno jako żywność funkcjonalna. Zywn Nauk. Technol. Ja. 2012, 1, 27–44. [Google Scholar]
- Orsavova, J.; Misurcova, L.; Ambrozova, J.V.; Vicha, R.; Mlcek, J. Fatty acids composition of vegetable oils and its contribution to dietary energy intake and dependence of cardiovascular mortality on dietary intake of fatty acids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 12871–12890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugała, M.; Zarzecka, K.; Sikorska, A. Prozdrowotne właściwości oleju rzepakowego. Postępy Fitoter. 2014, 2, 100–103. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Meng, G.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.-P. Correlation analysis of phenolic contents and antioxidation in yellow- and black-seeded Brassica Napus. Molecules 2018, 23, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wroniak, M.; Łukasik, D.; Maszewska, M. Porównanie stabilności oksydatywnej wybranych olejów tłoczonych na zimno z olejami rafinowanymi. Zywn Nauk. Technol. Ja. 2006, 1, 214–221. [Google Scholar]
- Krajewska, M.; Ślaska-Grzywna, B.; Szmigielski, M. The effect of the oregano addition on the chemical properties of cold-pressed rapeseed oil. Przem. Chem. 2018, 97, 1953–1956. [Google Scholar]
- Starek, A.; Sagan, A.; Kiczorowska, B.; Szmigielski, M.; Ślaska-Grzywna, B.; Andrejko, D.; Kozłowicz, K.; Blicharz-Kania, B.; Krajewska, M. Effects of oleoresins on the chemical properties of cold-pressed rapeseed oil. Przem. Chem. 2018, 97, 771–773. [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak-Łukasiak, K.; Zbikowska, A.; Krygier, K. Wpływ stosowania azotu na stabilność oksydacyjna mieszanin oleju rzepakowego z olejem lnianym. Żywn Nauk Technol. Ja. 2006, 13, 206–215. [Google Scholar]
- Asif, M. Health effects of omega-3,6,9 fatty acids: Perilla frutescens is a good example of plant oils. Orient Pharm. Exp. Med. 2011, 11, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulczyński, B.; Kobus-Cisowska, J.; Taczanowski, M.; Kmiecik, D.; Gramza-Michałowska, A. The chemical composition and nutritional value of chia seeds—Current state of knowledge. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zia-Ul-Haq, M.; Ahmad, S.; Calani, L.; Mazzeo, T.; del Rio, D.; Pellegrini, N.; de Feo, V. Compositional study and antioxidant potential of ipomoea hederacea jacq. and lepidium sativum l. seeds. Molecules 2012, 17, 10306–10321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimes, S.J.; Phillips, T.D.; Hahn, V.; Capezzone, F.; Graeff-Hönninger, S. Growth, yield performance and quality parameters of three early flowering chia (Salvia hispanica l.) genotypes cultivated in southwestern Germany. Agriculture 2018, 8, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara-Cruz, M.; Tovar, A.R.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; Medina-Vera, I.; Gil-Zenteno, L.; Hernandez-Viveros, I.; Lopez-Romero, P.; Ordaz-Nava, G.; Canizales-Quinteros, S.; Guillen Pineda, L.E.; et al. A dietary pattern including nopal, chia seed, soy protein, and oat reduces serum triglycerides and glucose intolerance in patients with metabolilic syndrome. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, K.; Majsterek, S.Z.; Ciesielska, N.; Sokołowski, R.; Klimkiewicz, K.; Zukow, W. The role of chia seeds in nutrition in geriatric patients. J. Educ. Health Sport 2016, 6, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Q.L.; Zhu, Y.D.; Huang, W.H.; Qi, Y.; Guo, B.L. Two new acylated flavonol glycosides from the seeds of Lepidium sativum. Molecules 2014, 19, 11341–11349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakran, M.; Selim, Y.; Zidan, N. A new isoflavonoid from seeds of Lepidium sativum L. and its protective effect on hepatotoxicity induced by paracetamol in male rats. Molecules 2014, 19, 15440–15451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN-EN ISO 665:2004. Nasiona Oleiste. Oznaczanie Wilgotności i Zawartości Substancji Lotnych; Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny: Warsaw, Poland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- PN-EN