Status and Challenges of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau’s Grasslands: An Analysis of Causes, Mitigation Measures, and Way Forward
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Methodology
2. Status of Grassland Degradation on the QTP
2.1. Quantification Attempts of Degraded Grasslands on the QTP
2.2. Drivers of Grassland Degradation on the QTP
2.3. Grassland Degradation as a Result of Anthropogenic Activities
2.4. Degradation Due to Intensive Overgrazing
2.5. Degradation Caused by Climate Change
2.6. Degradation Caused by Small Rodents
2.7. Other Uncertain Factors of Grassland Degradation on the QTP
2.8. Grassland Degradation Versus Livelihood Challenge on the QTP
3. Effects of Grassland Degradation on Biodiversity and Soil Properties on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau
3.1. Effects of Grassland Degradation on Plant Species Vegetation
3.2. Effects of Grassland Degradation on Soil Properties
4. Grassland Ecosystem Restoration and Rehabilitation Efforts: Improved Grassland Management Practices
4.1. Grassland Ecosystem Restoration Efforts at a Global Scale
4.2. Chinese Authority’s Interventions in Combating Grassland Degradation and Ensuring Ecological Restoration Across Grasslands and other Ecosystems in China
4.3. Grassland Ecosystem Restoration Outcomes on the QTP
5. Conclusions and the Way Forward
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dingguo, Y. Degradation and protection of grassland on the Qinghai-Tibet plateau Erosion, Debris Flows and Environment in Mountain Regions (Proceedings of the Chengdu Symposium, July 1992). IAHS Pub. 1992, 209, 471. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.K.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.Y.; Liu, S.L.; Dong, Q.M.; Zhou, H.K.; Yeomans, J.; Li, S.; Gao, X.X. Effect of grassland degradation on aggregate-associated soil organic carbon of alpine grassland ecosystems in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zamanianb, K.; Schleussa, P.; Zarebanadkoukic, M.; Kuzyakova, Y. Degradation of Tibetan grasslands: Consequences for carbon and nutrient cycles. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 252, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Dong, C.X.; Li, B.L.; Yao, Y.H. Biodiversity and conservation in the Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2002, 12, 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; Tang, W. Land Use and Land Cover Change in the Qinghai Lake Region of the Tibetan Plateau and Its Impact on Ecosystem Services. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shijin, W.; Lanyue, Z.; Yanqiang, W. Integrated risk assessment of snow disaster over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geomatics. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 740–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.L.; Gao, J.; Brierley, G.; Qiao, Y.M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.W. Rangeland Degradation on The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Implications for Rehabilitation. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscha, A.; Dörfera, C.; He, J.; Schmidt, K.; Scholtena, T. Predicting soil respiration for the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: An empirical comparison of regression models. Pedobiologia 2016, 59, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fang, J.; Smith, P.; Tang, Y.; Chen, A.; Ji, C.; Hu, H.; Rao, S.; Tan, K.U.N.; He, J.-S. Changes in topsoil carbon stock in the Tibetan grasslands between the 1980 and 2004. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 2723–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Gong, T.L.; Li, J.Y. Decadal trend of climate in the Tibetan Plateau—Regional temperature and precipitation. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 3056–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The Yak Second Edition “Conservation and Use of Animal Genetic Resources in Asia and the Pacific” Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Bangkok, Thailand. 2003. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/ad347e/ad347e0w.htm#TopOfPage (accessed on 22 October 2019).
- Cui, X.; Graf, H.F. Recent land cover changes on the Tibetan Plateau: A review. Clim. Chang. 2009, 94, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, S.K.; Sherman, K. Enhancing the resilience of coupled human and natural systems of alpine rangelands on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Rangel. J. 2015, 37, i–iii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, J.; Cui, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, F.; Pang, Z.; Xu, N. Changes in Biomass and Quality of Alpine Steppe in Response to N & P Fertilization in the Tibetan Plateau. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, J.; Zhang, J.; Nie, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Sun, H. Evolutionary diversifications of plants on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, L.; Duan, X.; Kong, F.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Hu, S. Influences of climate change on area variation of Qinghai Lake on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau since 1980s. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, T.; Xu, B.; Yang, X.; Jin, Y.; Ma, H.; Li, J. Review of researches on biomass carbon Stock in grassland ecosystem of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2012, 31, 1724–1731. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Y.; Yi, S.H.; Wu, Q.B.; Yang, K.; Ding, Y.J. The role of permafrost and soil water in distribution of alpine grassland and its NDVI dynamics on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Planet Chang. 2016, 147, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anon. Ecological Progress on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. 2018. Available online: http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/201807/19/WS5b4fd51aa310796df4df752c_3.html (accessed on 15 May 2019).
