Abstract
The karst area in Southwest China is facing the challenges of environmental degradation and agricultural safety. Intercropping is a green and efficient planting mode that can make full use of the differences in crops’ physiological and ecological characteristics and land and climate resources while considering the environmental and yield benefits. This study selected five treatments: Salvia miltiorrhiza monoculture, Dactylis glomerata intercropped with S. miltiorrhiza, Cichorium intybus intercropped with S.miltiorrhiza, Trifolium repens intercropped with S.miltiorrhiza, and Lolium perenne intercropped with S.miltiorrhiza. Using one-way ANOVA, principle component analysis (PCA), and linear correlation analysis, we analyzed the changes in the soil physicochemical factors and the coupling relationship between them in the intercropping mode. The results showed that at different soil depths, the soil bulk density in the intercropping mode was significantly lower than that in the single cropping mode (p < 0.05), and the soil water content and total porosity were significantly increased (p < 0.05). There were no significant differences in soil pH among the five models (p > 0.05), the content of soil organic matter was significantly higher than that in the single cropping mode (p < 0.05), and the content of nitrogen and phosphorus also showed different changes. The correlation analysis showed that there was no significant correlation between the pH and soil physical properties (p > 0.05); bulk density and chemical properties were negatively correlated, while the soil water content, field water-holding capacity, and total porosity were significantly positively correlated with the chemical properties (p > 0.05). Therefore, it is suggested to strengthen the management of agricultural grass intercropping, improve soil pore structure, regulate the distribution of soil water and fertilizer, and improve the resilience of agricultural systems in the karst area of southwest China.
1. Introduction
Intercropping is a traditional and efficient planting mode that can make full use of the advantages of time and space, reduce the loss of soil, water, light, fertilizer, and other resources, and increase diversity in crop production [1]. The research on intercropping patterns at home and abroad includes food crops and cash crops [2], green manure crops [3], medicinal crops [4], fodder crops, and so on [5,6]. Its advantages are reflected in increases in crop yields [7], suppression of weeds and insect pests [8], increases in unit land productivity [9], repair of soil pollution [10], and protection of the environment [11], all of which contribute to the development of modern agriculture. Compared with single planting, intercropping can maximize soil advantages, reduce soil water evaporation and leakage, improve crop water-use efficiency, and optimize the soil water environment for crop growth and development [12]. Changing root exudates and promoting the rapid growth of soil microorganisms can improve the metabolic abilities, increase the content of effective soil nutrients [13], regulate the soil microflora, prevent and control crop soil-borne diseases, change the functional diversity of microbial communities, improve the soil quality, and restore ecological balance [14].
Under the influence of its internal structure and external conditions, the weathering of the whole dolomite karst area in southwest China is strong, causing the mountains to be broken and the rock cementation force to be poor. Although the soil is continuous, the soil gravel content is rich, the saturated water conductivity is high, and the water-holding performance is poor. Because of these aspects, coupled with unreasonable human social and economic activities, the water and nutrients are easily leaked into the epikarst zone, resulting in nutrient loss [15,16,17,18]. The prevention of the loss of moisture and nutrients is the key to the efficient utilization of water and fertilizer in the dolomite karst soil. Most researchers have focused on aspects of the crop types in the Shibing dolomite karst area, such as on the irrigation and fertilization systems, plant density, spatial arrangements, cultivation and mulching measures, and environment [19,20,21,22,23]. There are few reports related to the effects of different intercropping patterns on the physical and chemical properties of the soil. In recent years, following the rural industrial revolution and the development of innovative industries in the Shibing area, good economic benefits have been obtained by planting S. miltiorrhiza in sandy soil with a high gravel content in accordance with the local conditions, but long-term and continuous cropping causes soil acidification and imbalances in the rhizosphere, ecosystem, and soil nutrition [24,25,26]. Thus, this paper selected S. miltiorrhiza and different kinds of forage in the Shibing dolomite karst area as the research objects. From the perspective of ecological planting, this study compared the physical and chemical properties of S. miltiorrhiza under four kinds of compound planting: Dactylis glomerata, Cichorium intybus, Trifolium repens, and Lolium perenne. The differences in physical and chemical properties between different layers of the S. miltiorrhiza soil were used to clarify the mechanisms of action of different intercropping modes on the soil moisture and nutrients and to screen for the intercropping plants that were suitable for the complex planting of S. miltiorrhiza in order to provide a basis for the construction of an efficient and ecological planting model of S. miltiorrhiza.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Basic Information
This study area was located in Shiqiao Village, Shibing County, Guizhou province, China (Figure 1). It is a typical dolomite karst mountain-canyon landform type, with large undulations in the area and an altitude of 530–1100 m. The demonstration area is dominated by a subtropical humid monsoon climate, and the vegetation types are mainly subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forests. The average annual temperature is 16.5 °C, the average annual precipitation is 1348.1 mm, the average annual sunshine duration is 1138.6 h, the annual average relative humidity is 79%, the forest coverage rate is 93.95%, the lithology is a thin layer of fine-grained dolomite of the Cambrian Gaotai Formation, the soil is mainly black lime soil, and some of the soil is rich in gravel [17,19]. The main crops are Oryza sativa, Zea mays, Nicotiana tabacum, Brassica napus, Capsicum annuum, Pseudostellaria heterophylla, S. miltiorrhiza, and other crops. There is a long history of agricultural cultivation in this area.
