Non-Linear Microscopy: A Well-Established Technique for Biological Applications towards Serving as a Diagnostic Tool for in situ Cultural Heritage Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Problem Statement: Factors that Cause Degradation of a Cultural Heritage (CH) Object
1.2. Diagnostic Imaging Methods in the Service of Cultural Heritage
1.2.1. Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS)
1.2.2. Holography
1.2.3. Multi-spectral Imaging
1.2.4. Raman Spectroscopy
1.2.5. Fourier-Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
1.2.6. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
1.2.7. Terahertz Time-Domain imaging (THz-TDI)
1.2.8. Laser-Induced Fluorescence Spectroscopy (LIF)
1.2.9. Photoacoustic Microscopy (PA)
1.2.10. Pump-Probe Spectroscopy
1.3. Non-linear Microscopy
1.4. Non-linear Imaging as a Tool to Serve Cultural Heritage Studies
1.5. Synergy of Non-linear Techniques with other Imaging Modalities
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Multi-Photon Excitation Fluorescence (MPEF)
2.2. Second and Third Harmonic Generation (SHG, THG)
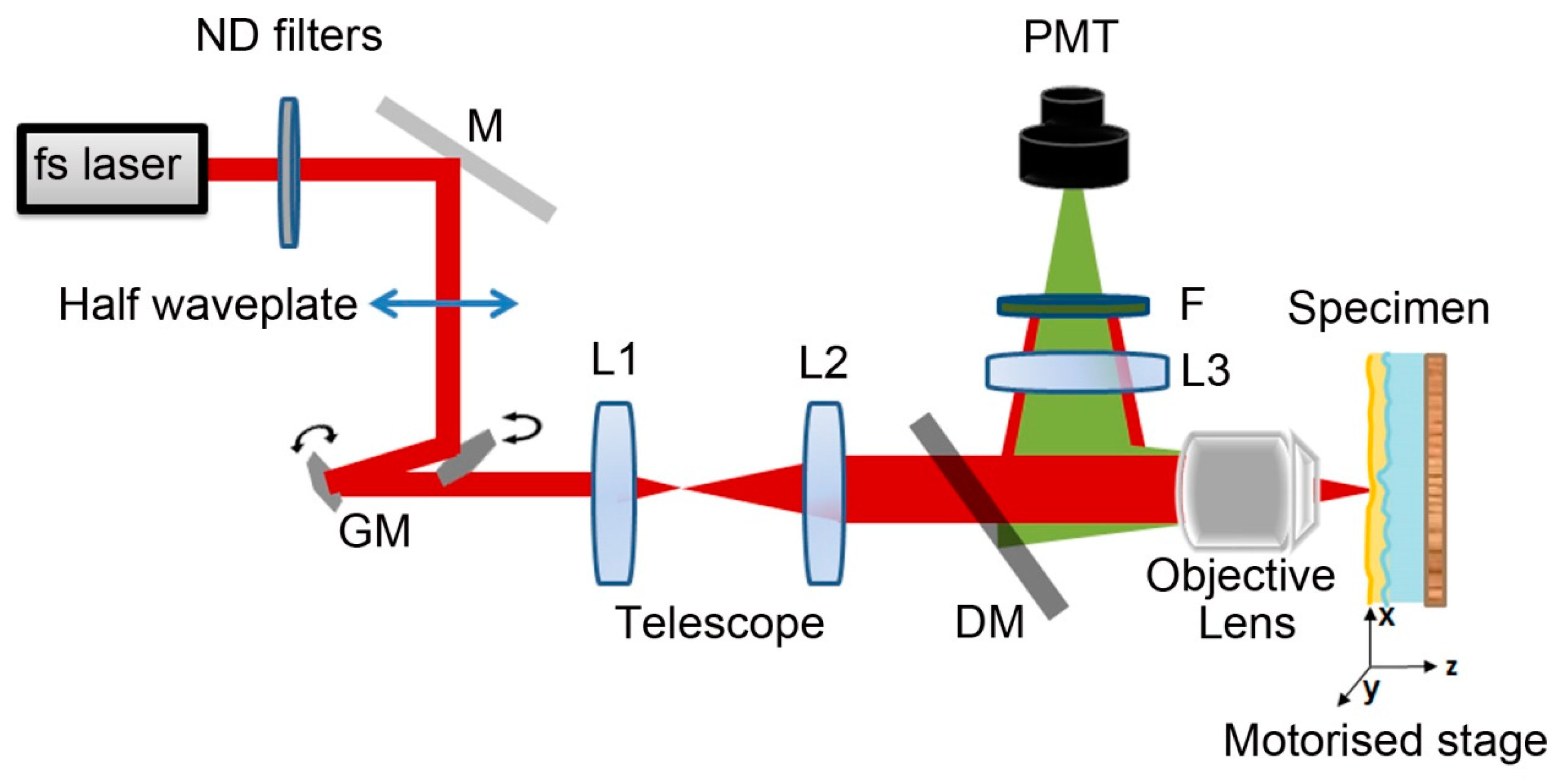
2.3. Experimental Apparatus—Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Layer Discrimination in Multi-layered Samples
3.2. Artificial Aging Studies
3.3. Towards the Construction of a Transportable System for in situ Applications
3.4. Microscope Specifications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carlyle, L. The Artist’s Assistant, Oil Painting Instruction Manuals and Handbooks in Britain 1800–1900 with Reference to Selected Eighteenth-Century Sources; Archetype Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Eastaugh, N.; Walsh, V.; Siddall, R.; Chaplin, T. Optical Microscopy of Historical Pigments; The Pigment Compendium: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Stoner, J.H.; Rushfield, R.A. Conservation of Easel Paintings; Routledge: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Miliani, C.; Monico, L.; Melo, M.J.; Fantacci, S.; Angelin, E.M.; Romani, A.; Janssens, K. Photochemistry of Artists’ Dyes and Pigments: Towards Better Understanding and Prevention of Colour Change in Works of Art. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7324–7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Area, M.C.; Cheradame, H. Paper aging and degradation: Recent findings and research methods. BioResources 2011, 6, 5307–5337. [Google Scholar]
- Kuchitsu, N.; Morii, M.; Sakai, S.; Unten, H. Simple evaluation of the degradation state of cultural heritage based on multi-view stereo. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2019, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palomar, T.; Oujja, M.; Castillejo, M.; Sabio, R.; Rincón, J.; García-Heras, M.; Villegas, M. Roman glasses from Augusta Emerita: Study of degradation pathologies using LIBS. In Sciene and Technology for the Conservation of Cultural Heritage; CRC Press: London, UK, 2013; pp. 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Melcher, M.; Wiesinger, R.; Schreiner, M. Degradation of Glass Artifacts: Application of Modern Surface Analytical Techniques. Accounts Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbrich, J.; Mai, C.; Militz, H. Evaluation of bacterial wood degradation by Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) measurements. J. Cult. Heritage 2012, 13, S135–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinnebier, R.E.; Runčevski, T.; Fischer, A.; Eggert, G. Solid-State Structure of a Degradation Product Frequently Observed on Historic Metal Objects. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 2638–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Song, H.; Cho, S.W.; Kim, C.E.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, K. Optical Measurements of Paintings and the Creation of an Artwork Database for Authenticity. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouli, P.; Selimis, A.; Georgiou, S.; Fotakis, C. Recent Studies of Laser Science in Paintings Conservation and Research. Accounts Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglos, D. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in heritage science. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botto, A.; Campanella, B.; Legnaioli, S.; Lezzerini, M.; Lorenzetti, G.; Pagnotta, S.; Poggialini, F.; Palleschi, V. Applications of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in cultural heritage and archaeology: A critical review. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2019, 34, 81–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglos, D.; Detalle, V. Cultural Heritage Applications of LIBS. Springer Ser. Opt. Sci. 2014, 182, 531–554. [Google Scholar]
