Effects of Drought Stress on Some Agronomic and Morpho-Physiological Traits in Durum Wheat Genotypes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Experimental Layout
2.2. Physiological Assay
2.3. Agro-Morphological Assay
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Variance, Range of Data, and Means Comparison
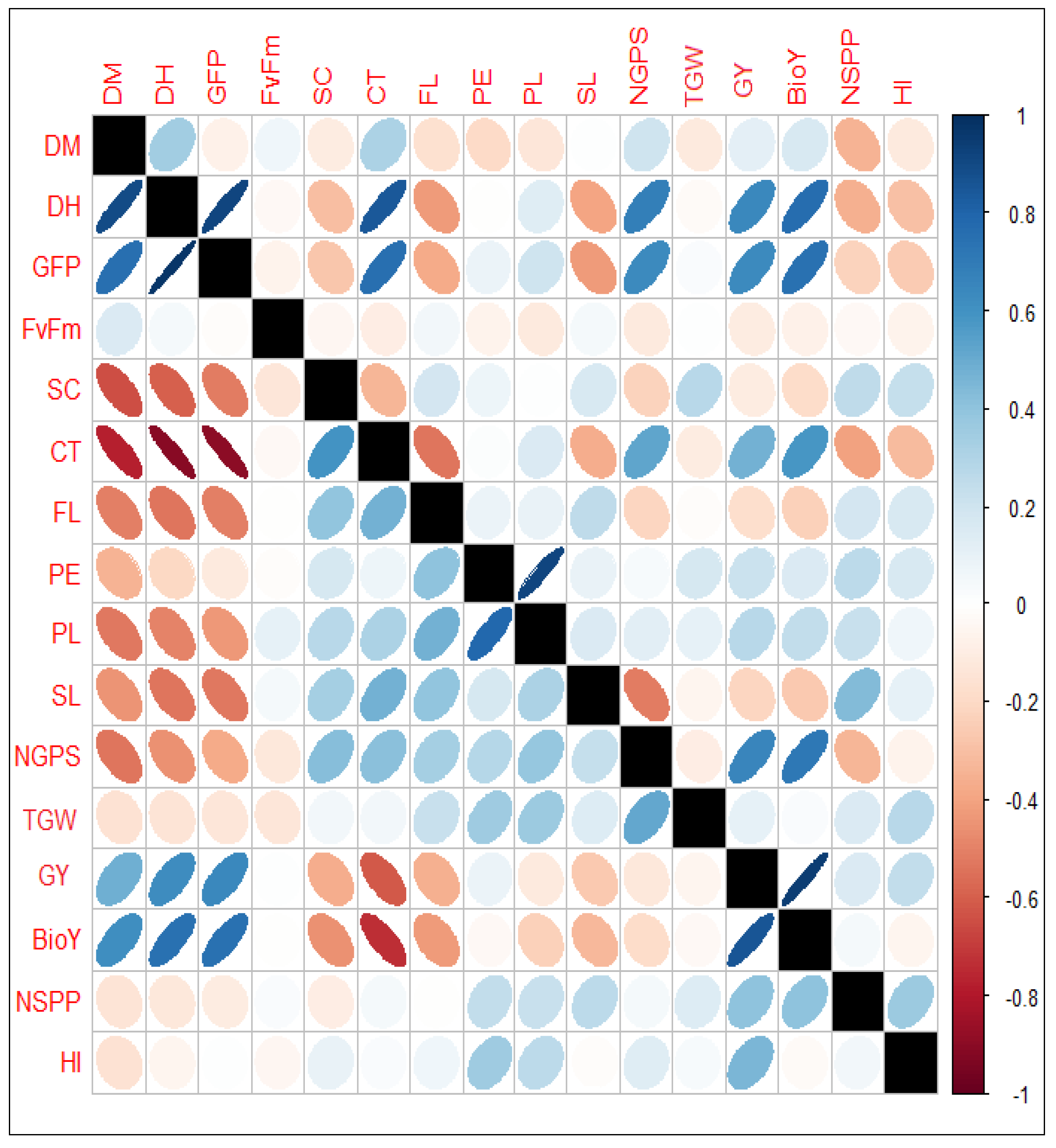
3.2. Association Among Measured Traits
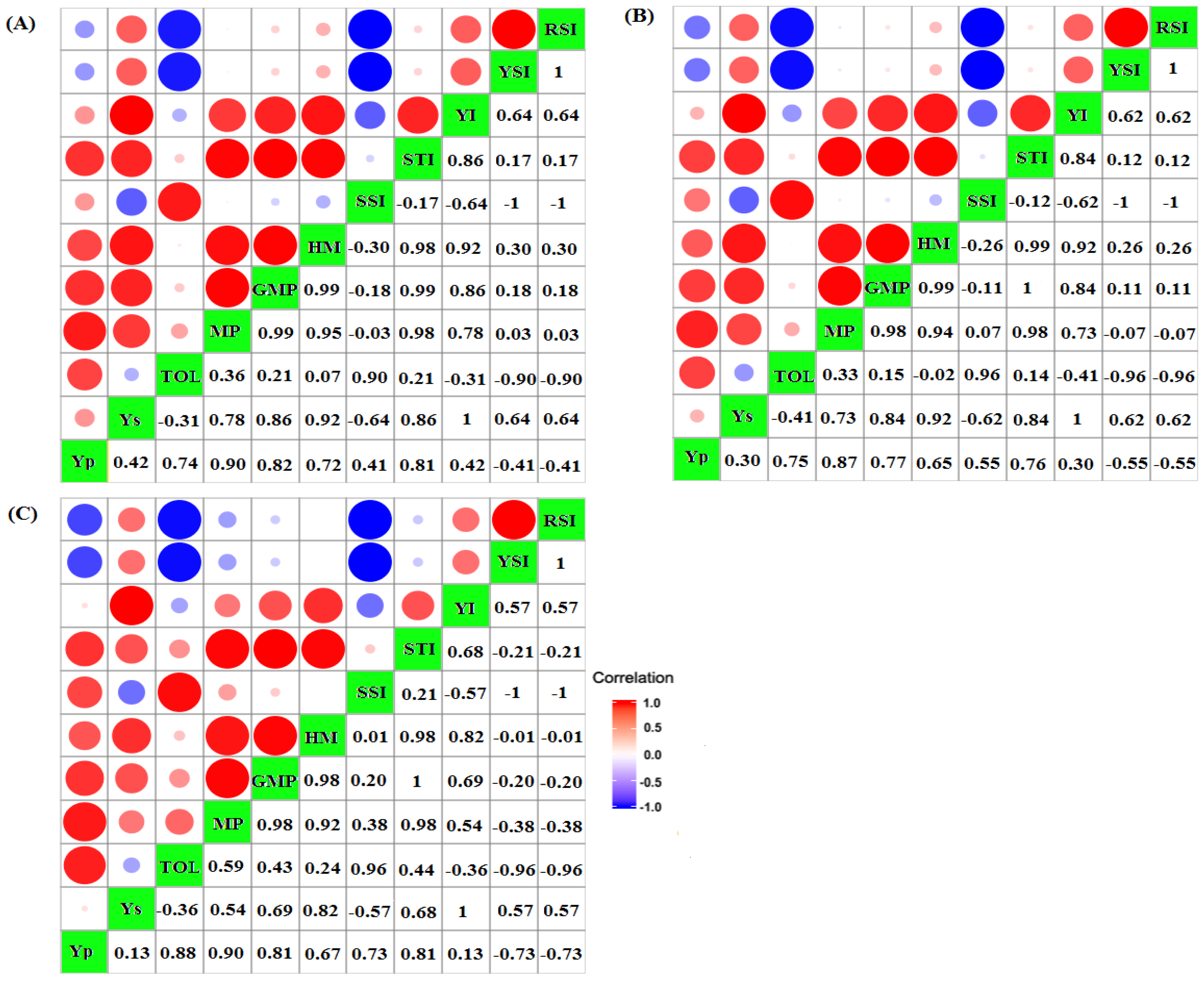
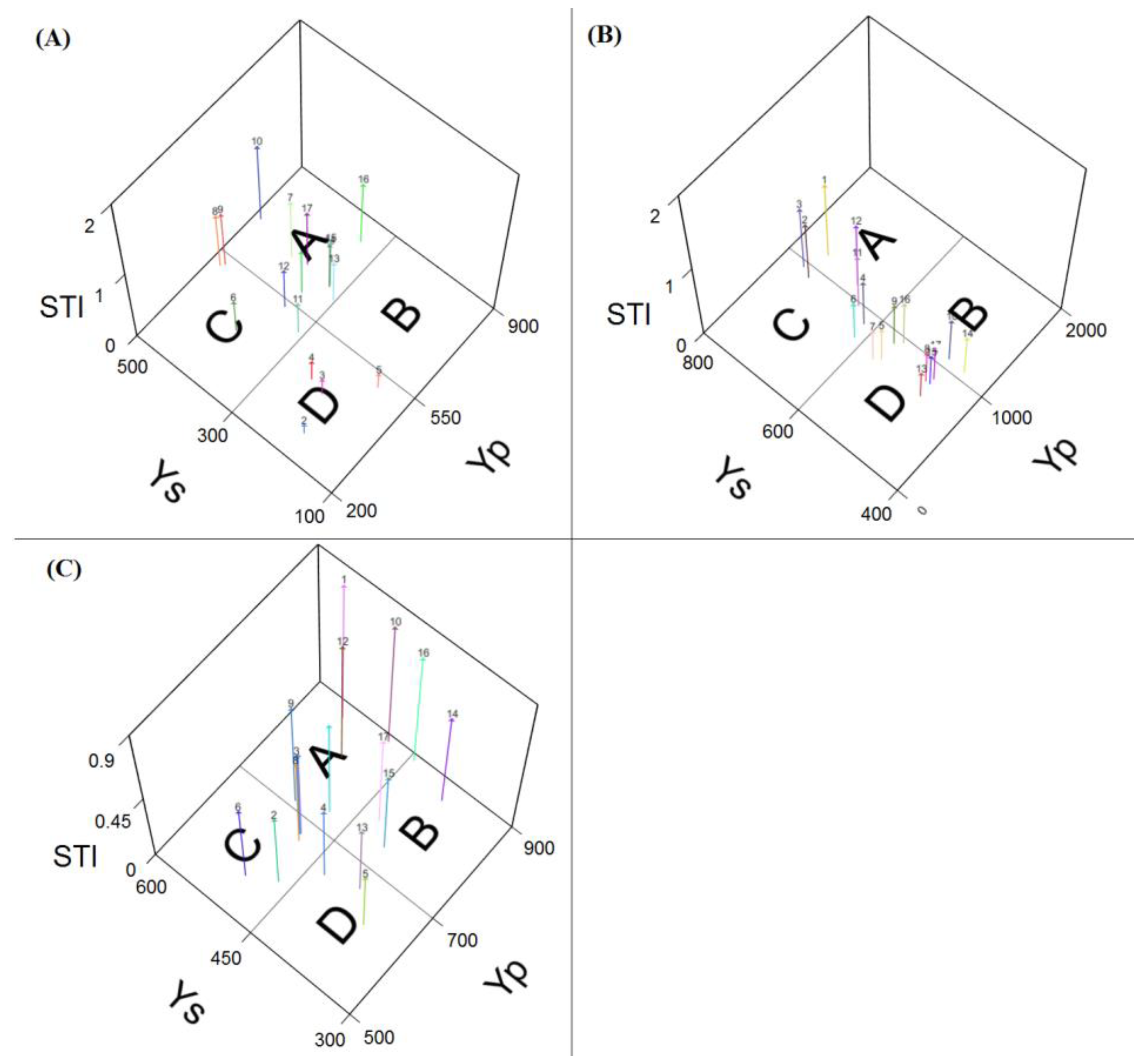
3.3. Screening Drought-Tolerant Genotypes Due to Yield-Based Indices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, H.G.M.D.; Sajjad, M.; Li, M.; Azmat, M.A.; Rizwan, M.; Maqsood, R.H.; Khan, S.H. Selection criteria for drought-tolerant bread wheat genotypes at seedling stage. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukid, F.; Dall’Asta, M.; Bresciani, L.; Mena, P.; Del Rio, D. Phenolic profile and antioxidant capacity of landraces, old and modern Tunisian durum wheat. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, F.; Sanchez-Garcia, M. Adaptation and stability analysis of ICARDA durum wheat elites across 18 countries. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 2419–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loss, S.P.; Siddique, K.H.M. Morphological and physiological traits associated with wheat yield increases in mediterranean environments. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1994; pp. 229–276. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, J.; Pour-Aboughadareh, A.; Fabriki Ourang, S.; Mehrabi, A.A.; Siddique, K.H.M. Wild relatives of wheat: Aegilops–Triticum accessions disclose differential antioxidative and physiological responses to water stress. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2018, 40, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, K.H.M.; Kirby, E.J.M.; Perry, M.W. Ear:stem ratio in old and modern wheat varieties; relationship with improvement in number of grains per ear and yield. Field Crop Res. 1989, 21, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Searle, L.R.; Mather, D.E.; Able, A.J.; Able, J.A. Morphological, physiological and yield responses of durum wheat to pre-anthesis water-deficit stress are genotype-dependent. Crop Pasture Sci. 2015, 66, 1024–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araus, J.L.; Slafer, G.A.; Royo, C.; Dolores Serret, M. Breeding for yield potential and stress adaptation in cereals. