Hybrid Deep Learning Algorithm with Open Innovation Perspective: A Prediction Model of Asthmatic Occurrence
Abstract
1. Introduction
Increase in Air Pollutants and Asthma
2. Related Research
2.1. Effects of Air Pollutants on Asthma
2.2. Effects of Meteorological Changes on Asthma
2.3. Prediction of the Asthmatic Occurrence
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Datasets
3.1.1. Asthmatic Occurrence
3.1.2. Atmospheric Environments
3.1.3. Meteorological Environments
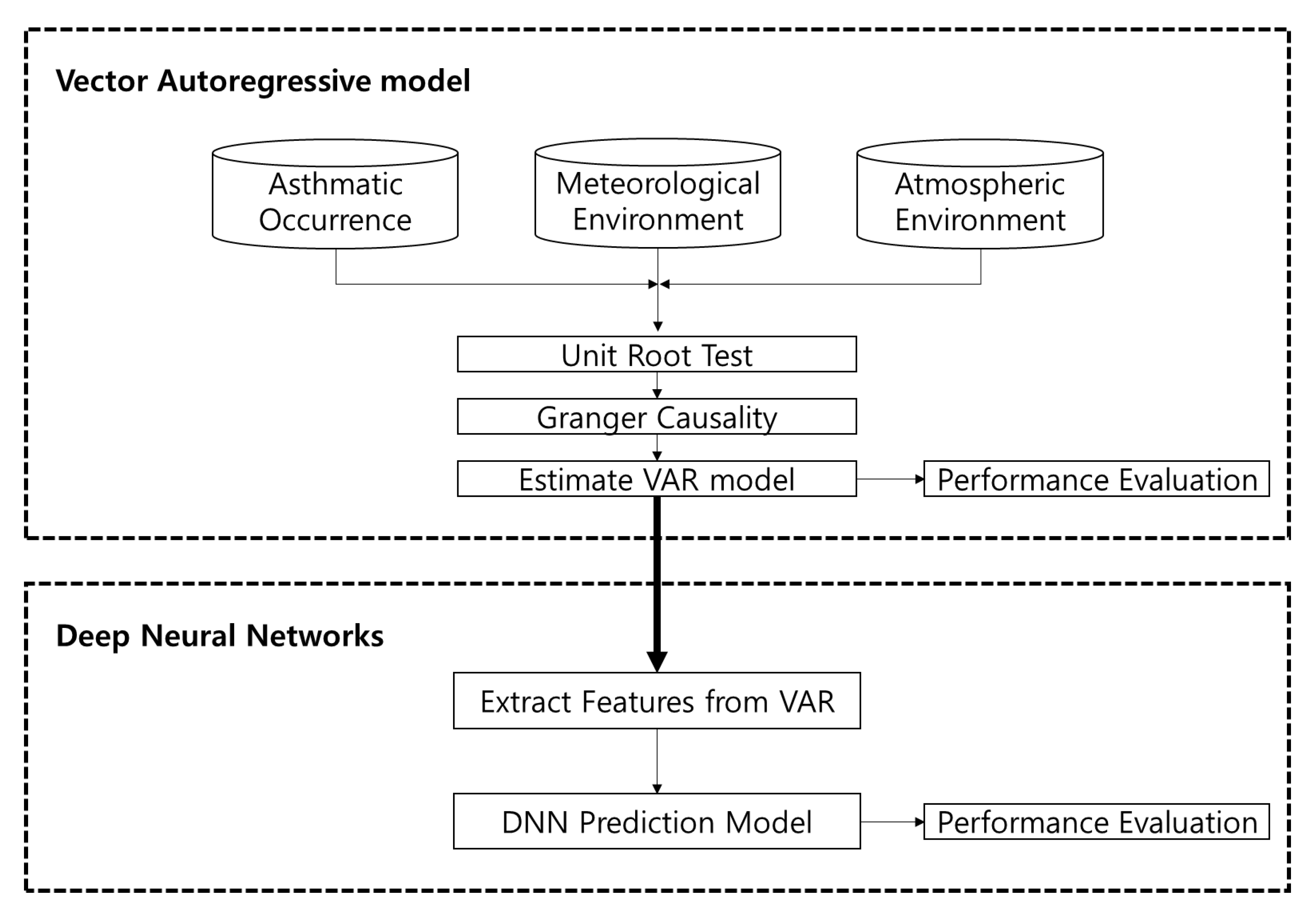
3.2. Methodology
3.2.1. Vector Autoregressive Model
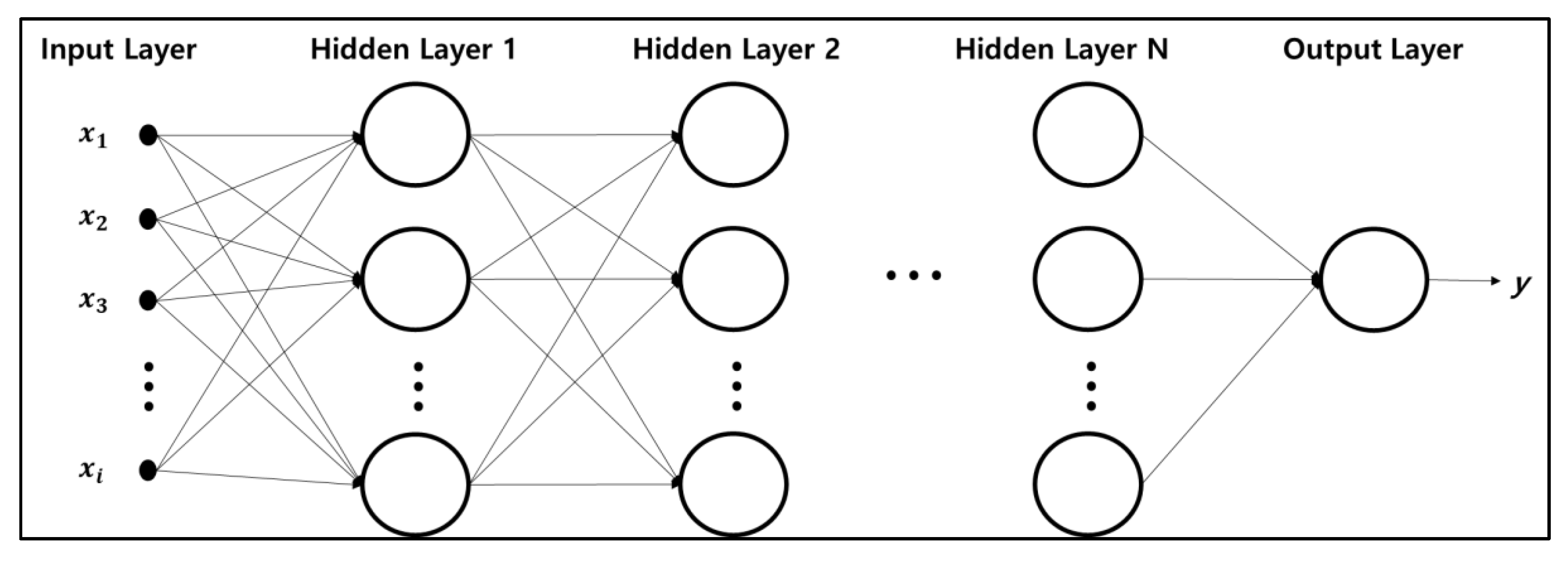
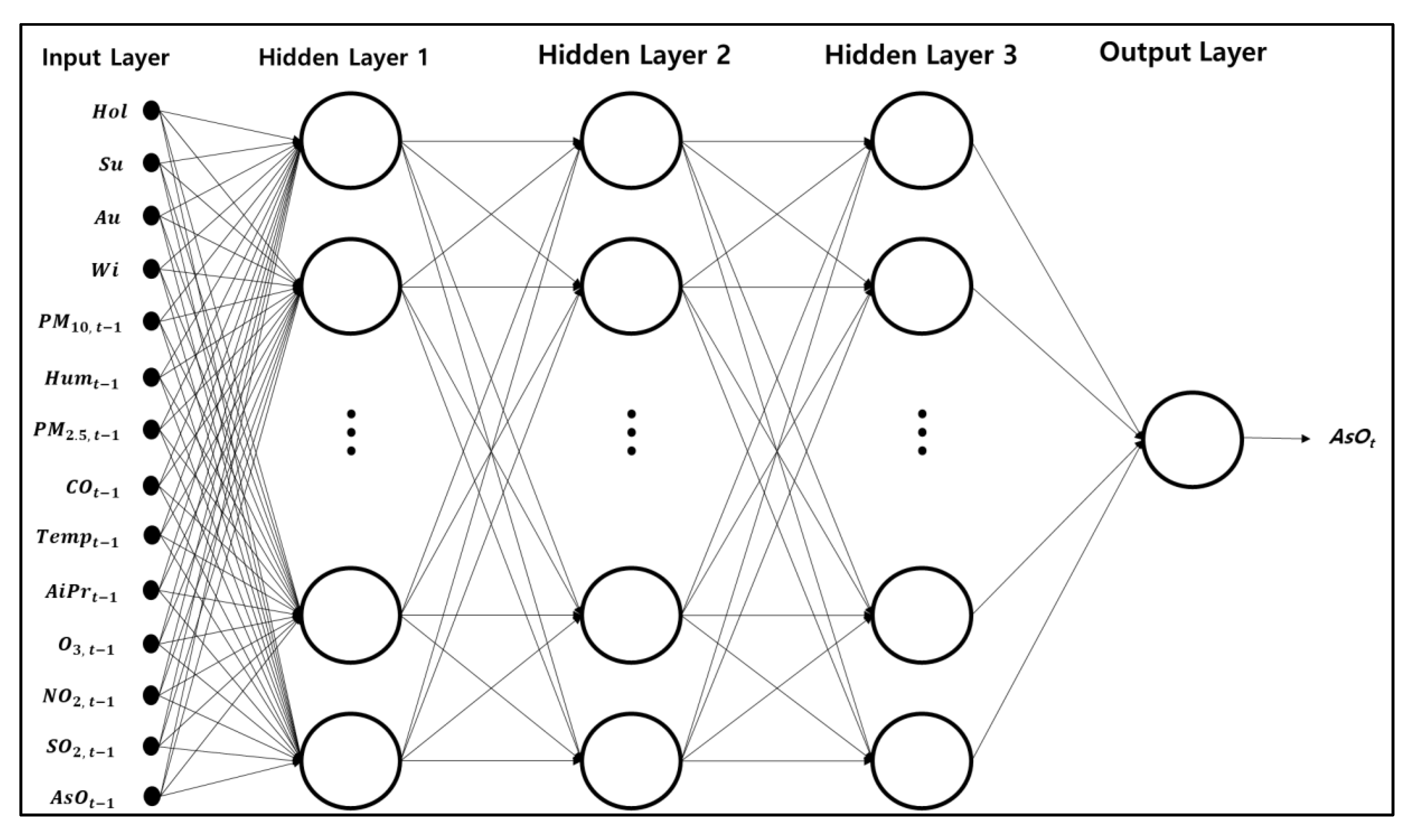
3.2.2. Hybrid Deep-Learning Model Based VAR & DNN
4. Results
4.1. Vector Autoregressive Model
4.1.1. Unit Root Test
4.1.2. Granger Causality
4.1.3. Estimation of VAR Model
4.2. Hybrid Deep Neural Networks
4.2.1. Extract Features from VAR Model
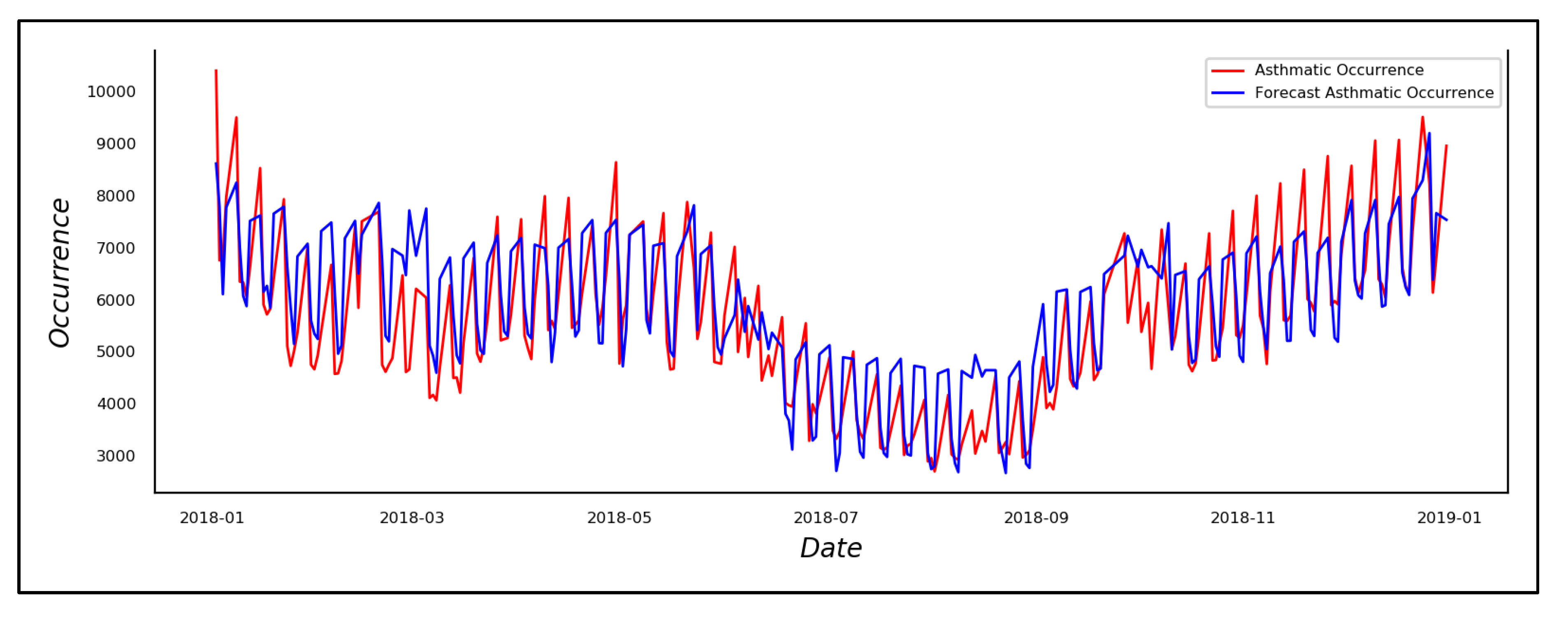
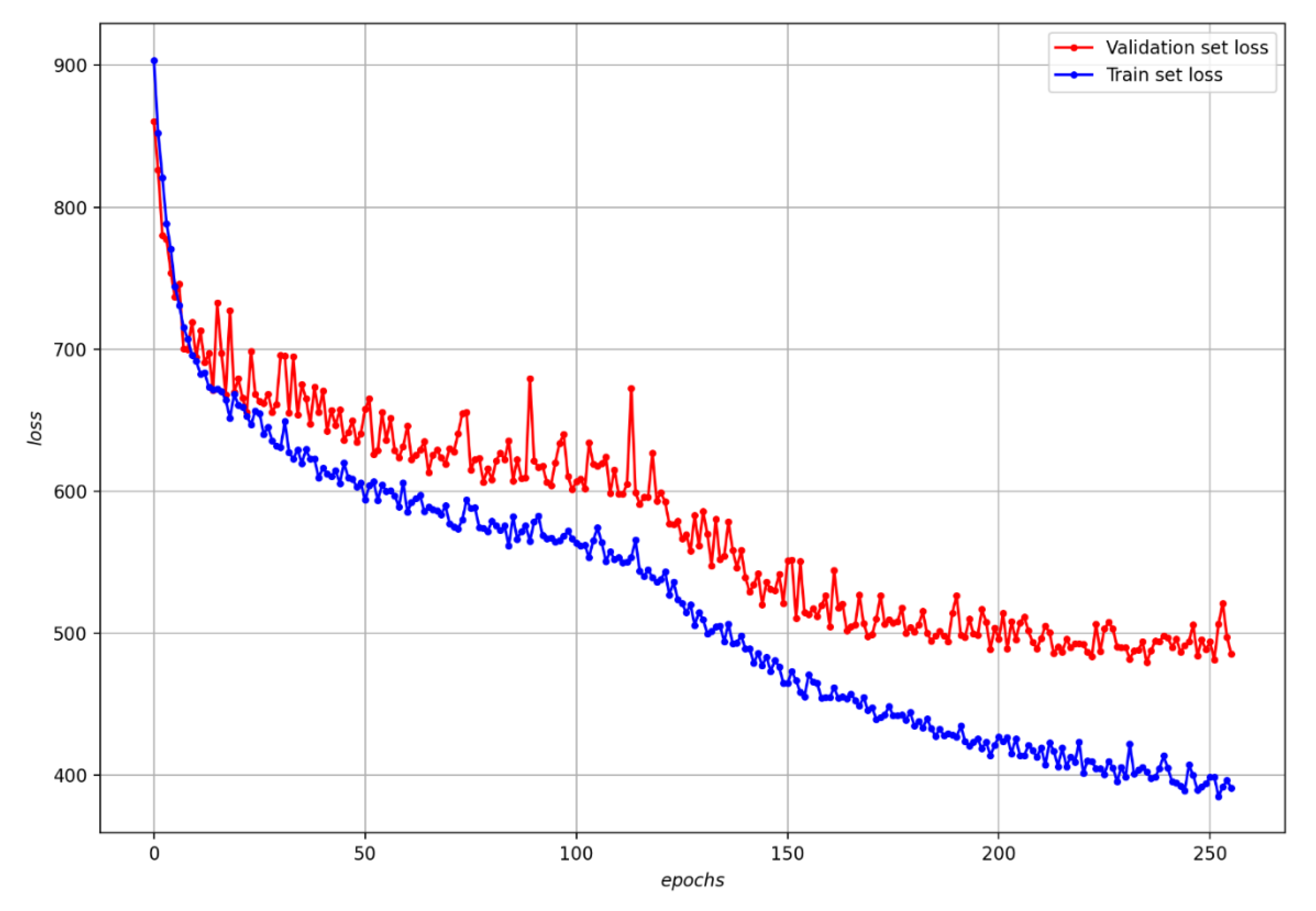
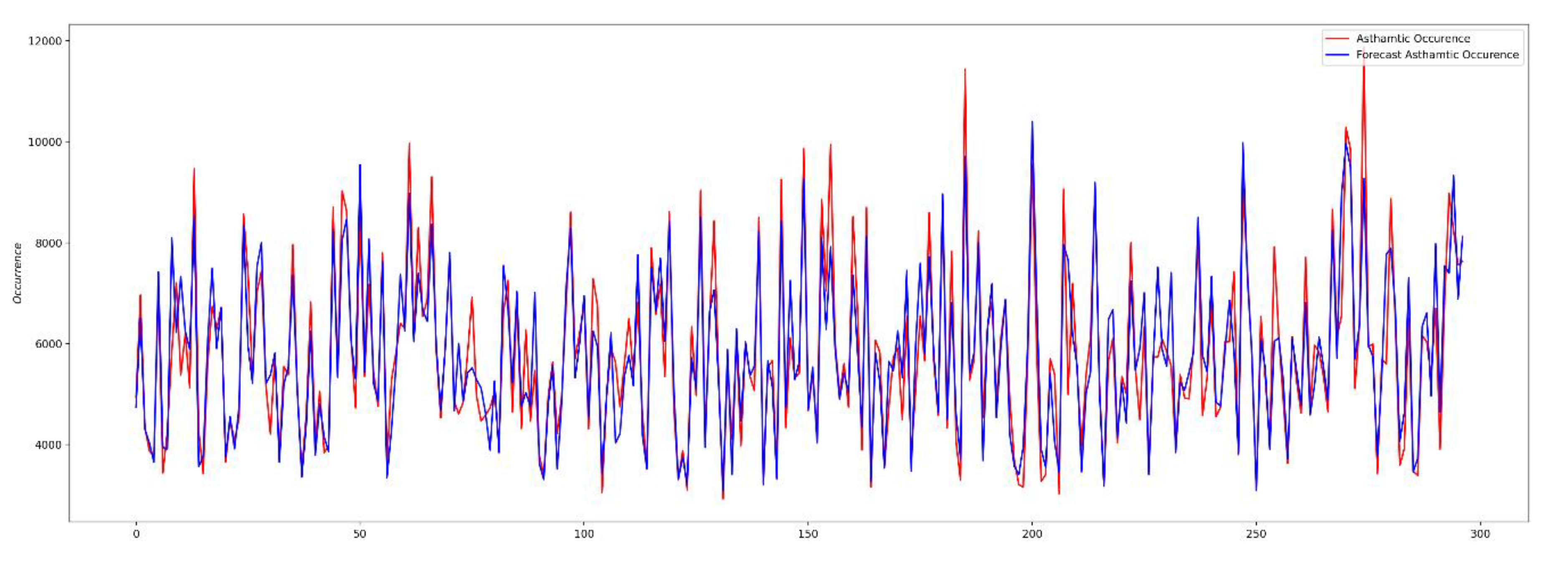
4.2.2. Performance Evaluation of Hybrid DNN
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kwon, H.J.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, M.S.; Ha, M.N.; Han, S.W. Cross-sectional Study on Respiratory Symptoms due to Air Pollution Using a Questionnaire. Korea J. Prev. Med. 1994, 27, 313–325. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, Y.W.; Lee, H.S.; Jang, Y.J. A Cluster Analysis on the Risk of Particulate Matter Focusing on Differences of Risk-Related Behaviors based on Public Segmentation. J. Public Relat. Res. 2016, 20, 201–235. [Google Scholar]
- Bert, B.; Stephen, T.H. Air Pollution and Health. The Lancet 2002, 360, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Nino, K.; Ira, B.T. Air Pollution: From Lung to Heart. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2005, 135, 697–702. [Google Scholar]
- Pope, C.A., III; Richard, T.B.; Michael, J.B.; Eugenia, E.C.; Daniel, K.; Kazuhiko, I.; George, D.T. Lung Cancer, Cardiopulmonary Mortality, and Long-term Exposure to Fine Particulate Air Pollution. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2002, 287, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Andrew, J.G.; Robert, B.D. Inflammatory Lung Injury after Bronchial Instillation of Air Pollution Particles. Am. J. of Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 704–708. [Google Scholar]
- Boris, Z.S.; Michael, T.K.; Robert, A.K. Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Injury. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 719–726. [Google Scholar]
