Acquirer’s Absorptive Capacity and Firm Performance: The Perspectives of Strategic Behavior and Knowledge Assets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Hypothesis Development
2.1. The Role of CBMA in Knowledge Acquisition
2.2. Absorptive Capacity and Sustainable Performance in CBMAs
2.3. Moderators: Acquiring Firm’s Strategic Behavior and Target Firm’s Knowledge
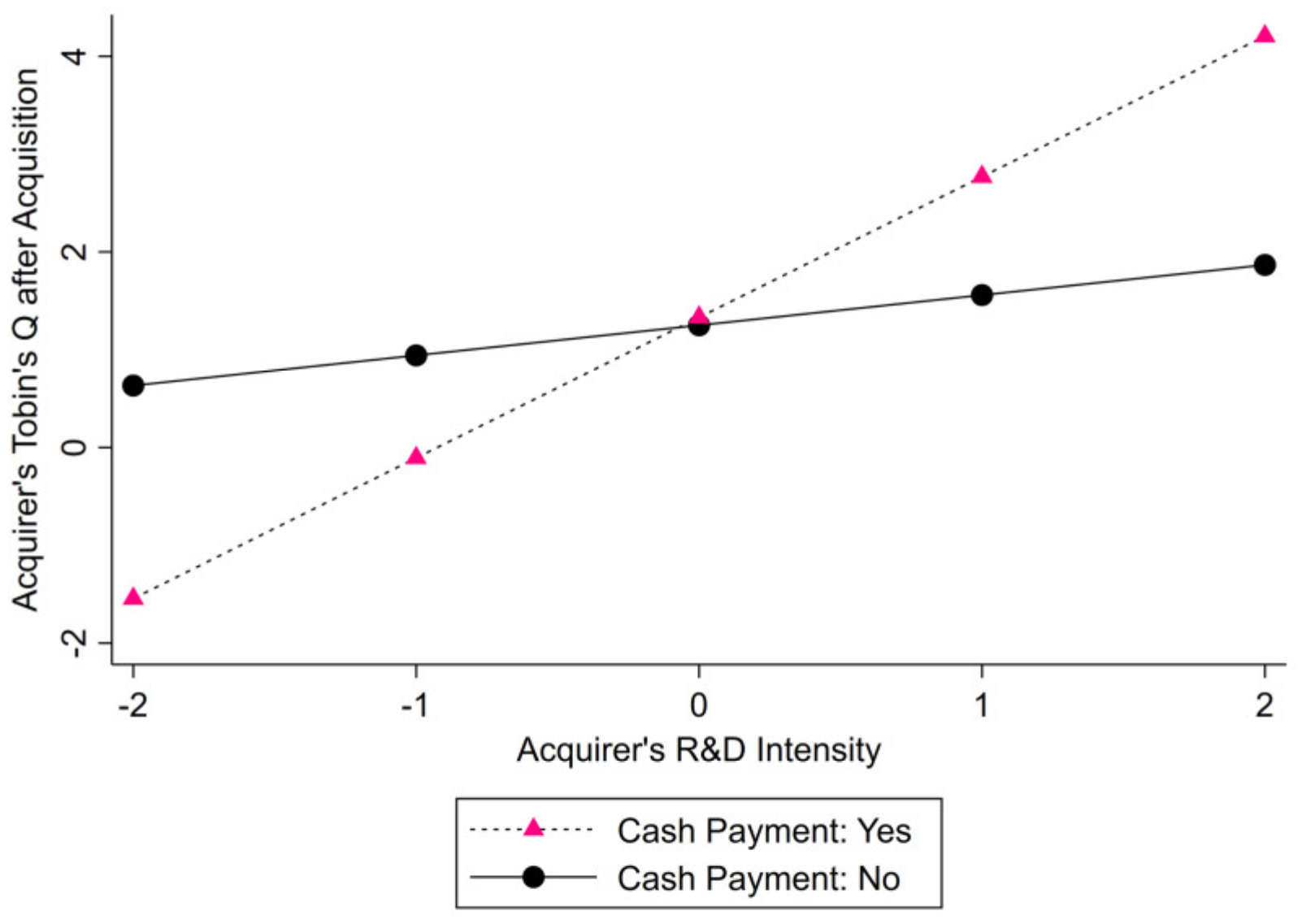
2.3.1. Acquirer’s Strategic Behavior: Payment Method of Cash
2.3.2. Acquirer’s Strategic Behavior: Past CBMA Experiences
2.3.3. Target Firm’s Knowledge: Amount of Strategic Assets
2.3.4. Target Firm’s Knowledge: High-Tech Industry
3. Data and Methodology
3.1. Sampling and Data Collection
3.2. Dependent Variable
3.3. Explanatory Variables
3.4. Control Variables
3.5. Estimation Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
4.2. OLS Regression
4.3. Robustness Test: Heckman Selection Model
4.4. Sensitivity Test: Domestic M&A vs. CBMA
5. Conclusions
5.1. Theoretical Implications
5.2. Managerial Implications
5.3. Limitations and Future Studies
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shimizu, K.; Hitt, M.A.; Vaidyanath, D.; Pisano, V. Theoretical foundations of cross-border mergers and acquisitions: A review of current research and recommendations for the future. J. Int. Manag. 2004, 10, 307–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capron, L.; Pistre, N. When do acquirers earn abnormal returns? Strateg. Manag. J. 2002, 23, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Torres, T.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, J.-L.; Pelechano-Barahona, E.; García-Muiña, F.E. A systematic review of research on sustainability in mergers and acquisitions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laamanen, T.; Keil, T. Performance of serial acquirers: Toward an acquisition program perspective. Strateg. Manag. J. 2008, 29, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, P.; Wang, B. The liability of opaqueness: State ownership and the likelihood of deal completion in international acquisitions by Chinese firms. Strateg. Manag. J. 2019, 40, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitt, M.; Pisano, V. Cross-border mergers and acquisitions: Challenges and opportunities. In Mergers and Acquisitions: Creating Integrative Knowledge; Pablo, A.L., Javidan, M., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, K.D.; Folta, T.B. Option value and entry timing. Strateg. Manag. J. 2002, 23, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Yang, M. Enhancing performance of cross-border mergers and acquisitions in developed markets: The role of business ties and technological innovation capability. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 81, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Mudambi, R.; Gray, S. Internationalization, innovation and institutions: The 3 I’s underpinning the competitiveness of emerging market firms. J. Int. Manag. 2013, 19, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Lin, R.; Mi, J.; Li, N. Improving enterprises’ cross-border M&A sustainability in the globalization age—Research on Acquisition and application of the foreign experience. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3180. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y. Building a strong foothold in an emerging market: A link between resource commitment and environment conditions. J. Manag. Stud. 2004, 41, 749–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitt, M.A.; Li, H.; Worthington, W.J., IV. Emerging markets as learning laboratories: Learning behaviors of local firms and foreign entrants in different institutional contexts. Manag. Organ. Rev. 2005, 1, 353–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulakh, P.S.; Kotabe, M.; Teegen, H. Export strategies and performance of firms from emerging economies: Evidence from Brazil, Chile, and Mexico. Acad. Manag. J. 2000, 43, 342–361. [Google Scholar]
- Beamish, P.W.; Delios, A. Japanese investment in transitional economies: Characteristics and performance. In Managing Organizational Change in Transition Economies; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Makino, S.; Beamish, P.W.; Zhao, N.B. The characteristics and performance of Japanese FDI in less developed and developed countries. J. World Bus. 2004, 39, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon-Gonzalez, R.; Tole, L. The Determinants of Mergers & Acquisitions in a Resource-Based Industry: What Role for Environmental Sustainability? Rev. Econ. Anal. 2015, 7, 111–134. [Google Scholar]
- Di Giovanni, J. What drives capital flows? The case of cross-border M&A activity and financial deepening. J. Int. Econ. 2005, 65, 127–149. [Google Scholar]
- Evenett, S. The cross-border mergers and acquisitions wave of the late 1990s. In Challenges to Globalization: Analyzing the Economics; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2004; pp. 411–470. [Google Scholar]
