A Practical Overview of Methodologies for Sampling and Analysis of Microplastics in Riverine Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sampling Strategies in Riverine Environments
3. Collection of the Aqueous Phase
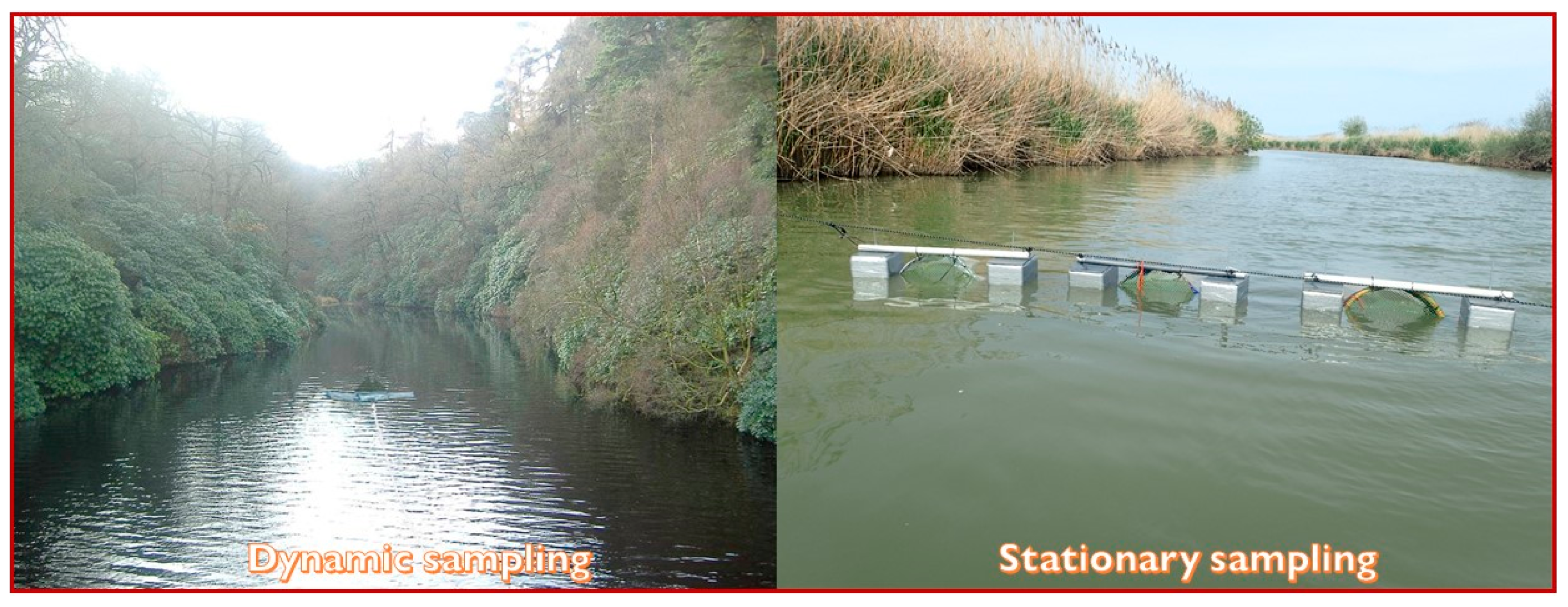
3.1. Dynamic Sampling
3.2. Stationary Sampling
4. Water Surface Sampling
5. Water Column Sampling
6. Expression of Results and Water Volume Calculation
- no. MPs per area (no. particles/km−2 or no. particles/m−2);
- no. MPs per volume (no. particles/m−3);
- mass of MPs per area (g MPs/km−2 or g MPs/m−2);
- mass of MPs per volume (g MPs/L−1 or g MPs/m−3);
7. Sediment Sampling
7.1. Collecting Sediments and Preservation
7.2. Expression of Results for Sediment Samples
- no. MPs per area (no. particles/km−2 or no. particles/m−2);
- no. MPs per volume (no. particles/m−3);
- no. MPs per mass (no. particles/kg−1 dry sediment);
- mass of MPs per area (g MPs/km−2 or g MPs/m−2);
- mass of MPs per volume (g MPs/L−1 or g MPs/cm−3),
8. Samples Processing
8.1. Water Samples Preparation
8.2. Sediment Samples Preparation
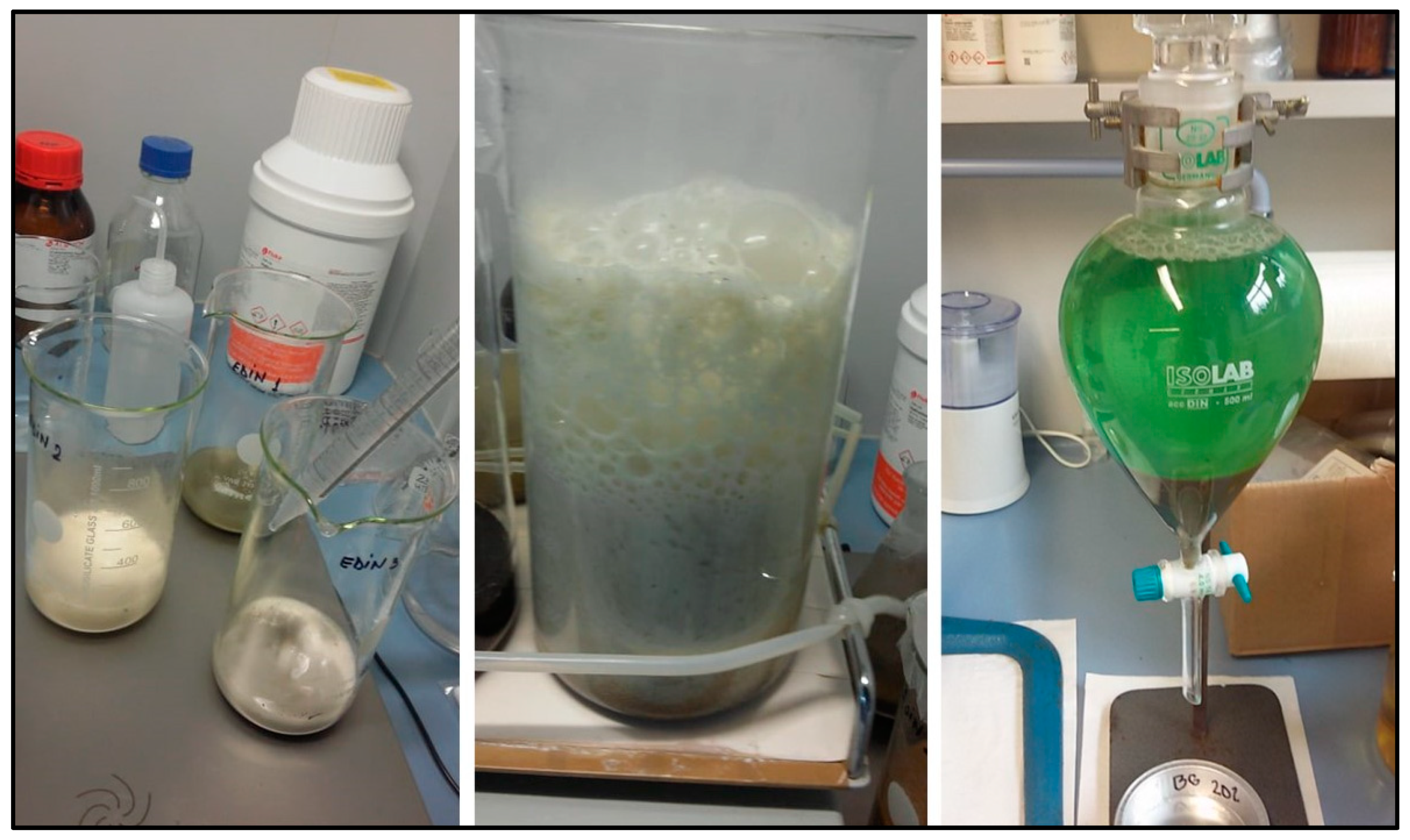
8.3. Sample Digestion
8.4. Density Separation and Filtration
9. Quantification and Identification
10. Quality Assurance and Quality Control of Analysis (QA/QC)
11. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, J.P.; Nash, R. Microplastics: Finding a consensus on the definition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.; Dimzon, I.K.; Eubeler, J.; Knepper, T.P. Analysis, occurrence, and degradation of microplastics in the aqueous environment. In Freshwater Microplastics: Emerging Environmental Contaminants? Wagner, M., Lambert, S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.; Wagner, M. The handbook of environmental chemistry. In Freshwater microplastics. Emerging Environmental Contaminants? Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lechner, A.; Keckeis, H.; Lumesberger-Loisl, F.; Zens, B.; Krusch, R.; Tritthart, M.; Glas, M.; Schludermann, E. The Danube so colourful: A potpourri of plastic litter outnumbers fish larvae in Europe’s second largest river. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 188, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Wal, M.; Van der Meulen, M.; Tweehuijsen, G.; Peterlin, M.; Palatinus, A.; Virsek, M.K.; Coscia, L.; Krsan, A. SFRA0025: Identification and Assessment of Riverine Input of (Marine) Litter: Final Report for the European Commission DG Environment under Framework Contract No ENV.D2/FRA/2012/0025. 2015, Volume 25, p. 208. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/marine/good-environmental-status/descriptor-10/pdf/iasFinal%20Report.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2020).
- Lebreton, L.C.M.; van der Zwet, J.; Damsteeg, J.-W.; Slat, B.; Andrady, A.; Reisser, J. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegfried, M.; Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Kroeze, C. Export of microplastics from land to sea. A modelling approach. Water Res. 2017, 127, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, T.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Seasonal microplastics variation in nival and pluvial stretches of the Rhine River—From the Swiss catchment towards the North Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanale, C.; Stock, F.; Massarelli, C.; Kochleus, C.; Bagnuolo, G.; Reifferscheid, G.; Uricchio, V.F. Microplastics and their possible sources: The example of Ofanto river in southeast Italy. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. MPs as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löder, M.G.J.; Gerdts, G. Methodology used for the detection and identification of MPs a critical appraisal. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Bergmann, M., Gutow, L., Klages, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; p. 