- Fredrik, N.; Per, G.; Lars, J.; Tom, B.; Niklas, B.; Robert, J.; Goran, P. Urban Air Pollution and Lung Cancer in Stockholm. Epidemiology 2000, 11, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laura, P.; Christophe, D.; Carmen, I.; Inmaculada, A.; Chiara, B.; Ferran, B.; Catherine, B.; Olivier, C.; Francisco, B.C.; Francesco, F.; et al. Chronic Burden of Near-roadway Traffic Pollution in 10 European Cities (APHEKOM network). Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 594–605. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.W.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, H.J. The Impact of Indoor Air Pollution on Asthma. Allergy Asthma Respir. Dis. 2017, 5, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.U.; Paek, D.M. Asthma and Air Pollution in Korea. Korean J. Epidemiol. 1995, 17, 64–75. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Son, J.Y.; Lee, J.T.; Kim, T.B.; Park, H.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, T.H.; Son, J.W.; Shin, D.H.; Park, S.S.; et al. Effect of Air Pollution on Acute Exacerbation of Adult Asthma in Seoul, Korea: A Case-crossover Study. Korean J. Med. 2010, 78, 450–456. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, G.; John, R.B. Outdoor Air Pollution and Asthma. Lancet 2014, 383, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar]
- Piotr, O.C.; Piotr, D.; Aneta, O.J.; Michalina, B.; Ernest, C.; Tomasz, O.; Patrycja, R.K.; Artur, B. A Preliminary Attempt at the Identification and Financial Estimation of the Native Health Effects of Urban and Industrial Air Pollution Based on the Agglomeration of Gdaǹsk. Sustainability 2020, 12, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Esther, R.; Nicole, A.H.J.; Patricia, H.N.V.; Bert, B. Personal and Outdoor Nitrogen Dioxide Concentration in Relation to Degree of Urbanization and Traffic Density. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 719–726. [Google Scholar]
- Andreas, R.; John, P.B.; Hendrik, N.; Claire, G.; Ulrike, N. Increase in Tropospheric Nitrogen Dioxide over China Observed from Space. Nature 2005, 437, 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.J.; Seo, J.H. Climate Change and Human Health. J. Korean Med. Assoc. 2011, 54, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KIM, M.K. The Survey of Nitrogen Dioxide in Indoor Environment. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Anal. 2010, 13, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Jane, Q.K. Air Pollution and Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 104, 717–722. [Google Scholar]
- Yutong, C.; Wilma, L.Z.; Dany, D.; Marta, B.; Paul, R.B.; Isabel, F.; Amadou, G.; Kees, D.H.; Kristian, H.; Stephane, M.; et al. Ambient Air Pollution, Traffic Noise and Adult Asthma Prevalence: A BioSHaRE Approach. European Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1502127. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, A.S. Climate Change and Air Pollution. J. Korean Med. Assoc. 2011, 54, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, Y.J.; Park, N.G.