The Possibilities of Preservation, Regeneration and Presentation of Industrial Heritage: The Case of Old Mint “A.D.” on Belgrade Riverfront
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Industrial Heritage and Relevant Charters
2.2. Practical Framework—Methodology of work on the elective course History and Theory 1—Visual Culture in Architectural Theory and Practice
3. Results
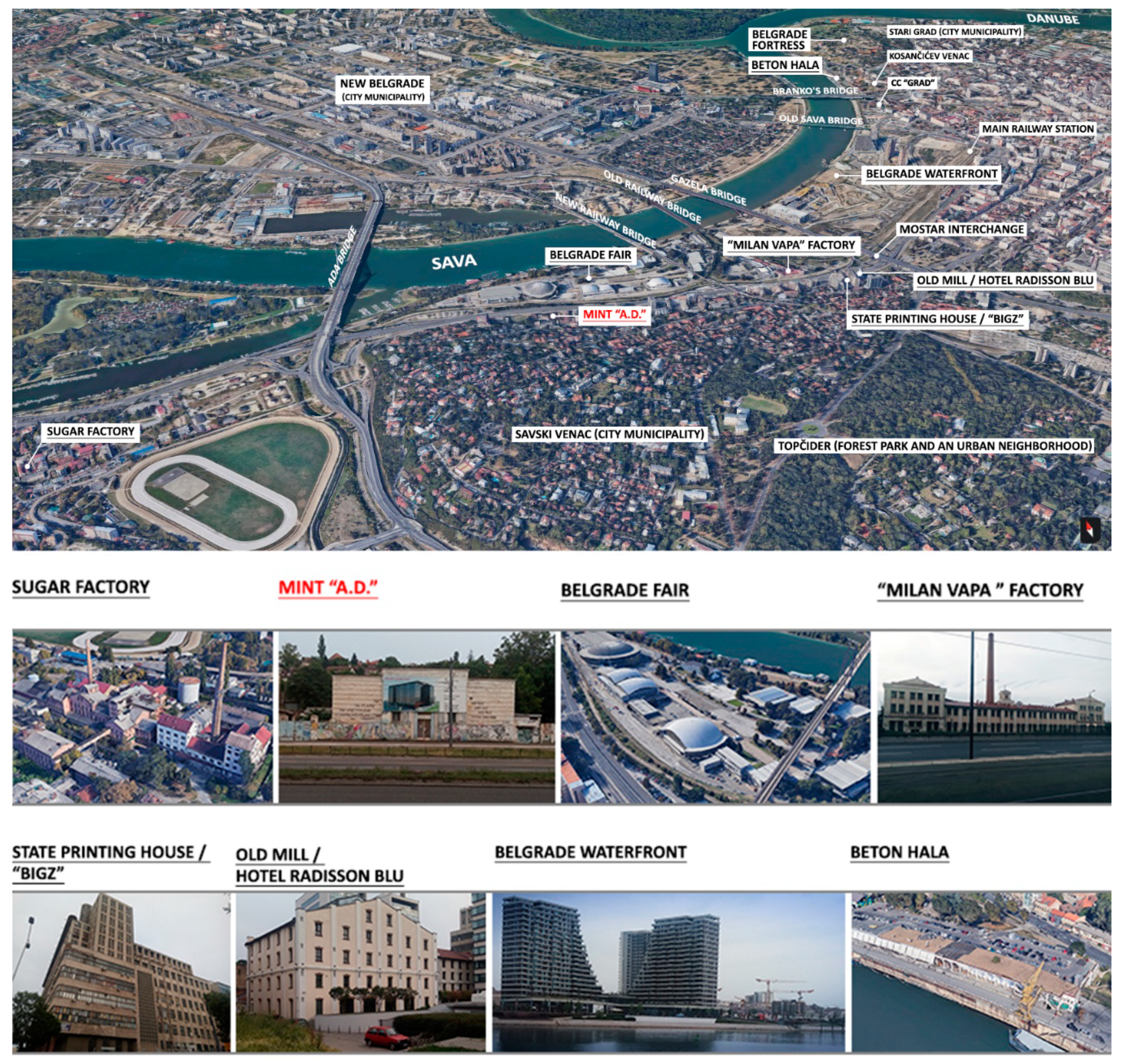
3.1. Industrial Heritage of Belgrade—Historical Overview
3.2. Industrial Heritage in Belgrade and the Main Challenges
3.3. Environmental and Sustainable Aspects of Adaptive Reuse Approach in Preserving Industrial Cultural Heritage
Environmental Aesthetics and Ethical Positions in Preservation of Architectural Cultural Heritage
