Investigation into Creep Characteristics and Model of Recycled Construction and Demolition Waste Used in Embankment Filler
Abstract
:1. Introduction
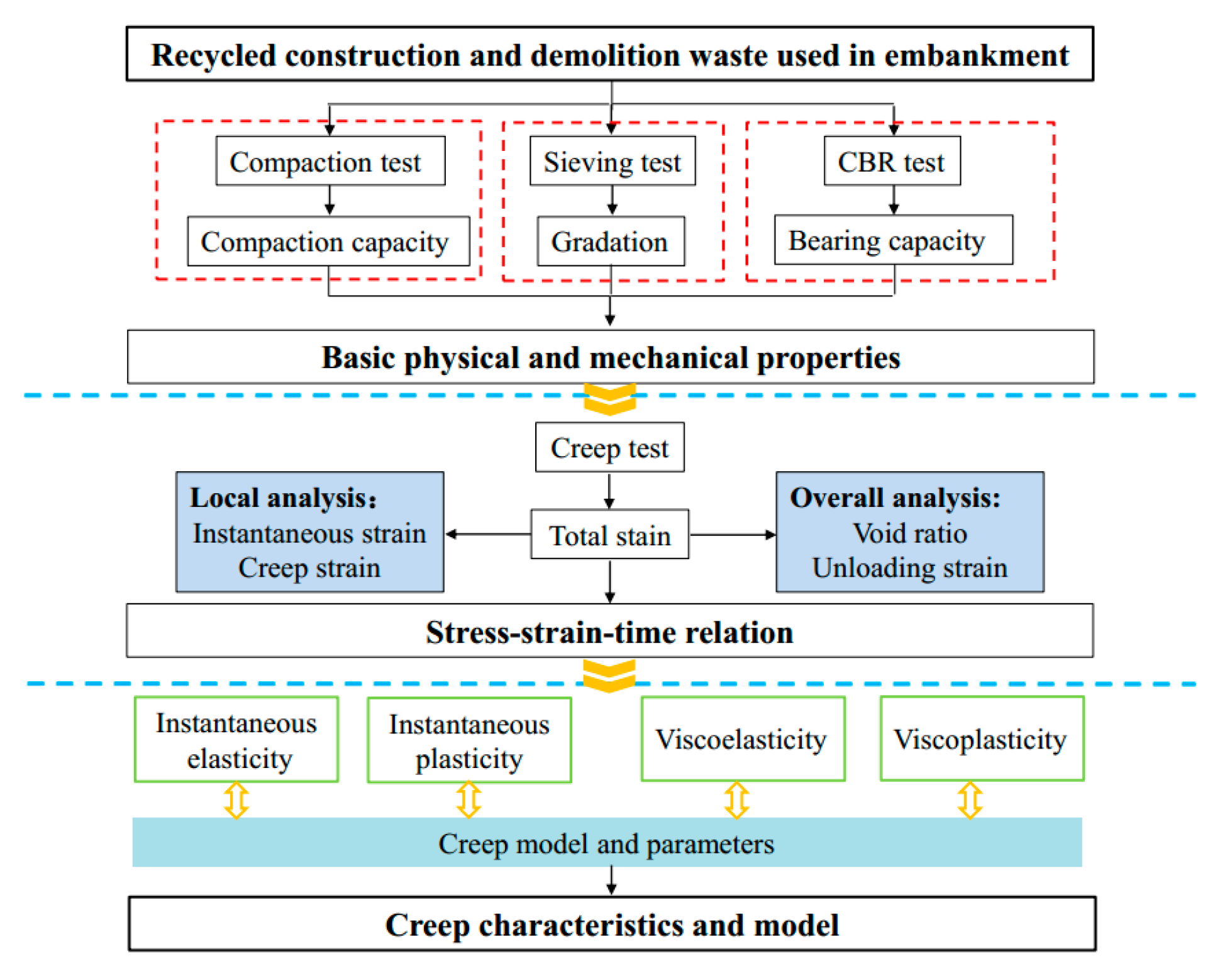
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
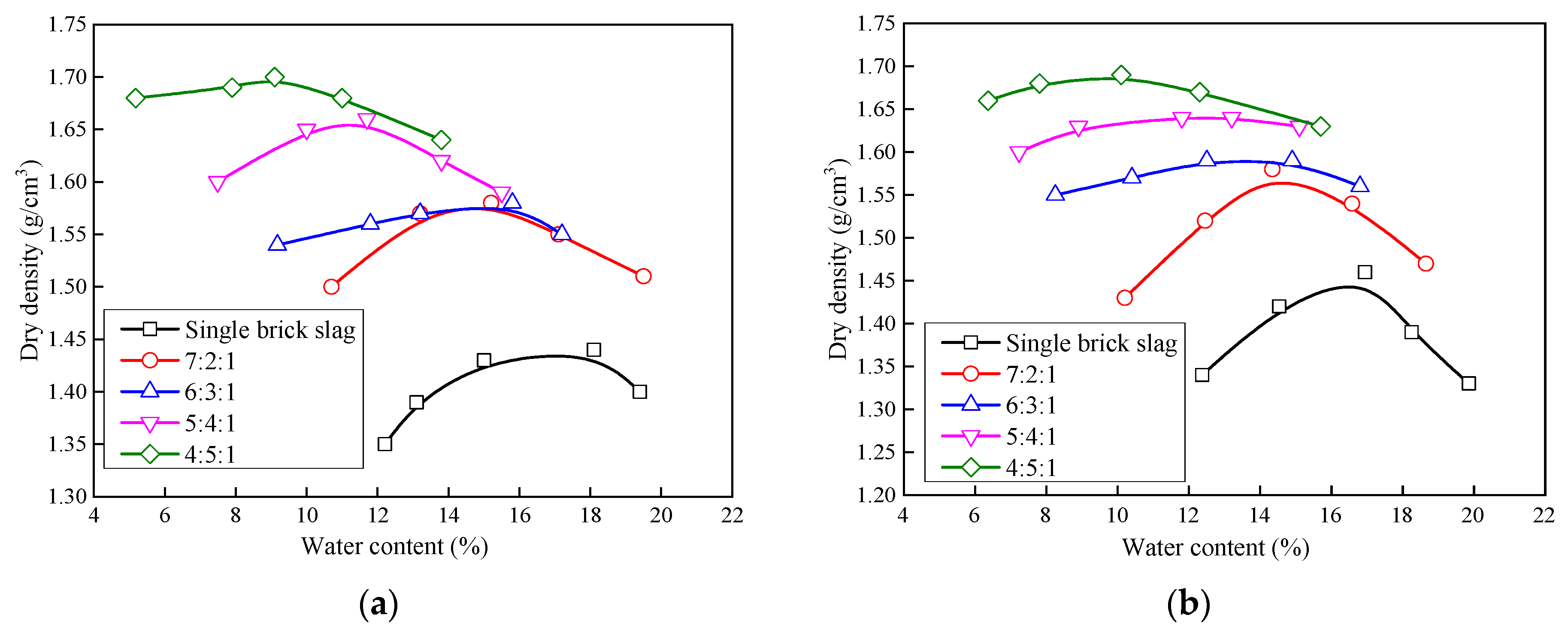
2.2. Compaction Test
2.3. Sieving Test
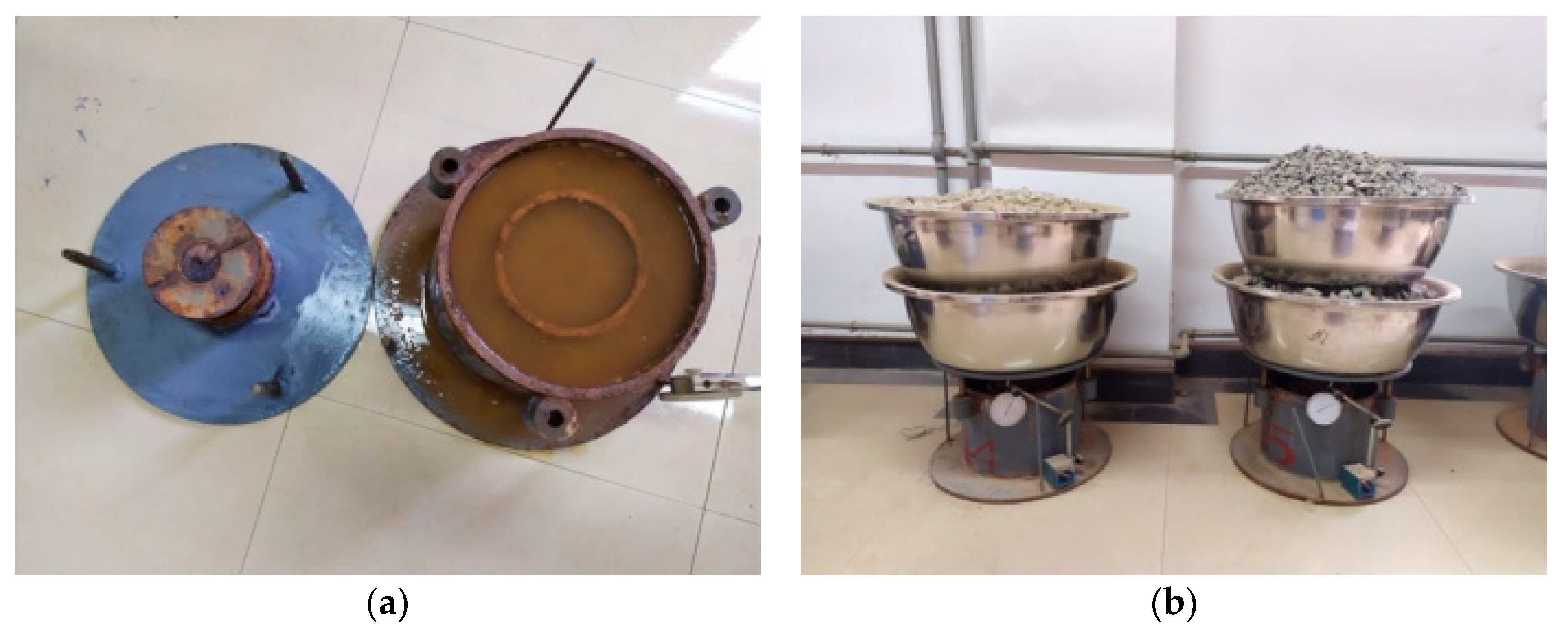
2.4. CBR Test
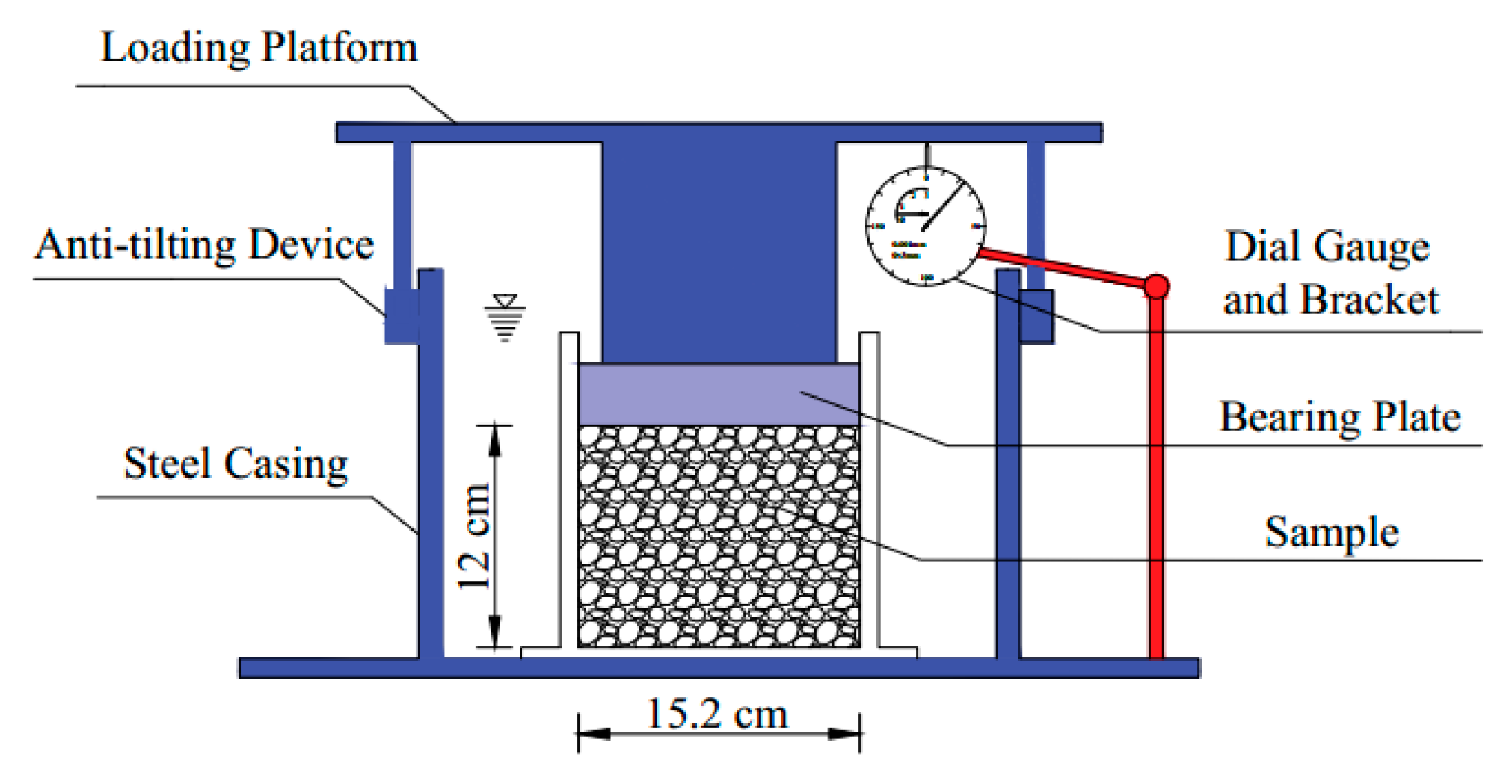
2.5. Creep Test
3. Results
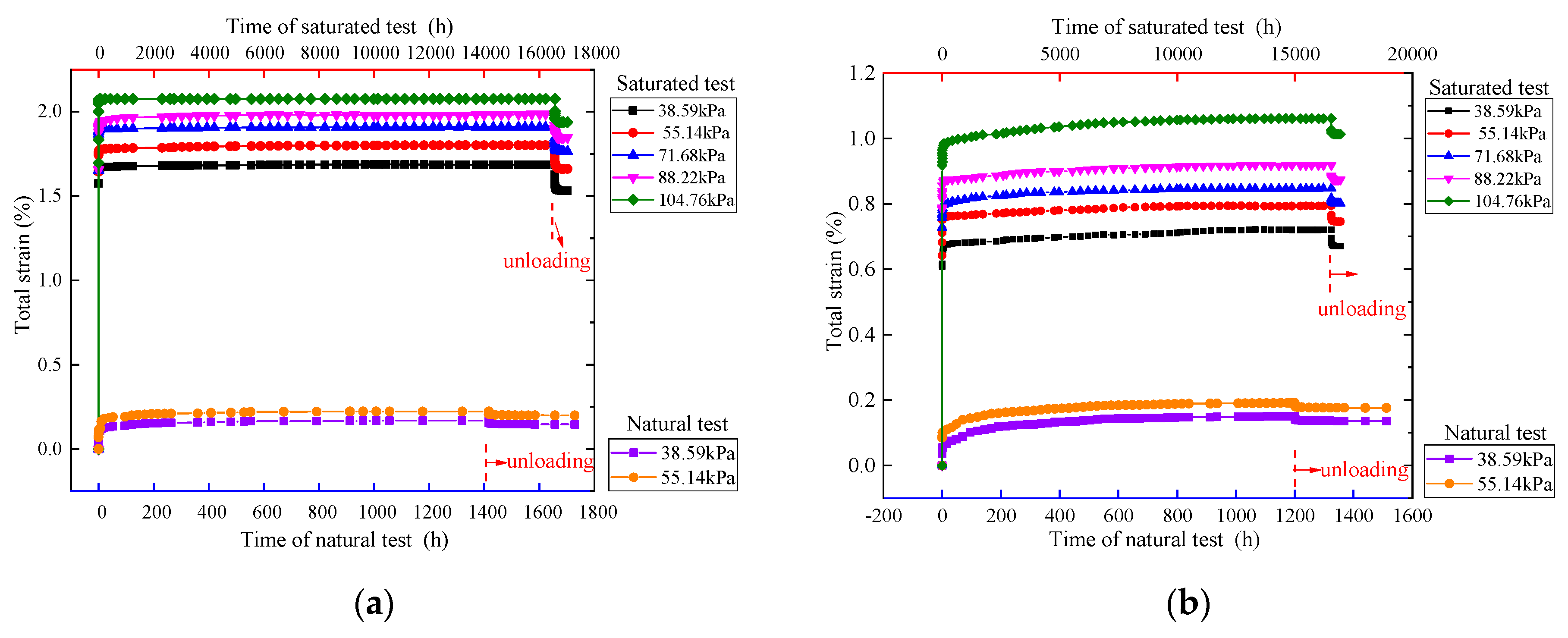
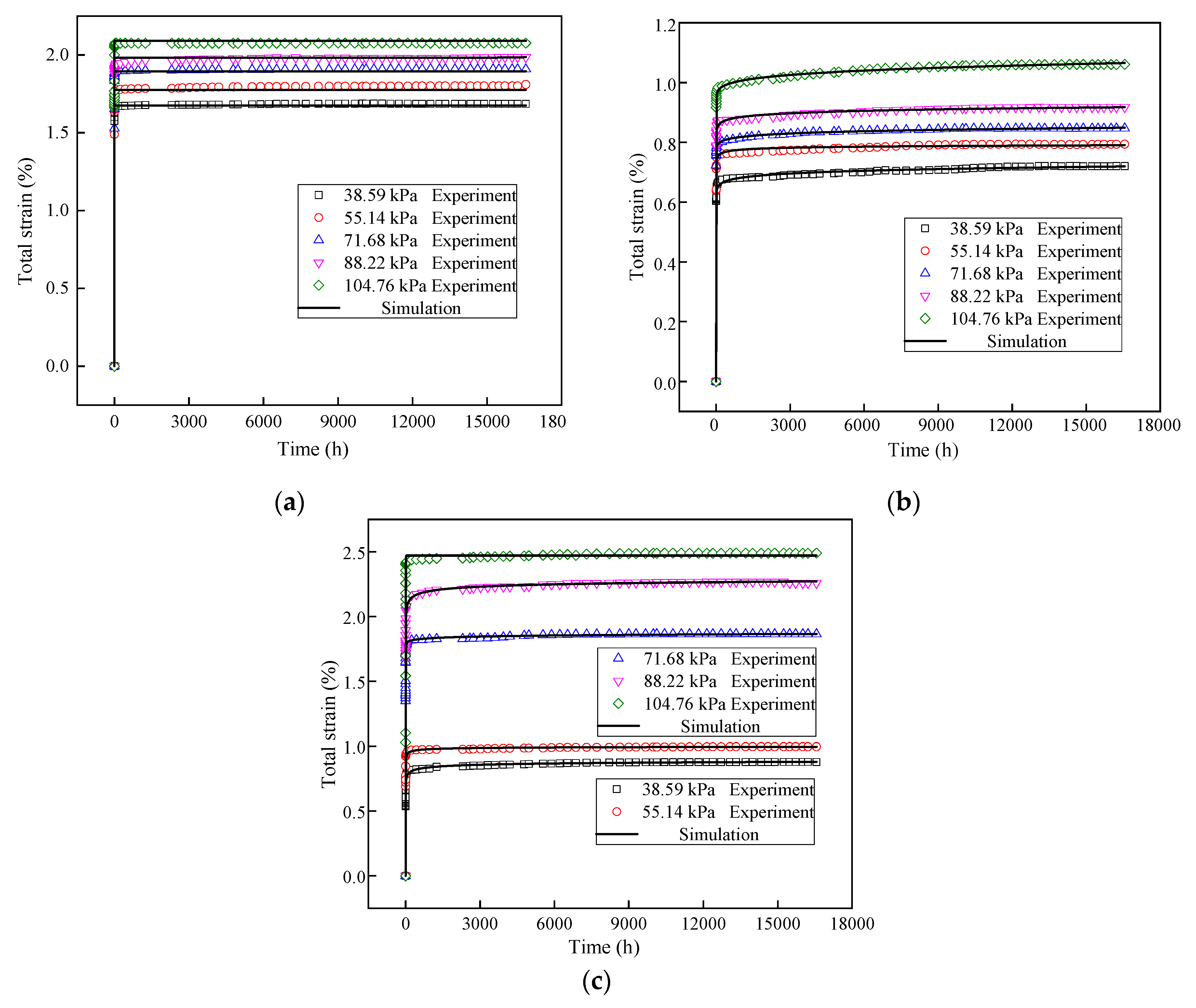
3.1. Analysis of Total Strain
3.2. Analysis of Void Ratio
3.3. Analysis of Instantaneous Strain
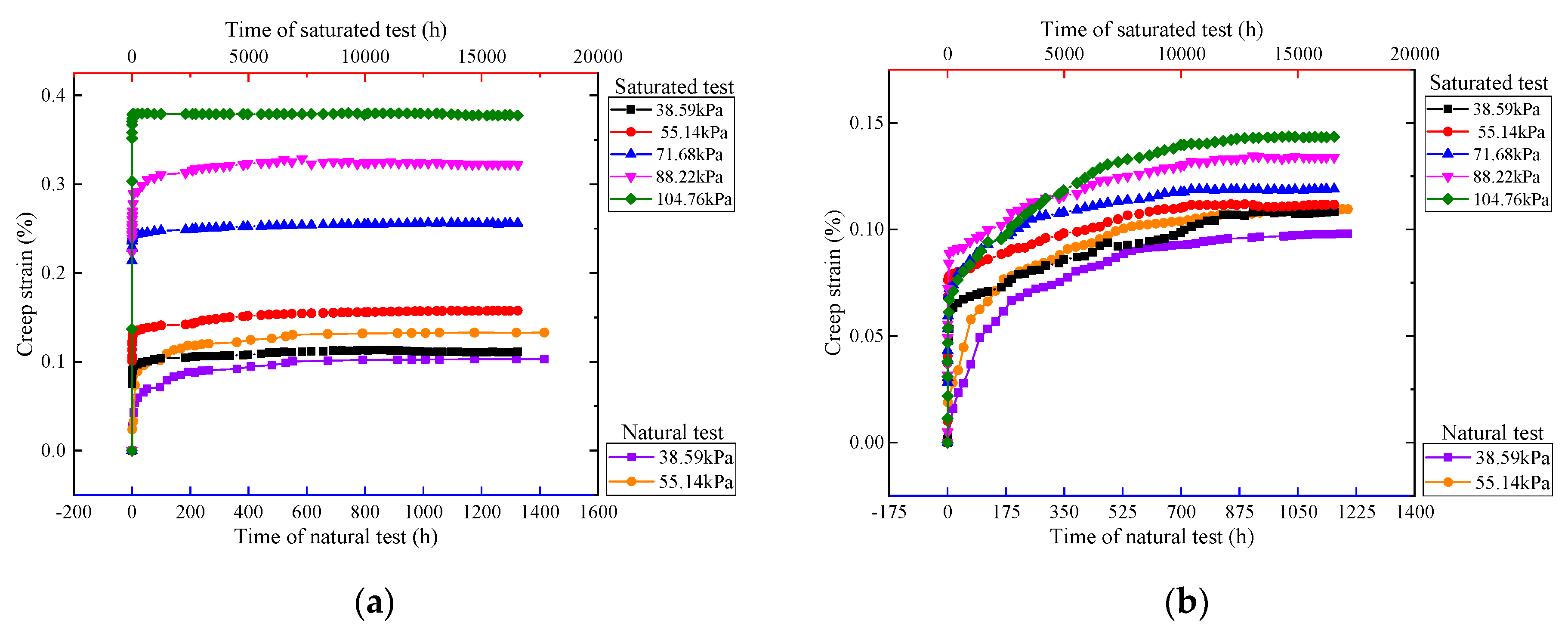
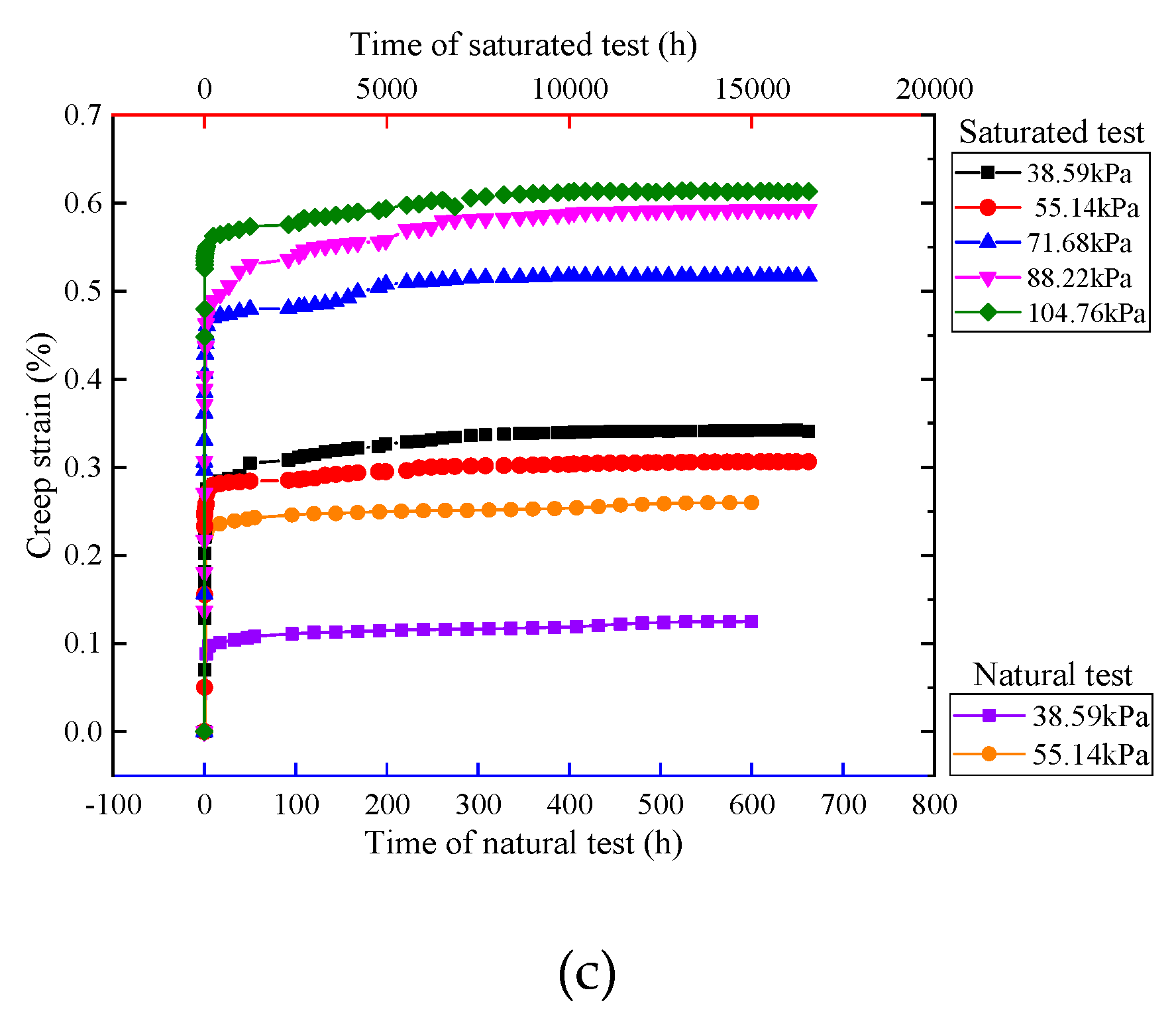
3.4. Analysis of Creep Strain
3.5. Analysis of Unloading Stain
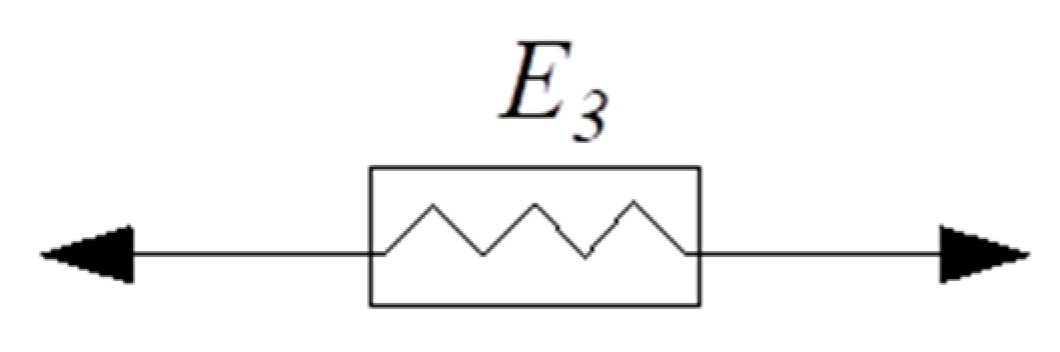
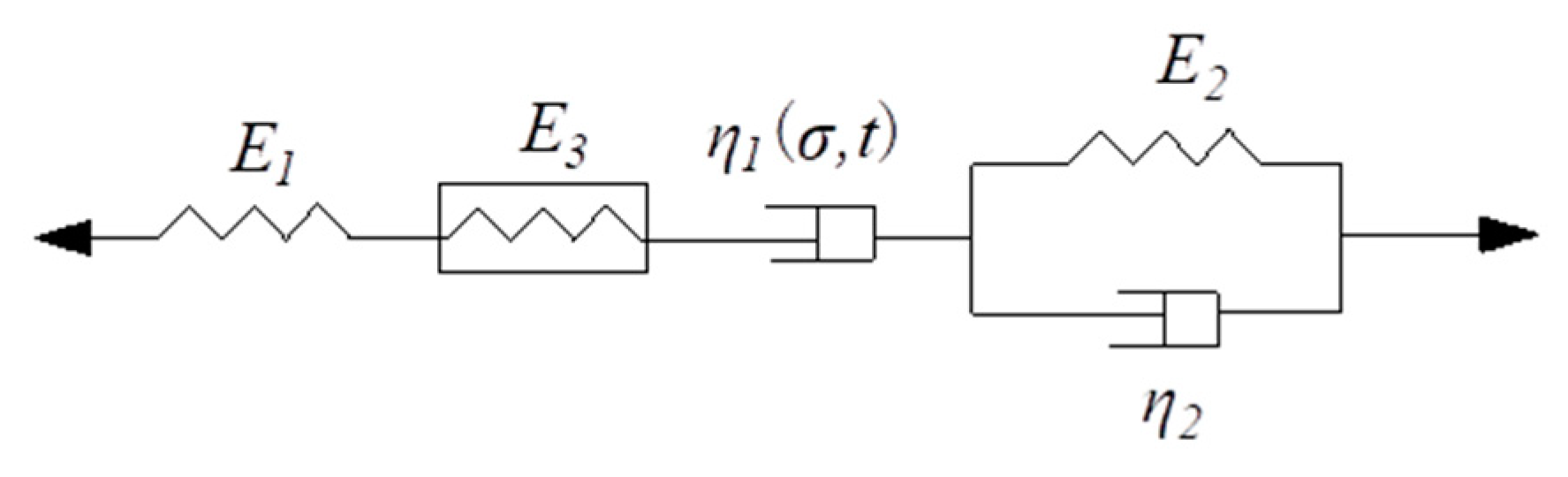
3.6. Creep Model and Parameters
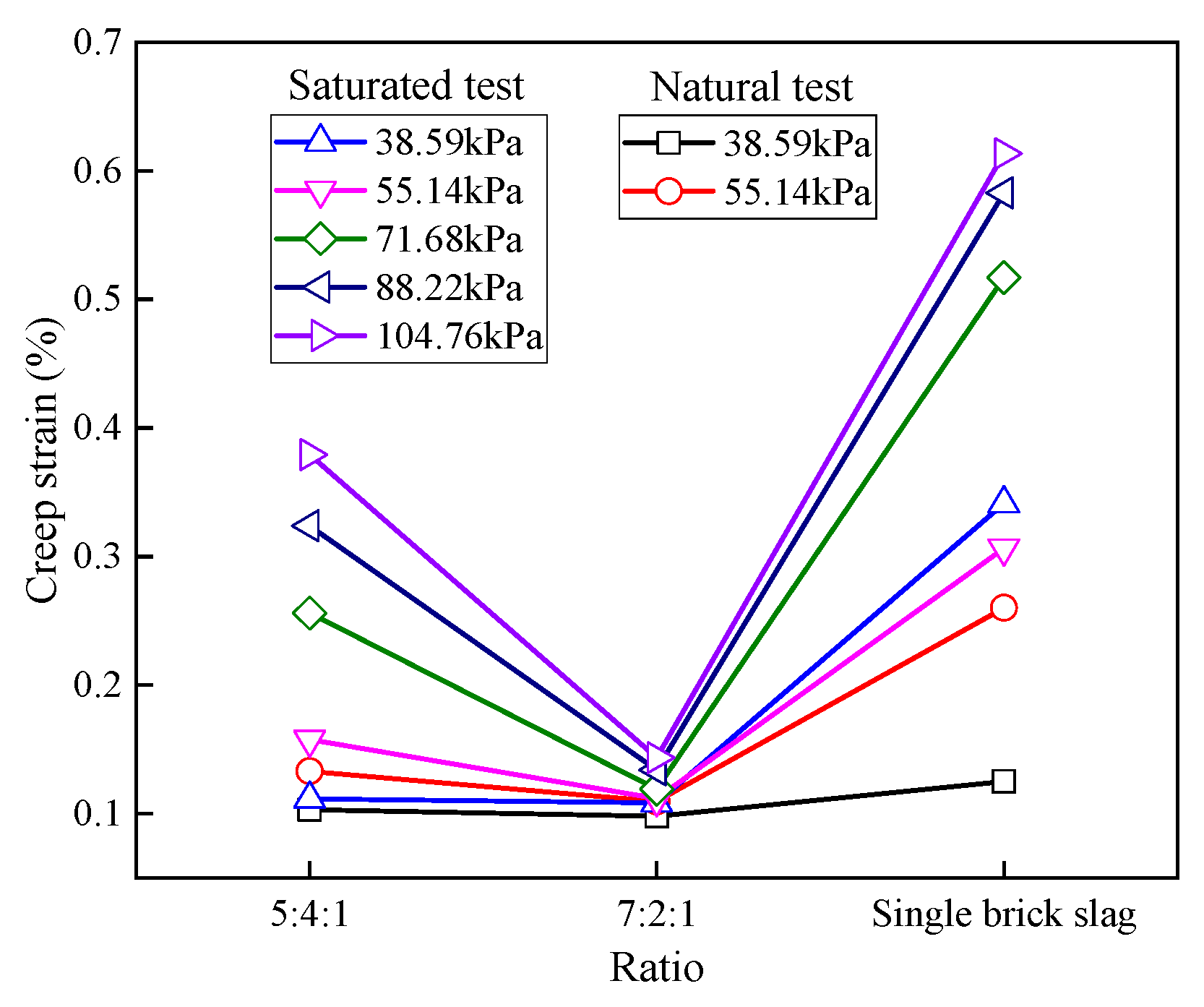
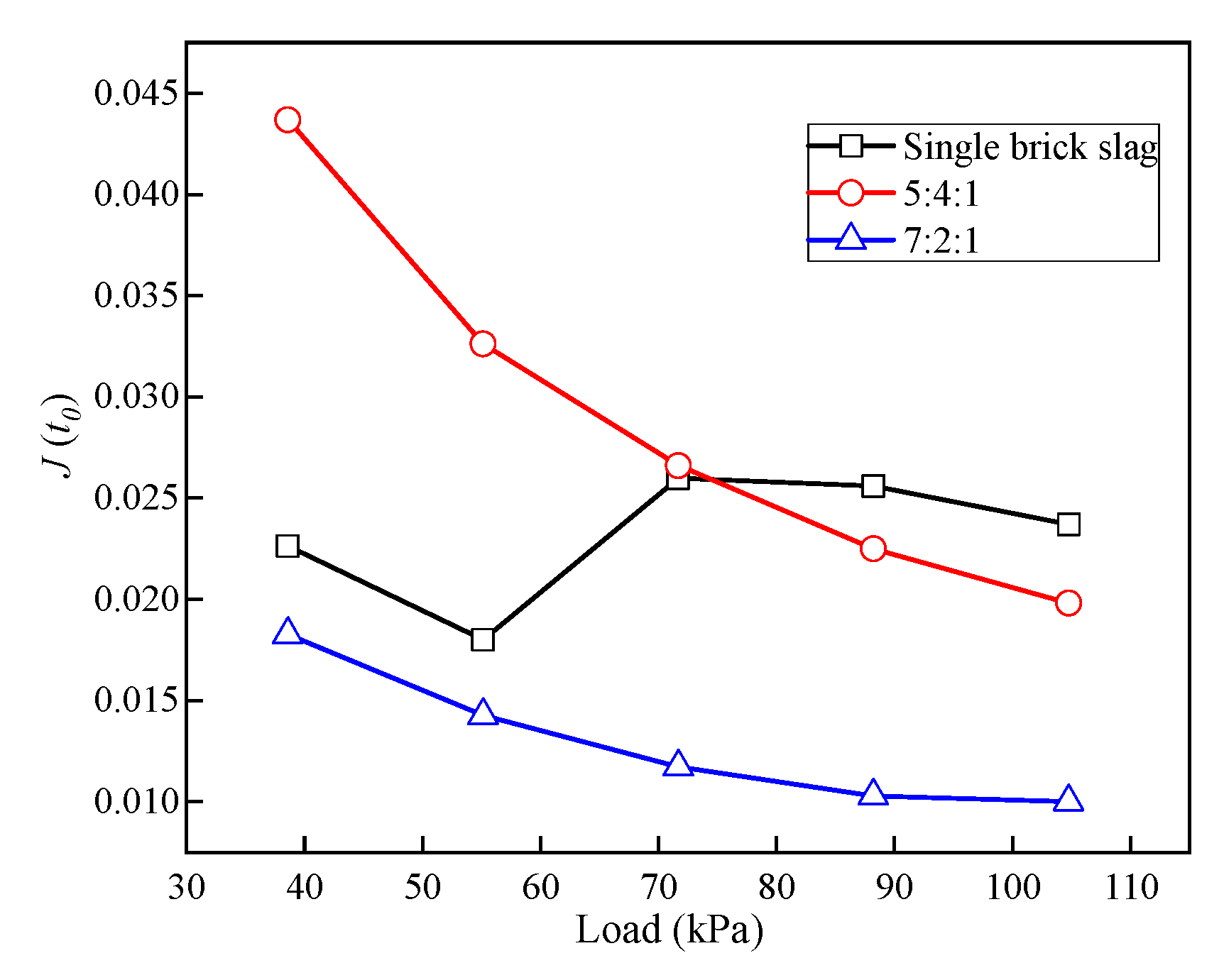
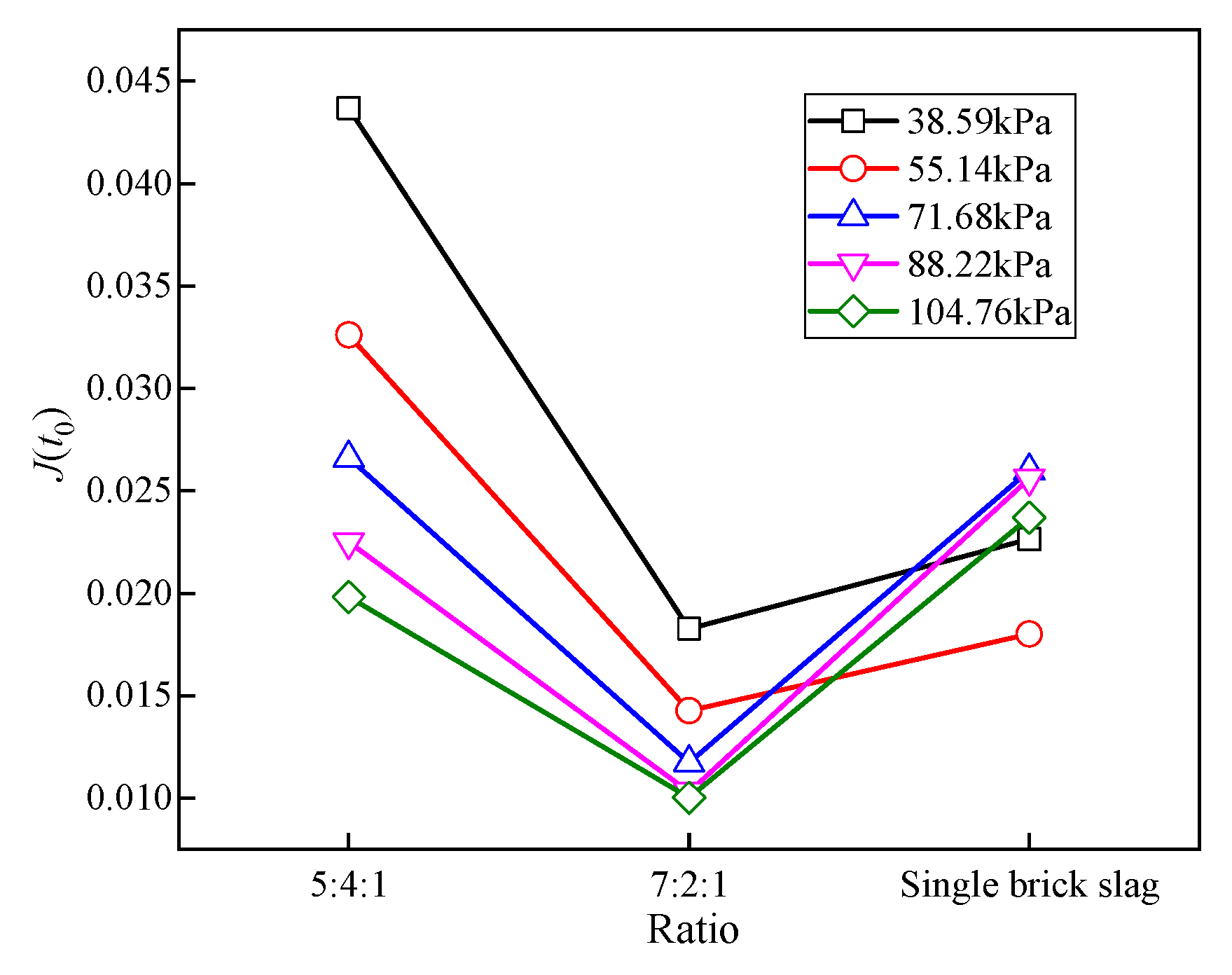
3.7. Influencing Factors of Creep Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, B.; Wang, X.; Kua, H.; Geng, Y.; Bleischwitz, R.; Ren, J. Construction and demolition waste management in China through the 3R principle. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 129, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbudo, A.; Agrela, F.; Ayuso, J.; Jiménez, J.R.; Poon, C.S. Statistical analysis of recycled aggregates derived from different sources for sub-base applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 28, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, R.; Silva, R.V.; de Brito, J.; Dhir, R. Use of recycled aggregates from construction and demolition waste in geotechnical applications: A literature review. Waste Manage. 2016, 49, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Conceição Leite, F.; dos Santos Motta, R.; Vasconcelos, K.L.; Bernucci, L. Laboratory evaluation of recycled construction and demolition waste for pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 2972–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cai, G.; Liu, S. Compression properties and micro-mechanisms of rubber-sand particle mixtures considering grain breakage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 187, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimanbeigi, A.; Edil, T.B. Compressibility of recycled materials for use as highway embankment fill. