Impact of Indo-Pacific Climate Variability on Rice Productivity in Bihar, India
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
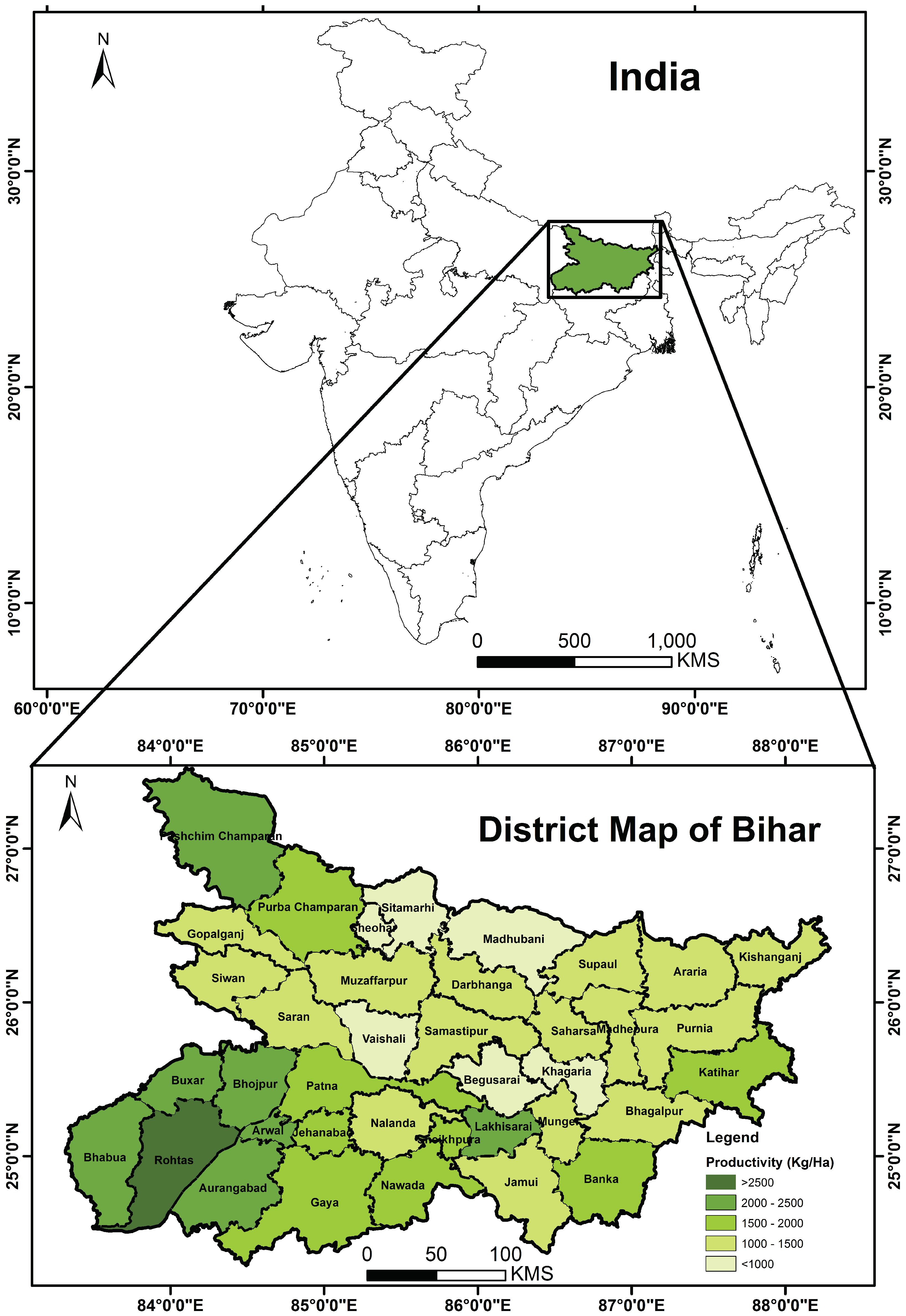
2.1. Study Area
2.2. District Wise Rice Productivity
2.3. Climate Variables/Indices and SST Data
2.4. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Climate Variability and Rice Productivity
3.2. Rainfall and Soil Moisture
3.3. Temperature
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DJF | December-January-February |
| JFM | January-February-March |
| FMA | February-March-April |
| AMJ | August-May-June |
| NDJ | November-December-January |
| MAM | March-April-May |
| MJJ | May-June-July |
| JAS | July-August-September |
| ASO | August-September-October |
| GOSAT | Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite |
| ENSO | El Niño-Southern Oscillation |
| SST | Sea Surface Temperature |
| SOI | Southern Oscillation Index |
| EMI | El Niño Modoki Index |
| DMI | Dipole mode index |
| TNI | Trans Niño Index |
| MI | Monsoon Index |
| IOD | Indian Ocean Dipole |
| PPMC | Pearson’s Product Moment Correlation |
| OLR | Outgoing Longwave Radiation |
| JAMSTEC | Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology |
| CGD | Climate and Global Dynamics Laboratory |
| AU | Tamil Nadu Agricultural University |
| DRDPAT | Directorate of Rice Development Patna |
| ONI | Ocean Niño Index |
| ICAR | Indian Council of Agricultural Research |
| TNIRRI | International Rice Research Institute |
| DES | Directorate of Economics and Statistics |
| WAOB | World Agricultural Outlook Board |
| UNICEF | United Nations Children’s Fund |
| NCAR | National Center for Atmospheric Research |
| GrADS | Grid Analysis and Display System |
References
- Whetton, P.; Rutherfurd, I. Historical ENSO teleconnections in the eastern hemisphere. Clim. Chang. 1994, 28, 221–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R. Impact of El Niño-southern oscillation on Indian foodgrain production. Int. J. Climatol. 2003, 23, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Mayo, Z.A. Impact of temperature and rainfall on rice production in Punjab, Pakistan. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 121, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellner, O.; Niyogi, D. Climate Variability and the U.S. Corn Belt: ENSO and AO Episode-Dependent Hydroclimatic Feedbacks to Corn Production at Regional and Local Scales. Earth Interact. 2015, 19, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; Sahu, N.; Behera, S.; Sayama, T.; Sahu, L.; Avtar, R.; Singh, R.B.; Yamada, M. Impact of Climate Variability on Crop Yield in Kalahandi, Bolangir, and Koraput Districts of Odisha, India. Climate 2019, 7, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, A.K.; Avm, I.; Das, N.N.; Khedun, C.P.; Singh, V.P.; Sivakumar, B.; Hansen, J.W. Anatomy of a local-scale drought: Application of assimilated remote sensing products, crop model, and statistical methods to an agricultural drought study. J. Hydrol. 