- Hur, J.; Parinduri, R.A.; Riyanto, Y.E. Cross-border M&A inflows and quality of country governance: Developing versus developed countries. Pac. Econ. Rev. 2011, 16, 638–655. [Google Scholar]
- Morck, R.; Yeung, B. Internalization: An event study test. J. Int. Econ. 1992, 33, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, O.; Betschinger, M.-A. Performance of domestic and cross-border acquisitions: Empirical evidence from Russian acquirers. J. Comp. Econ. 2012, 40, 413–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zack, M.H. Managing codified knowledge. Sloan Manag. Rev. 1999, 40, 45–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, P.J.; Koka, B.R.; Pathak, S. The reification of absorptive capacity: A critical review and rejuvenation of the construct. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2006, 31, 833–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, S.A.; George, G. Absorptive capacity: A review, reconceptualization, and extension. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2002, 27, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, P. Absorptive capacity and a failed cross-border M&A. Manag. Res. Rev. 2010, 33, 673–682. [Google Scholar]
- Yli-Renko, H.; Autio, E.; Tontti, V. Social capital, knowledge, and the international growth of technology-based new firms. Int. Bus. Rev. 2002, 11, 279–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junni, P.; Sarala, R.M. The role of absorptive capacity in acquisition knowledge transfer. Thunderbird Int. Bus. Rev. 2013, 55, 419–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zollo, M.; Singh, H. Deliberate learning in corporate acquisitions: Post-acquisition strategies and integration capability in US bank mergers. Strateg. Manag. J. 2004, 25, 1233–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changqi, W.; Ningling, X. Determinants of cross-border merger & acquisition performance of Chinese enterprises. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2010, 2, 6896–6905. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, S.; Volpin, P.F. Cross-country determinants of mergers and acquisitions. J. Financ. Econ. 2004, 74, 277–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkopf, L.; Nerkar, A. Beyond local search: Boundary-spanning, exploration, and impact in the optical disk industry. Strateg. Manag. J. 2001, 22, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeley, M.; King, D.; Covin, J. R&D investment level and environment as predictors of firm acquisition. J. Manag. Stud. 2006, 43, 1513–1536. [Google Scholar]
- Bresman, H.; Birkinshaw, J.; Nobel, R. Knowledge transfer in international acquisitions. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 1999, 30, 439–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Shenkar, O.; Lew, Y.K. Knowledge transfer from international joint ventures to local suppliers in a developing economy. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2015, 46, 656–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarala, R.M.; Vaara, E. Cultural differences, convergence, and crossvergence as explanations of knowledge transfer in international acquisitions. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2010, 41, 1365–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Q.; Tan, H. Acquirers’ prior related knowledge and post-acquisition integration. J. Organ. Chang. Manag. 2017, 30, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junni, P. Knowledge transfer in acquisitions: Fear of exploitation and contamination. Scand. J. Manag. 2011, 27, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranft, A.L.; Lord, M.D. Acquiring new technologies and capabilities: A grounded model of acquisition implementation. Organ. Sci. 2002, 13, 420–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reus, T.H. A knowledge-based view of mergers and acquisitions revisited: Absorptive capacity and combinative capability. In Advances in Mergers and Acquisitions; Finkelstein, S., Cooper, C.L., Eds.; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2012; pp. 69–88. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, P. Why do Chinese firms tend to acquire strategic assets in international expansion? J. World Bus. 2009, 44, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Tung, R.L. International expansion of emerging market enterprises: A springboard perspective. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2007, 38, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.I.; Roh, T. Chinese multinationals’ FDI motivations: Suggestion for a new theory. Int. J. Emerg. Mark. 2019, 14, 70–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, B.; Zander, U. Knowledge of the firm, combinative capabilities, and the replication of technology. Organ. Sci. 1992, 3, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, R.M. Toward a knowledge-based theory of the firm. Strateg. Manag. J. 1996, 17, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, B.; Zander, U. Knowledge of the firm and the evolutionary theory of the multinational corporation. