Abstract
China’s environmental regulation regime remains mainly government-oriented, consisting of the government environmental investment policy and the command–control policy. This paper first improves the traditional environment Copeland-Taylor model by including the above two types of government-oriented environment instruments. Then, based on a comprehensive firm-level dataset, we examine the effects of government-oriented environmental instruments on firms’ water pollutant emission abatement in the Yangtze River Economic zone. We find robust evidence of a significant decrease of 2.99% in chemical Oxygen Demand(COD) discharge and of 3.55% in ammonia nitrogen(NH3) discharge of firms in response to the government environmental investment policy, whereas the command–control instrument shows little effect on firms’ water pollutant emission reduction. Our results are robust when using alternative measurements for two types of environmental instruments. Additionally, we also find there exist heterogeneous effects across sub-samples: (1)comparing with large and medium firms, small and micro firms are more liable to be influenced by the two types of government-oriented environmental instruments; (2) the effect of two types of government-oriented environmental instruments is obviously significant in the intensive-water-pollution industry, whereas it is not obvious in clean industry; (3) the effect of government environmental investment is obvious on state-owned enterprises and domestic joint ventures, whereas the command–control policy has effectively reduced the water pollutant discharge for domestic joint ventures and private firms. Finally, this study also presents some future policy implications.
1. Introduction
Water environment management remains an important global public policy issue. With the acceleration of industrialization, China’s water quality has been deteriorated to one of the world’s worst. In recent years, the Chinese government has taken more stringent water environmental regulations to change this situation. This paper aims to explore the effect of China’s water management practice and offer some possible experience to other countries using the Yangtze River Economic Zone as a study area.
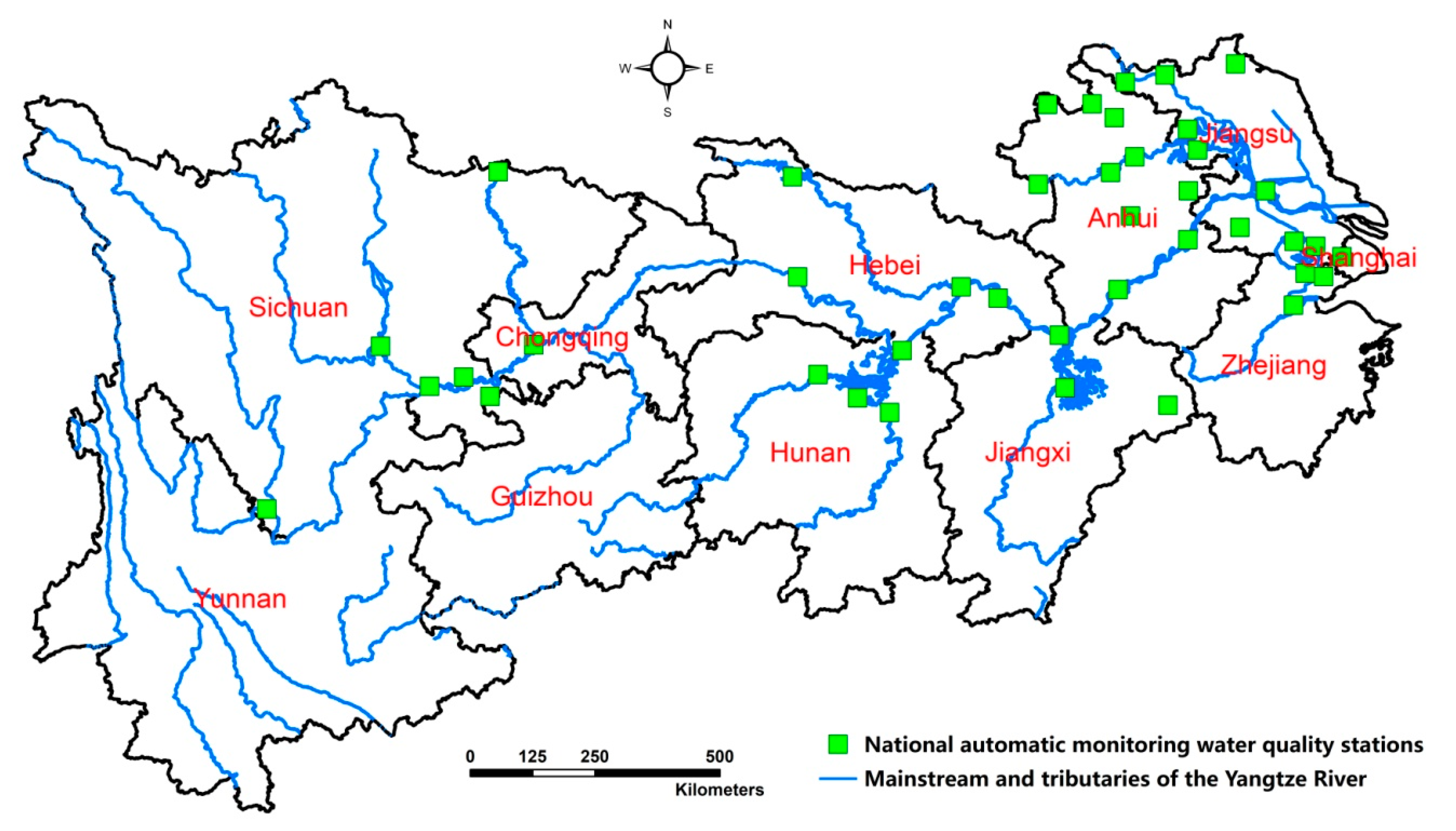
As the largest industrial base in China, the Yangtze River Economic Zone accounts for 43% of the total wastewater discharge and more than half of the total Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) discharge [1]. Meanwhile, as a most popular densely area in the world, the Yangtze River provides water for 500 million people. Thus, the water safety problem is very important in this area. Figure 1 shows the mainstream and tributaries of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Although China has kept reforming its environmental regulation regime from a government-oriented setting to a market-oriented setting, its current environmental regulation regime still remains one fold, dominated by non-market instruments, mainly including two types, command–control instrument and government environmental investment instrument. In contrast, the typical market-oriented environmental policies of pollution discharge fees and environmental protection tax are quite rare and immature. Until 2003, pollutant discharge fees have been collected nationally, and the mean sewage collection standards are only 0.7 RMB Yuan (0.1 USD) per Pollutant Equivalent discharge (per unit of pollution) according to the Administrative Regulations on Levy and Use of Pollutant Discharge Fee [2], which is only equivalent to half of the pollutant abatement cost [3]. In 2018, the Environmental Protection Tax Law took effect, under which the pollutant discharge fees are replaced by the environmental protection tax to address the issue of ineffective enforcement in levying pollution discharge fees. The tax rate for water pollutants is between 1.4 and 14 RMB Yuan (about US$0.202–US$2.202) and varies across provinces. In sharp contrast, government-oriented environmental instruments have played a dominant role in the past decades. Various kinds of command–control instruments, such as discharge standards, environmental-related laws, national automatic water quality monitoring stations (see Figure 1), regulations and policies of local government and central government have been published and enforced year after year to prevent water pollution. In addition, vast government financial funds have been allocated in establishing pollution treatment equipment, such as building sewage pollution treatment plants, building new or upgrading sewage pipe network systems, building new facilities for pollution control of livestock and poultry farms. In 2017, government environmental investment reached 953.9 billion RMB Yuan (136.27 billion USD) with an average growth rate of 12.68% from 2006 to 2017 [4].Thus, an interesting question has been posed: can China’s government-oriented environmental regulation reduce water pollution?
