Abstract
The atmosphere is a very sensitive medium to extraterrestrial forces, most importantly, solar electromagnetic radiation and energetic particle intrusion. This released intense solar activity can cause sudden disturbances in the Earth’s atmosphere and further create ground telecommunication interferences, blackouts, transportation problems, water supply problems, potential health effects, as well as natural disasters, such as forest fires. These extreme events can cause billions of dollars of damage and impact individuals, families, communities, and societies. For this reason, it is of crucial importance to investigate the connections between this extreme activity and natural disasters, and further develop ways to prevent, prepare against, and respond to them. The aim of this special issue is to engage a wide community of scientists to de-fragment broaden and improve our knowledge in this field. We invite researchers from all relevant fields to publish their recent investigations in this special issue.
1. Introduction
Keeping in mind that the Earth is permanently exposed to numerous influences coming from the outer space, its properties, especially in the atmosphere, are often significantly disturbed by extraterrestrial influences [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Although the relevant astrophysical phenomena can be from the deep Universe like, for example, radiation from the gamma to the UV part of the electromagnetic spectrum that occur in supernova explosions or other processes [7,8]. The solar radiation has the most important influence on the Earth’s layers [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18].
Generally speaking, the solar influence is very important for the Earth’s dynamics and life on our planet even if its radiation is not suddenly increased due to intensive processes on the Sun. It can be seen in many different ways in daytime and nighttime periods as well as in disturbances during sunrise and sunset periods. In addition, its influence can be very important for the possibility of detecting numerous astrophysical and terrestrial phenomena which do not affect intensively enough the locations considered to be dominated by solar effects [19]. Also, many investigations indicate detections of the ionospheric properties in periods around natural disasters like earthquakes [20] or tropical depression beginnings [21] during solar terminator.
However, unpredictable processes and events in the Earth are the consequences of extreme solar radiation. Among others, they can be connected with different types of natural disasters which interfere the process of sustainable development, and become more serious due to climate change and the increase in their frequency and intensity. Obviously, there is a need for a new approach that could include the prevention of natural disasters within the sustainable development cycle.
