Unprepared to Deal with Invasion: Pre-Service Teachers’ Perception, Knowledge and Attitudes toward Invasive Species
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Sample
2.2. Research Instrument
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Perception of IAS Impacts (Q4)
3.2. Knowledge of IAS Transmission Vectors (Q5)
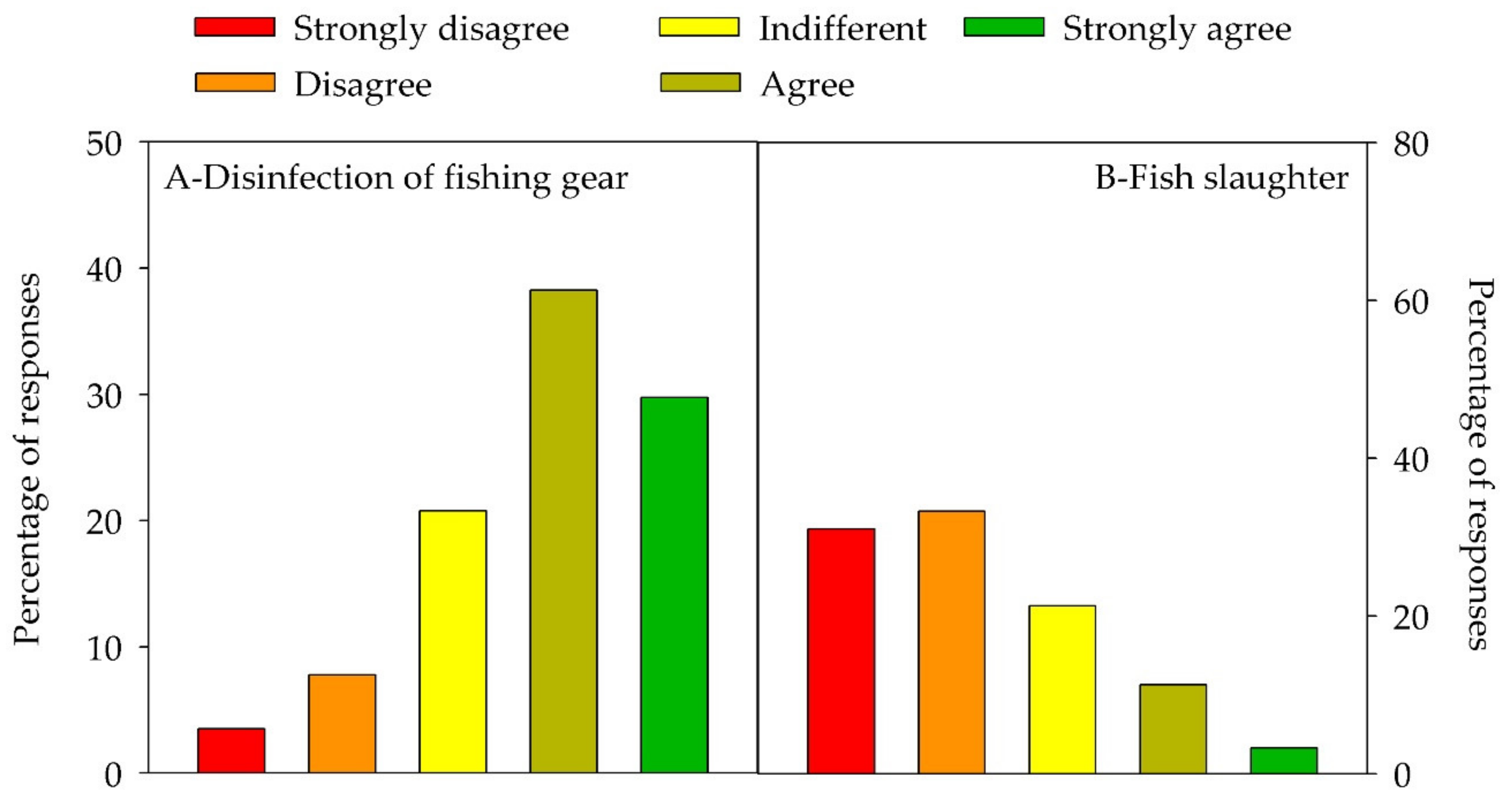
3.3. Attitudes about Control Methods (Q6–Q9)
3.4. Correlations between the Different Items of the Survey
3.5. Groups Comparison
4. Discussion
Final Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Butchart, S.H.M.; Walpole, M.; Collen, B.; Van Strien, A.; Scharlemann, J.P.W.; Almond, R.E.A.; Baillie, J.E.M.; Bomhard, B.; Brown, C.; Bruno, J.; et al. Global biodiversity: Indicators of recent declines. Science 2010, 328, 1164–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo, B.; Bacher, S.; Bradley, B.; Comín, F.A.; Gallien, L.; Jeschke, J.M.; Cascade, C.J.; Vilà, M. InvasiBES: Understanding and managing the impacts of invasive alien species on biodiversity and ecosystem Services. NeoBiota 2019, 50, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyšek, P.; Hulme, P.E.; Simberloff, D.; Bacher, S.; Blackburn, T.M.; Carlton, J.T.; Dawson, W.; Essl, F.; Foxcroft, L.C.; Genovesi, P.; et al. Scientists’ warning on invasive alien species. Biol. Rev. 2020, 95, 1511–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPBES. Summary for Policymakers of the Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services of the Intergovernmental Science—Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services; IPBES Secretariat: Bonn, Germany, 2019.
- Seebens, H.; Blackburn, T.M.; Dyer, E.E.; Genovesi, P.; Hulme, P.E.; Jeschke, J.M.; Pagad, S.; Pyšek, P.; Winter, M.; Arianoutsou, M.; et al. No saturation in the accumulation of alien species worldwide. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Llorente, M.; Martín-López, B.; González, J.A.; Alcorlo, P.; Montes, C. Social perceptions of the impacts and benefits of invasive alien species: Implications for management. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141, 2969–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capinha, C.; Essl, F.; Seebens, H.; Moser, D.; Pereira, H.M. The dispersal of alien species redefines biogeography in the Anthropocene. Science 2015, 348, 1248–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazón, S.; Melero, Y. Status, threats and management actions on the European mink Mustela lutreola (Linnaeus, 1761) in Spain: A review of the studies performed since 1992. Munibe Monogr. Nat. Ser. 2014, 3, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedia, I.; Almeida, D.; Rodeles, A.A.; Leunda, P.M.; Baquero, E.; Galicia, D.; Oscoz, J.; Elustondo, D.; Santamaría, J.M.; Miranda, R. Behavioral interactions and trophic overlap between invasive signal crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus (Decapoda, Astacidae) and native fishes in Iberian rivers. Water 2019, 11, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bacher, S.; Blackburn, T.M.; Essl, F.; Genovesi, P.; Heikkilä, J.; Jeschke, J.M.; Jones, G.; Keller, R.; Kenis, M.; Kueffer, C.; et al. Socio-economic impact classification of alien taxa (SEICAT). Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilà, M.; Basnou, C.; Pyšek, P.; Josefsson, M.; Genovesi, P.; Gollasch, S.; Nentwig, W.; Olenin, S.; Roques, A.; Roy, D.; et al. How well do we understand the impacts of alien species on ecosystem services? A pan-European, cross-taxa assessment. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2010, 8, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertolino, S.; Genovesi, P. Spread and attempted eradication of the grey squirrel (Sciurus carolinensis) in Italy, and consequences for the red squirrel (Sciurus vulgaris) in Eurasia. Biol. Conserv. 