1. Introduction
The mobile phone can generate social capital, leading to economic, social and political opportunities [
1]. Geser states that before the appearance of mobile phones, formal organizations had created sophisticated fixed telephone lines specifically for their structural and organizational purposes [
2]. Today, mobile phones are substituting most of the fixed phones and are adding new functions for the users, such as activity recognition using cell phone sensors [
3].
Information is especially useful for developing and sustaining a company’s competitiveness in terms of its products and services on the market [
4,
5,
6]. It is achieved by organizational control of information processes that involve information processing such as the acquisition, recording, organization, retrieval, display, or dissemination of information. Information processes have been considered from the information systems theories perspective. We considered the mobile phone as an instrument used by the individual to perform any generally recognized information processing: collect, organize, analyze, store (and retrieve), transmit (and receive), process and display. According to Encyclopedia Britannica, information processing is considered the acquisition, recording, organization, retrieval, display and dissemination of information [
7]. The European Commission provides a definition of information processing as “any operation or set of operations such as collection, recording, organization, structuring, storage, adaptation or alteration, retrieval, consultation, use, disclosure by transmission, dissemination or otherwise making available, alignment or combination, restriction, erasure or destruction” [
8] (p. 33). A similar definition of information processes can be extracted from Alter, who defines an information system as “a work system whose processes and activities are devoted to processing information, i.e., capturing, transmitting, storing, retrieving, manipulating, and displaying information” [
9] (p. 6).
Smartphones are able to realize any of these information processing types. The focus of human behavior defines the purpose of the information processing, differentiating professional and personal purposes. Hence, this study considers two types of information processes involving the use of mobile phones: personal and professional information processes.
Mobile phones are processing information through different software, accessing many kinds of information from different information channels. Information processes connect the user with these channels by the information transmitted or accessed through them (e.g., information processes appear in the use of e-mail, sms, Messenger, Whatsapp, GPS, Waze, etc.). Therefore, it becomes obvious that information processes cannot be treated separately from their related information channels. Due to their various kind of processed information, different software and diverse information channels, this study considers the different practical use of mobile phones in different information processes: games, getting evidence through audio-video recordings for the work done (only for professional purposes), messaging applications (e-mail, sms, Messenger, Whatsapp, etc.), movies/videos viewing applications, music-listening applications (including on-line radio), online stores, orientation applications (maps, GPS, Waze, etc.), phone calls (voice only), search for useful information on the Internet, social networks (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.), specialized applications made available by the company, and video calls.
What kind of information processes will bring benefits to companies? Just ones used for professional purposes? Or could even the information processes used by employees for private matters sustain their working tasks? This study puts forward several reasons for using mobile phones for personal information processes at work and also stresses the positive and negative effects of mobile phone use at work for personal purposes. However, enterprises need to learn how information should be used in order to generate profitability and be competitive on the market [
4], and how a culture of knowledge sharing could be promoted [
10].
Today, mobile phones are replacing computers and are used to call, text, send e-mails, run video conferences, do micro-blogging, interact on social-networks, surf the Internet, watch and share videos and pictures, play video games, and utilize a tremendous array of software-driven applications. The main positive aspects of cell phone use (CPU) reported by other studies comprise the following:
CPU is positively related to anxiety and satisfaction with life [
11];
CPU counts in positive use for organizations as it is important to have knowledge of market and share information and keep in touch with clients and superiors [
12,
13];
CPU has positive impact on the experience of work and the ability to effectively solve problems on the spot [
12];
Smartphone promotes autonomy in a workplace, making employees feel better [
13].
The main negative aspects to cell phone use (CPU) reported by previous studies include:
CPU disrupts physical activity behaviour, causing high frequency users to be less physically active and more sedentary in comparison to low frequency users [
14];
Smartphone users are obsessed with their smartphones [
15];
CPU is negatively related to academic performance [
11];
CPU in the manufacturing sector may not positively contribute to productivity gains [
13];
CPU dependence on smartphones at work may increase workers’ perception of their job performance and workplace social capital; however, on the negative side, it may lead to the emergence of smartphone addiction symptoms [
15];
CPU negatively affects attention as focus is on chatting, listening to music and other activities, while academic activities are neglected and left to suffer [
16];
Excessive use of smartphones separates people from realities [
13];
When employees use their smartphones to work on their projects from their work, sometimes they bring stress from their workplaces into their private lives at home, so they cannot separate their work and non-work lives [
13].