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the location of the test site.
With a random block design, the experiment was carried out in five planting modes with approximately the same latitude, longitude, elevation, and slope direction (Table 1). The area of each plot was 3 m × 6 m, and repeat 3 times for each plot. S. miltiorrhiza was planted with two rows per ridge, the ridge width was 70 cm, the row spacing was 20 cm, and the plant spacing was 30 cm. The area was sown on 23 March 2020, and the root propagation method was adopted with a sowing rate of 4 kg/hm−2. Forage was planted in furrows through the strip sowing method, and four rows of forage were planted in every other ridge of S. miltiorrhiza; the row spacing of the forage was 30 cm (Figure 2), and the sowing time was on 12 April, 2020. The seeding rate of T. repens was 5 kg/hm2, the seeding rate of C. intybus was 5 kg/hm2, and the seeding rate of D. glomerata and L. perenne was 15 kg/hm2. S. miltiorrhiza was planted in November 2019, and the forages were planted in March 2020. Before planting, the area was uniformly plowed, and compost was applied at a rate of 134 kg/hm2. No plowing, irrigation, or fertilizers were used during the growth process. Soil samples were collected after the forage was harvested. The tested S. miltiorrhiza root seedlings came from Bozhou Wanfeng Chinese Medicine Technology Co., Ltd. (Bozhou, China), and D. glomerate L.cv.Qiancao No. 4., C. intybus L.cv.puna Qianying., T. repens Yaqing, and L. perenne L.cv.nipuna were used. Before planting, the area was uniformly plowed, and compost was applied at a rate of 134 kg/hm2. No plowing, irrigation, or fertilizers were used during the growth process.

Table 1.
Location and information of the sampling points.
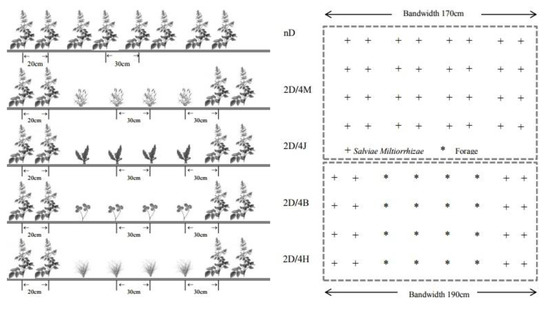
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the planting mode. Note: nD indicates the number of rows of the single crop of S. miltiorrhiza. 2D/4M, 2D/4J, 2D/4B, and 2D/4H indicate two rows of S. miltiorrhiza intercropped with four rows of D. glomerata, C. intybus, T. repens, or L. perenne, respectively.
2.2. Soil Sampling and Analysis
The soil samples were collected on 24 October, 2020. The S-type random sampling method was used to divide the samples into four layers. The sampling depths ranged from 0 to 20 cm: 0–5, 5–10, 10–15, and 15–20 cm, and repeated three times. Samples were brought back to the laboratory for natural air drying and removal of visible plant roots and gravel. Then, they were passed through 0.15 and 2 mm soil sieves and stored at room temperature.
The basic physical and chemical properties—soil bulk density, water content, and capillary porosity—were determined by using the cutting-ring method [27]. The soil pH was measured with the 1:1 soil–water ratio method and was also directly measured with a pH meter. The total N was estimated by titration of distillations after Kjeldahl readiness tests and examinations [28]. The total P in the soil was measured with the perchloric corrosive assimilation strategy technique [29]. Available P was analyzed by using molybdenum blue colorimetry [30]. Alkaline hydrolysis N was measured with the alkaline solution diffusion method [31], and soil organic matter was measured with the potassium dichromate oxidation–external heating method [28].
