Pollution, Sources and Human Health Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Different Land Use Types under the Background of Industrial Cities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
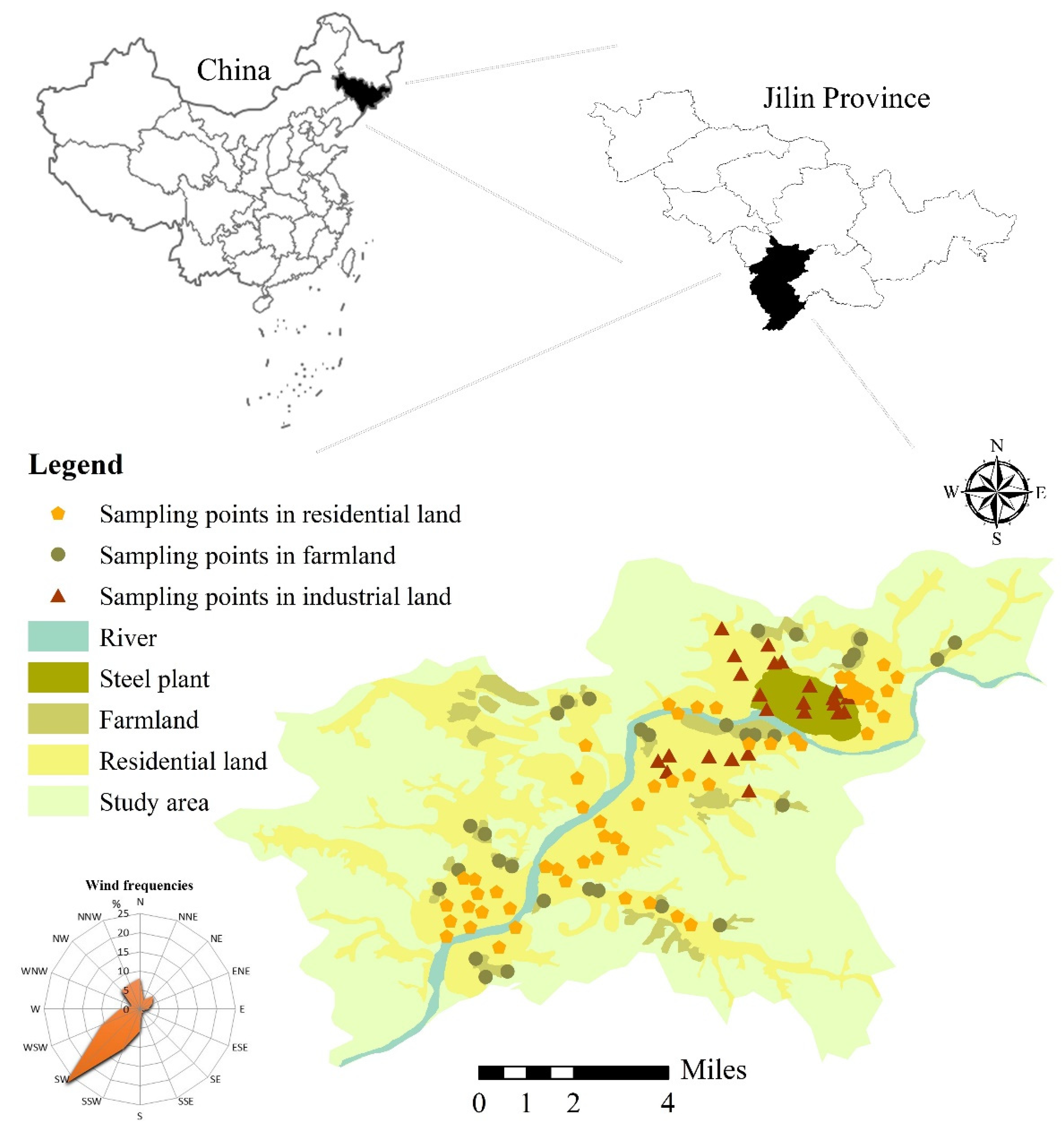
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Collection and Analysis
2.3. Method
2.3.1. Factor Analysis (FA)
2.3.2. Geo-Accumulation Index (Igeo)
2.3.3. Pollution Load Index (PLI)
2.3.4. Potential Ecological Risk Index
2.3.5. Heathy Risk Assessment
2.3.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Concentration of PTEs
3.2. Spatial Distribution of PTEs
3.3. Pollution Assessment of PTEs
3.4. Source Identification of PTEs
PC1: Cr, Cu, Ni
PC2: As, Zn
PC3: Pb
3.5. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment
3.6. Human Health Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.Y.; Liu, L.J.; Wang, Y.G.; Luo, G.P.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.L.; Hall, M.H.P.; Guo, R.C.; Wang, H.J.; Cui, J.H.; et al. Heavy metal contamination of urban soil in an old industrial city (Shenyang) in Northeast China. Geoderma 2013, 192, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xu, Y.F.; Hou, H.; Shangguan, Y.X.; Li, F.S. Source identification and health risk assessment of metals in urban soils around the Tanggu chemical industrial district, Tianjin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Feng, C.T.; Zeng, G.M.; Gao, X.; Zhong, M.Z.; Li, X.D.; Li, X.; He, X.Y.; Fang, Y.L. Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in surface soils in a typical coal mine city, Lianyuan, China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Cai, L.M.; Wen, H.H.; Luo, J.; Wang, Q.S.; Liu, X. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from a typical county-level city of Guangdong Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, J.; Jiao, W.B.; Qiu, H.; Chen, B.; Huang, X.X.; Kang, B. Origin and spatial distribution of heavy metals and carcinogenic risk assessment in mining areas at You’xi County southeast China. Geoderma 2018, 310, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.M.; Wang, Q.S.; Luo, J.; Chen, L.G.; Zhu, R.L.; Wang, S.; Tang, C.H. Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment for children near a large Cu-smelter in central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingkhwan, R.; Worakhunpiset, S. Heavy metal contamination near industrial estate areas in Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya Province, Thailand and human health risk assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Guo, D.K.; Liu, K.; Meng, H.; Zheng, Y.J.; Yuan, F.Q.; Zhu, G.H. Levels, sources, and spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils from a typical coal industrial city of Tangshan, China. Catena 2019, 175, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.T.; Chen, Z.L.; Xu, S.Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Bi, C.J.; Teng, J.Y. Potentially toxic metal contamination of urban soils and roadside dust in Shanghai, China. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.G.; Gao, Y.P.; Lin, Q. Contamination, bioaccessibility and human health risk of heavy metals in exposed-lawn soils from 28 urban parks in southern China’s largest city, Guangzhou. Appl. Geochem. 2016, 67, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Ahmed, K.; Habibullah, A.M.; Masunaga, S. Potential ecological risk of hazardous elements in different land-use urban soils of Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Khan, S.; Khan, A.; Alam, M. Soil contamination with cadmium, consequences and remediation using organic amendments. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1591–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.W.; Yang, L.S.; Li, Y.H.; Li, H.R.; Wang, W.Y.; Ye, B.X. Impacts of lead/zinc mining and smelting on the environment and human health in China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 2261–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, K.; Li, C.; Song, Z.F.; Gao, X.; Wu, M.X. Pollution and health risk assessment of carcinogenic elements As, Cd, and Cr in multiple media—A case of a sustainable farming area in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.X.; Zhang, J.Q.; Cao, T.H.; Li, S.J.; Chen, Y.N.; Liang, X.H.; Zhao, X.; Chen, J.W. Human health risk assessment of toxic elements in farmland topsoil with source identification in Jilin Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.Y.; Li, F.X.; Zhang, J.Q.; Chen, Y.N.; Cao, T.H.; Tong, Z.J.; Liu, X.P.; Liang, X.H.; Zhao, X. Comprehensive assessment of heavy metals pollution of farmland soil and crops in Jilin Province. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Qian, H.; Wang, H. Assessment of heavy metal (HM) contamination in agricultural soil lands in northern Telangana, India: An approach of spatial distribution and multivariate statistical analysis. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doabi, S.A.; Karami, M.; Afyuni, M.; Yeganeh, M. Pollution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soil, atmospheric dust and major food crops in Kermanshah province, Iran. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Ma, Z.W.; van der Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.W.; Huang, L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, I.C.; Devi, N.L.; Singh, V.K.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Spatial distribution, source analysis, and health risk assessment of heavy metals contamination in house dust and surface soil from four major cities of Nepal. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 1100–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.H.; Cai, L.M.; Wen, H.H.; Hu, G.C.; Chen, L.G.; Luo, J. An integrated approach to quantifying ecological and human health risks from different sources of soil heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Han, J.; Wei, Y.; Li, G.; Sun, Y. Potential ecological risk and health risk assessment of heavy metals and metalloid in soil around Xunyang mining areas. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Tripti, M.M.; Kiseleva, I.; Maiti, S.K.; Morozova, M. Toxic metal(loid)s contamination and potential human health risk assessment in the vicinity of century-old copper smelter, Karabash, Russia. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, A.A.; Zarei, A.; Esmaeilzadeh, M.; Taghavi, M.; Yousefi, M.; Yousefi, Z.; Sedighi, F.; Javan, S. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risks assessment in soils around an industrial zone in Neyshabur, Iran. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszecka-Kosowska, A.; Baran, A.; Wdowin, M.; Mazur-Kajta, K.; Czech, T. The contents of the potentially harmful elements in the arable soils of southern Poland, with the assessment of ecological and health risks: A case study. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 419–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Long, J.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Liao, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, C.; Wu, Q. Risk assessment and source identification of toxic metals in the agricultural soil around a Pb/Zn mining and smelting area in southwest China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.M.; Xu, Z.C.; Ren, M.Z.; Guo, Q.W.; Hu, X.B.; Hu, G.C.; Wan, H.F.; Peng, P.G. Source identification of eight hazardous heavy metals in agricultural soils of Huizhou, Guangdong Province, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 78, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; O’Connor, D.; Nathanail, P.; Tian, L.; Ma, Y. Integrated GIS and multivariate statistical analysis for regional scale assessment of heavy metal soil contamination: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistics in soil science: State-of-the-art and perspectives. Geoderma 1999, 89, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.; Oliver, M.A. Geostatistics for Environmental Scientists; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, S.; Scheifler, R.; Benslama, M.; Crini, N.; Lucot, E.; Brahmia, Z.; Benyacoub, S.; Giraudoux, P. Spatial distribution of heavy metal concentrations in urban, suburban and agricultural soils in a Mediterranean city of Algeria. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2294–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Jiang, Y. Chronicles of Tonghua City; Jilin People’s Publishing House: Chang Chun, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Romic, M.; Romic, D. Heavy metals distribution in agricultural topsoils in urban area. Environ. Geol. 2003, 43, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Al-Tabbaa, A.; Chen, H.; Mamic, I. Factor analysis and structural equation modelling of sustainable behavior in contaminated land remediation. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 84, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- CNEMC (The Chinese Environmental Monitoring Centre). The Background Values of Soil Elements in China; Chinese Environment Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, B.G.; Yang, L.S. A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem. J. 2010, 94, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Yang, Y.; Christakos, G.; Liu, Y.J.; Yang, X. Assessment of soil heavy metal pollution using stochastic site indicators. Geoderma 2019, 337, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkanson, L. An ecological Risk Index for Aquatic Pollution Control-A Sedimentological Approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Baptista, L.; De Miguel, E. Geochemistry and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: A tropical urban environment. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4501–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA United States Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/regional-removal-management-levels-rmls-users-guide (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- National Environment Protection Agency of China (SEPAC). Environmental Quality Standard for Soils (GB 15618-1995); Chinese Environment Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- National Environment Protection Agency of China (SEPAC). Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land (GB 15618-2018); Chinese Environment Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Keshavarzi, B.; Najmeddin, A.; Moore, F.; Moghaddam, P.A. Risk-based assessment of soil pollution by PTEs in the industrialized urban and peri-urban areas of Ahvaz metropolis, southwest of Iran. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 167, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Zong, Y.T.; Lu, S.G. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 120, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Han, L.N.; Zhang, J.Q.; Zhang, Y.C.; Lang, Q.L.; Li, F.X.; Aru, H.; Bao, Y.B.; Li, K.W.; Alu, S. Environmental risk assessment of metals in the volcanic soil of Changbai Mountain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.X.; Chao, S.H.; Liu, J.W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhang, A.C.; Cao, H.B. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, K.; Huang, B.; Xing, Z.; Hu, W.Y. Geochemical baseline establishment and ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in greenhouse soils from Dongtai, China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.H.; Chen, L.J.; Yu, L.; Guo, Z.B.; Shan, C.Q.; Lin, J.Q.; Gu, Y.G.; Yang, Z.B.; Yang, Y.X.; Shao, J.R.; et al. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of human exposure to oral bioaccessibility of heavy metals via urban street dusts from different functional areas in Chengdu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, B.Q.; Liang, T.; Wang, L.Q.; Li, K.X. Applications of stochastic models and geostatistical analyses to study sources and spatial patterns of soil heavy metals in a metalliferous industrial district of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Liao, R.M.; Ali, A.; Mahar, A.; Guo, D.; Li, R.H.; Sun, X.N.; Awasthi, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.Q. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil near a Pb/Zn smelter in Feng County, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 139, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Ilyas, A.; Akhter, G.; Bashir, A. Pollution assessment and source apportionment of selected metals in rural (Bagh) and urban (Islamabad) farmlands, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.Z.