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eerkes-Medrano, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Aldridge, D.C. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review of the emerging threats, identification of knowledge gaps and prioritisation of research needs. Water Res. 2015, 75, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Paul Chen, J. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review on occurrence, environmental effects, and methods for MPs detection. Water Res. 2018, 137, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, F.; Kochleus, C.; Bänsch-Baltruschat, B.; Brennholt, N.; Reifferscheid, G. Sampling techniques and preparation methods for microplastic analyses in the aquatic environment—A review. TrAC Trend Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fernández, D.; Hanke, G.; Tweehuysen, G.; Bellert, B.; Holzhauer, M.; Palatinus, A.; Hohenblum, P.; Oosterbaan, L. Riverine Litter Monitoring-Options and Recommendations; MSFD GES TG Marine Litter Thematic Report; JRC Technical Report; Joint Research Centre (JRC): Luxembourg, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.L.; Devriese, L.; Galgani, F.; Robbens, J.; Janssen, C.R. MPs in sediments: A review of techniques, occurrence and effects. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 111, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The physical impacts of MPs on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermsen, E.; Mintenig, S.M.; Besseling, E.; Koelmans, A.A. Quality criteria for the analysis of microplastic in biota samples: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10230–10240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Fernández, D.; Hanke, G.; Marin, J.V.; Cabañas, A.C. Modelling Floating Macro Litter Loads from Rivers to the Marine Environment Based on Visual Observations; European Geosciences Union General Assembly: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Methods for sampling and detection of microplastics in water and sediment: A critical review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubarenko, I.; Bagaev, A.; Zobkov, M.; Esiukova, E. On some physical and dynamical properties of microplastic particles in marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 108, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukulka, T.; Proskurowski, G.; Morét-Ferguson, S.; Meyer, D.W.; Lawet, K.L. The effect of wind mixing on the vertical distribution of buoyant plastic debris. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H. Transport of MPs in coastal seas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 199, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummel, C.D.; Jahnke, A.; Gorokhova, E.; Kühnel, D.; Schmitt-Jansen, M. Impacts of biofilm formation on the fate and potential effects of microplastic in the aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogi, H.; Bab, N.; Ishihara, S.; Shibata, Y. Sampling of Plastic Pellets by Two Types of Neuston Net and Plastic Pollution in the Sea. Bull. Fac. Fish. Hokkaido Univ. 1999, 50, 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- GESAMP. Sources, Fate and Effects of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Part Two of a Global Assessment; Kershaw, P.J., Rochman, C.M., Eds.; Rep. Stud. GESAMP.; IMO/FAO/UNESCO-IOC/UNIDO/WMO/IAEA/UN/ UNEP/UNDP Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection: London, UK, 2016; p. 220. [Google Scholar]
- Setälä, O.; Magnusson, K.; Lehtiniemi, M.; Norén, F. Distribution and abundance of surface water microlitter in the Baltic Sea: A comparison of two sampling methods. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michida, Y.; Chavanich, S.; Cózar Cabañas, A.; Hagmann, P.; Hinata, H.; Isobe, A.; Kershaw, P.; Kozlovskii, N.; Li, D.; Lusher, A.L.; et al. Guidelines for Harmonizing Ocean Surface Microplastic Monitoring Methods; Ministry of the Environment Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 2019.
