Low Cost, Multi-Pollutant Sensing System Using Raspberry Pi for Indoor Air Quality Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Low Cost Air Quality System
3. Measurements Using LCAQS
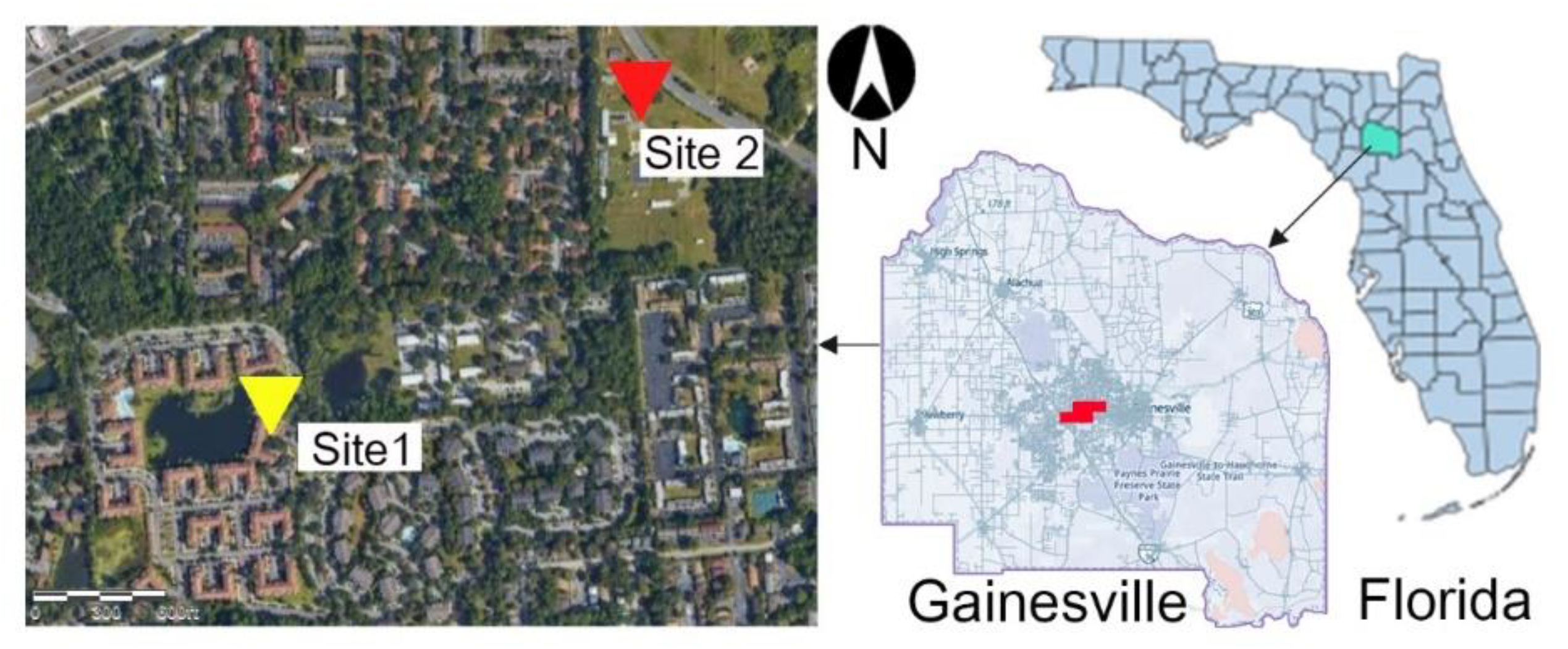
3.1. Site-Description
3.2. Measuring and Sampling Methods
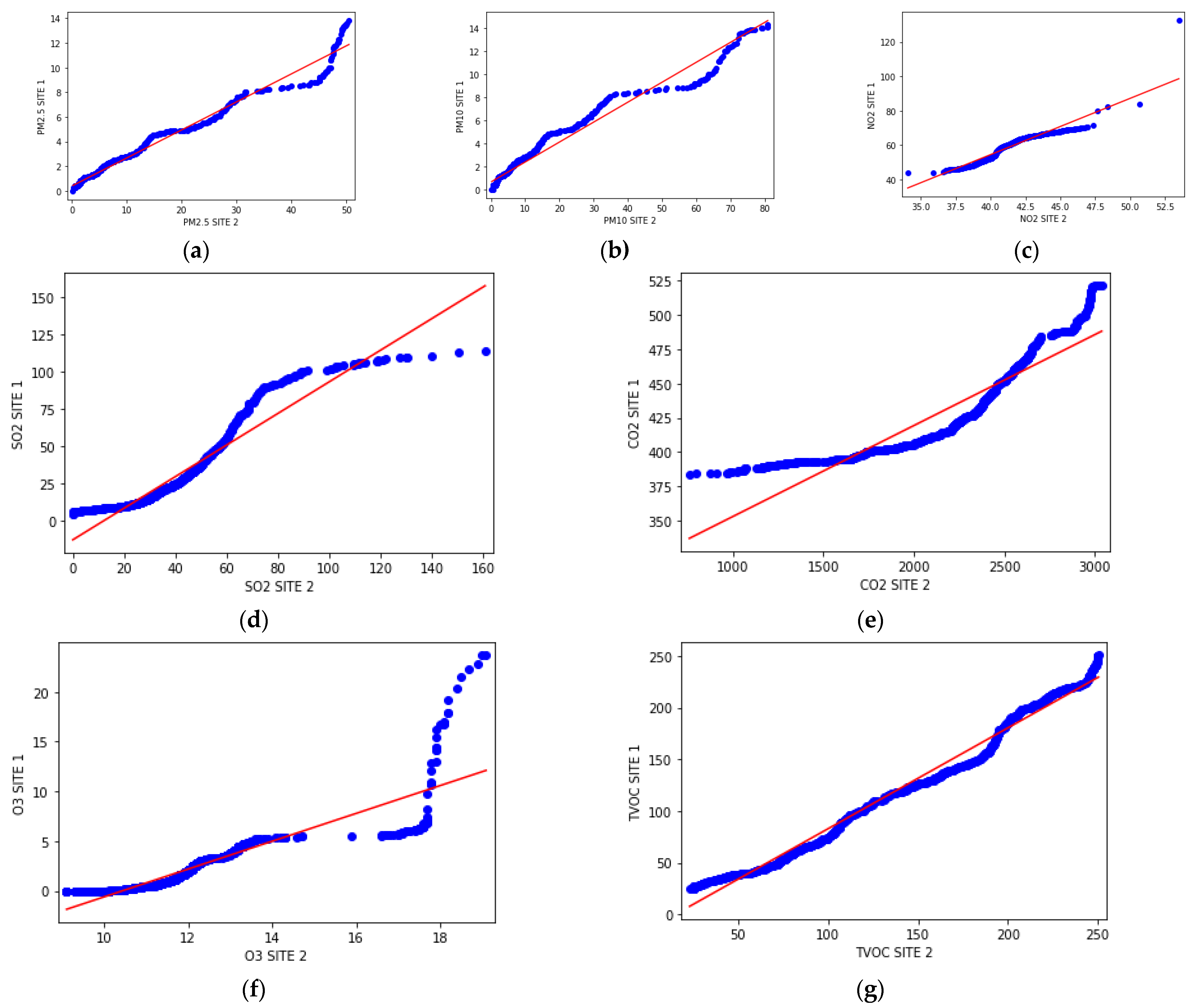
3.3. Data Analysis
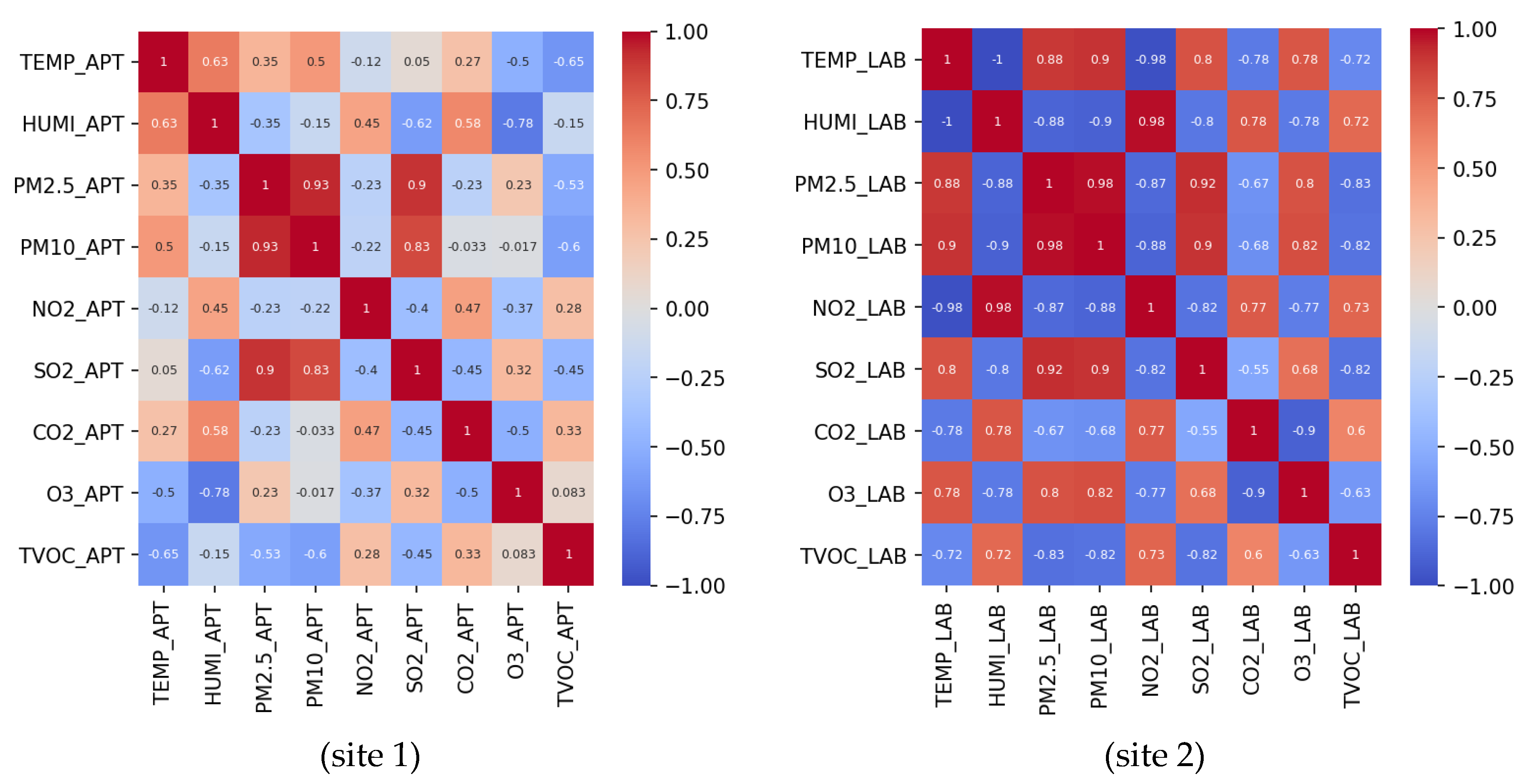
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ALA. The State of the Air 2020; American Lung Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 2020; pp. 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Pitarma, R.; Marques, G.; Ferreira, B.R. Monitoring Indoor Air Quality for Enhanced Occupational Health. J. Med. Syst. 2017, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, H.; Roser, M. Indoor Air Pollution. Our World Data 2020. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/indoor-air-pollution (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- Andersson, K. TVOC and health in non-industrial indoor environments report from a Nordic scientific consensus meeting at Langholmen in Stockholm, 1996. Indoor Air 1997, 7, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, Y.; Kadonosono, K.; Uchio, E. Clinical and allergological analysis of ocular manifestations of sick building syndrome. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2017, 11, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ahmed Abdul-Wahab, S.A.; En, S.C.F.; Elkamel, A.; Ahmadi, L.; Yetilmezsoy, K. A review of standards and guidelines set by international bodies for the parameters of indoor air quality. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, D.; Bourbeau, J. Building-Related Illnesses. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 1524–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Srinivasan, R. A systematic review of air quality sensors, guidelines, and measurement studies for indoor air quality management. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.G.; Kamal, A.S.; Morishita, M.; Dvonch, J.T.; Harkema, J.R.; Rohr, A.C. PM2.5-Induced cardiovascular dysregulation in rats is associated with elemental carbon and temperature-resolved carbon subfractions. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. A Standardized EPA Protocol for Characterizing Indoor Air Quality in Large Office Buildings; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Branco, P.T.B.S.; Nunes, R.A.O.; Alvim-Ferraz, M.C.M.; Martins, F.G.; Sousa, S.I.V. Children’s exposure to indoor air in urban nurseries—Part II: Gaseous pollutants’ assessment. Environ. Res. 2015, 142, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NAAQS. Primary National Ambient Air Quality Standard (NAAQS) for Sulfur Dioxide. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/so2-pollution/primary-national-ambient-air-quality-standard-naaqs-sulfur-dioxide (accessed on 26 July 2019).