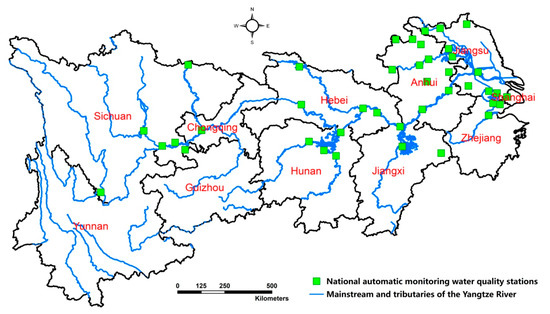
Figure 1.
The main stream and tributaries of the Yangtze River Economic Belt.
The effect of environmental regulation on water pollution reduction has been widely debated in previous literature [3,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. Most of the studies focus on developed countries. Sigman, List, and Keisere evaluated the effect of the Clean Water Act (CWA) in the United States [12,13,14,15,16]. The consensus has been reached that the CWA has substantially reduced the water pollution concentrations in the U.S., but giving different explanations. Sigman and List hold that, as a decentralized water environment policy reform, the CWA is effective for water quality improvement for the following three reasons: first, it has improved the management efficiency through transforming a centralized standard setting to a decentralized one; second, it is easier for state governments to obtain more information than the federal government and can respond quickly to emergencies; third, state governments can implement specific policies based on their own social economic situation. Therefore, it is more likely to achieve Pareto optimality under a decentralized environmental setting [12,13,14,15,16]. However, Sigman also pointed out that a decentralized environmental policy like CWA might bring out “a race to the bottom” in environmental protection, states having a free ride or being unable to realize economies of scale in water pollution control. According to his study, the externalities brought out by the CWA at the downstream area reached $17 million [14].Using water pollution data from 240,000 monitoring sites of all U.S. rivers, Keiser and Shapiro found that the CWA’s grants to municipal wastewater treatment plants contribute most to clean river water in U.S. [12].Unlike the CWA,-a decentralization regulation, the Water Framework Directive (WFD) in the EU has been considered as a centralization regulation. Deng et al. appraised the regulatory, administrative, monitoring, and public participation of the WFD and proposed what China can learn from it when moving towards institutional integration [17].
A few empirical papers evaluate the effect of water environmental regulation in developing countries. In India, Greenstone and Hanna prove that the decentralized water environment setting, the National River Conservation Plan, is almost completely ineffective because of a lack of environmental protection funds, a weak environmental institutional background, and difficulty in regional or department cooperation [9]. Although Brazil’s decentralized water management reform has somewhat reduced water pollution, it has also brought out a serious problem of free riding [17,18].
With China accelerating its water environment regulation reform, the research on the effect of various water environment management policies in China is also booming. The water environment regulations, such as water pollution reduction mandates implemented by the central government in the “Eleventh Five-Year Plan”, the “Twelfth Five-Year Plan”, and the River Chief Policy (RCP), a local government water quality management reform policy, have been discussed in many studies. Using the triple difference-in-difference method (DDD) and industry-level data along 24 major rivers in China from 1998 to 2008, Cai et al. study how the water pollution reduction mandates in 2001 triggered free riding among counties. The results reveal that the environmental regulation stringency is more lenient in downstream counties than in other counties, which causes the water polluting activities in downstream counties of a province to be 20% higher than in other counties [11]. Chen et al. also accumulate evidence that spatially differentiated water pollution regulation stringency will transfer pollution activities from the down reaches of the Yangtze River where regulations are more stringent to the middle and the upper reaches where regulations are less stringent [1].Using weekly or annual water pollution national monitoring data, some literature studies evaluate the policy effect of the RCP. No consensus has been reached on whether the RCP is effective on water pollution reduction [19,20,21]. The effect of the RCP depends on pollutants measured, river basin, and even the water pollution data used. When using provincial and national monitoring data, the contradictory results will be obtained [21]. In addition, the effect of the RCP depends on the length of time. After the implementation, a rapid and obvious effect can be seen on point-source water pollution, but the effect of the RCP levels off after several years of implementation [20].
This study is closely related to the literature on different types of environment regulations on water quality improvement. Using A-share market industrial listed company data, Wang et al. evaluate the effect of legislative environmental regulation and economic regulation on listed companies’ investment choice. Results show that there exists heterogeneity effect of different types of environmental regulation. Economic environmental regulation weakens the short-termism of corporation investment, and the legislative environmental regulation strengthens the short-termism of corporation investment [22]. This study stresses the transparency of environmental regulations, and the combination of different types of environmental regulation can enhance the effectiveness of the environmental regulation setting. Using the provincial data of China from 1997 to 2013, Shen explores the impact of the command and control regulation and the market environmental regulation on China’s industrial environmental efficiency, and found that the environmental regulations mainly improve the optimization of industrial environmental efficiency through technical effect and structural effect [23]. Although there is a trend of increasing stringency of environmental regulations, local governments respond differently to different types of environmental instruments in attracting Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), taking the “race-to-the-bottom” strategy for command and control environmental instruments and “race-to-the-top” strategy for autonomous environmental regulations [24]. The above literature studies divide environmental regulations into different types and explore their heterogeneous effects on company investment, industrial green development, and FDI attraction, but fail to focus on the impact of water pollution.