- Basset, A.; Sangiorgio, F.; Sabetta, L. Metodologie per la Determinazione Della Struttura Dimensionale di Fitoplancton e Macroinvertebrati Bentonici; ISPRA-Istituto Superiore per la Protezione e la Ricerca Ambientale: Roma, Italy, 2009.
- Tranter, D.J.; Smith, P.E. Filtration performance. In Zooplankton Sampling; Tranter, D.J., Fraser, J.H., Eds.; UNESCO Monographs on Oceanographic Methodology; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1968; pp. 27–56. [Google Scholar]
- Cutroneo, L.; Reboa, A.; Besio, G.; Borgogno, F.; Canesi, L.; Canuto, S.; Dara, D.; Enrile, F.; Forioso, I.; Greco, G.; et al. Microplastics in seawater: Sampling strategies, laboratory methodologies, and identification techniques applied to port environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 8938–8952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, C.B.; Quinn, B. Microplastic identification techniques. In Microplastic Pollutants, 1st ed.; Crawford, C.B., Quinn, B., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 219–267. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, F.; Grant, G.C. Guidelines for Zooplankton Sampling in Quantitative Baseline and Monitoring Programs; Special Scientific Report No. 83; Virginia Institute of Marine Science; US Envoronmental Protection Agency: Corvallis, OR, USA.
- UNESCO. Zooplankton Sampling. Monographs on Oceanographic Methodology; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1979; ISBN 92-3-101194-4.
- Eriksen, M.; Mason, S.; Wilson, S.; Box, C.; Zellers, A.; Edwards, W.; Farley, H.; Amato, S. Microplastic pollution in the surface waters of the Laurentian Great Lakes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 77, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, C.; Baker, J.; Bamford, H. Proceedings of the International Research Workshop on the Occurrence, Effects and Fate of Micro-Plastic Marine Debris; NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS-OR&R-30; NOAA: Silver Sping, MD, USA, 2008; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, P.G.; Suaria, G.; Perold, V.; Bornman, T.G.; Aliani, S. Sampling microfibres at the sea surface: The effects of mesh size and water depth. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113413. [Google Scholar]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Rocher, V.; Saad, M.; Renault, N.; Tassin, B. Microplastic contamination in an urban area: A case study in Greater Paris. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedermann, M.; Gmeiner, P.; Pessenlehner, S.; Haimann, M.; Hohenblum, P.; Habersack, H. A methodology for measuring microplastic transport in large or medium rivers. Water 2018, 10, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamminga, M.; Stoewer, S.C.; Fischer, E.K. On the representativeness of pump water samples versus manta sampling in microplastic analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254 Pt A, 112970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhong, S.; Yang, B.; Lu, D.; Zhong, Q. Distribution of microplastics in surface water and sediments of Qin river in Beibu Gulf, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, R.; Labrenz, M. Small microplastic sampling in water: Development of an encapsulated filtration device. Water 2018, 10, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, J.H.; Kwon, O.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Song, Y.K.; Shim, W.J. Marine neustonic microplastics around the southeastern coast of Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 96, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guven, O.; Gokdag, K.; Jovanovic, B.; Kideys, A.E. Microplastic litter composition of the Turkish territorial waters of the Mediterranean Sea, and its occurrence in the gastrointestinal tract of fish. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.J.; Warrack, S.; Langen, V.; Challis, J.K.; Hanson, M.L.; Rennie, M.D. Microplastic contamination in lake winnipeg, Canada. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooi, M.; Reisser, J.; Slat, B.; Ferrari, F.F.; Schmid, M.S.; Cunsolo, S.; Brambini, R.; Noble, K.; Sirks, L.-A.; Linders, T.E.W.; et al. The effect of particle properties on the depth profile of buoyant plastics in the ocean. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lenaker, P.L.; Baldwin, A.K.; Corsi, S.R.; Mason, S.A.; Reneau, P.C.; Scott, J.W. Vertical distribution of microplastics in the water column and surficial sediment from the Milwaukee River Basin to Lake Michigan. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12227–12237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlsson, T.M.; Kärrman, A.; Rotander, A.; Hassellöv, M. Comparison between manta trawl and in situ pump filtration methods, and guidance for visual identification of microplastics in surface waters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 5559–5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collignon, A.; Hecq, J.H.; Glagani, F.; Voisin, P.; Collard, F.; Goffart, A. Neustonic microplastic and zooplankton in the North Western Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCormick, A.R.; Hoellein, T.J.; London, M.G.; Hittie, J.; Scott, J.W.; Kelly, J.J. Microplastic in surface waters of urban rivers: Concentration, sources, and associated bacterial assemblages. Ecosphere 2016, 7, e01556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrows, A.; Neumann, C.; Berger, M.; Shaw, S. Grab vs. neuston tow net: A microplastic sampling performance comparison and possible advances in the field. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syakti, A.; Hidayati, N.; Jaya, Y.; Yude, R.; Suhendy, S.; Asia, L.; Wong-Wah-Chung, P.; Doumenq, P. Simultaneous grading of microplastic size sampling in the Small Islands of Bintan water, Indonesia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amélineau, F.; Bonnet, D.; Heitz, O.; Mortreux, V.; Harding, A.M.A.; Karnovsky, N.; Walkusz, W.; Fort, J.; Grémillet, D. Microplastic pollution in the Greenland Sea: Background levels and selective contamination of planktivorous diving seabirds. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, Y.Y.; Mak, C.W.; Liebich, C.; Lam, S.W.; Sze, E.T.; Chan, K.M. Microplastic pollution in the marine waters and sediments of Hong Kong. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Tassin, B. Sources and fate of microplastics in urban areas: A focus on Paris megacity. In Freshwater Microplastics. The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Wagner, M., Lambert, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campanale, C.; De Palma, C.P.; Bollino, B.