2003, 109, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shine, R.; Doody, J.S. Invasive species control: Understanding conflicts between researchers and the general community. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, S.L.; Hinchliffe, S.; McDonald, R.A. The parakeet protectors: Understanding opposition to introduced species management. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 229, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, R.T.; Richardson, D.M.; Shackleton, C.M.; Bennett, B.; Crowley, S.L.; Dehnen-Schmutz, K.; Estévez, R.A.; Fischer, A.; Kueffer, C.; Kull, C.A.; et al. Explaining people’s perceptions of invasive alien species: A conceptual framework. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 229, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espeja, A.G.; Couso, D. Introducing Model-Based Instruction for SSI Teaching in Primary Pre-service Teacher Education. In Science Teacher Education for Responsible Citizenship: Towards a Pedagogy for Relevance Through Socioscientific Issues; Evagorou, M., Nielsen, J.A., Dillon, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 153–171. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, J.S.C.; Wong, K.L.; Chan, K.K.H. Pre-service Secondary Science Teachers’ Beliefs About Teaching Socio-scientific Issues. In Science Teacher Education for Responsible Citizenship: Towards a Pedagogy for Relevance Through Socioscientific Issues; Evagorou, M., Nielsen, J.A., Dillon, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 21–39. [Google Scholar]
- Evagorou, M.; Dillon, J. Socio-scientific Issues as Promoting Responsible Citizenship and the Relevance of Science. In Science Teacher Education for Responsible Citizenship: Towards a Pedagogy for Relevance Through Socioscientific Issues; Evagorou, M., Nielsen, J.A., Dillon, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, C.; Luque, G.M.; Courchamp, F. The twenty most charismatic species. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dunn, M.; Marzano, M.; Forster, J.; Gill, R.M.A. Public attitudes towards “pest” management: Perceptions on squirrel management strategies in the UK. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 222, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcliffe, C.; Quinn, C.H.; Shannon, C.; Glover, A.; Dunn, A.M. Exploring the attitudes to and uptake of biosecurity practices for invasive non-native species: Views amongst stakeholder organisations working in UK natural environments. Biol. Invasions 2018, 20, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shannon, C.; Stebbing, P.D.; Quinn, C.H.; Warren, D.A.; Dunn, A.M. The effectiveness of e-Learning on biosecurity practice to slow the spread of invasive alien species. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 2559–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, A.; Park, K. Public attitudes to the management of invasive non-native species in Scotland. Biol. Conserv. 2007, 139, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindemann-Matthies, P. Beasts or beauties? Laypersons’ perception of invasive alien plant species in Switzerland and attitudes towards their management. NeoBiota 2016, 29, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waliczek, T.M.; Williamson, P.S.; Oxley, F.M. College student knowledge and perceptions of invasive species. HortTechnology 2017, 27, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larson, D.L.; Phillips-Mao, L.; Quiram, G.; Sharpe, L.; Stark, R.; Sugita, S.; Weiler, A. A framework for sustainable invasive species management: Environmental, social, and economic objectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, R.F. Using transformative learning theory to explore the mechanisms of citizen participation for environmental education on the removal of invasive species: The case of Green Island, Taiwan. Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2017, 13, 2665–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapitza, K.; Zimmermann, H.; Martín-López, B.; Wehrden, H. von Research on the social perception of invasive species: A systematic literature review. NeoBiota 2019, 43, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, R.T.; Adriaens, T.; Brundu, G.; Dehnen-Schmutz, K.; Estévez, R.A.; Fried, J.; Larson, B.M.H.; Liu, S.; Marchante, E.; Marchante, H.; et al. Stakeholder engagement in the study and management of invasive alien species. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 229, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, D.; Hansmann, R.; Činčera, J.; Radović, V.; Telešienė, A.; Balžekienė, A.; Vávra, J. Education for Environmental Citizenship and Responsible Environmental Behaviour. In Conceptualizing Environmental Citizenship for 21st Century Education; Hadjichambis, A.C., Reis, P., Paraskeva-Hadjichambi, D., Činčera, J., Pauw, J.B.-D., Gericke, N., Knippels, M.-C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 115–137. [Google Scholar]
- Parra, G.; Hansmann, R.; Hadjichambis, A.C.; Goldman, D.; Paraskeva-Hadjichambi, D.; Sund, P.; Sund, L.; Gericke, N.; Conti, D. Education for Environmental Citizenship and Education for Sustainability. In Conceptualizing Environmental Citizenship for 21st Century Education; Hadjichambis, A.C., Reis, P., Paraskeva-Hadjichambi, D., Činčera, J., Pauw, J.B.-D., Gericke, N., Knippels, M.-C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 149–160. [Google Scholar]
- Huxham, M.; Welsh, A.; Berry, A.; Templeton, S. Factors influencing primary school children’s knowledge of wildlife. J. Biol. Educ. 2006, 41, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, J.; Meñika, A.; Sanz-Azkue, I.; Ortuzar, A. Urban and Rural Children’s Knowledge on Biodiversity in Bizkaia: Tree Identification Skills and Animal and Plant Listing. Int. J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2018, 12, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballouard, J.M.; Brischoux, F.; Bonnet, X. Children prioritize virtual exotic biodiversity over local biodiversity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frumkin, H.; Bratman, G.N.; Breslow, S.J.; Cochran, B.; Kahn, P.H.; Lawler, J.J.; Levin, P.S.; Tandon, P.S.; Varanasi, U.; Wolf, K.L.; et al. Nature contact and human health: A research agenda. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Goodale, E.; Chen, J. How contact with nature affects children’s biophilia, biophobia and conservation attitude in China. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 177, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MECD. Real Decreto 126/2014, de 28 de Febrero, por el que se Establece el Currículo Básico de la Educación Primaria; Ministerio de Educación Cultura y Deporte: Madrid, Spain, 2014.
- MECD. Real Decreto 1105/2014, de 26 de Diciembre, por el que se Establece el Currículo Básico de la Educación Secundaria Obligatoria y del Bachillerato; Ministerio de Educación Cultura y Deporte: Madrid, Spain, 2015.