3.4. Educational Student Projects of Preservation, Regeneration and Presentation of the Old Mint “A.D.”
3.4.1. Analysis of Cultural and Historical Values of the Mint AD, Its Surroundings and Presentation of the Location in the Strategic Plan of Spatial Development of Belgrade
3.4.2. Results of the Educational Projects for the Revitalization of the Old Mint “A.D.”
Review of Student Projects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tasić, N.; Zotović, L.j.; Kalić, J.; Tričković, R.; Milosavljević, P.; Milić, D.; Maksimović, B.; Kojić, B.; Milićević, J.; Gligorijević, B.; et al. Istorija Beograda; Srpska akademija nauka i umetnosti: Belgrade, Serbia, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- TICCIH (The International Committee for the Conservation of the Industrial Heritage). The Nizhny Tagil Charter for the Industrial Heritage; TICCIH: Ceredigion, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, M.; Neaverson, P. Industrial Archaeology. In Principles and Practice; Routledge: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Council of Europe Industrial Heritage in Europe; Council of Europe, Parliamentary Assembly: Brussels, Belgium. 2013. Available online: http://assembly.coe.int/nw/xml/XRef/Xref-XML2HTML-en.asp?fileid=19512&lang=EN (accessed on 14 January 2020).
- ICOMOS (International Council of Monuments and Sites). Venice Charter for the Conservation and Restoration of Monuments and Sites; ICOMOS: Venice, Italy, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization). Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Council of Europe. Convention for the Protection of the Architectural Heritage of Europe; Council of Europe: Granada, Spain, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization). Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Petranović, B. Istorija Jugoslavije 1918–1988, Knjige 1,2,3; Nolit: Belgrade, Yugoslavia, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Ignjatović, A. Jugoslovenstvo u arhitekturi 1904–1941; Građevinska knjiga: Belgrade, Serbia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Belgrade, W. Available online: https://www.belgradewaterfront.com/en/ (accessed on 22 January 2020).
- Academy of Architecture of Serbia. Available online: https://aas.org.rs/tag/beograd-na-vodi/ (accessed on 22 January 2020).
- National Sustainable Development Strategy [Nacionalna strategija održivog razvoja]. Offcial Gazette of the Republic of Serbia [Službeni glasnik Republike Srbije] br. 57/2008; Službeni glasnik: Belgrade, Serbia, 3 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Museum of Science and Technology. Protocol for the Integral Protection of Industrial Heritage; MST: Belgrade, Serbia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lalović, K.; Živković, J.; Radosavlejvić, U.; Đukanović, Z. An Integral Approach to the Modeling of Information Support for Local Sustainable Development-Experiences of a Serbian Enabling Leadership Experiment. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikezić, A.; Marković, D. Place-Based Education in the Architectural Design Studio: Agrarian Landscape as a Resource for Sustainable Urban Lifestyle. Sustainability 2015, 7, 9711–9733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radosavljević, U.; Kuletin Ćulafić, I. Use of Cultural Heritage for Place Branding in Educational Projects: The Case of Smederevo and Golubac Fortresses on the Danube. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bottero, M.; D’Alpaos, C.; Oppio, A. Ranking of Adaptive Reuse Strategies for Abandoned Industrial Heritage in Vulnerable Contexts: A Multiple Criteria Decision Aiding Approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coscia, C.; Lazzari, G.; Rubino, I. Values, Memory, and the Role of Exploratory Methods for Policy-Design Processes and the Sustainable Redevelopment of Waterfront Contexts: The Case of Officine Piaggio (Italy). Sustainability 2018, 10, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ICOMOS (International Council of Monuments and Sites). The Nara Document on Authenticity; ICOMOS: Nara, Japan, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- ICOMOS (International Council of Monuments and Sites). The Nara+20: On Heritage Practices, Cultural Values and the Concept of Authenticity; ICOMOS: Nara, Japan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- ICOMOS (International Council of Monuments and Sites). International Cultural Tourism Charter: Managing Tourism at Places of Heritage Significance; ICOMOS: Mexico City, Mexico, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- World Summit on Sustainable Tourism. The 2015 World Charter for Sustainable Tourism +20; World Summit on Sistainable Tourism: Victoria-Gasteiz, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- TICCIH (The International Committee for the Conservation of the Industrial Heritage). Taipei Declaration for Asian Industrial Heritage. In Proceedings of the TICCIH Congress 15th Congress in Taipei, Taipei, Taiwan, 5–8 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Council of Europe. Council of Europe Framework Convention on the Value of Cultural Heritage for Society; Council of Europe: Faro, Portugal, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Council of Europe. European Landscape Convention; Council of Europe: Florence, Italy, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Council of Europe. Congress of Local and Regional Authorities of Europe. Manifesto for a New Urbanity: European Urban Charter II; Council of Europe: Congress of Local and Regional Authorities of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- TICCIH (The International Committee for the Conservation of the Industrial Heritage). Available online: https://ticcih.org (accessed on 7 February 2020).
