Clostridium difficile Infection Epidemiology over a Period of 8 Years—A Single Centre Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol
2.2. Ethical Statement
2.3. Diagnosis of CDI
2.4. Statistical Analysis
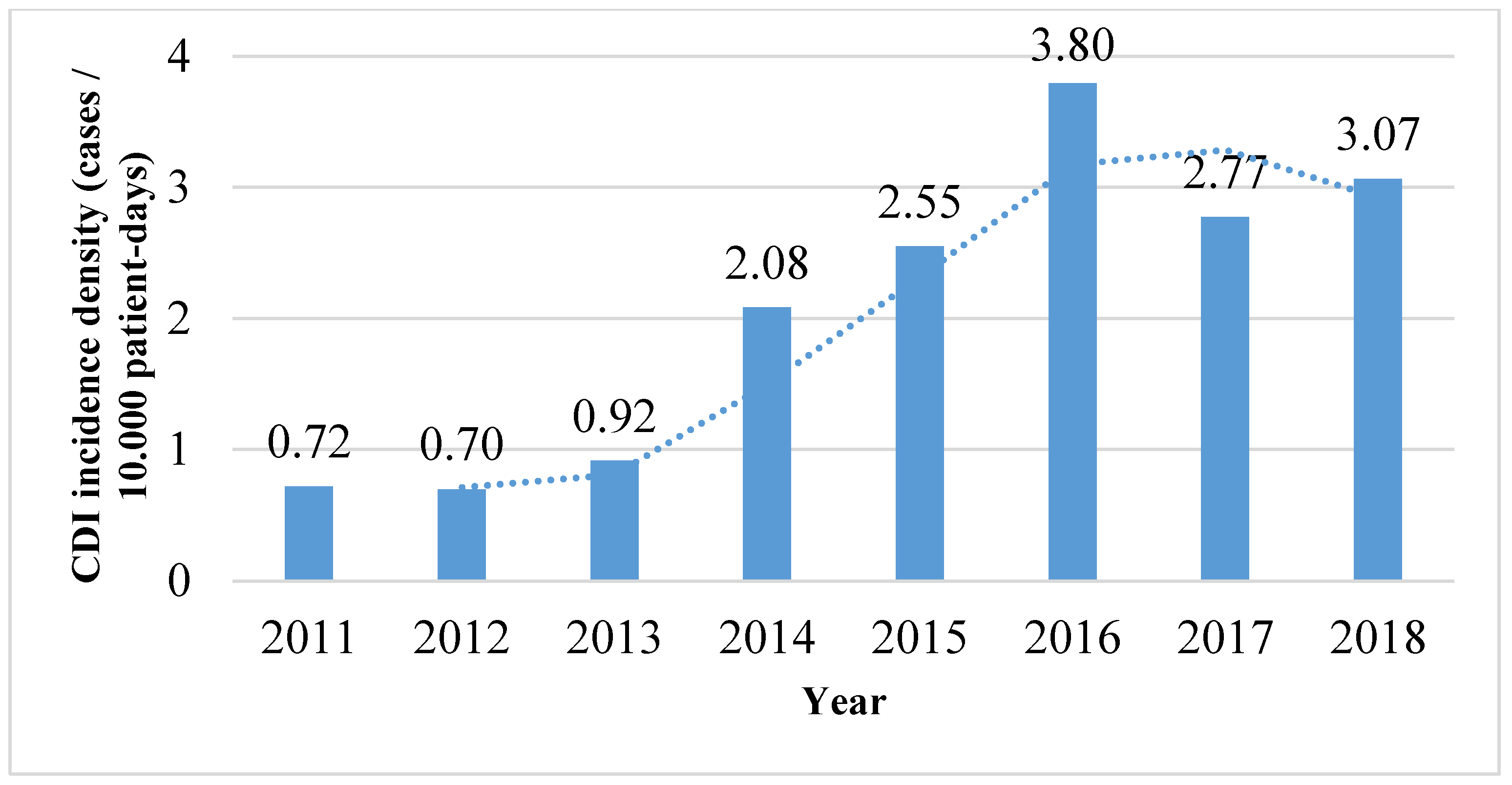
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodriguez-Palacios, A.; Borgmann, S.; Kline, T.R.; LeJeune, J.T. Clostridium difficile in foods and animals: History and measures to reduce exposure. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2013, 14, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McDonald, L.C.; Owings, M.; Jernigan, D.B. Clostridium difficile infection in patients discharged from US short-stay hospitals, 1996–2003. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartlett, J.G.; Gerding, D.N. Clinical recognition and diagnosis of Clostridium difficile infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, S12–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haque, M.; Sartelli, M.; McKimm, J.; Abu Bakar, M. Health care-associated infections—An overview. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 2321–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chai, J.; Lee, C.H. Management of Primary and Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection: An Update. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collins, D.A.; Riley, T.V. Clostridium difficile in Asia: Opportunities for One Health Management. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barker, A.K.; Alagoz, O.; Safdar, N.; Barker, A.K.; Alagoz, O.; Safdar, N. Interventions to Reduce the Incidence of Hospital-Onset Clostridium difficile Infection: An Agent-Based Modeling Approach to Evaluate Clinical Effectiveness in Adult Acute Care Hospitals. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 1192–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raviglione, M.; Maher, D. Ending infectious diseases in the era of the Sustainable Development Goals. Porto Biomed. J. 2017, 2, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsells, E.; Shi, T.; Leese, C.; Lyell, I.; Burrows, J.; Wiuff, C.; Campbell, H.; Kyaw, M.H.; Nair, H. Global burden of Clostridium difficile infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Glob. Health. 2019, 9, 010407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Consumption of Antibacterials for Systemic Use (ATC Group J01) in the Community (Primary Care Sector) in Europe, Reporting Year 2018. 2018. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/antimicrobial-consumption/database/rates-country/ (accessed on 18 November 2019).