Regarding the possible positive or negative influences when using mobile devices at work for personal purposes, in this study we outline the likely effects that may have an impact on individuals and organizations. These effects (either positive or negative) are related to productivity, efficiency, pace of work, work–life balance (WLB), colleagues from work and stress at work. Personal purposes are related to private life: communication with loved ones, interests regarding home-owning or other properties (e.g., car, personal goods, etc.), contact with friends and relatives, and also information regarding friends and relatives. These purposes have nothing to do with work tasks. Professional purposes are related to the work environment: work tasks, working with colleagues, working hours, deadlines for specific activities, etc. These purposes should not be related to personal issues. However, if we take into account that nowadays individuals work long hours every day and private matters are dealt with at the same time (and sometimes it becomes impossible to do so after working hours), then a work–life balance (WLB) is needed. The concept of WLB indicates to what extent the job allows employees to fulfill their personal life needs, considering their working hours. For WLB, mobile devices play a central role since they constantly provide workers with access to information, keeping them in touch with other people.
As these two issues recharge the engines of competitiveness—information and technology (mobile phone, the Internet, etc.), considering the return rates on digital investment [
17]—it is important for managers to give proper importance to this mix if they wish to create a business-friendly, sustainable and value-added business.
The mobile phone has become a device that many of us cannot not live without, with many aspects of our daily life being influenced by its use [
18]. Data included in the Human Development Index comprise a component on mobile phone subscription per 100 inhabitants, showing that the number of mobile subscriptions per 100 inhabitants in Romania between 2000–2010 grew by approximately 10.54 times, from 11.3 to 119.2, reaching a ratio of more than one subscription per inhabitant [
19]. As the percentage of the population using the Internet on various devices grew from 3.6% in 2006 to 59.5% in 2016 [
19], we can assume that the lives of Romanian workers have been influenced by the use of mobile phones and by Internet connectivity. Smartphone adoption by workers is similar all over the world; managers are facing the challenge of efficient integration of these new devices into the daily routine of their workers. It has been found that research is needed not only to determine how more mindful usage of technology influences employee engagement and effectiveness, but also to determine how the most effective norms around these practices could be created [
20].
Given the large variety of apps available for today’s smartphones, it is quite difficult to describe a complete taxonomy of areas in which these devices can be used. According to Yim and Gomez, mobile phones have three major intervention areas [
21]:
Communication with others, generating information, knowledge, emotional support, etc.;
The process of focusing on information, which is connected to occupational practices and widening of knowledge, and enriching them;
Flexibility in life at work.
The focus of our research is on the use of mobile phones at work, its main research question being how mobile phones are used by employees and for which purposes. We investigated several characteristics of the relationship between the use of mobile phones at work and which information processes are accessed by employees for personal and professional purposes, discovering that mobile phone use, as a knowledge-sharing instrument, is an important aspect at work. We consider that today, smartphones are the most used mobile devices on the market. In this study, we have not considered simple mobile phones, with no Internet connection, as nowadays these are rarely used. We also considered that any available use of a mobile phone involves the participation of an individual in an information process, since this device requires the user to acquire, record, organize, retrieve, display or disseminate information in relation to another individual or software. The phone calls, video calls, messaging, or use of any available apps involves the participation of an individual in an information process.
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Research Instrument, Data Collection and Sample
The aim of this study is to suggest two regression models to show which information processes are accessed by employees for personal and professional purposes when using mobile phones at work. It is a quantitative research that has been conducted using an online research questionnaire.
The questionnaire comprises 24 questions, with many sub-questions (items) that collected the ratings given by respondents on a 5-point Likert scale (1 = “never”; 5 = “very often” or 1 = “totally agree”; 5 = “totally disagree”), using rating names adapted to each question. Many of the items of this tool are related to information processes and information channels accessed through mobile phones, already discussed in the results of other studies [
1,
2,
13,
21,
26,
30,
35,
37,
40,
41,
44,
49], including perceptions of the behavior of managers related to the use of mobile devices at work, plus personal data covering nationality, age, gender, the highest level of education reached in a specific field. However, as this study focuses only on information processes used at work for personal or professional purposes, the additional collected data will be used in future research.
Along with the demographic variables, the whole questionnaire includes 95 items. The internal consistency of the items was tested only on 40 sub-questions in the questionnaire (those used for the current paper), excluding the items related to demographic variables. The Cronbach’s α coefficient of these research sub-questions had a value of 0.868 (details in
Table 1), higher than 0.600, which indicates that the internal consistency of the items has been reached.
This instrument was pretested at the beginning of July 2018 and was subsequently modified. It was pretested using interviews with 10 specialists in such fields as marketing research, marketing analysis, engineering and education, who provided feedback and ideas for modifying it. The interviews were conducted in order to ensure that the items of the questionnaire are understandable and easy to complete. The participants made improvements, depending on the nature of their experience, both in terms of question formulation, type of variables and statistical analysis. The main improvements that have been made to the questionnaire in the pre-testing phase were: the informational channels were listed in order to clarify the items (for example: messaging applications (E-mail, sms, Messenger, WhatsApp, etc.), social networks (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.)); a distinction was made between telephone calls (voice only) and video calls (video calls) and the possibility of not using the mobile phone at work at all was also considered.