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2015, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T. Application of construction and building debris as base and subbase materials in rigid pavement. J. Transp. Eng. 2003, 129, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.S.; Chan, D. Feasible use of recycled concrete aggregates and crushed clay brick as unbound road sub-base. Constr. Build. Mater. 2006, 20, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cai, G.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.; Puppala, A.J. Thermo-hydro-mechanical properties of bentonite-sand-graphite-polypropylene fiber mixtures as buffer materials for a high-level radioactive waste repository. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 141, 981–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Labuz, J.F.; Dai, S. Resilient modulus of base course containing recycled asphalt pavement. Transp. Res. Record. 2007, 2005, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melbouci, B. Compaction and shearing behaviour study of recycled aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2723–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.S.; Qiao, X.C.; Chan, D. The cause and influence of self-cementing properties of fine recycled concrete aggregates on the properties of unbound sub-base. Waste Manage. 2006, 26, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yu, N.; Li, Y. Methods for improving the microstructure of recycled concrete aggregate: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 242, 118164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, J.; Kong, X.; Chen, C.; Lehman, D.E. Mechanical and durability properties of sustainable self-compacting concrete with recycled concrete aggregate and fly ash, slag and silica fume. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 231, 117115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhy, A.; Pires, G.M.; del Barco Carrión, A.J.; Lo Presti, D.; Airey, G. Binder and mixture fatigue performance of plant-produced road surface course asphalt mixtures with high contents of reclaimed asphalt. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pires, G.M.; Lo Presti, D.; Airey, G.D. A practical approach to estimate the degree of binder activity of reclaimed asphalt materials. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2019, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavira, J.; Jiménez, J.R.; Ledesma, E.F.; López-Uceda, A.; Ayuso, J. Real-scale study of a heavy traffic road built with in situ recycled demolition waste. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegas, I.; Ibañez, J.A.; Lisbona, A.; de Cortazar, A.S.; Frías, M. Pre-normative research on the use of mixed recycled aggregates in unbound road sections. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 2674–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Soleimanbeigi, A.; Likos, W.J.; Edil, T.B. Creep response of compacted waste foundry sands for use as roadway embankment fill. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2019, 144, 04017115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantut, N.; Heap, M.; Meredith, P.; Baud, P. Time-dependent cracking and brittle creep in crustal rocks: A review. J. Struct. Geol. 2013, 52, 17–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwenya, B.T.; Main, I.G.; Elphick, S.C.; Crawford, B.R.; Smart, B.G. A constitutive law for low-temperature creep of water-saturated sandstones. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2001, 106, 21811–21826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, T.; Peng, C.; Qian, X.; Jie, Y. Experimental study on loading-creep coupling effect in rockfill material. Int. J. Geomech. 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Xu, M.; Song, E. An elastic-viscoplastic double-yield-surface model for coarse-grained soils considering particle breakage. Comput. Geotech. 2017, 85, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Consolidation analysis of nuozhadu high earth-rockfill dam based on the coupling of seepage and stress-deformation physical state. Int. J. Geomech. 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.S.; Cheng, Z.-L.; Zuo, Y.; Ding, H. CT triaxial rheological test on coarse-grained soils. Rock Soil Mech. 2014, 35, 2507–2514. [Google Scholar]
