Utilization of Fly Ashes from Fluidized Bed Combustion: A Review
Abstract
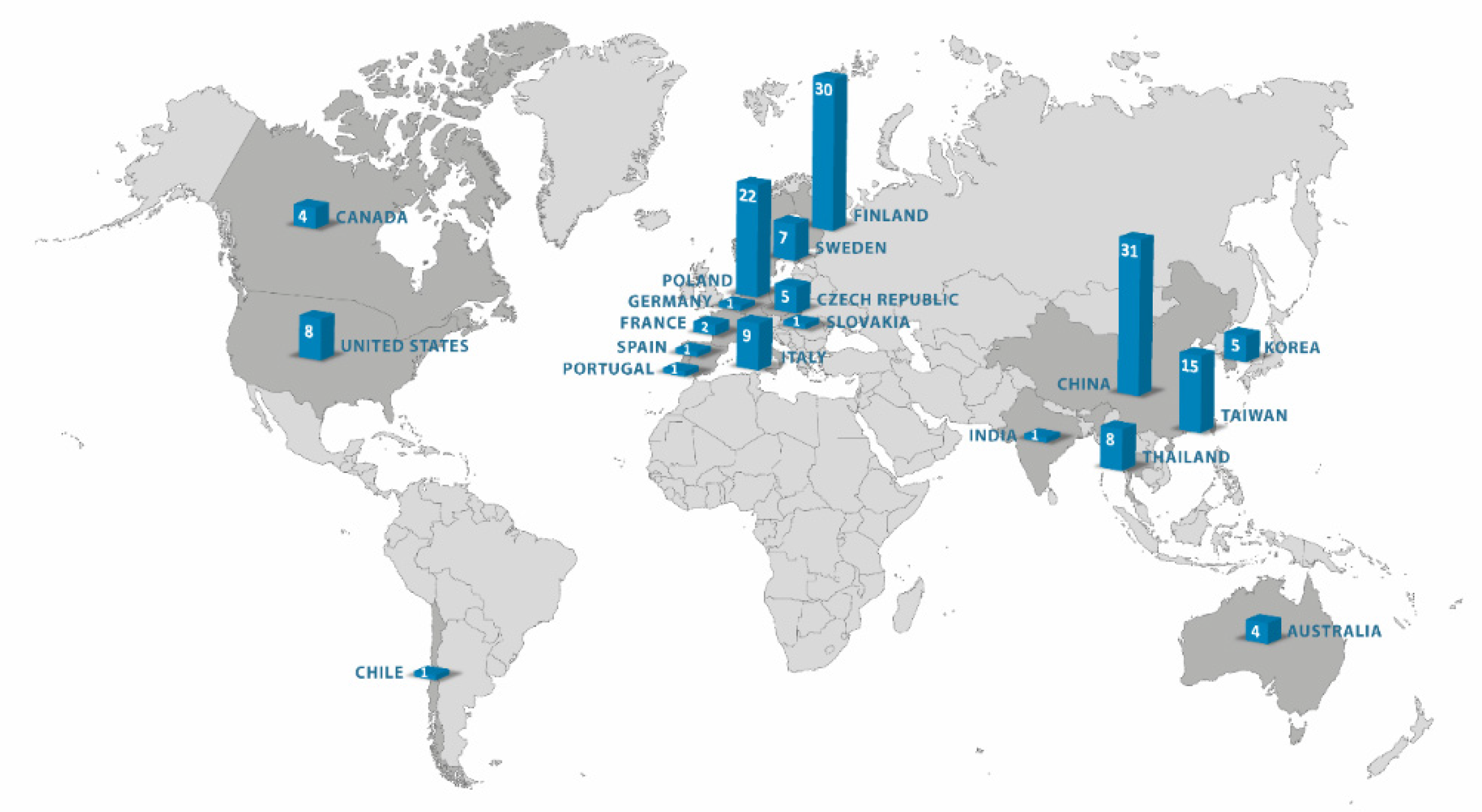
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. FBCFA Properties
3.1. Chemical and Mineralogical Properties
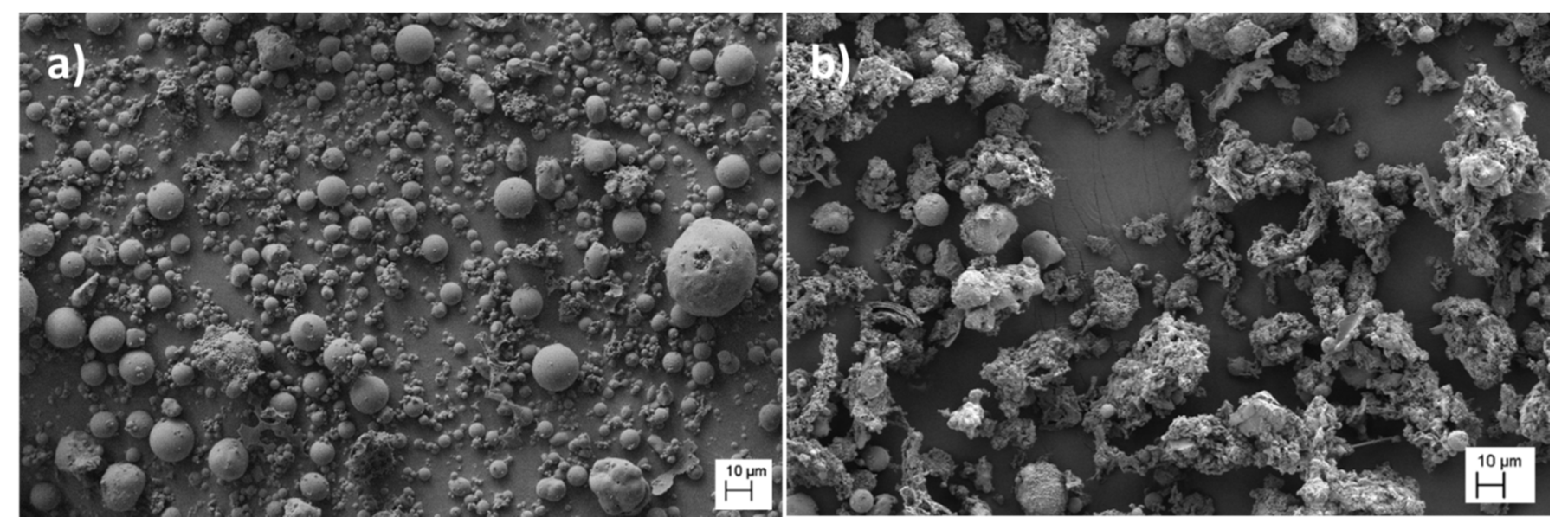
3.2. Morphological Properties
3.3. Particle Size of FBC Fly Ashes
4. FBCFA as a Soil Amendment
4.1. Fertilizers and Soil Improvers
4.2. Field Tests
5. FBCFA as a Construction Material
5.1. Partial Replacement of Cement in Concrete
5.2. Non-Cement Binder
5.2.1. Mixtures of Industrial Waste Materials
5.2.2. Self-Hardening of FBCFA
5.3. Aerated Concrete
5.4. Alkali-Activated FBCFA
5.5. Lightweight Aggregate Production
5.6. Cast-Concrete Products
6. FBCFA in Earth Construction
6.1. Mine Backfilling
6.2. Soil Stabilization
6.3. Road Construction
7. Other Applications of FBCFA
7.1. Recovery of Combustibles
7.2. SO2 Capture
7.3. CO2 Sequestration
7.4. Adsorbents and Catalysts
7.5. Filler Material in Polymer Composites
7.6. Acidic Wastewater Treatment
7.7. Waste Stabilization
8. Conclusions and Outlook
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deschamps, R.J. Using FBC and Stoker Ashes as Roadway Fill: A Case Study. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 1998, 124, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skousen, J.; Ziemkiewicz, P.; Yang, J.E. Use of coal combustion by-products in mine reclamation: Review of case studies in the USA. Geosyst. Eng. 2012, 15, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, M.; Rajabipour, F. Fluidized Bed Combustion (FBC) fly ash and its performance in concrete. ACI Mater. J. 2019, 116, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Kumar, S. Recovery of combustibles from electrostatic precipitator discharge. Waste Manag. Res. 2016, 34, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, K.M.; Sojobi, A.O.; Zhang, L.W. Green concrete: Prospects and challenges. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 1063–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, A.; Grutzeck, M.W.; Blanco, M.T. Alkali-activated fly ashes: A cement for the future. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Palomo, A. Characterisation of fly ashes. Potential reactivity as alkaline cements. Fuel 2003, 82, 2259–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, A.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Kovalchuk, G.; Ordoñez, L.M.; Naranjo, M.C. Opc-fly ash cementitious systems: Study of gel binders produced during alkaline hydration. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 2958–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fly Ash for Concrete—Part 1: Definition, Specifications and Conformity Criteria; British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2005.
- Lopes, M.H.; Freire, M.; Galhetas, M.; Gulyurtlu, I.; Cabrita, I. Leachability of automotive shredder residues burned in a fluidized bed system. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balampanis, D.E.; Pollard, S.J.T.; Simms, N.; Longhurst, P.; Coulon, F.; Villa, R. Residues characterisation from the fluidised bed combustion of East London’s solid recovered fuel. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 1318–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, C.-S.; Saylak, D.; Zollinger, D.G. Potential use of stockpiled circulating fluidized bed combustion ashes in manufacturing compressed earth bricks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2062–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, C.-S.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Saylak, D.; Zollinger, D.G.; Mejeoumov, G.G. Potential use of stockpiled circulating fluidized bed combustion ashes in controlled low strength material (CLSM) mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, T.R.; Kraus, R.N.; Sturzl, R.F.; Ramme, B.W. Design and testing Controlled Low-Strength Materials (CLSM) using clean coal ash. ASTM Spec. Tech. Publ. 1998, 1331, 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- Winschel, R.A.; Wu, M.M.; Burke, F.P. Synthetic aggregates from coal-fired fluidized-bed combustion residues. Coal Sci. Technol. 1995, 24, 1987–1990. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, A.; Basu, P.; Acharya, B. An investigation into partial capture of CO2 released from a large coal/petcoke fired circulating fluidized bed boiler with limestone injection using its fly and bottom ash. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomykala, R. Properties of solidified fly ash suspension heated at high temperature. In Proceedings of the Thirtieth annual International Pittsburgh Coal Conference, Beijing, China, 15–18 September 2013; Curran: Norwich, UK, 2013; Volume 3, pp. 2449–2464. [Google Scholar]
- González, A.; Moreno, N.; Navia, R.; Querol, X. Study of a Chilean petroleum coke fluidized bed combustion fly ash and its potential application in copper, lead and hexavalent chromium removal. Fuel 2010, 89, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Song, Y.; Li, B. An Attempt to Reduce Materials Cost of Autoclaved Aerated Concrete Production. Open Civ. Eng. J. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illikainen, M.; Tanskanen, P.; Kinnunen, P.; Körkkö, M.; Peltosaari, O.; Wigren, V.; Österbacka, J.; Talling, B.; Niinimäki, J. Reactivity and self-hardening of fly ash from the fluidized bed combustion of wood and peat. Fuel 2014, 135, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Qian, J.; Zhang, Z. Investigations of anhydrite in CFBC fly ash as cement retarders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, N.T.; Chang, T.-P.; Chen, C.-T.; Yang, T.-R. Cementitious properties and microstructure of an innovative slag eco-binder. Mater. Struct. 2016, 49, 2009–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.-A.; Chang, T.-P.; Shih, J.-Y.; Chen, C.-T.; Nguyen, T.-D. Sulfate resistance of low energy SFC no-cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 102, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-T.; Nguyen, H.-A.; Chang, T.-P.; Yang, T.-R.; Nguyen, T.-D. Performance and microstructural examination on composition of hardened paste with no-cement SFC binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 76, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.-A.; Chang, T.-P.; Chen, C.-T.; Yang, T.-R.; Nguyen, T.-D. Physical-chemical characteristics of an eco-friendly binder using ternary mixture of industrial wastes. Mater. Constr. 2015, 65, 064. [Google Scholar]