- TICCIH (The International Committee for the Conservation of the Industrial Heritage). Available online: https://ticcih.org/ticcih-in-chile-congress-xvii (accessed on 8 February 2020).
- TICCIH (The International Committee for the Conservation of the Industrial Heritage). Memorandum of Understanding between ICOMOS and TICCIH Regarding a Framework for Collaboration on the Conservation of Industrial heritage; TICCIH: Ceredigion, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- ERIH (European Route of Industrial Heritage). European Route of Industrial Heritage: Executive Summary: Our Common European Heritage; ERICH Secretariat Deutsche Gesellschaft für Industriekultur: Duisburg, Germany, 2001; Available online: https://www.erih.net/fileadmin/Mediendatenbank/Downloads/Masterplan___Infos/ERIH_I_summary.PDF (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- ERIH (European Route of Industrial Heritage). The Declaration of Duisburg; ERICH Secretariat Deutsche Gesellschaft für Industriekultur: Duisburg, Germany, 2001; Available online: https://www.erih.de (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- ICOMOS (International Council of Monuments and Sites). The ICOMOS Charter on Cultural Routes. In Proceedings of the 16th General Assembly of ICOMOS, Québec, QC, Canada, 29 September–5 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization). Recommendation on the Historic Urban Landscape; UNESCO World Heritage Centre: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization). Recommendation Concerning the Safeguarding and Contemporary Role of Historic Areas; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- ICOMOS (International Council of Monuments and Sites). Xi’an Declaration on the Conservation of the Setting of Heritage Structures, Sites and Areas; ICOMOS: Paris, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization). Vienna Memorandum on ‘World Heritage and Contemporary Architecture-Managing the Historic Urban Landscape’; UNESCO World Heritage Centre: Paris, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Congress of Local and Regional Authorities of Europe. Manifesto for a New Urbanity: European Urban Charter II.; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- ICOMOS (International Council of Monuments and Sites). The Québec Declaration on the Preservation of the Spirit of the Place; ICOMOS: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Regionalverband Ruhr. Available online: https://www.route-industriekultur.ruhr (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Report of the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development; United Nations: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Provisional Agenda; United Nations: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- ICPD. Programme of Action of the International Conference on Population and Development; ICPD: Cairo, Egypt, 1994; extended 2010. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Resolution adopted by General Assembly, 66/288. The future we want. Final document of the Rio+20 Conference. In Proceedings of the Rio+20 United Nations Conference Sustainable Development, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 20–22 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. United Nations Millennium Declaration; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Adoption of the Paris Agreement; United Nations: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Kyoto Protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change; United Nations: Kyoto, Japan, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Law on Ratification of the Kyoto Protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on climate change [Zakon o potvrđivanju Kjoto protokola uz okvirnu konvenciju Ujedinjenih Nacija o promeni klime]. Official Gazette of the Republic of Serbia [Službeni glasnik Republike Srbije] br. 88/07; Službeni glasnik: Belgrade, Serbia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Doha Amendment the Kyoto Protocol; United Nations: Doha, Qatar, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Muminović, E.; Radosavljević, U.; Beganović, D. Strategic Planning and Management Model for the Regeneration of Historic Urban Landscapes: The Case of Historic Center of Novi Pazar in Serbia. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radosavljević, U.; Đorđević, A.; Živković, J.; Lalović, K.; Đukanović, Z. Educational Projects for Linking Place Branding and Urban Planning in Serbia, European Planning Studies. 2019. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/09654313.2019.1701296 (accessed on 14 January 2020).
