Effects of Climate and Land-Cover Changes on Soil Erosion in Brazilian Pantanal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
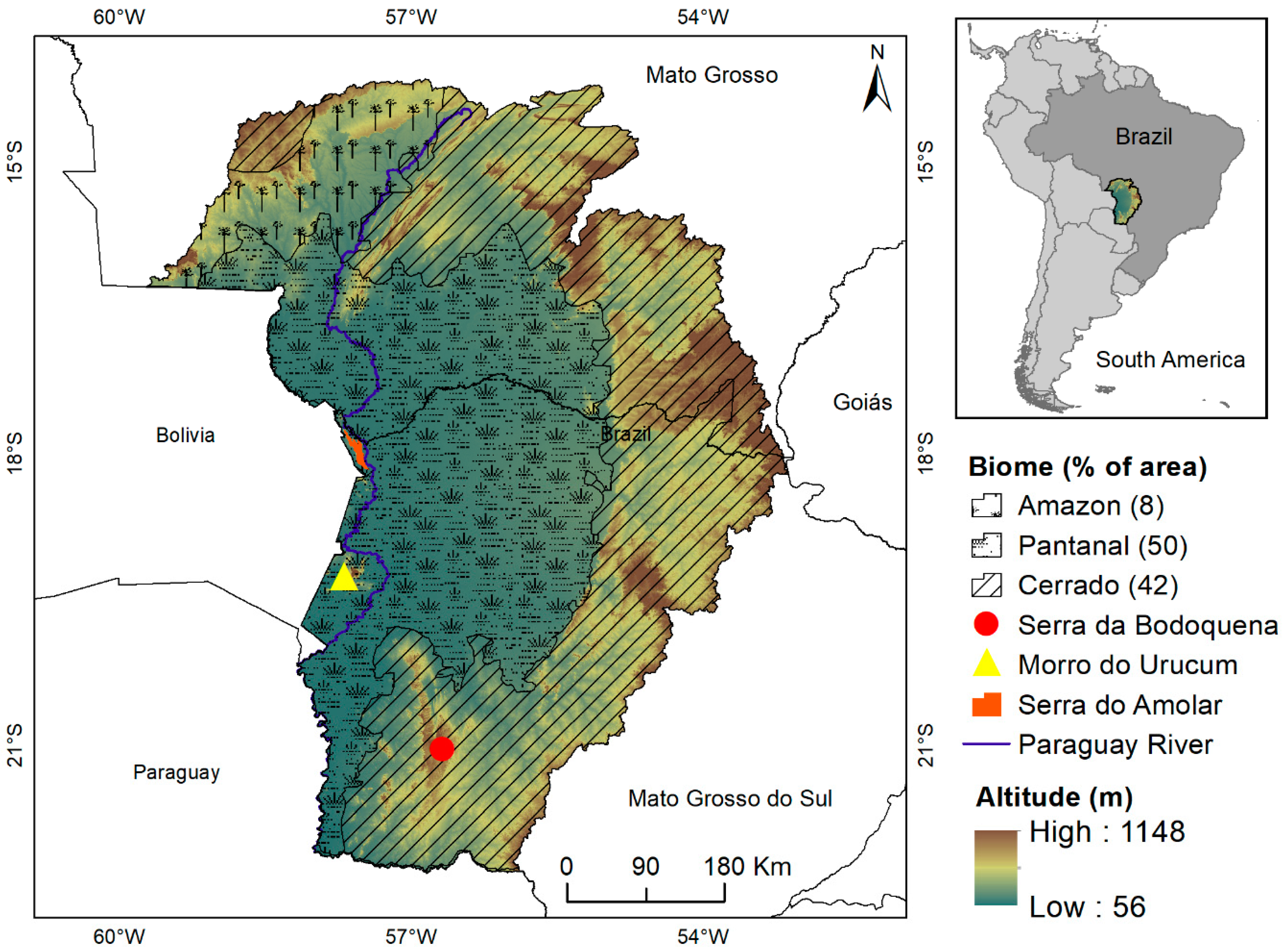
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Study Delineation
2.2.1. Computing the R- and C-Factors
2.2.2. Computing Four Other RUSLE Factors
2.2.3. Soil Erosion Simulations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. RUSLE Factors
3.2. Average Annual Soil Loss Estimation
3.3. Impacts of Climate Change and Land-Cover and Land-Use Change (LCLU)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alho, C. The World’s Largest Wetlands: Ecology and Conservation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; Available online: /core/books/worlds-largest-wetlands/3AB91B8482FF77B4A82DB83A8EFFB34E (accessed on 26 March 2018).