- Dung, N.T.; Chang, T.-P.; Chen, C.-T. Engineering and sulfate resistance properties of slag-CFBC fly ash paste and mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 63, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, N.T.; Chang, T.-P.; Yang, T.-R. Performance Evaluation of an Eco-Binder Made with Slag and CFBC Fly Ash. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2014, 26, 04014096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, N.T.; Chang, T.-P.; Chen, C.-T. Circulating fluidized bed combustion fly ash-activated slag concrete as novel construction material. ACI Mater. J. 2015, 112, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.-A.; Chang, T.-P.; Shih, J.-Y.; Chen, C.-T.; Nguyen, T.-D. Engineering properties and durability of high-strength self-compacting concrete with no-cement SFC binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 106, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohenoja, K.; Tanskanen, P.; Wigren, V.; Kinnunen, P.; Körkkö, M.; Peltosaari, O.; Österbacka, J.; Illikainen, M. Self-hardening of fly ashes from a bubbling fluidized bed combustion of peat, forest industry residuals, and wastes. Fuel 2016, 165, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.-P.; Vo, D.-H.; Hwang, C.-L. Engineering and durability properties of eco-friendly mortar using cement-free SRF binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozwiak-Niedzwiedzka, D. Estimation of chloride migration coefficient in air-entrained concretes containing fluidized bed combustion fly ash. Arch. Civ. Eng. 2012, 58, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, E.; Medri, V.; Landi, E.; Ballarin, B.; Miccio, F. Production and characterization of geopolymers based on mixed compositions of metakaolin and coal ashes. Mater. Des. 1980-2015 2014, 56, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Guo, C.; Qian, J.; Ding, T. Effect of the Ca-to-Si ratio on the properties of autoclaved aerated concrete containing coal fly ash from circulating fluidized bed combustion boiler. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 83, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomykała, R.; Kępys, W.; Łyko, P. The Influence of High Temperature on the Properties of Solidified Suspension Made of Ash from Fluidized Combustion of Lignite. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 1407–1411. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J.G.; Park, S.-M.; Chung, S.; Ahn, J.-W.; Kim, H.-K. Utilization of circulating fluidized bed combustion ash in producing controlled low-strength materials with cement or sodium carbonate as activator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 159, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yliniemi, J.; Nugteren, H.; Illikainen, M.; Tiainen, M.; Weststrate, R.; Niinimäki, J. Lightweight aggregates produced by granulation of peat-wood fly ash with alkali activator. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2016, 149, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Chi, M.; Huang, R. Characteristics of CFBC fly ash and properties of cement-based composites with CFBC fly ash and coal-fired fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamma, R.; Ball, R.J.; Tarelho, L.A.C.; Allen, G.C.; Labrincha, J.A.; Ferreira, V.M. Characterisation and use of biomass fly ash in cement-based materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Song, Y. Adsorption properties of CFBC ash–cement pastes as compared with PCC fly ash–cement pastes. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2016, 3, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhai, J.; Fu, X.; Sheng, G. Characterization of Fly Ashes from Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion (CFBC) Boilers Cofiring Coal and Petroleum Coke. Energy Fuels 2006, 20, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šiler, P.; Bayer, P.; Sehnal, T.; Kolářová, I.; Opravil, T.; Šoukal, F. Effects of high-temperature fly ash and fluidized bed combustion ash on the hydration of Portland cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 78, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karltun, E.; Saarsalmi, A.; Ingerslev, M.; Mandre, M.; Andersson, S.; Gaitnieks, T.; Ozolinčius, R.; Varnagiryte-Kabasinskiene, I. Wood Ash Recycling—Possibilities And Risks. In Sustainable Use of Forest Biomass for Energy; Managing Forest Ecosystems; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 79–108. ISBN 978-1-4020-5053-4. [Google Scholar]
- FINLEX ®-Viranomaisten määräyskokoelmat: Maa-ja metsätalousministeriö-01.09.2011 1784/14/2011. n.d. Available online: http://www.finlex.fi/fi/viranomaiset/normi/400001/37638 (accessed on 17 February 2020).
- Bekendtgørelse om anvendelse af bioaske til jordbrugsformål (Bioaskebekendtgørelsen)-retsinformation.dk. n.d. Available online: https://www.retsinformation.dk/forms/r0710.aspx?id=116609 (accessed on 17 February 2020).
- Luan, J.; Li, A.; Su, T.; Li, X. Translocation and toxicity assessment of heavy metals from circulated fluidized-bed combustion of oil shale in Huadian, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- REGULATION (EU) 2019/1009 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32019R1009 (accessed on 17 February 2020).
- Budhathoki, R.; Vaïsänen, A. Particle size based recovery of phosphorus from combined peat and wood fly ash for forest fertilization. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 146, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, O.; Nurmesniemi, H.; Pöykiö, R.; Watkins, G. Heavy metal concentrations in bottom ash and fly ash fractions from a large-sized (246MW) fluidized bed boiler with respect to their Finnish forest fertilizer limit values. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 1634–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, O.; Nurmesniemi, H.; Pöykiö, R.; Watkins, G. Comparison of the characteristics of bottom ash and fly ash from a medium-size (32 MW) municipal district heating plant incinerating forest residues and peat in a fluidized-bed boiler. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orava, H.; Nordman, T.; Kuopanportti, H. Increase the utilisation of fly ash with electrostatic precipitation. Miner. Eng. 2006, 19, 1596–1602. [Google Scholar]