The existing literature can be improved from the following aspects. First, existing literature studies often uses province-level, city-level data or water quality data from monitoring stations to measure pollution outcomes. However, the province or city-level water pollution data cannot reflect industry-specific pollution activity. In addition, point observations of water quality at monitoring sites cannot reflect firms’ pollution activity, which also include water pollutant from living sewage or agriculture activity. Second, most recent studies only investigate the effect of environmental regulation on water pollution reduction from an empirical perspective; few discuss the theoretical framework. Third, most studies focus on environmental regulation implemented in the U.S., the E.U., India, or Brazil, where the institutional background is quite different from China. Some literature explores the effect of different types of water environmental regulations in China, but most of them focus on the market-oriented environmental instruments. However, market-oriented environmental instruments have not played an important role in China; the mainstream environmental instruments still remain as government-oriented environmental instruments.
Therefore, compared with the existing research results, the contributions of this study appear in several ways: (1) using the comprehensive firm-level data from two sources, the Key National Monitoring Sources of Pollution Firms (KNMSPF)and the Annual Survey of Industrial Firms (ASIF), we thus can evaluate the effect of environmental regulations on manufacturing activity; (2) constructing a theoretical model by including two types of environmental instruments into the traditional Copeland–Taylor environment model to analyze the effect of different environmental instruments on firms’ water pollution abatement; (3) Considering China’s current one fold, mainly governmental-oriented environmental regulation setting, and the unavailability of the market-oriented environmental regulation data (the most commonly used measurements for market-oriented environmental regulation—pollution discharge fee or environmental protection tax only available at the provincial level), we mainly evaluate the effect of two types of governmental-oriented environmental regulations, i.e., government environmental investment policy and the command–control policy on firms’ water pollutant discharge.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows. Section 2 briefly presents the theoretical framework that helps to structure the subsequent analysis. Section 3 lays out the data and empirical methodology. Section 4 provides the main results and discusses heterogeneous effects of the different types of the environmental regulation on water pollution abatement. Section 5 concludes the study and provides policy implications.
2. Theoretical Framework
Following the classical environment economic model of Copeland and Taylor, Antweiler et al., this section frames the conceptual view of how environmental regulations reduce water pollution by including the command–control instrument and the government investment instrument. The model can help to motivate the empirical models [25,26].
2.1. Fundamental Assumption
We began by assuming that firms use two production inputs: capital K and labor L to produce dirty water product X and clean product Y with a constant return to scale. Assuming that only X generates water pollutant emission Z during production, Y does not generate water pollutant at all. If firms are unregulated, they will have no incentive to reduce pollution. In this case, the output of X is given by F (KX, LX), where F is defined as the potential output. In China, governments usually adopt two kinds of policy to eliminate or reduce pollution: government environmental investment policy and command–control policy. Government environmental investment policies include building new or upgrading sewage pipe network systems, building new sewage treatment plants in industrial agglomeration areas, etc. Those policies will not increase firms’ production costs, and the government takes on the burden of pollution treatment and remedies the environmental eternality caused by manufacturers. In contrast, command–control policy includes shutting down or relocating polluting plants, monitoring the pollution discharge of factories, working out water pollution emission standards, enacting protection laws and regulations, etc., which force dirty firms to allocate a proportion of production input (θ) to abate pollution, θ ∈ [0, 1]. Consequently, the actual output Y, X, and the total level of pollution emission Z can be given by:
where KY and LY represent the input of effective capital and effective labor required to produce Y, respectively. KX and LX represent the input of effective capital and effective labor required to produce X. θ is the pollution abatement cost of dirty product X, which is only positively associated with command–control intensity υ. We assume that the government environmental investment intensity is λ. Λ and υ are exogenous to the firms, thus the pollution emission function can be given by
where 0 < α < 1, A represents the technology level. Substituting Equation (4) into Equation (3), the pollution emission function of Z can be expressed as
The production function of X can be expressed as
From Equation (6), we can see that polluting product X is mainly determined by pollution emission Z, production function F, technology level A, and government environmental investment λ.
2.2. Firm’s Optimal Decision
In terms of the pollution supply, firms try to make their optimal decisions to minimize production costs by choosing the emissions intensity and the capital–labor input ratio: (1) choosing the capital–labor ratio. Assuming that the capital price r and the wage w are exogenous, the firms will choose the optimal capital–labor ratio to minimize the production cost CF, according to the following equation:
where αKF and αLF represent capital and labor demand. The first-order conditions for the choice of r and w are
(2) choosing the optimal emissions intensity. Given the production cost of the potential output CF and the pollution emission cost θ (which is determined by υ), the firms will choose the optimal ratio of pollution emission Z and potential output F to minimize the production cost, according to the following equation:
The optimal solution of Equation (9) is:
In terms of the pollution demand, because in a purely competitive market, the firms’ total revenue is equal to total cost, then the following equation should be satisfied:
where PX is the price of product X. Substituting Equation (11) into Equation (10), we can obtain the pollution emission intensity e:
From Equation (12), we can see that the pollution emission intensitye mainly depends on the price of product X, technology level, government environment investment intensity, and command–control intensity. If we define the industrial scale as follows:
where PX and PY denote the price of product X and product Y, and the share of the polluting product X in the total output value can be expressed as
then, the total pollution emission Z can be rewritten as
Combining Equation (12) with Equation (14) and taking logs to get our decomposition:
From Equation (16), we can see that the total pollution emission is positively associated with the industrial scale (S) and the industrial structure (φx) and negatively associated with the technology level (A), the command–control intensity (υ), and the government environmental investment intensity (λ). What interested us in this equation is the impact of the command–control intensity (υ) and the government environmental investment intensity (λ), which consist of the total environmental regulation intensity, and both are important reasons for the improvement of water pollution quality.