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2008, 27, 377–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, L.; Napoli, M.; Mancini, M.; Masella, P.; Cappelli, A.; Parenti, A.; Orlandini, S. Wheat grain composition, dough rheology and bread quality as affected by nitrogen and sulfur fertilization and seeding density. Agronomy 2020, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, A.; Oliva, N.; Cini, E. Stone milling versus roller milling: A systematic review of the effects on wheat flour quality, dough rheology, and bread characteristics. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recchia, L.; Cappelli, A.; Cini, E.; Garbati Pegna, F.; Boncinelli, P. Environmental sustainability of pasta production chains: An integrated approach for comparing local and global chains. Resources 2019, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.C. Further progress in crop water relations. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1997; pp. 293–338. [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan, M.M.; Block, A.; Christensen, S.A.; Allen, L.H.; Schmelz, E.A. The effects of climate change associated abiotic stresses on maize phy-tochemical defenses. Phytochem. Rev. 2018, 17, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institute. Base SAS 9.1 Procedures Guide; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pour-Aboughadareh, A.; Yousefian, M.; Moradkhani, H.; Moghaddam Vahed, M.; Poczai, P.; Siddique, K.H.M. iPASTIC: An online toolkit to estimate plant abiotic stress indices. Appl. Plant Sci. 2019, 7, e11278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketata, H.Y.; Yau, S.K.; Nachit, M. Relative Consistency Performance Across Environments; International Symposium on Physiology and Breeding of Winter Cereals for stressed Mediterranean Environments: Montpellier, France, 1989; pp. 391–400. [Google Scholar]
- Pour-Aboughadareh, A.; Omidi, M.; Naghavi, M.R.; Etminan, A.; Mehrabi, A.A.; Poczai, P.; Bayat, H. Effect of water deficit stress on seedling biomass and physio-chemical characteristics in different species of wheat possessing the D genome. Agronomy 2019, 9, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, G.; Prasad, V.; Fritz, A.K.; Kirkhan, M.; Gill, B. Response of Aegilops species to drought stress during reproductive stage of development. Funct. Plant Biol. 2012, 39, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaseem, M.F.; Qureshi, R.; Shaheen, H. Heat and their combination on the growth, yield and physiology of diverse wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes varying in sensitivity to heat and drought stress. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaju, O.; Reynolds, M.; Sparkes, D.; Foulkes, M. Relationships between large-spike phenotype, grain number, and yield potential in spring wheat. Crop Sci. 2009, 49, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnabas, B.; Jaeger, K.; Feher, A. The effect of drought and heat stress on reproductive processes in cereals. Plant. Cell. Environ. 2008, 31, 11–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etminan, A.; Pour-Aboughadareh, A.; Mohammadi, R.; Shoshtari, L.; Yousefiazarkhanian, M.; Moradkhani, H. Determining the best drought tolerance indices using artificial neural network (ANN): Insight into application of intelligent agriculture in agronomy and plant breeding. Cereal Res. Commun. 2019, 47, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolferus, R.; Ji, X.; Richards, R.A. Abiotic stress and control of grain number in cereals. Plant Sci. 2011, 181, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahenshah; Isoda, A. Effects of water stress on leaf temperature and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in cotton and peanut. Plant Prod. Sci. 2010, 13, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnoff, N. The role of active oxygen in the response of plants to water deficits and desiccation. New Phytol. 1993, 125, 27–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Isoda, A. Adaptive responses of soybean and cotton to water stress. I. Transpiration changes in relation to stomatal area and stomatal conductance. Plant Prod. Sci. 2005, 8, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Murchie, E.H.; Lawson, T. Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis: A guide to good practice and understanding some new applications. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 3983–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbe, E.; Calatayud, A. Applications of chlorophyll fluorescence imaging technique in horticultural research: A review. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 138, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour-Aboughadareh, A.; Ahmadi, J.; Mehrabi, A.A.; Etminan, A.; Moghaddam, M.; Siddique, K.H.M. Physiological responses to drought stress in wild relatives of wheat: Implications for wheat improvement. Acta Physiol. Plant 2017, 39, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietragalla, J.; Pask, A.J.D. Physiological Breeding II; Pietragalla, H., Pask, A.J.D., Mullan, D., Reynold, M.P., Eds.; CIMMYT: Mexico City, Mexico, 2012; pp. 