- Marengo, J.A.; Oliveira, G.S.; Alves, L.M. Climate Change Scenarios in the Pantanal. Dyn. Pantanal Wetl. S. Am. 2015, 37, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.T.S.; Nearing, M.A.; Moran, M.S.; Goodrich, D.C.; Wendland, E.; Gupta, H.V. Trends in water balance components across the Brazilian Cerrado. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 7100–7114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nearing, M.A.; Pruski, F.F.; O’Neal, M.R. Expected climate change impacts on soil erosion rates: A review. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2004, 59, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Fang, H. Impacts of climate change on water erosion: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2016, 163, 94–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares-Filho, B.S.; Campos, A.; Koberle, A.C.; Ribeiro, A.; Alvim, F.; Davis, J.L.; Rajão, R.; Maia, S.; Costa, W.L.S. Opções de Mitigação de Emissões de Gases de Efeito Estufa em Setores-Chave do Brasil. Agricultura, Florestas e Outros Usos do Solo (AFOLU); Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia, Inovações e Comunicações: Brasília, Brazil, 2018.
- Bergier, I.; Assine, M.L.; McGlue, M.M.; Alho, C.J.R.; Silva, A.; Guerreiro, R.L.; Carvalho, J.C. Amazon rainforest modulation of water security in the Pantanal wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marengo, J.A. Mudanças Climáticas Globais e Seus Efeitos Sobre a Biodiversidade Caracterização do Clima Atual e Definição das Alterações Climáticas Para o Território Brasileiro ao Longo do Século XXI.; Ministério do Meio Ambiente-Secretaria de Biodiversidade e Florestas: Brasília, Brazil, 2007; ISBN 978-85-7738-038-1.
- Bergier, I. Effects of highland land-use over lowlands of the Brazilian Pantanal. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.S.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Agriculture Handbook: Washington, WA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Batista, P.V.G.; Davies, J.; Silva, M.L.N.; Quinton, J.N. On the evaluation of soil erosion models: Are we doing enough? Earth Sci. Rev. 2019, 197, 102898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laflen, J.M.; Elliot, W.J.; Flanagan, D.C.; Meyer, C.R.; Nearing, M.A. WEPP-Predicting Water Erosion Using a Process-Based Model. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1997, 52, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- De Roo, A.P.J.; Wesseling, C.G.; Ritsema, C.J. Lisem: A Single-Event Physically Based Hydrological and Soil Erosion Model for Drainage Basins. I: Theory, Input and Output. Hydrol. Process. 1996, 10, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.C.; Quinton, J.N.; Smith, R.E.; Govers, G.; Poesen, J.W.A.; Auerswald, K.; Chisci, G.; Torri, D.; Styczen, M.E. The European Soil Erosion Model (EUROSEM): A dynamic approach for predicting sediment transport from fields and small catchments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. J. Br. Geomorphol. Group 1998, 23, 527–544. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/%28SICI%291096-9837%28199806%2923%3A6%3C527%3A%3AAID-ESP868%3E3.0.CO%3B2-5 (accessed on 29 November 2019). [CrossRef]
- Almagro, A.; Thomé, T.C.; Colman, C.B.; Pereira, R.B.; Marcato Junior, J.; Rodrigues, D.B.B.; Oliveira, P.T.S. Improving cover and management factor (C-factor) estimation using remote sensing approaches for tropical regions. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; Mcmahon, T.A. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2007, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, P.T.S.; Nearing, M.A.; Scott, R.L.; Rosolem, R.; da Rocha, H.R. The water balance components of undisturbed tropical woodlands in the Brazilian cerrado. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 2899–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lapola, D.M.; Martinelli, L.A.; Peres, C.A.; Ometto, J.P.H.B.; Ferreira, M.E.; Nobre, C.A.; Aguiar, A.P.D.; Bustamante, M.M.C.; Cardoso, M.F.; Costa, M.H.; et al. Pervasive transition of the Brazilian land-use system. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strassburg, B.B.N.; Brooks, T.; Feltran-Barbieri, R.; Iribarrem, A.; Crouzeilles, R.; Loyola, R.; Latawiec, A.E.; Oliveira Filho, F.J.B.; de M. Scaramuzza, C.A.; Scarano, F.R.; et al. Moment of truth for the Cerrado hotspot. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, A.A.; Rajão, R.; Costa, M.A.; Stabile, M.C.C.; Macedo, M.N.; dos Reis, T.N.P.; Alencar, A.; Soares-Filho, B.S.; Pacheco, R. Limits of Brazil’s Forest Code as a means to end illegal deforestation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7653–7658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajão, R.; Soares-Filho, B. Policies undermine Brazil’s GHG goals. Science 2015, 350, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Imeson, A.; Meusburger, K.