3. Empirical Model, Data Description, and Preliminary Analysis
3.1. Empirical Model
We sought to estimate the water pollution abatement effect of two different types of environmental regulations, as described in the theoretical model. A basic empirical econometric model can be established as follows:
where the dependent variable Yit is one of the firm’s pollution discharges (log form of COD or NH3) in city i in year t. CPT refers to the industrial scale(S) in the theoretical model, represented by the total fixed assetsof the water pollution intensive firm. ISTit refers to the industrial structure (φx) in the theoretical model, represented by the industrial output value of the water-pollution-intensive industry to the total output value of the manufacturing sectorin city i in year t. TCit refers to the technology level(A) in the theoretical model. Since this study focused on the water-polluted-firms’ activity, the technology should also be related to water saving and using. We use water-using efficiency to proxy for the technology level as in the following equation:
where TC is the technology level, and WTC and WTD refer to the industry water consumption and wastewater discharge, respectively. All of the above firm-level data come from the ASIF and the KNMSPF.
This paper focuses on items 5 and 6 in Equation (17), namely, the impact of command–control policy and government environmental investment policy on firms’ water pollutant discharge. In this paper, the number of environmental-related laws and regulations (LAW) and environmental protection investment (EI) is used to proxy for the above two types of environmental policies. δ1 and δ2 are the parameters of interest, which capture the impact of the command–control policy LAW and the government environmental investment policy EI on water pollution abatement. A negative and significant δ indicates that the environmental regulation can reduce a firm’s water pollutant discharge, while a positive and significant δ suggests that the environmental regulation cannot reduce a firm’s water pollutant discharge.
Since firms’ pollution activities vary across industries, we follow Chakraborty and Chatterjee and included industry fixed effects (μi) at the 4-digit Chinese Industrial Code (CIC)in Equation (17) to absorb the impact of industry-specific characteristics of water pollutant discharge [27]. νt are year fixed effects, which control for any time-specific shocks that affect all firms’ equally. The standard errors are clustered at the 4-digit CIC level.
Moreover, while estimating Equation (17), we also try to control for other simultaneous events which might potentially affect the estimation outcome. Two other most substantive events take place during the study period which might potentially affect the estimation outcome: (1) the “Eleventh Five-Year Plan” (released in 2006) set different COD discharge reduction targets for every province according to their GDP level and industrial output. We categorically control for these confounding effects by including the interaction of the industry fixed effects and year trend; (2) since 2007, cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt have successively carried out the River Chief Policy, under which government leaders are appointed as the River Chief and are responsible for the water environment. In cities where the RCP has been implemented, the water-polluted firms might be under higher stringent regulation, which will also confound the analysis. In order to control for these confounding effects, we included the following in Equation (17): time trend, interacting time trend and industry fixed effect.
3.2. Data Source
3.2.1. Firm-Level Data
This paper evaluates the proposed effect of two types of government-oriented environmental regulations on a firm’s pollution activity using firm-level data from two major sources. The first one is the Key National Monitoring Sources of Pollution Firms (KNMSPF), previously used by Wang et al. and Fan et al. [22,28]. The KNMSPF is compiled by the Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP), including over 80,000 key monitored polluted firms annually, which accounts for 85% of total pollution emissions of all firms in a county. The KNMSPF data include a firm’s name, address, output value, water use, energy use, and also emissions of major pollutants such as wastewater discharge, COD, ammonia nitrogen (NH3), industrial smoke (SO2), industrial smoke and solid waste, which we can use for empirical analysis.
The second major data source is the Annual Surveys of Industrial Firms (ASIF), compiled by China’s National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) and which covered around 310,000 manufacturing firms with annual sales of above 5 million RMB (US$700,000) before 2011, and firms with annual sales of above 20 million RMB (US$3,000,000) after 2011, contributing to about 95% of China’s total industrial output value. The ASIF data include information about firm revenues, capital stocks, employments, address, the 4-digit Chinese Industry Classification (CIC) industrial code, added value of output, ownership, and so forth, which has been used to study environmental regulation effects at the firm level by a handful of previous studies [29,30]. The ASIF data also include a firm code and firm name which allow us to match firms with data in the KNMSPF.
In addition, based on the method of Brandt et al., the merged ASIF and KNMSPF data are also processed as follows, excluding the observed values of less than eight employees, total assets less than fixed assets, and paid-up capital equal to or less than 0. The samples with negative output, fixed costs, and total assets are also deleted. The 2-digit factory price of manufactured goods is used as a deflator to adjust the output value to eliminate the influence of price fluctuations [27]. Since the latest available data of KNMSPF are from 2012, we use the cleaned cross-sectional data from 2003 to 2012, with 146,982 observations in total as the basis for this empirical analysis.
The data of total fixed assets (CPT) directly come from the ASIF. Pollutant emission (COD and NH3) and technology-level (TC) data are from the KNMSPF.
The industrial structure (INS) is constructed in two steps. First, we use the emission intensity (COD and NH3 emissions per RMB of output) to classify the water pollution and non-pollution industry [31,32,33]. The following ten 2-digit Chinese Industry Classification (CIC) industries account for 81.1% of total COD and for 85.9% of total NH3 discharged from industrial sectors: coal mining and washing industry (06), ferrous metal mining-selection (08), non-ferrous metal mining-selection (09), agricultural food processing (13), food manufacturing (14), beverage manufacturing (15), textiles (17), paper and paper products (22), oil processing, coking, and nuclear fuel processing industry (25), and chemical raw materials and chemical products manufacturing(26)(The First National Pollution Source Census Bulletin (2007), National Bureau of Statistics. Available at: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/tjgb/qttjgb/qgqttjgb/201002/t20100211_30641.html, 29 June 2020). Second, the industrial structure (INS) can be calculated as the proportion of water-polluted industry output to the total output of the manufacturing sector.
