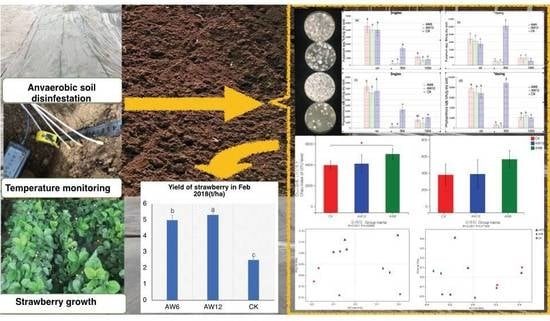
Composted Chicken Manure for Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation Increased the Strawberry Yield and Shifted the Soil Microbial Communities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Trials
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Fungal Soil-Borne Pathogen Analysis
2.4. Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
2.5. Strawberry Growth, Mortality and Yield
2.6. DNA Extraction and HTS Analysis
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
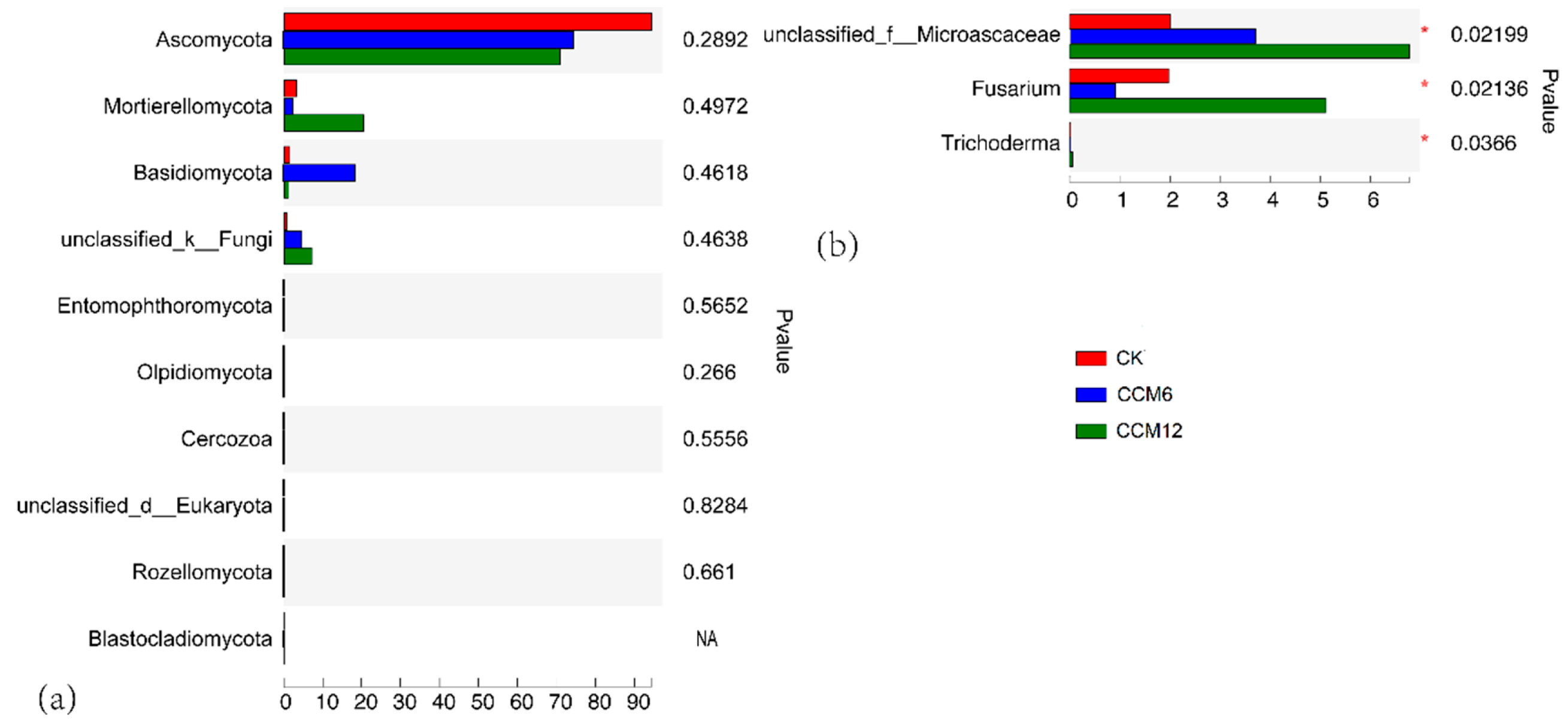
3.1. Fungi Soil-Borne Pathogens
3.2. Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.3. Strawberry Growth, Mortality Rate and Yield
3.4. Soil Microbial Diversity Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of ASD on Fungal Pathogens
4.2. Effect of ASD on the Soil Physicochemical Properties
4.3. Effect of ASD on Strawberry Growth and Yield
4.4. Effect of ASD on Soil Microbial Diversity and Community
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, D.; Yan, D.; Cao, A.; Fang, W.; Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Li, Y.; Ouyang, C.; Guo, M.; Wang, Q. Study on the Hydrolysis Kinetics of Dimethyl Disulfide. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yan, D.; Fang, W.; Huang, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, J.; Ouyang, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Chloropicrin Alternated with Biofumigation Increases Crop Yield and Modifies Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Strawberry Production. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sial, M.U.; Yu, H.; Cao, A. Combined Effect of a Reduced Dose of 1,3-Dichloropropene and Dimethyl Disulfide on Soilborne Pests and Tomato Growth. Crop Prot. 2019, 121, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajwa, H.A.; Klose, S.; Nelson, S.D.; Minuto, A.; Gullino, M.L.; Lamberti, F.; Lopez-Aranda, J.M. Alternatives to Methyl Bromide in Strawberry Production in the United States of America and the Mediterranean Region. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2003, 42, 220–244. [Google Scholar]
- López-Aranda, J.M.; Gómez, F.; Puga, M.; Zamora, R.; Daugovish, O.; Cotero, M.A. Chemical Soil Fumigation for Raspberry Nursery in Jalisco (Mexico). J. Berry Res. 2016, 6, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donley, N. The USA Lags behind Other Agricultural Nations in Banning Harmful Pesticides. Environ. Health 2019, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fennimore, S.A.; Serohijos, R.; Samtani, J.B.; Ajwa, H.A.; Subbarao, K.V.; Martin, F.N.; Daugovish, O.; Legard, D.; Browne, G.T.; Muramoto, J.; et al. Tif Film, Substrates and Nonfumigant Soil Disinfestation Maintain Fruit Yields. Calif. Agric. 2013, 67, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: FAOSTAT Database Collections. 2017. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org/ (accessed on 29 July 2020).