The questionnaire was distributed by e-mail and on social networks using a message that presented the study’s aim, so as to stimulate the curiosity of potential respondents and invite them to take part in the research. The invitation to fill in the questionnaire also contained a questionnaire link, and was sent by the authors of this study. To complete the questionnaire, the respondents needed 15 min.
As all the potential respondents could not be counted (as we used such social networks as Facebook), we have not computed the response rate. Nonetheless, 368 valid responses from professionals working in Romania in different fields of activity were collected online between mid-July and December of 2018, using convenience sampling.
Sample respondents (N = 368, see details in
Table 2) in the questionnaire included several socio-demographic characteristics, which can be summarized as follows: Romanian nationality; aged between 18 and over 48 (with the following distribution: 13% aged 18–23, 39% aged 24–29, 22% aged 30–35, 14% aged 36–41, 7% aged 42–47 and 5% aged over 48); gender (69% females and 31% males); highest level of education (with the following distribution: high school 5%, post-secondary 1%, undergraduate degree 42%, postgraduate degree 47% and phd degree 5%). The questionnaire was completed by people who work in organizations in various fields of production and services (see details in
Table A7).
3.2. Developed Variables And Models and Calculation Of Information Processes Intensity
The proposed regression models are multiple and linear, which implies that the target link between the variables is proportional, with the occurrence of at least two independent variables. The general form of the multiple linear model is [
50] (p. 90)
where:
β0 = constant
β1, β2, …, βp = regression coefficients for each independent variable
X1, X2, …, Xp = independent variables
Y = dependent variable
Ɛ = residual variable
In order to design the regression model showing which information processes are accessed by employees for their personal purposes when using mobile phones at work, we have used the dependent variable—use of mobile phone at work for personal purposes (with possible answers “Yes/No”)—and the independent variables—games, messaging applications (e-mail, sms, Messenger, Whatsapp, etc.), movies/videos viewing applications, music listening applications (including on-line radio), online stores, orientation applications (maps, GPS, Waze, etc.), phone calls (voice only), search for useful information on the Internet, social networks (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.), specialized applications made available by the company and video calls (with possible answers the using of these information processes on a scale from 1—minimum to 5—maximum).
For the regression model showing which information processes are accessed by employees for their professional purposes when using mobile phones at work, we have used the dependent variable—use of mobile phone at work for professional purposes (with possible answers “Yes/No”)—and the independent variables—games, getting evidence through audio-video recordings for the work done, messaging applications (e-mail, sms, Messenger, Whatsapp, etc.), movies/videos viewing applications, music listening applications (including on-line radio), online stores, orientation applications (maps, GPS, Waze, etc.), phone calls (voice only), search for useful information on the Internet, social networks (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.), specialized applications made available by the company and video calls (with possible answers the using of these information processes on a scale from 1—minimum to 5—maximum).
The dependent variables for both regression models were simple, in line with the aim of the study to confirm the action of using mobile phone at work for personal and/or professional purposes. As for the independent variables, these consist of the choices of respondents (in a declarative manner) in using mobile phones for specific information processes through their related channels.
We have selected the same independent variables as for dependent variables (the action of using mobile phone at work for personal/professional purposes) in order to maintain data comparability, except one independent variable—getting evidence through audio-video recordings for the work done—which is obviously specific only to professional purposes. To select the independent variables, we took two aspects into account: their discussion in previous studies, and whether they were realistic for the working environment in Romania.
In the analysis, we also have calculated the intensity of the use of information processes (in percentages), which represents an indicator related to the distance between minimum and maximum at which the mean of the use of information processes is located.
Using a scale with responses from 1 (minimum) to 5 (maximum) for using information processes, the distance between extremities is four intervals (therefore, it will result in the denominator value 5 − 1 = 4). To normalize the numerator between 0–4, it is necessary to subtract a point (so it will result in the numerator value mean − 1). Therefore, the following formula was used
To present synthetic results other than the regression analysis, we have used specific items and responses in the questionnaire that are described in the results section.
4. Results
Respondents were asked to specify the percentage of time spent on using mobile phones at the workplace for personal and professional purposes. The results are shown in
Table 3.
On one hand, 83.15% of respondents declared using mobile phones at work for personal purposes. On the other hand, 16.85% denied it. More specifically, respondents in the second category work mainly in the following areas: public administration, defence and public order, commerce, construction, the manufacturing and extractive industry, engineering, education, health services, financial and insurance services, transport.
Being a fairly wide range of industries, we may consider that the use of mobile phones at work for personal purposes is largely based on individual choice, and is clearly influenced by the personal characteristics of each person [
40]. Besides, the Pearson correlation coefficient between the use of mobile phones at work for personal purposes and field of activity (0.037) indicates a weak positive correlation (details in
Table A1).