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, D.S.; Eom, J.H.; Cho, M.C.; Yoon, S.J.; Jeong, H.S.; Song, H.G.; Sung, R.H.; et al. The Inflammatory Response in Mouse Lung after Acute Sulfur Dioxide Exposure. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 1994, 41, 328–338. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, G., Jr.; William, S.L.; Sheryl, L.T.; Karen, R.A.; Kenneth, W.C. Anti-inflammatory and Lung Function Effects of Montelukast in Asthmatic Volunteers Exposed to Sulfur Dioxide. CHEST 2001, 119, 402–408. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, R.M.; Thornton, C.A.; Lawrence, R.G.; Mark, D.; Kinnersley, R.P.; Ayres, J.R. Personal Exposure Monitoring of Particulate Matter, Nitrogen Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide, Including Susceptible Groups. Occupat. Environ. Med. 2002, 59, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristin, A.E.; Jill, S.H.; Philip, K.H.; Maria, F.; David, Q.R. Increased Ultrafine Particles and Carbon Monoxide Concentrations are Associated with Asthma Exacerbation among Urban Children. Environ. Res. 2014, 129, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Im, H.J.; LEE, S.Y.; Yun, K.J.; Ju, Y.S.; Kang, D.H.; Cho, S.H. A Case-crossover Study between Air Pollution and Hospital Emergency Room Visits by Asthma Attack. Korean J. Occupat. Environ. Med. 2000, 12, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, H.; Yamaya, M.; Yanai, M.; Ohrui, T.; Sasaki, H. Increased Blood Carboxyhaemoglobin Concentrations in Inflammatory Pulmonary Diseases. Thorax 2002, 57, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, J.B.; Jeffrey, W.S.; Charles, A.P.; Ross, J.S.; Russell, R.D. Observed Relationships of Ozone Air Pollution with Temperature and Emissions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L09803. [Google Scholar]
- Matthew, J.S.; Lyndsey, A.D.; Mitchel, K.; Dana, W.F.; Jeremy, A.S.; Lance, A.W.; Stefanie, E.S.; James, A.M.; Paige, E.T. Short-term Associations between Ambient Air Pollutants and Pediatric Asthma Emergency Department Visits. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 307–316. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, A.S.; Kazuhiko, I. Age-related Association of Fine Particles and Ozone with Severe Acute Asthma in New York City. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 367–373. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Z.; Xiaobin, L.; Liuhua, S.; Ge, T.; Cristine, T.L.; Sabine, L.; Julie, E.G. Concentration-response of Short-term Ozone Exposure and Hospital Admissions for Asthma in Texas. Environ. Int. 2017, 104, 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Gehui, W.; Liming, H.; Shixiang, G.; Songting, G.; Liansheng, W. Measurements of PM10 and PM2.5 in Urban Area of Nanjing, China and the Assessment of Pulmonary Deposition of Particle Mass. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 689–695. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Linyu, X. Comparative Study of PM10/PM2.5—Bound PAHs in Downtown Beijing, China: Concentrations, Sources and Health Risk. J. Clean. Product. 2018, 177, 674–683. [Google Scholar]