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Z.G.; Qu, Y.P.; Chai, F.H.; Hao, J.M. Atmospheric emissions estimation of Hg, As, and Se from coal-fired power plants in China, 2007. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3078–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, A.; Gereslassie, T.; Xu, Q.; Tang, X.J.; Wang, J. Concentrations, distribution, sources and ecological risk assessment of trace elements in soils from Wuhan, central China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastegari, M.M.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Sharifi, R.; Lahijanzadeh, A.; Kermani, M. Distribution, source identification and health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in urban areas of Isfahan province, Iran. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 132, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.Y.; Wang, F.F.; Xu, C.Q.; Pan, N.H.; Lin, J.K.; Zhao, R.; Yang, Y.Y.; Luo, H.P. Source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil based on PMF: A case study in Hexi Corridor, northwest China. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smichowski, P.; Gomez, D.; Frazzoli, C.; Caroli, S. Traffic-related elements in airborne particulate matter. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2007, 43, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Seijo, A.; Andrade, M.L.; Vega, F.A. Origin and spatial distribution of metals in urban soils. J. Soil. Sediment. 2017, 17, 1514–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, P.E.; Subramanian, K.S.; Jessiman, B.J. A multi-element profile of house dust in relation to exterior dust and soils in the city of Ottawa, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 267, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Q.Q.; Deng, M.H.; Japenga, J.; Li, T.Q.; Yang, X.E.; He, Z.L. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of agricultural soils in a typical peri-urban area in southeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.Z.; Duan, X.L.; Zhao, X.G.; Ma, J.; Dong, T.; Huang, N.; Sun, C.Y.; He, B.; Wei, F.S. Health risks from the exposure of children to As, Se, Pb and other heavy metals near the largest coking plant in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Q.; Li, Z.Y.; Lu, X.N.; Duan, Q.N.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

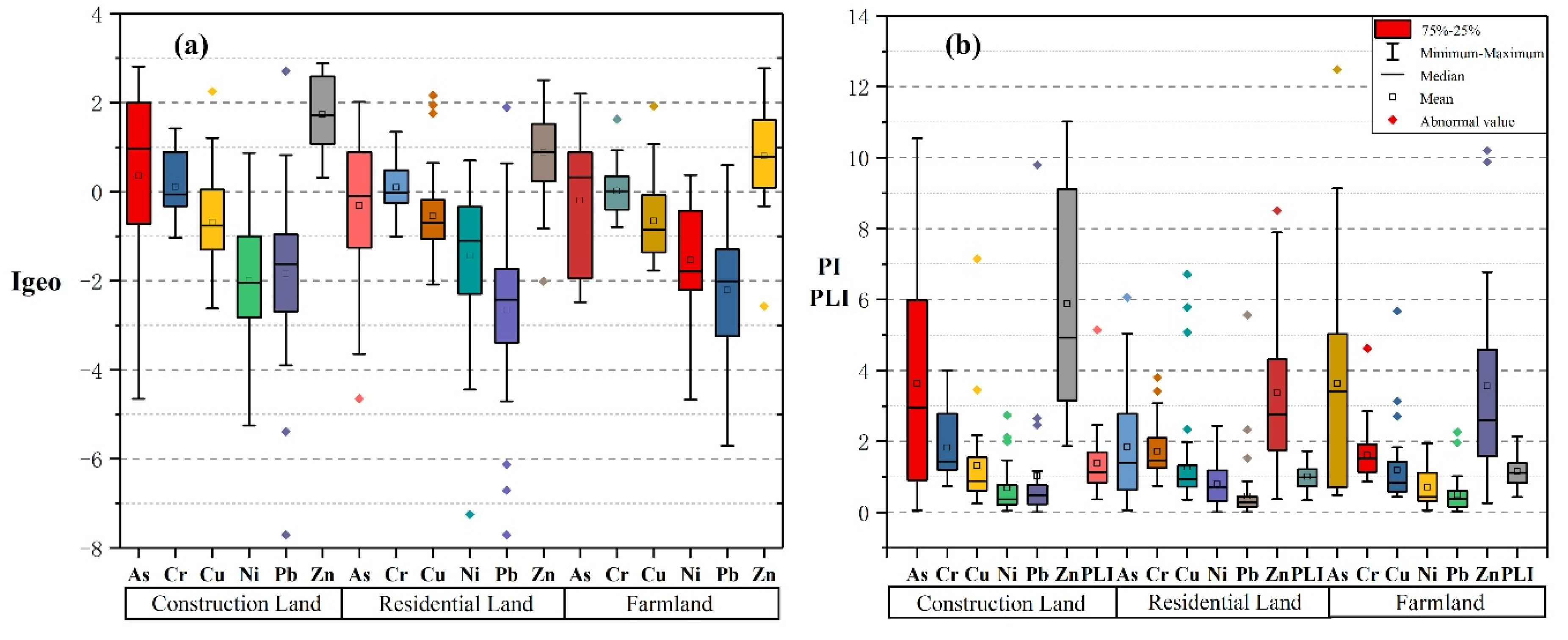




| Geo-Accumulation Index a | Pollution Load Index b | Potential Ecological Risk Index c | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Contamination Level | Value | Contamination Level | Value | Risk Degree |
| <0 | practically unpolluted | PLI ≤ 1 | unpolluted | < 40 | low risk |
| 0−1 | unpolluted to moderately polluted | 1 ≤ PLI ≤ 2 | unpolluted to moderately polluted | 40 ≤ < 80 | moderate risk |
| 1−2 | moderately polluted | 2 ≤ PLI ≤ 3 | moderately polluted | 80 ≤ < 160 | considerable risk |
| 2−3 | moderately to strongly polluted | 3 ≤ PLI ≤ 4 | moderately to highly polluted | 160 ≤ < 320 | high risk |