2015, 526, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagagnan, A.R.; Ouedraogo, I.; Fonta, W.M. Perceived Climate Variability and Farm Level Adaptation in the Central River Region of The Gambia. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashok, K.; Guan, Z.; Saji, N.H.; Yamagata, T. Individual and Combined Influences of ENSO and the Indian Ocean Dipole on the Indian Summer Monsoon. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 3141–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, N.B.S.; Ratnam, J.V.; Silva, R.V.; Parhi, P.; Duan, W.; Takara, K.; Singh, R.B.; Yamagata, T. El Nino Modoki connection to extremely-low streamflow of the Paranaiba River in Brazil. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 2014, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Mandal, M. Examining the impact of regional land use and land cover changes on temperature: The case of Eastern India. Spat. Inf. Res. 2019, 27, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Mandal, M. Impact of land use and land cover changes on temperature trends over India. Land Use Policy 2019, 89, 104238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, W.B.; Seager, R.; Baethgen, W.; Cane, M.; You, L. Synchronous crop failures and climate-forced production variability. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahu, N.; Yamashiki, Y.; Behera, S.; Takara, K.; Yamagata, T. Large Impacts of Indo-Pacific Climate Modes on the Extreme Streamflows of Citarum River in Indonesia. J. Glob. Environ. Eng. 2012, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, N.; Singh, R.B.; Kumar, P.; Silva, R.V.D.; Behera, S.K. La Niña Impacts on Austral Summer Extremely High-Streamflow Events of the Paranaíba River in Brazil. Adv. Meteorol. 2013, 2013, 461693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubilava, D.; Abdolrahimi, M. The El Niño impact on maize yields is amplified in lower income teleconnected countries. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 054008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.G.; Dawe, D.; Falcon, W.P.; Naylor, R.L. El Niño-Southern Oscillation Impacts on Rice Production in Luzon, the Philippines. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 1718–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.K.; Kumar, K.R.; Ashrit, R.G.; Deshpande, N.R.; Hansen, J.W. Climate impacts on Indian agriculture. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 1375–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskandar, I.; Mardiansyah, W.; Lestari, D.O.; Masumoto, Y. What did determine the warming trend in the Indonesian sea? Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2020, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropelewski, C.F.; Jones, P.D. An Extension of the Tahiti-Darwin Southern Oscillation Index. Mon. Weather Rev. 1987, 115, 2161–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Fan, Z. Choice of South Asian Summer Monsoon Indices. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 629–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashok, K.; Behera, S.K.; Rao, S.A.; Weng, H.; Yamagata, T. El Niño Modoki and its possible teleconnection. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K. The Climate Data Guide: Nino SST Indices (Nino 1+2, 3, 3.4, 4; ONI and TNI). In Climate Data Guide; UCAR: Boulder, CO, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Zhu, S.; Huang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Wu, B.; Liu, L. Spatiotemporal variations of drought and their teleconnections with large-scale climate indices over the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, N.; Panda, A.; Nayak, S.; Saini, A.; Mishra, M.; Sayama, T.; Sahu, L.; Duan, W.; Avtar, R.; Behera, S.; et al. Impact of Indo-Pacific Climate Variability on High Streamflow Events in Mahanadi River Basin, India. Water 2020, 12, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, D.A.; Weisberg, R.H. El Niño-Southern Oscillation-related ocean-atmosphere coupling in the western equatorial Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1998, 103, 18635–18648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, T.; Morioka, Y.; Behera, S. Indo-Pacific Climate Variability and Predictability; World Scientific: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.; Yamagata, T. Impacts of IOD, ENSO and ENSO Modoki on the Australian Winter Wheat Yields in Recent Decades. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soora, N.K.; Aggarwal, P.K.; Saxena, R.; Rani, S.; Jain, S.; Chauhan, N. An assessment of regional vulnerability of rice to climate change in India. Clim. Chang. 2013, 118, 683–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Xu, J. Assessing the impacts of temperature variations on rice yield in China. Clim. Chang. 2016, 138, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuecker, M.F.; Tigchelaar, M.; Kantar, M.B. Climate variability impacts on rice production in the Philippines. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koide, N.; Robertson, A.W.; Ines, A.V.; Qian, J.; Dewitt, D.G.; Lucero, A. Prediction of Rice Production in the Philippines Using Seasonal Climate Forecasts. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 552–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Datta, S.K. Principles and Practices of Rice Production; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- TNAU. Water Management; Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Directorate of Extension Education Tamil Nadu Agricultural University Coimbatore—641 003: Coimbatore, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- DRDPAT. Rice—A Status Paper; Directorate of Rice Development; Department of Agriculture & Co-Operation, Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India: Patna, India, 2014.