- Christian, S.; Nino, K.; Jean, P.B.; Philippe, L.; Werner, K.; Regula, R.; Christian, M.; Ursula, A.L. Short-Term Variation in Air Pollution and in Average Lung-Function Among Never-Smokers. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 163, 356–361. [Google Scholar]
- Jennifer, K.M.; John, R.B.; Tim, A.B.; Kathleen, M.M.; Helene, G.M.; Boriana, P.; Katharine, H.; Frederick, W.L.; Ira, B.T. Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on Wheeze in Asthmatic Children in Fresno, California. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1497–1502. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, F.W.S.; Tam, W.; Wong, T.W.; Lai, C.K.W.; Wong, G.W.K.; Leung, T.F.; Ng, S.S.S.; Hui, D.S.C. Effects of Air Pollution on Asthma Hospitalization Rates in Different =Age Groups in Hong Kong. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2007, 37, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutyajeet, S.; Chengsheng, J.; Jared, F.; Crystal, R.U.; Clifford, M.; Amir, S. Exposure to Extreme Heat and Precipitation Events Associated with Increased Risk of Hospitalization for Asthma in Maryland, USA. Environ. Health 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renato, A.; Giorgio, W.C.; Giovanni, P. Possible Role of Climate Changes in Variations in Pollen Seasons and Allergic Sensitizations during 27 Years. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010, 104, 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- Antonio, C.; Jane, F.; Emil, K.; Rory, J.S. Thunderstorm Associated Asthma: A Detailed Analysis of Environmental Factors. Br. Med. J. 1996, 312, 604–607. [Google Scholar]
- Katayoun, B.; Mary, M.D.W.; Carlo, M.; Larry, L.; Kadria, A.; John, S.; Mark, F. Economic Burden of Asthma: A Systematic Review. BMC Pulm. Med. 2009, 9, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Patrick, W.S.; Julia, F.S.; Vahram, H.G.; Brandon, S.; Denise, R.G.; Lin, S.L.; Gary, G. The Relationship between Asthma, Asthma Control and Economic Outcomes in the United States. J. Asthma 2014, 51, 769–778. [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet, J.; Dahl, R.; Khaltaev, N. Global Alliance against Chronic Respiratory Diseases. Eur. Respir. Soc. 2007, 29, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthew, M.; Denise, F.; Shaun, H.; Richard, B. The Global Burden of Asthma: Executive Summary of GINA Dissemination Committee Report. Allergy 2004, 59, 469–478. [Google Scholar]
