Spin Crossover in 3D Metal Centers Binding Halide-Containing Ligands: Magnetism, Structure and Computational Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results. Solid State.
2.1. d4 Complexes, HS (S = 2) and LS (S = 1)—Mn(III)
2.2. d5 Complexes, HS (S = 5/2) and LS (S = 1/2)—Fe(III)
2.3. d6 Complexes, HS (S=2) and LS (S=0)—Fe(II)
2.4. d7 Complexes, HS (S=3/2) and LS (S=1/2)—Co(II)
3. Results Solution
4. Computational Studies
5. Conclusions
6. Computational Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cambi, L.; Szegö, L. Über die Magnetische Susceptibilität der Komplexen Verbindungen. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1931, 64, 2591–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gütlich, P.; Garcia, Y.; Goodwin, H.A. Spin Crossover Phenomena in Fe(II) Complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2000, 29, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, Y.; Niel, V.; Muñoz, M.C.; Real, J.A. Spin Crossover in 1D, 2D and 3D Polymeric Fe(II) Networks. Top. Curr. Chem. 2004, 233, 229–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real, J.A.; Gaspar, A.B.; Muñoz, M.C.; Gütlich, P.; Ksenofontov, V.; Spiering, H. Bipyrimidine-Bridged Dinuclear Iron(II) Spin Crossover Compounds. Top. Curr. Chem. 2004, 233, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toftlund, H.; McGarvey, J.J. Iron(II) Spin Crossover Systems with Multidentate Ligands. Top. Curr. Chem. 2004, 233, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, H.A. Spin Crossover in Iron(II) Tris(diimine) and Bis(terimine) Systems. Top. Curr. Chem. 2004, 233, 59–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Koningsbruggen, P.J. Special Classes of Iron(II) Azole Spin Crossover Compounds. Top. Curr. Chem. 2004, 233, 123–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.L.; Money, V.A.; Goeta, A.E.; Howard, J.A.K. Structural Studies of Thermal- and Light-Induced Transitions in Iron(II) gSpin-Crossover Complexes. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2005, 8, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, F.; Liu, T.; Yuan, M.; Wang, Z.-M.; Gao, S. Spin Crossover in a Series of Iron(II) Complexes of 2-(2-Alkyl-2H-tetrazol-5-yl)-1,10-phenanthroline: Effects of Alkyl Side Chain, Solvent, and Anion. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 2541–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halcrow, M.A. The Spin-States and Spin-Transitions of Mononuclear Iron(II) Complexes of Nitrogen-Donor Ligands. Polyhedron 2007, 26, 3523–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larionov, S.V. Spin Transition in Iron(III) and Iron(II) Complexes. Russ. J. Coord. Chem. 2008, 34, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, K.S. Advances in Polynuclear Iron(II), Iron(III) and Cobalt(II) Spin-Crossover Compounds. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 2008, 3101–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, J.A.; Brooker, S. Spin Crossover in Iron(II) Complexes of 3,5-Di(2-pyridyl)-1,2,4-triazoles and 3,5-Di(2-pyridyl)-1,2,4-triazolates. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2008, 252, 2072–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salitros, I.; Madhu, N.T.; Boca, R.; Pavlik, J.; Ruben, M. Room-Temperature Spin-Transition Iron Compounds. Monatsh. Chem. 2009, 140, 695–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolny, J.A.; Paulsen, H.; Trautwein, A.X.; Schünemann, V. Density Functional Theory Calculations and Vibrational Spectroscopy on Iron Spin-Crossover Compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 2423–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halcrow, M.A. Iron(II) Complexes of 2,6-Di(pyrazol-1-yl)pyridines-A Versatile System for Spin-Crossover Research. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 2493–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olguín, J.; Brooker, S. Spin Crossover Active Iron(II) Complexes of Selected Pyrazole-Pyridine/Pyrazine Ligands. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 203–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gütlich, P.; Gaspar, A.B.; Garcia, Y. Spin State Switching in Iron Coordination Compounds. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 342–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, G.A.; Roubeau, O.; Aromí, G. Spin State Switching in 2,6-Bis(pyrazol-3-yl)pyridine (3-bpp) based Fe(II) Complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2014, 269, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchenko, G.; Khristov, A.V.; Varyukhin, V.N. Spin Crossover in Iron(II)-Containing Complex Compounds under a Pressure. Low. Temp. Phys. 2014, 40, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Villar, N.; Muñoz, M.C.; Real, J.A. Symmetry Breaking in Iron(II) Spin-Crossover Molecular Crystals. Magnetochemistry 2016, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, H.S.; Staniland, R.W.; Kruger, P.E. Spin Crossover in Homoleptic Fe(II) Imidazolylimine Complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 362, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boillot, M.-L.; Weber, B. Mononuclear Ferrous and Ferric Complexes. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2018, 21, 1196–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogue, R.W.; Singh, S.; Brooker, S. Spin Crossover in Discrete Polynuclear Iron(II) Complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 7303–7338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Koningsbruggen, P.J.; Maeda, Y.; Oshio, H. Iron(III) Spin Crossover Compounds. Top. Curr. Chem. 2004, 233, 259–324. [Google Scholar]
- Nihei, M.; Shiga, T.; Maeda, Y.; Oshio, H. Spin Crossover Iron(III) Complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2007, 251, 2606–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, D.J.; Harding, P.; Phonsri, W. Spin Crossover in Iron(III) Complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 313, 38–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, H.A. Spin Crossover in Cobalt(II) Systems. Top. Curr. Chem. 2004, 234, 23–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivokapic, I.; Zerara, M.; Lawson Daku, L.M.; Vargas, A.; Enachescu, C.; Ambrus, C.; Tregenna-Piggott, P.; Amstutz, N.; Krausz, E.; Hauser, A. Spin-Crossover in Cobalt(II) Imine Complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2007, 251, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, Y.; Gütlich, P. Thermal Spin Crossover in Mn(II), Mn(III), Cr(II) and Co(III) Coordination Compounds. Top. Curr. Chem. 2004, 234, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halcrow, M.A. Spin-Crossover Materials: Properties and Applications; Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Borshch, S.A. Comprehensive Inorganic Chemistry II, 2nd ed.; Reedijk, J., Poeppelmeier, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 469–480. [Google Scholar]