3.2.2. Environmental Regulation Data
The measure of environmental regulations differs across studies. The most popular approach is to use pollutant discharge fees or pollutant abatement cost as a proxy for environmental regulation stringency [34]. Obviously, pollutant discharge fee and pollutant abatement cost are both the market-based regulation. However, Our aim of this paper is to evaluate whether China’s dominant government-oriented can affect firms’ pollution activity. Therefore, in this paper, we use a number of environmental-related laws and regulations published by local government to proxy command–control policy, which comes from China’s Law and Regulation Database (Laws and Regulation Database. http://search.chinalaw.gov.cn/search2.html), and we use local government investment in environmental sanitation to proxy government environmental investment, which come from the city statistical yearbook. The government investment in environmental sanitation is deflated into real one by using the GDP deflator index for the year 2003. Table 1 summarizes all the above variables.

Table 1.
Summary of the descriptive statistics of all variables.
3.2.3. Preliminary Analysis
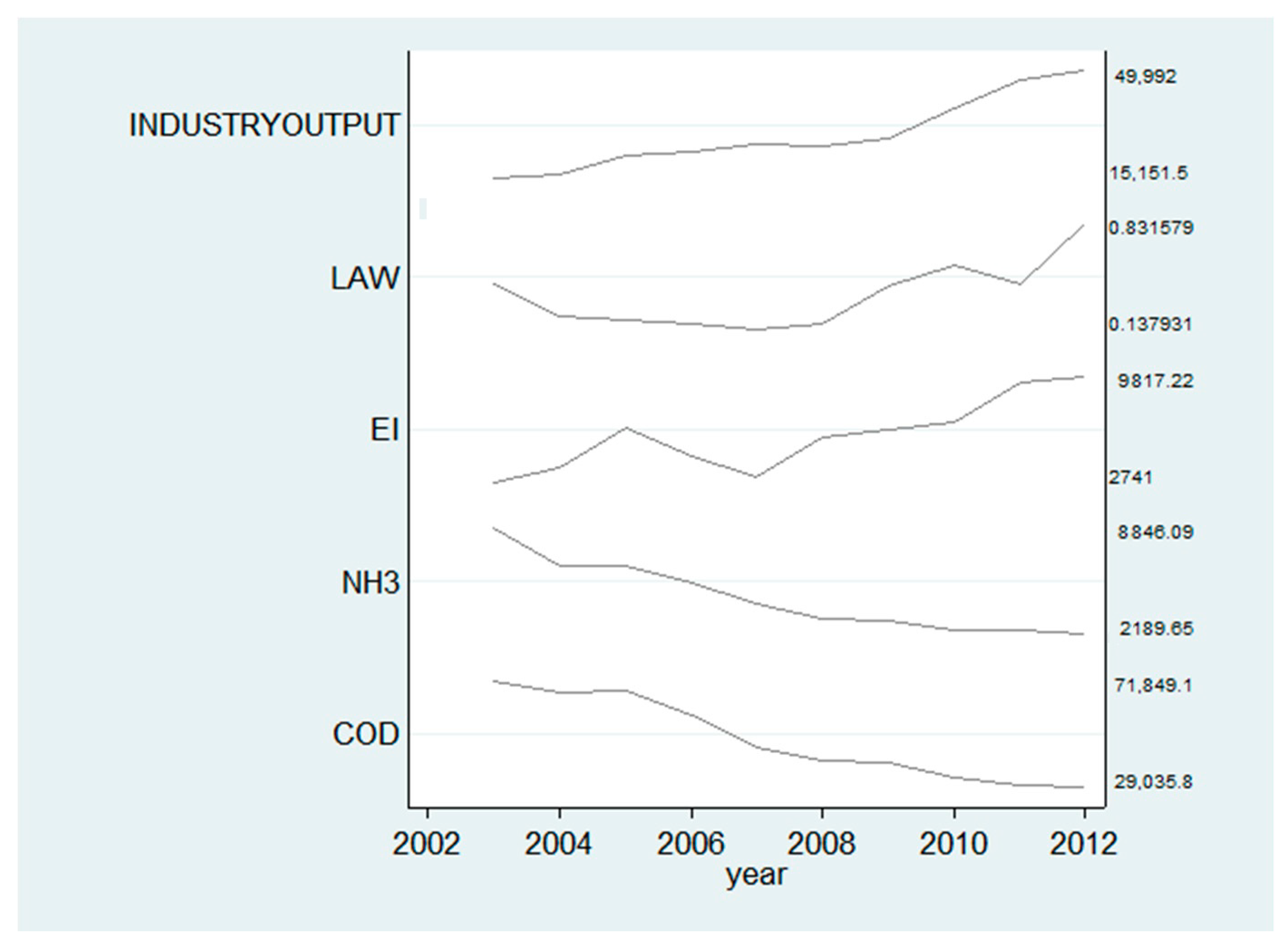
Figure 2 presents the time trend of annual average industry outputs, COD emissions and NH3 emissions of firms, number of annual average environmental laws and regulations as well as government environmental investment in the Yangtze River Economic Belt from 2002 to 2012. This figure shows that, during the study period, COD and NH3 emissions of firms experience a significant decrease when industry output kept rising. In contrast, the environmental laws and regulations as well as government environmental investment also have maintained the upward trend. This suggests that command–control policy and government environmental investment policy might have a positive effect on water pollutant emissions. However, this result is merely suggestive, and other factors and simultaneous events might also influence the firms’ water pollutant emissions. We will further conduct empirical tests in the next section to address these concerns.
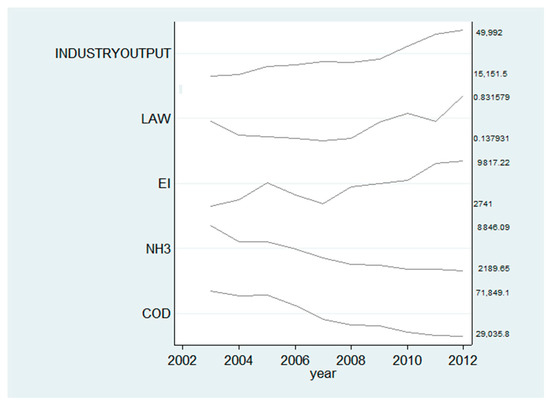
Figure 2.
The time trend of industrial output, COD and NH3 emissions of water-pollution-intensive firms in the Yangtze River from 2003 to 2012.
4. Empirical Results and Analysis
In this section, we first focus on our baseline outcomes of the effect of two types of environmental policies on firms’ water pollutant discharge. Then, we check the robustness of these results. Third, we provide heterogeneity in the effects across different firm sizes, industries, and ownerships.