- Biancone, P.; Secinaro, S.; Brescia, V.; Calandra, D. Management of Open Innovation in Healthcare for Cost Accounting Using EHR. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2019, 5, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.J.; Zhao, X.; Jung, K.; Yigitcanlar, T. The Culture for Open Innovation Dynamics. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, V.S. Monetary Policy and the US Housing Market: A VAR Analysis Imposing Sign Restrictions. J. Macroecon. 2008, 30, 977–990. [Google Scholar]
- Horng, M.S.; Chang, Y.W.; Wu, T.Y. Does Insurance Demand or Financial Development Pomote Economic Growth? Evidence from Taiwan. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2012, 19, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.L.; Hiroshi, M.; Joseph, V.; Yu, M.; David, L.B. Guiding Public Health Policy by Using Grocery Transaction Data to Predict Demand for Unhealthy Beverage. Stud. Comput. Intell. 2020, 843, 169–176. [Google Scholar]
- Public Data Portal. Available online: https://www.data.go.kr/data/15028050/fileData.do (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Air Korea. Available online: http://www.airkorea.or.kr (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Park, M.E.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, J.J.; Lee, H.C.; Cha, J.W.; Ryoo, S.B. Case Study of the Heavy Asian Dust Observed in Late February 2015. Atmosphere 2016, 26, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Meteorological Agency. Available online: http://data.kma.go.kr (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Sims, C.A. Macroeconomics and Reality. Econometrica 1980, 48, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.S.; Huh, N.K.; Kim, S.; Hur, H.Y. A Study on International Passenger and Freight Forecasting Using the Seasonal Multivariate Time Series Models. Commun. Appl. Methods 2010, 17, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutthichaimethee, P.; Chatchorfa, A.; Suyaprom, S. A Forecasting Model for Economic Growth and CO2 Emission Based on Industry 4.0 Political Policy under the Government Power: Adapting a Second-Order Autoregressive-SEM. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2019, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.J. An Empirical Analysis on the Relationship between Economic Growth and Income Inequality. Seoul Stud. 2014, 15, 95–111. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.H.; Nam, J.O. A Causality Analysis of the Hairtail Price by Distribution Channel Using a Vertor Autoregressive Model. J. Fish. Bus. Adm. 2015, 46, 93–107. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.H.; Kim, H.K. Financial Support and University Performance in Korean Universities: A Panel Data Approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, B.; Lu, H. Carbon Dioxide Emissions, Economic Growth, and Selected Types of Fossil Energy Consumption in China: Empirical Evidence from 1965 to 2015. Sustainability 2017, 9, 697. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.J.; Park, C. A Study on the Prospective in Korean Land Market Using Vector Auto-Regressive Model. Korean Spat. Plan. Rev. 2001, 31, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Méndez-Suárez, M.; García-Fernández, F.; Gallardo, F. Artificial Intelligence Modelling Framework for Financial Automated Advising in the Copper Market. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2019, 5, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Suh, T.; Roy, D.; Baucus, M. Emerging Technology and Business Model Innovation: The Case of Artificial Intelligence. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2019, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tereq, H.; Siby, J.P.; Radha, K.A.; Prakash, R.; Hossein, S. Short-term Load Forecasting Using Deep Neural Networks(DNN). In Proceedings of the IEEE 2017 North American Power Symposium, Morgantown, WV, USA, 17–19 September 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, J.J.; Kim, D.; Yan, M.-R. Open Innovation Engineering-Preliminary Study on New Entrance of Technology to Market. Electronics 2020, 9, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.J. Demand Pattern of the Global Passengers: Sea and Air Transport. J. Korea Port Econ. Assoc. 2011, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Karoliina, P.S.; Piia, A.; Markku, O.; Heikki, T. Climate Change and Electricity Consumption-witnessing Increasing or Decreasing Use and Costs? Energy Policy 2010, 38, 2409–2419. [Google Scholar]
- José, D.C.; José, C.P. The Corrected VIF (CVIF). J. Appl. Stat. 2011, 38, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar]
- Wujung, V.A.; Mbella, M.E. Entrepreneurship and Poverty Reduction in Cameroon: A Vector Autoregressive Approach. Arch. Bus. Res. 2014, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibuhtto, M.C. Modelling Colombo Consumer Price Index: A Vector Autoregressive Approach. J. Manag. 2014, 11, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, J.J.; Lee, D.; Ahn, H.; Park, K.; Yigitcanlar, T. Not Deep Learning but Autonomous Learning of Open Innovation for Sustainable Artificial Intelligence. Sustainability 2016, 8, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajcsák, Z. Implementing Open Innovation Using Quality Management System: The Role of Organizational Commitment and Customer Loyalty. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2019, 5, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Variables | Mean | Median | Kurtosis | Skewness | Percentiles | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 25th | 75th | Max | |||||
| Occurrence | 5859.59 | 5737.00 | 0.17 | 0.56 | 2699.00 | 4728.00 | 6724.00 | 11,881.00 |
| Variables | Mean | Median | Kurtosis | Skewness | Percentiles | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 25th | 75th | Max | |||||
| SO2 (ppm) | 0.005 | 0.005 | 3.321 | 1.216 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.013 |