Relationships between the extreme solar radiation and natural disasters are the subject of this special issue. The main goal is to point out the multi-discipline nature of research of extreme solar radiation influence on natural disasters. This includes studies in fields of solar physics, geophysics, social sciences, medicine, technology, telecommunications etc.
We invited researchers from the entire community to publish their recent investigations in this special issue of Sustainability.
2. Extreme Solar Radiation and Natural Disasters
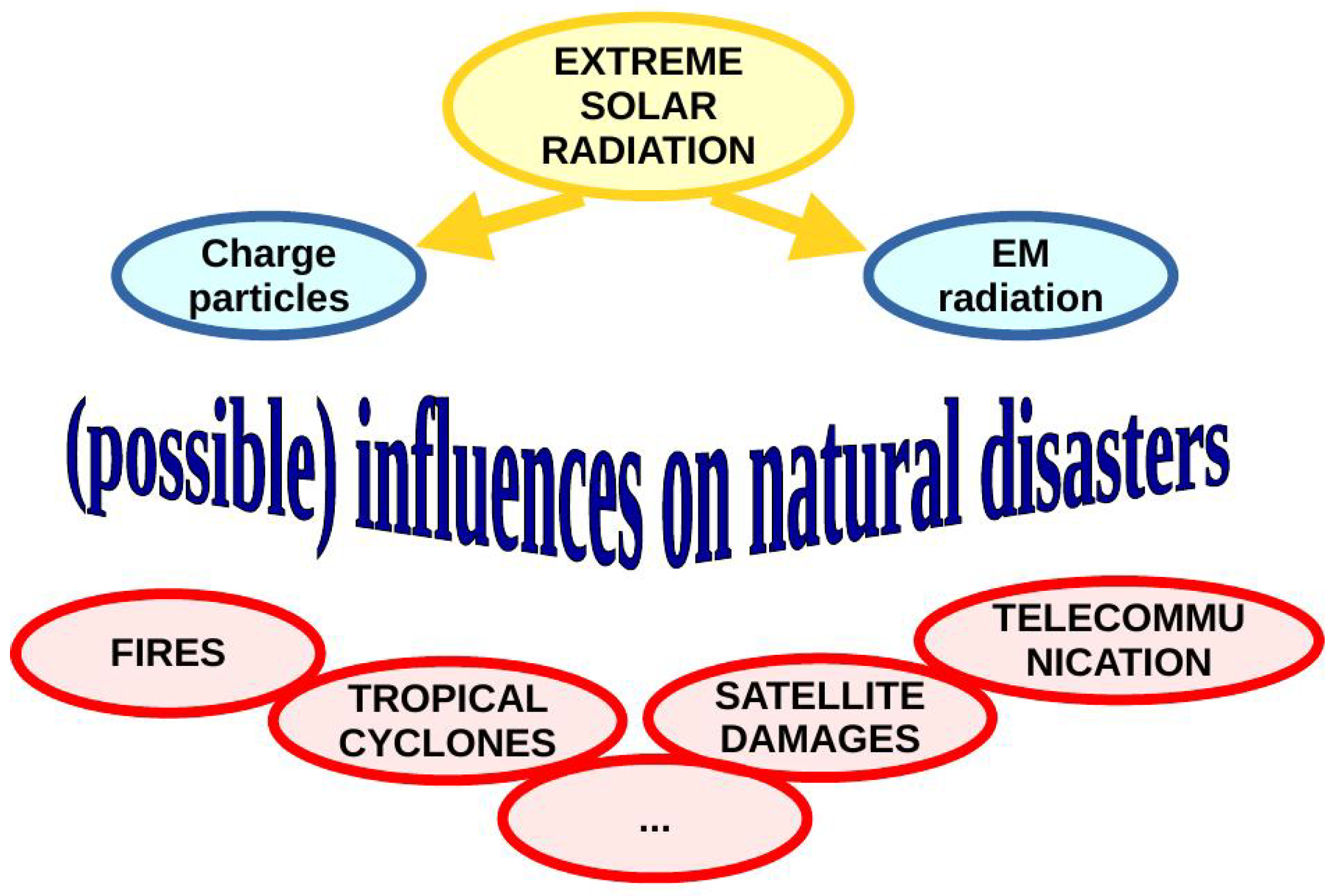
The extreme solar radiation is a consequence of sudden intensive processes in the Sun. There are two types of this radiation; charged particles emitted during coronal mass ejection and electromagnetic radiation primarily in the X-ray spectral domain induced by solar X-ray flares.
- Charged particles. The most important increase of the charged particles is the consequence of a coronal mass ejection (CME). This process, connected with magnetic reconnection on the Sun, can produce a significant increase of the charged particles coming to Earth, where, consequently, solar radiation influence varies on different terrestrial layers. First of all, very intensive disturbances can occur in the magnetic field which, on the other side, has influence on the charged particles’ paths. Generally, their influence primarily depends on altitude and latitude due to interactions with the atmospheric particles and the geomagnetic field effects on charged particles. Although the particle impact is the most important in the polar areas, many investigations point out their significant role in locations with anomalies in geomagnetic fields [22,23].
- Electromagnetic radiation (X-rays, UV). The most important extreme electromagnetic radiation coming from the Sun is the consequence of solar flares and lies in the X domain of EM spectrum. As investigations show, very intensive perturbations which are induced by this astrophysical phenomenon occur in the low ionosphere [24,25,26] with possible significant effects on propagations of electromagnetic waves which propagate in the ionosphere [27]. Also, the radiation in the UV region reaching the Earth’s surface can sometimes be significantly increased. As a consequence, serious health problems can occur.
Disasters occurring as the consequence of extreme solar radiation are numerous (see Figure 1). Many researches point to the connections between the increase of the charged particle densities and large natural disasters, for example forest fires [28], or tropical depressions [29]. These natural disasters directly affect life and nature on Earth and can have a significant influence on people and, generally, medical and social aspects of their lives. Also, it is well known that solar wind can damage or destroy satellites and its presence can affect satellite operation (see [30] and references therein). In addition, extreme solar radiation can significantly change the propagation of radio signals emitted by satellites or devices located on the ground (including blackout) [27,31] with consequences in many remote applications (positioning, telecommunications, Earth observations, etc.).