4.1. Baseline Result
We first test the effect of the command–control policy and the government environmental policy on firms’ pollutant emissions (COD and NH3). Table 2 reports two sets of estimation results from Equation (17); the log form of COD and NH3 discharges are used as the dependent variables, respectively. All columns include 4-digit fixed effects and year fixed effects. In columns (1) and (2), the estimated coefficients of government environmental investment (lnEI) to the log form of COD and NH3 discharges are −0.0287 and −0.0253, which are statistically significant at the 1% and the 5% levels, respectively. However, the estimated coefficients of command–control policy (LAW) are only statistically insignificant in column (2), and the value is much smaller than that of government environmental investment. Columns (3) and (4) include time trend and interactions of time trend and industry fixed effects to control for other simultaneous events that may affect the water pollutant discharge of dirty firms. After control for all these other effects, our main findings continue to hold. The estimated coefficients of government environmental investment (lnEI) to lnCOD and lnNH3 relatively decrease to −0.0299 and −0.0335, respectively, both statistically significant at the 1% level. This finding suggests that if the government environmental investment increases by 1%, firms’ COD and NH3 discharges will reduce by 2.99% and 3.35%, respectively. The estimated coefficients of command–control policy (LAW) in columns (3) and (4) are still statistically insignificant.

Table 2.
The estimated result of the basic model.
The results reveal that, although both of the two types of environmental regulations can reduce the water pollutant discharge of firms, the government environmental investment contributes most to firms’ pollutant abatement. The reason lies in at least two facts. First, government environmental investment can help to reduce water pollutant discharge by installing a sewage pipe network and establishing new sewage treatment equipment. Second, during the sample period, the environmental relative laws were not stringent enough or directly targeted at firms’ water pollution discharge, which shows little direct effect on water pollutant discharge. The results are in line with the work of Keiser and Shapiro, who found that the government’s grants ($100 per person-year) contributed most to the improvement of river water in the U.S. [10]. Our results also show that it is up to the government, not the dirty firm, to remedy and reduce pollution externalities caused by dirty production processes.
The coefficients of industry scale (lnCPT), industry structure (INS), and technology level (lnCPT) are exactly in compliance with the theoretical model. The expanding industrial scale (lnCPT) and the dirtying industry structure (INS) are associated with a COD and NH3 increase. The improvement of technology on water using (TC) can reduce water pollutant emission.
4.2. Robust Check
The way to measure environmental regulation intensity might affect the estimation result. With this in mind, we try to use an alternative method to measure the command–control policy and the government investment policy as a robust check. Specifically, investment in fixed assets of municipal public facilities construction (lnMUNICIPAL) is used to proxy for the government investment policy intensity, which comes from China’s urban construction statistical yearbook. We also collect the frequencies of environmental-related key words (TEXT), such as “environmental protection,”“ecological environment” in government work reports of all the sample cities, and use it as a proxy for the command–control policy. The results are presented in Table 3. Again, we find that the government environmental investment can reduce two types of water pollutants emission, but the command–control policy only reduces COD discharge. Our results are robust to using alternative measurements for two types of environmental regulation.

Table 3.
Coefficient on environmental regulations: alternate measurements.
4.3. Heterogeneity
Do all firms respond homogenously to environmental regulations? To address this concern, we explored the amount of heterogeneity involved in our benchmark findings conditioned by industry, firm size, and ownership.
4.3.1. Industry Heterogeneity
Different industries respond differently to environmental regulations. In Section 3, we divide the entire sample into the water-pollution-intensive industry and the other industry according to water-pollutant emitting intensity across industries. We re-estimate Equation (17) by including interaction terms of the environmental regulations and the industry dummies for the water-pollution-intensive industry and the other industry. If a firm’s 2-digit CIC code belongs to the above water-pollution-intensive industry, the variable would indicate 1 for that firm, and zero otherwise.
The regression results are reported in Table 4, which indicate that the effect of the environmental regulations vary across industrial groups. Generally, the results remain along the same trend with our previous estimation. The effect of the government environmental investment policy is more obvious than the command–control policy. The estimated coefficients of the government environmental investment to lnCOD and lnNH3 for water-pollution-intensive firms take significantly negative values. What is more, the absolute values of the estimated coefficients are much bigger than those in Table 2, which includes all samples. This indicates that the government environmental investment policy is more effective on water-pollution-intensive firms than other firms. Although the estimated coefficient of the command–control policy to lnCOD for water pollution firms is also significantly negative, the extent of the effect is comparatively small. This indicates that an additional environment law will decrease 1.08% of the total COD discharge. The reason is easy to understand. Comparing with other industries, the water-pollution-intensive industry has a higher level of pollution. Therefore, the effects of both kinds of water quality regulations are more obvious than for other industries.

Table 4.
Effects of the environmental regulations on water pollutant emissions, by industry.
4.3.2. Size Heterogeneity
Firms with a different size may respond to environmental instruments differently, because large firms are more likely to use green technology to reduce water pollutant discharge. Some literature studies find that pollution discharge has a negative relationship with the firm’s size [32]. According to the number of employees, we divide all sample industrial firms into large, medium, small, and micro firms (Statistical classification of large, medium, small and micro enterprises (2017), National Bureau of Statistics. Available at: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/tjbz/201801/t20180103_1569357.html, 30 June 2020, X is number of employee, the standard of large, medium, small, and micro firms are X ≥ 1000, 300 ≤ X < 1000, 20 ≤ X< 300, X < 20).
Table 5 reports estimation results from a regression that includes an interaction of environmental instruments with firm size. The estimated coefficients follow the same pattern as before: comparing with the government environmental policy, the command–control policy shows little effect on water pollution reduction. Although the coefficient of the command–control policy to NH3 discharge is significant for large firms, and the coefficient of the command–control policy to COD discharge is significant for small firms, the values are too small and have little economic meaning. Contrarily, the effect of the government environmental investment policy on COD and NH3 emission reduction is obviously significant among most of the sub-samples, i.e., small and micro firms. The reason might lie in the fact that, when applying the same advanced technology or establishing pollution treatment equipment, small firms’ marginal abatement costs are much higher than large firms because of their smaller quantities of production [34,35]. Thus, comparing with large firms, small firms are more unlikely to take responsibility for pollution control. When the government invests in water pollution control and treatment, small firms “free ride” it and reduce their water pollutant discharge.