- Lu, H.; Liu, G. Trends in temperature and precipitation on the Tibetan Plateau, 1961–2005. Clim. Res. 2010, 43, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.L.; Du, G.Z.; Liu, Z.H.; Thirgood, S. Effect of fencing and grazing on a Kobresia-dominated meadow in the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Plant Soil. 2009, 319, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Chen, Y.; Sun, W.; Huang, Y. Effects of grazing exclusion on soil carbon dynamics in alpine grasslands of the Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma 2019, 353, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Zu, J.; Paudel, B. Increasing sensitivity of alpine grasslands to climate variability along an elevational gradient on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuenkamp, L.; Prober, S.M.; Price, J.N.; Zobel, M.; Standish, R.J. Benefits of mycorrhizal inoculation to ecological restoration depend on plant functional type, restoration context and time. Fungal. Ecol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Shao, Q. The spatial and temporal characteristics of grassland degradation in the Three-River Headwaters region in Qinghai Province. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2008, 63, 364–377. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Shao, Q.; Liu, J.; Lu, Q. Improving ecological conservation and restoration through payment for ecosystem services in Northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 31, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.K.; Wen, L.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, X.X.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.Y. Soil-Quality Effects of Grassland Degradation and Restoration on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 2256–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Dong, S.K.; Yang, B.; Li, Y.Y.; Su, X.K. The effects of grassland degradation on plant diversity, primary productivity, and soil fertility in the alpine region of Asia’s headwaters. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 6903–6917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.; Dong, S.K.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Shi, J.J.; Wang, Y.L.; Ma, Y.S. Effect of degradation intensity on grassland ecosystem services in the alpine region of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, R.; Das, A.J. Climate Change and its Impact on Land Degradation: Imperative Need to Focus. J. Climatol. Weather Forecast. 2014, 2, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Perry, G.L.W.; Brierley, G.J. A spatial simulation model to assess controls upon grassland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 98, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassnacht, F.E.; Li, L.; Fritz, A. Mapping degraded grassland on the Eastern Tibetan Plateau with multi-temporal Landsat 8 data - where do the severely degraded areas occur? Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2015, 42, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Kelsey, K.C.; Yan, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Cheng, G.; Neff, J.C. Effects of grazing on ecosystem structure and function of alpine grasslands in Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau: A synthesis. Ecosphere 2017, 8, e01656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Adamowski, J.F.; Deo, R.C.; Xu, X.; Gong, Y.; Feng, Q. Grassland Degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: Reevaluation of Causative Factors. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 72, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Hu, H.; Sun, W.; Zhu, J.; Liu, G.; Zhou, W.; Shi, P. Effects of national ecological restoration projects on carbon sequestration in China from 2001 to 2010. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4039–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mirza, M.M.Q. Climate change and extreme weather events: Can developing countries adapt? Clim. Policy 2003, 3, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Managing soils and ecosystems for mitigating anthropogenic carbon emissions and advancing global food security. BioScience 2010, 60, 708–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, L.; Du, B.; Wei, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Sheng, W. Assessing the effects of ecological restoration approaches in the alpine rangelands of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- NDRC (National Development and Reform Commission of People’s Republic of China). Major Function Oriented Zoning of China; People’s Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2015. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Z.H.; Gibb, M.J.; Leiber, F.; Ismail, M.; Ding, L.M.; Guo, X.S.; Long, R.J. The sustainable development of grassland-livestock systems on the Tibetan plateau: Problems, strategies and prospects. Rangel. J. 2014, 36, 267–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, R.B. Rangeland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau: A review of the evidence of its magnitude and causes. J. Arid Environ. 2010, 74, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Gang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, J. Quantitative assess the driving forces on the grassland degradation in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, in China. Ecol. Inform. 2016, 33, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, M.C.; Jiao, B.; Beall, C.M.; Tsering, P. Development and Change in Rural Tibet. Asian Surv. 2003, 43, 758–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, L.W.; Meyer, H.; Meyer, N.; Reudenbach, C.; Bendix, J. A hyperspectral indicator system for rangeland degradation on the Tibetan Plateau: A case study towards spaceborne monitoring. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 39, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chang, S.; Hou, F. Grazing management options for restoration of alpine grasslands on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecosphere 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, J.F.; Chen, S.P.; Kato, T.; Zhou, G.S. A comparison of satellite-derived vegetation indices for approximating gross primary productivity of grasslands. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 67, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Gang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, J. Comparative assessment of grassland degradation dynamics in response to climate variation and human activities in China, Mongolia, Pakistan and Uzbekistan from 2000 to 2013. J. Arid. Environ. 2016, 135, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, H.; Huang, L.; Chen, C.; Lin, X.; Hu, Z.; Li, J. Grassland degradation remote sensing monitoring and driving factors quantitative assessment in China from 1982 to 2010. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 83, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Ma, Y.S. Qinghai Yak production system. In Conservation and Management of Yak Genetic Diversity; Miller, D.J., Craig, S.R., Rana, G.M., Eds.; ICIMOD: Kathmandu, Nepal, 1997; pp. 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.K.; Wu, Y.; Dong, S.K.; Wen, L.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, X.X. Effects of grassland degradation and re-vegetation on carbon and nitrogen storage in the soils of the Headwater Area Nature Reserve on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2015, 12, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.H.; Long, R. Formation causes and recovery of the “Black Soil Type” degraded alpine grassland in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Front. Agric. China 2007, 1, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Jinlan, W.; Xiaojiao, Z.; Shangli, S.; Wenxia, C. Effect of degradation and rebuilding of artificial grasslands on soil respiration and carbon and nitrogen pools on an alpine meadow of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 111, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, X.; Tang, Y.; Gu, S.; Zhou, L. Alpine grassland degradation and its control in the source region of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, China. Grassl. Sci. 2006, 51, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Shi, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Shao, H.; Xian, W.; Peng, P.; Li, Q. Monitoring the Grassland Change in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: A Case Study on Aba County. J. Indian Soc. Remote 2017, 46, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Yang, X.; Xu, X. Human-induced grassland degradation/restoration in the central Tibetan Plateau: The effects of ecological protection and restoration projects. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 83, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yi, S.; Qin, Y. The contribution of plateau pika disturbance and erosion on patchy alpine grassland soil on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: Implications for grassland restoration. Geoderma 2017, 297, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Ma, W.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z. The impacts of climate change and human activities on alpine vegetation and permafrost in the Qinghai-Tibet Engineering Corridor. Ecol. Ind. 2018, 93, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.C.; Peng, H.; Chen, F.; Dong, W.; Ning, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, Y.; He, S.; Shi, X.; et al. Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau peatland sustainable utilization under anthropogenic disturbances and climate change. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2017, 3, e01263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.; Lassoie, J.P.; Morreale, S.J.; Dong, S.K. A critical review of socioeconomic and natural factors in ecological degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Rangel. J. 2015, 37, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.X.; Li, Y.S.; Wang, Y.B.; Chen, L. Typical alpine wetland system changes on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in recent 40 years. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2007, 5, 481–491. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.X. Qinghai Geography; Qinghai People’s Publishing House: Xining, China, 2004. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, H. Influences of alpine ecosystem responses to climatic change on soil properties on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China. Catena 2007, 70, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, J.; Harris, W.; Shao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, N.; Li, Y. Effects of plateau pika (Ochotona curzoniae) on net ecosystem carbon exchange of grassland in the three rivers headwaters region, Qinghai-Tibet, China. Plant Soil 2013, 366, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenetahun, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y. Assessment of Range Land Degradation, Major Causes, Impacts, and Alternative Rehabilitation Techniques in Yabello Rangelands Southern Ethiopia. Preprints 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Cheng, G.W.; Li, W.P. Meta-analysis of relationships between environmental factors and aboveground biomass in the alpine grassland on the Tibetan Plateau. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.X.; Cheng, G.D. Eco-environmental changes and causative analysis in the source regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, China. Environmentalist 2000, 20, 221–232. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q. Prevention of Tibetan eco-environmental degradation caused by traditional use of biomass. Renew Sust. Energ. Rev. 2009, 13, 2562–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Tiessen, H. Effect of land use on soil degradation in alpine grassland soil, China. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, J.; Hu, Q.; Li, Y.; Tian, J.; Liao, C.; Xu, Y. Assessing revegetation effectiveness on an extremely degraded grassland, southern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, using terrestrial LiDAR and field data. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 282, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Are, K.S.; Huang, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Q. Livestock grazing significantly accelerates soil erosion more than climate change in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Evidenced from 137Cs and 210Pbex measurements. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 285, 106643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Jiang, C.; Cheng, T.; Bai, J. Grazing alters the phenology of alpine steppe by changing the surface physical environment on the northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Wu, J.; Gong, X.; Lang, X.; Wang, C.; Song, S.; Ali Ahmad, A. Effects of long term fencing on biomass, coverage, density, biodiversity and nutritional values of vegetation community in an alpine meadow of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 130, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Hou, G.; Liu, M.; Fu, G.; Zhan, T.; Zhou, H.; Haregeweyn, N. Effects of climatic and grazing changes on desertification of alpine grasslands, Northern Tibet. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.P.; Ding, Y.J.; Chen, R.S. Spatial and temporal of variations of alpine Vegetation cover in the source regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers of the Tibetan Plateau from 1982 to 2001. Environ. Geol. 2006, 50, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, B. The cause of black soil patch grassland in Qinghai province and management countermeasures. Grassl. China 1995, 51, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, R.B.; Samberg, L.H.; Yeh, E.T.; Smith, A.T.; Wang, W.Y.; Wang, J.B. Rangeland responses to pastoralists, grazing management on a tibetan steppe grassland, qinghai province, China. Rangel. J. 2016, 38, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.K.; Gao, Q.Z.; Liu, S.L.; Zhou, H.K.; Ganjurjav, H.; Wang, X.X. Climate change and human activities altered the diversity and composition of soil microbial community in alpine grasslands of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, A.; Wu, G. Change of cloud amount and the climate warming on the Tibetan Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L22704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, X.X.; Jiao, J.J. Review on climate change on the Tibetan Plateau during the last half-century. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 3979–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.K.; Shang, Z.H.; Gao, J.X.; Boone, R. Enhancing sustainability of grassland ecosystems through ecological restoration and grazing management in an era of climate change on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhu, B.; Zheng, J.; Xiong, Z.W.; Jiang, F.Q.; Han, L.W.; Wang, T.; Wang, M. Soil properties as indicators of desertification in an alpine meadow ecosystem of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J. Burrowing rodents as ecosystem engineers: The ecology and management of plateau zokor (myospalax fontanierii) in alpine meadow ecosystems on the Tibetan Plateau. Mammal. Rev. 2003, 33, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, C.G.; Lawton, J.H.; Shachak, M. Organisms as ecosystem engineers. Oikos 1994, 69, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.K.; Lassoie, J.; Wen, L.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.Y.; Li, J.P.; Li, Y.Y. Degradation of rangeland ecosystems in the developing world: tragedy of breaking coupled human-natural systems. Int. J. Sustain. Soc. 2012, 4, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.; Ikazaki, K.; Siriguleng, A.; Kadono, T.K. Grassland degradation caused by tourism activities in Hulunbuir, Inner Mongolia, China 8th International Symposium of the Digital Earth (ISDE8). Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2014, 18, 012137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.S.; Wang, Z.K.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Ran, C.Q. Response of Kobresia pygmaea and Stipa purpurea grassland communities in Northern Tibet to nitrogen and phosphate addition. Mt. Res. Dev. 2015, 35, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; Shen, Y.; Jia, W.; Li, J. Quantitative assessment of the relative roles of climate change and human activities in desertification processes on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau based on net primary productivity. Catena 2016, 147, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, B.O.; Koch, C.; Boldrini, I.I.; Vélez-Martin, E.; Hasenack, H.; Hermann, J.-M.; Overbeck, G.E. Grassland degradation and restoration: A conceptual framework of stages and thresholds illustrated by southern Brazilian grasslands. Nat. Conserv. 2015, 13, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, T.P. Restoration ecology and conservation biology. Restor. Ecol. 2000, 92, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Bello, F.; Vandewalle, M.; Reitalu, T. Evidence for scale- and disturbance-dependent trait assembly patterns in dry semi-natural grasslands. J. Ecol. 2013, 101, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, H.K.; Zhou, L. Biomass distribution pattern of degraded grassland in alpine meadow. Grassl. China 2005, 27, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- You, Q.L.; Min, J.Z.; Kang, S.C. Rapid warming in the Tibetan Plateau from observations and CMIP5 models in recent decades. Int. J. Climtol. 2016, 36, 2660–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Xue, X.; You, Q.; Huang, C.; Dong, S.; Liao, J.; Wang, T. Changes of soil properties regulate the soil organic carbon loss with grassland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.K.; Li, J.P.; Li, X.Y. Application of design theory for restoring the “black beach” degraded rangeland at the headwater areas of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Afr. J. Agr. Res. 2010, 5, 3542–3552. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Xue, X.; Peng, F.; You, Q.; Hao, A. Meta-analysis of the effects of grassland degradation on plant and soil properties in the alpine meadows of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 20, e00774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhai, Q.G.; Xu, F.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Wang, T.W. Resources in grassland of northern Tibet and its evolutionary trend – A case study of the Zainza area. Geol. Bull. China. 2003, 22, 991–998. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Tao, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Shi, P.; Yu, C. The impact of climate change and anthropogenic activities on alpine grassland over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 189, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Huang, C. The effects on birds of human encroachment on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2011, 16, 604–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Tong, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. Grassland dynamics in responses to climate variation and human activities in China from 2000 to 2013. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Han, W.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, H. Substantial gaps between the protection of biodiversity hotspots in alpine grasslands and the effectiveness of protected areas on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 278, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.R.; Li, S.; Li, F.; Dong, S.K.; Ma, F.L.; Zhu, S.C.; Zhou, H.K.; Stufkens, P. Plant functional groups asynchrony keep the community biomass stability along with the climate change- a 20-year experimental observation of alpine meadow in eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 282, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, T.F.D.; Qin, G.-K.; Plattner, M.; Tignor, S.K.; Allen, J.; Boschung, A.; Nauels, Y.; Xia, V.; Bex, P.M.; Midgley, P.M. IPCC (2013): Climate Change. The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 1535. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Guo, Y.; Xu, H.; Ganjurjav, H.; Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Liu, S. Climate change and its impacts on vegetation distribution and net primary productivity of the alpine ecosystem in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sci Total. Environ. 2016, 554, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Grassland restoration tackles the root of the problem (China’s Tibertannet News). 2019. Available online: https://en.tibet3.com/news/qinghai/2019-09-12/5016.html (accessed on 30 October 2019).