The SPSS 22.0 software was used for statistical analysis of the measured data. A one-way analysis of variance was performed, and the least significant difference (LSD) method was used to test the significance of the differences at the p < 0.05 level. The Origin 2018 software was used for drawing.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Different Intercropping Patterns on Soil Physical Properties
The soil bulk density in this experiment was between 1.1 and 1.5 g/cm3. In the soil layers of 0–5 and 10–15 cm, the soil bulk densities of the four intercropping methods were lower than that of the CK, and the difference was significant (Figure 3). In the 5–10 cm soil layer, the CK had the highest soil bulk density, which was not significantly different from the DM treatment. In the 15–20 cm soil layer, the bulk density of the soil treated with DJ was the highest, and the difference between CK and DJ was not significant. The soil water content of intercropped soil was higher than that of the monoculture (excluding the DM treatment), and it decreased with the increase in soil depth. The soil moisture content of the DM treatment in the 0–5 cm soil layer was lower than that of the monoculture, and the difference was not significant, while the soil moisture content of the four intercropping modes in the soil layer of 5–20 cm was higher than that of the monoculture, with a significant difference. The soil water-holding capacity in the field gradually decreased from the surface layer to the lower layers. Within the soil layer of 0–15 cm, the changing trends of the four intercropping patterns were inconsistent. Compared with the single cropping, the difference was not significant, but there was a significant difference in the bottom layer. The total porosity of the soil in the 0–5 cm soil layer was the highest in the DH treatment, and the difference was significant (p < 0.05). The total porosity in the 5–10 cm soil layer was highest in the D. glomerata treatment, and the difference between intercropping and single cropping was significant (p < 0.05). In the 10–15 cm soil layer, the total porosity of the DH treatment was significantly higher than that of the other treatments, and the difference between the DJ and DB treatments was not significant (p > 0.05). In the 15–20 cm soil layer, the total porosity of the DM treatment was the highest, and the DJ treatment was the lowest. There was no significant difference between the DB and CK treatments (p > 0.05).
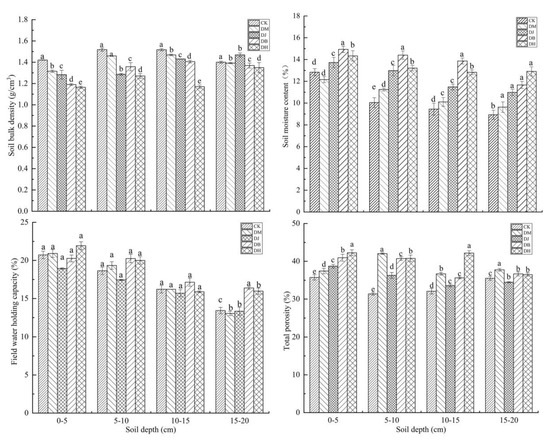
Figure 3.
Comparison of the soil physical properties in different treatments. DM = S. miltiorrhiza + D. glomerata intercropping; DJ = S. miltiorrhiza + C. intybus intercropping; DB = S. miltiorrhiza + T. repens intercropping; DH = S. miltiorrhiza + L. perenne intercropping. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.2. Characteristics of Soil Chemical Properties in Different Intercropping Modes
The intercropping patterns had different effects on the soil chemical properties in different soil layers, and the differences between the intercropping modes and monoculture were significant (Figure 4). In the 0–5 cm soil layer, intercropping had significant effects on SOM, AN, TP, and AP content. Compared with single cropping, the TN content of the soil treated with DH increased by 7.79%. The contents of AN and TP of the DM and DJ treatments were reduced by 15.12%, 9.35%, 7.69%, and 9.91%. The TN content of the DM treatment was not significantly different (p > 0.05). In the 5–10 cm soil layer, the content of SOM was significantly different in the intercropping pattern (p < 0.05). The TN content of the DM treatment was not significantly different from that of the CK. The contents of SOM, TN, AN, and AP in the DB treatment increased by 16.54%, 2.61%, 8.74%, and 14.29%. Compared with CK, the contents of SOM, TP, and AP in the DH treatment increased by 26.68%, 11.9%, and 33.83%. In addition, the TP and AP contents of the DM treatment were reduced by 2.77% and 3.26%, and there was a significant difference (p > 0.05). In the 10–15 cm soil layer, the SOM and TN contents were significantly different among the treatments (p < 0.05), the content of AN was significantly different, except for the DH treatment (p < 0.05), and the TP content of the soil showed no significant difference between the DM and DB treatments (p > 0.05). There was no significant difference in the AP content between the DH and DJ treatments (p > 0.05). In the 15–20 cm soil layer, the content of SOM was significantly different in all treatments, the TN content of DM and DJ was not significantly different from that of CK (p > 0.05), the AN content of DJ was not significantly different from that of CK (p > 0.05), the TP content of DJ and DM was not significantly different from that of CK (p > 0.05), and the AP content of DJ was not significantly different from that of CK (p > 0.05).