- Spengler, J.D.; Ferris, B.G.; Dockery, D.W.; Speizer, F.E. Sulfur Dioxide and Nitrogen Dioxide Levels Inside and Outside Homes and the Implications on Health Effects Research. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1979, 13, 1276–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.L.; Lynch, R.A.; Floyd, E.L.; Wang, J.; Bartels, J.N. Indoor air quality in classrooms: Environmental measures and effective ventilation rate modeling in urban elementary schools. Build. Environ. 2018, 136, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madureira, J.; Paciência, I.; Rufo, J.; Severo, M.; Ramos, E.; Barros, H.; de Oliveira Fernandez, E. Source apportionment of CO2, PM10 and VOCs levels and health risk assessment in naturally ventilated primary schools in Porto, Portugal. Build. Environ. 2016, 96, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltzer, J.M. Building-related illnesses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1994, 94, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civan, M.Y.; Elbir, T.; Seyfioglu, R.; Kuntasal, Ö.O.; Bayram, A.; Doğan, G.; Yurdakul, S.; Andiç, Ö.; Müezzinoğlu, A.; Sofuoglu, S.C.; et al. Spatial and temporal variations in atmospheric VOCs, NO2, SO2, and O3 concentrations at a heavily industrialized region in Western Turkey, and assessment of the carcinogenic risk levels of benzene. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 103, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Building Air Quality—A Guide for Building Owners and Facility Managers; EPA-402-F-91-102; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; pp. 1–228.
- WHO. WHO Guidelines for Indoor Air Quality: Selected Pollutants; WHO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2010; Volume 35. [Google Scholar]
- Gvozdić, V.; Kovač-Andrić, E.; Brana, J. Influence of Meteorological Factors NO2, SO2, CO and PM10 on the Concentration of O3 in the Urban Atmosphere of Eastern Croatia. Environ. Model. Assess. 2011, 16, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Seo, J.H.; Jeong, N.N.; Sohn, J.R. Effects of Legal Regulation on Indoor Air Quality in Facilities for Sensitive Populations—A Field Study in Seoul, Korea. Environ. Manag. 2019, 64, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbain, B.; Lerner, U.; Castell, N.; Cole-Hunter, T.; Popoola, O.; Broday, D.M.; Martinez Iniquez, T.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Jovasevic-Stojanovic, M.; Topalovic, D.; et al. An evaluation tool kit of air quality micro-sensing units. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, S.; Mayfield, M.; Coca, D.; Jubb, S.A.; Osammor, O. Analysing the performance of low-cost air quality sensors, their drivers, relative benefits and calibration in cities—A case study in Sheffield. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, A.L.; Griswold, W.G.; Abhijit, R.S.; Johnston, J.E.; Herting, M.M.; Thorson, J.; Collier-Oxandale, A.; Hannigan, M. Low-Cost air quality monitoring tools: From research to practice (A workshop summary). Sensors 2017, 17, 2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Kilaru, V.J.; Snyder, E.G.; Kaufman, A.; Dye, T.; Rutter, A.; Russel, A.; Hafner, H. Air Sensor Guidebook; National Exposure Research Laboratory: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Williams, R. Tools and Resources Webinar: Low Cost Air Quality Sensors; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Morawska, L.; Thai, P.K.; Liu, X.; Asumadu-Sakyi, A.; Ayoko, G.; Bartonova, A.; Bedini, A.; Chai, F.; Christensen, B.; Dunbabin, M.; et al. Applications of low-cost sensing technologies for air quality monitoring and exposure assessment: How far have they gone? Environ. Int. 2018, 116, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polidori, A.; Papapostolou, V.; Zhang, H. Laboratory Evaluation of Low-Cost Air Quality Sensors; South Coast AQMD: Diamond Bar, CA, USA, 2016.
- AQ-SPEC. Laboratory Evaluation Air Quality Egg 2018 Model; South Coast AQMD: Diamond Bar, CA, USA, 2018.