- Ciantia, M.O.; Castellanza, R.; Di Prisco, C. Experimental study on the water-induced weakening of calcarenites. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2015, 48, 441–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Song, E.-X. Particle mechanics modeling of creep behavior of rockfill materials under dry and wet conditions. Comput. Geotech. 2015, 68, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.F.; Zhou, M.L.; Li, J.L.; Sun, X.S.; Huang, Y.L. Creep degradation mechanism by water-rock interaction in the red-layer soft rock. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwano, R.; Jardine, R.J. On measuring creep behaviour in granular materials through triaxial testing. Can. Geotech. J. 2002, 39, 1061–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramthawee, P.; Jongpradist, P.; Sukkarak, R. Integration of creep into a modified hardening soil model for time-dependent analysis of a high rockfill dam. Comput. Geotech. 2017, 91, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Chang, X.; Zhou, C.; Liu, X. Creep analysis of high concrete-faced rockfill dam. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Biomed. 2010, 26, 1477–1492. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G. A new constitutive creep-damage model for rock salt and its characteristics. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2004, 41, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Greene, M.S.; Liu, W.K. Two-scale mechanism-based theory of nonlinear viscoelasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2012, 60, 199–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justo, J.; Durand, P. Settlement-time behaviour of granular embankments. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2000, 24, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, X.; Han, B.; Shu, Y. Recognition of creep model of layer composite rock mass and its application. J. Cent. South Univ. 2007, 14, 329–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyen, M.L.; Cook, R.F. Load–displacement behavior during sharp indentation of viscous–elastic–plastic materials. J. Mater. Res. 2003, 18, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadzadeh, M.; Soroush, A. Direct shear testing on a rockfill material. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2009, 34, 379. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Chang, P. Study of nonlinear rheology of improved expansive soil based on model theory and genetic creep theory. Rock Soil Mech. 2016, 37, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Profession Standard of the People’s Republic of China. Test Methods of Soils for Highway Engineering (JTG E40-2007); Ministry of Communications of the PRC: Beijing, China, 2007. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/fuwu/bmfw/zggjbzhglwyhgjbzxxcx/index.html (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Profession Standard of the People’s Republic of China. Technical specification for construction of highway subgrades (JTG F10-2006); Ministry of Communications of the PRC: Beijing, China, 2006. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/fuwu/bmfw/zggjbzhglwyhgjbzxxcx/index.html (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Yan, S.; Zhang, M.; Xie, Y. Properties of microscopic particle morphology and particle contact of renewable construction waste mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 207, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Yan, S.; Zhang, M.; Xia, J.; Xie, Y. Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on mechanical and porosity properties of recycled construction waste mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 210, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J. Rock rheological mechanics and its advance in engineering applications. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2007, 26, 1081–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wan, W.; Tang, J. Modeling of non-linear rheological behavior of hard rock using triaxial rheological experiment. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2017, 93, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Chen, J.; Zou, Q. A nonlinear creep damage model for salt rock. Int. J. Damage Mech. 2019, 28, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
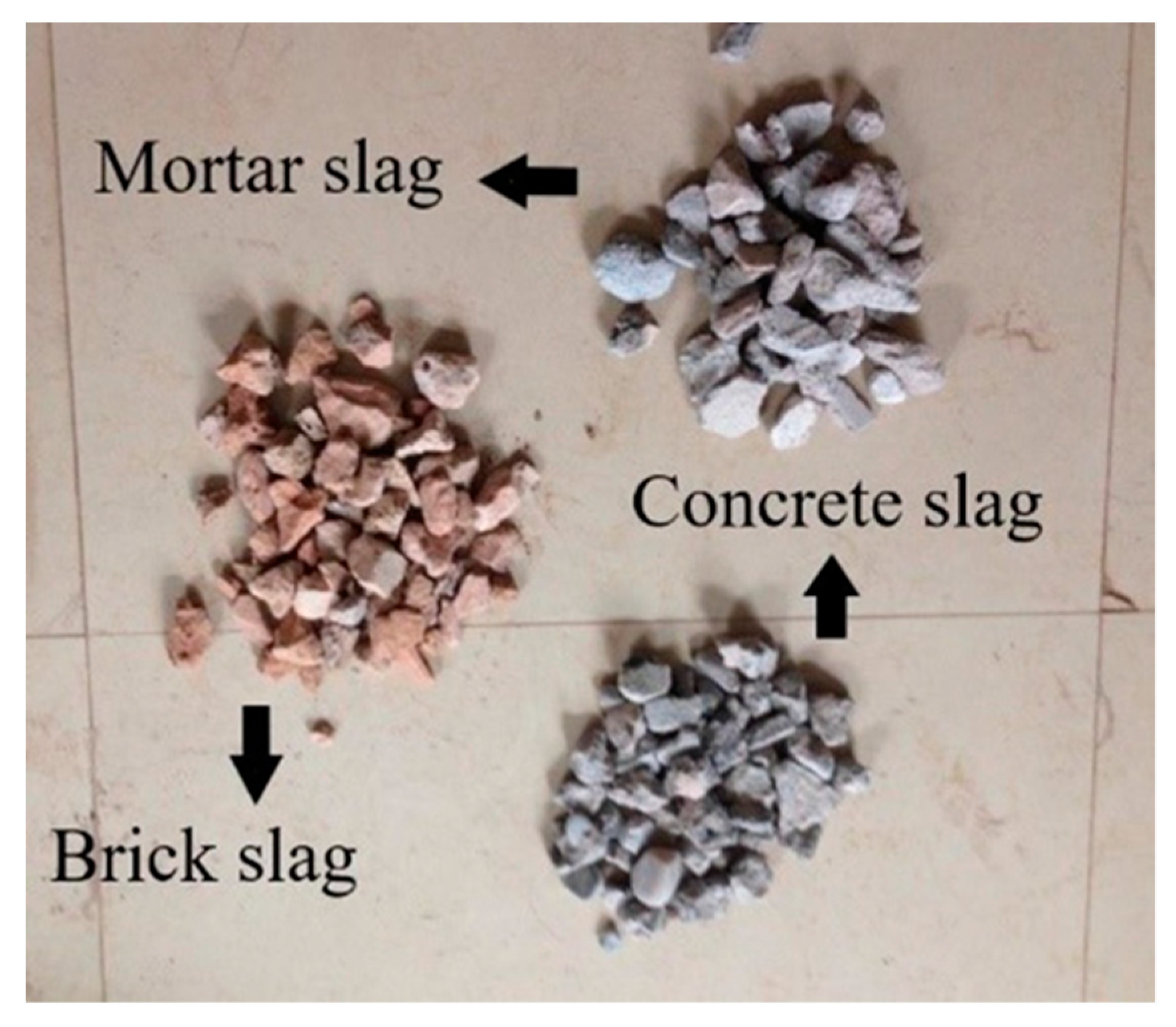


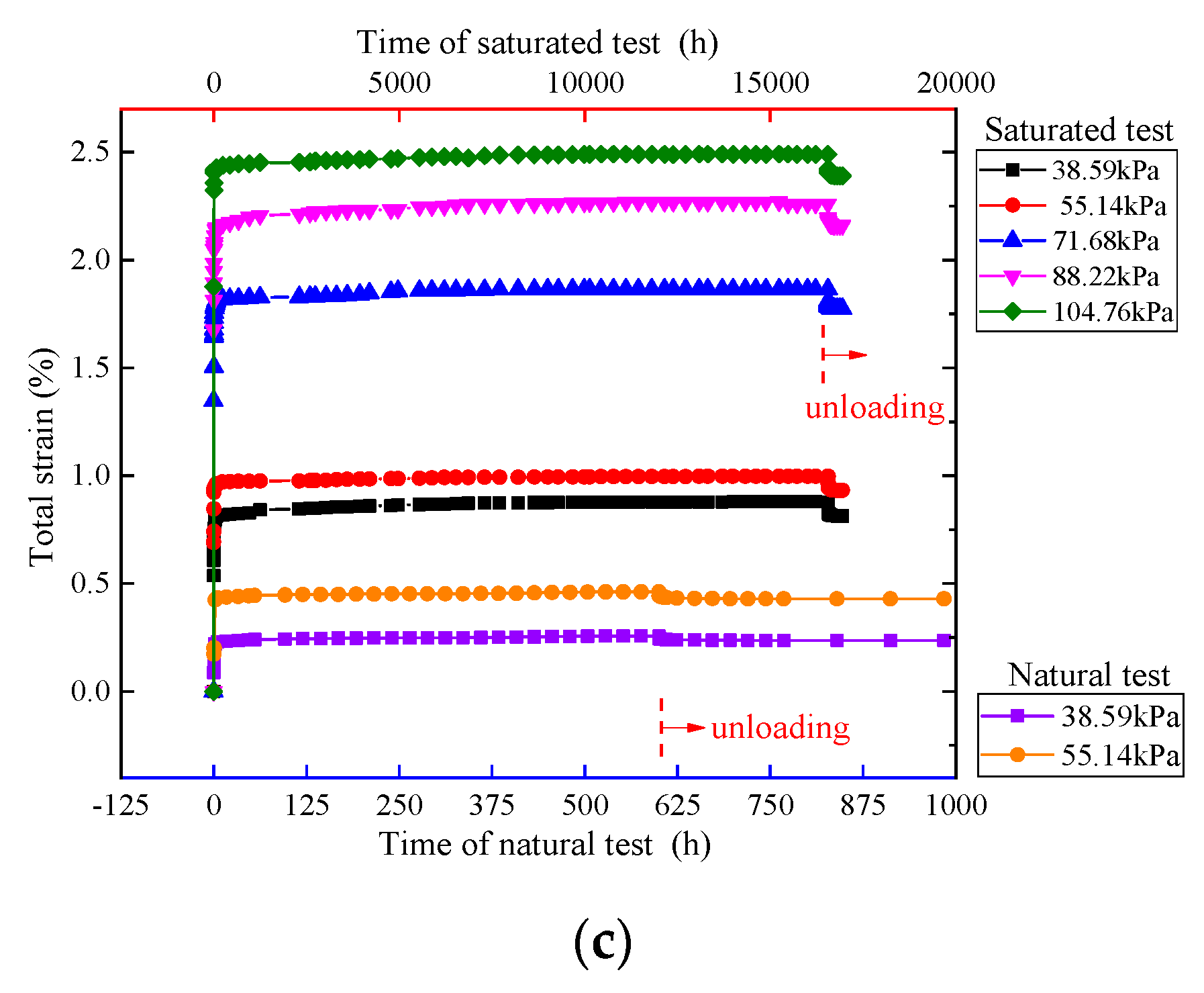

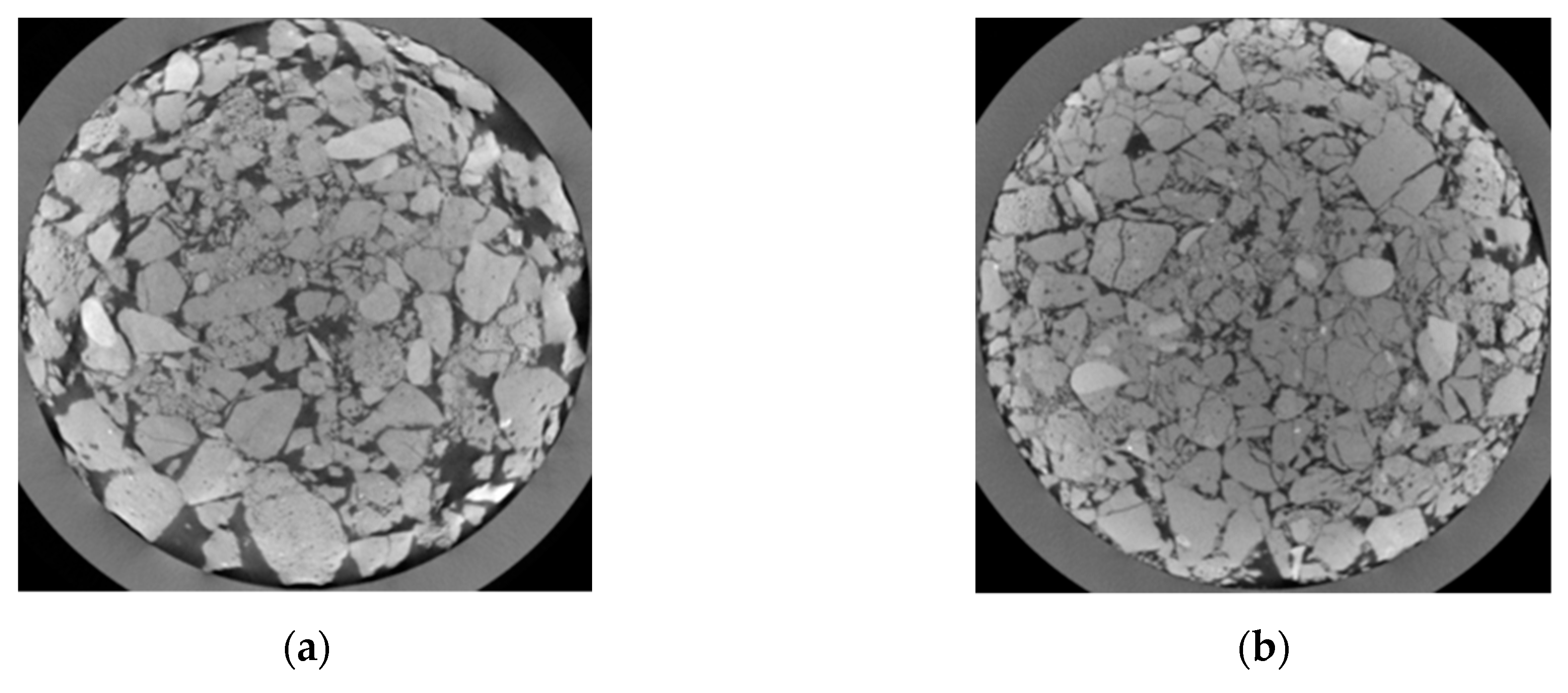
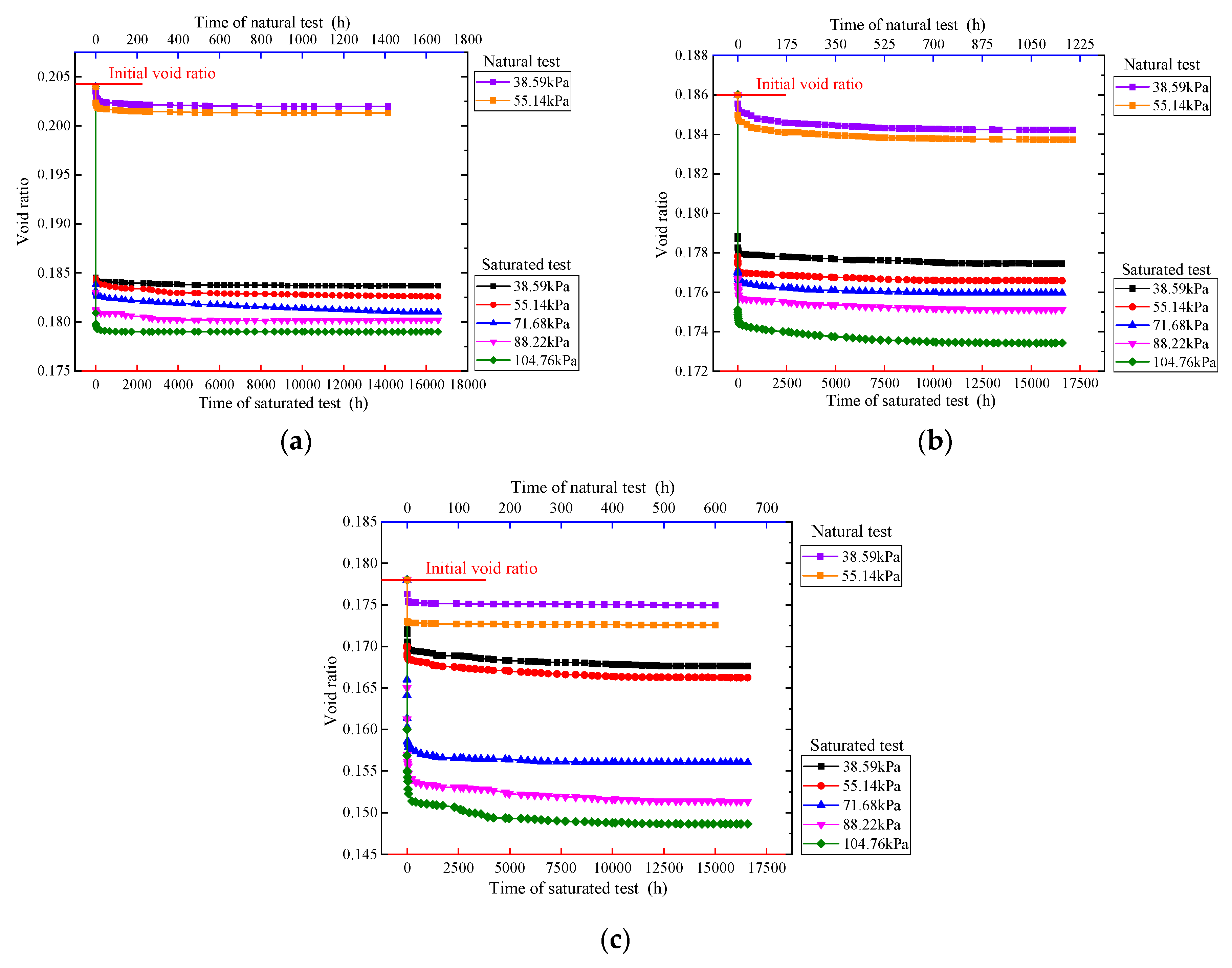
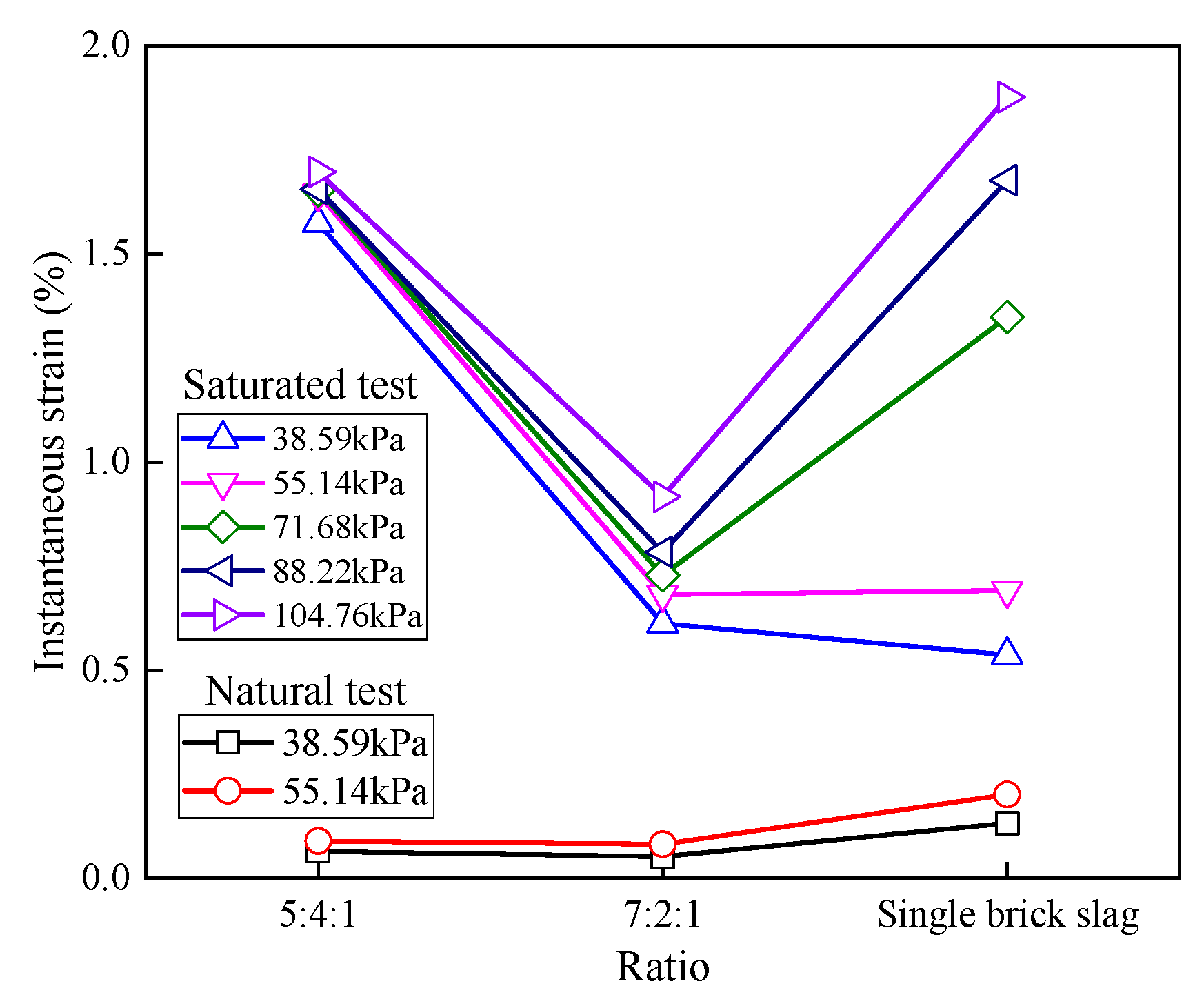


| Sample | Brick Slag (%) | Concrete Slag (%) | Mortar Slag (%) | Others (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 33 | 44 | 14 | 9 |
| Sample 2 | 35 | 45 | 13 | 7 |
| Sample 3 | 34 | 35 | 20 | 11 |
| Sample 4 | 36 | 34 | 20 | 10 |
| Recycled Aggregates | Concrete Slag | Mortar Slag | Brick Slag |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm3) | 2.57 | 2.01 | 1.61 |