Respondents were also asked if their bosses prohibit and penalize the use of mobile phone for personal purposes during work. The question had five possible answers on a scale from 1—minimum to 5—maximum (1 = “never”; 2 = “rarely”; 3 = “sometimes”; 4 = “very often”; 5 = “always”) and the results indicated an average of 1.71 with a standard deviation of 1.02. The distribution of the answers was: 61% never, 16% rarely, 18% sometimes, 3% very often, 2% always. As long as most of the respondents who are part of this research sample declared that their bosses do not prohibit or penalize the use of the mobile phone for personal purposes at work, the present study makes sense for using mobile devices for personal purposes at work.
A total of 68.75% of respondents declared using their mobile phone for work purposes, while 31.25% denied it (details in
Table 4). In a further analysis, individuals in the first category are currently working in the following fields of activity: public administration, commerce, information and telecommunications (IT), extractive industry, engineering, education, energy production and distribution, health services, financial and insurance services, shows, cultural and recreational activities, tourism, hotels and restaurants, and other areas.
According to the Pearson correlation coefficient (−0.133), there is a weak negative correlation between the field of activity and the use of a mobile phone for professional purposes correlation (details in
Table A2). The ability to use phones at work for such purposes depends on company size, company policy, leadership, etc.
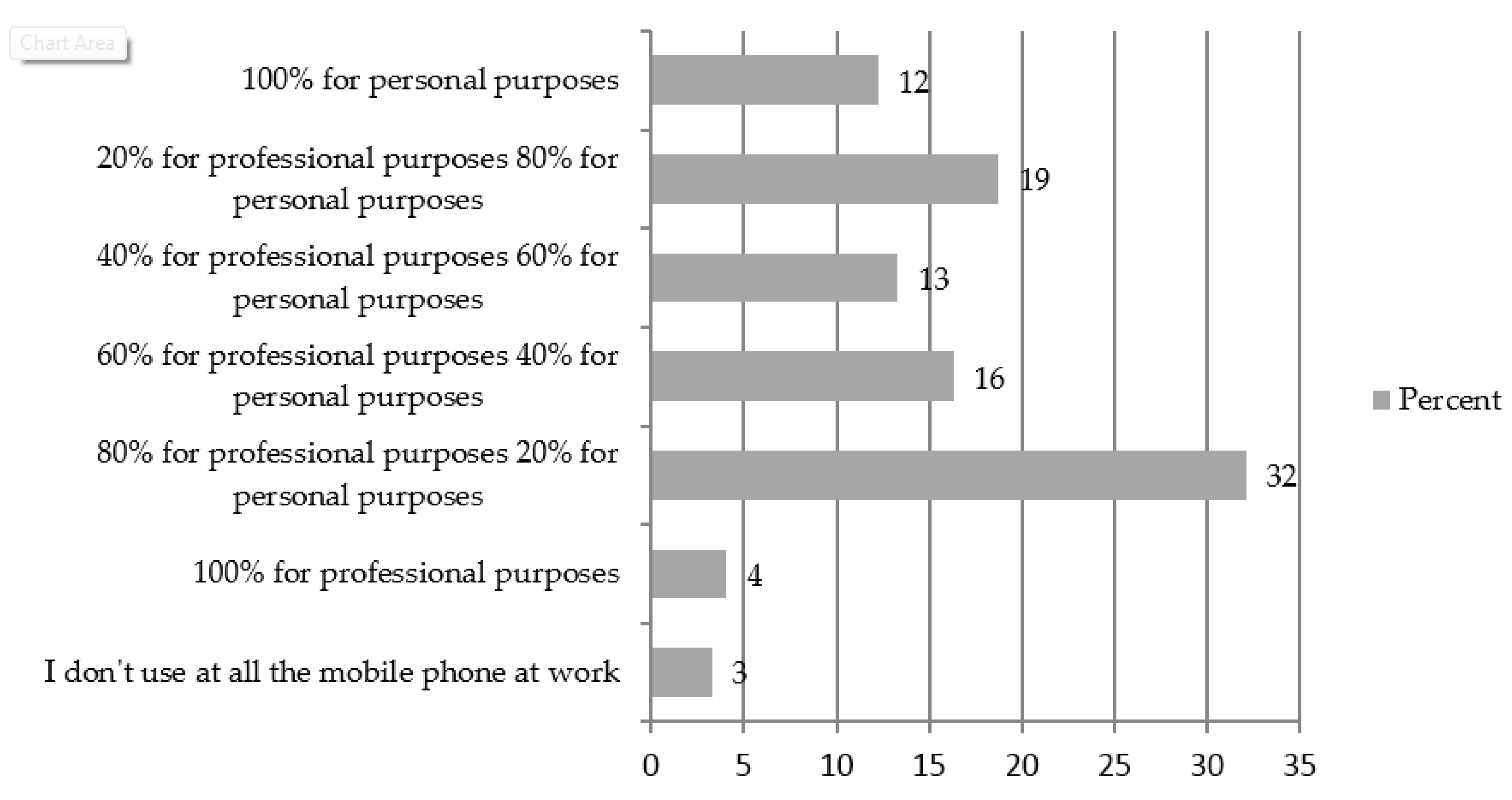
Most respondents (32%) reported using mobile phones at work, 80% for professional and 20% for personal purposes. Moreover, 19% admitted the opposite: the mobile phone is used by 20% of respondents for professional and by 80% for personal purposes. Finally, 16% of them use the mobile phone 60% for professional and 40% for personal purposes. Extremities indicate that 12% of respondents use their mobile phone strictly for personal purposes, and only 4% for professional purposes (see details in
Figure 1).