- Niu, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, G.; Liu, L.; Hua, L. Effects of grazing disturbance on plant diversity, community structure and direction of succession in an alpine meadow on Tibet Plateau, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, Q.; Chu, H.; Shi, J.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X. Grassland Community Composition Response to Grazing Intensity Under Different Grazing Regimes. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 71, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wen, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, L. Effects of Grazing Exclusion on Biomass Growth and Species Diversity among Various Grassland Types of the Tibetan Plateau. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, F.; Chen, W.; Liu, L.; Lu, C.; Smith, P. The density of active burrows of plateau pika in relation to biomass allocation in the alpine meadow ecosystems of the Tibetan plateau. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2015, 58, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, J.; Shi, Z.; Yang, X.; Harris, W. Relationships between plateau pika (Ochotona curzoniae) densities and biomass and biodiversity indices of alpine meadow steppe on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Joswiak, D.R. Impact of alpine meadow degradation on soil hydraulic properties over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2013, 478, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Chen, J.; Yi, S. Plateau Pikas burrowing activity accelerates ecosystem carbon emission from alpine grassland on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 84, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Mao, L.; Guo, Z. Effect of available burrow densities of plateau pika (Ochotona curzoniae) on plant niche of alpine meadow communities in the Qinghai- Tibet Plateau. Acta Bot. Sin. 2014, 34, 869–877. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.K.; Gao, H.W.; Xu, G.C.; Hou, X.Y.; Long, R.J.; Kang, M.Y.; Lassoie, P.J. Farmer and professional attitudes to the large-scale ban on livestock grazing of grasslands in China. Environ. Conserv. 2007, 34, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Liu, M.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Effects of fertility control in plateau pikas (Ochotona curzoniae) on diversity of native birds on Tibetan Plateau. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2015, 35, 164–169. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.L.; Ren, G.H.; Dong, Q.M.; Shi, J.J.; Wang, Y.L. Above- and belowground response along degradation gradient in an alpine grassland of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 2014, 42, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Wang, T. Aeolian desertification from the mid-1970s to 2005 in the Otindag Sand Dunes of Northern China. Environ. Geol. 2007, 51, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, Q.; Peng, C.; Wu, N.; Wang, Y.; Fang, X.; Wu, J. The impacts of climate change and human activities on biogeochemical cycles on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2940–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munsch, S.H.; Cordell, J.R.; Toft, J.D. Effects of shoreline armouring and overwater structures on coastal and estuarine fish: Opportunities for habitat improvement. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 54, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Redin, J.; Luque, S.; Poggio, L.; Smith, R.; Gimon, A. Spatial Bayesian belief networks as a planning decision tool for mapping ecosystem services trade-off on forested landscapes. Environ. Res. 2015, 144, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GOFC-GOLD. Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation in Developing Countries: A Sourcebook of Methods and Procedures for Monitoring, Measuring and Reporting, GOFC-GOLD Report version COP13-2; GOFC-GOLD Project Office: Wageningen, The Netherlands; Natural Resources: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Potschin, M.; Haines-Young, R.H. Rio + 10, sustainability science and Landscape Ecology. Landsc. Urban Plan 2006, 75, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potschin, M.B.; Haines-Young, R.H. Ecosystem services. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2011, 35, 575–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.K.; Beaulieu, J.J.; Eichmiller, J.J.; Fischer, J.R.; Franssen, N.R.; Gudder, D.A.; Sheibley, R.W. Nitrogen cycling and metabolism in the thalweg of a prairie river. J. Geophys. Res Biogeosci. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fan, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L. Dynamic response of water retention to grazing activity on grassland over the Three River Headwaters region. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 286, 106662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, G.L.; Lajoie, M.J.; Gustafson, H.H.; Sellers, D.L.; Nattermann, U.; Ellis, D.; Baker, D. Evolution of a designed protein assembly encapsulating its own RNA genome. Nature 2017, 552, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wayne, P.; Peggy, O.; Scott, L. An introduction to the Colorado Plateau Native Plant Initiative. In National Proceedings: Forest and Conservation Nursery Associations-2009; Proc. RMRS-P-62; Riley, L.E., Pinto, J.R., Dumroese, R.K., Eds.; Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2010; pp. 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.D. Integration of Ecological Restoration Experiment and Demonstration Research in Western China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Q.M.; Zhao, X.Q.; Wu, G.L.; Shi, J.J.; Ren, G.H. A review of formation mechanism and restoration measures of “black-soil-type” degraded grassland in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 2359–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdonald, T.; Gann, G.D.; Jonson, J.; Dixon, K.W. International Standards for the Practice of Ecological Restoration–Including Principles and Key Concepts; Society for Ecological Restoration: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Board, M.A. Millennium Ecosystem Assessment; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; Arge, R.; De Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B. The value of the world’ s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, G.C.; Matson, P.A. From theory to implementation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9455–9456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daily, D.C.; Alexander, S.; Ehrlich, P.R.; Goulder, L.; Lubchenco, J.; Matson, P.A.; Mooney, H.A.; Postel, S.; Schneider, S.H.; Tilman, D. Ecosystem Services: Benefits Supplied to Human Societies by Natural Ecosystems. Issues Ecol. 1997, 1, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Anthropogenic contributions dominate trends of vegetation cover change over the farming-pastoral ecotone of northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Okuoka, K.; Fujii, M.; Tanikawa, H.; Fujita, T.; Togawa, T.; Dong, L. Proliferation of district heating using local energy resources through strategic building-stock management: A case study in Fukushima, Japan. Front. Energy 2018, 12, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanten, B.T.V.; Berkel, D.B.V.; Meentemeyer, R.K.; Smith, J.W.; Tieskens, K.F.; Verburg, P.H. Continental-scale quantification of landscape values using social media data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12974–12979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, K.M.A.; Satterfield, T.; Goldstein, J. Rethinking ecosystem services to better address and navigate cultural values. Ecol. Econ. 2012, 74, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Groot, R.S.; Wilson, M.A.; Boumans, R.M. A typology for the classification, description and valuation of ecosystem functions, goods and services. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 41, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martín-López, B.; Iniesta-Arandia, I.; García-Llorente, M.; Palomo, I.; Casado-Arzuaga, I.; Del Amo, D.G.; Montes, C. Uncovering ecosystem service bundles through social preferences. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tengberg, A.; Fredholm, S.; Eliasson, I.; Knez, I.; Saltzman, K.; Wetterberg, O. Cultural ecosystem services provided by landscapes: Assessment of heritage values and identity. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 2, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smukler, S.M.; Jackson, L.E.; O’Geen, A.T.; Ferris, H. Environmental tradeoff assessment for best management practices on an organic farm in a Mediterranean-type climate. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 67, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farley, J.; Costanza, R. Payments for ecosystem services: From local to global. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 2060–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunder, S.; Engel, S.; Pagiola, S. Taking Stock: A Comparative Analysis of Payments for Environmental Services Programs in Developed and Developing Countries. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 65, 834–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopping, K.; Emily Yeh, E. Dismantling Assumptions about Grassland Degradation On the Tibetan Plateau 2018. Available online: https://www.colorado.edu/geography/2018/09/26/dismantling-assumptions-about-grassland-degradation-tibetan-plateau (accessed on 19 May 2019).
- Waldron, S.; Brown, C.; Longworth, J. Grassland degradation and livelihoods in China’s western pastoral region: A framework for understanding and refining China’s recent policy responses. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2010, 2, 298–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffner, U. Restoring grasslands of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. 2019. Available online: https://platform.cabi.org/Projects/Project/66013 (accessed on 10 November 2019).