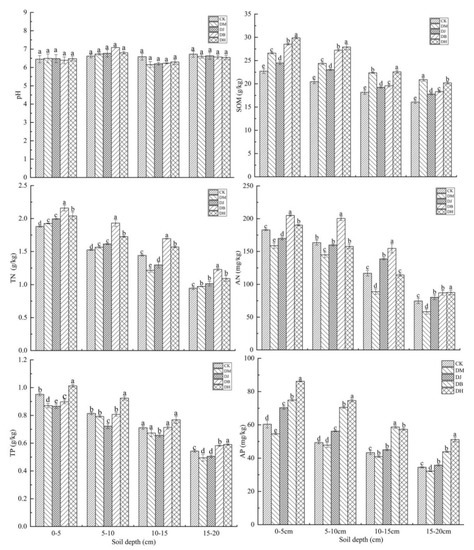
Figure 4.
Characteristics of the variations in soil chemical properties with different treatments. DM = S. miltiorrhiza + D. glomerata intercropping; DJ = S. miltiorrhiza + C. intybus intercropping; DB = S. miltiorrhiza + T. repens intercropping; DH = S. miltiorrhiza + L. perenne intercropping. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.3. Soil Physical and Chemical Characteristics with Different Treatments
A linear regression equation was used to analyze the correlations of the soil physical and chemical properties under different intercropping modes (Figure 5 and Figure 6). The results showed that the soil pH and physical indicators had an insignificant linear relationship (p > 0.05). The nitrogen, phosphorus, and organic matter content and field water-holding capacity in the soil had a strong positive correlation; they had a significant negative correlation with soil bulk density, but they had a significant positive correlation with soil moisture content. There was an insignificant linear relationship between the soil available nitrogen and total soil porosity, while organic matter had a strong positive correlation with the total soil porosity.
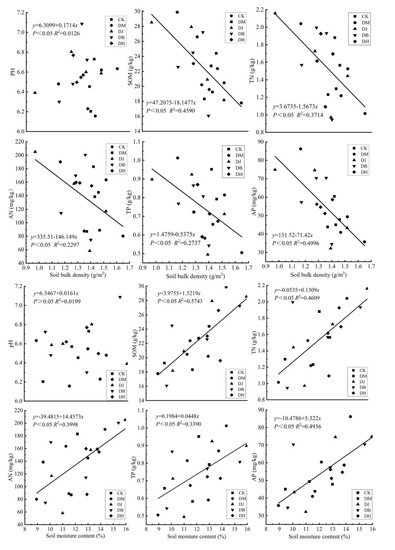
Figure 5.
Linear diagram of the correlation of bulk density and water content with chemical properties. DM = S. miltiorrhiza + D. glomerata intercropping; DJ = S. miltiorrhiza + C. intybus intercropping; DB = S. miltiorrhiza + T. repens intercropping; DH = S. miltiorrhiza + L. perenne intercropping. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05). pH = soil pH; SOM = soil organic matter; TN = total N; TP = total P; AN = alkaline hydrolysis N; AP = available P.
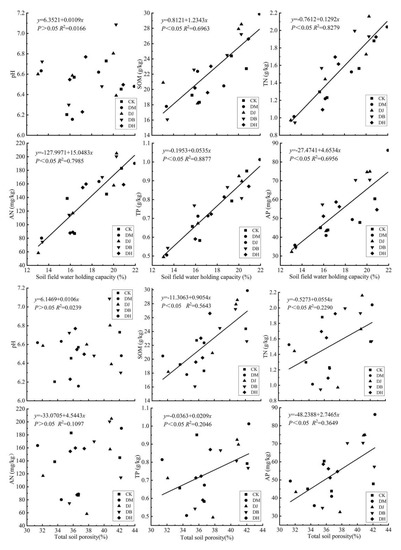
Figure 6.
Linear diagram of the correlation of the field water-holding capacity, total porosity, and chemical properties. DM = S. miltiorrhiza + D. glomerata intercropping; DJ = S. miltiorrhiza + C. intybus intercropping; DB = S. miltiorrhiza + T. repens intercropping; DH = S. miltiorrhiza + L. perenne intercropping. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05). pH = soil pH; SOM = soil organic matter; TN = total N; TP = total P; AN = alkaline hydrolysis N; AP = available P.
3.4. Principal Component Analysis of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
In order to further explore the impact of intercropping on the soil environment, principal component analysis was performed on the data from each sampling point. It was preliminarily found that the correlation coefficients between the various indicators were mostly greater than 0.3 (Table 2), indicating that there was a high degree of information repeatability between the factors, which met the requirements of principal component analysis. A further dimensionality reduction and two common factors were proposed, and the cumulative contribution rate of the common factors reached 80.10%, which indicated that the physical and chemical characteristics of the soil was reflected (Figure 7). As shown in Figure 7, the contribution rate of the first factor was 67.77%, and the order of correlation was: AP > TN > SOM > TP > CSL > AN > HSL > RZ > KXD > PH. This shows that the relationship between the pH and the physical and chemical properties of the soil was weak, and the correlation between the soil moisture and N and P was strong, indicating that water is more important for nutrient transport. The score of the first principal component in the DH treatment was much higher than those of other treatments. It was because that the root system of DH treatment was developed and dense, the interception effect was better, the water retention capacity was high, and the nutrient transfer was guaranteed.