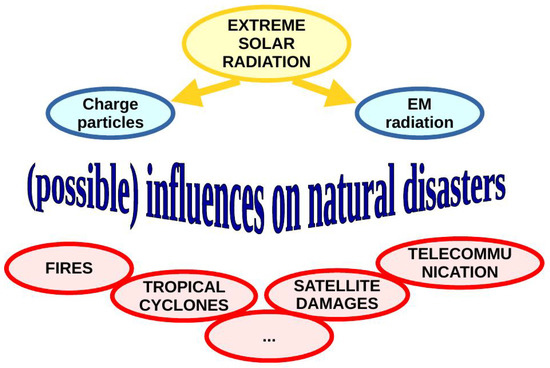
Figure 1.
Scheme of solar extreme radiation influence on natural disasters.
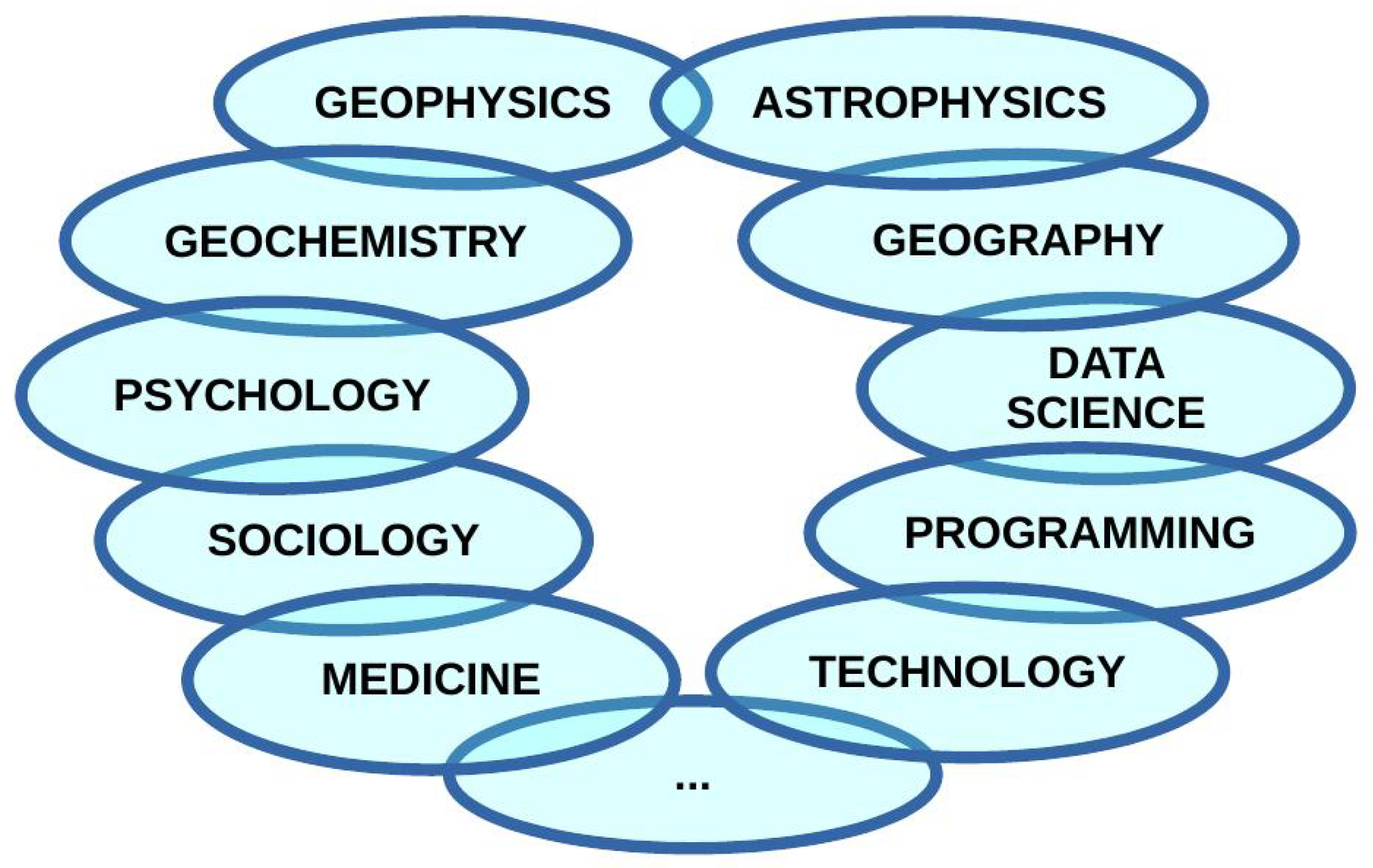
The importance of effects of natural disasters on human lives focused on in the research of scientists, engineers, programmers, and many other experts who work in different fields; natural sciences (astrophysics, geophysics, geochemistry, geography, etc.), medicine, social sciences (e.g., sociology, psychology), data science, programming, technology, etc. The scheme of disciplines which consider analyses and consequences of natural disasters (possibly) induced by the extreme solar radiation is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2.