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes, M.J.; Sylvester-Bradley, R.; Weightman, R.; Snape, J.W. Identifying physiological traits associated with improved drought resistance in winter wheat. Field Crop Res. 2007, 103, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafitte, H.R.; Blum, A.; Atlin, G. Using secondary traits to help identify drought tolerant genotypes. In Hardy Breeding Rice for Drought-Prone Environments; Fischer, K., Lafitte, S.R., Fukai, G., Atlin, B., Eds.; IRRI: Los Baños, CA, USA, 2003; pp. 38–39. [Google Scholar]
- Poursiahbidi, M.; Pour-Aboughadareh, A.; Tahmasebi, G.; Jasemi, S. Evaluation of genetic diversity and interrelationships of agro-morphological characters in durum wheat (Triticum durum desf.) lines using multivariate analysis. Int. J. Agric. Res. Rev. 2013, 3, 184–194. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Q.; Rudda, J.C.; Liua, S.; Jessupa, K.E.; Devkotaa, R.N.; Mahano, J.R. Yield determination and water use efficiency of wheat under water-limited conditions in the U.S. Southern High Plains. Crop Sci. 2013, 54, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, J.; Pour-Aboughadareh, A.; Fabriki Ourang, S.; Mehrabi, A.A.; Siddique, K.H.M. Screening wheat germplasm for seedling root architectural traits under contrasting water regimes: Potential sources of variability for drought adaptation. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2018, 64, 1351–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.K.; Andersen, S.B.; Ottosen, C.O.; Rosenqvist, E. Wheat cultivars selected for high Fv/Fm under heat stress maintain high photosynthesis, total chlorophyll, stomatal conductance, transpiration and dry matter. Physiol. Plant. 2015, 153, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, G.C.J. Effective selection criteria for assessing plant stress tolerance. In Proceedings of the AFCTWS Adaptation of Food Crops to Temperature and Water Stress, Shanhua, Taiwan, 13–18 August 1992; pp. 257–270. [Google Scholar]