- Giusto, E.; Gandino, F.; Greco, M.L.; Grosso, M.; Montrucchio, B.; Rinaudo, S. An investigation on pervasive technologies for IoT-based thermal monitoring. Sensors 2019, 19, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.E. Crowd-Sourced air quality studies: A review of the literature & portable sensors. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2016, 11, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, S.; Li, X. A cost-effective wireless sensor network system for indoor air quality monitoring applications. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 34, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Abdulghani, A.M.; Imran, M.A.; Abbasi, Q.H. Internet of Things (IoT) Enabled Smart Indoor Air Quality Monitoring System. ACM Int. Conf. Proc. Ser. 2020, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Pu’ad, M.F.; Gunawan, T.S.; Kartiwi, M.; Janin, Z. Performance evaluation of portable air quality measurement system using raspberry Pi for remote monitoring. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2019, 17, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Jasuja, A. Air quality monitoring system based on IoT using Raspberry Pi. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computing, Communication and Automation (ICCCA), Greater Noida, India, 5–6 May 2017; pp. 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.K.; Sircar, S.; Chatterjee, P.; Dutta, S.; Mitra, A.; Chatterjee, A.; Chattopadhyay, S.P.; Saha, H.N. A raspberry Pi controlled cloud based air and sound pollution monitoring system with temperature and humidity sensing. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 8th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 8–10 January 2018; pp. 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiruthika, R.; Umamakeswari, A. Low cost pollution control and air quality monitoring system using Raspberry Pi for Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Energy, Communication, Data Analytics and Soft Compututing (ICECDS), Chennai, India, 1–2 August 2017; pp. 2319–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkandari, A.A.; Moein, S. Implementation of monitoring system for air quality using raspberry Pi: Experimental study. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2018, 10, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.S.; Zanzinger, Z.; Debose, D.; Stephens, B. Open Source Building Science Sensors (OSBSS): A low-cost Arduino-based platform for long-term indoor environmental data collection. Build. Environ. 2016, 100, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, T.; Parkinson, A.; de Dear, R. Continuous IEQ monitoring system: Performance specifications and thermal comfort classification. Build. Environ. 2019, 149, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía, J.F.; Choy, S.L.; Mengersen, K.; Morawska, L. Methodology for assessing exposure and impacts of air pollutants in school children: Data collection, analysis and health effects—A literature review. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Risk of Bias Assesssment Instrument for Systematic; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Raspberry, P. Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ Datasheet; Raspberry Pi Ltd.: Milton, UK, 2016; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- DHT22. Digital-Output Relative Humidity & Temperature Sensor/Module AM2303, DHT22, Datasheet; Aosong Electron Co, Ltd.: Guangzhou, China, 2015; Available online: https://www.electroschematics.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/DHT22-datasheet.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Nova Fitness Co., Ltd. PM2.5 L. Laser PM2.5 Sensor. Available online: https://cdn-reichelt.de/documents/datenblatt/X200/SDS011-DATASHEET.pdf (accessed on 31 July 2019).
- SPEC Sensors. DGS-NO2 986-042, Digital Gas Sensor—Ozone. Available online: https://media.digikey.com/pdf/DataSheets/SPECSensorsPDFs/968-043_9-6-17.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2019).
- SPEC Sensors. DGS-SO2 986-042, Digital Gas Sensor—Ozone. Available online: https://www.spec-sensors.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/DGS-SO2-968-038.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2019).
- CO2Meter. K-30.K-30. Available online: https://img.ozdisan.com/ETicaret_Dosya/456729_1584920.PDF (accessed on 30 July 2019).
- Digi-Key Electronics. 968-034 D-C, Digital Gas Sensor—Carbon Monoxide. Available online: https://www.digikey.com/en/products/detail/spec-sensors-llc/968-034/6676880 (accessed on 26 July 2019).
- SPEC Sensors. DGS-O3, Digital Gas Sensor—Ozone. Available online: https://www.spec-sensors.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/DGS-O3-968-042_9-6-17.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2019).
- Ohmetch.io. UTHING::VOCTM™ Air-Quality USB Sensor Dongle. Available online: https://ohmtech.io/products/uthingvoc/#specifications (accessed on 10 June 2019).
- Mitsubishi Electric. TECHNICAL & SERVICE MANUAL. PEA-A18AA. PEA-A18AA. Available online: https://www.mitsubishitechinfo.ca/sites/default/files/PEA-A12-18AA4_Service_0.pdf (accessed on 28 June 2020).
- EPA. What is a MERV rating? Indoor Air Quality (IAQ). Available online: https://www.epa.gov/indoor-air-quality-iaq/what-merv-rating-1 (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- Goodman Air Conditioning and Health. GOODMAN GSX130481 4-tons 2 Ton Central Air Conditioner Air Handler Unit (Model AWUF24051BA). Available online: https://www.goodmanmfg.com/products/air-conditioners/13-seer-gsx13 (accessed on 8 June 2020).