- Osticioli, I.; Agresti, J.; Fornacelli, C.; Memmi, I.T.; Siano, S. Potential role of LIPS elemental depth profiling in authentication studies of unglazed earthenware artifacts. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2012, 27, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudiuso, R.; Dell’Aglio, M.; De Pascale, O.; Senesi, G.S.; De Giacomo, A. Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy for Elemental Analysis in Environmental, Cultural Heritage and Space Applications: A Review of Methods and Results. Sensors 2010, 10, 7434–7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papliaka, Z.E.; Philippidis, A.; Siozos, P.; Vakondiou, M.; Melessanaki, K.; Anglos, D. A multi-technique approach, based on mobile/portable laser instruments, for the in situ pigment characterization of stone sculptures on the island of Crete dating from Venetian and Ottoman period. Heritage Sci. 2016, 4, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westlake, P.; Siozos, P.; Philippidis, A.; Apostolaki, C.; Derham, B.; Terlixi, A.; Perdikatsis, V.; Jones, R.; Anglos, D. Studying Pigments on Painted Plaster in Minoan, Roman and Early Byzantine Crete. A Multi-Analytical Technique Approach. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 1413–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosma, K.; Andrianakis, M.; Hatzigiannakis, K.; Tornari, V. Digital holographic interferometry for cultural heritage structural diagnostics: A coherent and a low-coherence optical set-up for the study of a marquetry sample. Strain 2018, 54, e12263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Stoykova, E.; Berberova, N.; Park, J.; Nazarova, D.; Park, J.S.; Kim, Y.; Hong, S.; Ivanov, B.; Malinowski, N. Three-dimensional imaging of cultural heritage artifacts with holographic printers. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference and School on Quantum Electronics: Laser Physics and Applications, Sozopol, Bulgaria, 5 January 2017; Volume 10226, p. 102261. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.J.; Deng, F.; Brown, M.S. Visual enhancement of old documents with hyperspectral imaging. Pattern Recognit. 2011, 44, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedjam, R.; Cheriet, M. Historical document image restoration using multispectral imaging system. Pattern Recognit. 2013, 46, 2297–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H. Advances in Multispectral and Hyperspectral Imaging for Archaeology and Art Conservation. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 106, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kogou, S.; Neate, S.; Coveney, C.; Miles, A.; Boocock, D.; Burgio, L.; Cheung, C.S.; Liang, H. The origins of the Selden map of China: Scientific analysis of the painting materials and techniques using a holistic approach. Heritage Sci. 2016, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delaney, J.K.; Picollo, M. JAIC special issue on “Reflectance hyperspectral imaging to support documentation and conservation of 2D artworks”. J. Am. Inst. Conserv. 2019, 58, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anglos, D. Shedding light on the past: Optical technologies applied to cultural heritage. Heritage Sci. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nevin, A.; Spoto, G.; Anglos, D. Laser Spectroscopies for Elemental and Molecular Analysis in Art and Archaeology. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 106, 339–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, P.; Colomban, P.; Tournié, A.; Milande, V. Nondestructive on-site identification of ancient glasses: Genuine artefacts, embellished pieces or forgeries? J. Raman Spectrosc. 