- IRRI. Rice Almanac: Source Book for One of the Most Economic Activities on Earth; Maclean, J., Dawe, D., Hardy, B., Hettel, G.E., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Los Baños, Philippines, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Asada, H.; Matsumoto, J. Effects of rainfall variation on rice production in the Ganges-Brahmaputra Basin. Clim. Res. 2009, 38, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, W.; He, B.; Sahu, N.; Luo, P.; Nover, D.; Hu, M.; Takara, K. Spatiotemporal variability of Hokkaido’s seasonal precipitation in recent decades and connection to water vapour flux. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 3660–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finance Department. Economic Survey 2015–2016; Finance Department, Government of Bihar: Patna, India, 2016.
- ODCO. Census of India, Provisional Population Totals; Office of the Director of Census Operations: Patna, India, 2011.
- DES. Agricultural Statistics at a Glance; Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Government of India: New Delhi, India, 2011.
- Singh, S.K.; Singh, K.M.; Singh, R.P.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, U. Impact of Rainfall on Agricultural Production in Bihar: A Zone-Wise Analysis. Environ. Ecol. 2014, 32, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar]
- Haris, A.A.; Biswas, S.; Chhabra, V. Climate change impacts on productivity of rice (Oryza sativa) in Bihar. Indian J. Agron. 2014, 55, 295–298. [Google Scholar]
- Tesfaye, K.; Aggarwal, P.; Mequanint, F.; Shirsath, P.; Stirling, C.; Khatri-Chhetri, A.; Rahut, D. Climate Variability and Change in Bihar, India: Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable Crop Production. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.A.; Tahir, A.; Khurshid, N.; ul Husnain, M.I.; Ahmed, M.; Boughanmi, H. Economic effects of climate change-induced loss of agricultural production by 2050: A case study of Pakistan. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ICAR. State-Specific Technological Interventions for Higher Agricultural Growth; Indian Council of Agriculture Research: New Delhi, Indian, 2007.
- WAOB. Major World Crop Areas and Climatic Profiles; World Agricultural Outlook Board, United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1994.
- Naylor, R.; Falcon, W.; Rochberg, D.; Wada, N. Using El Niño/Southern Oscillation Climate Data to Predict Rice Production in Indonesia. Clim. Chang. 2001, 50, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, W.B.; Seager, R.; Baethgen, W.; Cane, M. Crop production variability in North and South America forced by life-cycles of the El Niño Southern Oscillation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 239, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashok, K.; Yamagata, T. The El Niño with a difference. Nature 2009, 461, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DRDPAT. Rice in India—A Handbook of Statistics 2007; Directorate of Rice Development, Department of Agriculture & Co-Operation, Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India: Patna, India, 2007.
- Finance Department. Economic Survey 2013–2014; Finance Department, Government of Bihar: Patna, India, 2014.
- Finance Department. Economic Survey 2014–2015; Finance Department, Government of Bihar: Patna, India, 2015.
- Finance Department. Economic Survey 2016–2017; Finance Department, Government of Bihar: Patna, India, 2017.
- El-Maayar, M.; Lange, M. A Methodology to Infer Crop Yield Response to Climate Variability and Change Using Long-Term Observations. Atmosphere 2013, 4, 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pai, D.S.; Sridhar, L.; Rajeevan, M.; Sreejith, O.P.; Satbhai, N.S.; Mukhopadyay, B. Analysis of the daily rainfall events over India using a new long period (1901–2010) high resolution (0.25° × 0.25°) gridded rainfall data set. MAUSAM 2014, 65, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Rajeevan, M.; Kshirsagar, S.R. Development of a high resolution daily gridded temperature data set (1969–2005) for the Indian region. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2009, 10, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dool, H.V.D.; Huang, J.; Fan, Y. Performance and analysis of the constructed analogue method applied to U.S. soil moisture over 1981–2001. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, R.W.; Smith, T.M.; Liu, C.; Chelton, D.B.; Casey, K.S.; Schlax, M.G. Daily High-Resolution-Blended Analyses for Sea Surface Temperature. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5473–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-Year Reanalysis Project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liebmann, B.; Smith, C.A. Description of a complete (interpolated) outgoing longwave 461 radiation dataset. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 1275–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, A.; S-y, W.; Promchote, P. Examination of the Climate Factors That Reduced Wheat Yield in Northwest India during the 2000s. Water 2019, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Stepaniak, D.P. Indices of El Niño Evolution. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 1697–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashok, K.; Guan, Z.; Yamagata, T. Impact of the Indian Ocean dipole on the relationship between the Indian monsoon rainfall and ENSO. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 4499–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izumo, T.; Vialard, J.; Lengaigne, M.; Montegut, C.D.; Behera, S.K.; Luo, J.; Cravatte, S.; Masson, S.; Yamagata, T. Influence of the state of the Indian Ocean Dipole on the following year’s El Niño. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Cai, W.; Lin, X. Dynamics of changing impacts of tropical Indo-Pacific variability on Indian and Australian rainfall. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, N.H.; Goswami, B.N.; Vinayachandran, P.N.; Yamagata, T. A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean. Nature 1999, 401, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JAMSTEC. SST DMI Dataset (Monthly from 1870 to Present); JAMSTEC: Kanagawa, Japan, 2017.