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Alewell, C. Soil Conservation in Europe: Wish or Reality?: Soil Conservation in Europe: Wish or Reality? Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1547–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alewell, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Panagos, P. Using the USLE: Chances, challenges and limitations of soil erosion modelling. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durigon, V.L.; Carvalho, D.F.; Antunes, M.A.H.; Oliveira, P.T.S.; Fernandes, M.M. NDVI time series for monitoring RUSLE cover management factor in a tropical watershed. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, P.T.S.; Rodrigues, D.B.B.; Sobrinho, T.A.; Panachuki, E. Estimating of the USLE topographic factor using three algorithms. Ambiente Agua Interdiscip. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 5, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J. Soil loss due to crop harvesting in the European Union: A first estimation of an underrated geomorphic process. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almagro, A.; Oliveira, P.T.S.; Nearing, M.A.; Hagemann, S. Projected climate change impacts in rainfall erosivity over Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, P.T.S.; Nearing, M.A.; Wendland, E. Orders of magnitude increase in soil erosion associated with land use change from native to cultivated vegetation in a Brazilian savannah environment. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2015, 40, 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares-Filho, B.; Rajão, R.; Merry, F.; Rodrigues, H.; Davis, J.; Lima, L.; Macedo, M.; Coe, M.; Carneiro, A.; Santiago, L. Brazil’s Market for Trading Forest Certificates. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MMA, C. Geoprocessamento; Ministério do Meio Ambiente: Brasilia, Barzil, 2018. Available online: http://www.mma.gov.br/governanca-ambiental/geoprocessamento (accessed on 6 November 2018).
- FAO. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014: International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; ISBN 978-92-5-108369-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mannigel, A.R.; E Carvalho, M.D.P.; Moreti, D.; Medeiros, L.D.R. Fator erodibilidade e tolerância de perda dos solos do Estado de São Paulo. Acta Scientiarum. Agron. 2008, 24, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.M.; Alcarde, C.; Hitomi, C. Natural Potential for Erosion for Brazilian Territory. In Soil Erosion Studies; Godone, D., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; ISBN 978-953-307-710-9. [Google Scholar]
- Pasquatto, M.C. Influência Do Uso e Ocupação Do Solo na Qualidade da Água e No Processo Erosivo Da Bacia de Captação Do Rio Barro Preto, Coronel Vivida (PR). Master’s Thesis, Universidade Tecnológica Federal do Paraná, Apucarana, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ruthes, J.M.; Tomazoni, J.C.; Guimarães, E.; Gomes, T.C. Propriedades do Solo da Bacia Hidrográfica do Rio Catorze que Intensificam a Erosão Laminar. Revista Brasileira de Geografia Física 2012, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, S.G.; Silva, M.L.N.; Avanzi, J.C.; Curi, N.; Fonseca, S. Cover-management factor and soil and water losses from eucalyptus cultivation and Atlantic Forest at the Coastal Plain in the Espírito Santo State, Brazil. Sci. For. 2010, 38, 517–526. [Google Scholar]
- Anache, J.A.A.; Bacchi, C.G.V.; Panachuki, E.; Sobrinho, T.A. Assessment of Methods for Predicting Soil Erodibility in Soil Loss Modeling. Geociências (São Paulo) 2016, 34, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Farr, T.G.; Rosen, P.A.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Roth, L.; et al. The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Loughlin, F.E.; Paiva, R.C.D.; Durand, M.; Alsdorf, D.E.; Bates, P.D. A multi-sensor approach towards a global vegetation corrected SRTM DEM product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 182, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desmet, P.J.J.; Govers, G. A GIS procedure for automatically calculating the USLE LS factor on topographically complex landscape units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- McCool, D.K.; Foster, G.R.; Mutchler, C.K.; Meyer, L.D. Revised slope length factor for the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Trans. ASAE 1989, 32, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, D.K.; Brown, L.C.; Foster, G.R. Revised slope steepness factor for the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdino, S. Distribuição Espacial do Fator Topográfico da Rusle na Bacia do Alto Paraguai.—Portal Embrapa. Available online: https://www.embrapa.br/territorial/busca-de-publicacoes/-/publicacao/1035988/distribuicao-espacial-do-fator-topografico-da-rusle-na-bacia-do-alto-paraguai (accessed on 16 March 2018).