| Water absorption (%) | 2.4 | 11.1 | 21.5 |
| Ratio | Optimum Moisture Content (%) | Maximum Dry Density (g/cm3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Group | Second Group | Average | First Group | Second Group | Average | |
| 4:5:1 | 8.7 | 9.3 | 9.0 | 1.69 | 1.69 | 1.69 |
| 5:4:1 | 10.8 | 11.4 | 11.1 | 1.66 | 1.64 | 1.65 |
| 6:3:1 | 14.6 | 14.2 | 14.4 | 1.58 | 1.59 | 1.59 |
| 7:2:1 | 14.8 | 15.6 | 15.2 | 1.57 | 1.57 | 1.57 |
| Brick slag | 16.6 | 16.2 | 16.4 | 1.45 | 1.44 | 1.45 |
| Ratio | Layer | d60 | d30 | d10 | Cu | Cc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4:5:1 | Upper layer | 25.6 | 11.2 | 4.0 | 6.4 | 1.2 |
| Middle layer | 24.6 | 11.4 | 2.8 | 8.8 | 1.9 | |
| Lower layer | 23.8 | 12.3 | 4.9 | 4.8 | 1.3 | |
| 5:4:1 | Upper layer | 25.6 | 10.4 | 2.1 | 12.2 | 2.0 |
| Middle layer | 23.0 | 10.1 | 2.1 | 11.0 | 2.1 | |
| Lower layer | 23.0 | 10.9 | 2.3 | 10.0 | 2.2 | |
| 6:3:1 | Upper layer | 25.6 | 10.4 | 2.1 | 12.2 | 2.0 |
| Middle layer | 23.0 | 10.1 | 2.1 | 11.0 | 2.1 | |
| Lower layer | 23.0 | 10.9 | 2.3 | 10.0 | 2.2 | |
| 7:2:1 | Upper layer | 20.6 | 10.2 | 2.1 | 9.8 | 2.4 |
| Middle layer | 18.1 | 8.8 | 2.2 | 7.8 | 1.9 | |
| Lower layer | 19.8 | 10.2 | 2.2 | 8.2 | 2.2 | |
| Brick slag | Upper layer | 19.6 | 10.4 | 2.2 | 8.9 | 2.5 |
| Middle layer | 17.2 | 9.0 | 2.1 | 8.2 | 2.2 | |
| Lower layer | 18.8 | 10.4 | 2.0 | 9.4 | 2.9 |
| Ratio | Compaction Work (kJ/m3) | Sample | Swelling Capacity (%) | Average (%) | CBR (%) | Average (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4:5:1 | 2677.2 | 1 | 0.0046 | 0.0049 | 77.27 | 79.97 |
| 2 | 0.0034 | 84.15 | ||||
| 3 | 0.0067 | 78.48 | ||||
| 5:4:1 | 1 | 0.0109 | 0.0097 | 96.32 | 97.61 | |
| 2 | 0.0166 | 97.71 | ||||
| 3 | 0.0017 | 98.82 | ||||
| 6:3:1 | 1 | 0.0083 | 0.0084 | 86.48 | 89.72 | |
| 2 | 0.0085 | 87.84 | ||||
| 3 | 0.0083 | 94.83 | ||||
| 7:2:1 | 1 | 0.0025 | 0.0022 | 82.23 | 80.62 | |
| 2 | 0.0017 | 80.16 | ||||
| 3 | 0.0025 | 79.48 | ||||
| Brick slag | 1 | 0.0028 | 0.0026 | 40.24 | 42.63 | |
| 2 | 0.0030 | 42.03 | ||||
| 3 | 0.0021 | 45.62 |
| Position of Filler Application (Below the Top of Roadbed)(m) | Minimum CBR (%) | Maximum Particle (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expressway and First Class Highway | Second Class Highway | Third and Fourth Class Highway | |||