ISO 659:2010. Nasiona Oleiste. Oznaczanie Zawartości Oleju (Metoda Odwoławcza); Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny: Warsaw, Poland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- PN-EN ISO 660:2010. Oleje i Tłuszcze Roślinne oraz Zwierzęce—Oznaczanie Liczby Kwasowej i Kwasowości; Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny: Warsaw, Poland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- PN-EN ISO 3960:2012. Oleje i Tłuszcze Roślinne oraz Zwierzęce—Oznaczanie Liczby Nadtlenkowej—Jodometryczne (Wizualne) Oznaczanie Punktu Końcowego; Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny: Warsaw, Poland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mathäus, B. Determination of the oxidative stability of vegetable oils by rancimat and conductivity and chemiluminescence measurements. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1996, 73, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar]
- PN-EN ISO 5508:1996. Oleje i Tłuszcze Roślinne oraz Zwierzęce—Analiza Estrów Metylowych Kwasów Tłuszczowych Metodą Chromatografii Gazowej; Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny: Warsaw, Poland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- PN-EN ISO 5509:2001. Oleje i Tłuszcze Roślinne oraz Zwierzęce—Przygotowanie Estrów Metylowych Kwasów tłuszczowych; Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny: Warsaw, Poland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- FAO/WHO. Codex Standard for Named Vegetable Oils. In Codex Alimentarius; ALINORM: Santa Croce, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Krygier, K.; Wroniak, M.; Grześkiewicz, S.; Obiedziński, M. Badanie wpływu zawartości nasion uszkodzonych na jakość oleju rzepakowego tłoczonego na zimno. Oilseed Crops 2000, 41, 587–596. [Google Scholar]
- Cichosz, G.; Czeczot, H. Stabilność oksydacyjna tłuszczów jadalnych—Konsekwencje zdrowotne. Bromatol. Chem. Toksyk. 2011, 44, 50–60. [Google Scholar]
- Krajewska, M.; Zdybel, B.; Andrejko, D.; Ślaska-Grzywna, B.; Tańska, M. Właściwości chemiczne wybranych olejów tłoczonych na zimno. Acta Agroph. 2017, 24, 579–590. [Google Scholar]
- Segura-Campos, M.R.; Ciau-Solis, N.; Rosado-Rubio, G.; Chel-Guerrero, L.; Betancur-Ancona, D. Physicochemical characterization of chia (Salvia hispanica) seed oil from Yucatán, México. Agric. Sci. 2014, 5, 220–226. [Google Scholar]
- Gokavi, S.S.; Malleshi, N.G.; Guo, M. Chemical composition of garden cress (Lepidium sativum) seeds and its fractions and use of bran as a functional ingredient. Plant Food Hum. Nutr. 2004, 59, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, B.R.; Shah, S.N.; Winkler-Moser, J.K.; Vaughn, S.F.; Evangelista, R.L. Composition and physical properties of cress (Lepidium sativum L.) and field pennycress (Thlaspi arvense L.) oils. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2009, 30, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruszewski, B.; Fąfara, P.; Ratusz, K.; Obiedziński, M. Ocena pojemności przeciwutleniającej i stabilności oksydacyjnej wybranych olejów roślinnych. Zesz. Probl. Post. Nauk Roln. 2013, 572, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak-Łukasik, K. Rola i znaczenie kwasów tłuszczowych omega-3. Zywn Nauk. Technol. Ja. 2011, 6, 24–35. [Google Scholar]
- Sawada, N.; Inoue, M.; Iwasaki, M.; Sasazuki, S.; Shimazu, T.; Yamaji, T.; Takachi, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Mizokami, M.; Tsugane, S. Consumption of n-3 fatty acids and fish reduces risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1468–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU) No 696/2014 of 24 June 2014 amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 as regards maximum levels of erucic acid in vegetable oils and fats and foods containing vegetable oils and fats. Off. J. EU 2014, L184, 1–2.
- Żmija, D. Zrównoważony rozwój rolnictwa i obszarów wiejskich w Polsce. Studia Ekonomiczne 2014, 166, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).