- Zaha, D.C.; Bungau, S.; Aleya, S.; Tit, D.M.; Vesa, C.M.; Popa, A.R.; Pantis, C.; Maghiar, O.A.; Bratu, O.G.; Furau, C.; et al. What antibiotics for what pathogens? The sensitivity spectrum of isolated strains in an intensive care unit. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaha, D.C.; Bungau, S.; Uivarosan, D.; Tit, D.M.; Maghiar, T.A.; Maghiar, O.; Pantis, C.; Fratila, O.; Rus, M.; Vesa, C.M. Antibiotic consumption and microbiological epidemiology in surgery departments: Results from a single study center. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langdon, A.; Crook, N.; Dantas, G. The effects of antibiotics on the microbiome throughout development and alternative approaches for therapeutic modulation. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Natarajan, M.; Walk, S.T.; Young, V.B.; Aronoff, D.M. A clinical and epidemiological review of non-toxigenic Clostridium difficile. Anaerobe 2013, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Bella, S.; Ascenzi, P.; Siarakas, S.; Petrosillo, N.; di Masi, A. Clostridium difficile Toxins A and B: Insights into Pathogenic Properties and Extraintestinal Effects. Toxins 2016, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leffler, D.A.; Lamont, J.T. Clostridium difficile infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marra, A.R.; Perencevich, E.N.; Nelson, R.E.; Samore, M.; Khader, K.; Chiang, H.-Y.; Chorazy, M.L.; Herwaldt, L.A.; Diekema, D.J.; Kuxhausen, M.F.; et al. Incidence and Outcomes Associated with Clostridium difficile Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e1917597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, S.H.; Gerding, D.N.; Johnson, S.; Kelly, C.P.; Loo, V.G.; McDonald, L.C.; Pepin, J.; Wilcox, M.H. Clinical practice guidelines for Clostridium difficile infection in adults: 2010 update by the society for healthcare epidemiology of America (SHEA) and the infectious diseases society of America (IDSA). Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2010, 31, 431–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sava, C.N.; Ritli, L.; Balmos, A.B.; Iuhas, A.R.; Marian, P.; Motorca, M.A.; Lele, L.A.; Straciuc, O.; Zaha, D.C.; Jurcă, M.C.; et al. Unusual extramedullary relapses in a case of common B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Case report and review of literature. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2019, 60, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Nale, J.Y.; Redgwell, T.A.; Millard, A.; Clokie, M.R.J. Efficacy of an Optimised Bacteriophage Cocktail to Clear Clostridium difficile in a Batch Fermentation Model. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crobach, M.J.T.; Vernon, J.J.; Loo, V.G.; Kong, L.Y.; Péchiné, S.; Wilcox, M.H.; Kuijper, E.J. Understanding Clostridium difficile colonization. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00021-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Institute of Statistics, 2019. Anuarul Statistic al Judetului Bihor. (In English: Statistical Yearbook of Bihor County). Available online: https://www.bihor.insse.ro/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/Anuar2018.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2020).