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 1993, 24, 625–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, K.Z.; Li, C.B. How knowledge affects radical innovation: Knowledge base, market knowledge acquisition, and internal knowledge sharing. Strateg. Manag. J. 2012, 33, 1090–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, B. Intellectual capital, financial performance and companies’ sustainable growth: Evidence from the Korean manufacturing industry. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hitt, M.A.; Pisano, V. The cross-border merger and acquisition strategy: A research perspective. Manag. Res. J. Iberoam. Acad. Manag 2003, 1, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Kim, J.; Park, B.I. Culture clashes in cross-border mergers and acquisitions: A case study of Sweden’s Volvo and South Korea’s Samsung. Int. Bus. Rev. 2015, 24, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, G.K.; Voigt, A. Do cultural differences matter in mergers and acquisitions? A tentative model and examination. Organ. Sci. 2008, 19, 160–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Xia, J.; Makino, S. How do high-technology firms create value in international M&A? Integration, autonomy and cross-border contingencies. J. World Bus. 2015, 50, 718–728. [Google Scholar]
- Hayward, M.L.; Hambrick, D.C. Explaining the premiums paid for large acquisitions: Evidence of CEO hubris. Adm. Sci. Q. 1997, 42, 103–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.B.; Altenborg, E. Incompatible strategies in international mergers: The failed merger between Telia and Telenor. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2008, 39, 508–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloodt, M.; Hagedoorn, J.; Van Kranenburg, H. Mergers and acquisitions: Their effect on the innovative performance of companies in high-tech industries. Res. Policy 2006, 35, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, S. Overcoming the liability of foreignness. Acad. Manag. J. 1995, 38, 341–363. [Google Scholar]
- Very, P.; Lubatkin, M.; Calori, R.; Veiga, J. Relative standing and the performance of recently acquired European firms. Strateg. Manag. J. 1997, 18, 593–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, F.; Matzler, K. Antecedents of M&A success: The role of strategic complementarity, cultural fit, and degree and speed of integration. Strateg. Manag. J. 2014, 35, 269–291. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, R.; Gupta-Mukherjee, S.; Jayaraman, N. Mars–Venus marriages: Culture and cross-border M&A. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2009, 40, 216–236. [Google Scholar]
- Morosini, P.; Shane, S.; Singh, H. National cultural distance and cross-border acquisition performance. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 1998, 29, 137–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, Y. Corporate cultural fit and performance in mergers and acquisitions. Hum. Relat. 1996, 49, 1181–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, S.; Haleblian, J. Understanding acquisition performance: The role of transfer effects. Organ. Sci. 2002, 13, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Roh, T. Proactive Divestiture and Business Innovation: R&D Input and Output Performance. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3874. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Peng, M.W.; Yang, H.; Sun, S.L. How do networks and learning drive M&As? An institutional comparison between China and the United States. Strateg. Manag. J. 2009, 30, 1113–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, W.M.; Levinthal, D.A. Absorptive capacity: A new perspective on learning and innovation. Adm. Sci. Q. 1990, 35, 128–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreras-Méndez, J.L.; Newell, S.; Fernández-Mesa, A.; Alegre, J. Depth and breadth of external knowledge search and performance: The mediating role of absorptive capacity. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2015, 47, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, S.A.; Hayton, J.C. The effect of international venturing on firm performance: The moderating influence of absorptive capacity. J. Bus. Ventur. 2008, 23, 195–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostopoulos, K.; Papalexandris, A.; Papachroni, M.; Ioannou, G. Absorptive capacity, innovation, and financial performance. J. Bus. Res. 2011, 64, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Ertug, G.; George, G. The capacity to innovate: A meta-analysis of absorptive capacity. Innovation 2018, 20, 87–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björkman, I.; Stahl, G.K.; Vaara, E. Cultural differences and capability transfer in cross-border acquisitions: The mediating roles of capability complementarity, absorptive capacity, and social integration. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2007, 38, 658–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, F.; Barkema, H. Learning through acquisitions. Acad. Manag. J. 2001, 44, 457–476. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, K.E.; Sinani, E. When and where does foreign direct investment generate positive spillovers? A meta-analysis. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2009, 40, 1075–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W. Knowledge transfer in intraorganizational networks: Effects of network position and absorptive capacity on business unit innovation and performance. Acad. Manag. J. 2001, 44, 996–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, P.; Wang, B. Do cross-border acquisitions create value? Evidence from overseas acquisitions by Chinese firms. Int. Bus. Rev. 2016, 25, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, A.; Du, M.; Bi, X.; Lodorfos, G. Cultural distance and value creation of cross-border M&A: The moderating role of acquirer characteristics. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2019, 63, 285–295. [Google Scholar]
- Hitt, M.A.; Ireland, R.D.; Camp, S.M.; Sexton, D.L. Strategic Entrepreneurship: Integrating Entrepreneurial and Strategic Management Perspectives. In Strategic Entrepreneurship: Creating a New Mindset; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hitt, M.A.; Tyler, B.B. Strategic decision models: Integrating different perspectives. Strateg. Manag. J. 1991, 12, 327–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.S.; Hitt, M.A.; Hoskisson, R.E.; Ireland, R.D. Resource complementarity in business combinations: Extending the logic to organizational alliances. J. Manag. 2001, 27, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makri, M.; Hitt, M.A.; Lane, P.J. Complementary technologies, knowledge relatedness, and invention outcomes in high technology mergers and acquisitions. Strateg. Manag. J. 2010, 31, 602–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Jo, G.S.; Kang, J. Is high-quality knowledge always beneficial? Knowledge overlap and innovation performance in technological mergers and acquisitions. J. Manag. Organ. 2018, 24, 258–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luypaert, M.; De Maeseneire, W. Antecedents of time to completion in mergers and acquisitions. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2015, 22, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.D.; Holcomb, T.R.; Certo, S.T.; Hitt, M.A.; Lester, R.H. Learning by doing: Cross-border mergers and acquisitions. J. Bus. Res. 2009, 62, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontis, N.; Wu, S.; Chen, M.C.; Cheng, S.J.; Hwang, Y. An empirical investigation of the relationship between intellectual capital and firms’ market value and financial performance. J. Intellect. Cap. 2005, 6, 159–176. [Google Scholar]
- King, D.R.; Slotegraaf, R.J.; Kesner, I. Performance implications of firm resource interactions in the acquisition of R&D-intensive firms. Organ. Sci. 2008, 19, 327–340. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, S.; Saadi, S.; Zhu, P. Finance, Does payment method matter in cross-border acquisitions? Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2013, 25, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccio, M.; Masulis, R.W. The choice of payment method in European mergers and acquisitions. J. Financ. 2005, 60, 1345–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.J. The method of payment in corporate acquisitions, investment opportunities, and management ownership. J. Financ. 1996, 51, 1227–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemmanur, T.J.; Paeglis, I.; Simonyan, K. The medium of exchange in acquisitions: Does the private information of both acquirer and target matter? J. Corp. Financ. 2009, 15, 523–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragozzino, R.; Reuer, J.J. Mind the information gap: Putting new selection criteria and deal structures to work in M&A. J. Appl. Corp. Financ. 2007, 19, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Bruton, G.D.; Oviatt, B.M.; White, M.A. Performance of acquisitions of distressed firms. Acad. Manag. J. 1994, 37, 972–989. [Google Scholar]
- Fowler, K.L.; Schmidt, D.R. Determinants of tender offer post-acquisition financial performance. Strateg. Manag. J. 1989, 10, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markides, C.C.; Ittner, C.D. Shareholder benefits from corporate international diversification: Evidence from US international acquisitions. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 1994, 25, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Woywode, M. Light-Touch Integration of Chinese Cross-Border M&A: The Influences of Culture and Absorptive Capacity. Thunderbird Int. Bus. Rev. 2013, 55, 469–483. [Google Scholar]