Table 2.
Matrix correlation table. RZ = soil bulk density; KXD = total soil porosity; CSL = field water-holding capacity; HSL = soil moisture content; pH = soil pH; SOM = soil organic matter; TN = total N; TP = total P; AN = alkaline hydrolysis N; AP = available P.
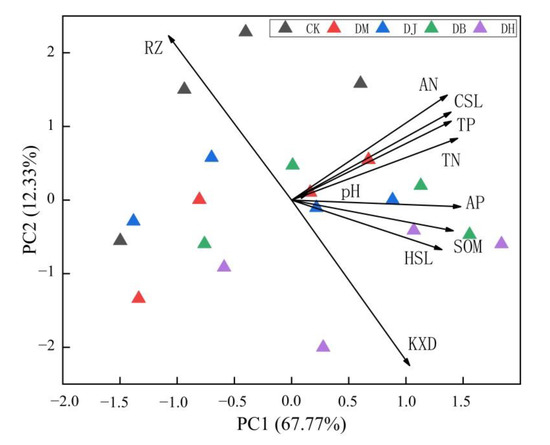
Figure 7.
Principal component analysis diagram.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Intercropping on Soil Physical Properties
Soil bulk density is an effective index for reflecting the physical properties of soil. It plays an important role in soil tightness, aeration, and drainage, as well as the growth of plant roots. In this experiment, the intercropping pattern was able to significantly reduce the soil bulk density, increase the total porosity, enhance the soil cultivability, and reduce the loss of nutrient elements. This conclusion was consistent with the findings of Ding [32] and Zhang [33]. Intercropping forage can increase the surface coverage and reduce the ineffective evaporation of surface water; at the same time, it can be used to intercept precipitation, intercept surface runoff, and adjust soil water content [34,35]. The effects of different species of forage on the soil water retention were obviously different. The soil water content increased with the use of the four types of intercropping forages, and DH provided the strongest soil water content. Ryegrass is a gramineous forage with many root systems and large numbers, and its water retention and water retention effects on soil were better than those of legumes and composite forages, which was consistent with the findings of Liu [36]. On the other hand, D. glomerata, which is also a gramineous forage, had a lower soil water content in the 0–5 cm soil layer than that obtained with monocropping, but the difference was not significant. This was mainly because the influence of S. miltiorrhiza on soil moisture was mainly on the surface of the soil. D. glomerata had a strong adaptability, with a higher above-ground biomass and greater water consumption than that obtained with single cropping. It was able to slow down the dissipation of soil moisture by regularly influences and controlling the water consumption of the forage. The field water-holding capacity of the C. intybus soil showed a downward trend compared with the monoculture, and the difference was not significant. Because its tap roots were conical, the lateral roots and fibrous roots were not developed, which led to the poor water-holding capacity of the soil and a decrease in the field water-holding capacity.
4.2. Effects of Intercropping on Soil Chemical Properties
There was no significant difference in soil pH under different intercropping planting methods (p > 0.05). The content of organic matter is an important indicator in the measurement of soil fertility, and it is closely related to mineral content; there was a positive correlation between nitrogen and organic matter. Intercropping can significantly improve organic matter content [37]. In this study, the organic matter and total nitrogen showed that the effect of intercropping L. perenne and T. repens in the 0–10 cm soil layer was significantly higher than that of intercropping D. glomerata and C. intybus (p < 0.05). The plant of L. perenne has luxuriant leaves, and there is a large amount of litter and dead branches in the later growth period [38]; the litter remains as the main source of organic matter input. The nutrient content of the litter of withered plant organs is returned to the soil, which may have a greater effect than with D. glomerata and C. intybus. T. repens, as legume herbage, has a root system that can coexist with rhizobia, and its biological nitrogen fixation ability is extremely strong. It takes advantage of its characteristic of covering the ground for a long time to effectively prevent the loss of surface water and fertilizer nutrients, promote the absorption of crops’ own nutrients, improve the organic matter content, increase the total nitrogen content, and cultivate fertility, which is consistent with the conclusions of studies by Song [39] in a tea garden, Zhang [40] in an orchard, and Jian [41] in farmland. All of these authors found that intercropping T. repens can effectively increase the organic matter and total nitrogen content. The total phosphorus content of soil treated with DM, DJ, and DB was significantly lower than that of soil treated with DH and CK. The available phosphorus content in the soil treated with DH and DB was higher than that of soil with the DM and DJ treatments, and the change trend was similar to that of the soil moisture content. The total phosphorus content of the soil treated with DM, DJ, and DB was significantly lower than that of soil treated with DH and CK. The available phosphorus content shows that DH and DB are better than DM and DJ, which is similar to the change trend of soil water content. Soil phosphorus is easily fixed and should not be lost with leaching. The soil water content affects the phosphorus diffusion rate, organic matter content affects the phosphorus adsorption and fixation, and the difference between the total phosphorus and available phosphorus content is related to the degree of soil leaching. In this study, the cultivation density of L. perenne was high and the plant gaps were small, so the soil leaching effect was weak; however, the density of D. glomerata and C. intybus cultivation was small and the plants were tall and thin, so the soil leaching effect was strong. Thus, the total phosphorus and available phosphorus content were lower than those of L. perenne.