| Type | Area (ha) | Rangeland (%) | Ecosystem | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperate meadow steppe | 3833 | 2.9 | ||
| Alpine meadow steppe | 5626 | 4.3 | ||
| Alpine steppe | 37,762 | 28.8 | ||
| Alpine desert steppe | 8679 | 6.6 | ||
| Temperate desert | 2084 | 1.6 | 58.8% | 23.0% |
| Alpine desert | 5967 | 4.9 | ||
| Temperate mountain meadow | 6067 | 4.6 | ||
| Alpine meadow | 58,652 | 44.6 | ||
| Total | 131,322 | 100.1 |
| Ecosystem Type and Location | Degradation Estimates/Assumptions | Comments | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Across QTP | 20–30% | Assumption | [47] |
| National level (China) | 90% | Assumption | [48] |
| Across QTP | 18.1% (1980) | FAO report | [49] |
| Across QTP | 28% (1990) | FAO report | [49] |
| Alpine grassland on QTP | 90% | Approximation | [50] |
| Black soil beach on QTP | 26% | Approximation | [50] |
| Alpine grassland QTP | 30% | Estimate | [51] |
| Alpine grassland on QTP | 90% | Assumption | [52] |
| Black soil beach on QTP | 35% | Estimate | [52] |
| Alpine meadow on QTP | 21% | Estimate | [53] |
| Across QTP | 57.19% (1996–2003) | Estimate | [54] |
| Across QTP | 19.55% (2003–2009) | Estimate | [54] |
| Across QTP | 40% | Assumption | [55] |
| Across QTP | 38.8% | Estimate | [42] |
| Soil Type | OM (%) | Total N (%) | Sample No |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alpine meadow soil | 10.7 | 0.47 | 11 |
| Subalpine meadow soil | 15.7 | 0.69 | 13 |
| Alpine steppe soil | 1.7 | 0.12 | 6 |
| Subalpine steppe soil | 3.1 | 0.20 | 8 |
| Alpine desert soil | 0.49 | 0.04 | 2 |
| Subalpine desert soil | 0.76 | 0.06 | 2 |
| Alpine frigid soil | 0.79 | 0.06 | 7 |
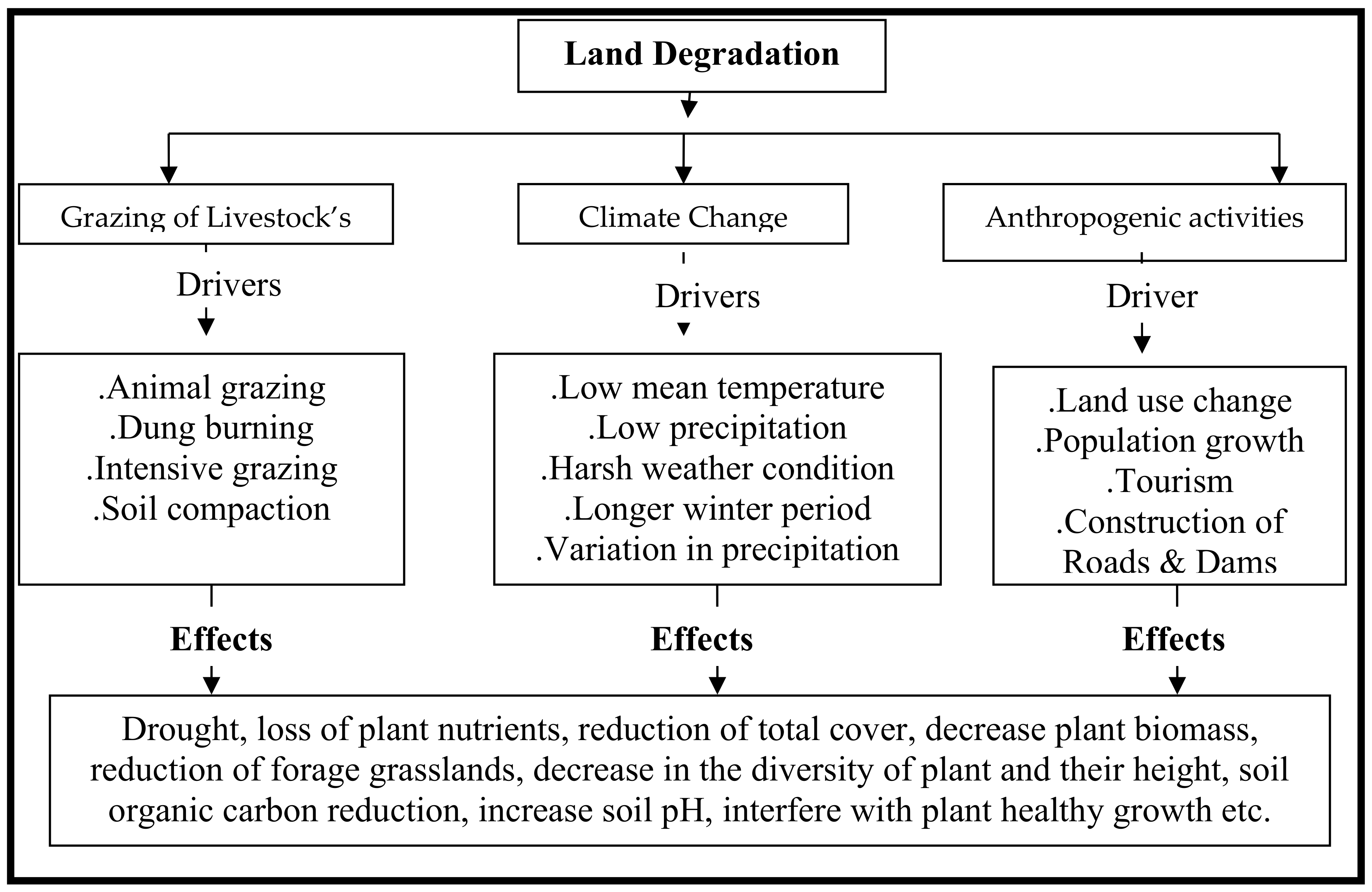
| Degradation Drivers of QTP Grasslands | Negative Effects | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Anthropogenic activities | Ploughing grasslands for crop cultivation resulted in extensive grassland degradation, stimulated desert exacerbation over time, reduced the carbon cycle of terrestrial ecosystem, and induced alpine ecosystem change. Road and railway construction affected the vigilance behavior and initial flight ability of wild birds, and decreased aboveground net primary productivity (ANPP). | [2,85,95,96,97,98] |
| 2. Climate change | Increased unstable plant biomass; decreased plant cover and aboveground and belowground biomass; stimulated desert exacerbation; declined river water quantity, storage, and flows; decreased grassland quality and species richness, limiting precipitation and temperature; reduced permafrost and glacier receding; altered soil carbon and nitrogen cycling; and transformed alpine meadow into shrubs. | [25,34,41,55,60,72,73,85,99,100,101] |