- Renard, K.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, J.A.; Dominguez, J.M.L.; Nearing, M.A.; Oliveira, P.T.S. A GIS-Based Procedure for Automatically Calculating Soil Loss from the UniversalSoil Loss Equation: GISus-M. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2015, 31, 907–917. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, P.T.S.; Wendland, E.; Nearing, M.A. Rainfall erosivity in Brazil: A review. Catena 2013, 100, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.T.; Rodrigues, D.B.; Sobrinho, T.A.; de Carvalho, D.F.; Panachuki, E. Spatial variability of the rainfall erosive potential in the state of Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil. Engenharia Agrícola 2012, 32, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sartori, M.; Philippidis, G.; Ferrari, E.; Borrelli, P.; Lugato, E.; Montanarella, L.; Panagos, P. A linkage between the biophysical and the economic: Assessing the global market impacts of soil erosion. Land Use Policy 2019, 86, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, A.D. O Futuro Climático da Amazônia:Relatório de Avaliação Científica; Articulação Regional Amazônica: Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2014; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Spera, S.A.; Galford, G.L.; Coe, M.T.; Macedo, M.N.; Mustard, J.F. Land-use change affects water recycling in Brazil’s last agricultural frontier. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 3405–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anache, J.A.A.; Wendland, E.; Rosalem, L.M.P.; Youlton, C.; Oliveira, P.T.S. Hydrological trade-offs due to different land covers and land uses in the Brazilian Cerrado. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 1263–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seidl, A.F.; de Silva, J.D.S.V.; Moraes, A.S. Cattle ranching and deforestation in the Brazilian Pantanal. Ecol. Econ. 2001, 36, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junk, W.J.; Nunes da Cunha, C. Pasture clearing from invasive woody plants in the Pantanal: A tool for sustainable management or environmental destruction? Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 20, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANA, S. Produto Parcial PP-02—Diagnóstico Consolidado da Região Hidrográfica do Rio Paraguai; Agência Nacional de Águas: Brasília, Brazil, 2017.
- ANA Plano de Recursos Hídricos da Região Hidrográfica do Rio Paraguai—PRH Paraguai. Available online: http://www3.ana.gov.br/portal/ANA/todos-os-documentos-do-portal/documentos-spr/prh-paraguai (accessed on 6 November 2018).
- Anache, J.A.A.; Flanagan, D.C.; Srivastava, A.; Wendland, E.C. Land use and climate change impacts on runoff and soil erosion at the hillslope scale in the Brazilian Cerrado. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonneaux, V.; Cheggour, A.; Deschamps, C.; Mouillot, F.; Cerdan, O.; Le Bissonnais, Y. Land use and climate change effects on soil erosion in a semi-arid mountainous watershed (High Atlas, Morocco). J. Arid Environ. 2015, 122, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poesen, J. Soil erosion in the Anthropocene: Research needs: Soil erosion in the Anthropocene. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 64–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, J.S.; Gesualdo, G.C.; Zamboni, P.A.P.; Vieira, N.O.M.; Mattos, T.S.; Carvalho, G.A.; Rodrigues, D.B.B.; Alves Sobrinho, T.; Oliveira, P.T.S. Water provisioning improvement through payment for ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, J.S.; Oliveira, P.T.S.; Zamboni, P.A.P.; Vieira, N.O.M.; Carvalho, G.A.; Macedo, M.C.M.; Araujo, A.R.; Montagner, D.B.; Sobrinho, A. Effects of long-term crop-livestock-forestry systems on soil erosion and water infiltration in a Brazilian Cerrado site. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| World Reference Base for Soil Classification | K-Factor (t h MJ−1 mm−1) | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Acrisols | 0.0228–0.0466 | [33] |
