Slope Orientation and Vegetation Effects on Soil Thermo-Hydraulic Behavior. An Experimental Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
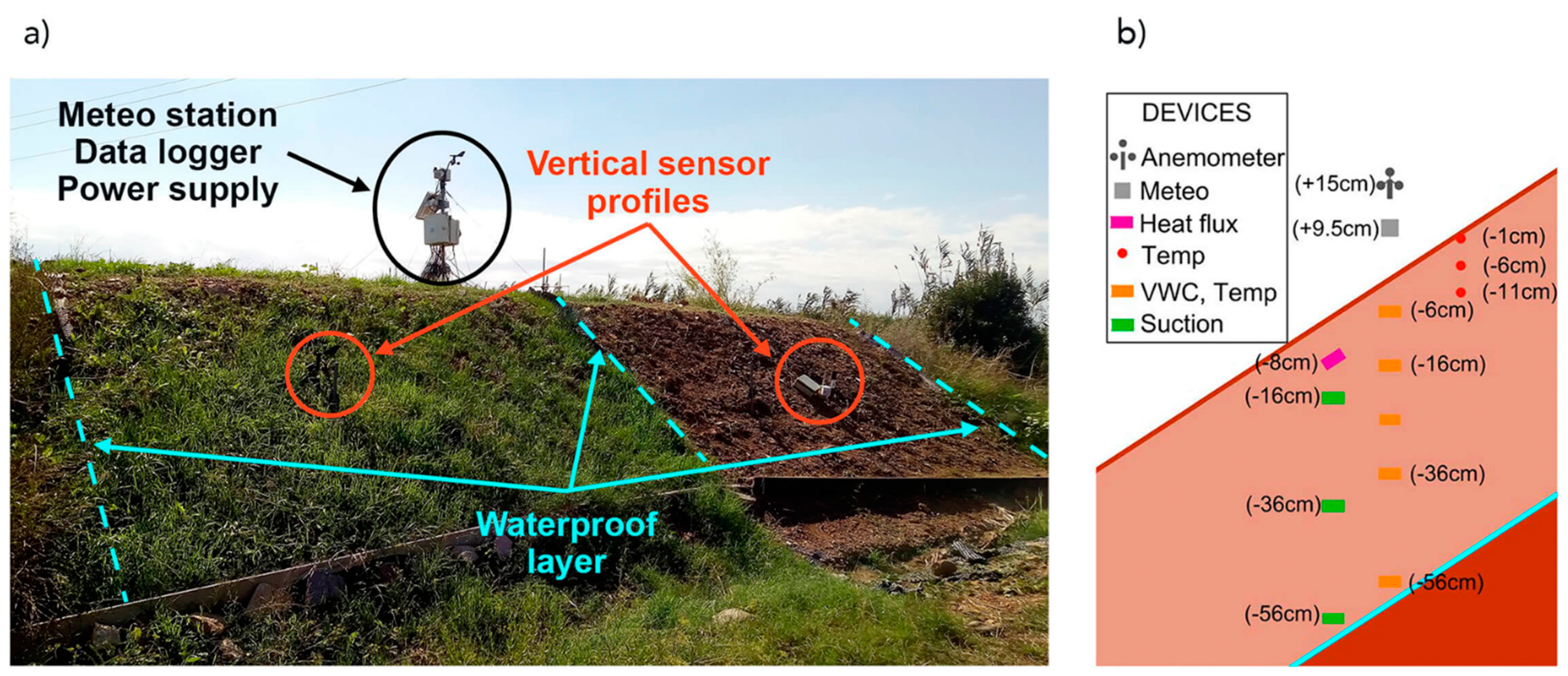
2.1. Site, Embankment and Monitoring Description
2.2. Characterization of the Vegetation Species
3. Results and Discussion
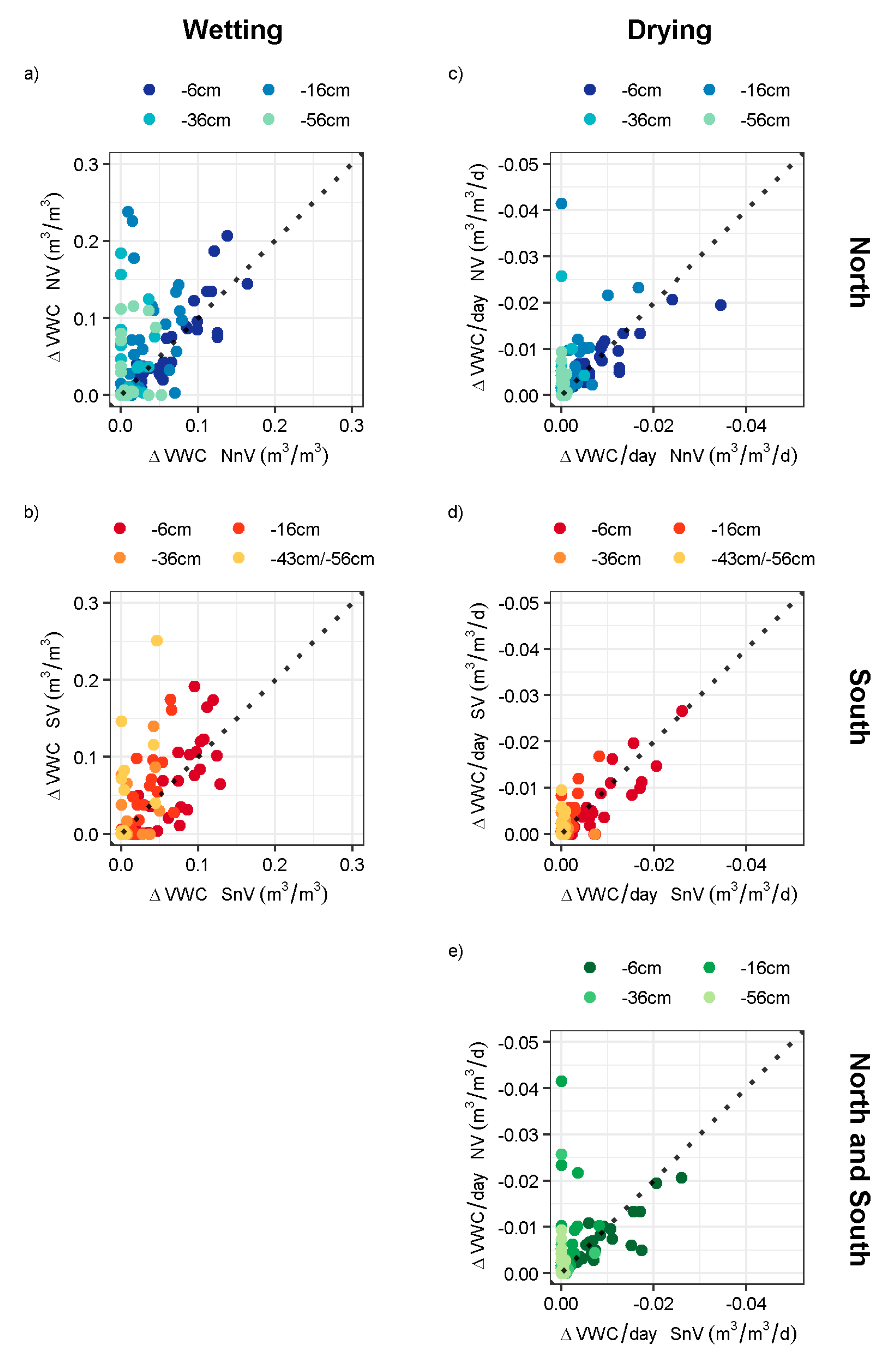
3.1. Hydraulic Aspects
3.2. Thermal Aspects
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boardman, J.; Poesen, J. Soil Erosion in Europe; Boardman, J., Poesen, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2006; ISBN 9780470859209. [Google Scholar]
- Spiker, E.C.; Gori, P.L. National Landslide Hazards Mitigation Strategy: A Framework for Loss Reduction; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Guzzetti, F.; Cardinali, M.; Reichenbach, P.; Cipolla, F.; Sebastiani, C.; Galli, M.; Salvati, P. Landslides triggered by the 23 November 2000 rainfall event in the Imperia Province, Western Liguria, Italy. Eng. Geol. 2004, 73, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petley, D. Global patterns of loss of life from landslides. Geology 2012, 40, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidle, R.C.; Bogaard, T.A. Dynamic earth system and ecological controls of rainfall-initiated landslides. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 159, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, D.G.; Rahardjo, H. Soil Mechanics for Unsaturated Soils; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1993; ISBN 9780470172759.