- Kuokkanen, T.; Pesonen, J.; Kaakinen, J.; Välimäki, I.; Illikainen, M. Comparison of standard methods for evaluating the metal concentrations in bio ash. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2017, 20, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuokkanen, T.; Pöykiö, R.; Nurmesniemi, H.; Rämö, J. Sequential leaching of heavy metals and sulfur in bottom ash and fly ash from the co-combustion of wood and peat at a municipal district heating plant. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2006, 18, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, M.; Harju-Oksanen, M.-L.; Watkins, G.; Ekroos, A.; Dahl, O. Feasibility assessment of inter-industry solid residue utilization for soil amendment—Trace element availability and legislative issues. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 67, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, M.; Watkins, G.; Dahl, O.; Nurmesniemi, H.; Pöykiö, R. Integration of solid residues from the steel and pulp and paper industries for forest soil amendment. J. Residuals Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Nurmesniemi, H.; Mäkelä, M.; Pöykiö, R.; Manskinen, K.; Dahl, O. Comparison of the forest fertilizer properties of ash fractions from two power plants of pulp and paper mills incinerating biomass-based fuels. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 104, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmesniemi, H.; Manskinen, K.; Pöykiö, R.; Dahl, O. Forest fertilizer properties of the bottom ash and fly ash from a large-sized (115 MW) industrial power plant incinerating wood-based biomass residues. J. Univ. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2012, 47, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Ohenoja, K.; Körkkö, M.; Wigren, V.; Österbacka, J.; Illikainen, M. Fly ash classification efficiency of electrostatic precipitators in fluidized bed combustion of peat, wood, and forest residues. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesonen, J.; Kuokkanen, T.; Rautio, P.; Lassi, U. Bioavailability of nutrients and harmful elements in ash fertilizers: Effect of granulation. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 100, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesonen, J.; Kuokkanen, V.; Kuokkanen, T.; Illikainen, M. Co-granulation of bio-ash with sewage sludge and lime for fertilizer use. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4817–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöykiö, R.; Nurmesniemi, H.; Keiski, R.L. Total and size fractionated concentrations of metals in combustion ash from forest residues and peat. Met. Summaarne Ja Fraktsioneeritud Sisaldus Puidujäätmete Ning Turba Põletustuhas 2009, 58, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöykiö, R.; Nurmesniemi, H.; Perämäki, P.; Kuokkanen, T.; Välimäki, I. Leachability of metals in fly ash from a pulp and paper mill complex and environmental risk characterization for eco-efficient utilization of the fly ash as a fertilizer. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2005, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Salgueiro, L.; Omil, B.; Merino, A.; Martínez-Carballo, E.; Simal-Gándara, J. Organic pollutants profiling of wood ashes from biomass power plants linked to the ash characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, N.C.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Carvalho, L.; Duarte, A.C.; Pereira, E.; Römkens, P.F.A.M.; Tarelho, L.A.C. Ashes from fluidized bed combustion of residual forest biomass: Recycling to soil as a viable management option. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 14770–14781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.P.; Vicente, E.D.; Gomes, A.P.; Nunes, M.I.; Alves, C.; Tarelho, L.A.C. Effect of industrial and domestic ash from biomass combustion, and spent coffee grounds, on soil fertility and plant growth: Experiments at field conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 15270–15277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, B.; Bolan, N.S.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Choppala, G.; Naidu, R. Effect of coal combustion products in reducing soluble phosphorus in soil II: Leaching study. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, B.; Bolan, N.S.; Kunhikrishnan, A. Effect of Clean Coal Combustion Products in Reducing Soluble Phosphorus in Soil I. Adsorption Study. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masto, R.E.; Sunar, K.K.; Sengupta, T.; Ram, L.C.; Rout, T.K.; Selvi, V.A.; George, J.; Sinha, A.K. Evaluation of the co-application of fly ash and sewage sludge on soil biological and biochemical quality. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Y.; Dou, Z.; Toth, J.D.; Ferguson, J. Use of flyash as environmental and agronomic amendments. Environ. Geochem. Health 2004, 26, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, I.; Hughes, R.E.; DeMaris, P.J. Formation and use of coal combustion residues from three types of power plants burning Illinois coals. Fuel 2001, 80, 1659–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottosen, L.M.; Jensen, P.E.; Kirkelund, G.M. Phosphorous recovery from sewage sludge ash suspended in water in a two-compartment electrodialytic cell. Waste Manag. 2016, 51, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Shen, L.; Sheng, C. Characterization of Biomass Ashes from Power Plants Firing Agricultural Residues. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamvuka, D.; Kaniadakis, G.; Pentari, D.; Alevizos, G.; Papapolikarpou, Z. Comparison of ashes from fixed/fluidized bed combustion of swine sludge and olive by-products. Properties, environmental impact and potential uses. Renew. Energy 2017, 112, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, A.; Åmand, L.-E.; Steenari, B.-M. Leaching of ashes from co-combustion of sewage sludge and wood-Part I: Recovery of phosphorus. Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, A.; Åmand, L.-E.; Steenari, B.-M. Leaching of ashes from co-combustion of sewage sludge and wood-Part II: The mobility of metals during phosphorus extraction. Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohenoja, K.; Körkkö, M.; Wigren, V.; Österbacka, J.; Illikainen, M. Increasing the utilization potential of fly ashes from fluidized bed combustion by mechanical treatments. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.B.; Zeto, S.K.; Ritchey, K.D.; Baligar, V.C. Mineral acquisition by maize grown in acidic soil amended with coal combustion products. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2001, 32, 1861–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codling, E.E.; Wright, R.J. Plant uptake of selenium arsenic and molybdenum from soil treated with coal combustion byproducts. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 1998, 7, 118–125. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, J.P.; Tarelho, L.; Gomes, A.P. Incorporation of biomass fly ash and biological sludge in the soil: Effects along the soil profile and in the leachate water. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 2023–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, P.; Rodrigues, D.; Mourinha, C.; Palma, P.; De Varennes, A.; Cruz, N.; Tarelho, L.A.C.; Rodrigues, S. Use of wastes from the pulp and paper industry for the remediation of soils degraded by mining activities: Chemical, biochemical and ecotoxicological effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huotari, N.; Tillman-Sutela, E.; Moilanen, M.; Laiho, R. Recycling of ash - For the good of the environment? For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 348, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.H.; Bland, A.E.; Wheeldon, J.M. Pressurized fluidized bed combustion ash 2. Soil and mine spoil amendment use options. Fuel 1997, 76, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, G.W.; Siddaramappa, R.; Wright, R.J.; Codling, E.E.; Gao, G. Evaluation of coal combustion byproducts as soil liming materials: Their influence on soil pH and enzyme activities. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1994, 17, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Riehl, A.; Elsass, F.; Duplay, J.; Huber, F.; Trautmann, M. Changes in soil properties in a fluvisol (calcaric) amended with coal fly ash. Geoderma 2010, 155, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodak, B.W.; Freitas, D.S.; De Oliveira Lima, G.J.E.; Dos Reis, A.R.; Schulze, J.; Guilherme, L.R.G. Beneficial use of Ni-rich petroleum coke ashes: Product characterization and effects on soil properties and plant growth. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, W.L.; Sharpley, A.N.; Pionke, H.B. Reducing soil phosphorus solubility with coal combustion by-products. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, W.L.; Sharpley, A.N.; Landa, J. Effectiveness of coal combustion by-products in controlling phosphorus export from soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, W.L.; Sharpley, A.N.; Gburek, W.J.; Pionke, H.B. Reducing phosphorus export from croplands with FBC fly ash and FGD gypsum. Fuel 1999, 78, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.; Zhang, G.Y.; Stout, W.L.; Toth, J.D.; Ferguson, J.D. Efficacy of alum and coal combustion by-products in stabilizing manure phosphorus. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atalay, A.; Bronick, C.; Mebrahtu, T.; Whitehead, B. Phosphorus immobilization and soil aggregation in chemically amended poultry litter used in corn/soybean rotation. J. Sustain. Agric. 2011, 35, 260–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-M.; Lin, L.-K.; Chang, T.-C. A preliminary assessment on reusage of flyash emitted from fluidized bed incineration of sludge cake. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 1997, 20, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M. Synthesis and characterization of mortars with circulating fluidized bed combustion fly ash and ground granulated blast-furnace slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behr-Andres, C.B.; Hutzler, N.J. Characterization and use of fluidized-bed-combustion coal ash. J. Environ. Eng. U. S. 1994, 120, 1488–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlica, J.; Brandstetr, J.; Odler, I. Possibilities of Utilizing Solid Residues from Pressured Fluidized Bed Coal Combustion (PSBC) for the Production of Blended Cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 1998, 28, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sata, V.; Jaturapitakkul, C.; Kiattikomol, K. Influence of pozzolan from various by-product materials on mechanical properties of high-strength concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 1589–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebök, T.; Šimoník, J.; Kulísek, K. The compressive strength of samples containing fly ash with high content of calcium sulfate and calcium oxide. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gao, J.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Y. Investigation of expansion properties of cement paste with circulating fluidized bed fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 157, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissanen Jouni; Ohenoja Katja; Kinnunen Paivo; Illikainen Mirja Partial Replacement of Portland-Composite Cement by Fluidized Bed Combustion Fly Ash. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 04017061. [CrossRef]
- Sinsiri, T.; Chindaprasirt, P.; Jaturapitakkul, C. Influence of fly ash fineness and shape on the porosity and permeability of blended cement pastes. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2010, 17, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strigáč, J.; Števulová, N.; Mikušinec, J.; Sobolev, K. The fungistatic properties and potential application of by-product fly ash from fluidized bed combustion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 159, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, G.; Zhai, J.; Li, Q.; Li, F. Utilization of fly ash coming from a CFBC boiler co-firing coal and petroleum coke in Portland cement. Fuel 2007, 86, 2625–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosti, L.; Van Zomeren, A.; Pels, J.R.; Comans, R.N.J. Technical and Environmental Performance of Lower Carbon Footprint Cement Mortars Containing Biomass Fly Ash as a Secondary Cementitious Material. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 134, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohenoja, K.; Wigren, V.; Österbacka, J.; Illikainen, M. Applicability of Fly Ash from Fluidized Bed Combustion of Peat, Wood, or Wastes to Concrete. Waste Biomass Valorization 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocuń-Wczelik, W.; Łagosz, A.; Kowalski, B.; Gawlicki, M. Calorimetry in testing waste materials from the brown coal combustion. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 118, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stryczek, S.; Brylicki, W.; Małolepszy, J.; Gonet, A.; Wiśniowski, R.; Kotwica, Ł. Potential use of fly ash from fluidal combustion of brown coal in cementing slurries for drilling and geotechnical works. Arch. Min. Sci. 2009, 54, 775–786. [Google Scholar]