- Reus, T.H.; Lamont, B.T. The double-edged sword of cultural distance in international acquisitions. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2009, 40, 1298–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, H.R. Organizational Learning from Performance Feedback: A Behavioral Perspective on Innovation and Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Haleblian, J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Rajagopalan, N. The influence of acquisition experience and performance on acquisition behavior: Evidence from the US commercial banking industry. Acad. Manag. J. 2006, 49, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dikova, D.; Sahib, P.R. Is cultural distance a bane or a boon for cross-border acquisition performance? J. World Bus. 2013, 48, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Porta, R.; Lopez-de-Silanes, F.; Shleifer, A.; Vishny, R. Investor protection and corporate governance. J. Financ. Econ. 2000, 58, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weber, Y.; Tarba, S.Y.; Reichel, A. A model of the influence of culture on integration approaches and international mergers and acquisitions performance. Int. Stud. Manag. Organ. 2011, 41, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amit, R.; Schoemaker, P.J. Strategic assets and organizational rent. Strateg. Manag. J. 1993, 14, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollinger, A.S.; Smith, R.D. Managing organizational knowledge as a strategic asset. J. Knowl. Manag. 2001, 5, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J.; Pisano, G.; Shuen, A. Dynamic capabilities and strategic management. Strateg. Manag. J. 1997, 18, 509–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalisin, M.D.; Smith, R.D.; Kline, D.M. In search of strategic assets. Int. J. Organ. Anal. 1997, 5, 360–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.; Alcácer, J. Knowledge seeking and location choice of foreign direct investment in the United States. Manag. Sci. 2002, 48, 1534–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gamayuni, R.R. The effect of intangible asset, financial performance and financial policies on the firm value. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2015, 4, 202–212. [Google Scholar]
- Riahi-Belkaoui, A. Intellectual capital and firm performance of US multinational firms. J. Intellect. Cap. 2003, 4, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, R.M.; Fracasso, E.M.; Schmidt, S.; Zen, A.C. Intellectual capital, absorptive capacity and product innovation. Manag. Decis. 2017, 55, 474–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, P.J.; Lubatkin, M. Relative absorptive capacity and interorganizational learning. Strateg. Manag. J. 1998, 19, 461–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, C.-F.; Chen, Y.-J.; Peng, J.-T. Manufacturing intelligence for semiconductor demand forecast based on technology diffusion and product life cycle. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2010, 128, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yli-Renko, H.; Autio, E.; Sapienza, H.J. Social capital, knowledge acquisition, and knowledge exploitation in young technology-based firms. Strateg. Manag. J. 2001, 22, 587–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Pavitt, K. The technological competencies of the world’s largest firms: Complex and path-dependent, but not much variety. Res. Policy 1997, 26, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, A.; Song, K.P.; Pettit, R.R. Value creation and destruction in cross-border acquisitions: An empirical analysis of foreign acquisitions of US firms. Strateg. Manag. J. 2002, 23, 921–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, J.G. Big samples and small effects: Let’s not trade relevance and rigor for power. Acad. Manag. J. 2010, 53, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Kapil, S. Explaining M&A performance: A review of empirical research. J. Strategy Manag. 2012, 5, 284–330. [Google Scholar]
- Sirmon, D.G.; Hitt, M.A. Contingencies within dynamic managerial capabilities: Interdependent effects of resource investment and deployment on firm performance. Strateg. Manag. J. 2009, 30, 1375–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-H.; Lin, C.-P. The impact of corporate charitable giving on hospitality firm performance: Doing well by doing good? Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2015, 47, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Miao, Y.; Su, C.-H.J.; Chen, M.-H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, T. Does Corporate charitable giving help sustain corporate performance in China? Sustainability 2019, 11, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruton, G.D.; Ahlstrom, D.; Wan, J.C. Turnaround in East Asian firms: Evidence from ethnic overseas Chinese communities. Strateg. Manag. J. 2003, 24, 519–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Barrionuevo, M.M.; García-Morales, V.J.; Molina, L.M. Validation of an instrument to measure absorptive capacity. Technovation 2011, 31, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schildt, H.; Keil, T.; Maula, M. The temporal effects of relative and firm-level absorptive capacity on interorganizational learning. Strateg. Manag. J. 2012, 33, 1154–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Wu, Y.-J.; Chang, C.; Wang, W.; Lee, C.-Y. The alliance innovation performance of R&D alliances—The absorptive capacity perspective. Technovation 2012, 32, 282–292. [Google Scholar]