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. Innovativo sistema di campionamento automatizzato per il monitoraggio di microplastiche in ambienti fluviali. In Proceedings of the RemTech Expo–Hub tecnologica Campania, Napoli, Italy, 26–28 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, K.L.; Obbard, J.P. Prevalence of microplastics in Singapore’s coastal marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagaev, A.; Khatmullina, L.; Chubarenko, I. Anthropogenic microlitter in the Baltic Sea water column. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Tian, Y.; Chen, T.; Tu, C.; Fu, C.; Luo, Y. Occurrence of microplastics in the water column and sediment in an inland sea affected by intensive anthropogenic activities. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanhai, L.D.K.; Gårdfeldt, K.; Lyashevska, O.; Hassellöv, M.; Thompson, R.C.; O’Connor, I. Microplastics in sub-surface waters of the Arctic Central Basin. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 130, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamminga, M.; Hengstmann, E.; Fischer, E.K. Microplastic analysis in the south Funen archipelago, Baltic Sea, implementing manta trawling and bulk sampling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 128, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covernton, G.A.; Pearce, C.M.; Gurney-Smith, H.J.; Chastain, S.G.; Ross, P.S.; Dower, J.F.; Dudas, S.E. Size and shape matter: A preliminary analysis of microplastic sampling technique in seawater studies with implications for ecological risk assessment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 667, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtene-Jones, W.; Quinn, B.; Gary, S.F.; Mogg, A.O.; Narayanaswamy, B.E. Microplastic pollution identified in deep-sea water and ingested by benthic invertebrates in the Rockall Trough, North Atlantic Ocean. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Jang, M.; Han, G.M.; Rani, M.; Lee, J.; Shim, W.J. A comparison of microscopic and spectroscopic identification methods for analysis of microplastics in environmental samples. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 93, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Vanreusel, A.; Mees, J.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastic pollution in deep-sea sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazey, F.M.; Ryan, P.G. Biofouling on buoyant marine plastics: An experimental study into the effect of size on surface longevity. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagaev, A.; Mizyuk, A.; Khatmullina, L.; Isachenko, I.; Chubarenko, I. Anthropogenic fibres in the Baltic Sea water column: Field data, laboratory and numerical testing of their motion. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, C.J.; Lattin, G.L.; Zellers, A.F. Quantity and type of plastic debris flowing from two urban rivers to coastal waters and beaches of Southern California. Revista da Gestão Costeira Integrada. J. Integr. Coast. Zone Manag. 2011, 11, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Gago, J.; Filgueiras, A.; Pedrotti, M.L.; Caetano, M.; Frias, J. Standardised Protocol for Monitoring Microplastics in Seawater; Deliverable 4.1. JPI-Oceans BASEMAN Project; JPI-Oceans: Brussels, Belgium, 2018; p. 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, M.R. Plastic pellets on New Zealand beaches. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1977, 8, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizetto, L.; Bussin, G.; Futter, M.N.; Butterfield, D.; Whitehead, P.G. A theoretical assessment of microplastic transport in river catchments and their retention by soils and river sediments. Environ. Sci. Process. Impact 2016, 18, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, H.A.; Brandsma, S.H.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Vethaak, A.D. Microplastics en route: Field measurements in the Dutch river delta and Amsterdam canals, wastewater treatment plants, North Sea sediments and biota. Environ. Int. 2017, 101, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolte, A.; Forster, S.; Gerdts, G.; Schubert, H. Microplastic concentrations in beach sediments along the German Baltic coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 99, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, B.; Murphy, F.; Ewins, C. Validation of density separation for the rapid recovery of microplastics from sediment. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, M.E.; Kroon, F.J.; Motti, C.A. Recovering microplastics from marine samples: A review of current practices. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 123, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Zuo, L.Z.; Peng, J.P.; Cai, L.Q.; Fok, L.; Yan, Y.; Li, H.X.; Xu, X.R. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in an urban river: A case study in the Pearl River along Guangzhou City, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imhof, H.K.; Ivleva, N.P.; Schmid, J.; Niessner, R.; Laforsch, C. Contamination of beach sediments of a subalpine lake with microplastic particles. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 867–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Faure, F.; Demars, C.; Wieser, O.; Kunz, M.; Alencastro, L.F. Plastic pollution in Swiss surface waters: Nature and concentrations, interaction with pollutants. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Thiel, M. Distribution and abundance of small plastic debris on beaches in the SE Pacific (Chile): A study supported by a citizen science project. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 87–88, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidoo, T.; Glassom, D.; Smit, A.J. Plastic pollution in five urban estuaries of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vianello, A.; Boldrin, A.; Guerriero, P.; Moschino, V.; Rella, R.; Sturaro, A.; Da Ros, L. Microplastic particles in sediments of Lagoon of Venice, Italy: First observations on occurrence, spatial patterns and identification. Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 2013, 130, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, R.A.; Avlijas, S.; Simard, M.A.; Ricciardi, A. Microplastic pollution in St. Lawrence River sediments. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 70, 1767–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobkov, M.B.; Esiukova, E.E. Microplastics in a marine environment: Review of methods for sampling, processing, and analyzing microplastics in water, bottom sediments, and coastal deposits. Oceanology 2018, 58, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Sample Preservation, Methods for Chemical Analysis of Water and Wastes; EPA-600/4-79-020; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1983; pp. 15–20.