- ANSI/ASHRAE. ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 62.1-2019, Ventilation for Acceptable Indoor Air Quality; American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Methods for Monitoring Indoor Air Quality in Schools; WHO: Bonn, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, R.; Schindler, C.; Eeftens, M.; Aguilera, I.; Ducret-Stich, R.E.; Ineichen, A.; Davey, M.; Phuleria, H.C.; Probst-Hensch, N.; Tsai, M.-Y.; et al. Modeling indoor air pollution of outdoor origin in homes of SAPALDIA subjects in Switzerland. Environ. Int. 2015, 82, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majd, E.; McCormack, M.; Davis, M.; Curriero, F.; Berman, J.; Connolly, F.; Leaf, P.; Rule, A.; Green, T.; Clemons-Erby, D.; et al. Indoor air quality in inner-city schools and its associations with building characteristics and environmental factors. Environ. Res. 2019, 170, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raysoni, A.U.; Stock, T.H.; Sarnat, J.A.; Chavez, M.C.; Sarnat, S.E.; Montoya, T.; Holguin, F.; Li, W.-W. Evaluation of VOC concentrations in indoor and outdoor microenvironments at near-road schools. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunyer, J.; Esnaola, M.; Alvarez-Pedrerol, M.; Forns, J.; Rivas, I.; López-Vicente, M.; Suades-Gonzalez, E.; Foraster, M.; Garcia-Esteban, R.; Basagana, X.; et al. Association between traffic-related air pollution in schools and cognitive development in primary school children: A prospective cohort study. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzyzanowski, M.; Cohen, A. Update of WHO air quality guidelines. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2008, 1, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurbenko, I.G. Detecting and tracking changes in ozone air quality. Air Waste 1994, 44, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seangkiatiyuth, K.; Surapipith, V.; Tantrakarnapa, K.; Lothongkum, A. Application of the AERMOD modeling system for environmental impact assessment of NO2 emissions from a cement complex. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.H.; Roh, J.; Park, W.M. Evaluation of PM10, CO2, airborne bacteria, TVOCs, and formaldehyde in facilities for susceptible populations in South Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scibor, M. Are we safe inside? Indoor air quality in relation to outdoor concentration of PM10 and PM2.5 and to characteristics of homes. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 48, 101537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chock, D.P.; Winkler, S.L.; Chen, C. A study of the association between daily mortality and ambient air pollutant concentrations in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2000, 50, 1481–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, M.F. Assessment of Ambient Air Quality Level at Different Areas inside Dammam University, Case Study. Met. Environ. Arid Land Agric. Sci. 2013, 142, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, O.J.; Abosede, O.O.; Sunday, F.B.; Ayooluwa, A.A.; Adetayo, A.J.; Ademola, S.J.; Alaba, A.F. Indoor air quality level of total volatile organic compounds (TVOCs) in a university offices. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 2872–2882. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.H.; Park, W.M. Indoor air concentrations of carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and ozone (O3) in multiple healthcare facilities. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 1487–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X. Monte Carlo simulation to control indoor pollutants from indoor and outdoor sources for residential buildings in Tianjin, China. Build. Environ. 2019, 165, 106376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
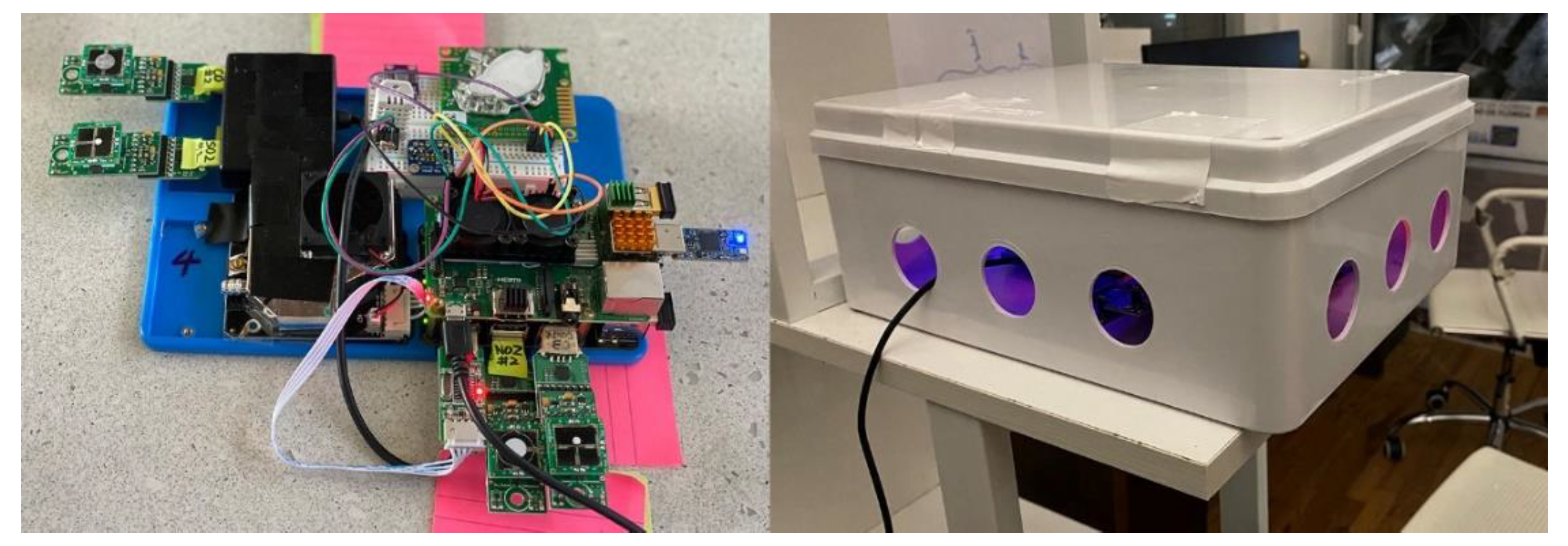
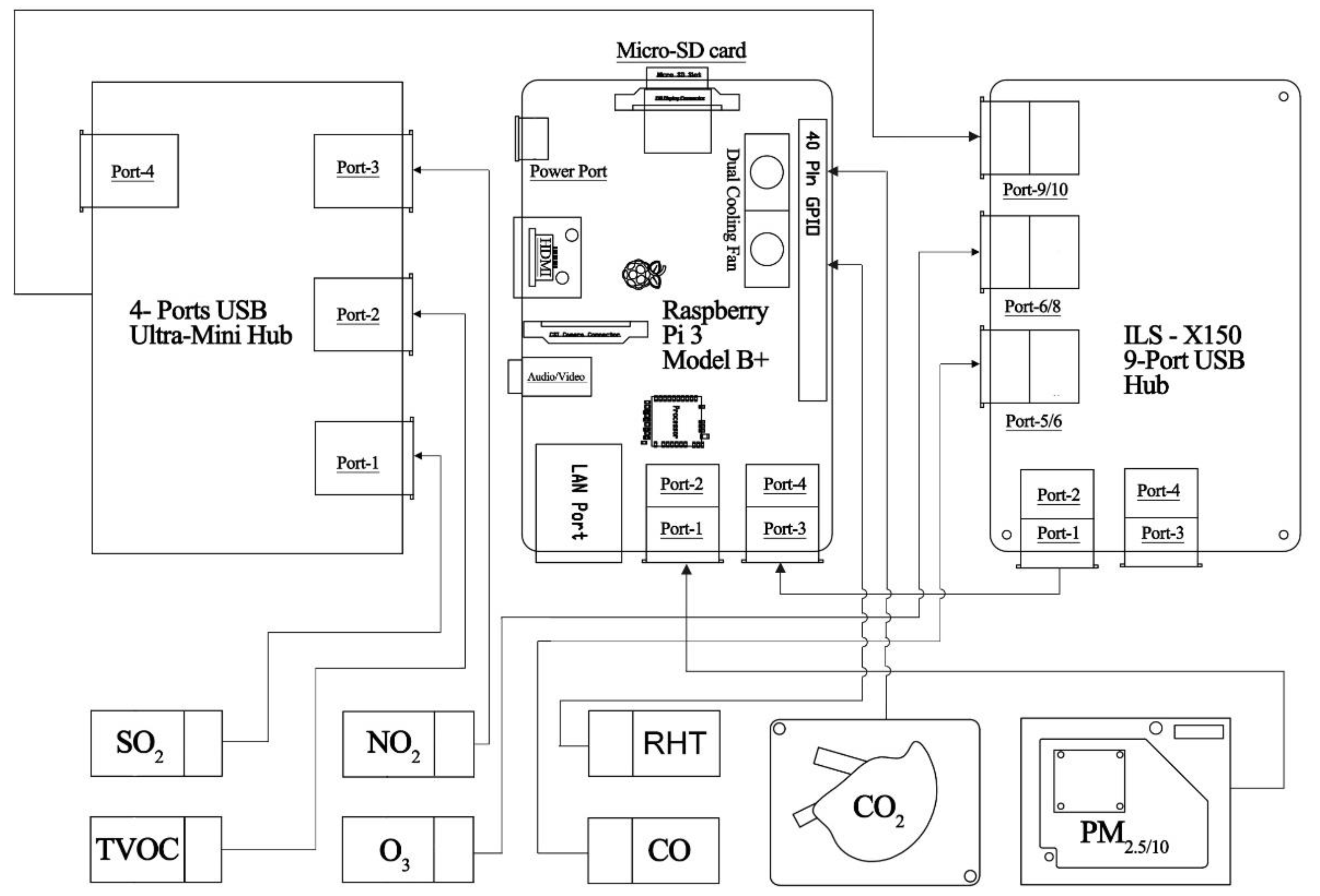


| Measured Parameter | Example Product | Manufacturer | Measuring Range | Accuracy (Repeatability) | Approx. Price (USD). 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RHT | DHT22 | Aosong Electronics | 40 °C–80 °C; 0% to 100% | ±0.5 °C; ±1% | ≤$10 |
| PM2.5/10 | SDS011 | Nova Fitness | 0.0–999.9 μg /m3 | 15%; ±10 μg/m3 | ≤$30 |
| NO2 | DGS-NO2 968-043 | SPEC Sensors | 0–10 ppm | ±15% | ≤$75 |
| SO2 | DGS-SO2 968-038 | SPEC Sensors | 0–20 ppm | ±15% | ≤$75 |
| CO2 | K-30 | CO2Meter | 0–5000 ppm | ±30% | ≤$80 |