It is natural for employees to use their mobile phone, depending on the nature of their work. For example, in the back office, it is normal for financial services to use mobile phone discussions in order to solve specific problems, while in the field of constructions, at the workplace, it is very important for the mobile phone to be used with caution when performing tasks in difficult working conditions. Finally, for the considered sample, the mobile phone shows its functionality, especially from a professional point of view.
4.1. Personal Use of Mobile Phone in Information Processes at Work
Respondents were asked to tick on a scale from 1 (never) to 5 (very often) how they use the mobile phone for personal purposes at work. This question does not go into personal details (how much time is dedicated to discussions, with whom are the discussions, what kind of information is being searched on the Internet, etc.). Instead, the item provides a global view of the types of information processes that are accessed at work and are not related to working tasks.
Table 5 shows the averages for each of the personal information processes taken into consideration and the significant differences between groups, considering the following demographic variables: gender, age and the highest level of education.
Most employees use text messaging applications (e-mail, sms, Messenger, Whatsapp, etc.) with an average of 3.59 out of five (intensity of use of 64.75%). The intensity of 64.75% was obtained as follows: (3.59 − 1)/4 × 100. Therefore, hypothesis H3 “Most often, the mobile phone is used for personal purposes in the workplace through messaging applications (e-mail, sms, Messenger, Whatsapp, etc.)” has been validated.
In addition, employees search for useful information on the Internet with an average of 3.43 and a level of intensity of 60.75%. Finally, they use phone calls (voice only) with an average of 3.34 (intensity of use—58.5%). The lowest average was recorded for games: 1.35, with intensity of use of only 8.75%.
The distribution for the considered sample is not normal, so that, in order to test the significant differences between groups considering demographic variables, was used the nonparametric test Kruskal Wallis. With 95% confidence, it can be stated that there are significant differences between males and females regarding the use of games for personal purposes at work. The results indicate significant differences between the considered age groups for personal use of mobile devices at work for: messaging applications (e-mail, sms, Messenger, Whatsapp, etc.), the search for useful information on the Internet, social networks (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.), music listening applications (including online radio), movies/videos viewing applications, video calls and games. Also, there are significant differences between groups that have different levels of education for personal use of mobile phone at work for movies/videos viewing applications and games.
The first four highest averages indicate that employees want to communicate with other people either through text messages or voice calls. Further, they want to be aware of what is happening outside their working environment, accessing useful information from the Internet, but also by using social networks. While the personal information processes that employees choose at work have previously been reported, the reasons why employees use mobile phones for personal purposes at work are listed below. Respondents were asked to tick on a scale from 1 (totally disagree) to 5 (totally agree) for what reasons they use mobile phone for personal purposes at work (see details in
Table 6).
The most common reason respondents give for using the mobile phone at work for personal purposes, is the need to know that loved ones are safe. Secondly, the same need for safety is related to personal goods or properties. At the same time, the mobile phone is useful for work–life balance, helping employees schedule their time after work. Again, the need to get information about friends or relatives is important, so employees connect to social networking in order to keep up with the news. All the reasons checked by respondents have an intensity level of over 55%, with an average over 3.20 from 5.
When the mobile phone is used in the workplace for personal purposes, depending on the working conditions (how close employees are working, if there are possible recreational facilities, etc.), individual positive or individual/collective negative effects may occur.
For the results below, respondents were asked to tick on a scale from 1 (totally disagree) to 5 (totally agree) for how they use the mobile phone for personal purposes at work. We considered that using the mobile phone at work for professional purposes is a positive behavior, hence, we asked the respondents only about the positive or negative effects of the personal use of the mobile phone. We developed a scale of answers based on information from the pretesting phase.