- Rahardjo, H.; Lim, T.T.; Chang, M.F.; Fredlund, D.G. Shear-strength characteristics of a residual soil. Can. Geotech. J. 1995, 32, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanapalli, S.K.; Fredlund, D.G.; Pufahl, D.E.; Clifton, A.W. Model for the prediction of shear strength with respect to soil suction. Can. Geotech. J. 1996, 33, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourie, A.B.; Rowe, D.; Blight, G.E. The effect of infiltration on the stability of the slopes of a dry ash dump. Géotechnique 1999, 49, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highland, L.M.; Bobrowsky, P. The Landslide Handbook—A Guide to Understanding Landslides; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2008; 129p, ISBN 978-141132226-4.
- Durán Zuazo, V.H.; Rodríguez Pleguezuelo, C.R. Soil-erosion and runoff prevention by plant covers. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 28, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nearing, M.A.; Jetten, V.; Baffaut, C.; Cerdan, O.; Couturier, A.; Hernandez, M.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Nichols, M.H.; Nunes, J.P.; Renschler, C.S.; et al. Modeling response of soil erosion and runoff to changes in precipitation and cover. Catena 2005, 61, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781107661820. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Meusburger, K.; Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Alewell, C. Soil erodibility in Europe: A high-resolution dataset based on LUCAS. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 479–480, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, H.; Gray, R.B.S. Biotechnical and Soil Bioengineering Slope Stabilization: A Practical Guide for Erosion Control; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1996; ISBN 978-0-471-04978-4. [Google Scholar]
- Jotisankasa, A.; Mairaing, W.; Tansamrit, S. Infiltration and stability of soil slope with vetiver grass subjected to rainfall from numerical modeling. In Unsaturated Soils: Research & Applications: Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Unsaturated Soils, UNSAT 2014, Sydney, Australia, 2–4 July 2014; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 1241–1247. ISBN 9781138001503. [Google Scholar]
- Igwe, P.U.; Ezeukwu, J.C.; Edoka, N.E.; Ejie, O.C.; Ifi, G.I. A Review of Vegetation Cover as a Natural Factor to Soil Erosion. Int. J. Rural Dev. Environ. Health Res. 2017, 1, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Ji, X.; Wang, S.; Ding, S. Relationships between Riparian Vegetation Pattern and the Hydraulic Characteristics of Upslope Runoff. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bochet, E.; Poesen, J.; Rubio, J.L. Runoff and soil loss under individual plants of a semi-arid Mediterranean shrubland: Influence of plant morphology and rainfall intensity. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2006, 31, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.H.; Osman, N. Shear Strength of a Soil Containing Vegetation Roots. Soils Found. 2008, 48, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chok, Y.H.; Jaksa, M.B.; Kaggwa, W.S.; Griffiths, D.V. Assessing the influence of root reinforcement on slope stability by finite elements. Int. J. Geo-Eng. 2015, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maffra, C.; Sousa, R.; Sutili, F.; Pinheiro, R. The Effect of Roots on the Shear Strength of Texturally Distinct Soils. Floresta Ambient. 2019, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greenway, D.R. Vegetation and Slope Stability. In Slope Stability: Geotechnical Engineering and Geomorphology; Anderson, M.G., Richards, K.S., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1987; pp. 187–230. [Google Scholar]
- Gens, A. Soil–environment interactions in geotechnical engineering. Géotechnique 2010, 60, 3–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahardjo, H.; Satyanaga, A.; Leong, E.C. Unsaturated soil mechanics for slope stabilization. Geotech. Eng. J. SEAGS AGSSEA 2012, 43, 48–58. [Google Scholar]
- Elia, G.; Cotecchia, F.; Pedone, G.; Vaunat, J.; Vardon, P.J.; Pereira, C.; Springman, S.M.; Rouainia, M.; Van Esch, J.; Koda, E.; et al. Numerical modelling of slope-vegetation-atmosphere interaction: An overview. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2017, 50, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, J.J.; Leung, A.K.; Ng, C.W.W.; Shao, W. Modelling hydro-mechanical reinforcements of plants to slope stability. Comput. Geotech. 2018, 95, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppin, N.J.; Richards, I.G. Use of Vegetation in Civil Engineering; Coppin, N.J., Richards, I.G., Eds.; Construction Industry Research and Information Association (CIRIA): London, UK, 1990; ISBN 978-086017-711-1. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, A.; Collison, A.J.C. Quantifying the mechanical and hydrologic effects of riparian vegetation on streambank stability. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2002, 27, 527–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preti, F.; Giadrossich, F. Root reinforcement and slope bioengineering stabilization by Spanish Broom (Spartium junceum L.). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1713–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eab, K.H.; Likitlersuang, S.; Takahashi, A. Laboratory and modelling investigation of root-reinforced system for slope stabilisation. Soils Found. 2015, 55, 1270–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capilleri, P.P.; Motta, E.; Raciti, E. Experimental Study on Native Plant Root Tensile Strength for Slope Stabilization. Procedia Eng. 2016, 158, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, T.J.; Horton, R. Soil Heat Flux. In Micrometeorology in Agricultural Systems; Agronomy Monograph no. 47; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 2005; pp. 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idso, S.B.; Aase, J.K.; Jackson, R.D. Net radiation—Soil heat flux relations as influenced by soil water content variations. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1975, 9, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, S.A.; Oliver, H.R.; Wallace, J.S.; Roberts, A.M. Soil heat flux and temperature variation with vegetation, soil type and climate. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1987, 39, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Parra, J.; Pulido, M.; Lozano-Fondón, C.; Schnabel, S. How do Soil Moisture and Vegetation Covers Influence Soil Temperature in Drylands of Mediterranean Regions? Water 2018, 10, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, C.W.W.; Woon, K.X.; Leung, A.K.; Chu, L.M. Experimental investigation of induced suction distribution in a grass-covered soil. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 52, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.W.W.; Garg, A.; Leung, A.K.; Hau, B.C.H. Relationships between leaf and root area indices and soil suction induced during drying-wetting cycles. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garg, A.; Leung, A.K.; Ng, C.W.W. Comparisons of soil suction induced by evapotranspiration and transpiration of S. heptaphylla. Can. Geotech. J. 2015, 52, 2149–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, L.M. Evaluating suction profile in a vegetated slope considering uncertainty in transpiration. Comput. Geotech. 2015, 63, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Ollauri, A.; Mickovski, S.B. Hydrological effect of vegetation against rainfall-induced landslides. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yildiz, A.; Graf, F.; Rickli, C.; Springman, S.M. Assessment of plant-induced suction and its effects on the shear strength of rooted soils. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Geotech. Eng. 2019, 172, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahardjo, H.; Satyanaga, A.; Leong, E.C.; Santoso, V.A.; Ng, Y.S. Performance of an instrumented slope covered with shrubs and deep-rooted grass. Soils Found. 2014, 54, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leung, A.K.; Garg, A.; Coo, J.L.; Ng, C.W.W.; Hau, B.C.H. Effects of the roots of Cynodon dactylon and Schefflera heptaphylla on water infiltration rate and soil hydraulic conductivity. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 3342–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garg, A.; Coo, J.L.; Ng, C.W.W. Field study on influence of root characteristics on soil suction distribution in slopes vegetated with Cynodon dactylon and Schefflera heptaphylla. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2015, 40, 1631–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bissonnais, Y.; Lecomte, V.; Cerdan, O. Grass strip effects on runoff and soil loss. Agronomie 2004, 24, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, V.U.; Tambe, D.T. Estimation of infiltration rate, run-off and sediment yield under simulated rainfall experiments in upper Pravara Basin, India: Effect of slope angle and grass-cover. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 119, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, P.; Zhao, X. Effects of rainfall intensity, underlying surface and slope gradient on soil infiltration under simulated rainfall experiments. CATENA 2013, 104, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergani, C.; Graf, F. Soil permeability, aggregate stability and root growth: A pot experiment from a soil bioengineering perspective. Ecohydrology 2016, 9, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.J.; Leung, A.K.; Ng, C.W.W.; So, P.S. Investigation of plant growth and transpiration-induced matric suction under mixed grass–tree conditions. Can. Geotech. J. 2017, 54, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fraccica, A.; Romero, E.; Fourcaud, T. Multi-scale effects on the hydraulic behaviour of a root-permeated and compacted soil. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.J.; Gao, Y.B.; Ferber, V. Simulating the water content and temperature changes in an experimental embankment using meteorological data. Eng. Geol. 2010, 114, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshioka, M.; Takakura, S.; Ishizawa, T.; Sakai, N. Temporal changes of soil temperature with soil water content in an embankment slope during controlled artificial rainfall experiments. J. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 114, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicalho, K.V.; Boussafir, Y.; Cui, Y.J. Performance of an instrumented embankment constructed with lime-treated silty clay during four-years in the Northeast of France. Transp. Geotech. 2018, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oorthuis, R.; Hürlimann, M.; Fraccica, A.; Lloret, A.; Moya, J.; Puig-Polo, C.; Vaunat, J. Monitoring of a full-scale embankment experiment regarding soil-vegetation-atmosphere interactions. Water (Switzerland) 2018, 10, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.W.W.; Ni, J.J.; Leung, A.K. Effects of plant growth and spacing on soil hydrological changes: A field study. Géotechnique 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, C.W. Abiotic stress tolerances (moisture, nutrients) and photosynthesis in endophyte-infected tall fescue. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1993, 44, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmi, A.A.; West, C.P. Endophyte infection effects on stomatal conductance, osmotic adjustment and drought recovery of tall fescue. New Phytol. 1995, 131, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilman, D.; Gao, Y.; Leitch, M.H. Some differences between eight grasses within the Lolium-Festuca complex when grown in conditions of severe water shortage. Grass Forage Sci. 1998, 53, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, F.Q.; Zhang, J.X. The Temporal Dynamics of Cynodon Dactylon Soil-Root System in Soil Conservation and Slope Reinforcement. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 838–841, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J. Effect of Cynodon dactylon community on the conservation and reinforcement of riparian shallow soil in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Ecol. Process. 2015, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Image J Web Page. Available online: https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ (accessed on 16 December 2020).
- Guswa, A.J. Effect of plant uptake strategy on the water-optimal root depth. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MPS-2 & MPS-6 Dielectric Water Potential Sensors Operator’s Manual (Version July 10, 2017). Available online: http://library.metergroup.com/Retired%20and%20Discontinued/Manuals/13755_MPS-2and6_Web.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2020).
- Schenk, H.J.; Jackson, R.B. The global biogeography of roots. Ecol. Monogr. 2002, 72, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.; Norum, D. The Effect of Soil Moisture on Infiltration As Related To Runoff and Recharge. In Proceedings of Hydrology Symposium; National Research Council of Canada Associate Committee on Geodesy and Geophysics Subcommittee on Hydrology: Otawa, ON, Canada, 1967; Volume 6, pp. 133–153. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Li, J.H.; Zhou, T.; Fredlund, D.G. Experimental study on unsaturated hydraulic properties of vegetated soil. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 103, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S. Robust Locally Weighted Regression and Smoothing Scatterplots. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oorthuis, R.; Vaunat, J.; Hürlimann, M.; Lloret, A.; Moya, J.; Puig-Polo, C.; Fraccica, A. Slope Orientation and Vegetation Effects on Soil Thermo-Hydraulic Behavior. An Experimental Study. Sustainability 2021, 13, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010014
Oorthuis R, Vaunat J, Hürlimann M, Lloret A, Moya J, Puig-Polo C, Fraccica A. Slope Orientation and Vegetation Effects on Soil Thermo-Hydraulic Behavior. An Experimental Study. Sustainability. 2021; 13(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleOorthuis, Raül, Jean Vaunat, Marcel Hürlimann, Antonio Lloret, José Moya, Càrol Puig-Polo, and Alessandro Fraccica. 2021. "Slope Orientation and Vegetation Effects on Soil Thermo-Hydraulic Behavior. An Experimental Study" Sustainability 13, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010014
APA StyleOorthuis, R., Vaunat, J., Hürlimann, M., Lloret, A., Moya, J., Puig-Polo, C., & Fraccica, A. (2021). Slope Orientation and Vegetation Effects on Soil Thermo-Hydraulic Behavior. An Experimental Study. Sustainability, 13(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010014