- Khalili, M.; Naghavi, M.R.; Pour–Aboughadareh, A.; Talebzadeh, J. Evaluating of drought stress tolerance based on selection indices in spring canola cultivars (Brassica napus L.). J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 4, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour–Siahbidi, M.M.; Pour–Aboughadareh, A. Evaluation of grain yield and repeatability of drought tolerance indices for screening chickpea (Cicer aritinum L.) genotypes under rainfed conditions. Iran. J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2013, 2, 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Naghavi, M.R.; Pour-Aboughadareh, A.R.; Khalili, M. Evaluation of drought tolerance indices for screening some of corn (Zea mays L.) Cultivars under environmental conditions. Not. Sci. Biol. 2013, 5, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, S.; Moghaddam, M.; Ghassemi, K.; Nishabouri, M.R. Genetic properties of drought resistance indices. J. Agric. Sci. Tech. 2001, 4, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Pour-Aboughadareh, A.; Etminan, A.; Abdelrahman, M.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Tran, L.S.P. Assessment of biochemical and physiological parameters of durum wheat genotypes at the seedling stage during polyethylene glycol-induced water stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Code | Pedigree | Name | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | Saji | Check variety | Iran |
| G2 | Zardak | Old variety | Iran |
| G3 | Sardari | Bread wheat old variety | Iran |
| G4 | TOPDY_18/FOCHA_1//ALTAR 86 | Breeding line | Iran |
| G5 | RASCON_37/4/MAGH72/RUFO//ALG86 | Breeding line | Iran |
| G6 | M84859 | Breeding line | ICARDA |
| G7 | M141979 | Breeding line | ICARDA |
| G8 | M141982 | Breeding line | ICARDA |
| G9 | M141994 | Breeding line | ICARDA |
| G10 | M141995 | Breeding line | ICARDA |
| G11 | M142005 | Breeding line | ICARDA |
| G12 | M142017 | Breeding line | ICARDA |
| G13 | M142025 | Breeding line | ICARDA |
| G14 | M142038 | Breeding line | ICARDA |
| G15 | M142045 | Breeding line | ICARDA |
| G16 | M142069 | Breeding line | ICARDA |
| G17 | M142070 | Breeding line | ICARDA |
| Source of Variation | Year (Y) | Stress (S) | YS | Replication/SY | Genotype (G) | GY | GS | GSY | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| df | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | |
| DH | ** | ** | ** | Ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | 0.48 |
| DM | ** | ** | ** | Ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | 0.76 |
| GFP | ** | ** | ** | Ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | 4.04 |
| PL | ** | ** | ** | * | ** | Ns | * | Ns | 15.89 |