2009, 40, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caggiani, M.C.; Colomban, P. Testing of Raman spectroscopy as a non-invasive tool for the investigation of glass-protected pastels. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2011, 42, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomban, P.; Tournié, A. On-site Raman identification and dating of ancient/modern stained glasses at the Sainte-Chapelle, Paris. J. Cult. Heritage 2007, 8, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badea, G.I.; Caggiani, M.C.; Colomban, P.; Mangone, A.; Teodor, E.D.; Teodor, E.S.; Radu, G.-L. Fourier Transform Raman and Statistical Analysis of Thermally Altered Samples of Amber. Appl. Spectrosc. 2015, 69, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peets, P.; Leito, I.; Pelt, J.; Vahur, S. Identification and classification of textile fibres using ATR-FT-IR spectroscopy with chemometric methods. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 173, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ion, R.M.; Boros, D.; Ion, M.L.; Dumitriu, I.; Fierascii, R.C.; Radovici, C.; Florea, G.; Bercu, C. Combined spectral analysis (EDXRF, ICP-AES, XRD, FTIR) for characterization of bronze roman mirror. Met. Int. 2008, 13, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Fierascu, R.C.; Avramescu, S.M.; Vasilievici, G.; Fierascu, I.; Paunescu, A. Thermal and spectroscopic investigation of Romanian historical documents from the nineteenth and twentieth century. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 123, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyuz, T.; Akyuz, S.; Balci, K.; Gulec, A. Investigations of historical textiles from the Imperial Pavilion (Hunkar Kasri) of the new mosque Eminonu-Istanbul (Turkey) by multiple analytical techniques. J. Cult. Heritage 2017, 25, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgitt, C.; Harris, S.; Cartwright, C.; Cruickshank, P. Assessing the potential of historic archaeological collections: A pilot study of the British Museum’s Swiss lake dwelling textiles. Br. Museum Techn. Res. Bull. 2011, 5, 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- La Russa, M.F.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Barone, G.; Crisci, G.M.; Mazzoleni, P.; Pezzino, A. The Use of FTIR and Micro-FTIR Spectroscopy: An Example of Application to Cultural Heritage. Int. J. Spectrosc. 2009, 2009, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miliani, C.; Rosi, F.; Daveri, A.; Brunetti, B.G. Reflection infrared spectroscopy for the non-invasive in situ study of artists’ pigments. App. Phys. A Mater. 2012, 106, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.; Nel, P.; Stuart, B. Non-invasive identification of polymers in cultural heritage collections: Evaluation, optimisation and application of portable FTIR (ATR and external reflectance) spectroscopy to three-dimensional polymer-based objects. Heritage Sci. 2019, 7, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wen, C.; Jin, M.; Duan, L.; Zhang, R.; Luo, C.; Xiao, J.; Ye, Z.; Gao, B.; Liu, P.; et al. FTIR Spectroscopy in Cultural Heritage Studies: Non-destructive Analysis of Chinese Handmade Papers. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2019, 35, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Cid, M.G.; Cucu, R.G.; Dobre, G.M.; Podoleanu, A.G.; Pedro, J.; Saunders, D. En-face optical coherence tomography—A novel application of non-invasive imaging to art conservation. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arecchi, T.; Bellini, M.; Corsi, C.; Fontana, R.; Materazzi, M.; Pezzati, L.; Tortora, A. A new tool for painting diagnostics: Optical coherence tomography. Opt. Spectrosc. 2006, 101, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Peric, B.; Hughes, M.; Podoleanu, A.G.; Spring, M.; Roehrs, S. Optical Coherence Tomography in archaeological and conservation science—A new emerging field. In Proceedings of the 1st Canterbury Workshop and School in Optical Coherence Tomography and Adaptive Optics, Canterbury, UK, 30 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Targowski, P.; Iwanicka, M. Optical Coherence Tomography: Its Role in the Non-Invasive Structural Examination and Conservation of Cultural Heritage Objects-A Review. App. Phys. A Mater. 