- Gudyma, I.; Maksymov, A.; Bobák, A. Nanophysics, Nanomaterials, Interface Studies, and Applications; NANO 2016, Springer Proceedings in Physics; Fesenko, O., Yatsenko, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; Volume 195. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlik, J.; Linares, J. Microscopic Models of Spin Crossover. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2018, 21, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calhorda, M.J.; Costa, P.J. Comprehensive Inorganic Chemistry II; Reedijk, J., Poeppelmeier, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 801–809. [Google Scholar]
- Desiraju, G.R.; Ho, P.S.; Kloo, L.; Legon, A.C.; Marquardt, R.; Metrangolo, P.; Politzer, P.; Resnati, G.; Rissanen, K. Definition of the Halogen Bond (IUPAC Recommendations 2013). Pure Appl. Chem. 2013, 85, 1711–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, I.-R.; Jeannin, O.; Clérac, R.; Rouzières, M.; Fourmigué, M. Spin-State Modulation of Molecular FeIII Complexes via Inclusion in Halogen-Bonded Supramolecular Networks. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 4989–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, R.; Lazar, H.; Barrett, S.A.; Kilner, C.A.; Asthana, S.; Carbonera, C.; Létard, J.F.; Halcrow, M.A.; Sheu, H.S.; Yasuda, N.; et al. Thermal and Light-Induced Spin-Transitions in Iron(II) Complexes of 2,6-Bis(4-halopyrazolyl)pyridines: The Influence of Polymorphism on a Spin-Crossover Compound. Dalton Trans. 2009, 125, 6656–6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, B.; Walker, F.A. Solution NMR Studies of Iron(II) Spin-Crossover Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 6794–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meer, M.; Rechkemmer, Y.; Breitgoff, F.D.; Dechert, S.; Marx, R.; Dörfel, M.; Neugebauer, P.; van Slageren, J.; Sarkar, B. Probing Bistability in FeII and CoII Complexes with an Unsymmetrically Substituted Quinonoid Ligand. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 8394–8403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, H.; Djomgoue, P.; Hörner, G.; Speck, J.M.; Rüffer, T.; Schaarschmidt, D. 1H NMR Spectroscopic Elucidation in Solution of the Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Spin Crossover for an Exceptionally Robust Fe2+ Complex. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 13798–13809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.H.; Nihei, M.; Wen, G.J.; Sun, B.W.; Oshio, H. Ambient-Temperature Spin-State Switching Achieved by Protonation of the Amino Group in [Fe(H2Bpz2)2(bipy-NH2)]. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 8147–8152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Jiménez, S.; Yang, M.; Stewart, I.; Garden, A.L.; Brooker, S. A Simple Method of Predicting Spin State in Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 18392–18396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devid, E.J.; Martinho, P.N.; Kamalakar, M.V.; Šalitroš, I.; Prendergast, Ú.; Dayen, J.-F.; Meded, V.; Lemma, T.; González-Prieto, R.; Evers, F.; et al. Spin Transition in Arrays of Gold Nanoparticles and Spin Crossover Molecules. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4496–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meded, V.; Bagrets, A.; Fink, K.; Chandrasekar, R.; Ruben, M.; Evers, F.; Bernand-Mantel, A.; Seldenthuis, J.S.; Beukman, A.; van der Zant, H.S.J. Electrical Control over the Fe(II) Spin Crossover in a Single Molecule: Theory and Experiment. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 245415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamachi, T.; Gruber, M.; Davesne, V.; Bowen, M.; Boukari, S.; Joly, L.; Scheurer, F.; Rogez, G.; Yamada, T.K.; Ohresser, P.; et al. Robust Spin Crossover and Memristance Across a Single Molecule. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopakumar, T.G.; Matino, F.; Naggert, H.; Bannwarth, A.; Tuczek, F.; Berndt, R. Electron-Induced Spin Crossover of Single Molecules in a Bilayer on Gold. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6262–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragonès, A.C.; Aravena, D.; Cerdá, J.I.; Acís-Castillo, Z.; Li, H.; Real, J.A.; Sanz, F.; Hihath, J.; Ruiz, E.; Díez-Pérez, I. Large Conductance Switching in a Single-Molecule Device through Room Temperature Spin-Dependent Transport. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefter, C.; Rat, S.; Costa, J.S.; Manrique-Juárez, M.D.; Quintero, C.M.; Salmon, L.; Séguy, I.; Leichle, T.; Nicu, L.; Demont, P.; et al. Current Switching Coupled to Molecular Spin-States in Large-Area Junctions. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 7508–7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.-H.; Liu, Q.-L.; Yang, L.-J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.-W.; You, C.-Q.; Sun, B.-W. Magnetic Observation of Above Room-Temperature Spin Transition in Vesicular Nano-Spheres. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 8061–8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, P.N.; Ortin, Y.; Gildea, B.; Gandolfi, C.; McKerr, G.; O’Hagan, B.; Albrecht, M.; Morgan, G.G. Inducing Hysteretic Spin Crossover in Solution. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 7461–7463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, C.; Morgan, G.G.; Albrecht, M. A Magnetic Iron(III) Switch with Controlled and Adjustable Thermal Response for Solution Processing. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 3726–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, N.G.; Feltham, H.L.C.; Gandolfi, C.; Albrecht, M.; Brooker, S. Towards Langmuir–Blodgett Films of Magnetically Interesting Materials: Solution Equilibria in Amphiphilic Iron(II) Complexes of a Triazole-Containing Ligand. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 3751–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlamp, S.; Thoma, P.; Weber, B. Influence of the Alkyl Chain Length on the Self-Assembly of Amphiphilic Iron Complexes: An Analysis of X-ray Structures. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 6462–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario-Amorin, D.; Dechambenoit, P.; Bentaleb, A.; Rouzières, M.; Mathonière, C.; Clérac, R. Multistability at Room Temperature in a Bent-Shaped Spin-Crossover Complex Decorated with Long Alkyl Chains. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravena, D.; Ruiz, E. Coherent Transport through Spin-Crossover Single Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 777–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baadji, N.; Piacenza, M.; Tugsuz, T.; Sala, F.D.; Maruccio, G.; Sanvito, S. Electrostatic Spin Crossover Effect in Polar Magnetic Molecules. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio, E.A.; Moth-Poulsen, K.; van der Zant, H.S.J.; Paaske, J.; Hedegård, P.; Flensberg, K.; Bendix, J.; Bjørnholm, T. Electrical Manipulation of Spin States in a Single Electrostatically Gated Transition-Metal Complex. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harzmann, G.D.; Frisenda, R.; van der Zant, H.S.J.; Mayor, M. Single-Molecule Spin Switch Based on Voltage-Triggered Distortion of the Coordination Sphere. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 13425–13430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisenda, R.; Harzmann, G.D.; Celis Gil, J.A.; Thijssen, J.M.; Mayor, M.; van der Zant, H.S.J. Stretching-Induced Conductance Increase in a Spin-Crossover Molecule. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 4733–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, O. Spin-Crossover Molecular Materials. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 1996, 1, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Létard, J.-F.; Guionneau, P.; Goux-Capes, L. Towards Spin Crossover Applications. Top. Curr. Chem. 2004, 235, 221–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.S.; Ruben, M. Emerging Trends in Spin Crossover (SCO) Based Functional Materials and Devices. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 346, 176–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Peng, H. Recent Advances in Self-Assembly of Spin Crossover Materials and their Applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 35, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, J.; Codjovi, E.; Garcia, Y. Pressure and Temperature Spin Crossover Sensors with Optical Detection. Sensors 2012, 12, 4479–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parr, R.G.; Yang, W. Density-Functional Theory of Atoms and Molecules; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, J.N. Spin-Forbidden Reactions: Computational Insight into Mechanisms and Kinetics. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2014, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ferbinteanu, M.; Marinescu, C.; Dobrinescu, A.; Ling, Q.-D.; Huang, W. Case Study on a Rare Effect: The Experimental and Theoretical Analysis of a Manganese(III) Spin-Crossover System. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 9839–9851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandurangan, K.; Gildea, B.; Murray, C.; Harding, C.J.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Morgan, G.G. Lattice Effects on the Spin-Crossover Profile of a Mononuclear Manganese(III) Cation. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 2021–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gildea, B.; Gavin, L.C.; Murray, C.A.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Harding, C.J.; Morgan, G.G. Supramolecular Modulation of Spin Crossover Profile in Manganese(III). Supramol. Chem. 2012, 24, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, A.J.; Trzop, E.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Dîrtu, M.M.; Garcia, Y.; Collet, E.; Morgan, G.G. Electronic vs. Structural Ordering in a Manganese(III) Spin Crossover Complex. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 17540–17543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirirak, J.; Harding, D.J.; Harding, P.; Murray, K.S.; Moubaraki, B.; Liu, L.; Telfer, S.G. Spin Crossover in cis Manganese(III) Quinolylsalicylaldiminates. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 2015, 2534–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, G.G.; Murnaghan, K.D.; Müller-Bunz, H.; McKee, V.; Harding, C.J. A Manganese(III) Complex that Exhibits Spin Crossover Triggered by Geometric Tuning. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 7192–7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, A.J.; Stepanovic, S.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Gruden-Pavlović, M.A.; García-Fernández, P.; Morgan, G.G. Challenges in Assignment of Orbital Populations in a High Spin Manganese(III) Complex. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 6702–6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, C.T.; Brewer, G.; May, L.; Sitar, J.; Wang, R. Spin Crossover in Heterodinuclear Iron(III) Schiff-Base Complexes. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1993, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallon, G.D.; McLachlan, G.A.; Moubaraki, B.; Murray, K.S.; O’Brien, L.; Spiccia, L. Mononuclear Chromium(III), Manganese(II) and Iron(III) Complexes of the Pentadentate Ligand 1;4-Bis(2-pyridylmethyl)-1;4;7-triazacyclononane. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1997, 2765–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Molina, R.; Mederos, A.; Dominguez, S.; Gili, P.; Ruiz-Pérez, C.; Castiñeiras, A.; Solans, X.; Lloret, F.; Real, J.A. Different Ground Spin States in Iron(III) Complexes with Quadridentate Schiff Bases: Synthesis; Crystal Structures; and Magnetic Properties. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 5102–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floquet, S.; Boillot, M.-L.; Rivière, E.; Varret, F.; Boukheddaden, K.; Morineau, D.; Négrier, P. Spin Transition with a Large Thermal Hysteresis Near Room Temperature in a Water Solvate of an Iron(III) Thiosemicarbazone Complex. New J. Chem. 2003, 27, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelentsov, V.V.; Bogdanova, L.G.; Ablov, A.V.; Gerbeleuand, N.V.; Dyatlova, C.V. Themomagnetic Studies of Fe(III) Complexes with Thiosemicarbazones of Substituted Ortho hydroxybenzaldehydes. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 1973, 18, 2654–2657. [Google Scholar]
- Zelentsov, V.V.; Mokshin, V.M.; Sobolev, S.S.; Shipilov, V.I. The Influence of Crystallization Water upon Magnetic Properties of Fe(III) Thiosemicarbazones. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 1984, 277, 900. [Google Scholar]