- Berchicci, L.; de Jong, J.P.; Freel, M. Remote collaboration and innovative performance: The moderating role of R&D intensity. Ind. Corp. Chang. 2016, 25, 429–446. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, G.S.; Park, G.; Kang, J. Unravelling the link between technological M&A and innovation performance using the concept of relative absorptive capacity. Asian J. Technol. Innov. 2016, 24, 55–76. [Google Scholar]
- Crook, T.R.; Ketchen, D.J., Jr.; Combs, J.G.; Todd, S.Y. Strategic resources and performance: A meta-analysis. Strateg. Manag. J. 2008, 29, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R. The strategic analysis of intangible resources. Strateg. Manag. J. 1992, 13, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kile, C.O.; Phillips, M.E. Using industry classification codes to sample high-technology firms: Analysis and recommendations. J. Account. Audit. Financ. 2009, 24, 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasija, D.; Liou, R.S.; Ellstrand, A. Navigating the new normal: Political affinity and multinationals’ post-acquisition performance. J. Manag. Stud. 2020, 57, 569–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatten, T.C.; Greve, G.I.; Brettel, M. Absorptive capacity and firm performance in SMEs: The mediating influence of strategic alliances. Eur. Manag. Rev. 2011, 8, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capron, L. The long-term performance of horizontal acquisitions. Strateg. Manag. J. 1999, 20, 987–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, P.M.; Serrasqueiro, Z.; Leitão, J. Is there a linear relationship between R&D intensity and growth? Empirical evidence of non-high-tech vs. high-tech SMEs. Res. Policy 2012, 41, 36–53. [Google Scholar]
- Dow, D.; Karunaratna, A. Developing a multidimensional instrument to measure psychic distance stimuli. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2006, 37, 578–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.; Porter, M.E.; Stern, S. Defining clusters of related industries. J. Econ. Geogr. 2016, 16, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-J. An examination of board and firm performance: Evidence from Taiwan. Int. J. Bus. Financ. Res. 2011, 5, 17–34. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E.; Tatham, R.L. Multivariate Data Analysis; Pearson: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1998; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, T.P. Modern Regression Techniques; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gulati, R.; Lavie, D.; Singh, H. The nature of partnering experience and the gains from alliances. Strateg. Manag. J. 2009, 30, 1213–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, L.S.; West, S.G.; Reno, R.R. Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.K.; Kim, J.M. The geography of block acquisitions. J. Financ. 2008, 63, 2817–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarba, S.Y.; Ahammad, M.F.; Junni, P.; Stokes, P.; Morag, O. The impact of organizational culture differences, synergy potential, and autonomy granted to the acquired high-tech firms on the M&A performance. Group Organ. Manag. 2019, 44, 483–520. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, B.-W.; Lee, Y.; Hung, S.-C. R&D intensity and commercialization orientation effects on financial performance. J. Bus. Res. 2006, 59, 679–685. [Google Scholar]
- Schaltegger, S.; Windolph, S.; Herzig, C. A longitudinal analysis of the knowledge and application of sustainability management tools in large German companies. Soc. Econ. 2012, 34, 549–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgelman, R.A. Strategy making as a social learning process: The case of internal corporate venturing. Interfaces 1988, 18, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.; Baek, C.; Lee, J.-D. Effects of knowledge accumulation strategies through experience and experimentation on firm growth. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 144, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.; Kim, J. The impact of experience on private target acquisition in high-technology industries. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reuer, J.J.; Ragozzino, R. The choice between joint ventures and acquisitions: Insights from signaling theory. Organ. Sci. 2012, 23, 1175–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martín-de Castro, G. Knowledge management and innovation in knowledge-based and high-tech industrial markets: The role of openness and absorptive capacity. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2015, 47, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuer, J.J.; Shenkar, O.; Ragozzino, R. Mitigating risk in international mergers and acquisitions: The role of contingent payouts. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2004, 35, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; White, R.S. The relative contributions of foreign technology and domestic inputs to innovation in Chinese manufacturing industries. Technovation 1997, 17, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, W.E.; Sinkula, J.M. Market orientation and the new product paradox. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2005, 22, 483–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purvis, B.; Mao, Y.; Robinson, D. Three pillars of sustainability: In search of conceptual origins. Sustain. Sci. 2019, 14, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arushanyan, Y.; Ekener, E.; Moberg, Å. Sustainability assessment framework for scenarios–SAFS. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2017, 63, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, R.H.; Peterson, N.D.; Arora, P.; Caldwell, K. Five approaches to social sustainability and an integrated way forward. Sustainability 2016, 8, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zijp, M.C.; Heijungs, R.; van der Voet, E.; van de Meent, D.; Huijbregts, M.A.; Hollander, A.; Posthuma, L. An identification key for selecting methods for sustainability assessments. Sustainability 2015, 7, 2490–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Variables | Domestic M&A (n = 325) | CBMA (n = 141) | Difference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| A_Tobin’sQ_3YR | 1.37 | 0.91 | 1.57 | 1.22 | −0.20 * |
| ln_size | 8.32 | 2.08 | 7.39 | 2.16 | 0.93 * |
| A_ROA | 0.04 | 0.15 | −0.01 | 0.38 | 0.06 * |
| A_Age | 52.80 | 45.40 | 49.60 | 49.20 | 3.29 |
| Deal_Duration | 105.00 | 80.90 | 89.00 | 80.50 | 15.99 * |
| ln_dealvalue | 5.88 | 1.85 | 5.16 | 2.00 | 0.73 * |
| A_M&Aexp_3YR | 2.66 | 3.06 | 2.69 | 4.48 | −0.04 |
| A_HighTech | 0.63 | 0.48 | 0.62 | 0.49 | 0.02 |
| Relatedness | 0.68 | 0.47 | 0.74 | 0.44 | −0.06 |
| T_HighTech | 0.67 | 0.47 | 0.58 | 0.49 | 0.08 * |
| Cash payment | 0.71 | 0.45 | 0.48 | 0.50 | 0.24 * |
| ln_intangible | 3.64 | 2.46 | 2.84 | 2.77 | 0.80 * |
| A_R&Dintensity | 0.12 | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0.98 | −0.13 * |
| Matching Method | Treated | Controls | Difference | T-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nearest | 1.53 | 1.26 | 0.264 | 2.04 |
| Kernel | 1.53 | 1.29 | 0.237 | 1.88 |
| Radius | 1.53 | 1.36 | 0.168 | 1.60 |
| Mahalanobis | 1.53 | 0.85 | 0.681 | 3.48 |
| Variables | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A_Tobin’sQ_3YR | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| 2 | ln_Size | −0.14 | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| 3 | A_ROA | 0.05 | 0.27 * | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| 4 | A_Age | −0.28 * | 0.48 * | 0.15 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| 5 | Deal__Duration | −0.08 | 0.31 * | 0.05 | 0.06 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| 6 | ln_Dealvalue | −0.08 | 0.62 * | 0.29 * | 0.28 * | 0.49 * | 1.00 | |||||||
| 7 | A_M&Aexp_3YR | 0.07 | 0.29 * | 0.14 | 0.04 | −0.02 | 0.19 * | 1.00 | ||||||
| 8 | A_HighTech | 0.32 * | −0.25 * | −0.12 | −0.39 * | 0.07 | −0.01 | 0.09 | 1.00 | |||||
| 9 | T_HighTech | 0.07 | −0.12 | −0.06 | −0.30 * | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.53 * | 1.00 | ||||
| 10 | Cash Payment | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.00 | −0.08 | −0.05 | 1.00 | |||
| 11 | Language | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.28 * | 0.04 | −0.15 | 0.09 | −0.15 | −0.13 | 1.00 | ||
| 12 | Relatedness | −0.10 | −0.13 | 0.21 * | 0.07 | −0.08 | 0.02 | −0.08 | −0.01 | 0.05 | 0.13 | −0.11 | 1.00 | |
| 13 | ln_Intangible | −0.09 | 0.33 * | 0.08 | 0.18 * | 0.20 * | 0.35 * | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.03 | −0.04 | 0.06 | −0.06 | 1.00 |
| 14 | A_R&Dintensity | 0.15 | −0.24 * | −0.53 * | −0.24 * | −0.07 | −0.14 | −0.07 | 0.25 * | 0.21 * | −0.10 | −0.06 | 0.00 | −0.18 * |
| Variables | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year Dummies | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ln_Size | −0.021 | −0.022 | −0.017 | −0.003 | −0.001 | 0.001 |
| (−0.67) | (−0.71) | (−0.55) | (−0.10) | (−0.02) | (0.04) | |
| A_ROA | 0.351 † | 0.395 * | 0.414 * | 0.480 * | 0.439 * | 0.506 ** |
| (1.77) | (1.99) | (2.10) | (2.50) | (2.27) | (2.65) | |
| A_Age | −0.002 | −0.002 | −0.001 | −0.001 | −0.001 | −0.001 |
| (−1.49) | (−1.45) | (−1.15) | (−1.21) | (−1.08) | (−1.12) | |
| Deal_Duration | -0.001 * | −0.001 * | −0.001 † | −0.001 | −0.001 † | −0.001 † |
| (−2.04) | (−2.13) | (−1.84) | (−1.62) | (−1.73) | (−1.68) | |
| ln_Dealvalue | 0.076 * | 0.077 * | 0.069 † | 0.062 † | 0.061 † | 0.061 † |
| (2.12) | (2.17) | (1.94) | (1.81) | (1.76) | (1.78) | |
| A_M&Aexp_3YR | 0.018 | −0.028 | 0.018 | 0.020 | 0.015 | −0.014 |