The results from
Table 7 show an interesting phenomenon: with an average of 3.17 out of 5 (54.25% intensity), employees have agreed that the mobile phone improves their efficiency, while with an average of 2.65 out of 5 (and intensity of 41.25%), they said they work more efficiently when they do not have the mobile phone next to them. Of course, there are many other negative effects that may occur at work when using mobile phone for personal purposes: slowing the pace of work, distracting attention, stress, and even disturbing other colleagues’ activities. Finally, the best benefit of using a mobile phone in the workplace for personal purposes is having a work–life balance, resulting in better productivity (with a mean of 3.18 out of 5).
The second hypothesis, related to personal purposes, H4 “There is a positive correlation between the use of mobile phone at the workplace for personal purposes and access to social networks (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.)”, has been validated too.
Mobile phone use in the workplace for personal purposes, related to accessing social networks (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.), is positively and weakly correlated, with a correlation coefficient of 0.386 (details in
Table 8). In other words, the more the mobile phone is used at work for personal purposes, the more social networks (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.) are among the information processes chosen by employees.
4.2. Professional Use of Mobile Phones in Information Processes at Work
The other hypothesis is related to professional purposes; H1 “There is a negative correlation between the use of mobile phone in the workplace for professional purposes and games applications” has been validated.
Mobile phone use in the workplace for professional purposes, related to accessing gaming applications, is negatively and very weakly correlated, with a correlation coefficient of −0.044 (details in
Table 9). In other words, the more the mobile phone is used in the workplace for professional purposes, the less it will be used for gaming applications.
Respondents were asked to tick on a scale from 1 (never) to 5 (very often) what they use the mobile phone for when using it for professional purposes at work. This question does not go into too many professional details, but provides a general view regarding the types of information processes that are accessed at work and are related to the working tasks.
Table 10 shows the averages for each of the professional information processes taken into consideration and the significant differences between groups considering the following demographic variables: gender, age and the highest level of education.
Most employees use the mobile phone at the working place for phone calls (voice only), with an average of 3.56 out of 5 (an intensity of use of 64%). Moreover, they search for useful information on the Internet, with an average of 2.91 and level of intensity of use of 47.75%. They also use messaging applications (e-mail, sms, Messenger, Whatsapp, etc.) with an average of 2.83 (level of intensity of use of 45.75%). Finally, they use specialized applications, made available by the company, with an average of 2.14 (an intensity of use level of 28.5%). Therefore, hypothesis H2—“Most often, the mobile phone it is used for professional purposes in the workplace through specialized applications made available by the company”—has not been validated.
The lowest average was recorded for games: 1.15, with an intensity of use of only 3.75%. The first four highest averages indicate that employees need to communicate, either through voice calls or text messages, with professionals from the work environment. Also, they need to access useful information from the Internet and use specialized applications made available by the company.
Using the nonparametric test Kruskal Wallis, with 95% confidence, it can be stated that there are significant differences between males and females in personal use of mobile devices at work for: orientation applications (maps, GPS, Waze, etc.) and getting evidence through audio-video recordings for the work done. The results indicate significant differences between the considered age groups for personal use of mobile phones at work for: phone calls (voice only) and messaging applications (e-mail, sms, Messenger, Whatsapp, etc.).
4.3. Personal versus Professional Use of Mobile Phone in Information Processes at Work
Taking into account the same types of information processes, we present in
Figure 2 a comparison between how often these processes are used for personal and professional purposes.
The biggest difference between the use of mobile phones in personal and professional information processes has been recorded for social networks (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.), which are most often used by employees for personal purposes. Then, there are big differences for messaging applications (e-mail, sms, Messenger, Whatsapp, etc.) and music listening applications (including on-line radio), which are more often used again for personal aims.
Regarding the specialized applications made available by the company, phone calls (voice only) and video calls, it seems that employees use them more for professional purposes at work. All the rest of the information processes analyzed are more intensely used for personal purposes.
4.4. Regression Analysis
4.4.1. A Model for Personal Use of Mobile Phones at Work and the Information Processes which They are Used for
Using backward regression analysis method, in the first version of the model, the use of the mobile phone in the workplace for personal purposes has been made for all the information processes that appear in the questionnaire (details in
Table A3). The final model indicates that the use of a mobile phone for personal purposes at workplace is only for: social networks (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.), phone calls (voice only) and messaging applications (e-mail, sms, Messenger, Whatsapp, etc.) (details in
Table A3). The best version of the model is the eighth, with an adjusted R
2 of 0.186 and an estimated standard error of 0.338 (details in
Table A3). For all model variants, p values are 0 (details in
Table A4), so the dependent variable are explained by the action of the independent variables. The eighth model has been chosen (details in
Table A4 and
Table 11).