- Bi, Y.M.; Tian, G.L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.N.; Zhang, F.F.; Zhang, L.S.; Sun, Z.J. Differential Effects of Two Earthworm Species on Fusarium wilt of Strawberry. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 126, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, G.J.; Mansouripour, S.M.; Hewavitharana, S.S. Strawberries at the Crossroads: Management of Soilborne Diseases in California Without Methyl Bromide. Phytopathology 2020, 110, 956–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butler, D.M.; Kokalis-Burelle, N.; Albano, J.P.; McCollum, T.G.; Muramoto, J.; Shennan, C.; Rosskopf, E.N. Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation (ASD) Combined with Soil Solarization as a Methyl Bromide Alternative: Vegetable Crop Performance and Soil Nutrient Dynamics. Plant Soil 2014, 378, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewavitharana, S.S.; Mazzola, M. Carbon Source-Dependent Effects of Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation on Soil Microbiome and Suppression of Rhizoctonia Solani AG-5 and Pratylenchus Penetrans. Phytopathology 2016, 106, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, U.; Augé, R.M.; Butler, D.M. A Meta-Analysis of the Impact of Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation on Pest Suppression and Yield of Horticultural Crops. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, S.L.; Kluepfel, D.A. Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation: A Chemical-Independent Approach to Pre-Plant Control of Plant Pathogens. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 2309–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, G.T.; Ott, N.; Poret-Peterson, A.; Gouran, H.; Lampinen, B. Efficacy of Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation for Control of Prunus Replant Disease. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramoto, J.; Shennan, C.; Zavatta, M.; Baird, G.; Toyama, L.; Mazzola, M. Effect of Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation and Mustard Seed Meal for Control of Charcoal Rot in California Strawberries. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2016, 16, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shennana, C.; Muramoto, J.; Mazzola, M.; Momma, N.; Kobara, Y.; Lamers, J.; Rosskopf, E.N.; Kokalis-Burelle, N.; Butler, D.M. Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation for Soil Borne Disease Control in Strawberry and Vegetable Systems: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Acta Hortic. 2014, 1044, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.H.; An, J.Y.; Hwang, J.; Kim, S.B.; Park, B.B. The Effects of Organic Manure and Chemical Fertilizer on the Growth and Nutrient Concentrations of Yellow Poplar (Liriodendron tulipifera Lin.) in a Nursery System. For. Sci. Technol. 2016, 12, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilston, E.L.; Pitt, D.; Groenhof, A.C. Composted Recycled Organic Matter Suppresses Soil-Borne Diseases of Field Crops. New Phytol. 2002, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Schuchardt, F.; Li, G.; Guo, R.; Zhao, Y. Effect of C/N Ratio, Aeration Rate and Moisture Content on Ammonia and Greenhouse Gas Emission during the Composting. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larney, F.J.; Hao, X. A Review of Composting as a Management Alternative for Beef Cattle Feedlot Manure in Southern Alberta, Canada. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 3221–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, S.T.; Gordon, T.R. Management of Fusarium wilt of Strawberry. Crop Prot. 2015, 73, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Identification and Characterization of a Bacillus subtilis strain TS06 as Bio-Control Agent of Strawberry Replant Disease (Fusarium and Verticilium Wilts). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komada, H. Development of a Selective Medium for Quantitative Isolation of Fusarium Oxysporum from Natural Soil. Rev. Plant Prot. Res. 1975, 8, 114–124. [Google Scholar]