| (1.29) | (−1.32) | (1.35) | (1.48) | (1.14) | (−0.64) | |
| A_HighTech | 0.477 *** | 0.462 *** | 0.410 ** | 0.326 ** | 0.396 ** | 0.330 ** |
| (3.78) | (3.68) | (3.24) | (2.65) | (3.21) | (2.68) | |
| T_HighTech | −0.248 * | −0.240 † | −0.223 † | −0.221 † | 0.017 | −0.091 |
| (−1.97) | (−1.92) | (−1.79) | (−1.83) | (0.13) | (−0.68) | |
| Cash Payment | 0.222 * | 0.213 * | 0.081 | 0.203 * | 0.172 † | 0.215 † |
| (2.10) | (2.03) | (0.72) | (2.01) | (1.68) | (1.94) | |
| Language | 0.100 † | 0.089 | 0.101 † | 0.085 | 0.086 | 0.074 |
| (1.83) | (1.64) | (1.87) | (1.62) | (1.63) | (1.41) | |
| Relatedness | 0.027 | 0.005 | 0.029 | 0.063 | 0.093 | 0.073 |
| (0.27) | (0.05) | (0.29) | (0.65) | (0.95) | (0.75) | |
| ln_Intangible | −0.019 | −0.016 | −0.016 | −0.067 ** | −0.023 | −0.056 * |
| (−0.89) | (−0.77) | (−0.79) | (−3.09) | (−1.11) | (−2.52) | |
| A_R&Dintensity | 0.351 *** | 0.077 | 0.308 *** | 0.339 *** | 3.080 *** | 1.592 * |
| (4.30) | (0.60) | (3.78) | (4.34) | (6.09) | (2.29) | |
| A_R&Dintensity A_M&Aexp_3YR | 0.308 ** (2.79) | 0.211 † (1.84) | ||||
| A_R&Dintensity Cash payment | 1.129 *** | −0.319 | ||||
| (3.31) | (−0.75) | |||||
| A_R&Dintensity ln_intangible | 0.415 *** | 0.311 *** | ||||
| (6.32) | (3.82) | |||||
| A_R&Dintensity T_HighTech | −2.787 *** | −1.456 * | ||||
| (−5.46) | (−2.11) | |||||
| Constant | 0.716 * | 0.846 ** | 0.733 * | 0.649 * | 0.455 | 0.614 * |
| (2.44) | (2.87) | (2.53) | (2.31) | (1.58) | (2.12) | |
| Observations | 141 | 141 | 141 | 141 | 141 | 141 |
| R2 | 0.186 | 0.200 | 0.206 | 0.254 | 0.238 | 0.268 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.133 | 0.147 | 0.153 | 0.204 | 0.187 | 0.214 |
| Log-likelihood | −622.535 | −618.421 | −616.740 | −602.133 | −607.115 | −597.627 |
| F | 3.551 *** | 3.749 *** | 3.885 *** | 5.110 *** | 4.684 *** | 4.953 *** |
| df(m) | 28 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 32 |
| Variables | Model 7 | |
|---|---|---|
| Year Dummy | Yes | |
| ln_size | 0.03 | (0.77) |
| A_ROA | 1.68 ** | (2.63) |
| A_Age | 0.00 | (0.97) |
| Deal_Duration | −0.00 | (−0.60) |
| ln_Dealvalue | −0.23 | (−1.48) |
| A_M&Aexp_3YR | −0.02 | (−0.85) |
| A_HighTech | 0.40 ** | (3.14) |
| T_HighTech | −0.36 | (−1.87) |
| Cash Payment | 0.23 * | (2.09) |
| Language | 0.05 | (1.32) |
| Relatedness | 0.06 | (0.61) |
| ln_Intangible | 0.07 | (1.02) |
| A_R&Dintensity | 1.73 * | (2.49) |
| A_R&Dintensity A_M&Aexp_3YR | 0.21 | (1.87) |
| A_R&Dintensity Cash Payment | −0.34 | (−0.79) |
| A_R&Dintensity ln_intangible | 0.30 *** | (3.73) |
| A_R&Dintensity T_HighTech | −1.56 * | (−2.26) |
| Constant | −0.20 | (−0.39) |
| Lambda | 1.10 | (1.94) |
| Observations | 465 | |
| R2 | 0.274 | |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.221 | |
| Log Likelihood | −595.70 | |
| F | 5.11 *** | |
| Df(m) | 32 | |
| AIC | 1257.40 | |
| BIC | 1394.08 | |
| Variables | Model 8 | Model 9 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Context) | (Domestic M&A) | (CBMA) | ||
| Year Dummy | Yes | Yes | ||
| ln_Size | −0.00 | (−0.09) | −0.01 | (−0.20) |
| A_ROA | 1.19 *** | (4.23) | 1.96 ** | (2.92) |
| A_Age | −0.00 | (−0.04) | −0.00 | (−1.14) |
| Deal_Duration | −0.00 | (−1.69) | −0.00 | (−1.03) |
| ln_Dealvalue | 0.07 | (1.37) | 0.05 | (0.85) |
| A_M&Aexp_3YR | −0.01 | (−0.80) | 0.02 | (0.75) |
| A_HighTech | 0.40 *** | (3.54) | 0.26 * | (2.05) |
| T_HighTech | −0.04 | (−0.30) | −0.10 | (−0.79) |
| Cash Payment | 0.06 | (0.71) | 0.17 | (1.65) |
| Relatedness | 0.26 ** | (3.17) | −0.10 | (−0.85) |
| ln_Intangible | −0.03 | (−1.08) | −0.02 | (−0.50) |
| A_R&Dintensity | 0.31 *** | (5.26) | 2.92 *** | (4.04) |
| Constant | 0.65 ** | (3.02) | 0.99 ** | (3.30) |
| Lambda | −0.10 | (−0.66) | −0.32 | (−1.28) |
| Observations | 325 | 141 | ||
| R2 | 0.233 | 0.331 | ||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.201 | 0.262 | ||
| F | 7.21 *** | 4.79 *** | ||
| Df(m) | 13 | 13 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, Y.; Lee, K.; Roh, T. Acquirer’s Absorptive Capacity and Firm Performance: The Perspectives of Strategic Behavior and Knowledge Assets. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8396. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208396
Bae Y, Lee K, Roh T. Acquirer’s Absorptive Capacity and Firm Performance: The Perspectives of Strategic Behavior and Knowledge Assets. Sustainability. 2020; 12(20):8396. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208396
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Yunjae, Kyungsuk Lee, and Taewoo Roh. 2020. "Acquirer’s Absorptive Capacity and Firm Performance: The Perspectives of Strategic Behavior and Knowledge Assets" Sustainability 12, no. 20: 8396. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208396
APA StyleBae, Y., Lee, K., & Roh, T. (2020). Acquirer’s Absorptive Capacity and Firm Performance: The Perspectives of Strategic Behavior and Knowledge Assets. Sustainability, 12(20), 8396. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208396