| 3−4 | strongly polluted | 4 ≤ PLI ≤ 5 | highly polluted | ≥ 320 | very high risk |
| 4−5 | strongly to extremely polluted | PLI > 5 | very highly polluted | ||
| ≥5 | extremely polluted | ||||
| Land Use Types | Values | As | Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residential land (57) | Max | 40.6 | 161.2 | 49.4 | 110 | 619 | 155.2 |
| Min | 0.4 | 31.6 | 0.2 | 5.8 | 27 | 0.2 | |
| Mean | 12.5 | 72.67 | 15.96 | 20.74 | 244.77 | 12.65 | |
| CV | 0.82 | 0.39 | 0.73 | 0.92 | 0.62 | 1.72 | |
| Grade a | 40 | 150 | 10 | 50 | 200 | 250 | |
| Industrial land (24) | Max | 70.6 | 169.8 | 55.6 | 117.2 | 802.2 | 273.2 |
| Min | 0.4 | 32 | 0.8 | 4 | 136.2 | 0.2 | |
| Mean | 24.33 | 76.85 | 13.87 | 21.54 | 427.86 | 28.31 | |
| CV | 0.84 | 0.50 | 1.11 | 1.08 | 0.56 | 1.91 | |
| Grade a | 40 | 150 | 40 | 50 | 200 | 250 | |
| Farmland (31) | Max | 46.2 | 195.8 | 39.4 | 93 | 742.8 | 63.2 |
| Min | 1.8 | 36.6 | 1.2 | 7.2 | 18.4 | 0.8 | |
| Mean | 13.41 | 68.50 | 14.25 | 19.48 | 258.95 | 13.72 | |
| CV | 0.83 | 0.43 | 0.70 | 0.87 | 0.76 | 0.99 | |
| Grade b | 40 | 150 | 70 | 50 | 90 | 200 | |
| Total | Max | 70.6 | 195.8 | 55.6 | 117.2 | 802.2 | 273.2 |
| Min | 0.4 | 31 | 0.2 | 4 | 18.4 | 0.2 | |
| Mean | 15.72 | 72.41 | 15.04 | 20.52 | 266.57 | 16.30 | |
| CV | 0.9 | 0.43 | 0.81 | 0.96 | 0.66 | 1.91 | |
| Background c | 6.7 | 42.4 | 20.3 | 16.4 | 72.8 | 27.9 |
| Elements | Rotated Component Matrix | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | |
| As | −0.369 | 0.738 | 0.064 |
| Cr | 0.711 | −0.054 | 0.284 |
| Cu | 0.851 | 0.053 | 0.016 |
| Ni | 0.716 | −0.215 | −0.085 |
| Pb | 0.084 | −0.114 | 0.952 |
| Zn | 0.129 | 0.847 | −0.218 |
| Elements | Health Index | Residential Land | Industrial Land | Farmland | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HQing | HQinh | HQder | HI | HQing | HQinh | HQder | HI | HQing | HQinh | HQder | HI | ||
| As | adults | 1.14 × 10−2 | 2.06 × 10−5 | 5.46 × 10−3 | 1.69 × 10−2 | 2.78 × 10−2 | 3.99 × 10−5 | 1.03 × 10−3 | 2.89 × 10−2 | 1.53 × 10−1 | 2.20 × 10−5 | 5.70 × 10−3 | 1.59 × 10−1 |
| children | 1.32 × 10−1 | 3.59 × 10−5 | 2.05 × 10−3 | 1.34 × 10−1 | 2.59 × 10−1 | 7.06 × 10−5 | 4.05 × 10−3 | 2.63 × 10−1 | 1.43 × 10−1 | 3.90 × 10−5 | 2.23 × 10−3 | 1.45 × 10−1 | |
| Cr | adults | 8.31 × 10−3 | 5.13 × 10−4 | 6.59 × 10−2 | 7.47 × 10−2 | 8.79 × 10−3 | 5.42 × 10−4 | 6.69 × 10−3 | 1.60 × 10−2 | 7.83 × 10−3 | 4.83 × 10−4 | 5.96 × 10−2 | 6.80 × 10−2 |
| children | 7.74 × 10−2 | 4.33 × 10−4 | 2.48 × 10−2 | 1.03 × 10−1 | 8.19 × 10−2 | 9.60 × 10−4 | 2.62 × 10−2 | 1.09 × 10−1 | 7.30 × 10−2 | 8.56 × 10−4 | 2.34 × 10−2 | 9.73 × 10−2 | |
| Ni | adults | 2.74 × 10−4 | 3.58 × 10−5 | 1.61 × 10−4 | 4.71 × 10−4 | 2.38 × 10−4 | 3.11 × 10−5 | 1.34 × 10−5 | 2.83 × 10−4 | 2.44 × 10-4 | 3.20 × 10−5 | 1.38 × 10−4 | 4.14 × 10−4 |
| children | 2.55 × 10−3 | 6.34 × 10−5 | 6.05 × 10−5 | 2.67 × 10−3 | 2.22 × 10−3 | 5.50 × 10−5 | 5.25 × 10−5 | 2.33 × 10−3 | 2.28 × 10−4 | 5.66 × 10−5 | 5.40 × 10−5 | 3.39 × 10−4 | |
| Cu | adults | 1.78 × 10−4 | 1.04 × 10−7 | 9.40 × 10−5 | 2.72 × 10-4 | 1.85 × 10−4 | 1.08 × 10−7 | 9.38 × 10−6 | 1.94 × 10−4 | 1.67 × 10−4 | 9.78 × 10−8 | 8.48 × 10−5 | 2.52 × 10−4 |
