A Scientometric Review of System Dynamics Applications in Construction Management Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Co-Authorship Analysis
3.2. Published Journals Analysis
3.3. Co-occurring Keywords Analysis
3.4. Article Citations Analysis
3.5. Regions Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Current Research Topics
4.2. Future Research Directions
4.2.1. Risk Management Research
4.2.2. Waste Management Research
4.2.3. Energy Management Research
4.2.4. Construction Productivity Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, L.; He, Q.; Jaselskis, E.J.; Xie, J. Construction Project Complexity: Research Trends and Implications. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2017, 143, 04017019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorvatn, T.; Wald, A. Project complexity and team-level absorptive capacity as drivers of project management performance. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2018, 36, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, R. Dynamic Simulation Model for Project Change-Management Policies: Engineering Project Case. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2019, 145, 05019008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papachristos, G.; Jain, N.; Burman, E.; Zimmermann, N.; Mumovic, D.; Davies, M.; Edkins, A. Low carbon building performance in the construction industry: A multi-method approach of project management operations and building energy use applied in a UK public office building. Energy Build. 2020, 206, 109609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Chini, A.R.; Lu, Y.; Shen, L. A dynamic model for assessing the effects of management strategies on the reduction of construction and demolition waste. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, H.; Cao, D. Dynamics of Collaborative Networks between Contractors and Subcontractors in the Construction Industry: Evidence from National Quality Award Projects in China. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2018, 144, 05018009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. Applying system dynamics to strategic decision making in construction. Front. Eng. Manag. 2017, 4, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, K.B.; Formoso, C.T. Requirements in performance measurement systems of construction projects from the lean production perspective. Front. Eng. Manag. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Le, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xia, B.; Skitmore, M.; Gao, X. System Dynamics Modeling for Construction Management Research: Critical Review and Future Trends. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2019, 25, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, P.E.; Mandal, P.; Li, H. Determining the causal structure of rework influences in construction. Constr. Manag. Econ. 1999, 17, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Lee, S.; Peña-Mora, F. Identification and Quantification of Non-Value-Adding Effort from Errors and Changes in Design and Construction Projects. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2012, 138, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Park, M.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, S. Hybrid Simulation Framework for Immediate Facility Restoration Planning after a Catastrophic Disaster. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2016, 142, 4016026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhatre, T.N.; Thakkar, J.J.; Maiti, J.; Van Der Wiele, T. Modelling critical risk factors for Indian construction project using interpretive ranking process (IRP) and system dynamics (SD). Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2017, 34, 1451–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Ng, S.T.; Skitmore, M. Influence of procurement systems to the success of sustainable buildings. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 1007–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yuan, H.; Wang, G.; Li, S.; Wu, G. Impacts of Lean Construction on Safety Systems: A System Dynamics Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zou, P.X. System dynamics analytical modeling approach for construction project management research: A critical review and future directions. Front. Eng. Manag. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, P.; Al-Hussein, M.; Ahmad, R. A scientometric analysis and critical review of computer vision applications for construction. Autom. Constr. 