- Achuthavarier, D.; Krishnamurthy, V.; Kirtman, B.P.; Huang, B. Role of the Indian Ocean in the ENSO-Indian Summer Monsoon Teleconnection in the NCEP Climate Forecast System. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 2490–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E. The Definition of El Niño. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 2771–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobell, D.B.; Hammer, G.L.; Mclean, G.; Messina, C.; Roberts, M.J.; Schlenker, W. The critical role of extreme heat for maize production in the United States. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, N.; Robertson, A.W.; Boer, R.; Behera, S.; DeWitt, D.G.; Takara, K.; Kumar, M.; Singh, R.B. Probabilistic seasonal streamflow forecasts of the Citarum River, Indonesia, based on general circulation models. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2017, 31, 1747–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Non-parametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theil, H. A rank-invariant method of linear and polynomial regression analysis, Part I. Proc. R. Neth. Acad. Arts Sci. 1950, 53, 386–392. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Sahdeo, A.; Guleria, S. Bihar Floods: 2007 (A Field Report); Technical Report; National Institute of Disaster Management, Ministry of Home Affairs: New Delhi, India, 2013.
- Auffhammer, M.; Ramanathan, V.; Vincent, J.R. Climate change, the monsoon, and rice yield in India. Clim. Chang. 2011, 111, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Zhang, T.; de Bruin, K.; Glomrød, S.; Shi, Q. Extreme weather impacts on maize yield: The case of Shanxi Province in China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, A.; Vu, T.; Veettil, A.V.; EntekhabI, D. Drought monitoring with soil moisture active passive (SMAP) measurement. J. Hydrol. 2017, 552, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finance Department. Economic Survey 2010–2011; Finance Department, Government of Bihar: Patna, India, 2011.
- Bhatnagar, M.K.; Faruqi, A.A.; Singh, U.P.; Sharma, S.C.; Khurana, S.; Khanna, D.; Chand, G. (Eds.) Annual Report 2010; India Meteorological Department: New Delhi, India, 2011.