- Remmele, M.; Lindemann-Matthies, P. Dead or alive? Teacher students’ perception of invasive alien animal species and attitudes towards their management. Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2020, 16, em1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, C.; Medina-Jerez, W.; Bryant, C. Cultivating environmental citizenship in teacher education. Teach. Educ. 2016, 27, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, D.; Sisk-Hilton, S. Nature and Environmental Education in Early Childhood. N. Educ. 2017, 13, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter-Beuschel, L.; Bögeholz, S. Knowledge of Student Teachers on Sustainable Land Use Issues–Knowledge Types Relevant for Teacher Education. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, C.; Gericke, N.; Höglund, H.-O.; Bergman, E. The barriers encountered by teachers implementing education for sustainable development: Discipline bound differences and teaching traditions. Res. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2012, 30, 185–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiebelkorn, F.; Menzel, S. Student Teachers’ Understanding of the Terminology, Distribution, and Loss of Biodiversity: Perspectives from a Biodiversity Hotspot and an Industrialized Country. Res. Sci. Educ. 2013, 43, 1593–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büssing, A.G.; Schleper, M.; Menzel, S. Do pre-service teachers dance with wolves? Subject-specific teacher professional development in a recent biodiversity conservation issue. Sustainability 2018, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gozlan, R. The cost of non-native aquatic species introductions in Spain: Fact or fiction? Aquat. Invasions 2010, 5, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardsley, D.; Edwards-Jones, G. Stakeholders’ perceptions of the impacts of invasive exotic plant species in the Mediterranean region. GeoJournal 2006, 65, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oxley, F.M.; Waliczek, T.M.; Williamson, P.S. Stakeholder opinions on invasive species and their management in the San Marcos River. HortTechnology 2016, 26, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verbrugge, L.N.H.; Van Den Born, R.J.G.; Lenders, H.J.R. Exploring public perception of non-native species from a visions of nature perspective. Environ. Manag. 2013, 52, 1562–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, S.K.; Miller, B.G.; Eitel, K.B.; Cohn, T.C. Assessing Teachers’ Environmental Citizenship Based on an Adventure Learning Workshop: A Case Study from a Social-ecological Systems Perspective. J. Sci. Teach. Educ. 2020, 31, 869–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, A. Environmental Citizenship and Pro-Environmental Behavior: Rapid Research and Evidence Review; Sustainable Development Research Network: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hadjichambis, A.C.; Reis, P. Introduction to the Conceptualisation of Environmental Citizenship for 21st Century Education. In Conceptualizing Environmental Citizenship for 21st Century Education; Hadjichambis, A.C., Reis, P., Paraskeva-Hadjichambi, D., Činčera, J., Pauw, J.B.-D., Gericke, N., Knippels, M.-C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld, J.; Clarke, A.; Nally, R.M.; Bond, N.; Lake, P.S. Flow permanence affects aquatic macroinvertebrate diversity and community structure in three headwater streams in a forested catchment. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 67, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-López, R.; Eugenio-Gozalbo, M.; Zuazagoitia, D.; Ruiz-González, A. Organic Learning Gardens in Higher Education: Do They Improve Kindergarten Pre-service Teachers’ Connectedness to and Conception of Nature? Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmori, A.; Santos, I.; Carbonell, R. The American mink Neovison vison (Schreber 1777) in Spain: Possible causes of its spread and interaction with other semi-aquatic mammals. Ecosistemas 2015, 24, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, R.; Valladolid, M.; Gómez, I. Life cycle and density of a newcomer population of zebra mussels in the Ebro River, Spain. In The Zebra Mussel in Europe; Van der Velde, G., Rajagopal, S., Bij de Vaate, A., Eds.; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Ladrera, R.; Gomà, J.; Prat, N. Effects of Didymosphenia geminata massive growth on stream communities: Smaller organisms and simplified food web structure. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceda-Veiga, A. Towards the conservation of freshwater fish: Iberian Rivers as an example of threats and management practices. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2012, 23, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waliczek, T.M.; Parsley, K.M.; Williamson, P.S.; Oxley, F.M. Curricula influence college student knowledge and attitudes regarding invasive species. HortTechnology 2018, 28, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.G.; White, P.C.L.; Stebbing, P.D.; Stentiford, G.D.; Dunn, A.M. Biosecurity and vector behaviour: Evaluating the potential threat posed by anglers and canoeists as pathways for the spread of invasive non-native species and pathogens. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, B.L.; Hernández, K.L.; Frangópulos, M.; Bauer, G.; Lorca, M.; Kilroy, C.; Spaulding, S. The invasion of the freshwater diatom Didymosphenia geminata in Patagonia: Prospects, Strategies, And implications for biosecurity of invasive microorganisms in continental waters. Conserv. Lett. 2012, 5, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENEC (European Network for Environmental Citizenship). Defining “Education for Environmental Citizenship”. Available online: http://enec-cost.eu/our-approach/education-for-environmental-citizenship/ (accessed on 19 October 2020).
- Simonneaux, L.; Simonneaux, J. Socio-scientific reasoning influenced by identities. Cult. Stud. Sci. Educ. 2009, 4, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadler, T.D.; Zeidler, D.L. The significance of content knowledge for informal reasoning regarding socioscientific issues: Applying genetics knowledge to genetic engineering issues. Sci. Educ. 2005, 89, 71–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnworth, M.J.; Watson, H.; Adams, N.J. Understanding Attitudes Toward the Control of Nonnative Wild and Feral Mammals: Similarities and Differences in the Opinions of the General Public, Animal Protectionists, and Conservationists in New Zealand (Aotearoa). J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2014, 17, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olszańska, A.; Solarz, W.; Najberek, K. To kill or not to kill—Practitioners’ opinions on invasive alien species management as a step towards enhancing control of biological invasions. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 58, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, J.A. Ethics and care: For animals, not just mammals. Animals 2019, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leandro, C.; Jay-Robert, P. Perceptions and representations of animal diversity: Where did the insects go? Biol. Conserv. 2019, 237, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Torrijos, L.; Kokko, H.; Makkonen, J.; Jussila, J.; Diéguez-Uribeondo, J. Mapping 15 years of crayfish plague in the Iberian Peninsula: The impact of two invasive species on the endangered native crayfish. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, D.; Ribeiro, F.; Leunda, P.M.; Vilizzi, L.; Copp, G.H. Effectiveness of FISK, an invasiveness screening tool for non-native freshwater fishes, to perform risk identification assessments in the Iberian Peninsula. Risk Anal. 2013, 33, 1404–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvira, B.; Almodóvar, A. Freshwater fish introductions in Spain: Facts and figures at the beginning of the 21st century. J. Fish Biol. 2001, 59, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermoso, V.; Clavero, M.; Blanco-Garrido, F.; Prenda, J. Invasive species and habitat degradation in Iberian streams: An analysis of their role in freshwater fish diversity loss. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.; Leunda, P.M. Non-native fish impacts on Mediterranean freshwater ecosystems: Current knowledge and research needs. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2012, 19, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Labajos, B.; Binimelis, R.; Monterroso, I.; Martinez-Alier, J. The arrival of Dreissena polymorpha and Silurus glanis in the Ebro River: Socio-economics of interlinked aquatic bioinvasions. In Assessing Biodiversity Risks with Socio-Economic Methods: The ALARM Experience; Rodriguez-Labajos, B., Spangenberg, J.H., Maxim, L., Martinez-Alier, J., Binimelis, R., Gallai, N., Kuldna, P., Monterroso, I., Peterson, K., Uustal, M., Eds.; PenSoft Publishers: Sofia, Bulgaria; PenSoft Publishers: Moscow, Russia, 2009; pp. 69–111. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi, R.A.; Pastre, C.M.; Vanderlei, L.C.M.; Godoy, M.F. Poincaré plot indexes of heart rate variability: Relationships with other nonlinear variables. Auton. Neurosci. 2013, 177, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Item | IPS | VKS |
|---|---|---|
| VKS | 0.307 * | |
| Always eliminate IAS | 0.197 * | 0.089 |
| Mink sterilization | 0.117 * | 0.136 * |
| Mink slaughter | 0.055 | 0.093 |
| Mink translocation | 0.157 * | 0.186 * |
| Mink none | −0.160 * | −0.205 * |
| Crab slaughtered by forestry agents | 0.150 * | 0.229 * |
| Crab slaughtered by citizens | 0.020 | −0.023 |
| Crab pesticides | −0.067 | −0.086 |
| Crab none | −0.134 * | −0.161 * |
| Obligating to disinfect | 0.298 * | 0.242 * |
| Invasive fish must be killed | 0.183 * | 0.171 * |
| Item | Baccalaureate Natural-Health Sciences (0)–Other Baccalaureates (1) | Early Childhood (0)–Primary (1) | Nature Association (0)–No (1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| IPS | 0 | - | - |
| VKS | - | - | 0 |
| Always eliminate IAS | - | - | - |
| Mink sterilization | - | - | 0 |
| Mink slaughter | - | - | - |
| Mink translocation | - | - | - |
| Crab slaughtered by forestry agents | - | - | - |
| Crab slaughtered by citizens | 0 | - | 0 |
| Crab pesticides | - | - | - |
| Crab none | - | - | - |
| Obligating to disinfect | - | - | - |
| Invasive fish must be killed | - | - | - |
| Score perception of impacts | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ladrera, R.; Robredo, B.; Ortega-Lasuen, U.; Díez, J.R.; Ruiz-González, A. Unprepared to Deal with Invasion: Pre-Service Teachers’ Perception, Knowledge and Attitudes toward Invasive Species. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10543. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122410543
Ladrera R, Robredo B, Ortega-Lasuen U, Díez JR, Ruiz-González A. Unprepared to Deal with Invasion: Pre-Service Teachers’ Perception, Knowledge and Attitudes toward Invasive Species. Sustainability. 2020; 12(24):10543. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122410543
Chicago/Turabian StyleLadrera, Rubén, Beatriz Robredo, Unai Ortega-Lasuen, José Ramón Díez, and Aritz Ruiz-González. 2020. "Unprepared to Deal with Invasion: Pre-Service Teachers’ Perception, Knowledge and Attitudes toward Invasive Species" Sustainability 12, no. 24: 10543. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122410543
APA StyleLadrera, R., Robredo, B., Ortega-Lasuen, U., Díez, J. R., & Ruiz-González, A. (2020). Unprepared to Deal with Invasion: Pre-Service Teachers’ Perception, Knowledge and Attitudes toward Invasive Species. Sustainability, 12(24), 10543. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122410543