2019, 107, 102947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuni, I.Y.; Shen, G.Q.; Osei-Kyei, R. Scientometric review of global research trends on green buildings in construction journals from 1992 to 2018. Energy Build. 2019, 190, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Tang, Z.-Y.; Zou, X. Mapping the Knowledge Domain of Smart-City Research: A Bibliometric and Scientometric Analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadegani, A.A.; Salehi, H.; Yunus, M.M.; Farhadi, H.; Fooladi, M.; Farhadi, M.; Ebrahim, N.A. A Comparison between Two Main Academic Literature Collections: Web of Science and Scopus Databases. Asian Soc. Sci. 2013, 9, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Le, Y.; Chan, A.P.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y. Review of the application of social network analysis (SNA) in construction project management research. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2016, 34, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Li, J.; Jin, R.; Ke, Y. A Holistic Review of Public-Private Partnership Literature Published between 2008 and 2018. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, C.; Cai, Y.; Lu, C.; Wang, H.; Yu, T. BIM-Based Visualization Research in the Construction Industry: A Network Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Nagy, Z. Comprehensive analysis of the relationship between thermal comfort and building control research—A data-driven literature review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2664–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X. A scientometric review of global BIM research: Analysis and visualization. Autom. Constr. 2017, 80, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.; Hu, W.; Dong, J.; Sun, B.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z. A Systematic Literature Review of Green and Sustainable Logistics: Bibliometric Analysis, Research Trend and Knowledge Taxonomy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Gao, S.; Cheshmehzangi, A.; Aboagye-Nimo, E. A holistic review of off-site construction literature published between 2008 and 2018. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 1202–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.R.; Martek, I.; Zavadskas, E.; Aibinu, A.A.; Arashpour, M.; Chileshe, N. Critical evaluation of off-site construction research: A Scientometric analysis. Autom. Constr. 2018, 87, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, B. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management and Construction Management: A Journal and a Profession Grow Together. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2017, 143, 02517004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Du, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Mao, G.; Zuo, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Huisingh, D. A review of the first twenty-three years of articles published in the Journal of Cleaner Production: With a focus on trends, themes, collaboration networks, low/no-fossil carbon transformations and the future. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 163, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.-N.; Lee, P.-C. Mapping knowledge structure by keyword co-occurrence: A first look at journal papers in Technology Foresight. Scientometrics 2010, 85, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, M.; Azab, S. Environmental and economic impact assessment of construction and demolition waste disposal using system dynamics. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 82, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Shen, L.; Hao, J.J.; Lu, W. A model for cost–benefit analysis of construction and demolition waste management throughout the waste chain. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Shen, L.; Skitmore, M.; Skitmore, M. A prototype system dynamic model for assessing the sustainability of construction projects. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2014, 32, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Wang, J. A system dynamics model for determining the waste disposal charging fee in construction. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 237, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H. A model for evaluating the social performance of construction waste management. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirzadeh, F.; Khanzadi, M.; Rezaie, M. Dynamic modeling of the quantitative risk allocation in construction projects. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2014, 32, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, Y.M.; Ali, M.J.A. A hybrid simulation approach for integrating safety behavior into construction planning: An earthmoving case study. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2016, 93, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, G.; Huang, Y.; Deng, L. Research on Investment Risk Management of Chinese Prefabricated Construction Projects Based on a System Dynamics Model. Buildings 2017, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasad, R.; Motawa, I. Dynamic demand risk assessment for toll road projects. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2015, 33, 799–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Li, C.Z.; Huang, W.; Xia, N. Schedule risk analysis of infrastructure projects: A hybrid dynamic approach. Autom. Constr. 2018, 95, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ding, L.; Love, P.E.; Edwards, D.J. Modeling tunnel construction risk dynamics: Addressing the production versus protection problem. Saf. Sci. 2016, 87, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yu, A.T.; Poon, C.S. An off-site snapshot methodology for estimating building construction waste composition—A case study of Hong Kong. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2019, 77, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shen, Q.; Alshawi, M. Measuring the impact of prefabrication on construction waste reduction: An empirical study in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 91, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Li, Z.; Tam, V.W. Identifying best design strategies for construction waste minimization. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 92, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yu, A.T.; Shen, L. Investigating the determinants of contractor’s construction and demolition waste management behavior in Mainland China. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, L.S.; Ahn, S.; Kim, T.W. System Dynamic Analysis of Impacts of Government Charges on Disposal of Construction and Demolition Waste: A Hong Kong Case Study. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ren, H.; Rotter, V.S. A system dynamics model for evaluating the alternative of type in construction and demolition waste recycling center—The case of Chongqing, China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Teng, Y.; Wang, D.; Gong, E. System dynamic analysis of construction waste recycling industry chain in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristino, T.M.; Neto, A.F.; Costa, A.F.B. Energy efficiency in buildings: Analysis of scientific literature and identification of data analysis techniques from a bibliometric study. Scientometrics 2018, 114, 1275–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, K.V.; Michael, L.K.; Mathew, A.O.; Nair, I.; Shaikh, T. Building energy efficiency using system dynamics approach—A case study in an academic block. Int.J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, A.; Al-Ghamdi, S.; Koç, M. Role of energy efficiency policies on energy consumption and CO2 emissions for building stock in Qatar. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 1409–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Chowdhury, M.; Issa, R.R.; Shi, W. Simulation of Dynamic Energy Consumption in Modular Construction Manufacturing Processes. J. Arch. Eng. 2018, 24, 04017034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebotareva, G.; Strielkowski, W.; Streimikiene, D. Risk assessment in renewable energy projects: A case of Russia. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunathilake, H.; Hewage, K.; Prabatha, T.; Ruparathna, R.; Sadiq, R. Project deployment strategies for community renewable energy: A dynamic multi-period planning approach. Renew. Energy 2020, 152, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzadi, M.; Kaveh, A.; Alipour, M.; Khanmohammadi, R. Assessment of labor productivity in construction projects using system dynamic approach. Sci. Iran. 2017, 24, 2684–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirzadeh, F.; Nojedehi, P. Dynamic modeling of labor productivity in construction projects. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2013, 31, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, M.P.; Shoar, S. A hybrid framework to model factors affecting construction labour productivity: Case study of Iran. J. Financ. Manag. Prop. Constr. 2019, 24, 630–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kofahi, Z.G.; Mahdavian, A.; Oloufa, A. System dynamics modeling approach to quantify change orders impact on labor productivity 1: Principles and model development comparative study. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seresht, N.G.; Fayek, A.R. Dynamic Modeling of Multifactor Construction Productivity for Equipment-Intensive Activities. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2018, 144, 04018091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, R.; Berg, S. Risks, Contracts, and Private-Sector Participation in Infrastructure. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2011, 137, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narbaev, T.; De Marco, A.; Orazalin, N. A multi-disciplinary meta-review of the public–private partnerships research. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2020, 38, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, C.; Udawatta, N. Optimizing the concession period of PPP projects for fair allocation of financial risk. Eng. Constr. Arch. Manag. 2019, 26, 2347–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Cheng, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z. Environmental Cost-Benefit Analysis of Prefabricated Public Housing in Beijing. Sustainability 2019, 11, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Z.; Shen, Q.; Xu, X.; Xue, F.; Sommer, L.; Luo, L. Schedule risk modeling in prefabrication housing production. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 153, 692–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, F.; Shao, Y.F.; Junaid, D.; Hanif, M.S. Cost-risk contingency framework for managing cost overrun in metropolitan projects: Using fuzzy-AHP and simulation. Int. J. Manag. Proj. Bus. 2020, 13, 1121–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-L.; Scorpio, D.E.; Kibert, C.J. Strategies for successful construction and demolition waste recycling operations. Constr. Manag. Econ. 1997, 15, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogaard, L.K.-S.; Riber, C.; Christensen, T.H. Quantifying capital goods for waste incineration. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xia, J.; Thompson, J.R.; Flower, R. Urban construction and demolition waste and landfill failure in Shenzhen, China. Waste Manag. 2017, 63, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinade, O.O.; Oyedele, L.O.; Ajayi, S.O.; Bilal, M.; Alaka, H.A.; Owolabi, H.A.; Bello, S.A.; Jaiyeoba, B.E.; Kadiri, K.O. Design for Deconstruction (DfD): Critical success factors for diverting end-of-life waste from landfills. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; Yan, G.; Shen, A.; Zheng, J. Dynamic simulation analysis of a construction and demolition waste management model under penalty and subsidy mechanisms. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 147, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, A.O. Smart road infrastructures that self-generate energy. Carreteras 2014, 4, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Ballarini, I.; Corgnati, S.P.; Corrado, V. Use of reference buildings to assess the energy saving potentials of the residential building stock: The experience of TABULA project. Energy Policy 2014, 68, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbazi, M.; Aktas, C.B. Energy efficiency of residential buildings in the U.S.: Improvement potential beyond IECC. Build. Environ. 2018, 142, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Kou, C.; Wang, H. Estimating city-level energy consumption of residential buildings: A life-cycle dynamic simulation model. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 240, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Xu, T.; Shen, P. Energy and behavioral impacts of integrative retrofits for residential buildings: What is at stake for building energy policy reforms in northern China? Energy Policy 2013, 52, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Oyedele, L.O.; Qadir, J.; Munir, K.; Ajayi, S.O.; Akinade, O.O.; Owolabi, H.A.; Alaka, H.A.; Pasha, M. Big Data in the construction industry: A review of present status, opportunities, and future trends. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2016, 30, 500–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porwal, A.; Hewage, K. Building Information Modeling (BIM) partnering framework for public construction projects. Autom. Constr. 2013, 31, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, R.; Perlman, A.; Barak, R. Construction safety training using immersive virtual reality. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2013, 31, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, A.S.; Camlic, R.; Peterson, P.A.; Nordheim, E.V. Quantitative Definition of Projects Impacted by Change Orders. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2002, 128, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingirige, B. Theorizing construction industry practice within a disaster risk reduction setting: Is it a panacea or an illusion? Constr. Manag. Econ. 2016, 34, 592–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