- Landry, C. The Creative City: A Toolkit for Urban Innovators; Comedia Earthscan Publishing for a Sustainable Future: London, UK; Sterling, VA, USA, 2008; pp. 166–167. [Google Scholar]
- Radosavljević, U.; Đorđević, A.; Živković, J. Business Improvement Districts as a Management Instrument for City Center’s Regeneration in Serbia. Facta Univ. Ser. Archit. Civ. Eng. 2015, 13, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lalović, K.; Radosavljević, U.; Đukanović, Z. Reframing Public Interest in the Implementation of Large Urban Projects in Serbia: The Case of Belgrade Waterfront Project. Facta Univ. Ser. Archit. Civ. Eng. 2015, 13, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikolić, M.; Pašić, D.; Milenković, A. Ispitivanje mogućnosti zaštite i revitalizacije livnice Panteliću Zemunu. Nasleđe 2018, XIX, 149–161. [Google Scholar]
- Roter Blagojević, M.; Nikolić, M. Predlog revitalizacije umetničke livnice Skulptura. Nasleđe 2012, XIII, 221–234. [Google Scholar]
- Vujović, B. Beograd u prošlosti i sadašnjosti; Izdavačka agencija Draganić: Belgrade, Serbia, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Janićijević, J.; Vujović, B.; Jovanović, M.; Kusovac, N.; Nemanjić, M.; Pantelić, N.; Srejović, D.; Stanić, D. Kulturna riznica Srbije; Izdavačka zadruga IDEA: Belgrade, Serbia, 1996; pp. 233–269. [Google Scholar]
- Roter Blagojević, M. The Modernization and Urban Transformation of the Belgrade in the 19th and Early 20th Century. In Planing Capital Cities: Belgrade, Bucurest, Sofia; Doytchinov, G., Đukić, A., Catalina, I., Eds.; Verlag der Technischen Universität Graz: Graz, Austria, 2015; pp. 20–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kulenović, R. Industrijsko Nasleđe Beograda; Muzej nauke i tehnike: Belgrade, Serbia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Katalog Nepokretnih Kulturnih Dobara Na Području Grada Beograda (The Cultural Properties in Belgrade). Available online: http://beogradskonasledje.rs/kd/zavod/savski_venac/zeleznicka_stanica.html (accessed on 6 April 2020).
- Vukotić-Lazar, M.; Roter Blagojević, M. The 1923 Belgrade Master Plan–historic town modernization. Planning Perspectives. 2017, pp. 1–8. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1080/02665433.2017.1408485 (accessed on 26 April 2020).
- Petrović, D. Istorija Industrije Beograda. Razvoj I Razmestaj Industrije Beograda U XIX I XX Veku; Srpsko geografsko društvo: Belgrade, Serbia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mihajlov, S. Nastanak i razvoj industrijske zone na desnoj obali Dunava u Beogradu od kraja 19. do sredine 20. veka. Nasleđe 2011, XII, 91–116. [Google Scholar]
- Djukić, A.; Vaništa Lazarević, E.; Vukmirović, M. Planning framework, projects, urban competitions and visions for development of Sava Amphitheatre. Izgradnja 2014, 3–4, 103–121. [Google Scholar]
- Law on Cultural Property [3акoн o културним дoбрима]. Official Gazette of the City of Belgrade [Službeni list grada Beograda]. No. 71/94,52/2011, 99/11. Available online: http://www.kultura.gov.rs/docs/dokumenti/propisi-iz-oblasti-kulture/zakon-o-kulturnim-dobrima.pdf (accessed on 26 April 2020).
- Obad Šćitaroci, M.; Bojanić Obad Šćitaroci, B. Heritage Urbanism. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milinković, M.; Ćorović, D.; Vuksanović-Macura, Z. Historical Enquiry as a Critical Method in Urban Riverscape Revisions: The Case of Belgrade’s Confluence. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katalog Nepokretnih Kulturnih Dobara Na Području Grada Beograda (The Cultural Properties in Belgrade). Available online: http://beogradskonasledje.rs/kd/zavod/stari_grad/beogradska_tvrdjava.html (accessed on 6 April 2020).
- Katalog Nepokretnih Kulturnih Dobara Na Području Grada Beograda (The Cultural Properties in Belgrade). Available online: http://beogradskonasledje.rs/kd/zavod/stari_grad/kosancicev_venac.html (accessed on 6 April 2020).