- Floquet, S.; Guillou, N.; Négrier, P.; Rivière, E.; Boillot, M.-L. The Crystallographic Phase Transition for a Ferric Thiosemicarbazone Spin Crossover Complex Studied by X-ray Powder Diffraction. New J. Chem. 2006, 30, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-Y.; Dai, J.-W.; Gagnon, K.J.; Cai, H.-L.; Yamamoto, T.; Einaga, Y.; Zhao, H.-H.; Kanegawa, S.; Sato, O.; Dunbar, K.R.; et al. A Neutral Fe(III) Compound Exhibiting a Two-Step Spin Transition and Dielectric Anomalies. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 14685–14688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupska, A.; Augustyniak-Jablokow, M.A.; Yablokov, Y.V.; Zelentsov, V.V.; Ulanov, V.A.; Mrozinski, J. EPR Discovery of a New Pressure-Induced Low-Spin Phase in (2Me–5Et–PyH)[Fe(Th–5Cl–Sa)2]. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2006, 110, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phonsri, W.; Macedo, D.S.; Davies, C.G.; Jameson, G.N.L.; Moubaraki, B.; Murray, K.S. Heteroleptic Iron(III) Schiff Base Spin Crossover Complexes: Halogen Substitution; Solvent Loss and Crystallite Size Effects. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 7020–7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-Y.; Dai, J.-W.; Shiota, Y.; Yoshizawa, K.; Kanegawa, S.; Sato, O. Multi-Step Spin Crossover Accompanied by Symmetry Breaking in an FeIII Complex: Crystallographic Evidence and DFT Studies. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 12948–12952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floquet, S.; Rivière, E.; Boukheddaden, K.; Morineau, D.; Boillot, M.-L. Neutral Ferric Complexes of Salicylaldehyde Thiosemicarbazone Ligands: An Exceptional Family of Complexes Exhibiting Discontinuous Spin Transition Behavior. Polyhedron 2014, 80, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Shiota, Y.; Kariyazaki, A.; Kanegawa, S.; Yoshizawa, K.; Sato, O. Heterometallic FeIII/K Coordination Polymer with a Wide Thermal Hysteretic Spin Transition at Room Temperature. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, T.; Okazawa, A.; Sato, O. Halogen Substituent Effect on the Spin-Transition Temperature in Spin-Crossover Fe(III) Compounds Bearing Salicylaldehyde 2-Pyridyl Hydrazone-Type Ligands and Dicarboxylic Acids. Inorganics 2017, 5, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Weyhermüller, T.; Eckhard, B.; Wieghardt, K.; Chaudhuri, P. Tuning of Spin Transition in Radical-Containing Iron(III) Complexes by Remote Ligand Substituents. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 7099–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enachescu, C.; Hauser, A.; Girerd, J.; Boillot, M. Photoexcitation and Relaxation Dynamics of Catecholato–Iron(III) Spin-Crossover Complexes. ChemPhysChem 2006, 7, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simaan, A.J.; Boillot, M.-L.; Rivière, E.; Boussac, A.; Girerd, J.-J. A Two-Step Spin Crossover in [(TPA)FeIII(cat)]BPh4. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 196–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collet, E.; Boillot, M.-L.; Hébert, J.; Moisan, N.; Servol, M.; Lorenc, M.; Toupet, L.; Cointe, B.L.; Tissot, A.; Sainton, J. Polymorphism in the Spin-Crossover Ferric Complexes [(TPA)FeIII(TCC)]PF6. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B 2009, 65, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissot, A.; Shepherd, H.J.; Toupet, L.; Collet, E.; Sainton, J.; Molnár, G.; Guionneau, P.; Boillot, M.-L. Temperature- and Pressure-Induced Switching of the Molecular Spin State of an Orthorhombic Iron(III) Spin-Crossover Salt. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 2013, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, A.I.S.; Dias, J.C.; Vieira, B.J.C.; Santos, I.C.; Branco, M.B.C.; Pereira, L.C.K.; Waerenborgh, J.C.; Almeida, M.; Belo, D.; Gama, V. A New Hybrid Material Exhibiting Room Temperature Spin-Crossover and Ferromagnetic Cluster-Glass Behavior. CrystEngComm 2009, 11, 2160–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phonsri, W.; Harding, D.J.; Harding, P.; Murray, K.S.; Moubaraki, B.; Gass, I.A.; Cashion, J.D.; Jameson, G.N.L.; Adams, H. Stepped Spin Crossover in Fe(III) Halogen Substituted Quinolylsalicylaldimine Complexes. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 17509–17518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, D.J.; Phonsri, W.; Harding, P.; Gass, I.A.; Murray, K.S.; Moubaraki, B.; Cashion, J.D.; Liu, L.; Telfer, S.G. Abrupt Spin Crossover in an Iron(III) Quinolylsalicylaldimine Complex: Structural Insights and Solvent Effects. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6340–6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, D.J.; Phonsri, W.; Harding, P.; Murray, K.S.; Moubaraki, B.; Jameson, G.N.L. Abrupt Two-Step and Symmetry Breaking Spin Crossover in an Iron(III) Complex: An Exceptionally Wide [LS–HS] Plateau. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 15079–15082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuroi, K.; Takahashi, K.; Mochida, T.; Sakurai, T.; Ohta, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Einaga, Y.; Mori, H. Synergistic Spin Transition between Spin Crossover and Spin-Peierls-like Singlet Formation in the Halogen-Bonded Molecular Hybrid System: [Fe(Iqsal)2][Ni(dmit)2]⋅CH3CN⋅H2O. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1983–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, B.J.C.; Dias, J.C.; Santos, I.C.; Pereira, L.C.J.; Gama, V.; Waerenborgh, J.C. Thermal Hysteresis in a Spin-Crossover FeIII Quinolylsalicylaldimine Complex, FeIII(5-Br-qsal)2Ni(dmit)2·solv: Solvent Effects. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 1354–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, B.J.C.; Coutinho, J.T.; Dias, J.C.; Nunes, J.C.; Santos, I.C.; Pereira, L.C.J.; Gama, V.; Waerenborgh, J.C. Crystal Structure and Spin Crossover Behavior of the [Fe(5-Cl-qsal)2][Ni(dmit)2]·2CH3CN Complex. Polyhedron 2015, 85, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phukkaphan, N.; Cruickshank, D.L.; Murray, K.S.; Phonsri, W.; Harding, P.; Harding, D.J. Hysteretic Spin Crossover Driven by Anion Conformational Change. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 9801–9804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phonsri, W.; Harding, P.; Murray, K.S.; Moubaraki, B.; Harding, D.J. Spin Crossover in Mixed Ligand Iron(III) Complexes. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 13747–13753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phonsri, W.; Harding, P.; Liu, L.; Telfer, S.G.; Murray, K.S.; Moubaraki, B.; Ross, T.M.; Jameson, G.N.L.; Harding, D.J. Solvent Modified Spin Crossover in an Iron(III) Complex: Phase Changes and an Exceptionally Wide Hysteresis. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 3949–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadehavan, S.A.; Cadoni, E.; Monni, N.; Pipaón, C.S.; Mascarós, J.