- Krutova, M.; Kinross, P.; Barbut, F.; Hajdu, A.; Wilcox, M.H.; Kuijper, E.J.; Survey Contributors. How to: Surveillance of Clostridium difficile infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CERTEST Clostridium Difficilegdh+ Toxin A+B. Available online: https://www.certest.es/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/IU-GX87V-v.01.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- Xpert® C. difficile BT. Available online: https://www.cepheid.com/en/tests/Healthcare-Associated-Infections/Xpert-C.-difficile-BT (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- Depestel, D.D.; Aronoff, D.M. Epidemiology of Clostridium difficile infection. J. Pharm. Pract. 2013, 26, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauer, M.P.; Notermans, D.W.; van Benthem, B.H.; Brazier, J.S.; Wilcox, M.H.; Rupnik, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Dissel, J.T.; Kuijper, E.J.; ECDIS Study Group. Clostridium difficile infection in Europe: A hospital-based survey. Lancet 2011, 377, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control). Clostridium Difficile Infections—Annual Epidemiological Report for 2016. 2018. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/healthcare-associated-infections-clostridium-difficile-infections-annual/ (accessed on 18 November 2019).
- Popescu, G.A.; Serban, R.; Pistol, A.; Niculcea, A.; Preda, A.; Lemeni, D.; Macovei, S.I.; Talapan, D.; Rafila, A.; Florea, D. The Recent emergence of Clostridium difficile infection in Romanian hospitals is associated with a high prevalence of polymerase chain reaction ribotype 027. Balk. Med. J. 2018, 35, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asempa, T.E.; Nicolau, D.P. Clostridium difficile infection in the elderly: An update on management. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 1799–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knetsch, C.W.; Kumar, N.; Forster, S.C.; Connor, T.R.; Browne, H.P.; Harmanus, C.; Sanders, I.M.; Harris, S.R.; Turner, L.; Morris, T.; et al. Zoonotic transfer of Clostridium difficile harboring antimicrobial resistance between farm animals and humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01384-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, C.; Taminiau, B.; Van Broeck, J.; Delmee, M.; Daube, G. Clostridium difficile in Food and Animals: A comprehensive review. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 932, 65–92. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, E.Y.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Martinez, E.M.; Pant, S.; Gandra, S.; Levin, S.A.; Goossens, H.; Laxminarayan, R. Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3463–E3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, K.A.; Khanafer, N.; Daneman, N.; Fisman, D.N. Meta-analysis of antibiotics and the risk of community-associated Clostridium difficile infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2326–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deshpande, A.; Pasupuleti, V.; Thota, P.; Pant, C.; Rolston, D.D.; Sferra, T.J.; Hernandez, A.V.; Donskey, C.J. Community-associated Clostridium difficile infection and antibiotics: A meta-analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1951–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vardakas, K.Z.; Trigkidis, K.K.; Boukouvala, E.; Falagas, M.E. Clostridium difficile infection following systemic antibiotic administration in randomised controlled trials: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 48, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Distribution of Antimicrobial Consumption by Antimicrobial Group. 2019. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/antimicrobial-consumption/database/distribution-by-antimicrobial-group/ (accessed on 20 November 2019).