- Ohenoja, K.; Tanskanen, P.; Peltosaari, O.; Wigren, V.; Österbacka, J.; Illikainen, M. Effect of particle size distribution on the self-hardening property of biomass-peat fly ash from a bubbling fluidized bed combustion. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 148, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissanen, J.; Ohenoja, K.; Kinnunen, P.; Romagnoli, M.; Illikainen, M. Milling of peat-wood fly ash: Effect on water demand of mortar and rheology of cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 180, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Guo, C.; Qian, J.; Liu, Y.; Cao, A. Adsorption mechanism of polycarboxylate-based superplasticizer in CFBC ash-Portland cement paste. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2014, 29, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Song, Y. Methods for the control of volume stability of sulfur-rich CFBC ash cementitious systems. Mag. Concr. Res. 2013, 65, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.-A.; Chang, T.-P.; Shih, J.-Y.; Chen, C.-T.; Nguyen, T.-D. Influence of circulating fluidized bed combustion (CFBC) fly ash on properties of modified high volume low calcium fly ash (HVFA) cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.-A.; Chang, T.-P.; Shih, J.-Y. Effects of sulfate rich solid waste activator on engineering properties and durability of modified high volume fly ash cement based SCC. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 20, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, A.; Soliman, N.; Xie, A.; Davidenko, T.; Tagnit-Hamou, A. Field trials with concrete incorporating biomass-fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.-A.; Chang, T.-P.; Shih, J.-Y. Engineering properties and bonding behavior of self-compacting concrete made with no-cement binder. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlaváček, P.; Šulc, R.; Šmilauer, V.; Rößler, C.; Snop, R. Ternary binder made of CFBC fly ash, conventional fly ash, and calcium hydroxide: Phase and strength evolution. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 90, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.H.; Choi, Y.C. Development of non-sintered zero-OPC binders using circulating fluidized bed combustion ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 178, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škvára, F.; Šulc, R.; Snop, R.; Peterová, A.; Šídlová, M. Hydraulic clinkerless binder on the fluid sulfocalcic fly ash basis. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 93, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, N.T.; Chang, T.-P.; Chen, C.-T. Hydration process and compressive strength of slag-CFBC fly ash materials without portland cement. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kledyński, Z.; Machowska, A.; Pacewska, B.; Wilińska, I. Investigation of hydration products of fly ash–slag pastes. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 130, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, A.; Marroccoli, M.; Montagnaro, F.; Tomasulo, M.; Valenti, G.L. Enhancement of selectivity toward ettringite during hydrothermal processes on fluidized bed combustion wastes for the manufacture of preformed building components. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 101887–101893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, A.; Calabrese, D.; Marroccoli, M.; Valenti, G.L.; Montagnaro, F. Study of the hydrothermal treatments of residues from fluidized bed combustors for the manufacture of ettringite-based building elements. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 126, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, Q.; Huang, K.; Ma, B.; Wu, B. Cementitious properties and hydration mechanism of circulating fluidized bed combustion (CFBC) desulfurization ashes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łaskawiec, K.; Gebarowski, P.; Małolepszy, J. Influence of Fluidized Ashes on Properties of Autoclaved Aerated Concrete. Mater. J. 2016, 113, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z. Utilization of circulating fluidized bed fly ash for the preparation of foam concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 54, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Guo, C.; Qian, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z. Effect of autoclave curing on hydration of anhydrite in CFBC fly ash. Mag. Concr. Res. 2015, 67, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinicki, M.A.; Zielinski, M. Frost salt scaling resistance of concrete containing CFBC fly ash. Mater. Struct. 2009, 42, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yan, Y.; Hu, Z. Utilization of circulating fluidized bed fly ash in preparing non-autoclaved aerated concrete production. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, K.G. Carbonation behavior of lightweight foamed concrete using coal fly ash. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 2016, 53, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinicki, M.A.; Zielinski, M. Air void system in concrete containing circulating fluidized bed combustion fly ash. Mater. Struct. 2008, 41, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinicki, M.A.; Zieliński, M. The influence of CFBC fly ash addition on phase composition of air-entrained concrete. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2008, 56, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Bílek, V.; Pařizek, L.; Kalina, L. Effect of the by-pass cement-kiln dust and fluidized-bed-combustion fly ash on the properties of fine-grained alkali-activated slag-based composites. Mater. Tehnol. 2015, 49, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Kasemsiri, P.; Poomsrisa-ard, S.; Posi, P. Fluidized bed coal-bark fly ash geopolymer with additives cured at ambient temperature. Int. J. GEOMATE 2019, 16, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Jenjirapanya, S.; Rattanasak, U. Characterizations of FBC/PCC fly ash geopolymeric composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Paisitsrisawat, P.; Rattanasak, U. Strength and resistance to sulfate and sulfuric acid of ground fluidized bed combustion fly ash–silica fume alkali-activated composite. Adv. Powder Technol. 2014, 25, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Thaiwitcharoen, S.; Kaewpirom, S.; Rattanasak, U. Controlling ettringite formation in FBC fly ash geopolymer concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 41, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Rattanasak, U.; Jaturapitakkul, C. Utilization of fly ash blends from pulverized coal and fluidized bed combustions in geopolymeric materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2011, 33, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Rattanasak, U. Utilization of blended fluidized bed combustion (FBC) ash and pulverized coal combustion (PCC) fly ash in geopolymer. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiamwijit, M.; Pachana, K.; Kaewpirom, S.; Rattanasak, U.; Chindaprasirt, P. Comparative study on morphology of ground sub-bituminus FBC fly ash geopolymeric material. Adv. Powder Technol. 2015, 26, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, Q.; Shen, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhai, J. Low-reactive circulating fluidized bed combustion (CFBC) fly ashes as source material for geopolymer synthesis. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Yan, C.; Duan, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, X.; Li, D. A comparative study of high- and low-Al2O3 fly ash based-geopolymers: The role of mix proportion factors and curing temperature. Mater. Des. 2016, 95, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Tafesse, M.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, H.-K. Incorporation of CFBC ash in sodium silicate-activated slag system: Modification of microstructures and its effect on shrinkage. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 123, 105771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yliniemi, J.; Pesonen, J.; Tiainen, M.; Illikainen, M. Alkali activation of recovered fuel–biofuel fly ash from fluidised-bed combustion: Stabilisation/solidification of heavy metals. Waste Manag. 2015, 43, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yliniemi, J.; Tiainen, M.; Illikainen, M. Microstructure and Physical Properties of Lightweight Aggregates Produced by Alkali Activation-High Shear Granulation of FBC Recovered Fuel-Biofuel Fly Ash. Waste Biomass Valorization 2016, 7, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, H.; Li, F.; Li, P.; Shen, L.; Zhai, J. Synthesis of geopolymer composites from blends of CFBC fly and bottom ashes. Fuel 2012, 97, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Lee, N.K.; Lee, H.K. Circulating fluidized bed combustion ash as controlled low-strength material (CLSM) by alkaline activation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shao, N.; Qin, J.; Kong, F.; Wang, C.; Wang, D. Strength and thermal behavior of low weight foam geopolymer using circulating fluidized bed combustion fly ash. J. Cent. South Univ. 2015, 22, 3633–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shao, N.; Wang, D.; Qin, J.; Huang, T.; Song, W.; Lin, M.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Z. Fabrication and properties of foam geopolymer using circulating fluidized bed combustion fly ash. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2014, 21, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Seo, J.H.; Lee, H.K. Binder chemistry of sodium carbonate-activated CFBC fly ash. Mater. Struct. 2018, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-M. Effects of circulating fluidized bed combustion fly ash on the properties of alkali-activated slag cement mortars. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2012, 20, 223–232. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.-H.; Huang, R.; Tsai, C.-J.; Lin, W.-T. Utilizing residues of CFB co-combustion of coal, sludge and TDF as an alkali activator in eco-binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 80, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvíl, J.; Kalousová, H.; Opravil, T. Optimization of alternative aggregates based on fluid combustion fly ashes. Mater. Sci. Forum 2016, 851, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, C.-S.; Jung, Y.S.; Saylak, D.; Mishra, S.K. Development of synthetic aggregate using off-ASTM specification ashes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 38, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yliniemi; Paiva; Ferreira; Tiainen; Illikainen Development and incorporation of lightweight waste-based geopolymer aggregates in mortar and concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 131, 784–792. [CrossRef]
- Naik, T.R.; Kraus, R.N.; Chun, Y.M.; Botha, F.D. Cast-Concrete Products Made with FBC Ash and Wet-Collected Coal-Ash. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2005, 17, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Qian, J.; You, C.; Hu, C. Use of circulating fluidized bed combustion fly ash and slag in autoclaved brick. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 35, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, Q.; Shen, L.F.; Zhao, H.; Zhai, J.P. Potential for manufacturing unfired-bricks using circulating fluidized bed combustion fly ash. Asian J. Chem. 2011, 23, 3449–3453. [Google Scholar]
- Húlan, T.; Trník, A.; Kaljuvee, T.; Uibu, M.; Štubňa, I.; Kallavus, U.; Traksmaa, R. The study of firing of a ceramic body made from illite and fluidized bed combustion fly ash. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 127, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardane, H.J.; Kannan, R.S.S.; Ziemkiewicz, P.F. Use of Waste Materials for Control of Acid Mine Drainage and Subsidence. J. Environ. Eng. 2003, 129, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, Y.P.; De, I.; Powell, E. A model study for blind pneumatic backfilling of fly ash in abandoned underground mines. Int. J. Surf. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2005, 19, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solem-Tishmack, J.K.; McCarthy, G.J.; Docktor, B.; Eylands, K.E.; Thompson, J.S.; Hassett, D.J. High-calcium coal combustion by-products: Engineering properties, ettringite formation, and potential application in solidification and stabilization of selenium and boron. Cem. Concr. Res. 1995, 25, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kępys, W.; Piotrowski, Z.; Pomykała, R.; Grzywa, A. Application of fly ash from biomass in suspension technologies. Inzynieria Miner. 2014, 15, 251–255. [Google Scholar]
- Uliasz-Bochenczyk, A.; Lyko, P. Waste from the cement industry—A Component of Sealing grouts. Gospod. Surowcami Miner. Kraków 2014, 30, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Liu, J.; Huang, X. Experimental Study of Stabilized Soil Utilizing Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion Desulfurization Ash with Carbide Slag and Desulfurization Gypsum. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/je/2015/459201/ (accessed on 13 December 2017).