Scheme of disciplines which consider analyses and consequences of natural disasters (possibly) induced by the extreme solar radiation.
3. Observations
Observations relevant for the research of the extreme solar radiation influence on natural disasters can be divided in two groups; observations of solar radiations by satellites and observations of terrestrial layers.
There are many satellites which monitor solar radiation like GOES satellites, ACE satellites, etc. They detect different types of particles and photons in several energy canals, which allows the modelling of radiation spectra of considered species.
Observation techniques of terrestrial parts that can be applied for natural disaster monitoring are numerous. They can be based on in situ measurements [32,33] or remote sensing from the ground or satellites [34,35].
Here we also want to point out the indirect influence of solar radiation on monitoring natural disasters using remote sensing techniques. Namely, different methods are based on electromagnetic wave propagation in the atmosphere. The characteristics of these propagations are significantly affected by the medium within which signals propagate and the changes in solar radiation can be an important source of errors or problems in disaster monitoring. The influence of radiation on particular observations depends on radiation intensity and its characteristics, observed area and observation technique. Namely, the intensity and spectrum of solar radiation in the medium within which signals propagate influence ionization rate and other plasma properties in the ionosphere. These radiation characteristics depend on the atmospheric properties above the area within which signal propagate (due to absorption and other changes in radiation before the relevant locations including the influence of the geomagnetic field on charged particles, which significantly depends on altitude and latitude) and on the properties inside this area (due to cross sections for numerous processes and geomagnetic field influence). On the other side, the deviation in propagation path depends on signal frequencies. For example, satellite signals with higher frequency have lower deviations than those with lower frequency. Also, depending on technique, signals can; (a) propagate from the ground, reflect at some altitude and come back to the Earth surface (ionospheric monitoring by ionosondes, digisondes, radars), (b) propagate in the Earth-ionosphere waveguide (the low ionospheric monitoring by radio waves), (c) propagate from the satellite to ground with (Synthetic Aperture Radars—SAR) or without (Global Navigation Satellite Signals—GNSS) reflection from the surface. Because of all these differences we can speak about two types of extreme solar radiation on natural disaster observations; increase in observation errors and impossibility of relevant observations.
4. Modelling
Generally speaking, the analyses of the extreme solar radiation influence on natural disasters can include modeling in several fields. These are some of them:
- Modelling of the radiation characteristics before its impact on the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Modelling of radiation propagation in the atmosphere.
- Modelling of processes which induce natural disasters.
- Modelling of the connection between radiation characteristics and processes which induce natural disasters.
These studies require the inclusion of observation data obtained in different types of observations (satellite or ground based measurements) as well as application of different existing models relevant to solar radiation [36,37], its propagation in the atmosphere [38], etc.
5. Summary
As it can be seen, the investigation of extreme solar radiation influence on natural disasters is a very complex task. These studies require cooperation of experts in natural, social and data sciences, engineers, programmers and people who work in many other connected fields. The goal of this special issue is to present both the differences in these sciences and the need for mutual activities in order to better understand the disasters and, most importantly to improve activities in organizations and activities during and after disasters. Also, it should have a special impact on indications of possible precursors of natural disasters which can be of essential importance to people’s reactions and, finally, which can save their lives.