4.3. Correlative Effects of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties in Different Intercropping Patterns
Soil is one of the most important sources of water and nutrients for crop growth and development. The level of soil fertility determines the abundance of crop yields. The distribution of soil moisture affects the migration and decomposition of nutrients and affects their absorption and utilization by crops. As the bulk density of soil becomes larger, the porosity and connectivity become weaker, the contact area between crop roots and soil decreases, and the circulation of nutrient elements between plant bodies and soil becomes slower [42]; thus, the bulk density can reduce the accumulation of nutrient elements. On the contrary, when the soil bulk density is low, the porosity becomes greater, and the water-holding capacity is strengthened, which increases the growth space for the crop root system and promotes its absorption of nutrients elements. Therefore, the soil nutrient content of the study area was at the maximum under the condition of low bulk density. As the total porosity of the soil increases, the amounts of water and air contained increase and the material exchange between soil microorganisms and plants becomes more frequent, which accelerates the hydrolysis of insoluble organic phosphorus compounds in the soil and the rate of nutrient returned, and it also increases the soil phosphorus content. The study of Li [43] showed that there was a significant positive correlation between the soil total phosphorus content and total porosity (p < 0.05), but in this study, the changes in phosphorus and nitrogen in the soil of the S. miltiorrhiza field were not obviously correlated with the total porosity, and only a weak positive correlation was shown. On one hand, the content of phosphorus in the soil was mainly affected by phosphorus mineral compounds and the soil in the dolomite karst area was affected by the weathering of the parent rock, so the soil phosphorus was scarce. The total porosity had little effect on the weathering and release of phosphorus minerals into the soil. On the other hand, the mineralization of soil nitrogen was strong in the dolomite karst area, and the organic nitrogen in the soil was mostly in the form of unstable inorganic compounds under the action of microorganisms. When the total porosity of soil increased, the nitrogen was emitted into the atmosphere in the form of ammonia [44], which can accelerate the loss of total nitrogen and available nitrogen in the soil of S. miltiorrhiza.
5. Conclusions
Salvia is a commodity among common medicinal materials, and growers mainly rely on artificial cultivation. Due to the increase in demand, as it is a rhizome crop, continuous large-scale single planting will cause continuous cropping obstacles, pests and diseases, and a lack of soil water and fertilizer. A principal component analysis and correlation analysis showed that intercropping S. miltiorrhiza can increase the soil water, improve soil bulk density, and increase soil organic matter, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Intercropping ryegrass can significantly increase the soil organic matter and phosphorus content, providing a strong basis for intercropping L. perenne in areas that lack soil phosphorus. The method of intercropping with forage can be used to reduce the pollution from pesticides and fertilizers in the soil environment, to explain the effect of S. miltiorrhiza intercropping on the soil water and fertilizer from the perspective of the soil, and to effectively realize the green and sustainable development of agricultural production. This study is only a preliminary study for constructing the best collocation of the ecological compound planting patterns of S. miltiorrhiza. The long-term dynamic change processes of the four intercropping patterns, the degree of influence of the soil environmental elements on intercropping, and the relationships of the quantitative indexes all need to be further studied in the future.