| children | 1.66 × 10−3 | 1.84 × 10−7 | 3.54 × 10−5 | 1.70 × 10−3 | 1.72 × 10−3 | 1.91 × 10−7 | 3.67 × 10−5 | 1.76 × 10−3 | 1.56 × 10−3 | 1.73 × 10−7 | 3.32 × 10−5 | 1.59 × 10−3 | |
| Zn | adults | 2.81 × 10−4 | 1.65 × 10−7 | 2.23 × 10−4 | 5.04 × 10−-4 | 4.89 × 10−4 | 2.88 × 10−7 | 3.74 × 10−5 | 5.27 × 10−4 | 2.96 × 10−4 | 1.74 × 10−7 | 2.25 × 10−4 | 5.21 × 10−4 |
| children | 2.62 × 10−3 | 2.92 × 10−7 | 8.37 × 10−5 | 2.70 × 10−3 | 4.56 × 10−3 | 5.09 × 10−7 | 1.46 × 10−4 | 4.71 × 10−3 | 2.76 × 10−3 | 3.08 × 10−7 | 8.83 × 10−5 | 2.85 × 10−3 | |
| Pb | adults | 1.24 × 10−3 | 7.25 × 10−7 | 1.31 × 10−3 | 2.55 × 10−3 | 2.77 × 10−3 | 1.62 × 10−6 | 2.82 × 10−4 | 3.05 × 10−3 | 1.34 × 10−3 | 7.86 × 10−7 | 1.37 × 10−3 | 2.71 × 10−3 |
| children | 1.15 × 10−2 | 1.28 × 10−6 | 4.93 × 10−4 | 1.20 × 10−2 | 2.59 × 10−2 | 2.87 × 10−6 | 1.10 × 10−3 | 2.70 × 10−2 | 1.25 × 10−2 | 1.39 × 10−6 | 5.34 × 10−4 | 1.30 × 10−2 | |
| Land Use Types | Health Index | As | Cr | Ni | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residential land | CRing | 6.56 × 10−5 | 1.29 × 10−4 | 3.80 × 10−7 | |
| CRinh | 1.04 × 10−7 | 1.71 × 10−6 | 7.50 × 10−9 | ||
| CRdermal | 3.38 × 10−6 | ||||
| TCR | 6.91 × 10−5 | 1.30 × 10−4 | 7.50 × 10−9 | 3.80 × 10−7 | |
| Industrial land | CRing | 1.29 × 10−4 | 1.36 × 10−4 | 8.52 × 10−7 | |
| CRinh | 2.05 × 10−7 | 1.80 × 10−6 | 6.51 × 10−9 | ||
| CRdermal | 2.29 × 10−6 | ||||
| TCR | 1.32 × 10−4 | 1.39 × 10−4 | 6.51 × 10−9 | 8.52 × 10−7 | |
| Farmland | CRing | 7.12 × 10−5 | 1.21 × 10−4 | 4.13 × 10−7 | |
| CRinh | 1.13 × 10−7 | 1.61 × 10−6 | 6.69 × 10−9 | ||
| CRdermal | 3.57 × 10−6 | ||||
| TCR | 7.49 × 10−5 | 1.23 × 10−4 | 6.69 × 10−9 | 4.13 × 10−7 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Q.; Peng, J.; Rong, G.; Tong, Z.; Liu, X. Pollution, Sources and Human Health Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Different Land Use Types under the Background of Industrial Cities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12052121
Xia Q, Zhang J, Chen Y, Ma Q, Peng J, Rong G, Tong Z, Liu X. Pollution, Sources and Human Health Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Different Land Use Types under the Background of Industrial Cities. Sustainability. 2020; 12(5):2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12052121
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Qing, Jiquan Zhang, Yanan Chen, Qing Ma, Jingyao Peng, Guangzhi Rong, Zhijun Tong, and Xingpeng Liu. 2020. "Pollution, Sources and Human Health Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Different Land Use Types under the Background of Industrial Cities" Sustainability 12, no. 5: 2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12052121
APA StyleXia, Q., Zhang, J., Chen, Y., Ma, Q., Peng, J., Rong, G., Tong, Z., & Liu, X. (2020). Pollution, Sources and Human Health Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Different Land Use Types under the Background of Industrial Cities. Sustainability, 12(5), 2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12052121