| PE | Ns | ** | Ns | ** | ** | Ns | Ns | Ns | 32.69 |
| FL | ** | Ns | Ns | * | ** | Ns | Ns | Ns | 12.84 |
| SL | ** | Ns | Ns | Ns | ** | Ns | Ns | Ns | 10.31 |
| NSPP | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | Ns | * | Ns | 21.01 |
| NGPS | ** | ** | ** | Ns | ** | Ns | * | Ns | 19.55 |
| TGW | Ns | ** | Ns | Ns | Ns | Ns | Ns | Ns | 17.69 |
| GY | ** | ** | * | ** | ** | ** | * | Ns | 26.56 |
| Bio | ** | ** | Ns | ** | Ns | ** | Ns | Ns | 21.89 |
| HI | ** | ** | * | Ns | ** | * | Ns | Ns | 13.68 |
| Fv/Fm | Ns | * | Ns | Ns | Ns | Ns | Ns | Ns | 10.74 |
| SC | ** | Ns | Ns | ** | Ns | Ns | Ns | Ns | 43.06 |
| CT | * | ** | ** | ** | Ns | * | Ns | Ns | 3.96 |
| Conditions | Genotype | DM | DH | GFP | PL | PE | FL | SL | NSPP | NGPS | TGW | GY (g/m2) | Bio (g/m2) | HI | Fv/Fm | SC | CT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control condition | G1 | 218 | 173 | 45 | 27.08 | 10.20 | 12.95 | 6.47 | 592 | 46 | 43.18 | 873.68 | 1968.15 | 45.29 | 0.75 | 43.30 | 33.74 |
| G2 | 216 | 171 | 44 | 32.56 | 13.64 | 16.36 | 6.97 | 530 | 30 | 45.28 | 463.77 | 1254.92 | 36.33 | 0.76 | 46.66 | 33.42 | |
| G3 | 214 | 172 | 42 | 30.75 | 12.78 | 13.39 | 9.45 | 896 | 24 | 44.25 | 672.87 | 1554.75 | 42.70 | 0.74 | 24.99 | 34.07 | |
| G4 | 217 | 175 | 42 | 24.47 | 7.75 | 13.61 | 6.70 | 432 | 43 | 43.85 | 645.57 | 1615.03 | 41.40 | 0.75 | 42.13 | 33.91 | |
| G5 | 218 | 176 | 41 | 27.20 | 9.14 | 17.97 | 7.39 | 450 | 46 | 40.70 | 622.35 | 1729.28 | 36.98 | 0.76 | 46.03 | 32.76 | |
| G6 | 216 | 173 | 42 | 27.14 | 10.75 | 13.39 | 6.36 | 447 | 44 | 39.30 | 565.03 | 1434.52 | 39.70 | 0.71 | 28.52 | 33.89 | |
| G7 | 218 | 170 | 47 | 32.64 | 15.69 | 14.61 | 7.56 | 591 | 46 | 41.93 | 675.25 | 1623.33 | 41.95 | 0.74 | 32.61 | 32.46 | |
| G8 | 215 | 173 | 42 | 32.72 | 15.89 | 13.72 | 7.53 | 603 | 41 | 42.62 | 663.45 | 1585.53 | 42.26 | 0.72 | 45.65 | 33.95 | |
| G9 | 218 | 172 | 45 | 30.31 | 13.67 | 16.00 | 6.67 | 537 | 45 | 45.33 | 711.72 | 1617.92 | 44.65 | 0.67 | 34.87 | 34.63 | |
| G10 | 217 | 170 | 47 | 29.92 | 13.69 | 14.94 | 6.11 | 644 | 43 | 44.91 | 887.90 | 1918.52 | 46.32 | 0.72 | 53.88 | 33.43 | |
| G11 | 217 | 174 | 43 | 28.17 | 11.67 | 14.94 | 6.08 | 548 | 44 | 45.42 | 732.38 | 1653.67 | 44.54 | 0.75 | 36.26 | 33.87 | |
| G12 | 217 | 170 | 47 | 26.06 | 10.81 | 16.20 | 6.39 | 56 | 49 | 42.72 | 817.67 | 1925.12 | 42.93 | 0.76 | 39.67 | 32.76 | |