| Cambisols | 0.0254–0.0441 | [33] |
| Chernozems | 0.0309 | [34] |
| Podzols | 0.3267 | [33] |
| Gleysols | 0.0044 | [33] |
| Ferralsols | 0.0061–0.0263 | [33] |
| Leptosols | 0.0196 | [35] |
| Arenosols | 0.1448 | [33] |
| Regosols | 0.1238 | [36] |
| Nitisols | 0.0081–0.0355 | [33] |
| Histosols | 0.0317 | [33] |
| Planosols | 0.0317 | [33] |
| Plinthosols | 0.017 | [37] |
| Vertisols | 0.04 | [34] |
| SOIL LOSS SIMULATION BASELINE | |
|---|---|
| Eta/HadGEM2-ES x Reference | Eta/MIROC5 x Reference |
| R-factor: 1961–2005 C-factor: 2012 | R-factor: 1961–2005 C-factor: 2012 |
| SOIL LOSS PROJECTED SCENARIOS | |
| Eta/HadGEM2-ES (RCP 4.5) x Reference | Eta/MIROC5 (RCP 4.5) x Reference |
| R-factor: 2007–2040 C-factor: 2020 | R-factor: 2007–2040 C-factor: 2020 |
| R-factor: 2007–2040 C-factor: 2035 | R-factor: 2007–2040 C-factor: 2035 |
| R-factor: 2041–2070 C-factor: 2050 | R-factor: 2041–2070 C-factor: 2050 |
| Eta/HadGEM2-ES (RCP 8.5) x Reference | Eta/MIROC5 (RCP 8.5) x Reference |
| R-factor: 2007–2040 C-factor: 2020 | R-factor: 2007–2040 C-factor: 2020 |
| R-factor: 2007–2040 C-factor: 2035 | R-factor: 2007–2040 C-factor: 2035 |
| R-factor: 2041–2070 C-factor: 2050 | R-factor: 2041–2070 C-factor: 2050 |
| Eta/HadGEM2-ES (RCP 4.5) x Low Carbon | Eta/MIROC5 (RCP 4.5) x Low Carbon |
| R-factor: 2007–2040 C-factor: 2020 | R-factor: 2007–2040 C-factor: 2020 |
| R-factor: 2007–2040 C-factor: 2035 | R-factor: 2007–2040 C-factor: 2035 |
| R-factor: 2041–2070 C-factor: 2050 | R-factor: 2041–2070 C-factor: 2050 |
| Eta/HadGEM2-ES (RCP 8.5) x Low Carbon | Eta/MIROC5 (RCP 8.5) x Low Carbon |
| R-factor: 2007–2040 C-factor: 2020 | R-factor: 2007–2040 C-factor: 2020 |
| R-factor: 2007–2040 C-factor: 2035 | R-factor: 2007–2040 C-factor: 2035 |
| R-factor: 2041–2070 C-factor: 2050 | R-factor: 2041–2070 C-factor: 2050 |
| Scenarios | Baseline | Projected (MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eta/HadGEM2-ES | 1961–2005 | Lowest | Highest |
| RCP 4.5 (2007–2040) | RCP 4.5 (2041–2070) | ||
| 8116 ± 1229 | 6906 ± 1066 | 7453 ± 1078 | |
| Eta/MIROC5 | 1961–2005 | Lowest | Highest |
| RCP 8.5 (2007–2040) | RCP 4.5 (2041–2070) | ||
| 8470 ± 1129 | 7622 ± 1134 | 8279 ± 1268 | |
| Scenarios | 2020 | 2035 | 2050 |
|---|---|---|---|
| a) Eta/HadGEM2-ES x Low Carbon | RCP 4.5 (2007–2040) | RCP 4.5 (2007–2040) | RCP 8.5 (2041–2070) |
| 16.02 ± 54.02 | 16.86 ± 56.43 | 18.25 ± 60.58 | |
| b) Eta/MIROC5 x Reference | RCP 4.5 (2007–2040) | RCP 4.5 (2007–2040) | RCP 4.5 (2041–2070) |
| 18.83 ± 61.73 | 19.89 ± 65.63 | 20.81 ± 67.87 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Colman, C.B.; Oliveira, P.T.S.; Almagro, A.; Soares-Filho, B.S.; Rodrigues, D.B.B. Effects of Climate and Land-Cover Changes on Soil Erosion in Brazilian Pantanal. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7053. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11247053
Colman CB, Oliveira PTS, Almagro A, Soares-Filho BS, Rodrigues DBB. Effects of Climate and Land-Cover Changes on Soil Erosion in Brazilian Pantanal. Sustainability. 2019; 11(24):7053. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11247053
Chicago/Turabian StyleColman, Carina B., Paulo Tarso S. Oliveira, André Almagro, Britaldo S. Soares-Filho, and Dulce B. B. Rodrigues. 2019. "Effects of Climate and Land-Cover Changes on Soil Erosion in Brazilian Pantanal" Sustainability 11, no. 24: 7053. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11247053
APA StyleColman, C. B., Oliveira, P. T. S., Almagro, A., Soares-Filho, B. S., & Rodrigues, D. B. B. (2019). Effects of Climate and Land-Cover Changes on Soil Erosion in Brazilian Pantanal. Sustainability, 11(24), 7053. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11247053