| CO | DGS-CO 968-034 | SPEC Sensors | 0–1000 ppm | ±15% | ≤$75 |
| Ozone | DGS-O3 968-042 | SPEC Sensors | 0–5 ppm | ±15% | ≤$75 |
| TVOC | uThing:VOC™ | Ohmetech.io | 0–500 IAQ index | ±15% | ≤$95 |
| Site 1 | Site 2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Parameters | Average ± SD | Min | Max | Median | Average ± SD | Min | Max | Median |
| PM2.5 (µg/m3) | 8.53 ± 11.9 | 0.20 | 50.5 | 3.60 | 2.33 ± 2.74 | 0.00 | 13.8 | 1.20 |
| PM10 (µg/m3) | 10.2 ± 16.1 | 0.20 | 80.9 | 3.90 | 2.43 ± 2.84 | 0.00 | 14.3 | 1.30 |
| NO2 (ppb) | 41.8 ± 2.02 | 34.1 | 53.5 | 41.8 | 60.3 ± 6.94 | 43.8 | 132 | 62.1 |
| SO2 (ppb) | 39.9 ± 20.7 | 0.01 | 161 | 37.6 | 29.6 ± 23.0 | 4.79 | 114 | 22.6 |
| CO2 (ppm) | 2195 ± 479 | 761 | 3039 | 2270 | 432 ± 34.6 | 384 | 522 | 424 |
| CO (ppb) | 1.05 ± 0.45 | 0.00 | 2.12 | 1.06 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Ozone (ppb) | 12.1 ± 1.84 | 9.10 | 19.1 | 11.9 | 2.37 ± 2.92 | 0.00 | 23.7 | 1.65 |
| TVOC | 139.2 ± 68.2 | 23.0 | 250 | 146 | 121 ± 67.1 | 25 | 250 | 123 |
| Temp. (℉) | 80.5 ± 0.73 | 76.6 | 81.7 | 80.7 | 75.5 ± 1.20 | 72.3 | 78.8 | 75.1 |
| Humidity (%) | 45.5 ± 1.61 | 44.3 | 62.8 | 54.5 | 70.4 ± 3.28 | 59.7 | 81.1 | 71.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Srinivasan, R.; Ganesan, V. Low Cost, Multi-Pollutant Sensing System Using Raspberry Pi for Indoor Air Quality Monitoring. Sustainability 2021, 13, 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010370
Zhang H, Srinivasan R, Ganesan V. Low Cost, Multi-Pollutant Sensing System Using Raspberry Pi for Indoor Air Quality Monitoring. Sustainability. 2021; 13(1):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010370
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, He, Ravi Srinivasan, and Vikram Ganesan. 2021. "Low Cost, Multi-Pollutant Sensing System Using Raspberry Pi for Indoor Air Quality Monitoring" Sustainability 13, no. 1: 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010370
APA StyleZhang, H., Srinivasan, R., & Ganesan, V. (2021). Low Cost, Multi-Pollutant Sensing System Using Raspberry Pi for Indoor Air Quality Monitoring. Sustainability, 13(1), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010370