- Tang, H.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Song, L.; Wu, Z.; Xu, H. Properties and mechanism of CFBC fly ash-cement based stabilizers for lake sludge. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2012, 27, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, C.-S.; Su Jung, Y.; Saylak, D. Evaluation of synthetic aggregates using off-ASTM specification ashes as road base course materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 38, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, N.M.; Schultz, S.; Sander, P.; Schopp, L. Beneficial use of CFB ash in pavement construction applications. Fuel 2009, 88, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwański, M.; Buczyński, P.; Mazurek, G. Optimization of the road binder used in the base layer in the road construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mráz, V.; Valentin, J.; Suda, J.; Kopecký, L. Experimental assessment of fly-ash stabilized and recycled mixes. J. Test. Eval. 2015, 43, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.J.; Bergeson, K.L. Long-term strength and durability of hydrated fly-ash road bases. Transp. Res. Rec. 2001, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Balunaini, U.; Prezzi, M. Forensic examination of severe heaving of embankment constructed with fluidized bed combustion ash. Transp. Res. Rec. 2007, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, H.; Fu, X.; Chen, C.; Zhai, J. Effects of circulating fluidized bed combustion (CFBC) fly ashes as filler on the performances of asphalt. Asia Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 4, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnaro, F.; Salatino, P.; Bernardo, G.; Telesca, A.; Valenti, G.L. Reuse of Fly Ash from a Fluidized Bed Combustor for Sulfur Uptake: The Role of Ettringite in Hydration-Induced Reactivation. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 1822–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, G.; Telesca, A.; Valenti, G.L.; Montagnaro, F. Role of Ettringite in the Reuse of Hydrated Fly Ash from Fluidized-Bed Combustion as a Sulfur Sorbent: A Hydration Study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 4054–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Charland, J.-P.; Anthony, E.J.; Jia, L. A Study on the Reactivation of Five Fly Ashes from Commercial Circulating Fluidized Bed (CFB) Boilers. Energy Fuels 2004, 18, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Manovic, V.; He, I.; Anthony, E.J. Reuse of Spent Sorbents from FBC for SO2 Capture by Simultaneous Reactivation and Pelletization. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, C.; Seo, J.; Choi, M.; Cho, J.; Ahn, J.; Cho, K. Utilization of CFBC fly ash as a binder to produce in-furnace desulfurization sorbent. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.J.; Lee, K.G. Carbonation Behavior of fly ash with circulating fluidized bed combustion (CFBC). J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 2015, 52, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaschik, J.; Jaschik, M.; Warmuziński, K. The utilisation of fly ash in CO2 mineral carbonation. Chem. Process Eng. 2016, 37, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, B.; Girón, R.P.; Suárez-Ruiz, I.; Fuente, E. From fly ash of forest biomass combustion (FBC) to micro-mesoporous silica adsorbent materials. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 105, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grela, A.; Hebda, M.; Łach, M.; Mikuła, J. Thermal behavior and physical characteristics of synthetic zeolite from CFB-coal fly ash. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 220, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, N.; Zhang, P.; Song, L.; Kang, M.; Lu, Z.; Zheng, R. Stearic acid coating on circulating fluidized bed combustion fly ashes and its effect on the mechanical performance of polymer composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 279, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbacz, A.; Sokołowska, J.J. Concrete-like polymer composites with fly ashes - Comparative study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 38, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.; Moreno, N.; Navia, R.; Querol, X. Development of a non-conventional sorbent from fly ash and its potential use in acid wastewater neutralization and heavy metal removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamon, M.; Katsumi, T.; Sano, Y. MSW fly ash stabilized with coal ash for geotechnical application. J. Hazard. Mater. 2000, 76, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hou, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, D. Feasibility study on solidification of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash with circulating fluidized bed combustion coal fly ash. Waste Manag. Res. 2009, 27, 258–266. [Google Scholar]