2012, 106, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Striova, J.; Fontana, R.; Barucci, M.; Felici, A.; Marconi, E.; Pampaloni, E.; Raffaelli, M.; Riminesi, C. Optical devices provide unprecedented insights into the laser cleaning of calcium oxalate layers. Microchem. J. 2016, 124, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanicka, M.; Tymińska-Widmer, L.; Rouba, B.J.; Kwiatkowska, E.A.; Sylwestrzak, M.; Targowski, P. Through-Glass Structural Examination of Hinterglasmalerei by Optical Coherence Tomography. In Lasers in the Conservation of Artworks VIII—Proceedings of the International Conference on Lasers in the Conservation of Artworks VIII, LACONA VIII; CRC Press: Sibiu, Romania, 2011; pp. 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Kunicki-Goldfinger, J.; Targowski, P.; Góra, M.; Karaszkiewicz, P.; Dzierżanowski, P. Characterization of Glass Surface Morphology by Optical Coherence Tomography. Stud. Conserv. 2009, 54, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.-L.; Winkler, A.; Klein, J.; Wall, A.; Barto, J. Using Optical Coherence Tomography to Characterize the Crack Morphology of Ceramic Glaze and Jade. In Selected Topics in Optical Coherence Tomography; IntechOpen: Shanghai, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Iwanicka, M.; Kwiatkowska, E.A.; Sylwestrzak, M.; Targowski, P. Application of optical coherence tomography (OCT) for real time monitoring of consolidation of the paint layer in Hinterglasmalerei objects. SPIE Opt. Metrol. 2011, 8084, 80840. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.; Lange, R.; Peric, B.; Spring, M. Optimum spectral window for imaging of art with optical coherence tomography. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 111, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flammini, M.; Bonsi, C.; Ciano, C.; Giliberti, V.; Pontecorvo, E.; Italia, P.; DelRe, E.; Ortolani, M. Confocal Terahertz Imaging of Ancient Manuscripts. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2017, 38, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catapano, I.; Soldovieri, F. A Data Processing Chain for Terahertz Imaging and Its Use in Artwork Diagnostics. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2017, 38, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, A. Terahertz and Cultural Heritage Science: Examination of Art and Archaeology. Technologies 2016, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhrström, L.; Fischer, B.M.; Bitzer, A.; Wallauer, J.; Walther, M.; Rühli, F. Terahertz Imaging Modalities of Ancient Egyptian Mummified Objects and of a Naturally Mummified Rat. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Boil. 2015, 298, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.B.; Mourou, M.; Whitaker, J.; Duling, I.; Williamson, S.; Menu, M.; Mourou, G.; Iii, I.D. Terahertz imaging for non-destructive evaluation of mural paintings. Opt. Commun. 2008, 281, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, K. Case Studies of THz Pulsed TDI. In Metallography in Archaeology and Art; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 4, pp. 85–144. [Google Scholar]
- Dandolo, C.L.K.; Jepsen, P.U.; Christensen, M.C. Characterization of European lacquers by terahertz (THz) reflectometric imaging. In Proceedings of the 2013 Digital Heritage International Congress (DigitalHeritage), Marseille, France, 28 October–1 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Skryl, A.S.; Jackson, J.B.; Bakunov, M.I.; Menu, M.; Mourou, G.A. Terahertz time-domain imaging of hidden defects in wooden artworks: Application to a Russian icon painting. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, E.; Fukunaga, K. Terahertz Imaging Applied to the Examination of Artistic Objects. Stud. Conserv. 2015, 60, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seco-Martorell, C.; López-Domínguez, V.; Arauz-Garofalo, G.; Redo-Sanchez, A.; Palacios, J.; Tejada, J. Goya’s artwork imaging with Terahertz waves. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 17800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grönlund; Johansson, A.; Barup, K.; Svanberg, S. Hällström Remote Multicolor Excitation Laser-Induced Fluorescence Imaging. Laser Chem. 2006, 2006, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fantoni, R.; Caneve, L.; Colao, F.; Fiorani, L.; Palucci, A.; Dell’Erba, R.; Fassina, V. Laser-induced fluorescence study of medieval frescoes by Giusto de’ Menabuoi. J. Cult. Heritage 2013, 14, S59–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Hernández, A.; Oujja, M.; Sanz, M.; Carrasco, E.; Detalle, V.; Castillejo, M. Analysis of heritage stones and model wall paintings by pulsed laser excitation of Raman, laser-induced fluorescence and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy signals with a hybrid system. J. Cult. Heritage 2018, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tserevelakis, G.J.; Fovo, A.D.; Melessanaki, K.; Fontana, R.; Zacharakis, G. Photoacoustic signal attenuation analysis for the assessment of thin layers thickness in paintings. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 123, 123102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tserevelakis, G.J.; Vrouvaki, I.; Siozos, P.; Melessanaki, K.; Hatzigiannakis, K.; Fotakis, C.; Zacharakis, G. Photoacoustic imaging reveals hidden underdrawings in paintings. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tserevelakis, G.J.; Pozo-Antonio, J.S.; Siozos, P.; Rivas, T.; Pouli, P.; Zacharakis, G. On-line photoacoustic monitoring of laser cleaning on stone: Evaluation of cleaning effectiveness and detection of potential damage to the substrate. J. Cult. Heritage 2019, 35, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, W.S.; Fischer, M.C.; Tong, Y. Novel Nonlinear Contrast Improves Deep-Tissue Microscopy. Laser Focus World. 2007, 43, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, T.; Fu, D.; Warren, W.S. Nonlinear Absorption Microscopy. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009, 85, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samineni, P.; DeCruz, A.; Villafaña, T.E.; Warren, W.S.; Fischer, M.C. Pump-probe imaging of historical pigments used in paintings. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 1310–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villafana, T.E.; Brown, W.P.; Delaney, J.K.; Palmer, M.; Warren, W.S.; Fischer, M.C. Femtosecond pump-probe microscopy generates virtual cross-sections in historic artwork. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1708–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Warren, W.S.; Fischer, M.C. Spectroscopic Differentiation and Microscopic Imaging of Red Organic Pigments Using Optical Pump–Probe Contrast. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 12686–12691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stentz, A.J.; Boyd, R.W. Nonlinear optics. In The Handbook of Photonics, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Stockert, J.C.; Blazquez-Castro, A.; Stockert, J.C.; Blazquez-Castro, A. Non-linear Optics. In Fluorescence Microscopy in Life Sciences; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, UAE, 2017; pp. 642–686. [Google Scholar]
- Filippidis, G.; Tserevelakis, G.J.; Selimis, A.; Fotakis, C. Nonlinear Imaging Techniques as Non-Destructive, High-Resolution Diagnostic Tools for Cultural Heritage Studies. Appl. Phys. A 2015, 118, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, M.; Tsafas, V.; Melessanaki, K.; Filippidis, G. Applications of non-linear imaging microscopy techniques to cultural heritage objects. Insight Non Destr. Test. Cond. Monit. 2018, 60, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Mari, M.; Cheung, C.S.; Kogou, S.; Johnson, P.; Filippidis, G. Optical coherence tomography and non-linear microscopy for paintings—A study of the complementary capabilities and laser degradation effects. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 19640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fovo, A.D.; Fontana, R.; Striová, J.; Pampaloni, E.; Barucci, M.; Raffaelli, M.; Mercatelli, R.; Pezzati, L.; Cicchi, R. Nonlinear optical imaging techniques (NLO) for painting investigation. In Proceedings of the LACONA XI Lasers in the Conservation of Artworks XI, 20–23 September 2016; NCU Press Torun: Krakow, Poland.