We hope that the special issue will have an impact on the entire scientific community and will also be helpful in education (graduate study level). For these reasons we invite researchers from all relevant fields to publish their recent investigations in this special issue.
Author Contributions
Writing, review and editing A.N., V.A.S., and M.R.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of Serbia, grant numbers 176002, III44002 and III47007.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the administrative and technical support of the Sustainability team. This work is made within projects of the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of Serbia, grant numbers 176002, III44002 and III47007.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bondur, V.G.; Pulinets, S.A.; Kim, G.A. Role of variations in galactic cosmic rays in tropical cyclogenesis: Evidence of Hurricane Katrina. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2008, 422, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artamonova, I.; Veretenenko, S. Effect of solar and galactic cosmic rays on the duration of macrosynoptic processes. Geomagn. Aeron. 2013, 53, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artamonova, I.; Veretenenko, S. Atmospheric pressure variations at extratropical latitudes associated with Forbush decreases of galactic cosmic rays. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 2491–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veretenenko, S.; Ogurtsov, M. Regional and temporal variability of solar activity and galactic cosmic ray effects on the lower atmosphere circulation. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 49, 770–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veretenenko, S.; Thejll, P. Influence of energetic Solar Proton Events on the development of cyclonic processes at extratropical latitudes. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 409, 012237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozhnoi, A.; Shalimov, S.; Solovieva, M.; Levin, B.; Hayakawa, M.; Walker, S. Tsunami-induced phase and amplitude perturbations of subionospheric VLF signals. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2012, 117, 9313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, U.S.; Lehtinen, N.G.; Moore, R.C.; Hurley, K.; Boggs, S.; Smith, D.M.; Fishman, G.J. Massive disturbance of the daytime lower ionosphere by the giant γ-ray flare from magnetar SGR 1806-20. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 8103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nina, A.; Simić, S.; Srećković, V.A.; Popović, L.Č. Detection of short-term response of the low ionosphere on gamma ray bursts. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 8250–8261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanović, M. Investigation of solar influence on the terrestrial processes: Activities in Serbia. J. Geogr. Inst. Cvijic 2018, 68, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, A.; Menk, F.; Maurya, A.K.; Singh, R.; Veenadhari, B. Response of the low-latitude D region ionosphere to extreme space weather event of 14–16 December 2006. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2015, 120, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitter, E.D. Modeling solar flare induced lower ionosphere changes using VLF/LF transmitter amplitude and phase observations at a midlatitude site. Ann. Geophys. 2013, 31, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boberg, F.; Lundstedt, H. Solar wind electric field modulation of the NAO: A correlation analysis in the lower atmosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabis, I.; Troshichev, O. Influence of short-term changes in solar activity on baric field perturbations in the stratosphere and troposphere. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2000, 62, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, K.; Kirov, B.; Knížová, P.K.; Mošna, Z.; Kouba, D.; Asenovska, Y. Solar influences on atmospheric circulation. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2012, 90, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, M.; Bell, C.; Woollings, T.; Harrison, R.; Gray, L.; Haigh, J. Top-down solar modulation of climate: Evidence for centennial-scale change. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 034008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazos, M.; Mendoza, B.; Gimeno, L. Analysis of precursors of tropical cyclogenesis during different phases of the solar cycle and their correlation with the Dst geomagnetic index. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2015, 133, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorović, N.; Vujović, D. Effect of solar activity on the repetitiveness of some meteorological phenomena. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 2430–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voiculescu, M.; Usoskin, I.; Condurache-Bota, S. Clouds blown by the solar wind. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 045032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nina, A.; Čadež, V.M.; Popović, L.