| G13 | 218 | 170 | 47 | 27.06 | 10.53 | 16.06 | 6.56 | 567 | 40 | 44.78 | 663.80 | 1597.25 | 42.13 | 0.77 | 49.69 | 32.56 | |
| G14 | 217 | 173 | 44 | 30.81 | 13.95 | 15.36 | 7.22 | 668 | 42 | 41.98 | 862.75 | 1955.50 | 44.69 | 0.76 | 44.64 | 32.69 | |
| G15 | 218 | 174 | 44 | 31.33 | 14.45 | 16.53 | 7.20 | 486 | 40 | 44.98 | 742.03 | 1734.97 | 42.81 | 0.78 | 37.67 | 33.11 | |
| G16 | 218 | 170 | 47 | 33.28 | 16.25 | 14.95 | 6.39 | 667 | 47 | 45.72 | 888.57 | 1996.20 | 44.21 | 0.73 | 40.89 | 33.15 | |
| G17 | 219 | 174 | 44 | 30.42 | 13.00 | 16.22 | 6.92 | 544 | 47 | 45.44 | 771.25 | 1678.73 | 45.41 | 0.74 | 53.93 | 32.91 | |
| LSD (0.05) | 1.13 | 2.69 | 2.93 | 6.92 | - | 2.89 | 1.37 | 19.64 | 3.93 | - | 99.53 | 191.69 | 6.65 | - | - | - | |
| LSD (0.01) | 1.51 | 3.57 | 3.89 | 9.20 | - | 3.84 | 1.82 | 26.13 | 5.22 | - | 132.37 | 254.94 | 8.85 | - | - | - | |
| Drought condition | G1 | 214 | 175 | 39 | 23.50 | 7.02 | 16.31 | 6.91 | 472 | 35 | 25.18 | 546.63 | 1501.47 | 37.00 | 0.72 | 38.95 | 40.55 |
| G2 | 213 | 176 | 37 | 24.47 | 9.25 | 16.49 | 7.22 | 532 | 24 | 25.42 | 466.30 | 1396.67 | 30.26 | 0.77 | 35.08 | 38.47 | |
| G3 | 214 | 179 | 36 | 23.03 | 6.92 | 12.69 | 8.00 | 628 | 19 | 22.99 | 486.15 | 1398.95 | 32.66 | 0.78 | 25.79 | 40.80 | |
| G4 | 214 | 179 | 35 | 21.94 | 6.06 | 13.70 | 6.37 | 391 | 33 | 27.47 | 430.50 | 1267.92 | 33.10 | 0.79 | 27.70 | 40.09 | |
| G5 | 218 | 179 | 38 | 16.86 | 3.97 | 16.47 | 7.35 | 297 | 29 | 19.06 | 356.17 | 1227.82 | 27.75 | 0.80 | 42.94 | 40.58 | |
| G6 | 216 | 174 | 41 | 26.53 | 9.39 | 15.15 | 6.83 | 463 | 24 | 27.61 | 500.62 | 1484.22 | 35.88 | 0.74 | 42.25 | 39.55 | |
| G7 | 214 | 174 | 40 | 23.00 | 9.11 | 13.55 | 7.39 | 513 | 34 | 24.57 | 485.77 | 1471.17 | 33.46 | 0.76 | 37.19 | 40.85 | |
| G8 | 215 | 174 | 41 | 24.03 | 10.72 | 13.33 | 7.50 | 528 | 33 | 22.18 | 481.48 | 1490.62 | 32.83 | 0.76 | 58.19 | 40.70 | |
| G9 | 214 | 176 | 38 | 23.69 | 9.30 | 16.14 | 6.50 | 463 | 30 | 20.93 | 518.60 | 1449.02 | 35.46 | 0.78 | 39.59 | 40.24 | |
| G10 | 217 | 176 | 41 | 25.22 | 9.50 | 16.36 | 6.03 | 527 | 34 | 24.76 | 482.88 | 1492.25 | 32.59 | 0.77 | 32.29 | 40.78 | |
| G11 | 214 | 176 | 37 | 23.08 | 7.56 | 15.17 | 6.81 | 449 | 33 | 21.89 | 477.90 | 1356.65 | 34.85 | 0.78 | 41.64 | 40.52 | |
| G12 | 214 | 176 | 38 | 26.22 | 9.39 | 15.44 | 6.39 | 462 | 32 | 25.34 | 513.08 | 1539.08 | 33.91 | 0.75 | 40.53 | 40.55 | |
| G13 | 215 | 175 | 39 | 25.33 | 9.33 | 16.94 | 6.97 | 403 | 35 | 24.29 | 387.62 | 1240.62 | 31.85 | 0.76 | 47.66 | 40.43 | |