- Filippidis, G.; Mari, M.; Kelegkouri, L.; Philippidis, A.; Selimis, A.; Melessanaki, K.; Sygletou, M.; Fotakis, C. Assessment of In-Depth Degradation of Artificially Aged Triterpenoid Paint Varnishes Using Nonlinear Microscopy Techniques. Microsc. Microanal. 2015, 21, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippidis, G.; Melessanaki, K.; Fotakis, C. Second and third harmonic generation measurements of glues used for lining textile supports of painted artworks. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 2161–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psilodimitrakopoulos, S.; Gavgiotaki, E.; Melessanaki, K.; Tsafas, V.; Filippidis, G. Polarization Second Harmonic Generation Discriminates Between Fresh and Aged Starch-Based Adhesives Used in Cultural Heritage. Microsc. Microanal. 2016, 22, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latour, G.; Echard, J.-P.; Didier, M.; Schanne-Klein, M.-C. In situ 3D characterization of historical coatings and wood using multimodal nonlinear optical microscopy. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 24623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latour, G.; Robinet, L.; Dazzi, A.; Portier, F.; Deniset-Besseau, A.; Schanne-Klein, M.C. Correlative Nonlinear Optical Microscopy and Infrared Nanoscopy Reveals Collagen Degradation in Altered Parchments. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faraldi, F.; Tserevelakis, G.J.; Filippidis, G.; Ingo, G.M.; Riccucci, C.; Fotakis, C. Multi photon excitation fluorescence imaging microscopy for the precise characterization of corrosion layers in silver-based artifacts. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 111, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Mao, Y.; Flueraru, C. Jade detection and analysis based on optical coherence tomography images. Opt. Eng. 2010, 49, 063602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.-L.; Lu, C.-W.; Hsu, I.-J.; Yang, C.-C. The Use of Optical Coherence Tomography for Monitoring the Subsurface Morphologies of Archaic Jades. Archaeometry 2004, 46, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Winkler, A.M.; Barton, J.K.; Vandiver, P.B. Using optical coherence tomography to examine the subsurface morphology of chinese glazes. Archaeometry 2009, 51, 808–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pircher, M.; Bajraszewski, T.; Strlic, M.; Kolar, J.; Hitzenberger, C.K.; Targowski, P. Optical Coherence Tomography for Examination of Parchment Degradation. Laser Chem. 2006, 2006, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vazquez-Calvo, C.; Martínez-Ramírez, S.; De Buergo, M.A.; Fort, R. The Use of Portable Raman Spectroscopy to Identify Conservation Treatments Applied to Heritage Stone. Spectrosc. Lett. 2012, 45, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Culka, A.; Jehlička, J. Identification of gemstones using portable sequentially shifted excitation Raman spectrometer and RRUFF online database: A proof of concept study. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2019, 134, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierlinger, N.; Schwanninger, M. Chemical Imaging of Poplar Wood Cell Walls by Confocal Raman Microscopy. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, D.; Chen, S.; Liu, Q. Review of Fluorescence Suppression Techniques in Raman Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2015, 50, 387–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemann, M.A. In situ micro-Raman spectroscopy on minerals on-site in the Grotto Hall of the New Palace, Park Sanssouci, in Potsdam. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2006, 37, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehlička, J.; Culka, A.; Bersani, D.; Vandenabeele, P. Comparison of seven portable Raman spectrometers: Beryl as a case study. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2017, 48, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colomban, P.; Tournié, A.; Maucuer, M.; Meynard, P. On-Site Raman and XRF Analysis of Japanese/Chinese Bronze/brass Patina—The Search for Specific Raman Signatures. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2012, 43, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquier, M.; Colomban, P.; Milande, V. Raman and Infrared Analysis of Glues Used for Pottery Conservation Treatments. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2009, 40, 1641–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, C.; Paris, C.; Le Hô, A.-S.; Bellot-Gurlet, L.; Echard, J.-P. A joint use of Raman and infrared spectroscopies for the identification of natural organic media used in ancient varnishes. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2010, 41, 1494–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro, K.; Pessanha, S.; Proietti, N.; Princi, E.; Capitani, D.; Carvalho, M.L.; Madariaga, J.M. Noninvasive and nondestructive NMR, Raman and XRF analysis of a Blaeu coloured map from the seventeenth century. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannucci, E.; Pastorelli, R.; Zerbi, G.; Bottani, C.E.; Facchini, A. Recovery of ancient parchment: Characterization by vibrational spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2000, 31, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tserevelakis, G.J.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Siozos, P.; Zacharakis, G. Uncovering the Hidden Content of Layered Documents by Means of Photoacoustic Imaging. Strain 2019, 55, e12289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, A.; Barberis, L.; Bearman, R.; Marengo, M. Portable non-invasive imaging method for monitoring the conservation of frescoes. 2015 Digital Heritage 2015, 2, 449–452. [Google Scholar]
- Salerno, E.; Tonazzini, A.; Grifoni, E.; Lorenzetti, G.; Legnaioli, S.; Lezzerini, M.; Marras, L.; Pagnotta, S.; Palleschi, V. Analysis of Multispectral Images in Cultural Heritage and Archaeology. J. Laser Appl. Spectrosc. 2014, 1, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Pouli, P.; Zafiropulos, V.; Balas, C.; Doganis, Y.; Galanos, A. Laser cleaning of inorganic encrustation on excavated objects: Evaluation of the cleaning result by means of multi-spectral imaging. J. Cult. Heritage 2003, 4, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakis, V.; Loukaiti, A.; Pouli, P. A spectral imaging methodology for determining on-line the optimum cleaning level of stonework. J. Cult. Heritage 2010, 11, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaleri, T.; Buscaglia, P.; Migliorini, S.; Nervo, M.; Piccablotto, G.; Piccirillo, A.; Pisani, M.; Puglisi, D.; Vaudan, D.; Zucco, M. Pictorial Materials Database: 1200 Combinations of Pigments, Dyes, Binders and Varnishes Designed as a Tool for Heritage Science and Conservation. Appl. Phys. A 2017, 123, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, T.; Löffler, T.; Saito, T.; Yukihira, N.; Deninger, A.; Fukunaga, K. A portable all-electronic THz scanner for the inspection of structural earthquake damage in Japanese buildings. In Proceedings of the 2012 37th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves, Wollongong, NSW, Australia, 23–28 September 2012; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga, K.; Cortes, E.; Cosentino, A.; Stünkel, I.; Leona, M.; Iii, I.N.D.; Mininberg, D.T. Investigating the use of terahertz pulsed time domain reflection imaging for the study of fabric layers of an Egyptian mummy. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. Rapid Publ. 2011, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koch-Dandolo, C.L.; Filtenborg, T.; Fukunaga, K.; Skou-Hansen, J.; Jepsen, P.U. Reflection terahertz time-domain imaging for analysis of an 18th century neoclassical easel painting. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 5123–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipfel, W.R.; Williams, R.M.; Webb, W.W. Nonlinear magic: Multiphoton microscopy in the biosciences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehberg, M.; Krombach, F.; Pohl, U.; Dietzel, S. Label-Free 3D Visualization of Cellular and Tissue Structures in Intact Muscle with Second and Third Harmonic Generation Microscopy. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cox, G.; Kable, E.; Jones, A.; Fraser, I.; Manconi, F.; Gorrell, M.D. 3-Dimensional imaging of collagen using second harmonic generation. J. Struct. Boil. 2003, 141, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavgiotaki, E.; Filippidis, G.; Markomanolaki, H.; Kenanakis, G.; Agelaki, S.; Georgoulias, V.; Athanassakis, I. Distinction between breast cancer cell subtypes using third harmonic generation microscopy. J. Biophotonics 2016, 10, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, M.; Filippidis, G.; Palikaras, K.; Petanidou, B.; Fotakis, C.; Tavernarakis, N. Imaging ectopic fat deposition in caenorhabditis elegans muscles using nonlinear microscopy. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2015, 78, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palikaras, K.; Mari, M.; Petanidou, B.; Pasparaki, A.; Filippidis, G.; Tavernarakis, N. Ectopic Fat Deposition Contributes to Age-Associated Pathology in Caenorhabditis Elegans. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filippidis, G.; Gualda, E.J.; Melessanaki, K.; Fotakis, C. Nonlinear imaging microscopy techniques as diagnostic tools for art conservation studies. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.P.; Houle, M.