| CO (ppm) | 0.564 | 0.520 | 1.388 | 1.217 | 0.280 | 0.443 | 0.636 | 1.251 |
| O3 (ppm) | 0.020 | 0.020 | −0.377 | 0.374 | 0.003 | 0.012 | 0.027 | 0.053 |
| NO2 (ppm) | 0.037 | 0.036 | 0.084 | 0.547 | 0.014 | 0.028 | 0.045 | 0.082 |
| PM10 (1 µg/m3) | 46.763 | 43.393 | 122.845 | 7.150 | 7.975 | 31.768 | 57.227 | 555.692 |
| PM2.5 (1 µg/m3) | 24.348 | 22.154 | 2.249 | 1.229 | 3.275 | 15.373 | 30.378 | 87.821 |
| Variables | Mean | Median | Kurtosis | Skewness | Percentiles | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 25th | 75th | Max | |||||
| Temperature (°C) | 13.28 | 14.40 | −1.06 | −0.27 | 14.80 | 3.50 | 23.10 | 33.70 |
| Humidity (%) | 58.54 | 58.60 | −0.36 | 0.15 | 21.80 | 47.60 | 68.10 | 97.00 |
| Air Pressure (hPa) | 1006.09 | 1006.70 | −0.66 | −0.07 | 981.0 | 999.60 | 1012.50 | 1026.20 |
| Variables | At the Level | First Difference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t-Statistics | p-Value | t-Statistics | p-Value | ||
| Asthmatic Occurrence | AsO | −2.8965 | 0.0457 ** | −2.8965 | 0.0457 ** |
| Atmospheric Environment | SO2 | −4.5497 | 0.0001 *** | −4.5497 | 0.0001 *** |
| CO | −4.0074 | 0.0013 ** | −4.0074 | 0.0013 ** | |
| O3 | −2.7408 | 0.0672 * | −11.6995 | <0.0001 *** | |
| NO2 | −8.5039 | <0.0001 *** | −8.5039 | <0.0001 *** | |
| PM10 | −5.4865 | <0.0001 *** | −5.4865 | <0.0001 *** | |
| PM2.5 | −8.7544 | <0.0001 *** | −8.7544 | <0.0001 *** | |
| Meteorological Environment | Temp | −2.2999 | 0.1719 | −4.3413 | 0.0003 *** |
| Hum | −4.2481 | 0.0005 *** | −4.2481 | 0.0005 *** | |
| AiPr | −2.0903 | 0.2484 | −12.9901 | <0.0001 *** | |
| Dependent Variables | AsO | SO2 | CO | O3 | NO2 | PM10 | PM2.5 | Temp | Hum | AiPr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AsO | 1.00 | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | 0.21 | <0.01 *** | 0.03 ** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | 0.05 ** |
| SO2 | <0.01 *** | 1.00 | <0.01 *** | 0.08 * | <0.01 *** | 0.14 | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** |
| CO | <0.01 *** | 0.23 | 1.00 | 0.05 ** | <0.01 *** | 0.10 * | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** |
| O3 | 0.35 | 0.07 * | <0.01 *** | 1.00 | <0.01 *** | 0.72 | 0.15 | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** |
| NO2 | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | 0.06 * | <0.01 *** | 1.00 | 0.07 * | 0.19 | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** |
| PM10 | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | 0.40 | <0.01 *** | 1.00 | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | 0.36 |
| PM2.5 | 0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | 0.03 ** | <0.01 *** | 0.04 ** | 1.00 | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** |
| Temp | 0.06 * | <0.01 ** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | 0.17 | <0.01 *** | 1.00 | 0.03 ** | <0.01 *** |