Table 5.
Effects of the environmental regulations on water pollutant emissions, by size.
4.3.3. Ownership Heterogeneity
The effects of environmental regulations may vary across firms’ ownership structure. The ASIF includes the information of ownership, under which all firms are divided into the following: state-owned enterprises (SOE), collective-owned enterprises, domestic joint ventures, private enterprises, foreign-invested enterprises and Hong Kong-, Macao-, and Taiwan-invested enterprises(In the whole sample firms, state-owned enterprises (SOE), collective-owned enterprises, domestic joint ventures, private enterprises, foreign-invested enterprises account for 5.53%, 4.43%, 22.64%, 41.38%, 26.01% of the total observations accordingly).Because the number of Hong Kong-, Macao-, and Taiwan-invested enterprises is quite small, we combined it into foreign-invested enterprises. In total, we got 4 types of ownership. Different ownership categories of firms are indicated by a dummy variable. Then, we re-estimate Equation (17) by including interaction terms of the environmental regulations and the ownership dummies.
The results are shown in Table 6. The estimated coefficients demonstrate that the effect of two types of environmental regulations is indeed heterogeneous across firms of ownership structure. The decrease in water pollutant discharge as a response to the government environmental investment policy is significantly in the SOEs, domestic joint ventures, and foreign-invested firms group. The reason may lie in the fact that government tends to establish new sewage treatment plants in industrial agglomeration areas where SOEs, joint venture enterprises, and foreign-invested firms are located, more so than firms of other ownership types. In other words, the government mainly remedies the water pollution externality for SOEs, joint venture enterprises, and foreign-invested firms. Contrary to the government environmental investment policy, the effect of the command–control policy is only significantly negative in joint venture enterprises and private firms, whereas the effect is insignificant on SOEs, collective-owned enterprises as well as foreign-invested firms. Our empirical result is consistent with Cai et al., who find that private firms are more sensitive to the environmental instruments than SOEs and foreign-invested firms [9]. Previous literature studies offer some possible explanations for these results. For example, comparing with SOEs and foreign-invested enterprises, private firms and domestic joint enterprises are less likely to acquire loans from commercial banks, which causes them a lack of financial resources to apply environmentally friendly technologies and results in emitting more pollutants [36]. However, SOEs take more social responsibility and are more likely to restrain their pollution emission behavior. Foreign firms used to face higher environmental standards in their home countries. Thus, they tend to apply environmentally friendly technology even in countries where environmental standards are relatively week, which results in less pollutant discharge [37]. Therefore, SOEs and foreign-invested firms are less influenced by the command–control policy, which accumulates supportive evidence for the work of [38].

Table 6.
Effects of the environmental regulations on water pollutant emissions, by ownership.
5. Conclusions and Implications
Within the improved framework of the Copeland–Taylor model, this study explored the effect of the two main types of China’s government-oriented environmental regulation on heavy-water-polluted firms’ discharge. According to the results, in the period of 2003–2013, the two types of water pollution index, COD and NH3, were reduced by 2.99% and 3.35%, respectively, with the increase of 1% of government environmental investment. However, the command–control policy shows little effect on firms’ water pollutant discharge abatement. Like other countries, government environmental investment is the main reason for water pollution reduction; the effect of the command–control policy is comparatively less obvious on a firm’s water pollutant emission. Our findings remain robust when using alternative measurements for environmental policies. The effects of the environmental regulations vary across sub-samples. The two types of government-oriented environmental instruments are both effective for the water pollution industry, but the extent of the effect of the command–control policy is very small. The government environmental investment policy has an obvious impact on SOEs, domestic joint ventures, and foreign-invested firms. The water pollution social externality caused by the above three types of firms has been burdened by government. However, the command–control policy is effective for domestic joint ventures and private firms. In other words, domestic joint ventures and private firms have been forced to be responsible for their own water pollution actions.
From the above analysis, this paper derives the following policy implications. (1) Under the current Chinese environmental regulation regime, it is up to the government, not the private firms, to remedy the pollution externalities caused by firms, under which the initiative of firms cannot be stimulated to apply advanced environmentally friendly technology and finally lead to the whole environment regulation being inefficient. According to the theoretical model, the command–control policy can force private firms to be responsible for their own pollution action. Therefore, the Chinese government should adhere to more command–control policies and improve its stringency, so that private firms have to bear the burden of their own pollution discharge. (2) Our study proves, more or less, that any kinds of environmental instruments can reduce the water pollutant discharge effectively. As some literature studies point out, the key point of China’s current environmental regime is relatively one fold, mainly government-oriented, and a good environmental regime should not be based on “which one is best?” but rather on “it should be a mix of instruments,” and that the best environmental regulation regime should be a mix of instruments [39,40]. Therefore, the urgent task for the Chinese government is to use more types of environmental regulation instruments, such as market-incentive policies and voluntary policies, to transform from a one fold, government-oriented environmental regime to a multi-fold, market-oriented environmental management regime. (3) Firms with different characteristics respond heterogeneously to the water quality regulations [41]. To make differential water quality regulations for firms from different industries, with different sizes and ownership structures, can improve the efficiency of water environmental regulations. Especially, for domestic joint ventures and private firms, which account for 61.99% and 55.78% of the total COD and NH3 emissions during the study period, respectively, they should be regulated by more stringent command–control policies (Calculated with the KNMSPF data by the author). In addition, some financial supports should be given to these kinds of firms to help them establish water pollutant treatment equipment. The market incentive policies also should be applied to stimulate them to apply environmentally friendly technology. Public supervision policies also can be used to put pressure on these firms.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L. conceived the research idea and revised the paper. Y.D. conducted the model simulations and data analysis. Y.S., writing—original draft. L.J. revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by Jiangxi Social Science Planning Fund (16YJ15); Key projects of Jiangxi science and Technology Department (20192BAA208014); Nanchang Hangkong University Open Fund Project (ER201909388; ER202009232).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, Z.; Kahn, M.E.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. The consequences of spatially differentiated water pollution regulation in China. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2018, 88, 468–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Council. Administrative Regulations on Levy and Use of Pollutant Discharge Fee. 2003. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2003/content_62565.htm (accessed on 28 April 2020).