| G14 | 215 | 178 | 37 | 26.14 | 9.21 | 16.02 | 7.45 | 396 | 35 | 25.16 | 384.60 | 1295.82 | 30.89 | 0.74 | 44.82 | 40.12 | |
| G15 | 216 | 176 | 40 | 22.06 | 7.70 | 15.36 | 6.95 | 397 | 29 | 22.85 | 399.22 | 1303.02 | 32.55 | 0.75 | 43.01 | 40.88 | |
| G16 | 214 | 176 | 38 | 24.20 | 9.53 | 15.45 | 6.61 | 422 | 32 | 24.45 | 443.23 | 1278.68 | 35.26 | 0.78 | 38.10 | 39.45 | |
| G17 | 214 | 175 | 39 | 26.08 | 11.83 | 16.28 | 6.61 | 433 | 31 | 24.70 | 425.23 | 1172.57 | 37.36 | 0.80 | 44.55 | 40.26 | |
| LSD (0.05) | 2.13 | 1.53 | 2.54 | - | 5.54 | 3.92 | 1.37 | 195.10 | 11.66 | 12.27 | 58.63 | - | - | - | 17.44 | - | |
| LSD (0.01) | 2.83 | 2.03 | 3.37 | - | 7.37 | 5.21 | 1.82 | 259.48 | 15.51 | 16.33 | 77.98 | - | - | - | 23.19 | - | |
| Control | 217.57 | 172.75 | 44.82 | 29.52 | 12.57 | 15.13 | 6.93 | 576.22 | 42.27 | 43.67 | 721.17 | 1696.67 | 42.60 | 0.74 | 41.25 | 33.37 | |
| Stress | 214.88 | 176.29 | 38.58 | 23.84 | 8.57 | 15.34 | 6.93 | 457.52 | 31.19 | 24.05 | 457.99 | 1374.50 | 33.39 | 0.76 | 40.01 | 40.28 | |
| Relative change † | 1.24 | −2.05 | 13.91 | 19.23 | 31.83 | −1.42 | 0.06 | 20.60 | 26.21 | 44.93 | 36.49 | 18.99 | 21.62 | −3.56 | 3.01 | −20.71 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pour-Aboughadareh, A.; Mohammadi, R.; Etminan, A.; Shooshtari, L.; Maleki-Tabrizi, N.; Poczai, P. Effects of Drought Stress on Some Agronomic and Morpho-Physiological Traits in Durum Wheat Genotypes. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5610. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145610
Pour-Aboughadareh A, Mohammadi R, Etminan A, Shooshtari L, Maleki-Tabrizi N, Poczai P. Effects of Drought Stress on Some Agronomic and Morpho-Physiological Traits in Durum Wheat Genotypes. Sustainability. 2020; 12(14):5610. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145610
Chicago/Turabian StylePour-Aboughadareh, Alireza, Reza Mohammadi, Alireza Etminan, Lia Shooshtari, Neda Maleki-Tabrizi, and Peter Poczai. 2020. "Effects of Drought Stress on Some Agronomic and Morpho-Physiological Traits in Durum Wheat Genotypes" Sustainability 12, no. 14: 5610. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145610
APA StylePour-Aboughadareh, A., Mohammadi, R., Etminan, A., Shooshtari, L., Maleki-Tabrizi, N., & Poczai, P. (2020). Effects of Drought Stress on Some Agronomic and Morpho-Physiological Traits in Durum Wheat Genotypes. Sustainability, 12(14), 5610. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145610