- Rosenfield, K. Beton Hala Waterfront Center / Sou Fujimoto Architects, ArchDaily. 2012. Available online: https://www.archdaily.com/286381/beton-hala-waterfront-center-sou-fujimoto-architects/ISSN0719-8884 (accessed on 3 May 2020).
- Vaništa Lazarević, E. Urban Regeneration Tools (City Branding) in Belgrade after the Democratic Change in 2000–Social Frame. In Planing Capital Cities: Belgrade, Bucurest, Sofia; Doytchinov, G., Đukić, A., Catalina, I., Eds.; Verlag der Technischen Universität Graz: Graz, Austria, 2015; pp. 174–187. [Google Scholar]
- Roter Blagojević, M.; Nikolić, M. Dilemmas and Problems in Active Reuse of Belgrade Industrial Architecture–The Case Study of the Sava River Area. In e-Monographic Publication of ICOMOS Slovenia: Protection and Reuse of Industrial Heritage: Dilemmas, Problems, Examples; Ifko, S., Stokin, M., Eds.; ICOMOS Slovenia: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2017; pp. 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Katalog Nepokretnih Kulturnih Dobara Na Području Grada Beograda (The Cultural Properties in Belgrade). Available online: http://beogradskonasledje.rs/kd/zavod/savski_venac/zgrada_drzavne_stamparije.html (accessed on 19 April 2020).
- Katalog Nepokretnih Kulturnih Dobara Na Području Grada Beograda (The Cultural Properties in Belgrade). Available online: http://beogradskonasledje.rs/kd/zavod/savski_venac/fabrika_hartije_milana_vape.html (accessed on 19 April 2020).
- Katalog Nepokretnih Kulturnih Dobara Na Području Grada Beograda (The Cultural Properties in Belgrade). Available online: http://beogradskonasledje.rs/kd/zavod/savski_venac/hala_1_beogradskog_sajma.html (accessed on 19 April 2020).
- Katalog Nepokretnih Kulturnih Dobara Na Području Grada Beograda (The Cultural Properties in Belgrade). Available online: http://beogradskonasledje.rs/kd/zavod/cukarica/fabrika_secera.html (accessed on 19 April 2020).
- Djukić, A.; Špirić, A.; Vujičić, T. Urban Design Competition and Megaprojects in a Context of Identity of Cultural Heritage: Case Study Belgrade’s Riverfronts. In e-Monographic Publication of ICOMOS Slovenia: Protection and Reuse of Industrial Heritage: Dilemmas, Problems, Examples; Ifko, S., Stokin, M., Eds.; ICOMOS Slovenia: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2017; pp. 59–71. [Google Scholar]
- Katalog Nepokretnih Kulturnih Dobara Na Području Grada Beograda (The Cultural Properties in Belgrade). Available online: http://beogradskonasledje.rs/kd/zavod/stari_grad/termoelektrana_snaga_i_svetlost.html (accessed on 19 April 2020).
- Drobnjak, B.; Nikolić, M. Bauhaus i njegova refleksija na formiranje umetničkih praksi na eks-jugoslovenskim kulturnim prostorima (Bauhaus and its Reflection on Forming of the Artistic Practices in the Ex-Yugoslav Cultural Region). Arhit. I Urban. 2019, 49, 7–17. [Google Scholar]
- “BBC Dream Builders”-Interview with Norman Foster. Interview conducted by Razia Iqbal (BBC World Service, 16.06.2013, London, United Kingdom). Available online: https://www.fosterandpartners.com/media/1028028/NF-BBC-Dream_Builders_transcript.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Foster and Partners. 2020. Available online: https://www.fosterandpartners.com/expertise/sustainability/ (accessed on 4 January 2020).
- General Urban Plan for Belgrade [Generalni urbanistički plan Beograda]. Official Gazette of the City of Belgrade [Službeni list grada Beograda]; Službeni glasnik: Belgrade, Serbia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization). The UNESCO Recommendation on the Historic Urban Landscape; UNESCO World Heritage Centre: Paris, France, 2019; Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/hul/ (accessed on 22 January 2020).
- Latham, D. Creative Re-Use of Buildings; Donhead Publishing: Shaftesbury, UK, 2000; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Yung, E.H.K.; Chan, E.H.W. Implementation challenges to the adaptive reuse of heritage buildings: Towards the goals of sustainable, low carbon cities. Habitat Int. 2012, 36, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocca, F. The Role of Cultural Heritage in Sustainable Development: Multidimensional Indicators as Decision-Making Tool. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. The WHO special initiative for mental health (2019–2023): Universal health coverage for mental health; World Health Organization, 2019. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/310981 (accessed on 26 January 2020).