Č.; Srećković, V.A. Diagnostics of plasma in the ionospheric D-region: Detection and study of different ionospheric disturbance types. Eur. Phys. J. D 2017, 71, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, O.; Hayakawa, M.; Oudoh, T.; Kawai, E. Precursory effects in the subionospheric VLF signals for the Kobe earthquake. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1998, 105, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nina, A.; Radovanović, M.; Milovanović, B.; Kovačević, A.; Bajčetić, J.; Popović, L.Č. Low ionospheric reactions on tropical depressions prior hurricanes. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 60, 1866–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanović, M.M.; Vyklyuk, Y.; Milenković, M.; Vuković, D.B.; Matsiuk, N. Application of adaptive neuro-fuzzy interference system models for prediction of forest fires in the USA on the basis of solar activity. Therm. Sci. 2015, 19, 1649–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyklyuk, Y.; Radovanović, M.; Milovanović, B.; Leko, T.; Milenković, M.; Milošević, Z.; Milanović Pešić, A.; Jakovljević, D. Hurricane genesis modelling based on the relationship between solar activity and hurricanes. Nat. Hazards 2017, 85, 1043–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, A.; Singh, R.; Singh, R. Solar flare induced D-region ionospheric perturbations evaluated from VLF measurements. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2014, 350, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nina, A.; Čadež, V.; Bajčetić, J.; Andrić, M.; Jovanović, G. Responses of the ionospheric D-region to periodic and transient variations of the ionizing solar Lyα radiation. J. Geogr. Inst. Cvijic 2017, 67, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srećković, V.A.; Šulić, D.; Vujčić, V.; Jevremović, D.; Vyklyuk, Y. The Effects of Solar Activity: Electrons in the Terrestrial Lower Ionosphere. J. Geogr. Inst. Cvijic 2017, 67, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajčetić, J.; Nina, A.; Čadež, V.M.; Todorović, B.M. Ionospheric D-Region Temperature Relaxation and Its Influences on Radio Signal Propagation After Solar X-Flares Occurrence. Therm. Sci. 2015, 19, S299–S309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.; Radovanovic, M. Solar activity as a possible cause of large forest fires—A case study: Analysis of the Portuguese forest fires. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 394, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyklyuk, Y.; Radovanović, M.M.; Stanojević, G.B.; Milovanović, B.; Leko, T.; Milenković, M.; Petrović, M.; Yamashkin, A.A.; Pešić, A.M.; Jakovljević, D.; et al. Hurricane genesis modelling based on the relationship between solar activity and hurricanes II. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2018, 180, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, R.B.; Glauert, S.A.; Meredith, N.P.; Boscher, D.; Maget, V.; Heynderickx, D.; Pitchford, D. Space weather impacts on satellites and forecasting the Earth’s electron radiation belts with SPACECAST. Space Weather 2013, 11, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankov, S.; Warnant, R.; Stegen, K. Trans-ionospheric GPS signal delay gradients observed over mid-latitude Europe during the geomagnetic storms of October–November 2003. Adv. Space Res. 2009, 43, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirazzini, R.; Leppänen, L.; Picard, G.; Lopez-Moreno, J.I.; Marty, C.; Macelloni, G.; Kontu, A.; Von Lerber, A.; Tanis, C.M.; Schneebeli, M.; et al. European In-Situ Snow Measurements: Practices and Purposes. Sensors 2018, 18, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Acqua, F.; Iannelli, G.C.; Torres, M.A.; Martina, M.L. A Novel Strategy for Very-Large-Scale Cash-Crop Mapping in the Context of Weather-Related Risk Assessment, Combining Global Satellite Multispectral Datasets, Environmental Constraints, and In Situ Acquisition of Geospatial Data. Sensors 2018, 18, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benevides, P.; Nico, G.; Catalão, J.; Miranda, P.M.A. Bridging InSAR and GPS Tomography: A New Differential Geometrical Constraint. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, P.; Catalão, J.; Nico, G. Sentinel-1 Interferometric SAR Mapping of Precipitable Water Vapor Over a Country-Spanning Area. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2993–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dere, K.P.; Landi, E.; Young, P.R.; Del Zanna, G.; Landini, M.; Mason, H.E. CHIANTI—An atomic database for emission lines. IX. Ionization rates, recombination rates, ionization equilibria for the elements hydrogen through zinc and updated atomic data. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 498, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Zanna, G.; Dere, K.P.; Young, P.R.; Landi, E.; Mason, H.E. CHIANTI—An atomic database for emission lines. Version 8. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 582, A56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, A.; Chacko, O. Attenuation of solar radiation in the atmosphere. Sol. Energy 1980, 24, 347–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).