| Hum | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | 1.00 | <0.01 *** |
| AiPr | 0.40 | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 ** | 0.04 ** | 0.02 ** | <0.01 *** | <0.01 *** | 1.00 |
| Lag | AIC | BIC | HQIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | −5.454 | −5.140 | −5.333 |
| 1 | −8.327 | −7.386 * | −7.964 |
| 2 | −8.582 | −7.014 | −7.977 * |
| 3 | −8.726 | −6.531 | −7.879 |
| 4 | −8.828 | −6.006 | −7.740 |
| 5 | −9.136 | −5.686 | −7.805 |
| 6 | −9.219 * | −5.142 | −7.646 |
| 7 | −9.137 | −4.434 | −7.323 |
| 8 | −9.026 | −3.695 | −6.970 |
| 9 | −8.952 | −2.994 | −6.654 |
| 10 | −8.869 | −2.284 | −6.329 |
| Variables | Coefficient | t-Statistics | p-Value | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2138.343 | 6.425 | <0.001 *** | − | |
| −1717.088 | 26.210 | <0.001 *** | 1.190 | |
| −1359.116 | −11.449 | <0.001 *** | 2.528 | |
| −275.489 | −2.571 | 0.010 ** | 1.980 | |
| 174.505 | 1.449 | 0.147 | 2.560 | |
| 9.245 | 1.204 | 0.229 | 1.153 | |
| 2575.587 | 0.558 | 0.577 | 1.171 | |
| −54.148 | −4.059 | <0.001 *** | 1.317 | |
| −4.435 | −0.849 | 0.396 | 4.271 | |
| 292.689 | 0.551 | 0.581 | 7.890 | |
| −0.995 | −0.568 | 0.570 | 2.645 | |
| 3.472 | 1.191 | 0.234 | 1.666 | |
| 12,668.225 | 1.865 | 0.062 * | 5.915 | |
| 95,442.851 | 2.062 | 0.039 ** | 2.670 | |
| 0.383 | 14.864 | <0.001 *** | 2.090 |
| Model | Learning Rate | Epoch | Performance Evaluation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | MSE | RMSE | MAPE | |||
| Hybrid DNN | 0.001 | 300 | 479.31 | 473,295.40 | 687.96 | 8.20 |
| VAR | − | − | 668.50 | 71,750.20 | 847.20 | 13.17 |
| DNN | 0.001 | 300 | 691.22 | 818,571.94 | 904.75 | 11.87 |
| LSTM | 0.001 | 100 | 821.72 | 1140,624.00 | 1068.00 | 15.01 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Jang, Y.-J.; Lee, C.-H.; Choi, J.-H.; Sung, T.-E. Hybrid Deep Learning Algorithm with Open Innovation Perspective: A Prediction Model of Asthmatic Occurrence. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156143
Kim M-S, Lee J-H, Jang Y-J, Lee C-H, Choi J-H, Sung T-E. Hybrid Deep Learning Algorithm with Open Innovation Perspective: A Prediction Model of Asthmatic Occurrence. Sustainability. 2020; 12(15):6143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156143
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Min-Seung, Jeong-Hee Lee, Yong-Ju Jang, Chan-Ho Lee, Ji-Hye Choi, and Tae-Eung Sung. 2020. "Hybrid Deep Learning Algorithm with Open Innovation Perspective: A Prediction Model of Asthmatic Occurrence" Sustainability 12, no. 15: 6143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156143
APA StyleKim, M.-S., Lee, J.-H., Jang, Y.-J., Lee, C.-H., Choi, J.-H., & Sung, T.-E. (2020). Hybrid Deep Learning Algorithm with Open Innovation Perspective: A Prediction Model of Asthmatic Occurrence. Sustainability, 12(15), 6143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156143