- Masago, H.; Yoshikawa, M.; Fukada, M.; Nakanishi, N. Selective Inhibition of Pythium Spp. on a Medium for Direct Isolation of Phytophthora Spp. from Soils and Plants. Phytopathology 1977, 77, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinner, F.; Öhlinger, R.; Kandeler, D.E.; Margesin, R. Methods in Soil Biology. In Methods in Soil Biology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1995; pp. 386–389. [Google Scholar]
- Shidan, B. (Ed.) Soil Agrochemical Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, N.; Tan, G.; Wang, H.; Gai, X. Effect of Biochar Additions to Soil on Nitrogen Leaching, Microbial Biomass and Bacterial Community Structure. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2016, 74, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massart, S.; Olmos, A.; Jijakli, H.; Candresse, T. Current Impact and Future Directions of High Throughput Sequencing in Plant Virus Diagnostics. Virus Res. 2014, 188, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-Filtering Vastly Improves Diversity Estimates from Illumina Amplicon Sequencing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massart, S.; Martinez-Medina, M.; Jijakli, M.H. Biological Control in the Microbiome Era: Challenges and Opportunities. Biol. Control 2015, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Wang, Q.; Yan, D.; Ma, T.; Liu, P.; Shen, J.; Li, Y.; Ouyang, C.; Guo, M.; Cao, A. Evaluation of Chloropicrin as a Soil Fumigant against Ralstonia Solanacarum in Ginger (Zingiber Officinale Rosc.) Production in China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messiha, N.A.S.; Van Diepeningen, A.D.; Wenneker, M.; Van Beuningen, A.R.; Janse, J.D.; Coenen, T.G.C.; Termorshuizen, A.J.; Van Bruggen, A.H.C.; Blok, W.J. Biological Soil Disinfestation (BSD), a New Control Method for Potato Brown Rot, Caused by Ralstonia Solanacearum Race 3 Biovar 2. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2007, 117, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheuerell, S.J.; Sullivan, D.M.; Mahaffee, W.F. Suppression of Seedling Damping-off Caused by Pythium Ultimum, P. Irregulare, and Rhizoctonia Solani in Container Media Amended with a Diverse Range of Pacific Northwest Compost Sources. Phytopathology 2005, 95, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oka, Y.; Shapira, N.; Fine, P. Control of Root-Knot Nematodes in Organic Farming Systems by Organic Amendments and Soil Solarization. Crop Prot. 2007, 26, 1556–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termorshuizen, A.J.; van Rijn, E.; van der Gaag, D.J.; Alabouvette, C.; Chen, Y.; Lagerlöf, J.; Malandrakis, A.A.; Paplomatas, E.J.; Rämert, B.; Ryckeboer, J.; et al. Suppressiveness of 18 Composts against 7 Pathosystems: Variability in Pathogen Response. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 2461–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, J.; Cai, Z.; Huang, X. Watermelon Planting Is Capable to Restructure the Soil Microbiome That Regulated by Reductive Soil Disinfestation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 129, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamliel, A.; van Bruggen, A.H.C. Maintaining Soil Health for Crop Production in Organic Greenhouses. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 208, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bruggen, A.H.C.; Gamliel, A.; Finckh, M.R. Plant Disease Management in Organic Farming Systems. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sollins, P.; Homann, P.; Caldwell, B.A. Stabilization and Destabilization of Soil Organic Matter: Mechanisms and Controls. Geoderma 1996, 74, 65–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancon, N.Q.; Edwards, C.A.; Bierman, P.; Welch, C.; Metzger, J.D. Influences of Vermicomposts on Field Strawberries: 1. Effects on Growth and Yields. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 93, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowlick, S.; Takehara, T.; Kaku, N.; Ueki, K.; Ueki, A. Proliferation of Diversified Clostridial Species during Biological Soil Disinfestation Incorporated with Plant Biomass under Various Conditions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 8365–8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amos, H.; Obi, C.I.; Audu, I. Effect of Chicken Manure on the Performance of Vegetable Maize (Zea Mays Saccharata) Varieties under Irrigation. Discourse J. Agric. Food Sci. 2013, 1, 190–195. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.Q.; Wen, T.; Zhang, J.B.; Meng, L.; Zhu, T.B.; Liu, L.L. Control of Soil-Borne Pathogen Fusarium Oxysporum by Biological Soil Disinfestation with Incorporation of Various Organic Matters. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2015, 143, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Wang, L.Y.; Zhou, Z.; Mbadinga, S.M.; Zhou, L.; Liu, J.F.; Yang, S.Z.; Gu, J.D.; Mu, B.Z. High Frequency of Thermodesulfovibrio Spp. and Anaerolineaceae in Association with Methanoculleus Spp. in a Long-Term Incubation of n-Alkanes-Degrading Methanogenic Enrichment Culture. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sekiguchi, Y.; Yamada, T.; Hanada, S.; Ohashi, A.; Harada, H.; Kamagata, Y. Anaerolinea Thermophila Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov. and Caldilinea Aerophila Gen. Nov., sp. Nov., Novel Filamentous Thermophiles That Represent a Previously Uncultured Lineage of the Domain Bacteria at the Subphylum Level. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1843–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.Y.; Gao, J.F.; Pan, K.L.; Li, D.C.; Zhang, L.F.; Wang, S.J. Shifts in Bacterial Community Composition and Abundance of Nitrifiers during Aerobic Granulation in Two Nitrifying Sequencing Batch Reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 251, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Di Gioia, F.; Zhao, X.; Ozores-Hampton, M.; Swisher, M.E.; Hong, J.; Kokalis-Burelle, N.; DeLong, A.N.; Rosskopf, E.N. Optimizing Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation for Fresh Market Tomato Production: Nematode and Weed Control, Yield, and Fruit Quality. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 218, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poret-Peterson, A.T.; Albu, S.; McClean, A.E.; Kluepfel, D.A. Shifts in Soil Bacterial Communities as a Function of Carbon Source Used during Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, A.; Kaku, N.; Ueki, K. Role of Anaerobic Bacteria in Biological Soil Disinfestation for Elimination of Soil-Borne Plant Pathogens in Agriculture. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 6309–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ran, W.