- Knoll, K.L.; Behr-Andres, C. Fluidized-Bed-Combustion Ash for the Solidification and Stabilization of a Metal-Hydroxide Sludge. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1998, 48, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vinter, S.; Montanes, M.T.; Bednarik, V.; Hrivnova, P. Stabilization/solidification of hot dip galvanizing ash using different binders. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 320, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, A. Durability of stabilised galvanic sewage sludge against the impact of sea water and sulfate solutions. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2012, 38, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymkiewicz, A.; Hycnar, J.J.; Fraš, A.; Przystaś, R.; Józefiak, T.; Baic, I. Application of fluidized bed combustion ashes for enhancement of mining waste management. Inzynieria Miner. 2012, 13, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pesonen, J.; Yliniemi, J.; Illikainen, M.; Kuokkanen, T.; Lassi, U. Stabilization/solidification of fly ash from fluidized bed combustion of recovered fuel and biofuel using alkali activation and cement addition. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, R.; Lapa, N.; Lopes, H.; Gulyurtlu, I.; Mendes, B. Stabilization/solidification of fly ashes and concrete production from bottom and circulating ashes produced in a power plant working under mono and co-combustion conditions. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 2009–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
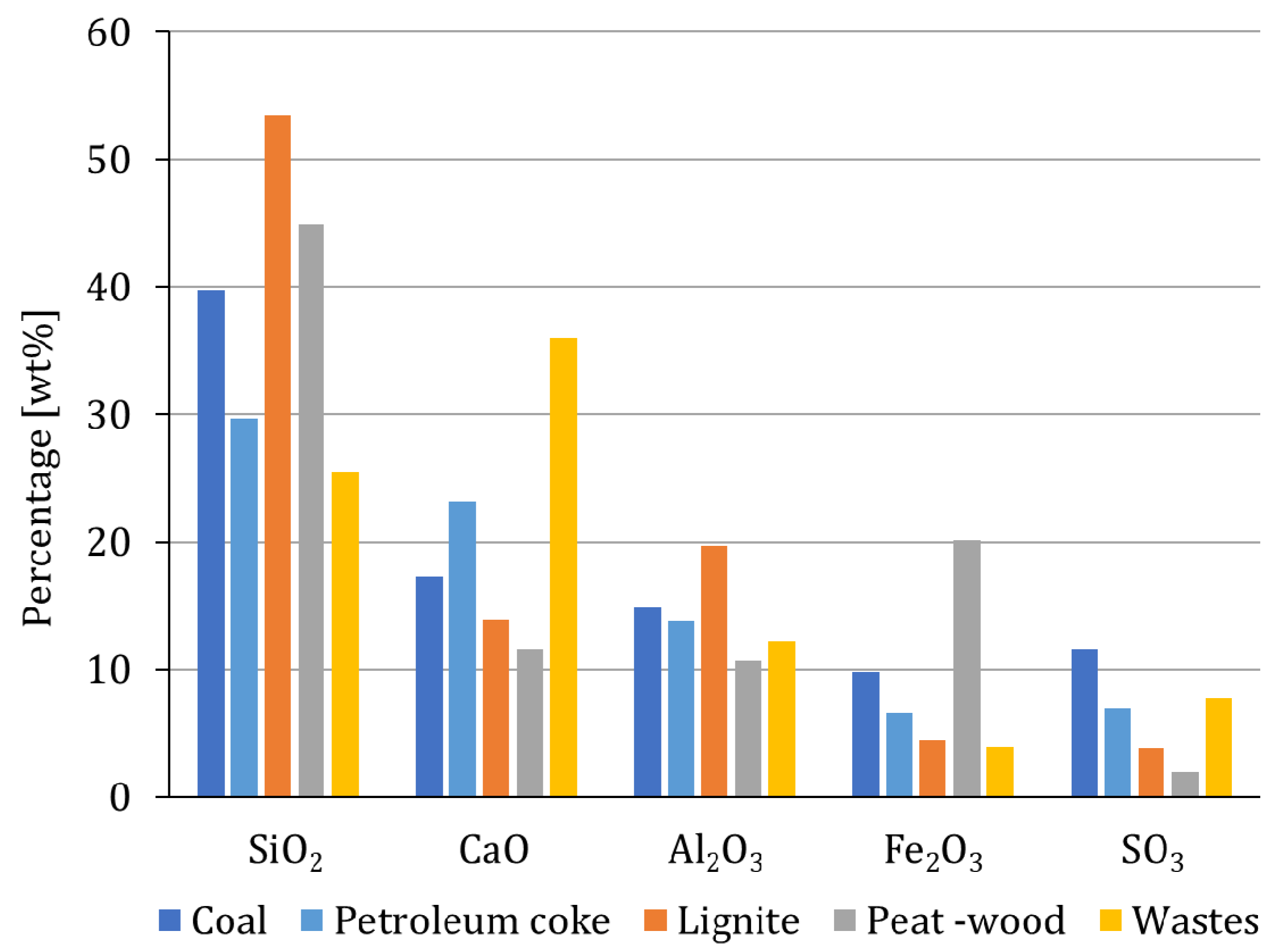
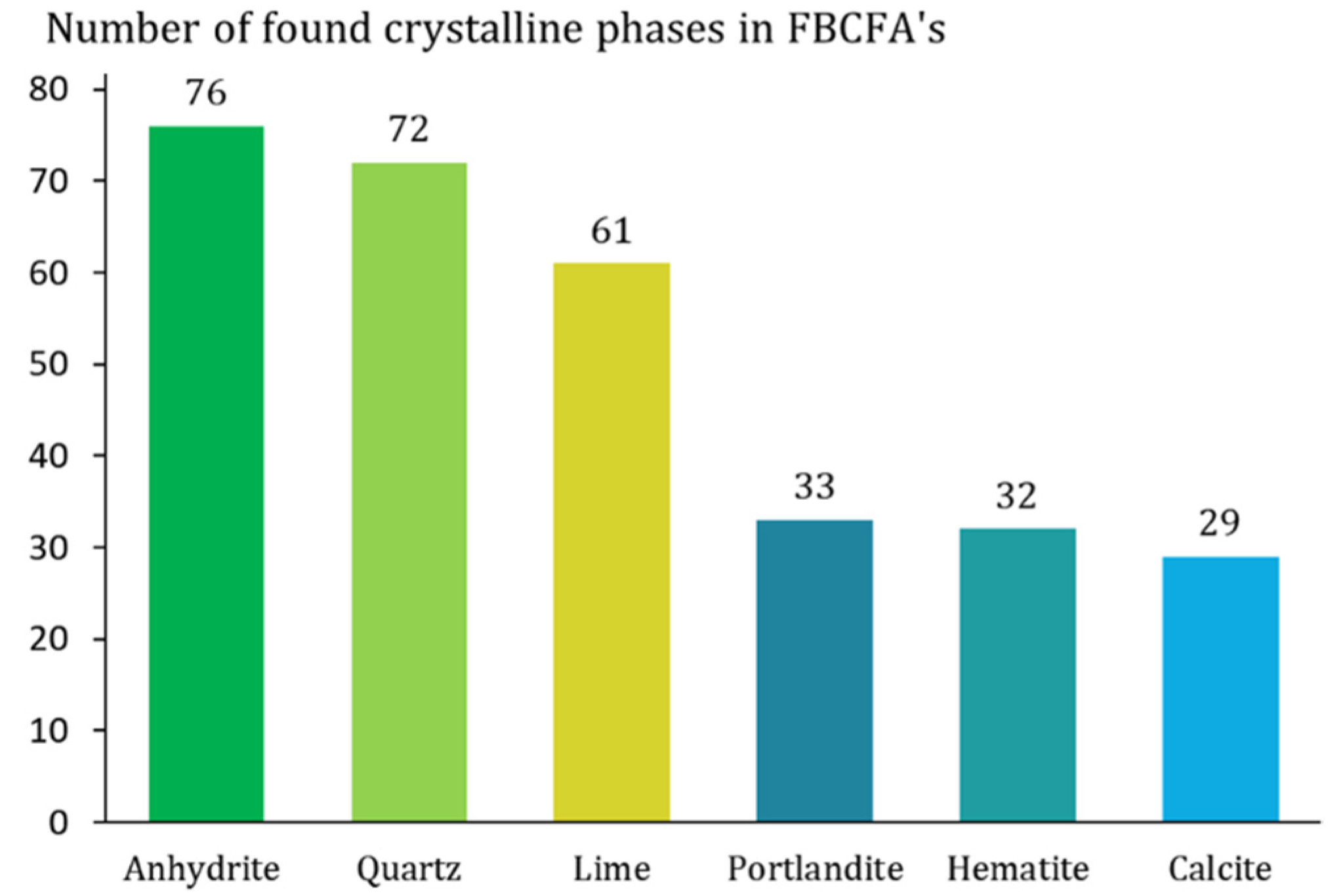

| Min. [%] | Max. [%] | |
|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 0.22 [16] | 53.5 [17] |
| Al2O3 | 0.10 [18] | 50.98 [19] |
| Fe2O3 | 0.10 [18] | 27.9 [20] |
| CaO | 1.40 [21] | 56.8 [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29] |
| SO3 | 0.50 [30] | 40.6 [31] |
| MgO | 0.15 [32] | 7.10 [33] |
| As (mg/kg) | Cd (mg/kg) | Cr (mg/kg) | Cu (mg/kg) | Ni (mg/kg) | Pb (mg/kg) | Zn (mg/kg) | Ca (%) | K + P (%) | Neutralizing Value %Ca | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Finland a | 25/40 | 2.5/25 | 300 | 600/700 | 100/150 | 100/150 | 1500/4500 | 6/- | 2 | -/10 |
| Denmark | 5/20 b | 100 | 60 | 120/250 c |
| Application | Number of Studies | Limitations/Important Information etc. |
|---|---|---|
| Soil amendment | 46 | - Only for fly ashes from pure biomass combustion - Low amount of hazardous elements - Source for phosphorous and calcium |
| Construction | 67 | - Chemical composition often suitable for cement substitution - Usually fly ashes have pozzolanic activity - Contain reactive minerals (portlandite, lime, anhydrite) - Irregular shape → higher porosity - Initial setting time usually increases |
| Earth construction | 14 | - Mine backfilling material - Immobilizing some hazardous elements via stabilization/solidification method - Decreased resistant against frost and water |
| Combustion plant internal use | 8 | - Re-combustion of fly ashes containing high unburnt carbon - SO2 and CO2 capture with lime-containing fly ashes |
| Other | 13 | - adsorbents, filler material, waste stabilization, … |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ohenoja, K.; Pesonen, J.; Yliniemi, J.; Illikainen, M. Utilization of Fly Ashes from Fluidized Bed Combustion: A Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2988. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12072988
Ohenoja K, Pesonen J, Yliniemi J, Illikainen M. Utilization of Fly Ashes from Fluidized Bed Combustion: A Review. Sustainability. 2020; 12(7):2988. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12072988
Chicago/Turabian StyleOhenoja, Katja, Janne Pesonen, Juho Yliniemi, and Mirja Illikainen. 2020. "Utilization of Fly Ashes from Fluidized Bed Combustion: A Review" Sustainability 12, no. 7: 2988. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12072988
APA StyleOhenoja, K., Pesonen, J., Yliniemi, J., & Illikainen, M. (2020). Utilization of Fly Ashes from Fluidized Bed Combustion: A Review. Sustainability, 12(7), 2988. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12072988