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Fileman, E.; Halsband, C.; Goodhead, R.; Moger, J.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastic ingestion by zooplankton. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6646–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.P.; Otero, V.; Sobral, P. Evidence of microplastics in samples of zooplankton from Portuguese coastal waters. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 95, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivar do Sul, J.A.; Costa, M.F. The present and future of microplastic pollution in the marine environment. Environ. Pollut. 1983, 185, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballent, A.; Corcoran, P.L.; Madden, O.; Helm, P.A.; Longstaffe, F.J. Sources and sinks of microplastics in Canadian Lake Ontario nearshore, tributary and beach sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Vidal, A.; Thompson, R.C.; Canals, M.; de Haan, W.P. The imprint of microfibres in southern European deep seas. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsing, S.; Kochleus, C.; Buchinger, S.; Brennholt, N.; Stock, F.; Reifferscheid, G. A new approach in separating microplastics from environmental samples based on their electrostatic behavior. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebezeit, G.; Dubaish, F. MPs in beaches of the East Frisian Islands Spiekeroog and Kachelotplate. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 89, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claessens, M.; Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Vandegehuchte, M.B.; Janssen, C.R. New techniques for the detection of microplastics in sediments and field collected organisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 70, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Webb, H.; Lindeque, P.K.; Fileman, E.S.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Isolation of microplastics in biota-rich seawater samples and marine organisms. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Löder, M.G.J.; Imhof, H.K.; Ladehoff, M.; Löschel, L.A.; Lorenz, C.; Mintenig, S.; Piehl, S.; Primpke, S.; Schrank, I.; Laforsch, C.; et al. Enzymatic purification of microplastics in environmental samples. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 14283–14292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Experimental development of a new protocol for extraction and characteriszation of microplastics in fish tissues: First observations in commercial species from Adriatic Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 111, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehaut, A.; Cassone, A.-L.; Frère, L.; Hermabessiere, L.; Himber, C.; Rinnert, E.; Rivière, G.; Lambert, C.; Soudant, P.; Huvet, A.; et al. Microplastics in seafood: Benchmark protocol for their extraction and characterization. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 215, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thielea, C.J.; Hudsona, M.D.; Russellb, A.E. Evaluation of existing methods to extract microplastics from bivalve tissue: Adapted KOH digestion protocol improves filtration at single-digit pore size. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2019, 142, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühn, S.; van Werven, B.; van Oyen, A.; Meijboom, A.; Rebolledo, E.L.B.; van Franeker, J.A. The use of potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution as a suitable approach to isolate plastics ingested by marine organisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catarino, A.I.; Thompson, R.; Sanderson, W.; Henry, T.B. Development and optimization of a standard method for extraction of microplastics in mussels by enzyme digestion of soft tissues. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtene-Jones, W.; Quinn, B.; Murphy, F.; Garya, S.F.; Narayanaswamya, B.E. Optimisation of enzymatic digestion and validation of specimen preservation methods for the analysis of ingested microplastics. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nuelle, M.T.; Dekiff, J.H.; Remy, D.; Fries, E. A new analytical approach for monitoring microplastics in marine sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenfeng, W.; Jun, W. Investigation of microplastics in aquatic environments: An overview of the methods used, from field sampling to laboratory analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanvey, J.; Lewis, P.; Lavers, J.; Crosbie, N.; Posa, K.; Clarke, B. A review of analytical techniques for quantifying microplastics in sediments. Anal. Methods 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, R.R.; Lusher, A.L.; Olsen, M.; Nizzetto, L. Validation of a method for extracting microplastics from complex, organic-rich, environmental matrices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7409–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masura, J.; Baker, J.; Foster, G.; Courtney, A. Laboratory Methods for the Analysis of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Recommendations for Quantifying Synthetic Particles in Waters and Sediments; NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS-OR&R-48; NOAA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Frias, J.P.; Nash, R.; Pagter, E.; O’Connor, I. Standardised Protocol for Monitoring Microplastics in Sediments; Technical Report; BASEMAN Project; JPI-Oceans: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Bagnuolo, G.; Savino, I.; Uricchio, V.F. The problem of microplastics and regulatory strategies in Italy. In Plastics in the Aquatic Environment-Stakeholders Role against Pollution; Stock, F., Reifferscheid, G., Brennholt, N., Kostianaia, E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Nieva, J.; Perales, J.A.; Gonzales-Leal, J.M.; Rojo-Nieto, R. A new analytical technique for extraction and quantification of microplastics in marine sediments focused on the easy implementation and repeatability. Anal. Meth. 2017, 9, 6371–6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagter, E.; Frias, J.; Nash, R. Microplastics in Galway Bay: A comparison of sampling and separation methods. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, P.L.; Biesinger, M.C.; Grifi, M. Plastics and beaches: A degrading relationship. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppock, R.L.; Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.K.; Queirós, A.M.; Galloway, T.S. A small-scale, portable method for extracting microplastics from marine sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kedzierski, M.; Tilly, V.L.; Bourseau, P.; Bellegou, H.; César, G.; Sire, O.; Bruzaud, S. Microplastic elutriation system. Part A: Numerical modeling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermsen, E.; Pompe, R.; Besseling, E.; Koelmans, A.A. Detection of low numbers of microplastics in North Sea fish using strict quality assurance criteria. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, W.J.; Hongab, S.H.; Eoab, S.E. Identification methods in microplastic analysis: A review. Anal. Methods 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Navarro, J.; Castrillón-Santana, M.; Gómez, M.; Herrera, A.; Marín-Reyes, P.A. Automatic counting and classification of microplastic particles. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods, Funchal, Portugal, 16 January 2018; pp. 646–652. [Google Scholar]
- Chaczko, Z.; Wajs-Chaczko, P.; Tien, D.; Haidar, Y. Detection of microplastics using machine learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics (ICMLC), Kobe, Japan, 7–10 July 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo-Navarro, J.; Castrillón-Santana, M.; Santesarti, E.; De Marsico, M.; Martínez, I.; Raymond, E.; Gómez, M.; Herrera, A. SMACC: A system for microplastics automatic counting and classification. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 25249–25261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmayr, V.; Sahin, A.; Sæmundsson, B.; Buhmann, J.M. Instance segmentation for the quantification of microplastic fiber images. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of WACV 2020, Aspen, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020; Available online: IEEE Xplore (accessed on 5 July 2020).