The model for the considered sample (N = 368) for the use of the mobile phone at work for personal purposes has significance levels for the variables less than 0.05 (0.013; 0.000; 0.000; 0.046; −0.055), and is the following:
The use of mobile phones in the workplace for personal purposes is very low (it achieves a score of 0.5 out of a maximum of 5), when employees do not use the mobile phone at all for: phone calls (voice only), messaging applications, social networking, and specialized applications made available by the company. This mobile phone use for personal purposes increases by 0.588 when employees are using mobile phone for: phone calls (voice only), messaging applications, social networking and specialized applications made available by the company—each of them growing by one unit (0.500 − 0.048 × 1 + 0.091 × 1 + 0.073 × 1 − 0.028 × 1 = 0.588). It is interesting that when employees use their mobile phones for voice calls and specialized applications made available by the company, the general trend of time spent on the phone for personal purposes decreases.
In other words, once personal interests have been resolved by phone calls (voice only) or through specialized applications made available by the company, the time spent on the phone for personal purposes should decrease. The model clearly indicates that the biggest productive time spent for personal purposes appears in messaging applications (e-mails, sms, Messenger, Whatsapp, etc.) and social networks (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.).
4.4.2. A Model for Professional Use of Mobile Phones at Work and the Information Processes Which They Are used for
The first version of the regression model obtained through the backward method links the use of the mobile phone at the workplace for professional purposes with all the information processes that appear in the questionnaire (details in
Table A5). The final model indicates that the use of mobile phones at the workplace for professional purposes is only for: phone calls (voice only), online stores and search for useful information on the Internet (details in
Table A5). The optimal version of the model is the tenth, with an adjusted R
2 of 0.331, and an estimated standard error of 0.380 (details in
Table A5). For all model variants, p values are 0 (details in
Table A6), so the dependent variable are explained by the action of the independent variables. Again, the analysis has confirmed that the tenth model is to be chosen (details in
Table A6 and
Table 12).
The model for the considered sample (N = 368) for the use of the mobile phone at work for professional purposes has significance levels for the variables less than 0.05 (0.378, 0.000, 0.001, 0.05), and is the following:
The use of mobile phones at the workplace for professional purposes is very low (with a score of 0.051 out of a maximum of 5), when employees do not use the mobile phone at all for: phone calls (voice only), and to search for useful information on the Internet and online stores. The use of the mobile phone at the workplace for professional purposes increases by 0.201 when the mobile phone is used by employees for: phone calls (voice only), and the search for useful information on the Internet and online stores, with each of them growing by one unit (0.051 + 0.160 × 1 + 0.056 × 1 − 0.066 × 1 = 0.201). As employees use their mobile phone for online stores, the general trend of time spent on the phone for professional purposes decreases.
In other words, once the professional interests of searching for useful information about online stores have been resolved, the time spent on the phone for professional purposes should decrease. The model clearly indicates that the biggest consumers of work time for work purposes are telephone conversations (voice only) and the searches for useful information on the Internet.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
The use of mobile phones at work has two separate behavioural components. Employees use the devices for several information processes, some being related to work and others to their personal life. Most of them are involved in both personal and professional informational processes, during their working hours. The effects of the use of mobile phones/smartphones at work can be perceived as positive or negative, based on the resulting productivity [
40,
42]. The time spent on the use of mobile phones at work cannot be implicitly considered a waste. If it is spent on solving personal problems, social networks, personal leisure or comfort-related activities, it reduces working time, thus reducing productivity. However, that time can also be spent for professional purposes, thus having positive effects such as keeping the workers in touch with managers and customers, keeping employees up to date with information on the market and regarding the organizational environment, helping employees quickly access important information from public or specialized sources, using specialized software for doing their work. As our study has shown what information processes people access where they live and work, it contributes to possible future research on social sustainability [
51]. We support this aspect, due to the fact that social sustainability promotes well-being at the workplace and information regarding the impact of technology on employees. Since this study shows what personal and professional information processes are accessed by employees at work, the results should be interesting for decision-makers in companies.
The aim of our research was to propose two regression models that capture what information processes are accessed by employees for personal and professional purposes when using the mobile phone at work.
In the first part of the quantitative analysis (mostly with descriptive statistics), we found that only 3% reported not using the mobile phone at work, with 4% using it only for professional purposes, and 12% only for personal purposes (details in
Figure 1). Even if the time on the mobile phone is spent for personal interests, the overall effect might still be positive for the organization. We have found that employees reduce their level of stress related to personal issues by staying informed about their loved ones and their goods (see details in
Table 6), thus creating a relaxed, less stressful, positive working environment. Results also stress that the biggest difference between the use of personal and professional information processes, in which the mobile phone is used at work, has been recorded for social networks (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.), which are most often used by employees for personal purposes. The biggest differences in favor of professional purposes have been found in the use of specialized applications made available by the company, phone calls (voice only) and video calls that employees use more for professional purposes at work.