- China News. China Will Make a Major Adjustment to the 11-Year-Old Emission Fee Collection Standard. Available online: http://www.chinanews.com/gn/2014/09-05/6568114.shtml (accessed on 18 September 2020).
- China Industry Information. Available online: http://www.chyxx.com/industry/201904/732895.html (accessed on 18 September 2020).
- Strumpf, K.S.; Oberholzer-Gee, F. Endogenous policy decentralization: Testing the central tenet of economic federalism. J. Political Econ. 2002, 110, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, A. Environmental regulatory competition: A status report and some new evidence. Natl. Tax J. 2003, 56, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chay, K.; Greenstone, M. Does Air Quality Matter? Evidence from the Housing Market. J. Political Econ. 2005, 113, 376–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernauer, T.; Kuhn, P.M. Is there an environmental version of the Kantian peace? Insights from water pollution in Europe. Eur. J. Int. Relat. 2010, 16, 77–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenstone, M.; Hanna, R. Environmental regulations, air and water pollution, and infant mortality in India. Am. Econ. Rev. 2014, 104, 3038–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, M.E.; Li, P.; Zhao, D. Water pollution progress at borders: The role of changes in China’s political promotion incentives. Am. Econ. J. Econ. Policy 2015, 7, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Chen, Y.; Gong, Q. Polluting thy neighbor: Unintended consequences of China’s pollution reduction mandates. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2016, 76, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiser, D.A.; Shapiro, J.S. Consequences of the Clean Water Act and the demand for water quality. Q. J. Econ. 2019, 134, 349–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigman, H. International spillovers and water quality in rivers: Do countries free ride? Am. Econ. Rev. 2002, 92, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigman, H. Letting States Do the Dirty Work: State Responsibility for Federal Environmental Regulation. Available online: https://www.nber.org/papers/w9451 (accessed on 18 September 2020).
- Sigman, H. Transboundary spillovers and decentralization of environmental policies. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2005, 50, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, J.A.; Bulte, E.H.; Shogren, J.F. “Beggar thy neighbor”: Testing for free riding in state-level endangered species expenditures. Public Choice 2002, 111, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Brombal, D.; Farah, P.D.; Moriggi, A.; Critto, A.; Zhou, Y.; Marcomini, A. China’s water environmental management towards institutional integration. A review of current progress and constraints vis-a-vis the European experience. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipscomb, M.; Mobarak, A.M. Decentralization and pollution spillovers: Evidence from the re-drawing of county borders in Brazil. Rev. Econ. Stud. 2016, 84, 464–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.R.; Jin, G.; Fang, X. Does environmental regulation cause pollution to transfer nearby. Econ. Res. J. 2018, 52, 44–59. [Google Scholar]
- She, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yuan, H. Is China’s River Chief Policy effective? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shi, X.; Wu, H.; Liu, L. Trade-off between economic development and environmental governance in China: An analysis based on the effect of river chief system. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 60, 101403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, J.J.; Zhang, B. Environmental regulation, emissions and productivity: Evidence from Chinese COD-emitting manufacturers. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2018, 92, 54–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Li, S.L.; Huang, L.X. Different types of environmental regulation and the green transformation of Chinese industry: Path selection and mechanism analysis. Nankai Econ. Stud. 2018, 5, 95–114. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, W.X.; Wei, W.J. Local government competition and envirionmental regulation heterogeneity: Race to the bottom or race to the top? China Soft Sci. 2018, 11, 76–93. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Copeland, B.R.; Taylor, M.S. North-South trade and the environment. Q. J. Econ. 1994, 109, 755–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antweiler, W.; Copeland, B.R.; Taylor, M.S. Is free trade good for the environment? Am. Econ. Rev. 2001, 91, 877–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Chatterjee, C. Does environmental regulation indirectly induce upstream innovation? New evidence from India. Res. Policy 2017, 46, 939–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Going Green in China: Firms’ Responses to Stricter Environmental Regulations (No. w26540). Available online: https://www.nber.org/papers/w26540 (accessed on 18 September 2020).
- Brandt, L.; Van Biesebroeck, J.; Zhang, Y. Creative accounting or creative destruction? Firm-level productivity growth in Chinese manufacturing. J. Dev. Econ. 2012, 97, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, L.; Van Biesebroeck, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. WTO accession and performance of Chinese manufacturing firms. Am. Econ. Rev. 2017, 107, 2784–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, B.R.; Taylor, M.S. Trade, growth, and the environment. J. Econ. Lit. 2004, 42, 7–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, R.E.; Wheeler, D.; Hettige, H. Economic Development, Environmental Regulation, and the International Migration of Toxic Industrial Pollution, 1960-88; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; Volume 1062. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, F.D.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, C.M.; Shan, Y.B. Spatial relocation and mechanism of pollution-intensive industries in Jiangsu Province. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2013, 33, 789–796. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Brunnermeier, S.B.; Cohen, M.A. Determinants of environmental innovation in US manufacturing industries. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2003, 45, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.A.; Elliott, R.J.; Shimamoto, K. Industrial characteristics, environmental regulations and air pollution: An analysis of the UK manufacturing sector. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2005, 50, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Wheeler, D.; Huq, M.; Zhang, C. Water Pollution Abatement by Chinese Industry: Cost Estimates and Policy Implications; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lanjouw, J.O.; Mody, A. Innovation and the international diffusion of environmentally responsive technology. Res. Policy 1996, 25, 549–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Moon, J.J.; Yin, H. Does international economic integration lead to a cleaner production in China? Prod. Oper. Manag. 2014, 23, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, J. Different types of environmental regulations and heterogeneous influence on “green” productivity: Evidence from China. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 132, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, E.Y.; Meng, Z.; Song, Y. Environmental regulation, green technological innovation, and eco-efficiency: The case of Yangtze river economic belt in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 155, 119993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X. Integrating the MCR and DOI models to construct an ecological security network for the urban agglomeration around Poyang Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 141868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).