- Primpke, S.; Dias, P.A.; Gerdts, G. Automated identification and quantification of microfibres and MPs. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 2138–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primpke, S.; Cross, R.K.; Mintenig, S.M.; Simon, M.; Vianello, A.; Gerdts, G.; Vollertsen, J. Toward the systematic identification of MPs in the environment: Evaluation of a new independent software tool (simple) for spectroscopic analysis. Appl. Spectrosc. 2020, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermabessiere, L.; Himber, C.; Boricaud, B.; Kazour, M.; Amara, R.; Cassone, A.-L.; Laurentie, M.; Paul-Pont, I.; Soudant, P.; Dehaut, A.; et al. Optimization, performance, and application of a pyrolysis-GC/MS method for the identification of microplastics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 6663–6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dekiff, J.H.; Remy, D.; Klasmeier, J.; Fries, E. Occurrence and spatial distribution of microplastics in sediments from Norderney. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 186, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.L.; Thomas, K.V.; Luo, Z.; Gowen, A.A. FTIR and Raman imaging for microplastics analysis: State of the art, challenges and prospects. Trac Trend Anal.Chem. 2019, 119, 115629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, G.; Schmidt, T.C.; Schram, J. Analytical methodologies for monitoring micro(nano)plastics: Which are fit for purpose? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käppler, A.; Fischer, M.; Scholz-Böttcher, B.M.; Oberbeckmann, S.; Labrenz, M.; Fischer, D.; Eichhorn, K.J.; Voit, B. Comparison of μ-ATR-FTIR spectroscopy and py-GCMS as identification tools for microplastic particles and fibers isolated from river sediments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5313–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dümichen, E.; Braun, U.; Senz, R.; Fabian, G.; Sturm, H. Assessment of a new method for the analysis of decomposition gases of polymers by a combining thermogravimetric solid-phase extraction and thermal desorption gas chromatography mass spectrometry. J. Chrom. A 2014, 1354, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, E.; Minor, E.C.; Schreiner, K. Microplastic abundance and composition in western Lake Superior as determined via microscopy, Pyr-GC/MS, and FTIR. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1787–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, E.; Dekiff, J.H.; Willmeyer, J.; Nuelle, M.-T.; Ebert, M.; Remy, D. Identification of polymer types and additives in marine microplastic particles using pyrolysis-GC/MS and scanning electron microscopy. Environ. Sci. Proc. Improv. 2013, 15, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peñalver, R.; Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; López-García, I.; Hernández-Córdoba, M. An overview of microplastics characterization by thermal analysis. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymanski, D.; Goldbeck, C.; Humpf, H.U.; Fürst, P. Analysis of microplastics in water by micro-Raman spectroscopy: Release of plastic particles from 691 different packaging into mineral water. Water Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käppler, A.; Fischer, D.; Oberbeckmann, S.; Schernewski, G.; Labrenz, M.; Eichhorn, K.J.; Voit, B. Analysis of environmental microplastics by vibrational microspectroscopy: FTIR, Raman or both? Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 8377–8391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corami, F.; Rosso, B.; Bravo, B.; Gambaro, A.; Barbante, C. A novel method for purification, quantitative analysis and characterisation of microplastic fibers using Micro-FTIR. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, S.A.; Welch, V.G.; Neratko, J. Synthetic polymer contamination in bottled water. Front Chem. 2018, 6, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Comnea-Stancu, I.R.; Wieland, K.; Ramer, G.; Schwaighofer, A.; Lendl, B. On the identification of rayon/viscose as a major fraction of microplastics in the marine environment: Discrimination between natural and manmade cellulosic fibers using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Appl Spectrosc. 2017, 7, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anger, P.M.; von der Esch, E.; Baumann, T.; Elsner, M.; Niessner, R.; Ivleva, N.P. Raman microspectroscopy as a tool for microplastic particle analysis. Trend Anal. Chem. 2018, 109, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dümichen, E.; Barthel, A.-K.; Braun, U.; Bannick, C.G.; Brand, K.; Jekel, M.; Senz, R. Analysis of polyethylene microplastics in environmental samples, using a thermal decomposition method. Water Res. 2015, 85, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Scholz-Bottcher, B.M. Simultaneous trace identification and quantification of common types of microplastics in environmental samples by pyrolysis-gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5052–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funck, M.; Yildirim, A.; Nickel, C.; Schram, J.; Schmidt, T.C.; Tuerk, J. Identification of microplastics in wastewater after cascade filtration using Pyrolysis-GC–MS. Methods X 2020, 7, 100778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, R.; Altmann, K.; Sommerfeld, T.; Braun, U. Quantification of microplastics in a freshwater suspended organic matter using different thermoanalytical methods—Outcome of an interlaboratory comparison. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2020, 104829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, Z.; Kintzi, A.; Muñoz, K.; Schaumann, G.E. A simple method for the selective quantification of polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene plastic debris in soil by pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2020, 147, 104803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dümichen, E.; Eisentraut, P.; Bannick, C.G.; Barthel, A.K.; Senz, R.; Braun, U. Fast identification of microplastics in complex environmental samples by a thermal degradation method. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisentraut, P.; Dümichen, E.; Ruhl, A.S.; Jekel, M.; Albrecht, M.; Gehde, M.; Braun, U. Two birds with one stonedfast and simultaneous analysis of microplastics: Microparticles derived from thermoplastics and tire wear. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5–10, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, G.A. Microplastics in Aquatic Systems: An Assessment of Risk (Summary of Critical Issues and Recommended Path Forward); Water Environment & Reuse Foundation (WE&RF): Alexandria, Egypt, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Connors, K.A.; Dyer, S.D.; Belanger, S.E. Advancing the quality of environmental microplastic research. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 1697–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Bakir, A.; Burton, G.A.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastic as a vector for chemicals in the aquatic environment: Critical review and model-supported reinterpretation of empirical studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3315–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Kooi, M.; Erich, M.; Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.E.; Dekker, S.C.; Koelmans, A.A.; van Wezel, A.P. A systems approach to understand microplastics measured in riverine surface waters and sediments in prep. Water Res. 2019, 176, 115723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Nor, N.H.M.; Hermsen, E.; Kooi, M.; Mintenig, S.M.; De France, J. Microplastics in freshwaters and drinking water: Critical review and assessment of data quality. Water Res. 2019, 155, 410–422. [Google Scholar]
- Estahbanati, S.; Fahrenfeld, N.L. Influence of wastewater treatment plant discharges on microplastic concentrations in surface water. Chemosphere 2016, 162, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zou, X.; Li, B.; Yao, Y.; Zang, Z.; Li, Y.; Yu, W.; Wang, W. Preliminary study of the source apportionment and diversity of microplastics: Taking floating microplastics in the South China Sea as an example. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodall, L.C.; Gwinnett, C.; Packer, M.; Thompson, R.C.; Robinson, L.F.; Paterson, G.L.J. Using a forensic science approach to minimize environmental contamination and to identify microfibres in marine sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesch, C.; Elert, A.M.; Wörner, M.; Braun, U.; Klein, R.; Paulus, M. Assuring quality in microplastic monitoring: About the value of clean-air devices as essentials for verified data. Sci. Rep. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, M.; Digka, N.; Anastasopoulou, A.; Tsangaris, C.; Mytilineou, C. Anthropogenic microfibres pollution in marine biota. A new and simple methodology to minimize airborne contamination. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 113, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sampling Device | Advantages | Disadvantages | Costs $ | Time (Minutes) | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nondiscrete sampling devices | Manta net | Sampling of large volumes of water; The lateral wings allow the floating of the device and the sampling of the water surface. | Expensive equipment; Requires boat; The lower limit of detection is 333 μm; Clogging problems; Risk of sample contamination; Underestimation of the total buoyant microplastic amounts. | ~3500 | 15–240 | [34,41,42,46,47,48,49,50,51] |
| Neuston net | Sampling of large volumes of water; Widely used (useful for compare positions). | Expensive equipment; Requires a boat; The lower limit of detection is 333 μm; Clogging problems; Risk of sample contamination; Underestimation of the total buoyant microplastic amounts. | ~2300 | 30 | [34,52,53,54,55] | |
| Plankton net | The lower limit of detection is 100 μm; Sampling of medium volumes of water; Possibility to sample the water column. | Expensive equipment; Requires a boat; Clogging problems; Sampling of lower volumes of water compared to Manta trawl; Risk of sample contamination; Underestimation of the total buoyant microplastic amounts. | ~2400 | 30 | [26,34,56,57,58] | |
| MP traps | Possibility to sample in several points of the water stream; Possibility to choose mesh dimensions from 100 µm to 333 µm. | Expensive equipment; May involve difficulty in anchoring to the riverbed; In the presence of a low flow rate, samples the first 15 cm of water; Risk of contamination. | ~1200 | 30 | [35] | |
| Autosampler | Well-known and precise volume of filtered water; Minimises the risk of contamination; Allows a dimensional separation of the particles directly in the field. | Costly equipment; Difficult and heavy to transport and deploy; May be very fragile; Requires electric energy; Requires a large amount of instrumentation. | 10,000–70,000 | - | [45,59] | |
| Pumping systems | Allows the user to sample smaller MPs and fibre loss is limited; Well-known and precise volume of filtered water; Allows standardisation of sampling. | Sampling of a small volume of water; Requires energy to work; Requires boat; It can be challenging to transport and apply. Allows the sampling of a single point; Requires the transport of bulky samples to the lab; Sampling is less representative; -Risk of sample contamination. | 300–1000 | 15–180 | [30,34,43,44,51,60] | |
| Discrete sampling devices | Niskin bottles/Jars/Bottles/Buckets/Rosette/Integrated water sampler (IWS)/Ruttner bottles/Friedinger bottles/Bernatowicz bottles | Relatively quick and straightforward to use; Rosette provides multi-point measurements; Allows sampling at different depths; Allows the user to sample smaller MPs and fibre loss is limited; Well-known and precise volume of filtered water; Allows standardisation of sampling. | Requires boat; Rosette can be challenging to transport; Sampling of a small volume of water; May be very fragile; Requires the transport of bulky samples to the lab; Sampling is less representative; Risk of sample contamination. | Very variable (300–50,000) | 15–30 | [34,35,58,61,62,63,64,65,66] |
| Devices for surface microlayer | Stainless-steel sieves/Rotating Drum Sampler | Does not require specialised equipment; Quick and straightforward to use; Well-known and precise volume of filtered water; Allows choice of mesh size; Allows a dimensional separation of the particles directly in the field. | Sampling of medium/low volumes of water; Requires the transport of significant volume of water to the lab; Manual transfer of water with buckets; Potential contamination by the apparatus. | From 50 | Depending on mesh size | [34,60,67] |
| Reagents | Method | Costs | Hazard | Pros | Cons | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HNO3 | 20 mL of HNO3 (22.5 M), 2 h heating (∼100 °C), hot filtration (∼80 °C) | $38.00 for 1 L | Oxidiser, corrosive | Efficient in organic digestion | Possible degradation of PS, PA, and PE, makes the plastic yellow | [16,95,98,99] |