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Shen, Q.; Shen, S.; Xu, Y. Biocontrol of Fusarium wilt Disease in Muskmelon with Bacillus Subtilis Y-IVI. BioControl 2013, 58, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loria, R.; Bukhalid, R.A.; Fry, B.A.; King, R.R. Plant Pathogenicity in the Genus Streptomyces. Plant Dis. 1997, 81, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harman, G.E. Overview of Mechanisms and Uses of Trichoderma spp. Phytopathology 2006, 96, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.; Sosnoskie, L.M.; Cabrera, J.A.; Qin, R.; Hanson, B.D.; Gerik, J.S.; Wang, D.; Browne, G.T.; Thomas, J.E. Fumigation Efficacy and Emission Reduction Using Low-Permeability Film in Orchard Soil Fumigation. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Trials | Fusarium spp. (cfu g−1) * | Phytophthora spp. (cfu g−1) * |
|---|---|---|
| Trial I (Jingjiao) | 4955 | 6539 |
| Trial II (Daxing) | 5455 | 6789 |
| Media * Category | Ingredients | Composition | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fusarium spp. | A | K2HPO4 (2 g), KCl (1 g), MgSO4 (1 g), L-Asparagine (4 g), D Galactose (40 g), Agar (30 g). | Komada [24] |
| B | Fe-Na EDTA (0.02 g), Na2B4O7.10H2O (2 g), Oxgall (1 g), streptomycin sulfate (1 g), Pentachloronitrobenzene (PCNB) (1.5 g). | ||
| Phytophthora spp. | A | Agar (34 g), glucose (40 g). | Masago [25] |
| B | Pentachloronitrobenzene (PCNB) (0.15 g), Ampicillin (0.03 g), Rifampicina (0.02 g). |
| Treatment | NH4+-N (mg/kg) | NO3−-N (mg/kg) | Available Phosphorus (mg/kg) | Available Potassium (mg/kg) | Organic Matter (mg/kg) | Oxidation-Reduction Potential (mV) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCM 6 | 16.1 ± 1.17 a | 92 ± 1 a | 942 ± 134 a | 773 ± 86 b | 17.0 ± 0.45 a | 182 ± 18 b | 7.59 ± 0.88 a |
| CCM 12 | 19.6 ± 1.52 a | 100 ± 21 a | 977 ± 82 a | 882 ± 69 a | 17.1 ± 2.9 a | 171 ± 22 b | 7.32 ± 0.56 a |
| CK | 13.8 ± 3.60 b | 55 ± 33 b | 906 ± 73 a | 750 ± 93 b | 13.9 ±1.9 b | 213 ± 16 a | 7.76 ± 0.53 a |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Z.; Massart, S.; Yan, D.; Cheng, H.; Eck, M.; Berhal, C.; Ouyang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cao, A. Composted Chicken Manure for Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation Increased the Strawberry Yield and Shifted the Soil Microbial Communities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6313. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166313
Song Z, Massart S, Yan D, Cheng H, Eck M, Berhal C, Ouyang C, Li Y, Wang Q, Cao A. Composted Chicken Manure for Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation Increased the Strawberry Yield and Shifted the Soil Microbial Communities. Sustainability. 2020; 12(16):6313. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166313
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Zhaoxin, Sebastien Massart, Dongdong Yan, Hongyan Cheng, Mathilde Eck, Chadi Berhal, Canbin Ouyang, Yuan Li, Qiuxia Wang, and Aocheng Cao. 2020. "Composted Chicken Manure for Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation Increased the Strawberry Yield and Shifted the Soil Microbial Communities" Sustainability 12, no. 16: 6313. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166313
APA StyleSong, Z., Massart, S., Yan, D., Cheng, H., Eck, M., Berhal, C., Ouyang, C., Li, Y., Wang, Q., & Cao, A. (2020). Composted Chicken Manure for Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation Increased the Strawberry Yield and Shifted the Soil Microbial Communities. Sustainability, 12(16), 6313. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166313