The most unexpected result was the top positions of the two opinions regarding the positive effects of the use of mobile phones during work, with averages higher than the other six negative effects identified (details in
Table 7). Employees say the most important effects of using mobile phones for personal interests are that they help them be more productive because they keep their work–life balance, and that phones used in the workplace for personal purposes improve their efficiency. A study based on the opinions of managers might show a different perspective.
The personal use of mobile devices was more intense than the professional use in eight application categories out of eleven, showing an imbalance between the personal and professional use of mobile phones at work (details in
Figure 2). Yet, since the mobile phone was originally designed as a personal device, the fact that today it is used in a significant proportion for professional purposes is a beneficial fact, convincing many employers not to prohibit its use during work. Moreover, the study has shown that the possibility of using the mobile phone during working time for personal purposes reduces the stress of the employees related to personal life uncertainties and risks (details in
Table 6), and creates a work environment based on trust, leading to increased employee performance.
In the second part of the quantitative analysis, we have analysed the two regression models. Summarizing the findings, the first hypothesis “There is a negative correlation between the use of mobile phone in the workplace for professional purposes and games applications”, the third hypothesis “Most often, the mobile phone it is used for personal purposes in the workplace through messaging applications (e-mail, sms, Messenger, Whatsapp, etc.)”, and the fourth hypothesis “There is a positive correlation between mobile phone use in the workplace for personal purposes and accessing Social networks (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.)”, have been validated. The second hypothesis—“Most often, the mobile phone is used for professional purposes in the workplace through specialized applications made available by the company”—has not been validated. Both regression models provide empirical evidence for these hypotheses (validated or not): the biggest productive time consumers for personal purposes are messaging applications (e-mail, sms, Messenger, Whatsapp, etc.) and social networks (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.) and the biggest consumers of work time for work purposes are telephone conversations (voice only) and searches for useful information on the Internet.
Our results proved that preferences for using mobile phones for personal purposes through messaging and social networks (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.) remain somewhat stable [
12,
40,
45,
48]. The on-line stores, orientation applications (maps, GPS, Waze, etc.), music listening applications (including on-line radio), watching movies and videos, video calls and playing games were statistically excluded by the calculated regression model for personal use of mobile phones at work. Also, our study has proven that games are not used on the mobile devices at the workplace for professional purposes [
30]. Regarding the use of mobile phones at work for professional purposes through specialized applications made available by the company, there is currently little emphasis on this, although there are opinions arguing that the use of mobile phones at work should be regulated by a constant procedure [
35]. The study proved that the use of specialized applications made available by the company leads to a decrease in the time spent for personal purposes, but the regression model for the professional use of the mobile phone didn’t reveal a significant impact of this kind of applications. In fact, the specialized applications made available by the company, messaging applications, orientation applications (maps, GPS, Waze, etc.), social networks (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.), getting evidence through audio-video recordings for the work done, video calls, movies/videos viewing applications, music listening applications (including on-line radio) and games were statistically excluded by the calculated regression model for professional use of mobile phones at work.
We consider that the use of mobile devices at work for personal interests, firstly, through the use of messaging applications, then for searching information on the Internet and, with a lower intensity, for voice-calls (details in
Table 5), shows that the length of worktime interruption for the satisfaction of personal interests is important. The employees show they prefer uses that require shorter times, even if this reduces the consistency of the transferred information.
In using mobile devices for professional interests, the order of intensity of use is reversed. On the first place are voice-calls, followed by the search for information on the Internet. The use of messaging applications is in third place (details in
Table 10). We consider that this order shows that, in the case of professional use of mobile devices, the quality of the information flow is more important and not the time invested in the transfer process.
Considering the limitations of this study, we must point out that respondents were only from Romania, without using a sampling scheme, hence the results are not relevant for other geographical areas. Yet, given the worldwide behavioral similarities in the use of smart phones, we expect that similar general studies in other countries could show similar results. We collected data on industries in which the respondents work, in order to be able to analyze their diversity, not for a sampling scheme. In the questionnaire, we used the Classification of Activities of the National Romanian Economy [
52] to gain a global view of the fields of activities in which employees are currently working (details in
Table A7). Hence, the resulting sample has no representativeness for each industry and the number of nominated industries (17) is very high relative to the total number of 368 respondents (with an average of 22 respondents/industry), which shows that no industry is predominant. This paper is limited regarding any influences from different industries on the usage of mobile phones and any significant differences between industries in terms of mobile phone usage. Thus, further research on specific industries might show different results, due to the specificity of potential uses of mobile phones in each industry or even in each type of job. Further lines of research on our topic could concentrate on analyzing the collected data on personal and professional information processes at work, taking into consideration the socio-demographic data of respondents.
Another limitation is the restriction of the applications of mobile phones to a classification of relevant categories, which we used during data collection. This classification covers most of the uses of smartphones but, given the versatility of applications that can be hosted by mobile devices, we cannot claim to have covered all their potential uses.