| HCl | 4 mL of HCl at 20% | $36.00 for 1 L | Corrosive, acute toxicity | Efficient in organic digestion (82.6%) of complex matrices (clams) | Degradation of polymers | [96,100,104] |
| NaOH | 20 mL of NaOH (10 M) at 60 °C for 24 h | $62.63 for 1 kg | Corrosive | Digestion efficiency up to 90%, stimulated by the rise of molarity and temperature | Degradation of PET and PVC | [16,96,104,107] |
| KOH | 20 mL of KOH (1 M) at 18–21 °C for two days | $85.72 for 1 kg | Corrosive, irritant | Good organic digestion efficiency | Requires lots of time, degradation of some polymers as cellulose acetate and some biodegradable plastics | [16,96,99,101] |
| H2O2 | 20 mL H2O2 at 30% plus 20 mL of FeSO4 * 7H2O (0.05 M) at 70 °C in stirring | $27.67 for 1 L | Corrosive, harmful | Efficient in organic digestion | At high concentrations could degrade the polymers | [10,16,104,108] |
| Cellulase, lipase, chitinase, protease, proteinase-K | 5 mL of Protease A-01 + 25 mL of Tris-HCl buffer, 1 mL of Lipase FE-01 + 25 mL of Tris-HCl buffer; 5 mL of Amylase TXL + 25 mL of NaOAc buffer, 1 mL of Cellulase TXL + 25 mL of NaOAc buffer; 1 mL of Chitinase + 25 mL of NaOAc buffer | Protease A-01 1 kg $48.34; Lipase FE-01 1 kg $48.34; Amylase TXL 1 Kg $36.50; Cellulase TXL 1 kg $43.95 | No danger | Good inorganic and biological material digestion; does not affect the polymers | Expensive, requires lots of time | [15,16,96,97] |
| Abbreviation | Polymer | Density (g/cm−3) |
|---|---|---|
| PS | Polystyrene | 0.01–1.06 |
| PP | Polypropylene | 0.85–0.92 |
| LDPE | Low-density polyethylene | 0.89–0.93 |
| HPDE | High-density polyethylene | 0.94–0.98 |
| Freshwater | 1.00 | |
| Seawater | 1.025 | |
| PA, PA 6,6 | Polyamide, Nylon 6,6 | 1.12–1.15 |
| PC | Polycarbonate | 1.20–1.22 |
| PU | Polyurethane | 1.20–1.26 |
| PET | Polyethene terephthalate | 1.38–1.41 |
| PVC | Polyvinyl chloride | 1.38–1.41 |
| PTFE | Polytetrafluoroethylene | 2.10–2.30 |
| Chemical Formula | Reagent Name | Water Solubility (g/L) | Density (g/cm−3) | Toxicity | Costs | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaCl | Sodium chloride | 358 at 20 °C | 1.0–1.2 | Low | $34.64 for 1 kg | [104,109,110,111,112,113] |
| Na2WO4 · 2H2O | Sodium tungstate dihydrate | 742 at 25 °C | 1.40 | Low | $224.92 for 500 g | [109,112] |
| NaBr | Sodium bromide | 905 at 20 °C | 1.37–1.40 | Low | $118.51 for 1 kg | [23,77,109] |
| 3Na2WO4·9WO3·H2O | Sodium polytungstate | 3100 at 20 °C | 1.40 | Low | $235.27 for 100 g | [109,113] |
| ZnCl2 | Zinc chloride | 4320 at 20 °C | 1.6–1.8 | High | $143.34 for 1 kg | [16,104,108,109,114] |
| ZnBr2 | Zinc bromide | 4470 at 20 °C | 1.71 | High | $166 for 500 g | [23,77,109] |
| NaI | Sodium iodide | 1793 at 20 °C | 1.80 | High | $159.46 for 500 g | [16,109,114,115] |
| Methodology | Advantages | Disadvantages | Lower Size Limit | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fourier transform infrared coupled to microscopy (μ-FTIR) | Easy to use Many particles can be analysed simultaneously Automatisation available Short time of analysis for single particles Evaluation of size and shape Detecting the intensity of oxidation Report particles with shape and size information Transmission and reflection mode Nondestructive Less expensive than Raman and thermoanalytical techniques | Difficulty in characterising black particles Long time of analysis to measure multiple particles Measures huge areas without particles Detectors have to be cooled with liquid nitrogen The analysis requires expert personnel Huge data sets (several GB per filter) No total mass determination Expensive | ~10–20 μm | [10,123,126,127,134,135,136,137] |
| Raman spectroscopy | Evaluation of size and shape Many particles can be analysed simultaneously Automatisation available Detecting the intensity of oxidation Staining possible Thermoelectrically cooled (TEC) detectors obviate the necessity for liquid nitrogen cooling Report particles with shape and size information Nondestructive Filter contributions can be subtracted out It is possible to detect additives, pigments, and plasticisers | More time-consuming measurements with respect to FTIR-spectroscopy The analysis requires expert personnel Interference of biological and inorganic contaminants No total mass determination Expensive | ~1 μm | [99,122,126,127,134,138] |
| Pyrolysis–Gas Chromatography–Mass spectrometry (Py–GC–MS) | More holistic approach to characterise, in a single analysis, additives and plasticiser, in addition to polymer category Powerful for mass determination | No particle number information No evaluation of size and shape Particles can be analysed singularly About 40 min of analysis for each particle determination The analysis requires expert personnel Destructive Expensive | ~50/100 μm | [35,122,130,131,139,140,141,142,143] |
| Thermal Extraction Desorption–Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (TED–GC–MS | More holistic approach to characterise, in a single analysis, additives and plasticiser, in addition to polymer category Powerful for mass determination | No particle number information No evaluation of size and shape Particles can be analysed singularly About 40 min of analysis for each particle determination The analysis requires expert personnel Destructive Expensive | ~50/100 μm | [123,139,142,144,145] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campanale, C.; Savino, I.; Pojar, I.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. A Practical Overview of Methodologies for Sampling and Analysis of Microplastics in Riverine Environments. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6755. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12176755
Campanale C, Savino I, Pojar I, Massarelli C, Uricchio VF. A Practical Overview of Methodologies for Sampling and Analysis of Microplastics in Riverine Environments. Sustainability. 2020; 12(17):6755. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12176755
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampanale, Claudia, Ilaria Savino, Iulian Pojar, Carmine Massarelli, and Vito Felice Uricchio. 2020. "A Practical Overview of Methodologies for Sampling and Analysis of Microplastics in Riverine Environments" Sustainability 12, no. 17: 6755. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12176755
APA StyleCampanale, C., Savino, I., Pojar, I., Massarelli, C., & Uricchio, V. F. (2020). A Practical Overview of Methodologies for Sampling and Analysis of Microplastics in Riverine Environments. Sustainability, 12(17), 6755. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12176755