| 3. Grazing | Altered the surface of the grassland physical environment, changed the belowground biomass, accelerated soil erosion and the loss of soil nutrients, increased landscape fragmentation, altered the plant life form as well as the plant population, decreased the plant species abundance, altered the composition and structure of plant communities, decreased soil moisture, and negatively influenced grassland vegetation. | [2,22,69,70,71,102,103,104,105] |
| 4. Burrowing activities of rodents; pikas (Ochotona curzoniae) and zoko (Eospalax fontanierii) | Decreased biomass productivity, stimulated the expansion of bare patches, damaged alpine meadow vegetation, declined ecosystem production, lowered plant cover and soil nutrient plant productivity, and reduced grassland ecosystem functions and services. | [34,106,107,108,109,110,111,112] |
| 5. Other activities | The harsh environment and natural disasters stimulated the decline in plant cover and the conversion of rangelands into agricultural lands. Archaic livestock husbandry approach and privatization have also contributed to the decline in vegetation cover, reduction in plant productivity, and acceleration of topsoil erosion. Downward drainage of water resulted in the drying of topsoil and permafrost decline reduced the activities of soil microbes. | [34,41,42,60,84,113,114,115] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fayiah, M.; Dong, S.; Khomera, S.W.; Ur Rehman, S.A.; Yang, M.; Xiao, J. Status and Challenges of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau’s Grasslands: An Analysis of Causes, Mitigation Measures, and Way Forward. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12031099
Fayiah M, Dong S, Khomera SW, Ur Rehman SA, Yang M, Xiao J. Status and Challenges of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau’s Grasslands: An Analysis of Causes, Mitigation Measures, and Way Forward. Sustainability. 2020; 12(3):1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12031099
Chicago/Turabian StyleFayiah, Moses, ShiKui Dong, Sphiwe Wezzie Khomera, Syed Aziz Ur Rehman, Mingyue Yang, and Jiannan Xiao. 2020. "Status and Challenges of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau’s Grasslands: An Analysis of Causes, Mitigation Measures, and Way Forward" Sustainability 12, no. 3: 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12031099
APA StyleFayiah, M., Dong, S., Khomera, S. W., Ur Rehman, S. A., Yang, M., & Xiao, J. (2020). Status and Challenges of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau’s Grasslands: An Analysis of Causes, Mitigation Measures, and Way Forward. Sustainability, 12(3), 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12031099