-R.G.; Abhervé, A.; Avarvi, N.; Marchiò, L.; Arca, M.; Mercuri, M.L. Structural Diversity in a New Series of Halogenated Quinolyl Salicylaldimides-Based FeIII Complexes Showing Solid-State Halogen-Bonding/Halogen···Halogen Interactions. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 4187–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Léon, M.; Coronado, E.; López-Jordà, M.; Waerenborgh, J.C. Multifunctional Magnetic Materials Obtained by Insertion of Spin-Crossover FeIII Complexes into Chiral 3D Bimetallic Oxalate-Based Ferromagnets. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 9122–9130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-León, M.; Coronado, E.; López-Jordà, M. 2D Bimetallic Oxalate-Based Ferromagnets with Inserted [Fe(4-Br-sal2-trien)]+ and [Fe(3-R-sal2-trien)]+ (R = Br, Cl and CH3O) FeIII Spin-Crossover Complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 5–6, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhervé, A.; Clemente-León, M.; Coronado, E.; Gómez-García, C.J.; Verneret, M. Luminescent Dinuclear Cu(I) Complexes Containing Rigid Tetraphosphine Ligands. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 12014–12026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, Y.; Murai, N.; Ishimae, H.; Suzuki, M.; Mori, S.; Takahashi, M.; Nakamura, M.; Toshino, K.; Ikeue, T. Spin-Crossover Between High-Spin (S = 5/2) and Low-Spin (S = 1/2) States In Six-Coordinate Iron(III) Porphyrin Complexes Having Two Pyridine-N Oxide Derivatives. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herchel, R.; Trávnícek, Z. 5-Aminotetrazole Induces Spin Crossover In Iron(III) Pentadentate Schiff Base Complexes: Experimental and Theoretical Investigations. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 16279–16288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger, C.; Augustín, P.; Nemec, I.; Trávníček, Z.; Oshio, H.; Boča, R.; Renz, F. Spin Crossover in Iron(III) Complexes with Pentadentate Schiff Base Ligands and Pseudohalido Coligands. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 5–6, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, C.; Augustín, P.; Dlhán, L.; Pavlik, J.; Moncol, J.; Nemec, I.; Boča, R.; Renz, F. Iron(III) Complexes with Pentadentate Schiff-Base Ligands: Influence of Crystal Packing Change and Pseudohalido Coligand Variations On Spin. Polyhedron 2015, 87, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, P.N.; Vicente, A.I.; Realista, S.; Saraiva, M.S.; Melato, A.I.; Brandão, P.; Ferreira, L.P.; Carvalho, M.D. Solution and Solid State Properties of Fe(III) Complexes Bearing N-Ethyl-N-(2-Aminoethyl)Salicylaldiminate Ligands. J. Organomet. Chem. 2014, 760, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, A.I.; Joseph, A.; Ferreira, L.P.; Carvalho, M.D.; Rodrigues, V.H.N.; Duttine, M.; Diogo, H.P.; da Piedade, M.E.M.; Calhorda, M.J.; Martinho, P.N. Dynamic Spin Interchange In A Tridentate Fe(III) Schiff-Base Compound. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 4251–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, A.I.; Ferreira, L.P.; Carvalho, M.D.; Rodrigues, V.H.N.; Dîrtu, M.; Garcia, Y.; Calhorda, M.J.; Martinho, P.N. Selecting The Spin Crossover Profile with Controlled Crystallization of Mononuclear Fe(III) Polymorphs. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 7013–7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.F.; Joseph, A.; Diogo, H.P.; da Piedade, M.E.M.; Ferreira, L.P.; Carvalho, M.D.; Barroso, S.; Romão, M.J.; Calhorda, M.J.; Martinho, P.N. Irreversible Magnetic Behaviour Caused by the Thermosalient Phenomenon in an Iron(III) Spin Crossover Complex. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 25, 2976–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonprab, T.; Harding, P.; Murray, K.S.; Phonsri, W.; Telfer, S.G.; Alkas, A.; Ketkaew, R.; Tantirungrotechai, Y.; Jameson, G.N.L.; Harding, D.J. Solvatomorphism and Anion Effects in Predominantly Low Spin Iron(III) Schiff Base Complexes. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 12449–12458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, A.M.; Shehab, O.R. Structural Studies and Quantum Chemical Calculations of Cr(III), Fe(III) and Ru(III) Bromazepam Complexes. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 31, 3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.H.; Kao, S.P. Mossbauer Study of the Effect of Intraligand Substituents on the Spin Crossover in Solid (Dithiocyanato)BIS(N-Substituted-Phenyl-2-Pyridinaldimine) Iron (II). J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 1985, 32, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phonsri, W.; Macedo, D.S.; Vignesh, K.R.; Rajaraman, G.; Davies, C.G.; Jameson, G.N.L.; Moubaraki, B.; Ward, J.S.; Kruger, P.E.; Chastanet, G.; et al. Halogen Substitution Effects on N2O Schiff Base Ligands in Unprecedented Abrupt FeII Spin Crossover Complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 7052–7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phonsri, W.; Davies, C.G.; Jameson, G.N.L.; Moubaraki, B.; Ward, J.S.; Kruger, P.E.; Chastanet, G.; Murray, K.S. Symmetry Breaking Above Room Temperature In An Fe(II) Spin Crossover Complex with An N4O2 Donor Set. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 1374–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda-Sowa, T.; Isobe, R.; Yamao, N.; Fukumasu, T.; Okubo, T.; Maekawa, M. Variety of Spin Transition Temperatures of Iron(II) Spin Crossover Complexes with Halogen Substituted Schiff-Base Ligands, HqsalX (X = F, Cl, Br, and I). Polyhedron 2017, 136, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real, A.; Zarembowitch, J.; Kahn, O.; Solans, X. Magnetic Interaction and Spin Transition In Iron(II) Dinuclear Compounds. Crystal Structure of (μ-2,2’-Bipyrimidine)Bis[(2,2’-Bipyrimidine)Bis(Thiocyanato)Iron(II)]. Inorg. Chem. 1987, 26, 2939–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enamullah, M.; Linert, W.; Gutmann, V. Vibrational Spectroscopy On Iron(II) Spin-Crossover Complexes with 4-Substituted 2,6-Bis(Benzimidazol-2′-Yl)Pyridine. Vib. Spectrosc. 1995, 9, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linert, W.; Konecny, M.; Renz, F. Spin-State Equilibria In Non-Aqueous Solution and Quantum-Mechanical Investigations of Iron(II) and Nickel(II) Complexes with 4-Substituted 2,6-Bis(Benzimidazol-2-Yl)Pyridines. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1994, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linert, W.; Enamullah, M.; Gutmann, V.; Jameson, R.F. Spin-Crossover Complexes in Solution. III. Substituent- and Solvent Effects on the Spin-Equilibrium of 4-Substituted Iron(II)-2,6-Bis-(Benzimidazol-2′-Yl)-Pyridine Systems. Monatsh. Chem. 1994, 125, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, H.; Duelund, L.; Zimmermann, A.; Averseng, F.; Gerdan, M.; Winkler, H.; Toftlund, H.; Trautwein, A.X. Substituent Effects on the Spin-Transition Temperature in Complexes with Tris(pyrazolyl) Ligands. Monatsh. Chem. 2003, 134, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, K.; Suemura, N.; Yoneda, K.; Kawata, S.; Kaizaki, S. Substituent Effect of The Coordinated Pyridine In A Series of Pyrazolato Bridged Dinuclear Diiron(II) Complexes On The Spin-Crossover Behavior. Dalton Trans. 2005, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bréfuel, N.; Shova, S.; Lipkowski, J.; Tuchagues, J.-P. FeII Bi-Stable Materials Based on Dissymmetrical Ligands: N4 Schiff Bases Including 2-Pyridyl and 5-Methylimidazol-4-yl Rings Yield Various FeII Spin-Crossover Phenomena around 300 K. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 5467–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, R.; Kilner, C.A.; Halcrow, M.A. Iron(II) Complexes with A Terpyridine Embrace Packing Motif Show Remarkably Consistent Cooperative Spin-Transitions. Chem. Commun. 2007, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, L.J.K.; Shepherd, H.J.; Comyn, T.P.; Beldé, C.; Cespedes, O.; Chastanet, G.; Halcrow, M.A. Decoupled Spin Crossover and Structural Phase Transition in a Molecular Iron(II) Complex. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 4805–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonera, C.; Kilner, C.A.; Letard, J.-F.; Halcrow, M.A. Anion Doping As A Probe of Cooperativity In The Molecular Spin-Crossover Compound [FeL2][BF4]2 (L = 2,6-di{pyrazol-1-yl}pyridine). Dalton Trans. 2007, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, L.J.K.; Kulmaczewski, R.; Mohammed, R.; Dudley, S.; Barrett, S.A.; Little, M.A.; Deeth, R.J.; Halcrow, M.A. A Unified Treatment of the Relationship Between Ligand Substituents and Spin State in a Family of Iron(II) Complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4327–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdiell, I.C.; Kulmaczewski, R.; Halcrow, M.A. Iron(II) Complexes of 2,4-Dipyrazolyl-1,3,5-triazine Derivatives—The Influence of Ligand Geometry on Metal Ion Spin State. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 8817–8828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhu, N.T.; Salitros, I.; Schramm, F.; Klyatskaya, S.; Fhur, O.; Ruben, M. Above Room Temperature Spin Transition In A Series of Iron(II) Bis(Pyrazolyl)Pyridine Compounds. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2008, 11, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, A.; Ishida, T. Pybox-Iron(II) Spin-Crossover Complexes with Substituent Effects from the 4-Position of the Pyridine Ring (Pybox = 2,6-Bis(oxazolin-2-yl)pyridine). Inorganics 2017, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, S.M.; Leita, B.A.; Offermann, D.A.; Duriska, M.B.; Moubaraki, B.; Chapman, K.W.; Halder, G.J.; Murray, K.S. Spin-Crossover Studies on a Series of 1D Chain and Dinuclear Iron(II) Triazine-Dipyridylamine Compounds. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 2007, 1073–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medlycott, E.A.; Hanan, G.S.; Abedin, T.S.M.; Thompson, L.K. The Effect of Steric Hindrance On The Fe(II) Complexes of Triazine-Containing Ligands. Polyhedron 2008, 27, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, T.M.; Moubaraki, B.; Neville, S.M.; Batten, S.R.; Murray, K.S. Polymorphism and Spin Crossover In Mononuclear FeII Species Containing New Dipyridylamino-Substituted S-Triazine Ligands. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 1512–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, H.S.; Ross, T.M.; Chilton, N.F.; Gass, I.A.; Moubaraki, B.; Chastanet, G.; Paradis, N.; Lètard, J.-F.; Vignesh, K.R.; Rajaraman, G.; et al. Crown-Linked Dipyridylamino-Triazine Ligands and Their Spin-Crossover Iron(II) Derivatives: Magnetism, Photomagnetism and Cooperativity. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 16494–16509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wannarit, N.; Roubeau, O.; Youngme, S.; Gamez, P. Subtlety of the Spin-Crossover Phenomenon Observed with Dipyridylamino-Substituted Triazine Ligands. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 2013, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannarit, N.; Roubeau, O.; Youngme, S.; Teat, S.J.; Gamez, P. Influence of Supramolecular Bonding Contacts on the Spin Crossover Behaviour of Iron(II) Complexes from 2,2′-Dipyridylamino/s-triazine Ligands. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 7120–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannarit, N.; Nassirinia, N.; Amani, S.; Masciocchi, N.; Youngme, S.; Roubeau, O.; Teat, S.J.; Gamez, P. Drastic Effect of Lattice Propionitrile Molecules on the Spin-Transition Temperature of a 2,2′-Dipyridylamino/s-triazine-Based Iron(II) Complex. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 9827–9836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.-P.; Qi, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, J.-J.; Zhu, D.; Liu, X.-Q.; You, X. Spin-Crossover in a Trans-[FeL2(NCS)2] Family (L = Triaryltriazole): Remote Substituent Effects on Spin Transition Modes and Temperature. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 10144–10152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.G.; Jeon, I.-R.; Harris, T.D. Electronic Effects of Ligand Substitution on Spin Crossover in a Series of Diiminoquinonoid-Bridged FeII2 Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.; Djukic, B.; Lemaire, M.T. Synthesis of Bromine- or Aryl-Substituted Ditopic Schiff Base Ligands and their Bimetallic Iron(II) Complexes: Electronic and Magnetic Properties. Transit. Metal Chem. 2014, 39, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, A.D.; Tinant, B.; Muffler, K.; Wolny, J.A.; Schünemann, V.; Garcia, Y. Relevance of Supramolecular Interactions, Texture and Lattice Occupancy in the Designer Iron(II) Spin Crossover Complexes. J. Solid State Chem. 2009, 182, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naggert, H.; Rudnik, J.; Kipgen, J.; Bernien, M.; Nickel, F.; Arruda, L.M.; Kuch, W.; Näther, C.; Tuczek, F. Vacuum-Evaporable Spin-Crossover Complexes: Physicochemical Properties in the Crystalline Bulk and in Thin Films Deposited from the Gas Phase. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 7870–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, H.; Djomgoue, P.; Hörner, G.; Heider, S.; Lochenie, C.; Weber, B.; Rüffner, T.; Schaarschmidt, D. Spin State Variability in Fe2+ Complexes of Substituted (2-(Pyridin-2-yl)-1,10-phenanthroline) Ligands as Versatile Terpyridine Analogues. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 6218–6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petzold, H.; Djomgoue, P.; Hörner, G.; Lochenie, C.; Weber, B.; Rüffer, T. Bis-Meridional Fe2+ Spin crossover Complexes of Phenyl and Pyridyl Substituted 2-(Pyridin-2-yl)-1,10-Phenanthrolines. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natke, D.; Unruh, D.; Dreyer, B.; Klimke, S.; Jahns, M.; Preiss, A.; Sindelar, R.; Klingelhöfer, G.; Renz, F. Tuning Spin Transitions of Iron(II)-dpp Systems. Hyperfine Interact. 2018, 239, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.-H.; Sun, X.-L.; Gu, L.; Qiu, D.; Li, Z.; Gu, Z.-G. A Family of Homochiral Spin-Crossover Iron(II) Imidazole Schiff-Base Complexes. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shylin, S.I.; Gural’skiy, I.A.; Bykov, D.; Demeshko, S.; Dechert, S.; Meyer, F.; Hauka, M.; Fritsky, I.O. Iron(II) Isothiocyanate Complexes with Substituted Pyrazines: Experimental and Theoretical Views on their Electronic Structure. Polyhedron 2015, 87, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, H.; Fei, B.; Chen, X.Q.; Tong, M.L.; Ksenofontov, V.; Gural’skiy, I.A.; Bao, X. Multiple Spin Phases in a Switchable Fe(II) Complex: Polymorphism and Symmetry Breaking Effects. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 3352–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stassen, A.F.; Dova, E.; Ensling, J.; Schenk, H.; Gütlich, P.; Haasnoot, J.G.; Reedijk, J. Spin Crossover in Hexakis(1-(2-chloroethyl)-tetrazole)iron(II) Complexes, Synthesis and Magnetic Properties. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2002, 335, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stassen, A.F.; Grunert, M.; Dova, E.; Müller, M.; Weinberger, P.; Wiesinger, G.; Schenk, H.; Linert, W.; Haasnoot, J.G.; Reedijk, J. Magnetic, 57Fe Mössbauer, and IR Monitoring of the Thermal Spin Transition in a New Family of Iron(II) Spin-Transition Complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 2003, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Knoll, C.; Seifried, M.; Welch, J.M.; Giester, G.; Reissner, M.; Weinberger, P. Halogenated Alkyltetrazoles for the Rational Design of FeII Spin-Crossover Materials: Fine-Tuning of the Ligand Size. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 5271–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.V.; Davis, I.; DeGayner, J.A.; Arman, H.D.; Tonzetich, Z.J. Iron Pincer Complexes Incorporating Bipyridine: A Strategy for Stabilization of Reactive Species. Organometallics 2017, 36, 4928–4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, L. Synthesis; Crystal Structure and Magnetism of Two Cobalt(II). Complexes with Imino and Nitronyl Nitroxides. Transit. Met. Chem. 2015, 40, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Harriman, K.L.M.; Brunet, G.; Pialat, A.; Gabidullin, B.; Murugesu, M. Reversible Redox, Spin Crossover, and Superexchange Coupling in 3d Transition-Metal Complexes of Bis-Azinyl Analogues of 2,2′:6′,2′′-Terpyridine. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 2018, 1212–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloshin, Y.Z.; Varzatskii, O.A.; Novikov, V.V.; Strizhakova, N.G.; Vorontsov, I.I.; Vologzhanina, A.V.; Lyssenko, K.A.; Romanenko, G.V.; Fedin, M.V.; Ovcharenko, V.I.; et al. Tris-Dioximate Cobalt(I,II,III) Clathrochelates: Stabilization of Different Oxidation and Spin States of an Encapsulated Metal Ion by Ribbed Functionalization. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 2010, 5401–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolganov, A.V.; Belov, A.S.; Novikov, V.V.; Vologzhanina, A.V.; Romanenko, G.V.; Budnikova, Y.G.; Zelinskii, G.E.; Buzin, M.I.; Voloshin, Y.Z. First Iron and Cobalt(II) Hexabromoclathrochelates: Structural, Magnetic, Redox, and Electrocatalytic Behavior. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 2476–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, V.V.; Ananyev, I.V.; Pavlov, A.A.; Fedin, M.V.; Lyssenko, K.A.; Voloshin, Y.Z. Spin-Crossover Anticooperativity Induced by Weak Intermolecular Interactions. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushuev, M.B.; Krivopalov, V.P.; Peresypkina, E.V.; Virovets, A.V.; Shvedenkov, Y.G.; Sheludyakova, L.A.; Semikolenova, N.V.; Zakharov, V.A.; Larionov, S.V. Complexes of Copper(II) and Cobalt(II) Halides with 4-(3,5-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-6-methyl-2-phenylpyrimidine: Synthesis, Structures, and Properties. Russ. J. Coord. Chem. 2009, 35, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.M.; Peters, J.C. Spin-State Tuning at Pseudotetrahedral d7 Ions: Examining the Structural and Magnetic Phenomena of Four-Coordinate [BP3]CoII-X Systems. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 7148–7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.-H.; Qiu, D.; Pang, C.-Y.; Li, Z.; Gu, Z.-G. Chiral Tetrahedral Iron(II) Cages: Diastereoselective Subcomponent Self-assembly, Structure Interconversion and Spin-Crossover Properties. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatur, S.M.; Shepard, S.G.; Higgins, R.F.; Shores, M.P.; Damrauer, N.H. A Synthetically Tunable System To Control MLCT Excited-State Lifetimes and Spin States in Iron(II) Polypyridines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 4493–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enamullah, M.; Linert, W. Substituent- and Solvent-Effects on the Stability of Iron(II)-4-X-2,6-bis-(benzimidazol-2′-yl)pyrdine Complexes Showing Spin-Crossover in Soltution. J. Coord. Chem. 1996, 40, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, K.; Huttner, G.; Zsolnai, L.; Schober, P. Complexes of Cobalt(II) Chloride with the Tripodal Trisphosphane triphos: Solution Dynamics, Spin-Crossover, Reactivity, and Redox Activity. Inorg. Chem. 1997, 36, 5457–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.; Eaves, B.; Parker, D.; Claxton, R.; Ray, P.S.; Slattery, S.J. Inductive Influence of 4′-Terpyridyl Substituents on Redox and Spin State Properties of Iron(II) and Cobalt(II) Bis-terpyridyl Complexes. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2006, 359, 2400–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorarinsdottir, A.E.; Gaudette, A.I.; Harris, T.D. Spin-Crossover and High-Spin Iron(II) Complexes as Chemical Shift 19F Magnetic Resonance Thermometers. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 2448–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vela, S.; Paulsen, H. Cooperativity in Spin Crossover Systems. An Atomistic Perspective on the Devil’s Staircase. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 9478–9488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vela, S.; Paulsen, H. Deciphering Crystal Packing Effects in the Spin Crossover of Six [FeII(2-pic)3]Cl2 Solvatomorphs. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neese, F. The ORCA Program System. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2012, 2, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiher, M.; Salomon, O.; Hess, B.A. Reparameterization of Hybrid Functionals Based on Energy Differences of States of Different Multiplicity. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2001, 107, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, O.; Reiher, M.; Hess, B.A. Assertion and Validation of the Performance of the B3LYP⋆ Functional for the First Transition Metal Row and the G2 Test Set. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 4729–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.; Horn, H.; Ahlrichs, R. Fully Optimized Contracted Gaussian Basis Sets for Atoms Li to Kr. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 97, 2571–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigend, F. Accurate Coulomb-Fitting Basis Sets for H to Rn. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kossmann, S.; Neese, F. Comparison of Two Efficient Approximate Hartee–Fock approaches. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2009, 481, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D.; Johnson, E.R. A Density-Functional Model of the Dispersion Interaction. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 123, 154101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A Consistent and Accurate Ab Initio Parametrization of Density Functional Dispersion Correction (DFT-D) for the 94 Elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimme, S.; Ehrlich, S.; Goerigk, L. Effect of the Damping Function in Dispersion Corrected Density Functional Theory. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossi, M.; Rega, N.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V. Energies, Structures, and Electronic Properties of Molecules in Solution with the C-PCM Solvation Model. J. Comput. Chem. 2003, 24, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.N.; Aschi, M.; Schwarz, H.; Koch, W. The Singlet and Triplet States of Phenyl Cation. A Hybrid Approach for Locating Minimum Energy Crossing Points Between Non-Interacting Potential Energy Surfaces. Theor. Chem. Acc. 1999, 99, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemcraft Program. Available online: http://www.chemcraftprog.com/index.html (accessed on 31 August 2019).
- Macrae, C.F.; Bruno, I.J.; Chisholm, J.A.; Edgington, P.R.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Rodriguez-Monge, L.; Taylor, R.; van de Streek, J.; Wood, P.A. Mercury CSD 20-New Features for the Visualization and Investigation of Crystal Structures. J. Appl. Cryst. 2008, 41, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

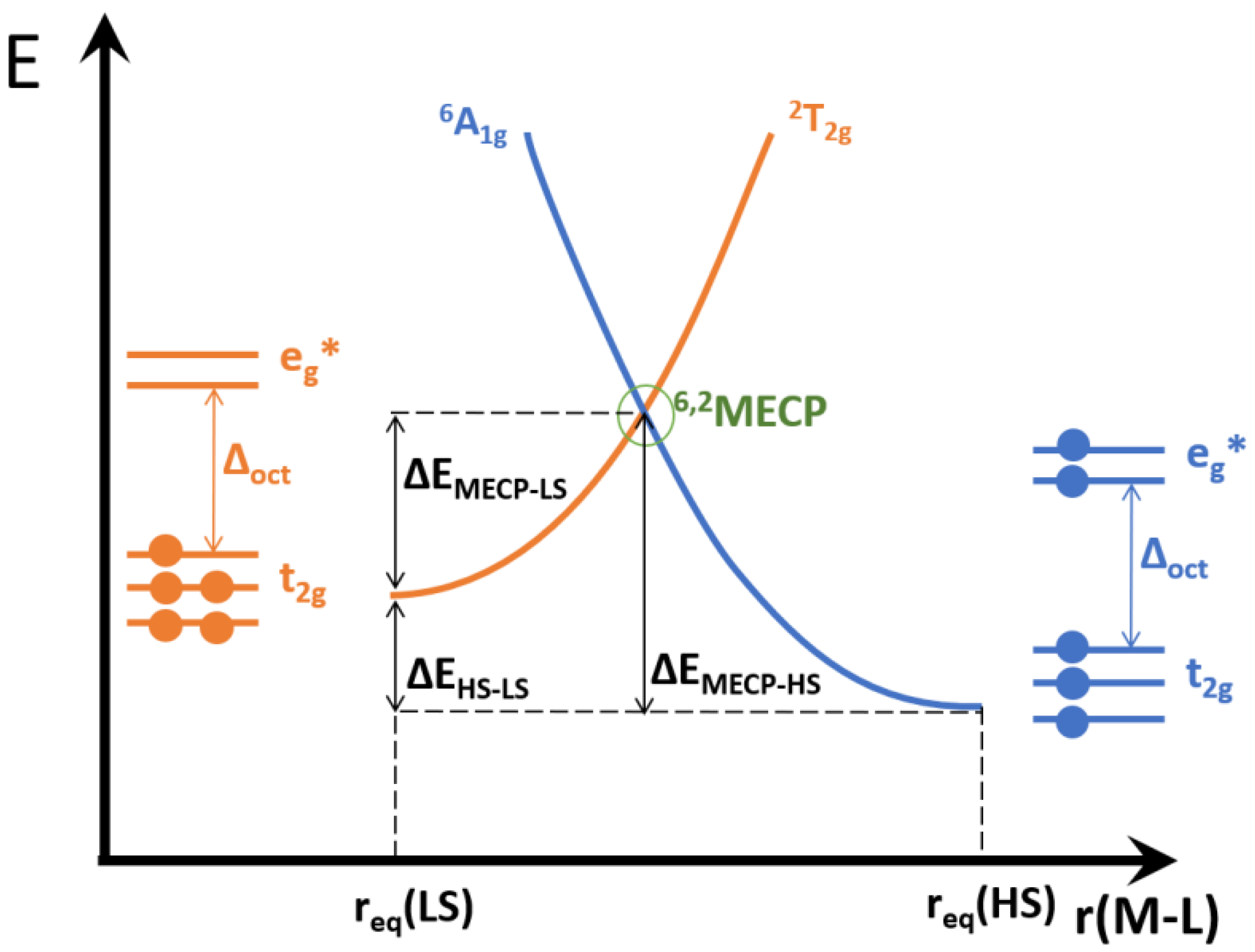










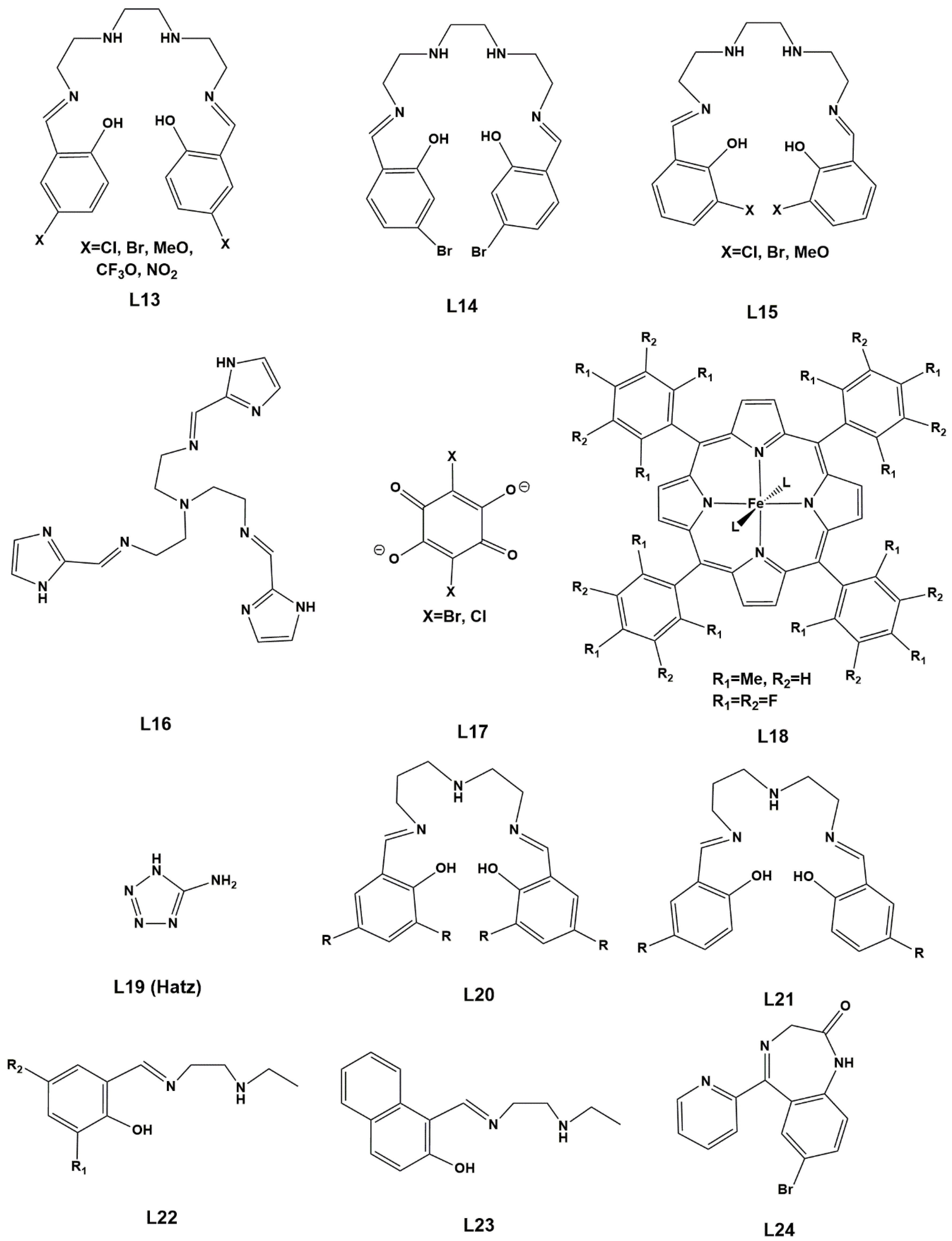






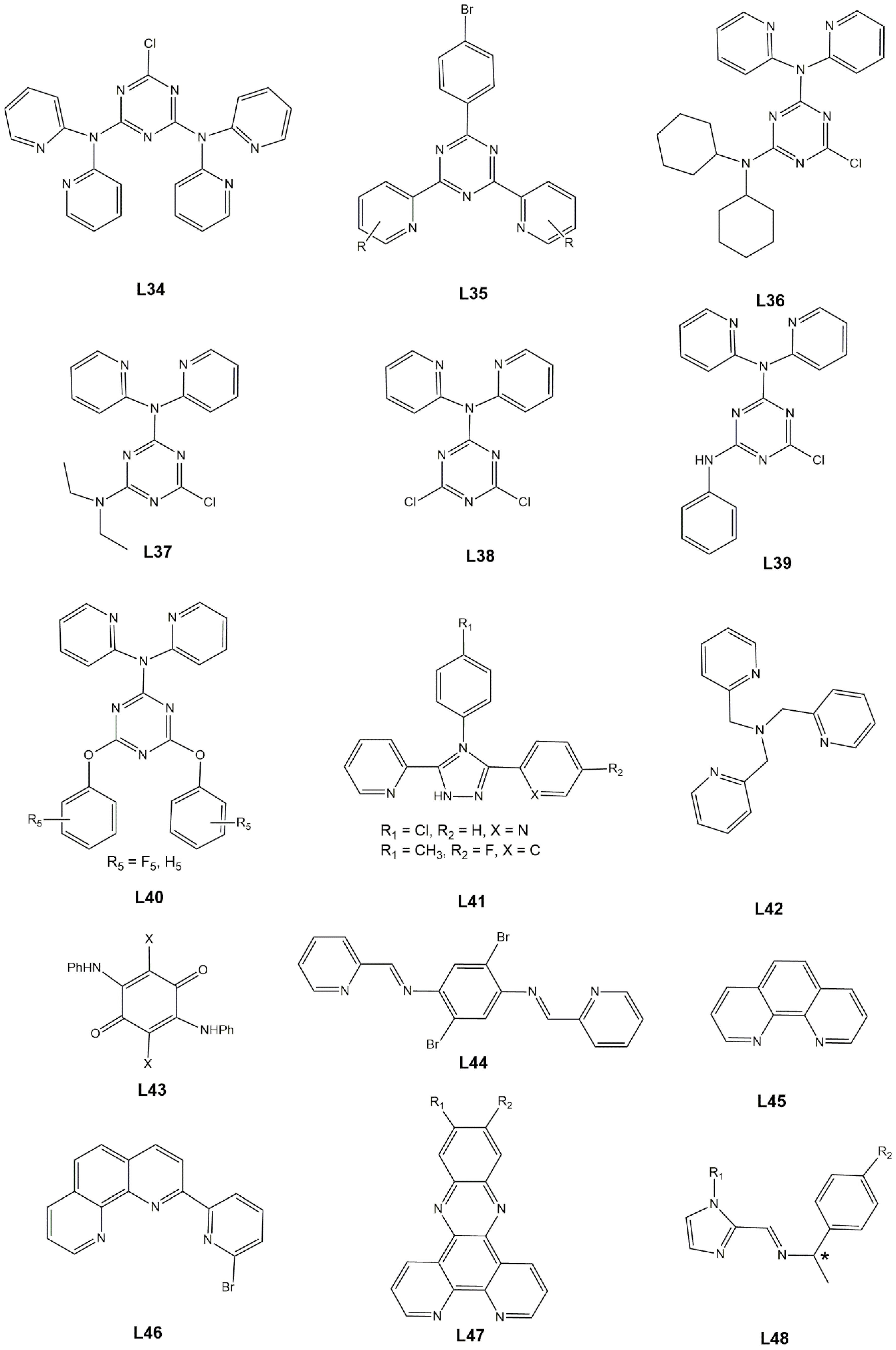





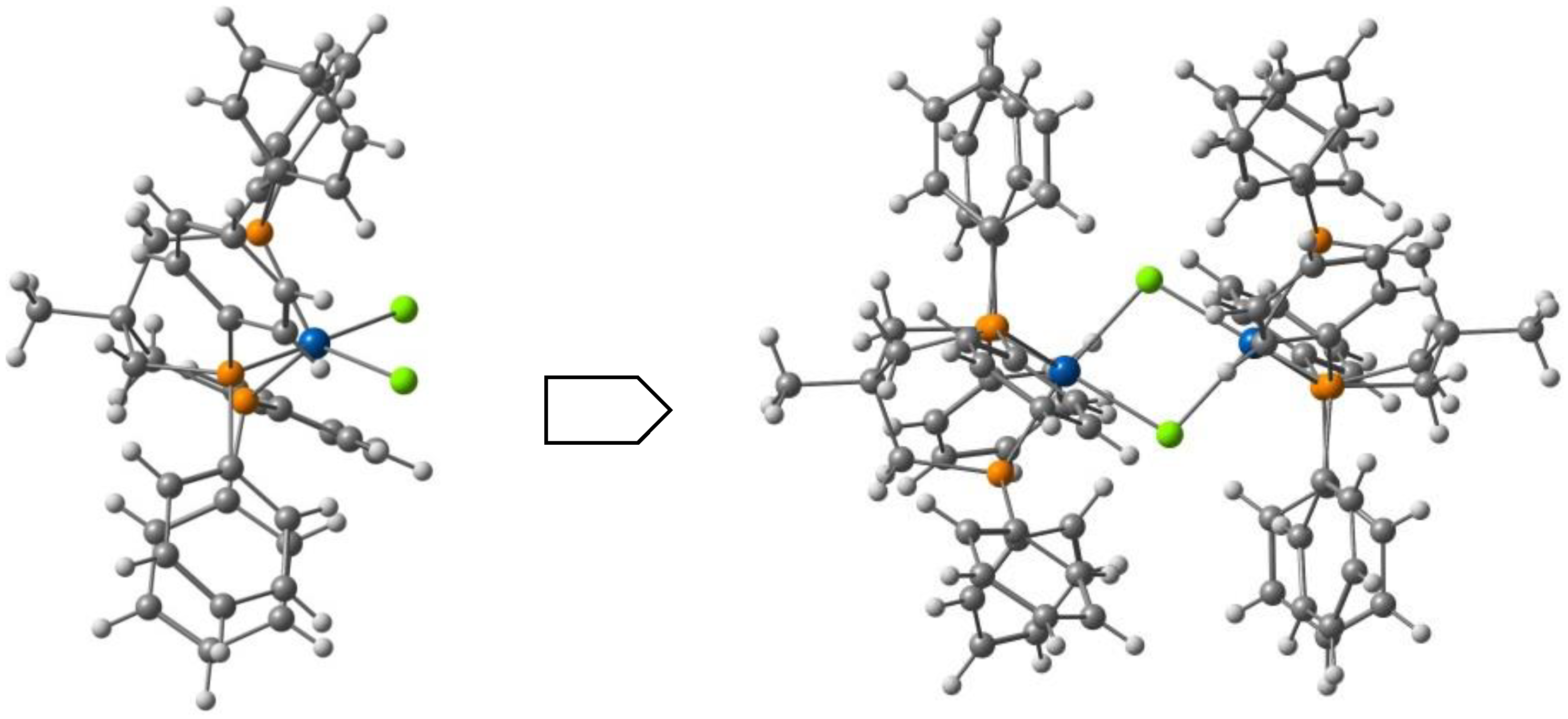
| Anion (Solv) | ΔEHS-LS (X-Ray) | ΔEHS-LS (Opt) | ΔEMECP-LS (X-Ray) | ΔEMECP-HS (Opt) | Δoct | ~T1/2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ClO4− (C2H5OH), 2e | 125.0 | 14.2 | 22.8 | 8.6 | 7016 | 120 |
| BF4− (C2H5OH), 2c | 155.4 | 0.2 | 2.4 | 2.2 | 7601 | 160 |
| CF3SO3− (C2H5OH), 2d | 140.9 | 26.1 | 32.3 | 6.3 | 10,089 | 200 |
| ClO4− (CH3CN), 2f | 148.5 | 39.2 | 7.2 | −31.9 | 11,735 | LS |
| Halogen | ΔEHS-LS (Opt) | ΔEMECP-LS | ΔEMECP-HS | Δoct | ~T1/2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | 5.6 | 15.3 | 9.7 | 6692 | 290 |
| Cl | 5.9 | 12.7 | 6.7 | 7586 | 320 |
| Br | 4.4 | 7.8 | 3.4 | 8329 | 340 |
| I | 3.7 | 11.9 | 8.2 | 9984 | LS |
| Halogen Cation+Anion | Entry | ΔEHS-LS (Opt) | ΔEMECP-LS | ΔEMECP-HS | Δoct | ~T1/2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl | 1 | −5.5 | 12.7 | 18.2 | 4281 | - |
| Br | 2 | −6.4 | 11.3 | 17.6 | 4349 | - |
| Cl + Cl (ani) | 3 | 9.1 | −4.4 | −13.5 | 6952 | 260 |
| Cl + Br (ani) | 4 | −20.8 | 41.5 | 62.3 | 5088 | 200 |
| Br + Cl (ani) | 5 | 9.6 | 13.8 | 4.2 | 6959 | 400 |
| Br + Br (ani) | 6 | −19.2 | 77.1 | 96.3 | 4902 | 320 |
| (Pseudo)halide X | ΔEHS-LS (Opt) | ΔEMECP-LS | ΔEMECP-HS | Δoct | T1/2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LBr | |||||
| N3− | 3.4 | 10.1 | 6.7 | 6296 | 143 |
| Cl− | 0.4 | 7.9 | 7.5 | 6631 | HS |
| NCS− | 3.8 | 10.5 | 6.6 | 10,608 | HS |
| NCSe− | 4.5 | 11.2 | 6.6 | 11,048 | 320 |
| LCl | |||||
| Cl− | 0.9 | 8.2 | 7.3 | 6892 | HS |
| NCS− | 3.4 | 10.6 | 7.2 | 7813 | 280 |
| NCSe− | 4.2 | 11.2 | 6.9 | 7967 | 293 |

| Halogen | ΔEHS-LS (X-Ray) | ΔEHS-LS (Opt) | ΔEMECP-LS | ΔEMECP-HS | Δoct | ~T1/2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl | 44.87 | 2.3 | 10.3 | 8.1 | 9988 | 310 |
| Br | 134.98 | 26.4 | 10.4 | −16.0 | 4556 | 342 |
| I | 85.94 | 7.8 | 11.4 | 3.6 | 7355 | 295 |
| Halogen | ΔEHS-LS (X-ray) | ΔEHS-LS (Opt) | Δoct | ~T1/2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H [131] | - | 4.2 | 2458 | 270 |
| Br | 170.5 | 0.7 | 3095 | 307 |
| I | 220.42 | 0.6 | 4016 | 332 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martinho, P.N.; Martins, F.F.; Bandeira, N.A.G.; Calhorda, M.J. Spin Crossover in 3D Metal Centers Binding Halide-Containing Ligands: Magnetism, Structure and Computational Studies. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2512. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12062512
Martinho PN, Martins FF, Bandeira NAG, Calhorda MJ. Spin Crossover in 3D Metal Centers Binding Halide-Containing Ligands: Magnetism, Structure and Computational Studies. Sustainability. 2020; 12(6):2512. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12062512
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartinho, Paulo N., Frederico F. Martins, Nuno A. G. Bandeira, and Maria José Calhorda. 2020. "Spin Crossover in 3D Metal Centers Binding Halide-Containing Ligands: Magnetism, Structure and Computational Studies" Sustainability 12, no. 6: 2512. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12062512
APA StyleMartinho, P. N., Martins, F. F., Bandeira, N. A. G., & Calhorda, M. J. (2020). Spin Crossover in 3D Metal Centers Binding Halide-Containing Ligands: Magnetism, Structure and Computational Studies. Sustainability, 12(6), 2512. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12062512