-A.; Popov, K.; Nicklaus, M.; Couture, C.-A.; Laliberté, M.; Brabec, T.; Ruediger, A.; Carr, A.J.; Price, A.J.; et al. Imaging and Modeling Collagen Architecture from the Nano to Micro Scale. Biomed. Opt. Express 2014, 5, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villafana, T.E.; Delaney, J.K.; Warren, W.S.; Fischer, M.C. High-resolution, three-dimensional imaging of pigments and support in paper and textiles. J. Cult. Heritage 2016, 20, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tserevelakis, G.J.; Tsafas, V.; Melessanaki, K.; Zacharakis, G.; Filippidis, G. Combined multiphoton fluorescence microscopy and photoacoustic imaging for stratigraphic analysis of paintings. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 1154–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oujja, M.; Psilodimitrakopoulos, S.; Carrasco, E.; Sanz, M.; Philippidis, A.; Selimis, A.; Pouli, P.; Filippidis, G.; Castillejo, M. Nonlinear imaging microscopy for assessing structural and photochemical modifications upon laser removal of dammar varnish on photosensitive substrates. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 22836–22843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filippidis, G.; Massaouti, M.; Selimis, A.; Gualda, E.J.; Manceau, J.M.; Tzortzakis, S. Nonlinear Imagig and THz Diagnostic Tools in the Service of Cultural Heritage. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 106, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fovo, A.D.; Sanz, M.; Mattana, S.; Oujja, M.; Marchetti, M.; Pavone, F.; Cicchi, R.; Fontana, R.; Castillejo, M. Safe limits for the application of nonlinear optical microscopies to cultural heritage: A new method for in-situ assessment. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Doelen, G.A.; Van den Berg, K.J.; Boon, J.J. Comparative Chromatographic and Massspectrometric Studies of Triterpenoid Varnishes: Fresh Material and Aged Samples from Paintings. Stud. Conserv. 1998, 43, 249–264. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Wise, F.W. Recent advances in fibre lasers for nonlinear microscopy. Nat. Photon. 2013, 7, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualda, E.J.; Filippidis, G.; Melessanaki, K.; Fotakis, C. Third-harmonic generation and multi-photon excitation fluorescence imaging microscopy techniques for online art conservation diagnosis. Appl. Spectrosc. 2009, 63, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Modality | Advantages | Limitations | CH objects - Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| NLM |
| Varnishes [79], lining glues [80,81], historical coatings [82], parchments [83], paint [75], corrosion layer [84] | |
| OCT |
| Varnish and glaze layers of paintings [43], semi-transparent solids [44,85,86], glazed ceramics [87], parchment [88], underdrawings [42,44] | |
| Raman | Rocks and minerals [93], gemstones [94], corrosion layers [95], glues [96], varnishes [97], pigments on stone sculptures [18] or on painted plaster [19], paper [98], parchments and inks [99] | ||
| Photoacoustic |
|
| Acrylic paints on canvas [65], sketch lines and underdrawings [66], multi-layered documents and paper sheets [100], graffiti cleaning on white marble [67] |
| Multi-spectral imaging |
| Distribution and identification of several pigments across a map [25], monitor the cleaning of marbles [103,104], multi-variate combinations of pictorial materials [105] | |
| THz |
| Fabric and mummies [55,107], western wall paintings [56], oil paintings [61,108], Japanese panel paintings and screens [60] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mari, M.; Filippidis, G. Non-Linear Microscopy: A Well-Established Technique for Biological Applications towards Serving as a Diagnostic Tool for in situ Cultural Heritage Studies. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041409
Mari M, Filippidis G. Non-Linear Microscopy: A Well-Established Technique for Biological Applications towards Serving as a Diagnostic Tool for in situ Cultural Heritage Studies. Sustainability. 2020; 12(4):1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041409
Chicago/Turabian StyleMari, Meropi, and George Filippidis. 2020. "Non-Linear Microscopy: A Well-Established Technique for Biological Applications towards Serving as a Diagnostic Tool for in situ Cultural Heritage Studies" Sustainability 12, no. 4: 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041409
APA StyleMari, M., & Filippidis, G. (2020). Non-Linear Microscopy: A Well-Established Technique for Biological Applications towards Serving as a Diagnostic Tool for in situ Cultural Heritage Studies. Sustainability, 12(4), 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041409