| Fill embankment | Upper roadbed (0-0.30) | 8 | 6 | 5 | 100 |
| Lower roadbed (0.30-0.80) | 5 | 4 | 3 | 100 | |
| Upper embankment (0.80-1.50) | 4 | 3 | 3 | 150 | |
| Lower embankment (>1.50) | 3 | 2 | 2 | 150 | |
| Cut embankment | 0-0.30 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 100 |
| 0.30-0.80 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 100 | |
| Loading Level | Load (kPa) | Simulated Embankment Depth (m) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 38.59 | 0.000 |
| 2 | 55.14 | 0.885 |
| 3 | 71.68 | 1.770 |
| 4 | 88.22 | 2.655 |
| 5 | 104.76 | 3.540 |
| Ratio | Condition | (kPa) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5:4:1 | Saturated test | 38.59 | 1.686 | 1.574 | 0.111 | 0.060 | 1.514 | 0.095 | 0.016 |
| 55.14 | 1.811 | 1.644 | 0.167 | 0.061 | 1.583 | 0.088 | 0.078 | ||
| 71.68 | 1.909 | 1.653 | 0.256 | 0.065 | 1.588 | 0.079 | 0.177 | ||
| 88.22 | 1.979 | 1.656 | 0.324 | 0.067 | 1.589 | 0.073 | 0.251 | ||
| 104.76 | 2.076 | 1.697 | 0.379 | 0.072 | 1.624 | 0.066 | 0.313 | ||
| Natural test | 38.59 | 0.168 | 0.065 | 0.103 | 0.012 | 0.053 | 0.009 | 0.094 | |
| 55.14 | 0.223 | 0.090 | 0.133 | 0.015 | 0.075 | 0.008 | 0.125 | ||
| 7:2:1 | Saturated test | 38.59 | 0.721 | 0.613 | 0.108 | 0.025 | 0.587 | 0.025 | 0.083 |
| 55.14 | 0.794 | 0.682 | 0.112 | 0.028 | 0.654 | 0.020 | 0.091 | ||
| 71.68 | 0.847 | 0.728 | 0.119 | 0.030 | 0.698 | 0.015 | 0.104 | ||
| 88.22 | 0.918 | 0.784 | 0.134 | 0.032 | 0.752 | 0.012 | 0.121 | ||
| 104.76 | 1.061 | 0.917 | 0.144 | 0.035 | 0.882 | 0.013 | 0.131 | ||
| Natural test | 38.59 | 0.150 | 0.052 | 0.098 | 0.008 | 0.044 | 0.006 | 0.092 | |
| 55.14 | 0.192 | 0.082 | 0.110 | 0.008 | 0.074 | 0.007 | 0.102 | ||
| Brick slag | Saturated test | 38.59 | 0.878 | 0.537 | 0.341 | 0.027 | 0.510 | 0.038 | 0.304 |
| 55.14 | 0.998 | 0.691 | 0.306 | 0.030 | 0.661 | 0.035 | 0.271 | ||
| 71.68 | 1.865 | 1.348 | 0.517 | 0.057 | 1.291 | 0.034 | 0.483 | ||
| 88.22 | 2.259 | 1.676 | 0.583 | 0.066 | 1.611 | 0.033 | 0.550 | ||
| 104.76 | 2.490 | 1.876 | 0.614 | 0.072 | 1.804 | 0.028 | 0.586 | ||
| Natural test | 38.59 | 0.257 | 0.132 | 0.125 | 0.011 | 0.121 | 0.010 | 0.115 | |
| 55.14 | 0.461 | 0.201 | 0.260 | 0.016 | 0.185 | 0.016 | 0.243 |