- Chiang, S.-R.; Lai, C.-C.; Ho, C.-H.; Chen, C.-M.; Chao, C.-M.; Wang, J.-J.; Cheng, K.-C. Prolonged Mechanical Ventilation Assistance Interacts Synergistically with Carbapenem for Clostridium difficile Infection in Critically Ill Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, N.A.; Smith, B.A.; Lewis, S.S. Novel and emerging sources of Clostridioides difficile infection. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1008125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usai, D.; Donadu, M.; Bua, A.; Molicotti, P.; Zanetti, S.; Piras, S.; Corona, P.; Ibba, R.; Carta, A. Enhancement of antimicrobial activity of pump inhibitors associating drugs. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2019, 13, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernandez-Garcia, R.; Garza-Gonzalez, E.; Miller, M.; Arteaga-Muller, G.; Galvan-de los Santos, A.M.; Camacho-Ortiz, A. Application of the ATLAS score for evaluating the severity of Clostridium difficile infection in teaching hospitals in Mexico. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 19, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hensgens, M.P.M.; Goorhuis, A.; Dekkers, O.M.; van Benthem, B.H.B.; Kuijper, E.J. All-cause and disease-specific mortality in hospitalized patients with Clostridium difficile infection: A multicenter cohort study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hota, S.S.; Achonu, C.; Crowcroft, N.S.; Harvey, B.J.; Lauwers, A.; Gardam, M.A. Determining mortality rates attributable to Clostridium difficile infection. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fatima, R.; Aziz, M. The hypervirulent strain of Clostridium difficile: NAP1/B1/027—A brief overview. Cureus 2019, 11, e3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banawas, S.S. Clostridium difficile Infections: A global overview of drug sensitivity and resistance mechanisms. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, A.M.; Wuerth, B.A.; Wiemken, T.L.; Arnold, F.W. Prevalence of Clostridium difficile infection presenting to US EDs. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 33, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafer, N.; Toure, A.; Chambrier, C.; Cour, M.; Reverdy, M.E.; Argaud, L.; Vanhems, P. Predictors of Clostridium difficile infection severity in patients hospitalised in medical intensive care. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 8034–8041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos-Schaller, O.; Boisset, S.; Seigneurin, A.; Epaulard, O. Recurrence and death after Clostridium difficile infection: Gender-dependant influence of proton pump inhibitor therapy. Springerplus 2016, 5, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boone, J.H.; Goodykoontz, M.; Rhodes, S.J.; Price, K.; Smith, J.; Gearhart, K.N.; Carman, R.J.; Kerkering, T.M.; Wilkins, T.D.; Lyerly, D.M. Clostridium difficile prevalence rates in a large healthcare system stratified according to patient population, age, gender, and specimen consistency. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 31, 1551–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schousboe, M.; Barrett, R.; Wildbore, A.M. Clostridium difficile–related 30-day mortality: A case-control study. Infect. Dis. Clin. Pract. 2013, 21, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karas, J.A.; Bradshaw, S.; Mahmud, W.; Enoch, D.A. Mortality in hospitalized older adults associated with Clostridium difficile infection at a district hospital. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2010, 2, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pechal, A.; Lin, K.; Allen, S.; Reveles, K. National age group trends in Clostridium difficile infection incidence and health outcomes in United States community hospitals. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Negrut, N.; Nistor-Cseppento, D.C.; Khan, S.A.; Pantis, C.; Maghiar, T.A.; Maghiar, O.; Aleya, S.; Rus, M.; Tit, D.M.; Aleya, L.; et al. Clostridium difficile Infection Epidemiology over a Period of 8 Years—A Single Centre Study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4439. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114439
Negrut N, Nistor-Cseppento DC, Khan SA, Pantis C, Maghiar TA, Maghiar O, Aleya S, Rus M, Tit DM, Aleya L, et al. Clostridium difficile Infection Epidemiology over a Period of 8 Years—A Single Centre Study. Sustainability. 2020; 12(11):4439. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114439
Chicago/Turabian StyleNegrut, Nicoleta, Delia Carmen Nistor-Cseppento, Shamim Ahmad Khan, Carmen Pantis, Teodor Andrei Maghiar, Octavian Maghiar, Selim Aleya, Marius Rus, Delia Mirela Tit, Lotfi Aleya, and et al. 2020. "Clostridium difficile Infection Epidemiology over a Period of 8 Years—A Single Centre Study" Sustainability 12, no. 11: 4439. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114439
APA StyleNegrut, N., Nistor-Cseppento, D. C., Khan, S. A., Pantis, C., Maghiar, T. A., Maghiar, O., Aleya, S., Rus, M., Tit, D. M., Aleya, L., Rahdar, A., & Bungau, S. (2020). Clostridium difficile Infection Epidemiology over a Period of 8 Years—A Single Centre Study. Sustainability, 12(11), 4439. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114439