Author Contributions
K.X. and Y.C. conceptualized the framework, acquired the funding, and supervised the overall project; Q.X. collected samples and data; Q.X. and Y.C. processed samples, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript; S.S. and Y.C. edited the manuscript; K.X. and Q.X. reviewed the final manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Key Project of Science and Technology Program of Guizhou Province: Poverty Alleviation Model and Technology Demonstration for Ecoindustries Derived from the Karst Desertification Control (No. 5411 2017 Qiankehe Pingtai Rencai), the Project of the National Key Research and Development Program of China in the 13th Five-Year Plan Period: Ecological Industry Model and Integrated Technology Demonstration of the Karst Plateau–Gorge Rocky Desertification Control (No. 2016YFC0502607), and the World Top Discipline Program of Guizhou Province: Karst Ecoenvironment Sciences (No.125 2019 Qianjiao Keyan Fa).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study did not involve humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
No participants were involve for any survey in this research. While no questionnaire and survey were done for this research. There is no humans and/or animals involves in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Brooker, R.W.; Bennett, A.E.; Cong, W.F.; Daniell, T.J.; George, T.S.; Hallett, P.D.; Hawes, C.; Iannetta, P.P.M.; Jones, H.G.; Karley, A.J.; et al. Improving intercropping: A synthesis of research in agronomy, plant physiology and ecology. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celette, F.; Findeling, A.; Gary, C. Competition for nitrogen in an unfertilized intercropping system: The case of an association of grapevine and grass cover in a Mediterranean climate. Eur. J. Agron. 2009, 30, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madembo, C.; Mhlanga, B.; Thierfelder, C. Productivity or stability? Exploring maize-legume intercropping strategies for smallholder Conservation Agriculture farmers in Zimbabwe. Agric. Syst. 2020, 185, 102921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, B.B.; Wang, H.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, M.; Yang, R.Y. Variation in microbial community structure in the rhizosphere soil of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge under three cropping modes. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 4832–4843. [Google Scholar]
- Tueche, J.R.; Hauser, S. Maize (Zea mays L.) yield and soil physical properties as affected by the previous plantain cropping systems, tillage and nitrogen application. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 115, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetteh, E.N.; Abunyewa, A.A.; Tuffour, H.O.; Berchie, J.N.; Acheampong, P.P.; Twum-Ampofo, K.; Dawoe, E. Rubber and plantain intercropping: Effects of different planting densities on soil characteristics. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutsamba, E.F.; Nyagumbo, I.; Mupangwa, W. Forage and maize yields in mixed crop-livestock farming systems. NJAS-Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2019, 92, 100317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.; Zhu, C.; Bai, J.; Wu, X.; Lin, T. Intercropping garlic at different planting times and densities for insect pest or crop yield and value management in tobacco fields. Entomol. Res. 2020, 50, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariz, C.M.; Costa, C.; Crusciol, A.C.; Meirelles, P.R.L.; Castilhos, A.M.; Andreotti, M.; Costa, N.R.; Martello, J.M.; Souza, D.M.; Sarto, J.R.W.; et al. Production and Soil Responses to Intercropping of Forage Grasses with Corn and Soybean Silage. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 2541–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.W.; Lin, L.J.; Liao, M.A.; Liu, J.; Liang, D.; Xia, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Deng, H.H. Effects of intercropping with different Solanum plants on the physiological characteristics and cadmium accumulation of Solanum nigrum. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavo, D.S.; Moitinho, M.R.; Silva, B.D.O. Effects of long-term no-tillage systems with different succession cropping strategies on the variation of soil CO2 emission. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 413–424. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.J.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.D.; Qiu, Y. The effects of land use on soil moisture variation in the Danangou catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. CATENA 2003, 54, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.K.; Wu, S.J.; Han, X.H. Organic carbon, nitrogen accumulation, and soil aggregate dynamics as affected by vegetation restoration patterns in the Loess Plateau of China—Science Direct. CATENA 2021, 196, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.S.; Lin, H.P.; Meng, C.F.; Jiang, P.K.; Fu, W.J. Effects of intercropping grasses on soil organic carbon and microbial community functional diversity under Chinese hickory (Carya cathayensis) stands. Eur. J. Soil Res. 2014, 52, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.X.; Wang, S.J.; Zhou, D.Q.; Li, Y.L. Differential Weathering and Pedogenetic Characteristics of Carbonate Rocksand Their Effect on the Development of Rock Desertification in Karst Regions. Acta Min. Sin. 2002, 22, 308–314. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.C.; Lian, Y.Q.; Qin, X.Q. Rocky desertification in Southwest China: Impacts, causes, and restoration. Earth Sci. Rev. 2014, 132, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Gu, Z.F.; Lu, Y.Y.; Liu, Z.K. The Experimental Study of Dolomite Dissolution and Pore Characteristics in Shibing, Guizhou. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2015, 26, 413–418. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, X.G.; Peng, T.; Wang, S.J.; Cai, X.L.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.B.; Meng, F.D.; Zhang, L. Agent and Activated Carbon as Soil Amendments on Dolomite Slopes—A Case Study of Perennial Ryegrass. Earth Environ. 2017, 45, 229–235. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.J.; Cao, X.; Yuan, S.; Wang, W.Y.; Feng, Y.Z.; Qiao, B. Effects of Long-term Conservation Tillage on Soil Nutrients in Sloping Fields in Regions Characterized by Water and Wind Erosion. Sci. Rep. 2015, 10, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’Dayegamiye, A.; Nyiraneza, J.; Grenier, M.; Bipfubusa, M.; Drapeau, A. The Benefits of Crop Rotation Including Cereals and Green Manures on Potato Yield and Nitrogen Nutrition and Soil Properties. Adv. Crop Sci. Technol. 2017, 279, 172–185. [Google Scholar]