| Ratio | (kPa) | (kPa) | (kPa) | (kPa·h) | (kPa) | (kPa·h) | a | b | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5:4:1 | 38.59 | 6.42e2 | 4.35e2 | 2.10e3 | 25.48 | 1.17 | 2.84 | 0.72 | 0.9974 |
| 55.14 | 9.01e2 | 6.73e2 | 3.64e3 | 34.83 | 1.02 | 1.93 | 0.89 | 0.9780 | |
| 71.68 | 1.10e3 | 9.60e2 | 4.61e3 | 45.14 | 1.00 | 1.45 | 0.98 | 0.9741 | |
| 88.22 | 1.33e3 | 1.27e3 | 7.24e3 | 55.52 | 1.00 | 1.37 | 0.97 | 0.9622 | |
| 104.76 | 1.45e3 | 1.68e3 | 8.28e3 | 64.49 | 1.00 | 1.25 | 1.00 | 0.9264 | |
| 7:2:1 | 38.59 | 1.52e3 | 4.35e2 | 2.10e3 | 65.71 | 1.03 | 2.35 | 0.75 | 0.9967 |
| 55.14 | 1.98e3 | 6.73e2 | 3.64e3 | 84.27 | 1.02 | 1.93 | 0.86 | 0.9916 | |
| 71.68 | 2.39e3 | 9.60e2 | 4.61e3 | 102.72 | 1.01 | 1.83 | 0.86 | 0.9994 | |
| 88.22 | 2.78e3 | 1.27e3 | 7.24e3 | 117.33 | 1.01 | 1.77 | 0.86 | 0.9971 | |
| 104.76 | 2.99e3 | 1.68e3 | 8.72e3 | 118.77 | 1.02 | 1.88 | 0.78 | 0.9988 | |
| Brick slag | 38.59 | 1.41e3 | 1.10e3 | 6.25e3 | 75.71 | 1.00 | 1.48 | 0.94 | 0.9499 |
| 55.14 | 1.85e3 | 1.69e3 | 1.03e4 | 83.36 | 1.00 | 1.40 | 0.97 | 0.9379 | |
| 71.68 | 1.25e3 | 2.23e3 | 2.46e4 | 55.54 | 1.01 | 1.24 | 0.97 | 0.9514 | |
| 88.22 | 1.34e3 | 2.80e3 | 4.95e4 | 54.78 | 1.01 | 1.24 | 0.95 | 0.9739 | |
| 104.76 | 1.46e3 | 4.00e3 | 6.53e4 | 58.06 | 1.00 | 1.17 | 0.97 | 0.7743 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Yan, S.; Liu, L.; Yang, J. Investigation into Creep Characteristics and Model of Recycled Construction and Demolition Waste Used in Embankment Filler. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051924
Li Z, Yan S, Liu L, Yang J. Investigation into Creep Characteristics and Model of Recycled Construction and Demolition Waste Used in Embankment Filler. Sustainability. 2020; 12(5):1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051924
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhe, Shihao Yan, Lulu Liu, and Jia Yang. 2020. "Investigation into Creep Characteristics and Model of Recycled Construction and Demolition Waste Used in Embankment Filler" Sustainability 12, no. 5: 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051924
APA StyleLi, Z., Yan, S., Liu, L., & Yang, J. (2020). Investigation into Creep Characteristics and Model of Recycled Construction and Demolition Waste Used in Embankment Filler. Sustainability, 12(5), 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051924