- Thakur, A.K.; Kassam, A.; Stoop, W.A.; Uphoff, N. Modifying rice crop management to ease water constraints with increased productivity, environmental benefits, and climate-resilience. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 235, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pray, C.; Nagarajan, L.; Li, L.; Huang, J.; Hu, R.; Selvaraj, K.N.; Napasintuwong, O.; Chandra Babu, R. Potential impact of biotechnology on adaption of agriculture to climate change: The case of drought tolerant rice breeding in Asia. Sustainability 2011, 3, 1723–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, W.; Zou, S.; Chen, Y.; Nover, D.; Fang, G.; Wang, Y. Sustainable water management for cross-border resources: The Balkhash Lake Basin of Central Asia, 1931–2015. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avtar, R.; Singh, C.K.; Shashtri, S.; Mukherjee, S. Identification of erosional and inundation hazard zones in Ken-Betwa river linking area, India, using remote sensing and GIS. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 182, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avtar, R.; Kumar, P.; Oono, A.; Saraswat, C.; Dorji, S.; Hlaing, Z. Potential application of remote sensing in monitoring ecosystem services of forests, mangroves and urban areas. Geocarto Int. 2016, 32, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, N.; Saini, A.; Behera, S.K.; Sayama, T.; Sahu, L.; Nguyen, V.T.V.; Takara, K. Why apple orchards are shifting to the higher altitudes of the Himalayas? PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saseendran, S.A.; Singh, K.K.; Rathore, L.S.; Singh, S.V.; Sinha, S.K. Effects of Climate Change on Rice Production in the Tropical Humid Climate of Kerala, India. Clim. Chang. 2000, 44, 494–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.G.; Watanabe, S.; Nakata, M.; Takemura, T. Response of the atmospheric hydrological cycle over the tropical Asian monsoon regions to anthropogenic aerosols and its seasonality. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2018, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.G.; Annamalai, H. Climate change and the South Asian summer monsoon. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Year | Anomalous Percentage Deviated | Climatic Phase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ONI | NIÑO 3 | SOI | ||
| 1991–1992 | −12.05 | MJJ(1991)-JAS(1991)+ve | - | MAM(1991)-JJA(1991)-ve |
| 1992–1993 | −29.76 | ASO(1991)-JAS(1992)+ve | NDJ(1991)-AMJ(1992)+ve | MAM(1992)-JJA(1992)-ve |
| 2004–2005 | −35.3 | JJA(2004)-JAS(2004)+ve | - | MAM(2004)-JJA(2004)-ve |
| 2005–2006 | −10.03 | ASO(2005)-JAS(2005)+ve | NDJ(2004)-DJF(2005)+ve | MAM(2005)-JJA(2005)-ve |
| 2009–2010 | −23.51 | JJA(2009)-JAS(2009)+ve | - | MAM(2009)-JJA(2009)-ve |
| After Effects of Flood Occurrence in 2008 | ||||
| 2010–2011 | −38.52 | JJA(2010)-JAS(2010)+ve | NDJ(2009)-FMA(2010)+ve | - |
| Variable | z Value | Sen’s Slope | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfall | −1.611 | −1.954 | 0.107 |
| Temperature (Max.) | 3.48 | 0.04 | 0.0005 |
| Temperature (Mean) | 4.087 | 0.035 | 0.00004 |
| Temperature (Min.) | 3.34 | 0.035 | 0.00084 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sahu, N.; Saini, A.; Behera, S.; Sayama, T.; Nayak, S.; Sahu, L.; Duan, W.; Avtar, R.; Yamada, M.; Singh, R.B.; et al. Impact of Indo-Pacific Climate Variability on Rice Productivity in Bihar, India. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7023. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177023
Sahu N, Saini A, Behera S, Sayama T, Nayak S, Sahu L, Duan W, Avtar R, Yamada M, Singh RB, et al. Impact of Indo-Pacific Climate Variability on Rice Productivity in Bihar, India. Sustainability. 2020; 12(17):7023. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177023
Chicago/Turabian StyleSahu, Netrananda, Atul Saini, Swadhin Behera, Takahiro Sayama, Sridhara Nayak, Limonlisa Sahu, Weili Duan, Ram Avtar, Masafumi Yamada, R. B. Singh, and et al. 2020. "Impact of Indo-Pacific Climate Variability on Rice Productivity in Bihar, India" Sustainability 12, no. 17: 7023. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177023
APA StyleSahu, N., Saini, A., Behera, S., Sayama, T., Nayak, S., Sahu, L., Duan, W., Avtar, R., Yamada, M., Singh, R. B., & Takara, K. (2020). Impact of Indo-Pacific Climate Variability on Rice Productivity in Bihar, India. Sustainability, 12(17), 7023. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177023