- Somasundaram, J.; Salikgram, M.; Sinha, N.K. Conservation agriculture effects on soil properties and crop productivity in a semiarid region of India. Soil Res. 2019, 57, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Luo, X.J.; Wang, X.S.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.L. Evolution Characteristics of Plant Communities in the Karst Area of Dolomites, Southeastern Guizhou Province. Acta Bot. Boreali Occident. Sin. 2019, 39, 2064–2071. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Zeng, C.; Xiao, S.Z.; He, J.H.; Di, Y.N.; Gong, X.Y.; Xiao, H. Preliminary Study on Hydrological and Hydrochemical Regime of a Typical Humid Subtropical Dolomite Catchment, a Case Study in the Huangzhou River Basin, Shibing County, Guizhou Province. Earth Environ. 2020, 48, 279–293. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.Y.; Weiner, J.; Shi, X.J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.R.; Zhu, M. Effect of reductive soil disinfestation on the chemical and microbial characteristics of rhizosphere soils associated with Salvia miltiorrhiza production in three cropping systems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 160, 103865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Heijden, M.G.A.; Bardgett, R.D.; Van Straalen, N.M. The unseen majority: Soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.W.; Liu, C.J.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Q.H.; Zhang, W.L.; Yang, P.; Feng, B.L. Responses of rhizosphere soil properties, enzyme activities and microbial diversity to intercropping patterns on the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.K. Soil and Agro-Chemical Analysis Methods; Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 1999; pp. 255–266. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.; Mulvaney, C. Total nitrogen. In Methods of Soil Analysis, 2nd ed.; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Sommers, L.E.; Nelson, D.W. Determination of total phosphorus in soils: A rapid perchloric acid digestion procedure. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1972, 36, 902–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, R.H.; Kurtz, L.T. Determination of total, organic, and available forms of phosphorus in soils. Soil Sci. 1945, 59, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M.Y.; Li, Y.; Xiong, K.N. Response of soil physical and chemical properties to Rocky desertification succession in South China Karst. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 6303–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.F.; Cao, Y.Q.; Yao, X.H.; Fu, S.L.; Zhang, P.A.; Lou, X.L. Effects of Intercropping with Different Green Manures on Soil Nutrient Loss in Camellia oleifera Field. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 32, 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.P. Influence of Scrophularia ningpoensis-tobacco intercropping on bacterial community structure in soil. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2017, 26, 120–130. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.; Chai, Q.; Zhao, C. Water utilization in intercropping: A review. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 241, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.J.; Liu, X.J.; Wu, Y.; Tong, C.C.; Lin, F. Effects of Medicago sativa-Triticale wittmack intercropping system on rhizosphere soil nutrients and bacterial community in semi-arid region of Northwest China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.S.; Chen, Z.Y.; Liu, F.; Pu, T.D. Impacts of Different Forage Species and Biochar Application on Soil Moisture. Bull. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 39, 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, S.Z.; Wang, Y.; Ning, T.Y.; Li, N.; Zhao, H.X.; Wang, B.W.; Li, Z.J.; Chi, S.Y. Continued no-till and subsoiling improved soil organic carbon and soil aggregation levels. Agron. J. 2014, 10, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.C. Study of Grass-Legume Intercropping System in Terms of Competition Indices and Monetary Advantage Index under Acid Lateritic Soil of India. Am. J. Exp. Agric. 2011, 1, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.Q.; Xiao, R.L.; Peng, W.X.; Wang, J.R.; Li, S.H.; Liu, X.F. Effects of intercropping white clover in tea plantation on soil environment in subtropical hilly region. Chin. J. Ecol. 2006, 25, 281–285. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.D.; Li, T.C.; Zhang, D.Y.; Jia, M.L.; Guo, H.; Li, J.K.; Cao, W.D. Effects of Interplanting White Clover on Soil Total Organic Carbon and Light Organic Carbon Fraction in Apple Orchard. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2014, 25, 810–818. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, Z.L.; Zhao, L.L.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, F.; Huang, J.X. Effect of intercrop of maize||white clover on maize photosynthesis, yield, and soil respiration with different row spacing in a Karst area. Pratacult Sci. 2019, 36, 480–489. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.H.; Li, Q.X.; Wang, X.Q.; Jia, Z.Q.; Chen, X.J. Root Distribution and Soil Properties under Caragana intermedia Plantations in Alpine Sandy Land. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 50, 840–846. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Wang, D.M.; Ding, C.; Liu, R.S.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.L. Soil infiltration characteristics and its influencing factors of typical vegetation type in Loess Alpine region. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 110–120. [Google Scholar]
- Walkup, J.; Freedman, Z.; Kotcon, J.; Morrissey, E.M. Pasture in crop rotations influences microbial biodiversity and function reducing the potential for nitrogen loss from compost. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 304, 107122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).