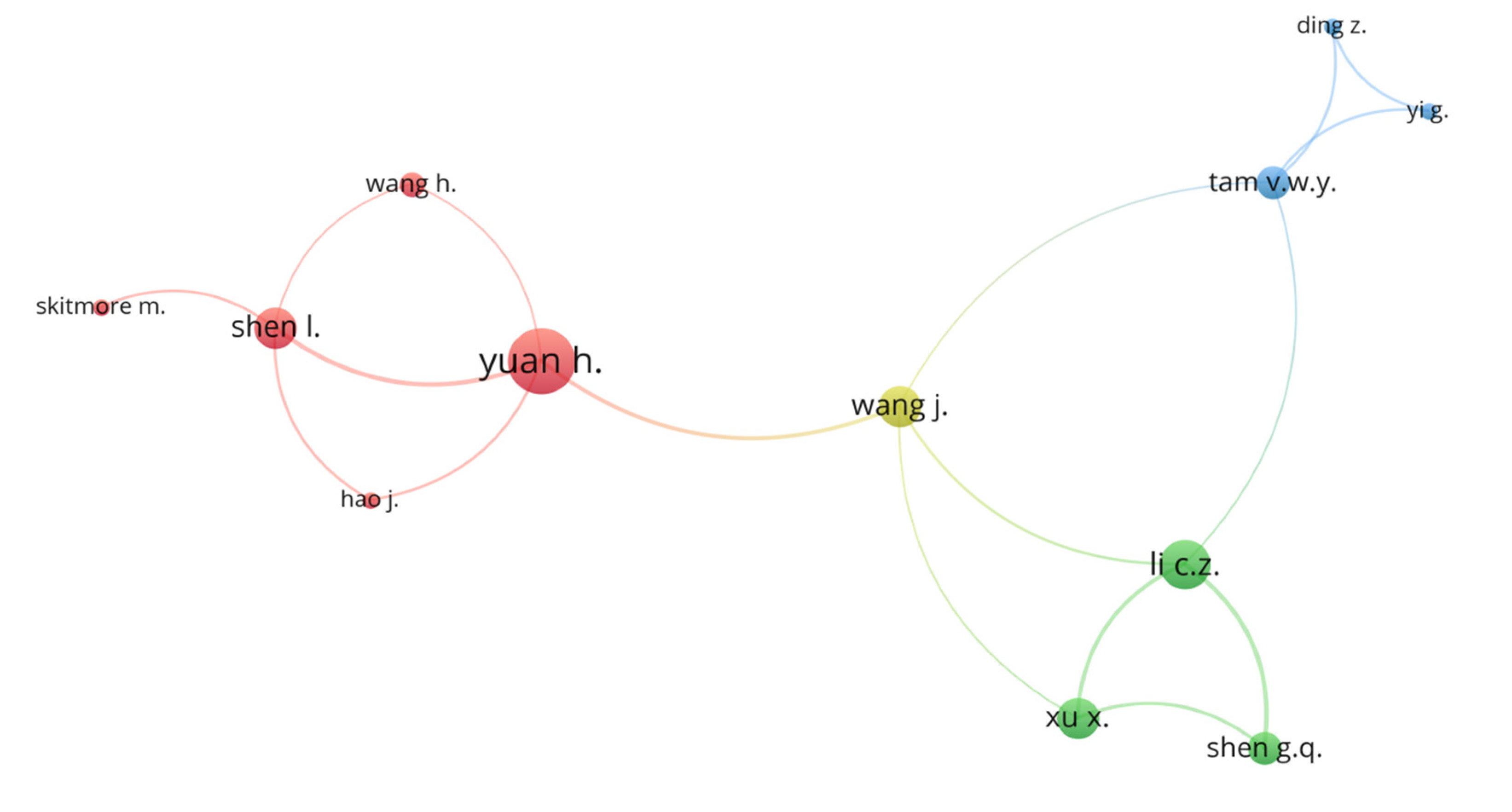





| Scholar | Affiliation | Documents | Citations | Avg. Pub. Year | Avg. Citations | Avg. Norm. Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shen L. | Chongqing University | 5 | 335 | 2012 | 67 | 2.31 |
| Yuan H. | Guangzhou University | 8 | 331 | 2014 | 41 | 2.36 |
| Tam V.W.Y. | University of Western Sydney | 4 | 143 | 2017 | 36 | 4.68 |
| Wang J. | Shenzhen University | 5 | 128 | 2016 | 26 | 1.89 |
| Li C.Z. | Shenzhen University | 6 | 150 | 2017 | 25 | 2.50 |
| Shen G.Q. | Hong Kong Polytechnic University | 4 | 93 | 2017 | 23 | 2.32 |
| Xu X. | Swinburne University of Technology | 5 | 44 | 2018 | 9 | 1.77 |
| Full Name of Journal Sources | Acronym | Documents | Citations | Avg. Citations | Avg. Norm. Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waste Management | WM | 3 | 192 | 64 | 3.68 |
| Resources, Conservation and Recycling | RCR | 5 | 316 | 63 | 1.99 |
| Accident Analysis and Prevention | AAP | 4 | 221 | 55 | 2.59 |
| International Journal of Project Management | IJPM | 4 | 182 | 46 | 2.25 |
| Mathematical and Computer Modelling | MCM | 3 | 61 | 20 | 1.58 |
| Journal of Construction Engineering and Management | JCEM | 13 | 189 | 15 | 1.23 |
| Journal of Management in Engineering | JME | 5 | 72 | 14 | 1.66 |
| Journal of Cleaner Production | JCP | 19 | 231 | 12 | 2.68 |
| Keywords | Occurrences | Avg. Pub. Year | Avg. Citations | Avg. Norm. Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Construction Waste | 27 | 2016 | 28 | 1.95 |
| Construction Safety | 8 | 2016 | 24 | 1.75 |
| Sustainability | 8 | 2016 | 9 | 1.06 |
| Productivity | 7 | 2017 | 9 | 1.04 |
| Energy Efficiency | 4 | 2018 | 5 | 1.57 |
| Policy | 4 | 2016 | 5 | 0.37 |
| Risk Management | 4 | 2016 | 2 | 0.21 |
| Critical Success Factors | 3 | 2018 | 7 | 2.15 |
| Carbon Emission | 3 | 2016 | 7 | 0.6 |
| Article | Title | Citations | Norm. Citations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yuan, Chini, Lu and Shen [5] | A dynamic model for assessing the effects of management strategies on the reduction of construction and demolition waste | 83 | 3.70 |
| Marzouk and Azab [33] | Environmental and economic impact assessment of construction and demolition waste disposal using system dynamics | 83 | 2.77 |
| Yuan et al. [34] | A model for cost-benefit analysis of construction and demolition waste management throughout the waste chain | 83 | 2.26 |
| Zhang et al. [35] | A prototype system dynamic model for assessing the sustainability of construction projects | 76 | 2.54 |
| Yuan and Wang [36] | A system dynamics model for determining the waste disposal charging fee in construction | 63 | 2.11 |
| Yuan [37] | A model for evaluating the social performance of construction waste management | 60 | 2.67 |
| Region | Documents | Citations | Avg. Pub. Year | Avg. Citations | Avg. Norm. Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 71 | 825 | 2016 | 12 | 1.27 |
| United States | 39 | 545 | 2016 | 14 | 1.01 |
| Australia | 30 | 469 | 2016 | 16 | 1.73 |
| Iran | 24 | 176 | 2017 | 7 | 0.76 |
| Hong Kong | 20 | 534 | 2015 | 27 | 1.95 |
| South Korea | 18 | 259 | 2016 | 14 | 0.90 |
| United Kingdom | 16 | 195 | 2015 | 12 | 0.88 |
| Canada | 15 | 341 | 2015 | 23 | 0.87 |
| Germany | 2 | 67 | 2015 | 34 | 1.09 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; Yang, K.; Lai, X.; Antwi-Afari, M.F. A Scientometric Review of System Dynamics Applications in Construction Management Research. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7474. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187474
Wu Z, Yang K, Lai X, Antwi-Afari MF. A Scientometric Review of System Dynamics Applications in Construction Management Research. Sustainability. 2020; 12(18):7474. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187474
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zezhou, Kaijie Yang, Xiaofan Lai, and Maxwell Fordjour Antwi-Afari. 2020. "A Scientometric Review of System Dynamics Applications in Construction Management Research" Sustainability 12, no. 18: 7474. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187474
APA StyleWu, Z., Yang, K., Lai, X., & Antwi-Afari, M. F. (2020). A Scientometric Review of System Dynamics Applications in Construction Management Research. Sustainability, 12(18), 7474. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187474