- United Nations. Our Common Future: Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development—Brundtland Report; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/5987our-common-future.pdf (accessed on 19 January 2020).
- Evans, J.; Jones, P. Rethinking Sustainable Urban Regeneration: Ambiguity, Creativity, and the Shared Territory. Environ. Plan. A 2008, 40, 1416–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Berardinis, P.; Rotilio, M.; Capannolo, L. Energy and Sustainable Strategies in the Renovation of Existing Buildings: An Italian Case Study. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Günçe, K.; Mısırlısoy, D. Assessment of Adaptive Reuse Practices through User Experiences: Traditional Houses in the Walled City of Nicosia. Sustainability 2019, 11, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radosavljević, U.; Đorđević, A.; Lalović, K.; Živković, J.; Đukanović, Z. Nodes and Networks: The Generative Role of Cultural Heritage for Urban Revival in Kikinda. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, J.; Lee, J. Adaptive Reuse of Apartments as Heritage Assets in the Seoul Station Urban Regeneration Area. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Medici, S.; De Toro, P.; Nocca, F. Cultural Heritage and Sustainable Development: Impact Assessment of Two Adaptive Reuse Projects in Siracusa, Sicily. Sustainability 2020, 12, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howkins, J. The Creative Economy How People Make Money from Ideas; The Penguin Press: London, UK, 2001; pp. 86–87. [Google Scholar]
- Harries, K. The Ethical Function of Architecture; MIT Press: Massachusetts, NE, USA, 2000; p. 270. [Google Scholar]
- Delancey, C. Architecture can Save the World: Building and Environmental Etics. In the Philosophical Forum; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK; Malden, MA, USA, 2004; Volume 35, pp. 147–159. [Google Scholar]
- Gradska Opština Savski Venac (Municipality Savski Venac). 2016. Available online: https://www.savskivenac.rs/cir/o-opstini/ (accessed on 18 April 2020).
- Bogunović, S. Arhitektonska Enciklopedija Beograda XIX I XX Veka (I); Beogradska knjiga: Belgrade, Serbia, 2005; pp. 355–356. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlović, M. Nikola Nestorović; Orion art: Belgrade, Serbia, 2017; p. 46. [Google Scholar]
- Pacific Gas and Electric Company. Inclusion of Solar Reflectance and Thermal Emittance Prescriptive Requirements for Residential Roofs in Title 24; Pacific Gas and Electric Company: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2006; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Solecki, W.D.; Rosenzweig, C.; Cox, J.; Parshall, L.; Rosenthal, J.; Hodges, S. Potential Impact of Green Roofs on the Urban Heat Island Effect. In Green Roofs in the New York Metropolitan Region; Rosenzweig, C., Gaffin, S., Parshall, L., Eds.; Columbia University Center for Climate Systems Research and NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies: New York, NY, USA, 2006; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Simić, I.; Stupar, A.; Djokić, V. Building the Green Infrastructure of Belgrade: The Importance of Community Greening. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
















© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikolić, M.; Drobnjak, B.; Kuletin Ćulafić, I. The Possibilities of Preservation, Regeneration and Presentation of Industrial Heritage: The Case of Old Mint “A.D.” on Belgrade Riverfront. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5264. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135264
Nikolić M, Drobnjak B, Kuletin Ćulafić I. The Possibilities of Preservation, Regeneration and Presentation of Industrial Heritage: The Case of Old Mint “A.D.” on Belgrade Riverfront. Sustainability. 2020; 12(13):5264. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135264
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikolić, Marko, Boško Drobnjak, and Irena Kuletin Ćulafić. 2020. "The Possibilities of Preservation, Regeneration and Presentation of Industrial Heritage: The Case of Old Mint “A.D.” on Belgrade Riverfront" Sustainability 12, no. 13: 5264. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135264
APA StyleNikolić, M., Drobnjak, B., & Kuletin Ćulafić, I. (2020). The Possibilities of Preservation, Regeneration and Presentation of Industrial Heritage: The Case of Old Mint “A.D.” on Belgrade Riverfront. Sustainability, 12(13), 5264. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135264





